Finite element analysis of the buckling of the liner of composite pressure vessel with depression
-
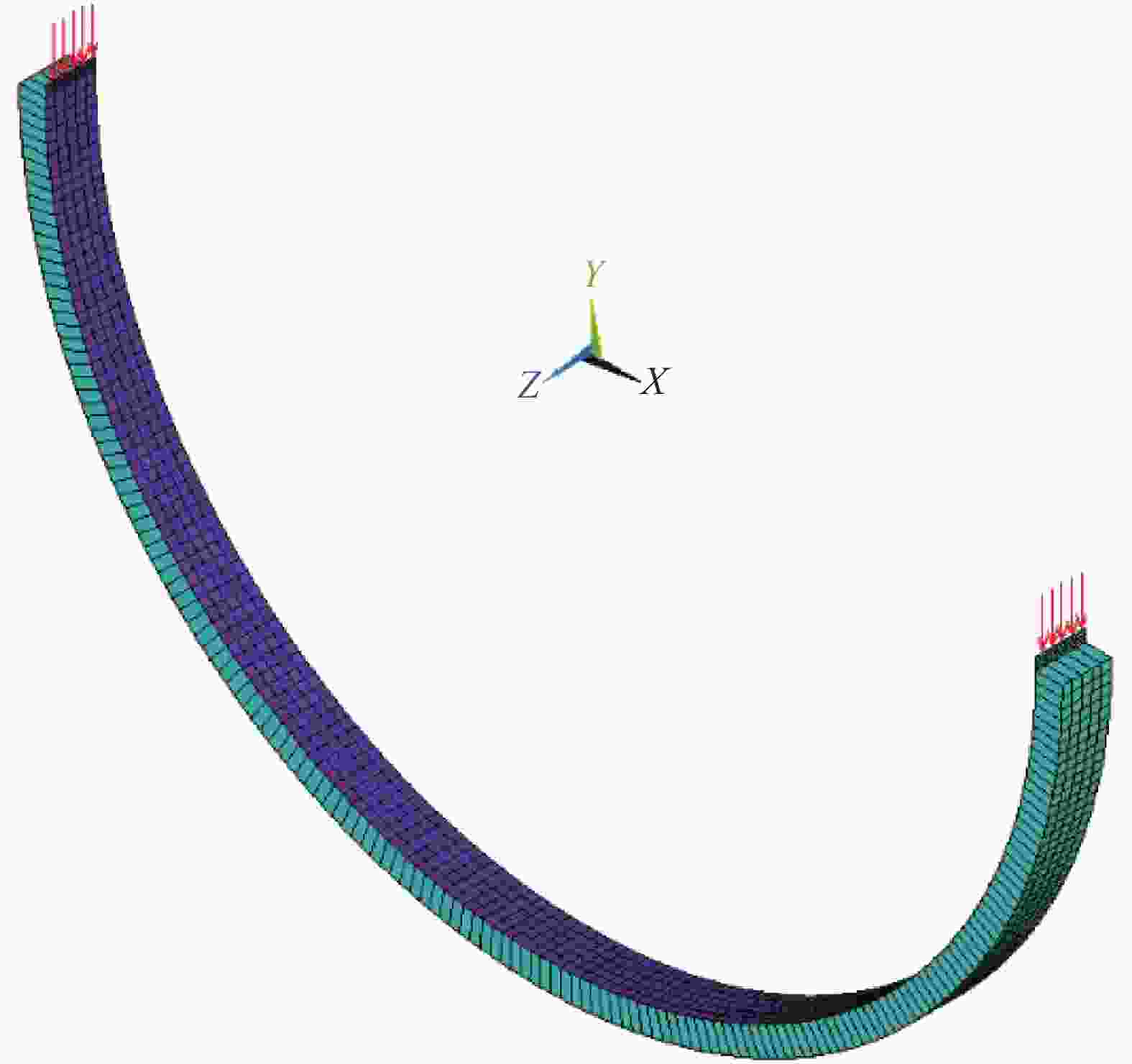
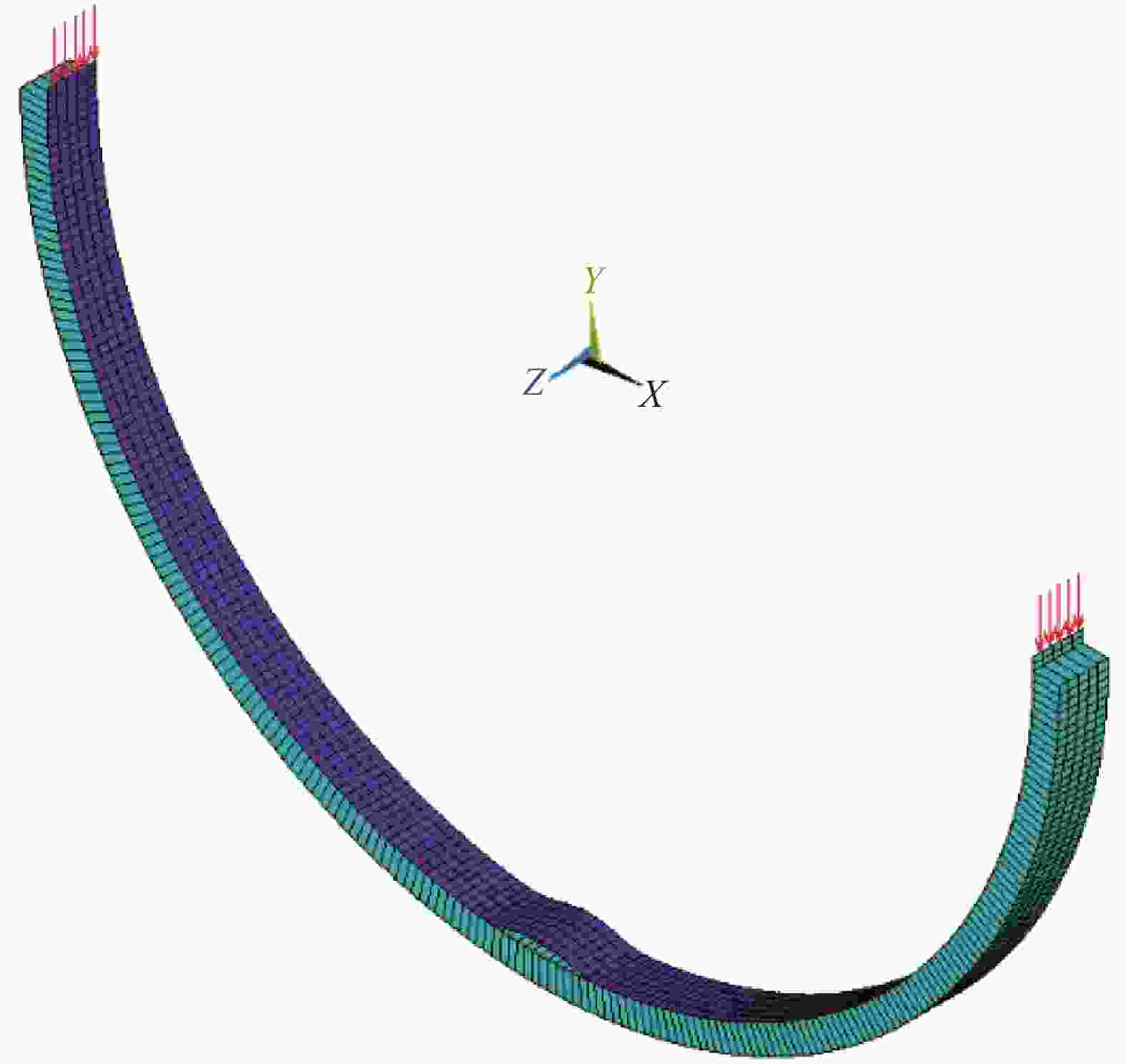
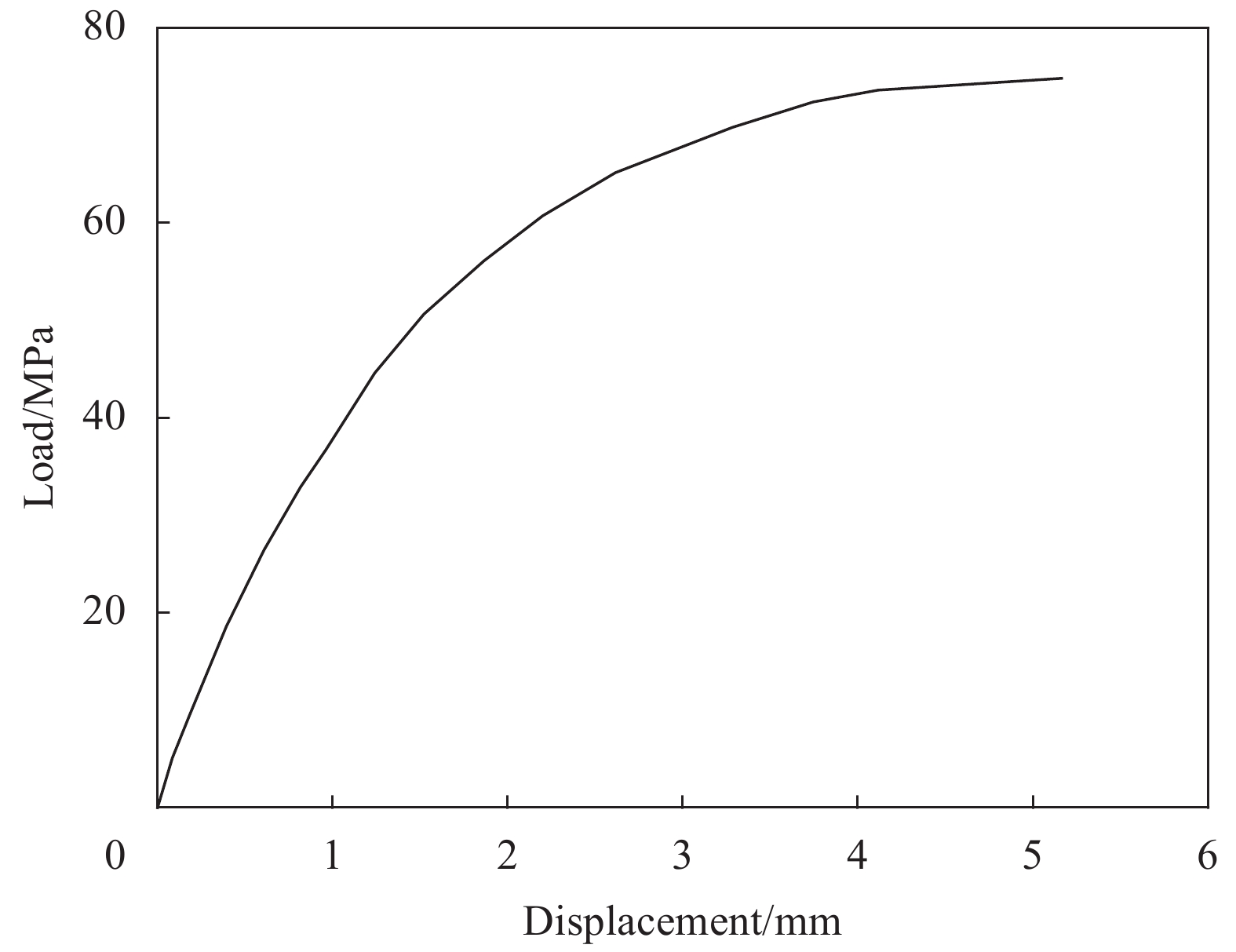
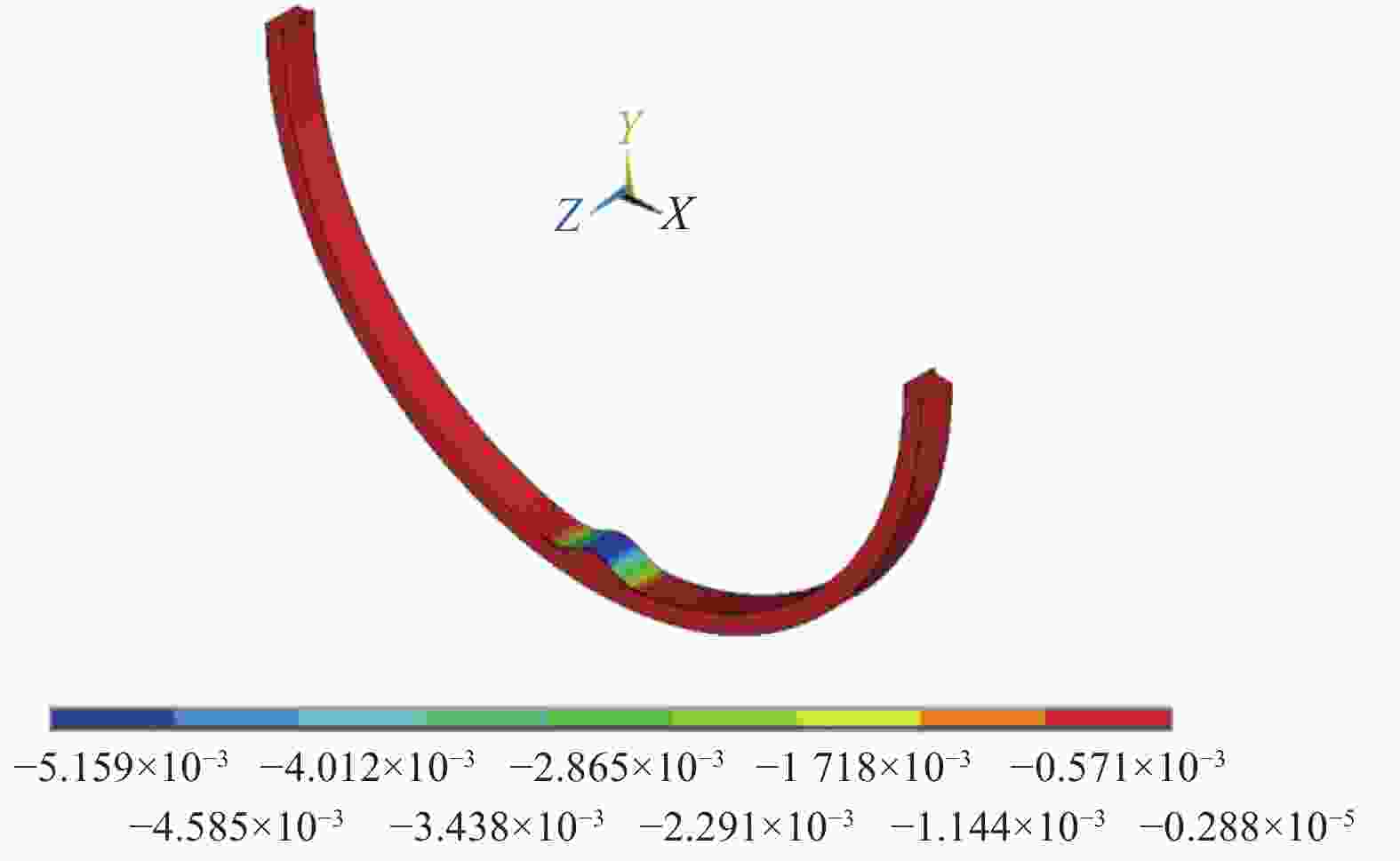
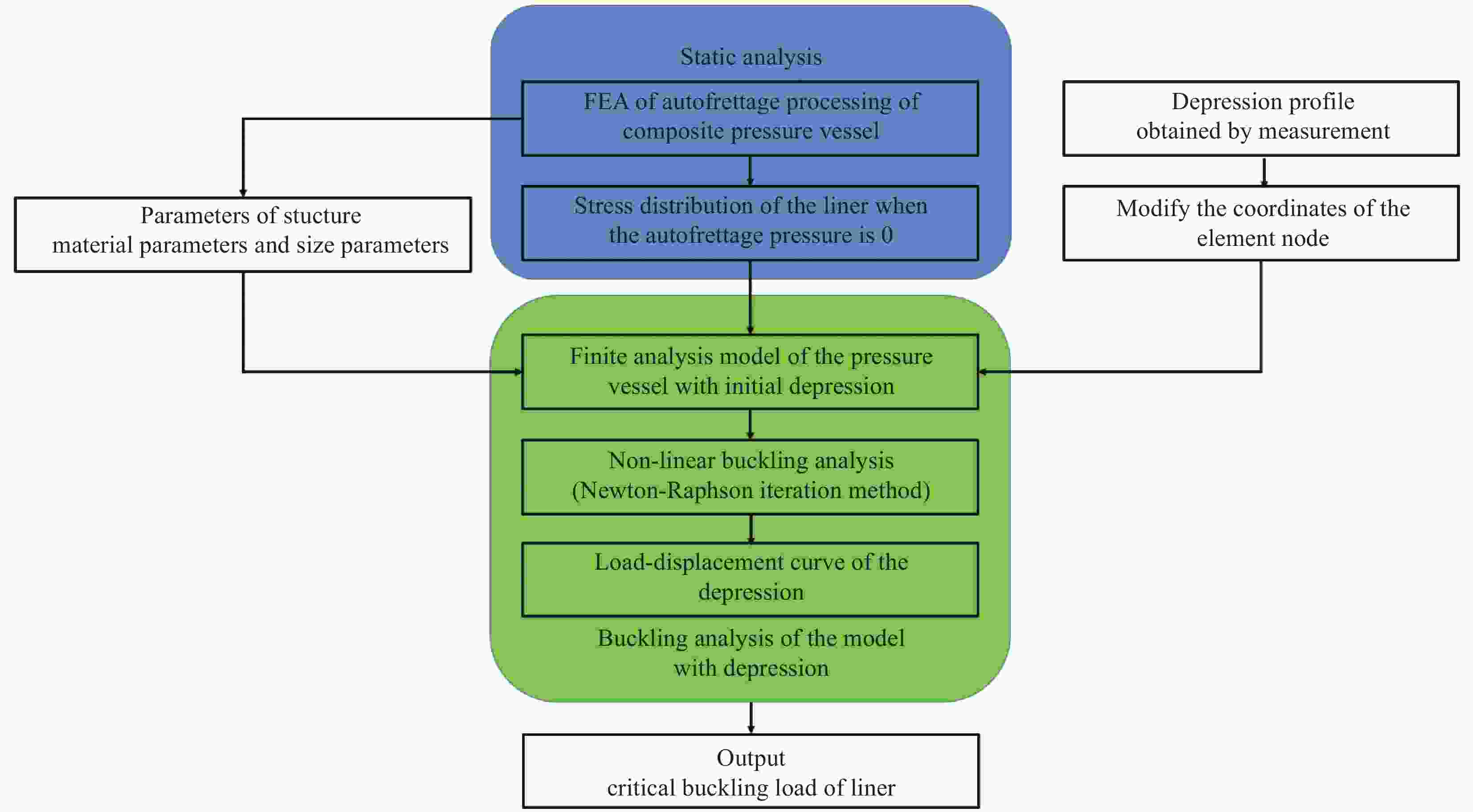
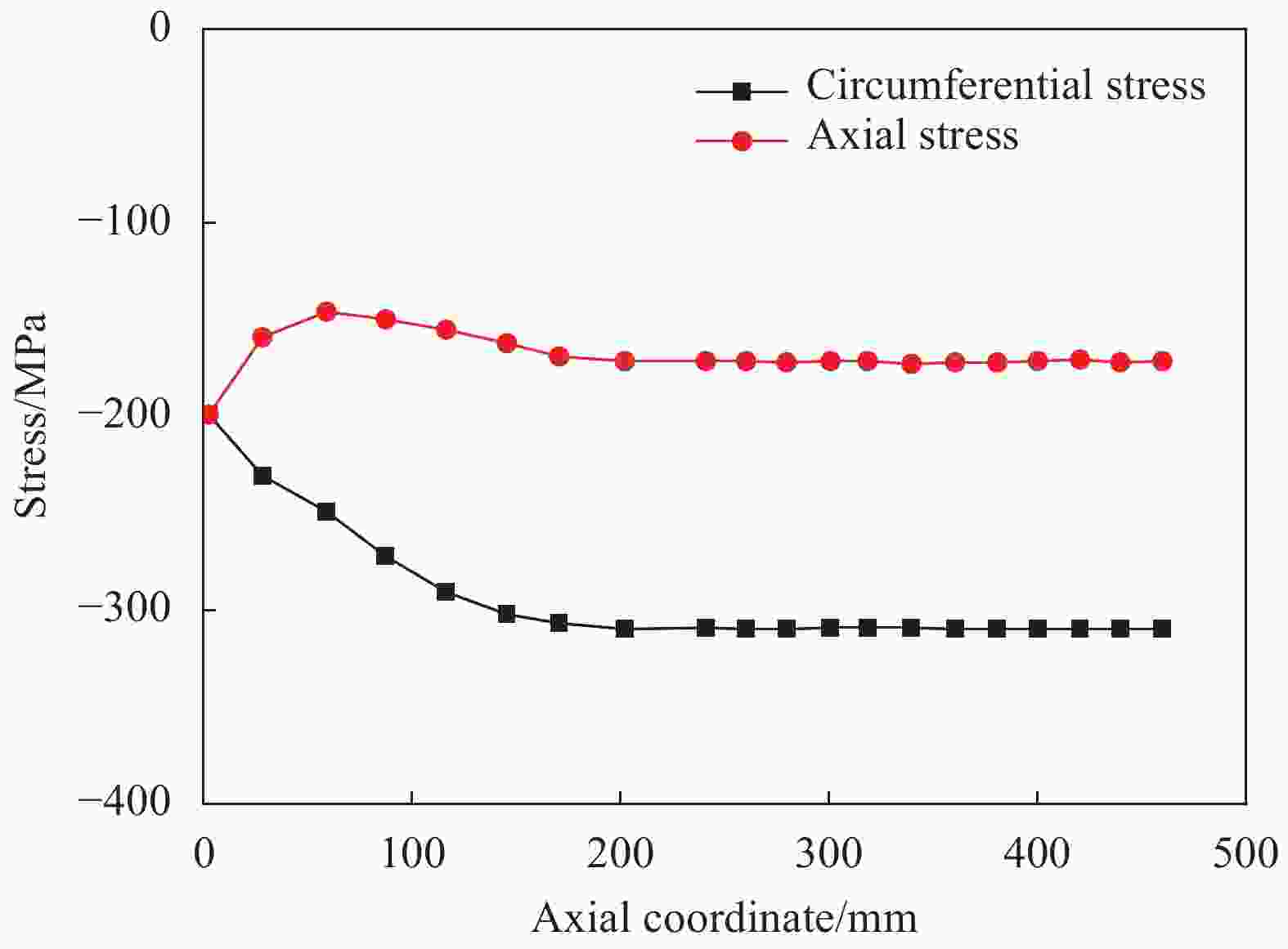
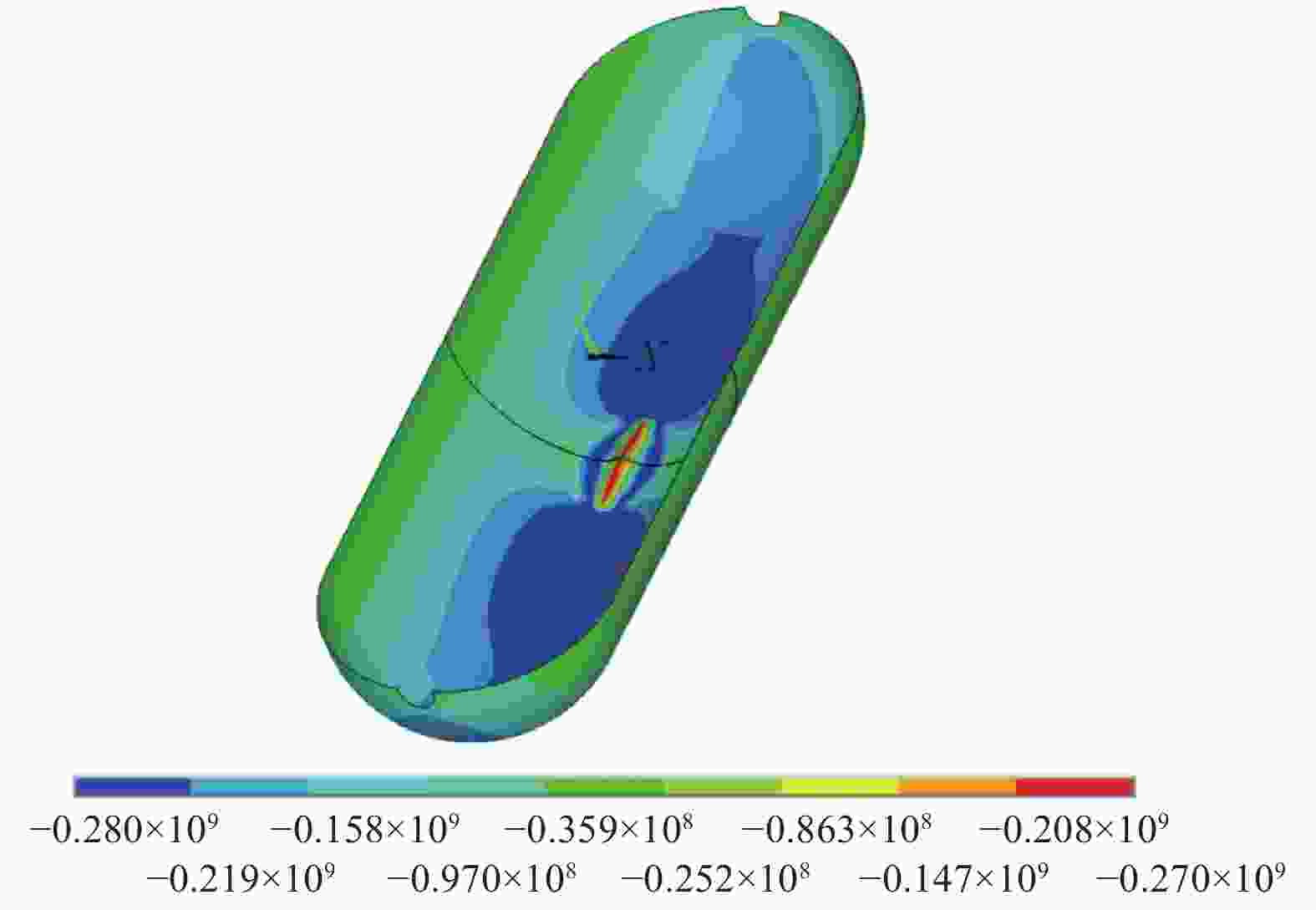
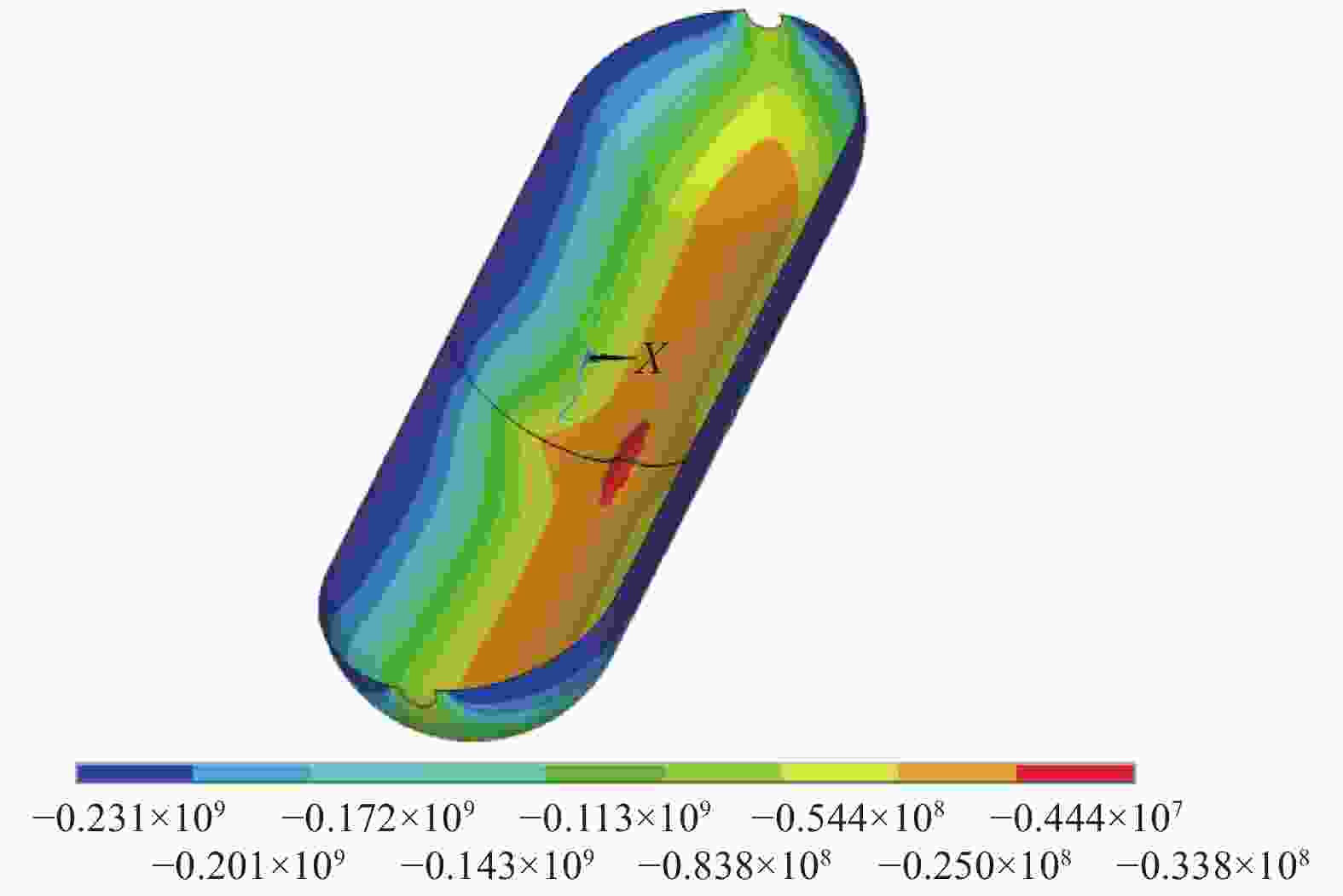
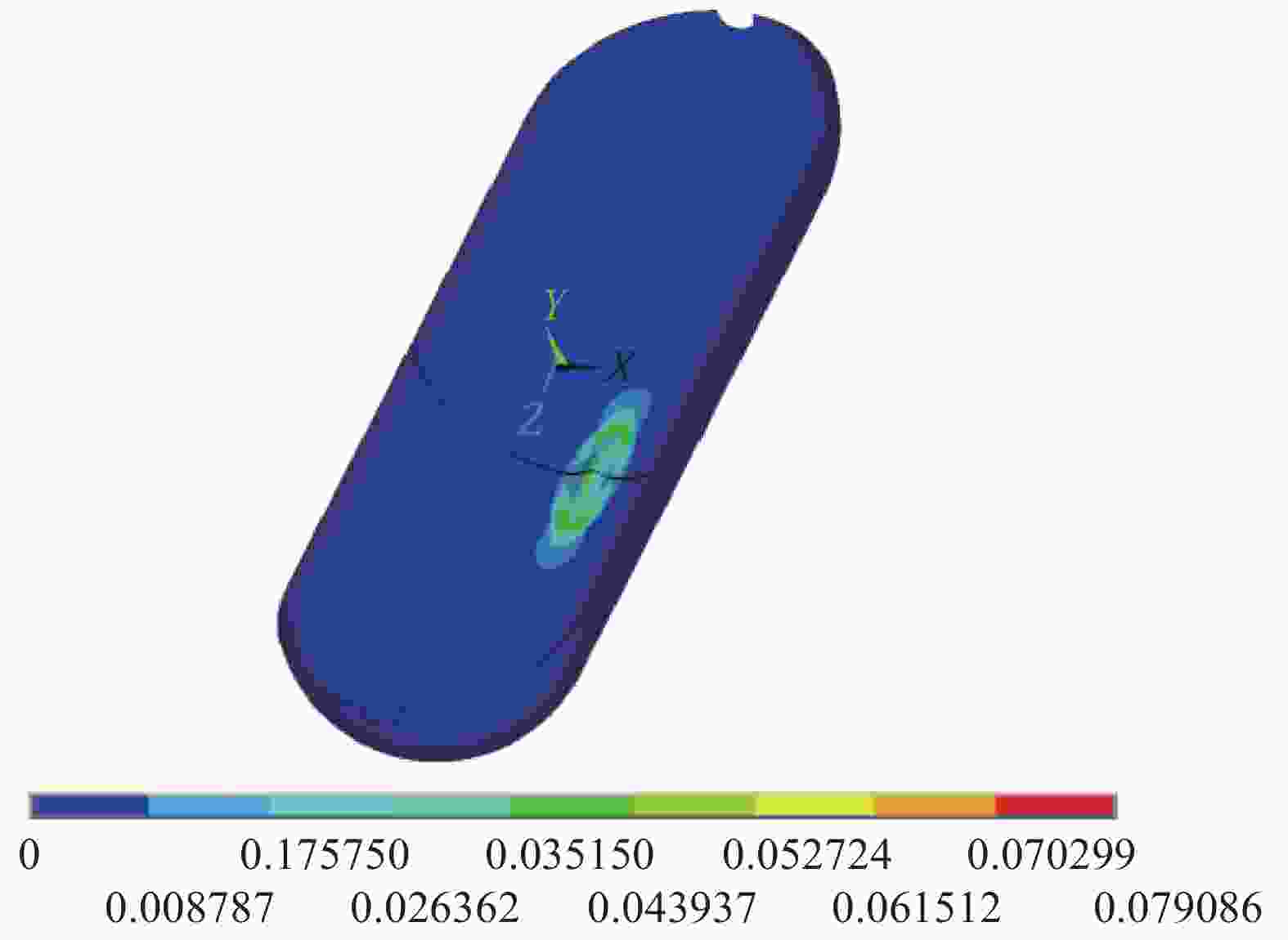
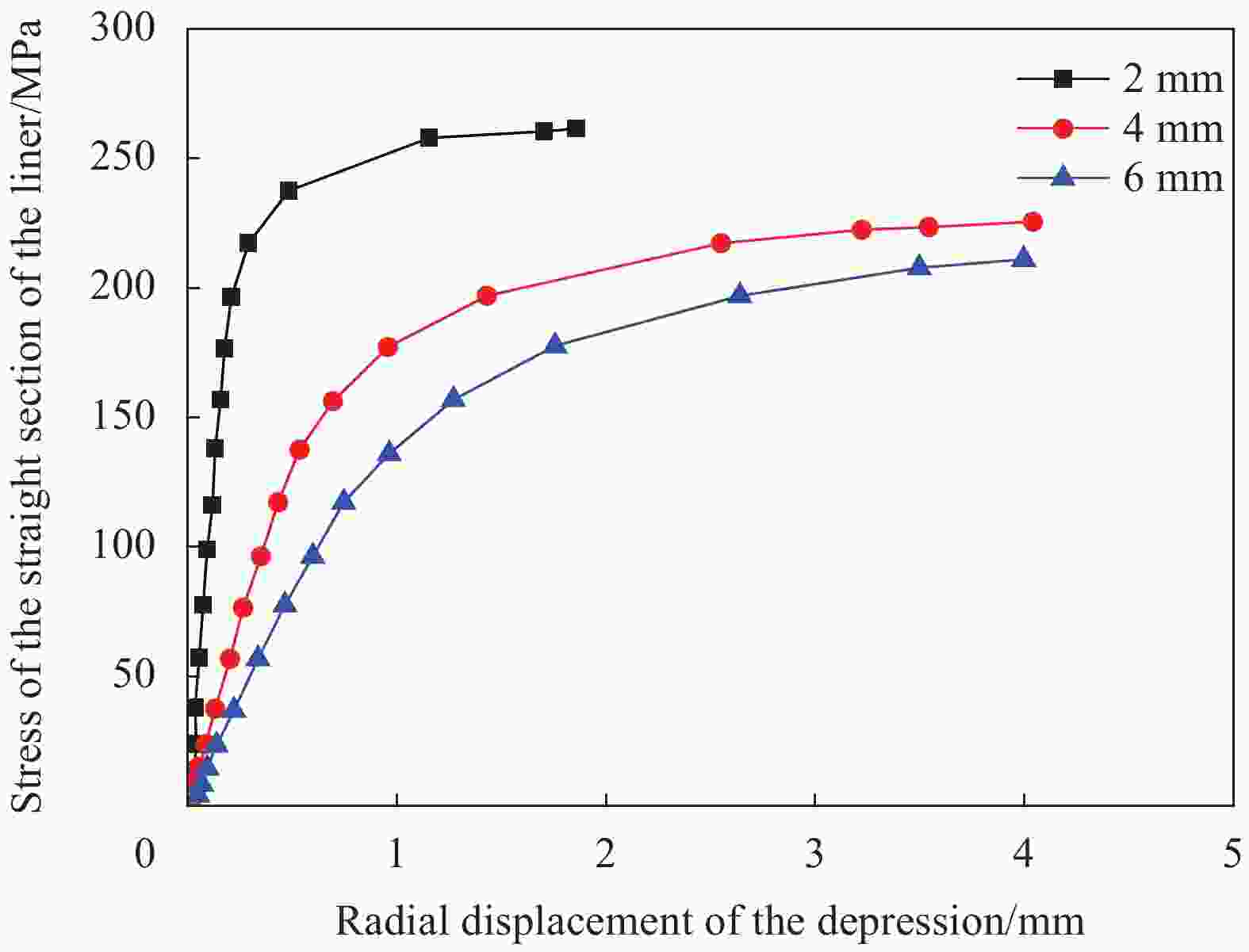
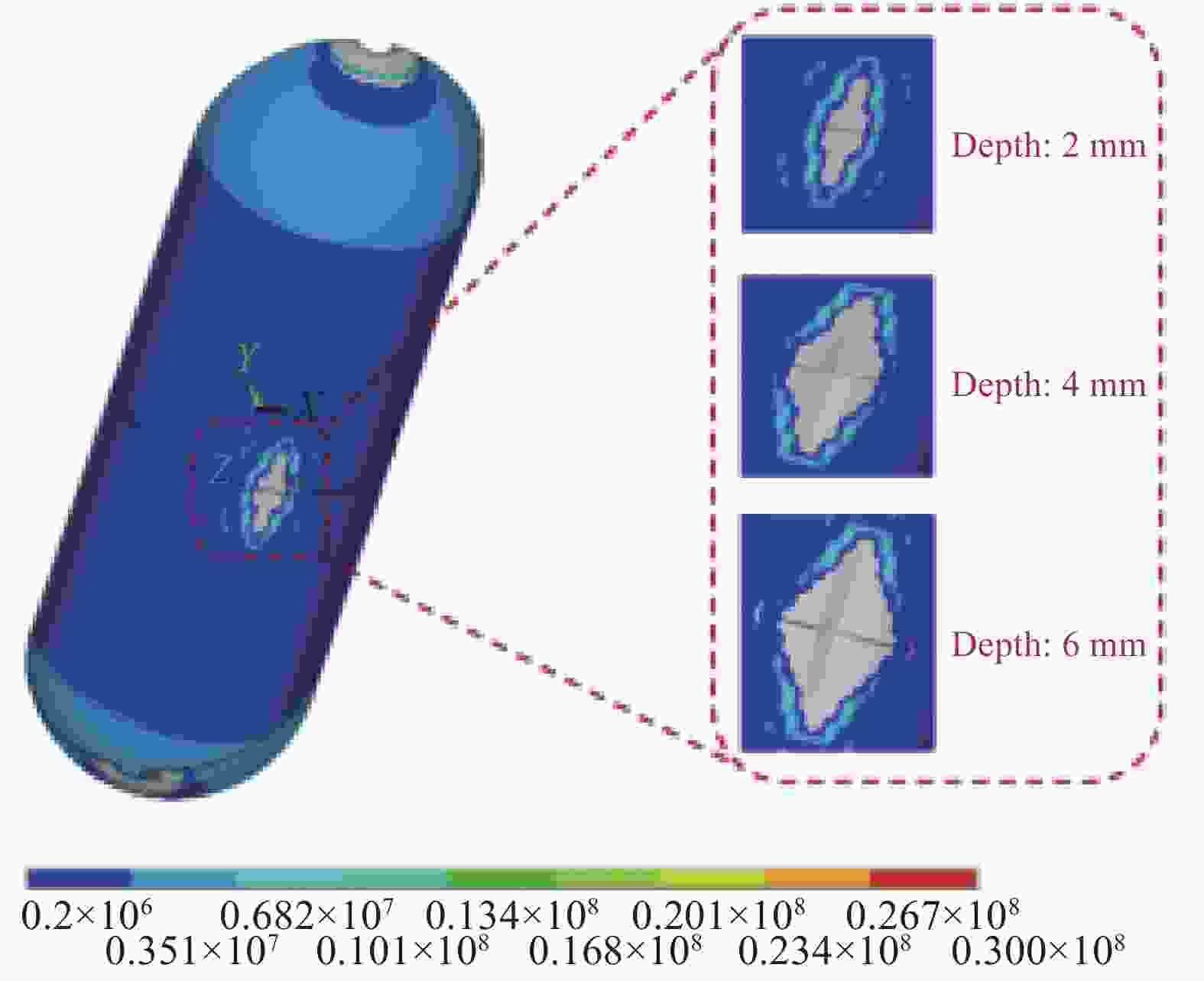
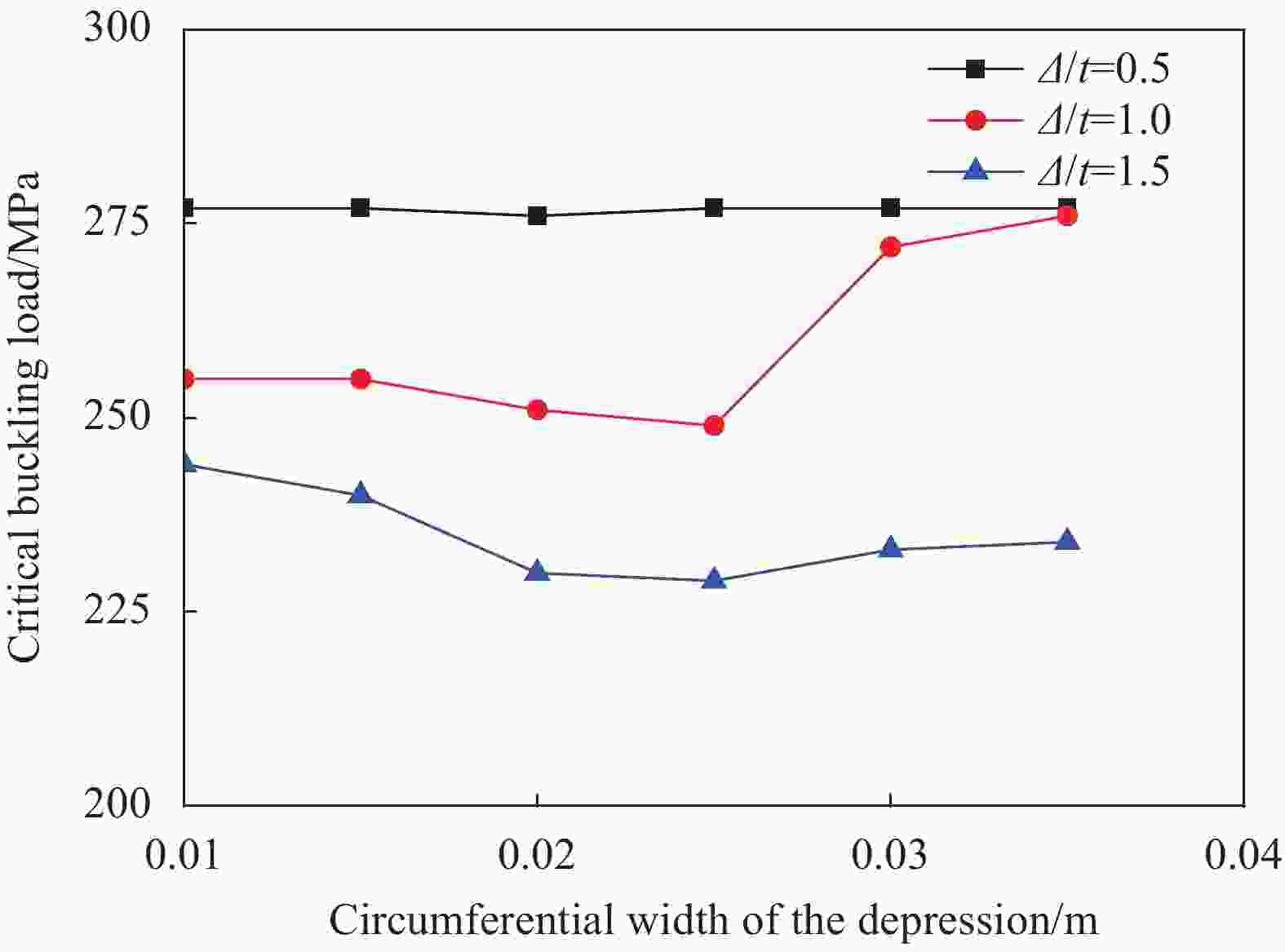
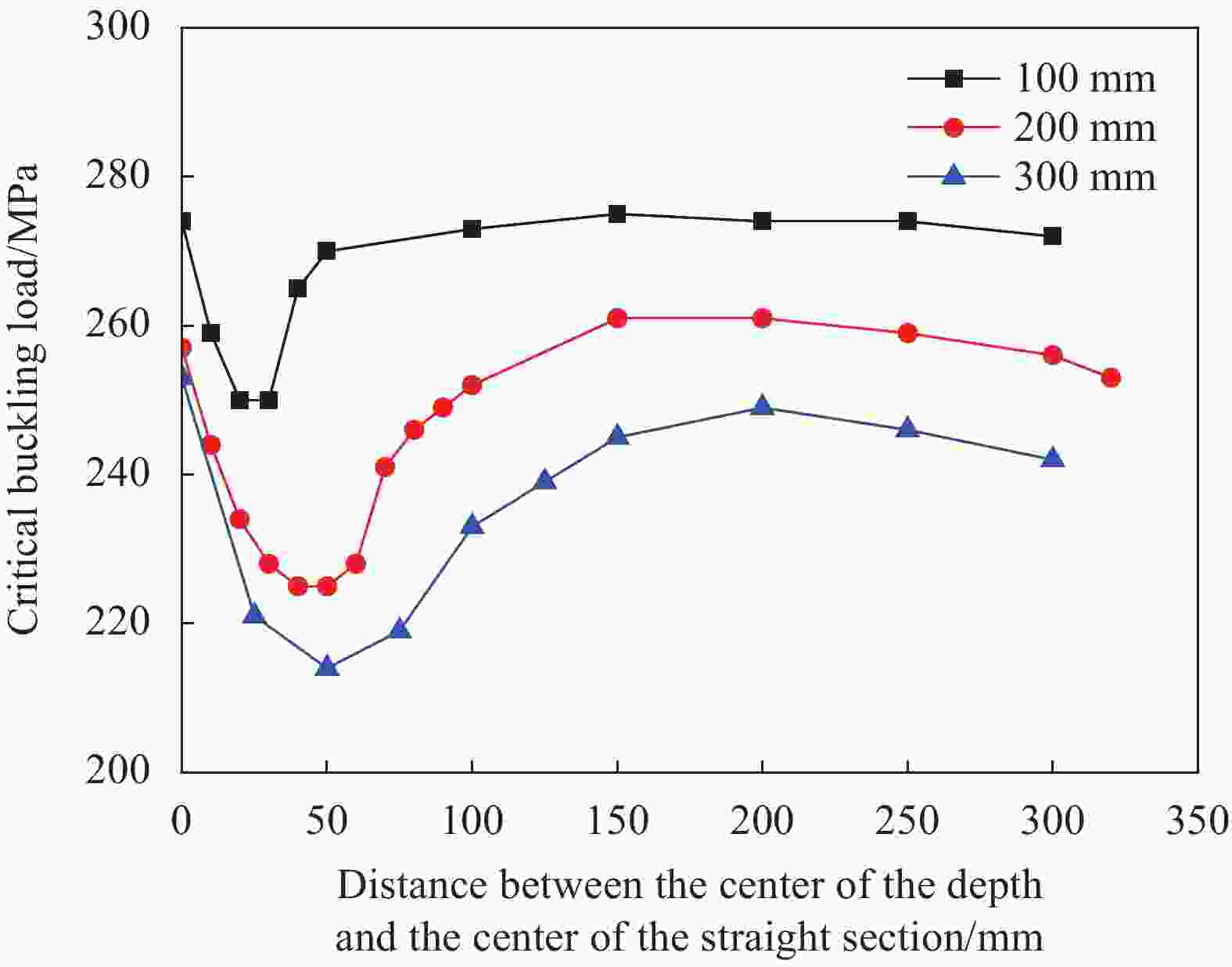
摘要: 提出了一种复合材料压力容器含凹陷金属内胆屈曲的三维有限元分析方法。基于平面应变假设,建立了含凹陷半圆环收缩屈曲分析模型,通过修改有限元模型中内胆的节点坐标,将内胆初始凹陷引入模型中,采用非线性迭代法逐步增大面内载荷,实现了含凹陷半圆环的收缩屈曲分析。在此基础上,建立复合材料压力容器含凹陷内胆的三维有限元分析模型,同时考虑自紧工艺后内胆残余应力的环向分量与轴向分量,实现了复合材料压力容器自紧工艺后含凹陷内胆的屈曲分析。以130 L球形封头薄壁铝合金内胆全缠绕复合材料压力容器为例,分析了含凹陷内胆的临界屈曲载荷以及屈曲发生时内胆的应力及变形。结果显示,含初始缺陷的内胆在自紧工艺之后屈曲模式为局部屈曲;初始凹陷深度越大,临界屈曲载荷越低;与直筒段中部的距离为凹陷轴向宽度1/2的区域和直筒段靠近封头的金属内胆区域存在凹陷易发生屈曲,是金属内胆的薄弱环节。Abstract: A method for buckling analysis of liner of composite pressure vessel with depression was proposed. Based on the assumption of plane strain, the shrinkage buckling analysis model of the semicircular ring with depress-ion was established, and the depression was introduced into the finite element analysis model by modifying the coordinates of nodes. The nonlinear iterative method was used to gradually increase the in-plane load, and the shrinkage buckling analysis of the semicircular ring with depression was analyzed. On this basis, a three-dimensional finite element analysis model of composite pressure vessel containing a liner with depression was established, the hoop and axial components of the residual stress of the liner after autofrettage was considered to analysis the buckling of the liner with depression after autofrettage of composite pressure vessel. Taking a 130 L spherical head and thin-walled aluminum alloy liner full-wound composite pressure vessel as an example, the critical buckling load of the liner and the stress and deformation of the liner when buckling occurred were analyzed. The results show that the buckling mode of the liner with initial depression after autofrettage is local buckling; the greater the initial depression depth, the lower the critical buckling load; the area where the distance from the middle of the straight section is 1/2 of the axial width of the depression and near the head of the straight section is prone to buckling, which is the weakness zone of the metal liner.
-
Key words:
- composite materials /
- pressure vessels /
- liner /
- buckling /
- finite element analysis
-
表 1 金属内胆材料的力学性能
Table 1. Mechanical properties of the metal liner material
Young’s modulus/GPa Poisson’s ratio Yield strength/MPa Ultimate strength/MPa 74 0.28 300 320 表 2 T300碳纤维/环氧树脂缠绕层的力学性能
Table 2. Mechanical properties of the winding T300 carbon fiber/epoxy layers
EX/GPa EY/GPa EZ/GPa μX μY μZ GXY/GPa GYZ/GPa GXZ/GPa 135 10 10 0.32 0.32 0.32 7 5 5 Notes: E, μ, G—Elastic modulus, Poisson’s ratio and shear modulus, respectively. -
[1] HWANG T K, PARK J B, KIM H G. Evaluation of fiber material properties in filament wound composite pressure vessels[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science & Manufacturing,2012,43(9):1467-1475. [2] LEI Z, WANG J, LI S. Influence of fiber slippage coefficient distributions on the geometry and performance of compo-site pressure vessels[J]. Polymer Composites,2016,37(1):315-321. doi: 10.1002/pc.23183 [3] HWANG T K, KIM H G. Experimental and analytical approach for the size effect on the fiber strength of CFRP[J]. Polymer Composites,2013,34(4):598-606. doi: 10.1002/pc.22461 [4] CEN International Standard. ISO111192 Gas cylinders of composite construction specification and test methods part 2 fully wrapped fiber reinforced composite gas cylinders with load sharing metal liners[S]. Switzerland: International Organization for Standardization, 2002. [5] 赫晓东, 王荣国, 矫维成, 等. 先进复合材料压力容器[M]. 北京: 科学出版社, 2016: 10-16.HE Xiaodong, WANG Rongguo, JIAO Weicheng, et al. Advanced composite pressure vessel[M]. Beijing: Science Press, 2016: 10-16(in Chinese). [6] BAI H, YANG B, HUI H, et al. Experimental and numerical investigation of the strain response of the filament wound pressure vessels subjected to pressurization test[J]. Polymer Composites,2019,40(5):4427-4441. [7] 郑传祥. 复合材料压力容器[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2006: 26-38.ZHENG Chuanxiang. Composite pressure vessel[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2006: 26-38(in Chinese). [8] 孙直, 任明法, 陈浩然. 含金属内衬的复合材料缠绕薄壁容器自紧设计的工程方法[J]. 复合材料学报, 2011, 28(2):217-221.SUN Zhi, REN Mingfa, CHEN Haoran. An engineering algorithm of autofrettage technique for composite overwrapped pressure vessels with metal inner[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2011,28(2):217-221(in Chinese). [9] 陈亮. 碳纤维复合材料缠绕气瓶数值分析[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2013.CHEN Liang. Numerical analysis of carbon fiber compo-site winding vessel[D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2013(in Chinese). [10] HU Z H, LIU H J, WANG R G, et al. The study on buckling deformation of composite pressure vessel based on acoustic emission signals[J]. Advanced Materials Research,2009,87/88:445-450. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/AMR.87-88.445 [11] OMARA A M, GUICE L K, STRAUGHAN W T, et al. Buckling models of thin circular pipes encased in rigid cavity[J]. Journal of Engineering Mechanics,1997,123(12):1294-1301. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)0733-9399(1997)123:12(1294) [12] CHICUREL R. Shrink buckling of thin circular rings[J]. Journal of Applied Mechanics,1968,35(3):608-610. doi: 10.1115/1.3601259 [13] VASILIKIS D, KARAMANOS S. Closure to “more on mechanics of confined thin-walled cylinders subjected to external pressure”[J]. Applied Mechanics Reviews,2013,66(1):1-15. [14] 王荣国, 赫晓东, 胡照会, 等. 超薄金属内衬复合材料压力容器的结构分析[J]. 复合材料学报, 2010, 27(4):135-142.WANG Rongguo, HE Xiaodong, HU Zhaohui, et al. Structure analysis of composite pressure vessel with ultra-thin metallic liner[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2010,27(4):135-142(in Chinese). [15] 陈亮, 孙红卫, 陈国清, 等. 碳纤维缠绕复合气瓶自紧力和疲劳的数值模拟[J]. 宇航材料工艺, 2012, 42(4):16-20. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2330.2012.04.004CHEN Liang, SUN Hongwei, CHEN Guoqing, et al. Numerical simulation of autofrettage and fatigue of filament wound pressure vessel[J]. Aerospace Materials and Technology,2012,42(4):16-20(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-2330.2012.04.004 [16] SUN C, SHAW W, VINOGRADOV A M. One-way buckling of circular rings confined within a rigid boundary[J]. Journal of Pressure Vessel Technology,1995,117(2):162-169. doi: 10.1115/1.2842105 [17] EL-SAWY K M, SWEEDAN A M I. Effect of local wavy imperfections on the elastic stability of cylindrical liners sub-jected to external uniform pressure[J]. Tunnelling and Underground Space Technology,2010,25(6):702-713. doi: 10.1016/j.tust.2010.04.002 [18] PHOENIX S, KEZIRIAN M. Analysis of potential Ti-liner buckling after proof in kevlar/epoxy COPV[C]. California:AIAA/ASME/ASCE/AHS/ASC Structures, Structural Dyna-mics, & Materials Conference, 2006: 1-25. [19] 徐坤山, 仇性启, 魏仁超. 压力容器原始制造缺陷危害性分析[J]. 机械设计与制造, 2015, 11(11):21-25. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3997.2015.11.006XU Kunshan, QIU Xingqi, WEI Renchao. Perniciousness analysis of original manufacturing defects in pressure vessel[J]. Machinery Design & Manufacture,2015,11(11):21-25(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3997.2015.11.006 [20] 周丹. 铝内衬碳纤维全缠绕复合材料气瓶结构分析与优化设计[D]. 武汉: 武汉理工大学, 2016.ZHOU Dan. Structure analysis and optimized design of fully wrapped carbon-fiber reinforced aluminum lined composite gas cylinder[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University of Technology, 2016(in Chinese). -






 下载:
下载: