A wideband, transparent and flexible microwave metamaterial absorber
-
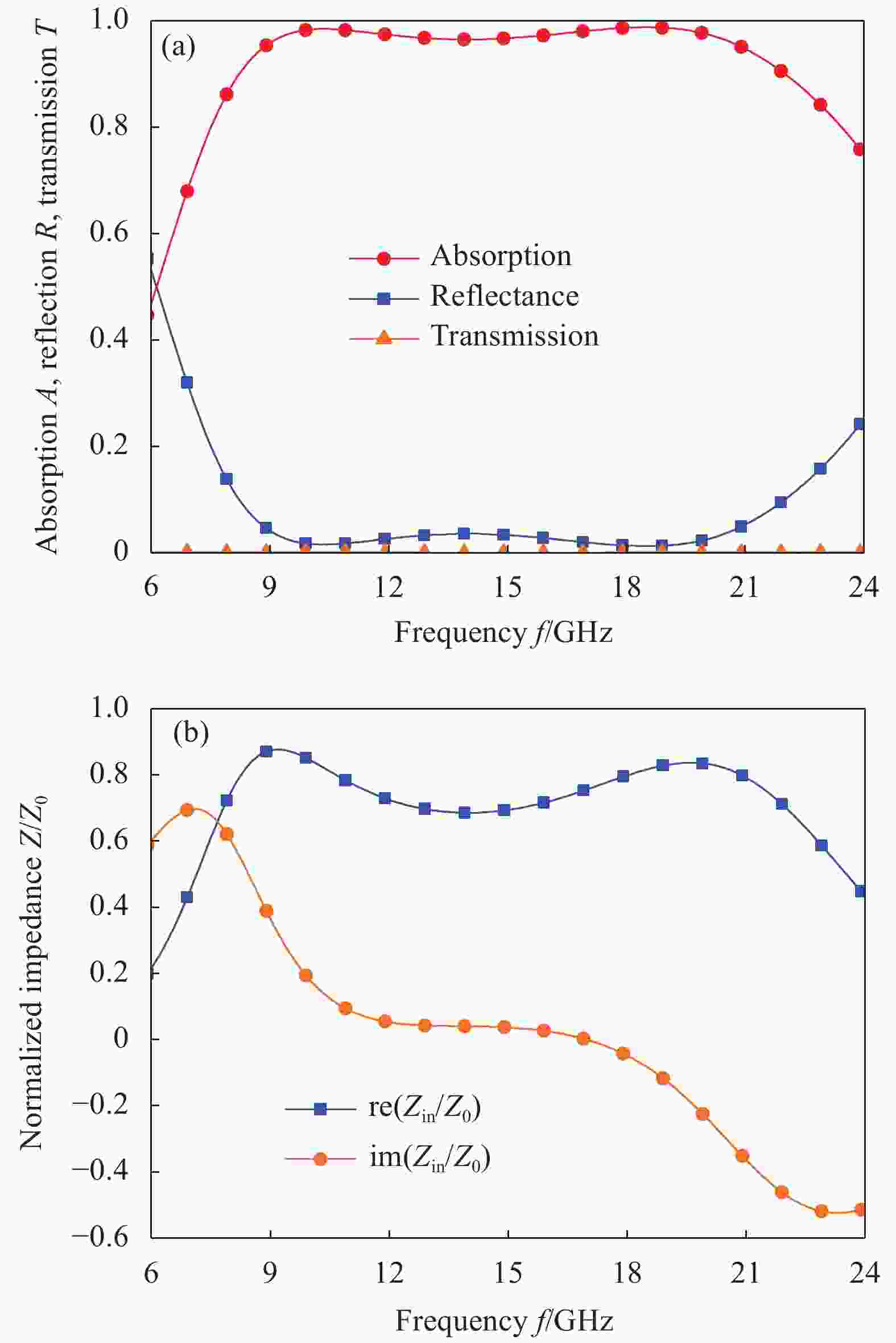
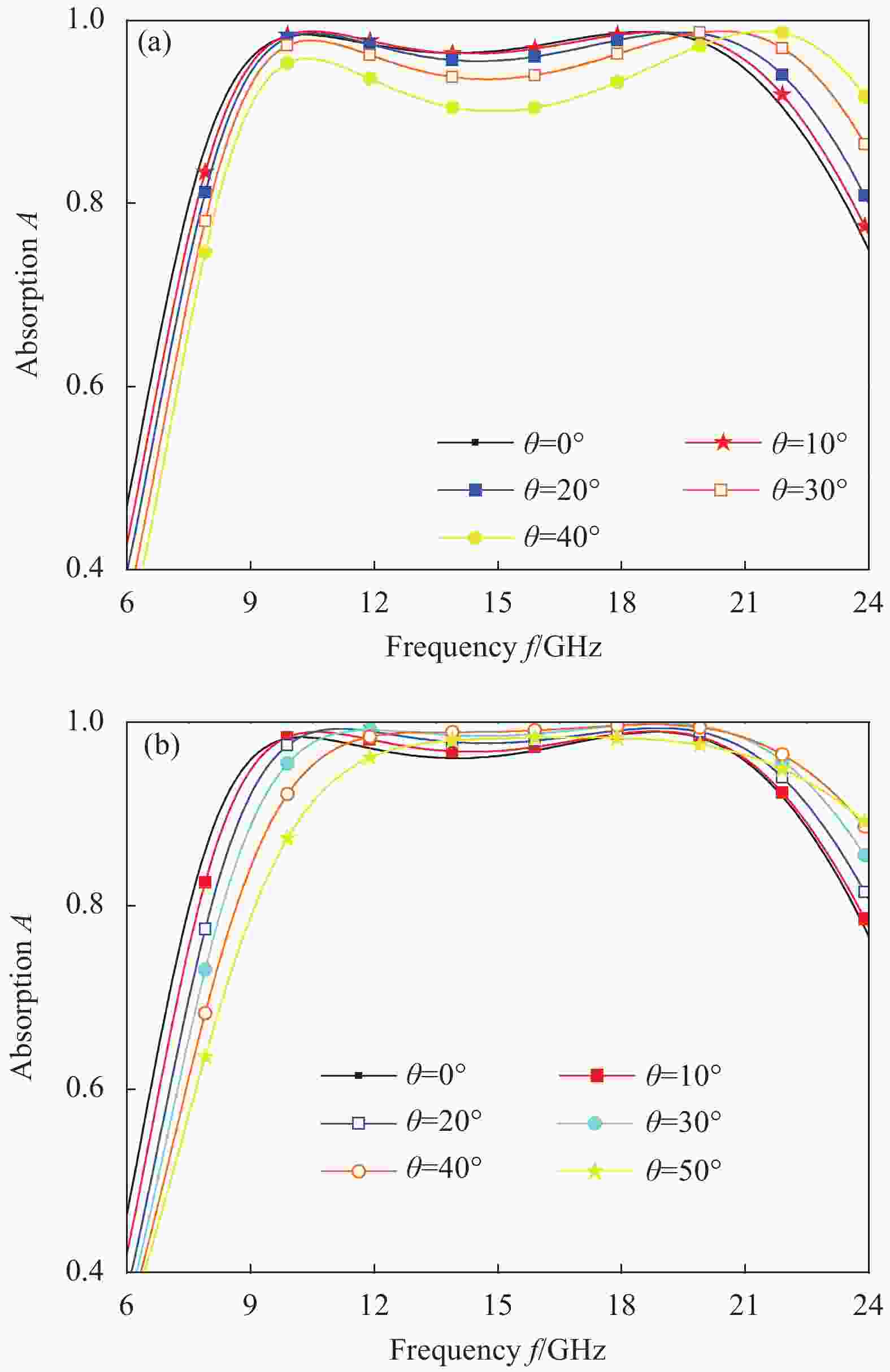
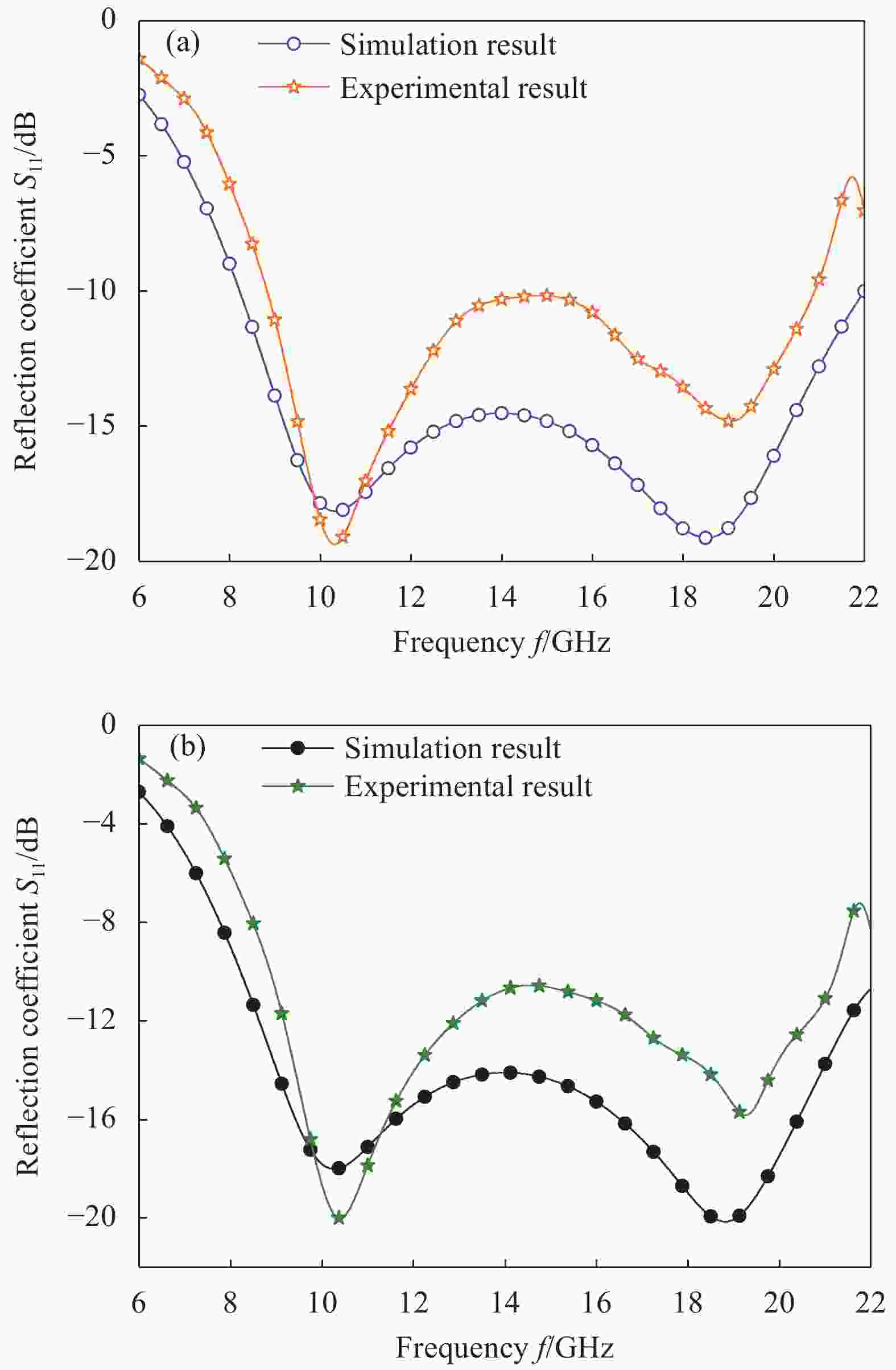
摘要: 超材料作为一种新型人工复合材料,因其独特的电磁特性,已成为物理学、材料学和电磁学界的研究热点。本文提出了一款兼具微波宽频吸收和透明、柔性特点的超材料。该反射型超材料共3层,分别为周期单元吸波层、介质基板和反射底板。基于阻抗匹配理论推导的吸波层阻抗匹配曲线,为宽频吸波优化设计提供了准确、高效的理论指导。仿真结果表明,当超材料总厚度仅为最大截止波长的0.091时,微波吸收率高于90%的频率范围为8.2~22 GHz,总带宽达13.8 GHz,相对带宽为91.4%,实现了微波宽频吸收。同时,由于周期单元为对称结构,该超材料对入射电磁波极化特性不敏感。另外,通过选用聚氯乙烯(PVC)和氧化铟锡(ITO)材料,该超材料还同时具备光学透明和柔性的特点,因此在武器装备的视窗雷达隐身和共形雷达隐身方面具有潜在的应用价值。Abstract: As a new type of artificial composite material, metamaterials have attracted numerous attentions in the fields of physics, materials science and electromagnetics for its unique electromagnetic properties. A transparent and flexible metamaterial with wideband microwave absorption properties was proposed in this work. The reflection-type metamaterial was composed of a microwave absorption layer, a dielectric substrate and a reflective backplane. The impedance matching curves of the microwave absorption layer was deduced based on the impedance matching theory to improve the accuracy and efficiency of the wideband optimization design. Simulated results show that absorption higher than 90% can be achieved in the frequency band ranging from 8.2-22 GHz, corresponding to a total wideband of 13.8 GHz. The relative bandwidth reaches up to 91.4%, realizing wideband absorption while the thickness of the metamaterial is only 0.091 times the upper-cutoff wavelength. In addition, the metamaterial absorber is insensitive to polarization angle since its unit cell is symmetrical. Moreover, by rationally selecting materials of polyvinyl chloride (PVC) and indium tin oxide (ITO), the metamaterial absorber in this work is optically transparent and flexible, thus quite suitable for window radar stealth and equipment conformal stealth.
-
Key words:
- new composite material /
- metamaterial /
- wideband absorption /
- transparent /
- flexible
-
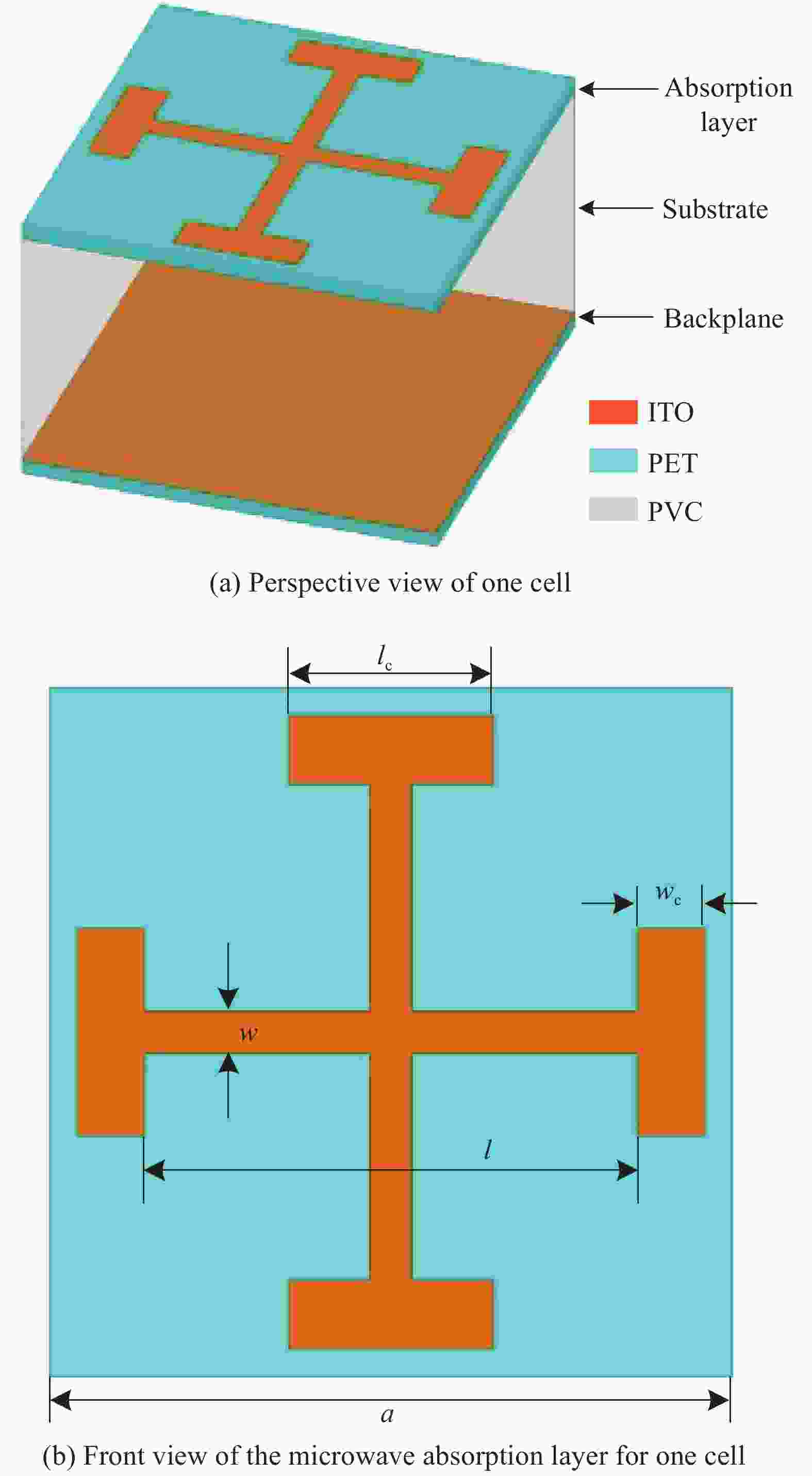
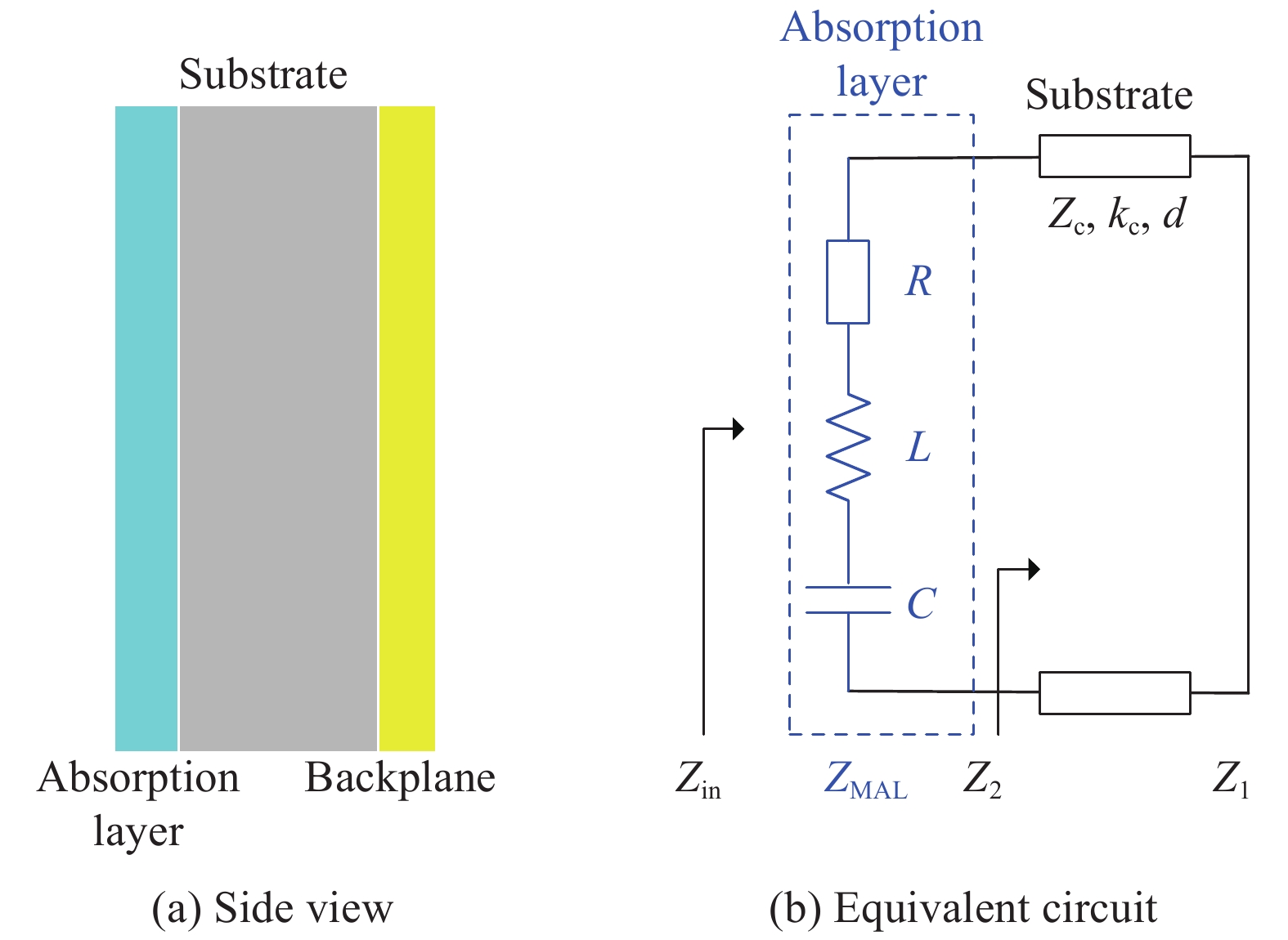
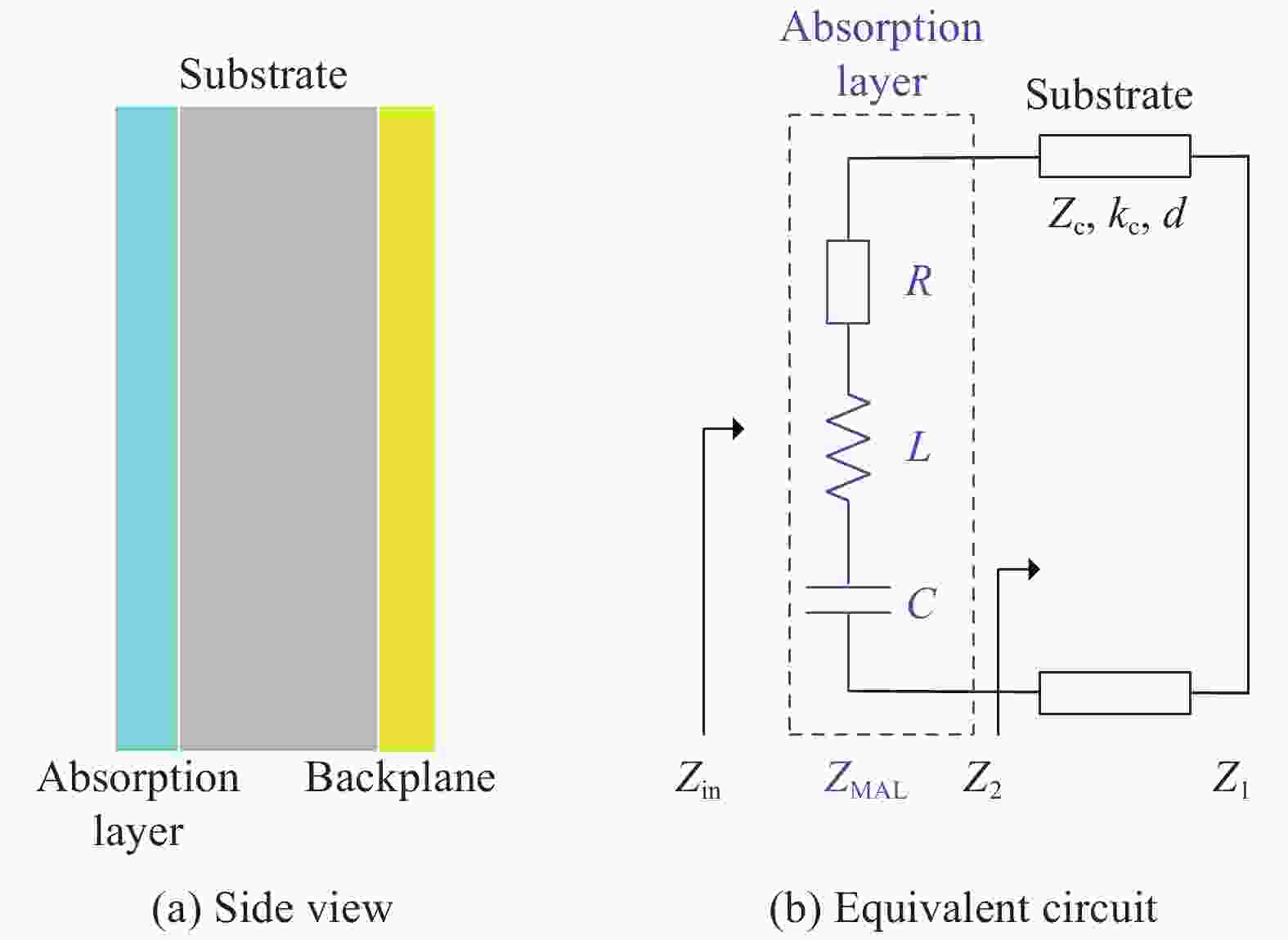
图 1 反射型超材料
Figure 1. Reflection-type metamaterial
Zin—Input impedance of the metamaterial absorber; ZMAL—Impedance of the absorption layer; R—Equivalent resistance; L—Equivalent inductance; C—Equivalent capacitance; Z2—Input impedance of the substrate; Z1—Impedance of the backplane; Zc— Characteristic impedance of the substrate; kc—Propagation constant of the substrate; d—Thickness of the substrate
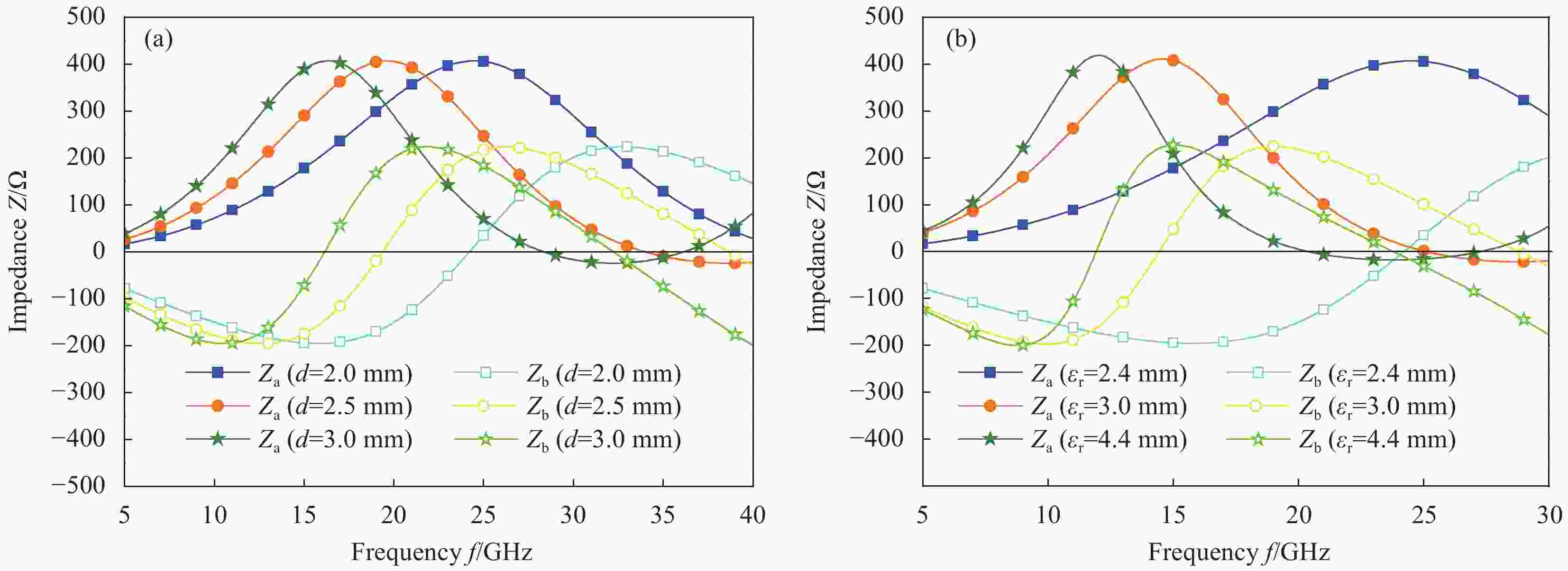
图 2 吸波层理想阻抗随介质板厚度 (a) 和介质板介电常数 (b) 实部变化曲线
Figure 2. Ideal impedance of the microwave absorption layer as a function of thickness of the dielectric substrate (a) and the real part of relative dielectric constant (b) of the dielectric substrate
Za—Real part of the ideal impedance of the absorbing layer; Zb—Imaginary part of the ideal impedance of the absorbing layer; d—Thickness of dielectric substrate
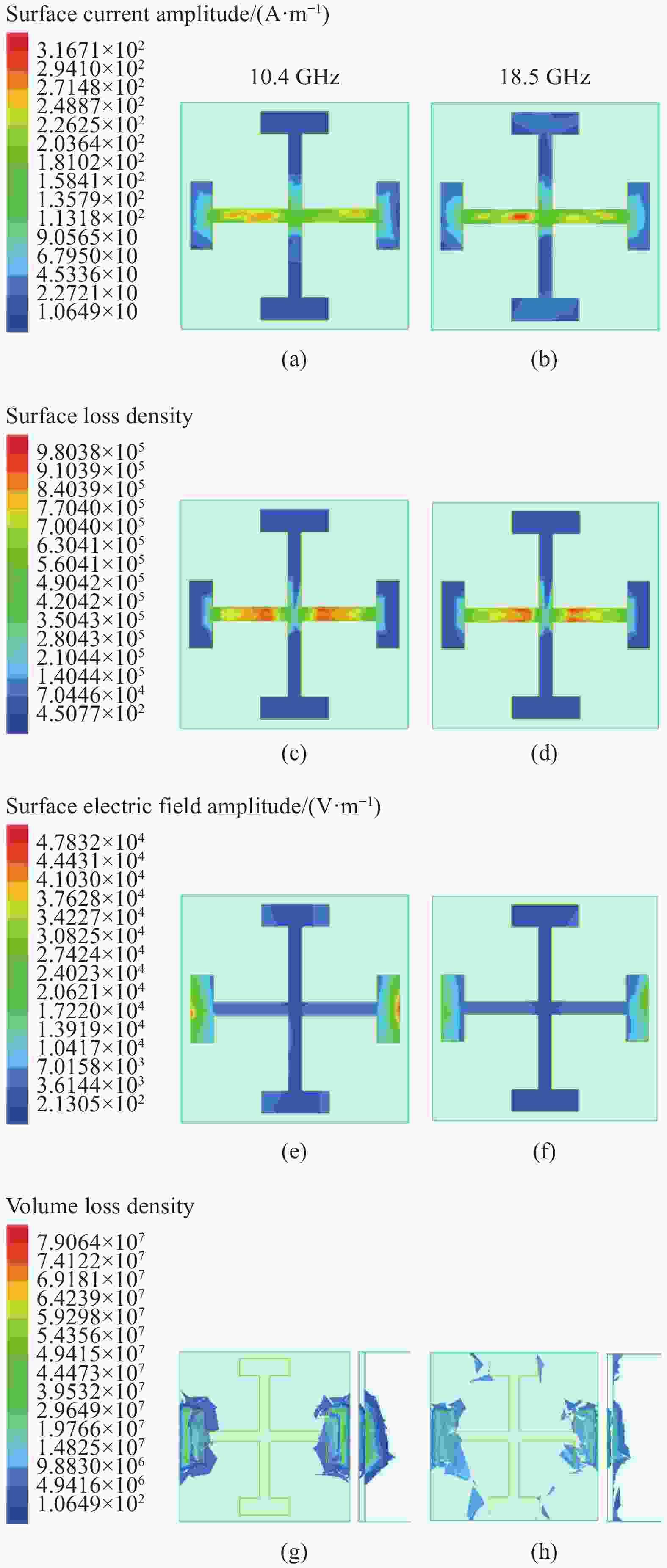
图 7 平面波垂直入射时超材料在10.4 GHz和18.5 GHz的电磁响应:((a)、(b)) 面电流幅值 J;((c)、(d)) 面损耗密度;((e)、(f)) 面电场幅值E;((g)、(h)) 体损耗密度
Figure 7. Electromagnetic responses of the metamaterial under the plane wave normal incidence at 10.4 GHz and 18.5 GHz: ((a), (b)) Magnitude of the surface current J; ((c), (d)) Surface loss density; ((e), (f)) Magnitude of the surface electric field E; ((g), (h)) Top views (left) and side views (right) of volume loss density
表 1 本文与相关文献超材料性能比较
Table 1. Performance comparison between the metamaterial absorber in this work and its counterparts
References Bandwidth (absorption higher than 90%) Relative bandwidth/% Thickness/mm Flexibility Transparency [19] 7.8-14.7(6.9) 61.3 5 No No [21] 5.8-12.2(6.4) 71.1 4.9 Yes Yes [23] 7-12.8(5.8) 58.6 3.4 No No [24] 4.3-18.7(14.4) 125.2 5.8 No Yes [26] 6-16.5(10.5) 93 4 Yes Yes [34] 7.6-12.8(5.2) 51 2 No No This work 8.2-22(13.8) 91.4 3 Yes Yes -
[1] CUI T J, SMITH D R, LIU R P. Metamaterials: Theory, design and application[M]. NY: Springer, 2010: 2. [2] 冯一军, 朱博, 徐培华, 等. 电磁超材料在微波吸波材料中的应用探索[J]. 中国材料进展, 2013, 32(8):473-479.FENG Yijun, ZHU Bo, XU Peihua, et al. Exploration on metamaterial applications to microwave absorbers[J]. Mateials China,2013,32(8):473-479(in Chinese). [3] 赵晓鹏, 刘亚红. 微波超材料与超表面中波的行为[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2016: 26-40.ZHAO Xiaopeng, LIU Yahong. Behaviors of microwave in metamaterials and metasurfaces[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2016: 26-40(in Chinese). [4] 罗先刚. 亚波长电磁学(下册)[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2017: 118-144.LUO Xian'gang. Sub-wavelength electromagnetics (Vol. 2)[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2017: 118-144(in Chinese). [5] 吕通, 张辰威, 刘甲, 等. 吸波超材料研究进展[J]. 复合材料学报, 2021, 38(1):25-35.LV Tong, ZHANG Chenwei, LIU Jia, et al. Research progress in metamaterial absorber[J]. Acta Materiae Compo-sitae Sinica,2021,38(1):25-35(in Chinese). [6] CHEN H T, TAYLOR A J, YU N. A review of metasurfaces: Physics and applications[J]. Reports on Progress in Physics,2016,79:076401. doi: 10.1088/0034-4885/79/7/076401 [7] LI A B, SINGH S, SIEVENPIPER D. Metasurfaces and their applications[J]. Nanophotonics,2018,7(6):989-1011. doi: 10.1515/nanoph-2017-0120 [8] 贺敬文, 董涛, 张岩. 太赫兹波前调制超表面器件研究进展[J]. 红外与激光工程, 2020, 49(9):20201033. doi: 10.3788/IRLA20201033HE Jingwen, DONG Tao, ZHANG Yan. Development of metasurfaces for wavefront modulation in terahertz waveband[J]. Infrared and Laser Engineering,2020,49(9):20201033(in Chinese). doi: 10.3788/IRLA20201033 [9] 唐小燕, 柯友煌, 井绪峰, 等. 基于透射型几何相位编码超表面的太赫兹波束自由操控[J]. 光子学报, 2021, 50(1):0116002.TANG Xiaoyan, KE Youhuang, JING Xufeng, et al. Free manipulation of terahertz wave based on the transmission type geometric phase coding metasurface[J]. Acta Photonica Sinica,2021,50(1):0116002(in Chinese). [10] AKRAM M R, DING G W, CHEN K, et al. Ultrathin single layer metasurfaces with ultra-wideband operation for both transmission and reflection[J]. Advanced Materials,2020,32(12):1907308. doi: 10.1002/adma.201907308 [11] LI Y, LIN J, GUO H J, et al. A tunable metasurface with switchable functionalities: From perfect transparency to perfect absorption[J]. Advanced Optical Materials,2020,8:1901548. doi: 10.1002/adom.201901548 [12] 李海鹏, 吴潇, 丁海洋, 等. 基于复合超构表面的宽带圆极化双功能器件设计[J]. 物理学报, 2021, 70(2):027803.LI Haipeng, WU Xiao, DING Haiyang, et al. Wideband circularly-polarized bifunction devices employing composite metasurfaces[J]. Acta Physica Sinica,2021,70(2):027803(in Chinese). [13] 商婷婷, 赵敏, 赵建平, 等. 基于极化转化超表面的雷达散射截面减缩[J]. 通信技术, 2021, 54(1):19-24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0802.2021.01.003SHANG Tingting, ZHAO Min, ZHAO Jianping, et al. Radar cross-section reduction based on polarization conversion metasurface[J]. Communications Technology,2021,54(1):19-24(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-0802.2021.01.003 [14] RAN Y Z, SHI L H, WANG J B, et al. Ultra-wide band linear-to-circular polarization converter with ellipse-shaped metasurfaces[J]. Optical Communication,2019,451:124-128. doi: 10.1016/j.optcom.2019.06.049 [15] ZHENG G X, MUHLENBERND H, KENNEY M, et al. Meta-surface holograms reaching 80% efficiency[J]. Nature Nano-technology,2015,10(4):308-312. doi: 10.1038/nnano.2015.2 [16] LANDY N I, SAJUYIGBE S, MOCK J J, et al. Perfect metamaterial absorber[J]. Physical Review Letters,2008,100:207402. doi: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.100.207402 [17] SHEN X P, CUI T J, ZHAO J M, et al. Polarization-independent wide-angle triple-band metamaterial absorber[J]. Optics Express,2011,19(10):9401. doi: 10.1364/OE.19.009401 [18] LI H, YUAN L H, ZHOU B, et al. Ultrathin multiband gigahertz metamaterial absorbers[J]. Journal of Applied Physics,2011,110:014909. doi: 10.1063/1.3608246 [19] DING F, CUI Y X, GE X C, et al. Ultra-broadband microwave metamaterial absorber[J]. Applied Physics Letters,2012,100:103506. doi: 10.1063/1.3692178 [20] 蒲明博. 亚波长结构材料的宽带频率响应特性研究[D]. 北京: 中国科学院大学, 2013.PU Mingbo. Study on the broadband frequency response of subwavelength metamaterial[D]. Beijing: University of Chinese Academy of Science, 2013(in Chinese). [21] JANG T, YOUN H, SHIN Y J, et al. Transparent and flexible polarization-independent microwave broadband absorber[J]. ACS Photonics,2014,1:279-284. doi: 10.1021/ph400172u [22] 张辉彬. 基于电磁谐振的宽频周期吸波结构设计[D]. 成都: 电子科技大学, 2010.ZHANG Huibin. Design of broadband periodic absorbing structure based on electromagnetic resonances[D]. Chengdu: University of Electronic Science and Technology of China, 2010(in Chinese). [23] NGUYEN T T, LIM S. Angle- and polarization-insensitive broadband metamaterial absorber using resistive fan-shaped resonators[J]. Applied Physics Letters,2018,112:021605. doi: 10.1063/1.5004211 [24] MIN P P, SONG Z C, YANG L, et al. Transparent ultrawideband absorber based on simple patterned resistive meta-surface with three resonant modes[J]. Optics Express,2020,28(13):19518-19530. doi: 10.1364/OE.396812 [25] DENG G S, LV K, SUN H X, et al. An ultra-broadband and optically transparent metamaterial absorber based on multilayer indium-tin-oxide structure[J]. Journal of Physics D: Applied Physics,2021,54(16):165301. doi: 10.1088/1361-6463/abdb6a [26] DENG R X, ZHANG K, LI M L, et al. Targeted design, analysis and experimental characterization of flexible microwave absorber[J]. Materials and Design,2019,162:119-129. doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2018.11.038 [27] 江孝伟, 武华. 吸收波长和吸收效率可控的超材料吸收器[J]. 物理学报, 2021, 70(2):027804. doi: 10.7498/aps.70.20201173JIANG Xiaowei, WU Hua. Metamaterial absorber with controllable absorption wavelength and absorption efficiency[J]. Acta Physica Sinica,2021,70(2):027804(in Chinese). doi: 10.7498/aps.70.20201173 [28] ZHAO J, CHENG Q, CHEN J, et al. A tunable metamaterial absorber using varactor diodes[J]. New Journal of Physics,2013,15(4):43049-43059. doi: 10.1088/1367-2630/15/4/043049 [29] LI A B, LUO Z J, WAKATSUCHI H, et al. Nonlinear, active, and tunable metasurfaces for advanced electromagnetics applications[J]. IEEE Access,2017,5(99):27439-27452. [30] LI H Y, COSTA F, WANG Y, et al. A wideband multifunctional absorber/reflector with polarization-insensitive performance[J]. IEEE Transactions on Antennas and Propogation,2020,68(6):5033-5038. doi: 10.1109/TAP.2019.2957709 [31] ZHANG J, WEI X Z, RUKHLENKO I D, et al. Electrically tunable metasurface with independent frequency and amplitude modulations[J]. ACS Photonics,2020,7:265-271. [32] 院伟. 磁性吸波材料低频带宽拓展研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉理工大学, 2016.YUAN Wei. Extending the low-frequency absorption bandwidth of magnetic-based composites[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University of Technology, 2016(in Chinese). [33] 卫家. 吸收频率可调范围宽的铁氧体基超材料及其带宽拓展[D]. 武汉: 武汉理工大学, 2016.WEI Jia. Ferrite based metamaterial absorber with tunableabsorption in wide-range and its bandwidth extension[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University of Technology, 2016(in Chinese). [34] GAO H T, WANG J J, XU B C, et al. Broadband metamaterial absorber based on magnetic substrate and resistance rings[J]. Materials Research Express,2019,6:045803. doi: 10.1088/2053-1591/aaf988 [35] HE Z D, WU L W, LIU Y, et al. Ultrawide bandwidth and large-angle electromagnetic wave absorption based on triple-nested helix metamaterial absorbers[J]. Journal of Applied Physics,2020,127(17):174901. doi: 10.1063/5.0001885 [36] HE Z D, LU Y, WU L W, et al. Combination of EG/Fe/Fe3O4 composites and hollowed out chiral metamaterials toward ultrathin, ultralight, broadband, polarization-insensitive, and wide-angle absorbers[J]. Advanced Materials Interfaces,2020,7(13):2000219. [37] LI W, WU T L, WANG W, et al. Broadband patterned magnetic microwave absorber[J]. Journal of Applied Physics,2014,116(4):044110. doi: 10.1063/1.4891475 [38] LONG C, YIN S, WANG W, et al. Broadening the absorption bandwidth of metamaterial absorbers by transverse magnetic harmonics of 210 mode[J]. Scientific Reports,2016,6:21431. doi: 10.1038/srep21431 [39] LI W, WU T L, WANG W, et al. Integrating non-planar metamaterials with magnetic absorbing materials to yield ultra-broadband microwave hybrid absorbers[J]. Applied Physics Letters,2014,104(2):022903. doi: 10.1063/1.4862262 [40] HU D W, CAO J, LI W, et al. Optically transparent broadband microwave absorption metamaterial by standing-up closed-ring resonators[J]. Advanced Optical Materials,2017,5(13):1700109. doi: 10.1002/adom.201700109 [41] LI W, WEI J, WANG W, et al. Ferrite-based metamaterial microwave absorber with absorption frequency magnetically tunable in a wide range[J]. Materials and Design,2016,110:27-34. doi: 10.1016/j.matdes.2016.07.118 -





 下载:
下载: