Preparation and application of Fmoc-Dphenylalanine/hyaluronic acid composite double-network hydrogel
-
摘要:
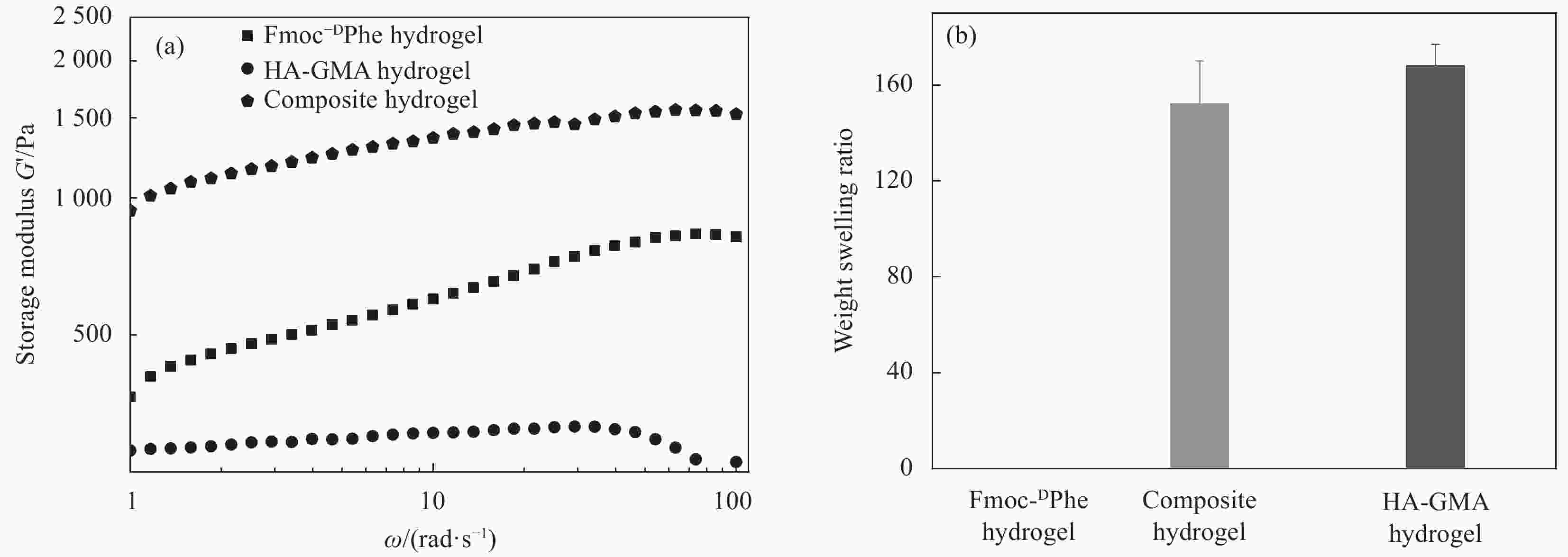
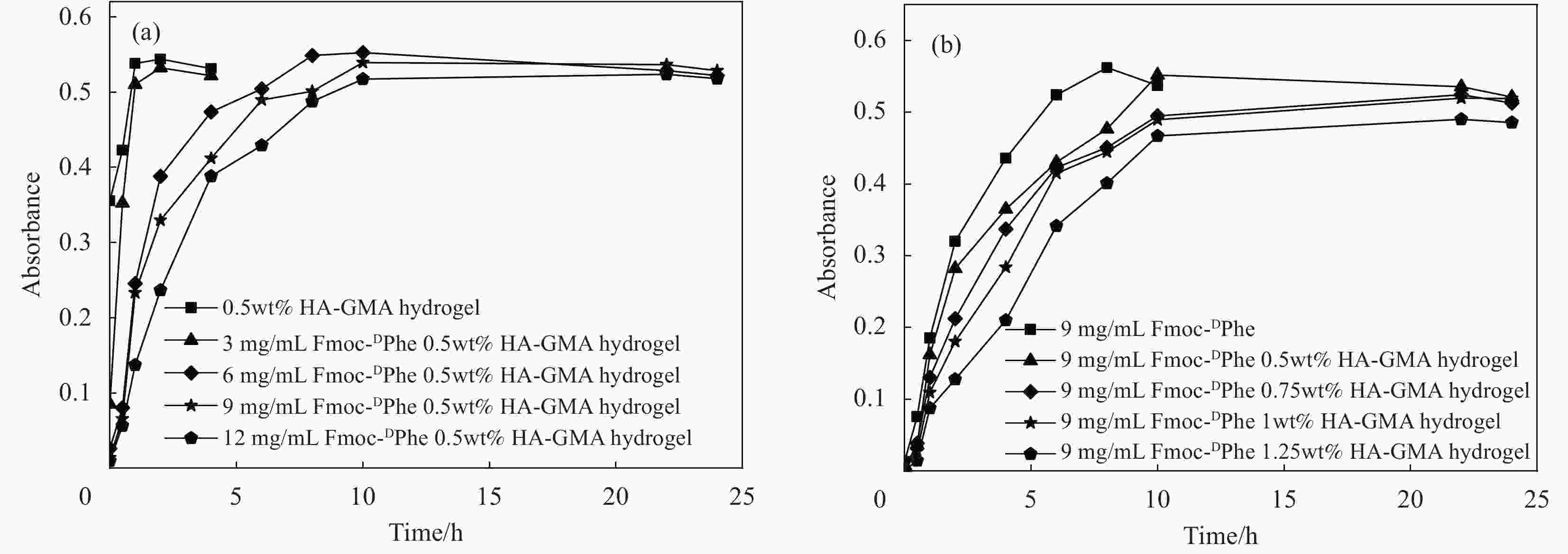
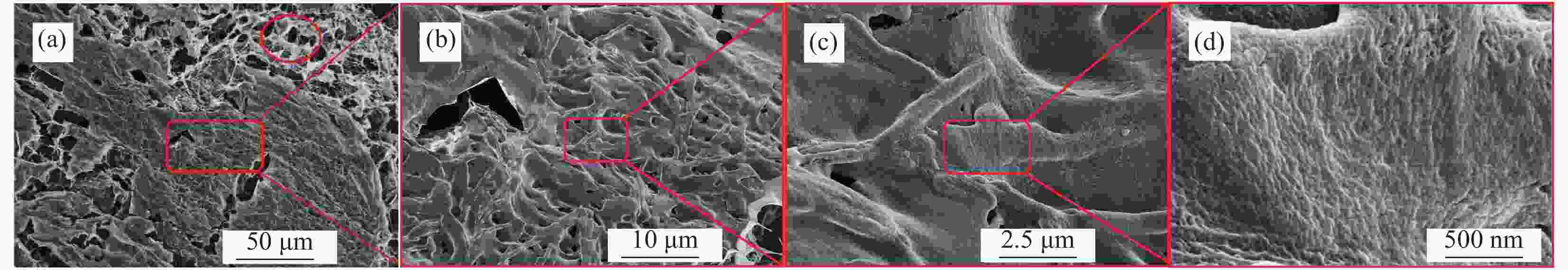
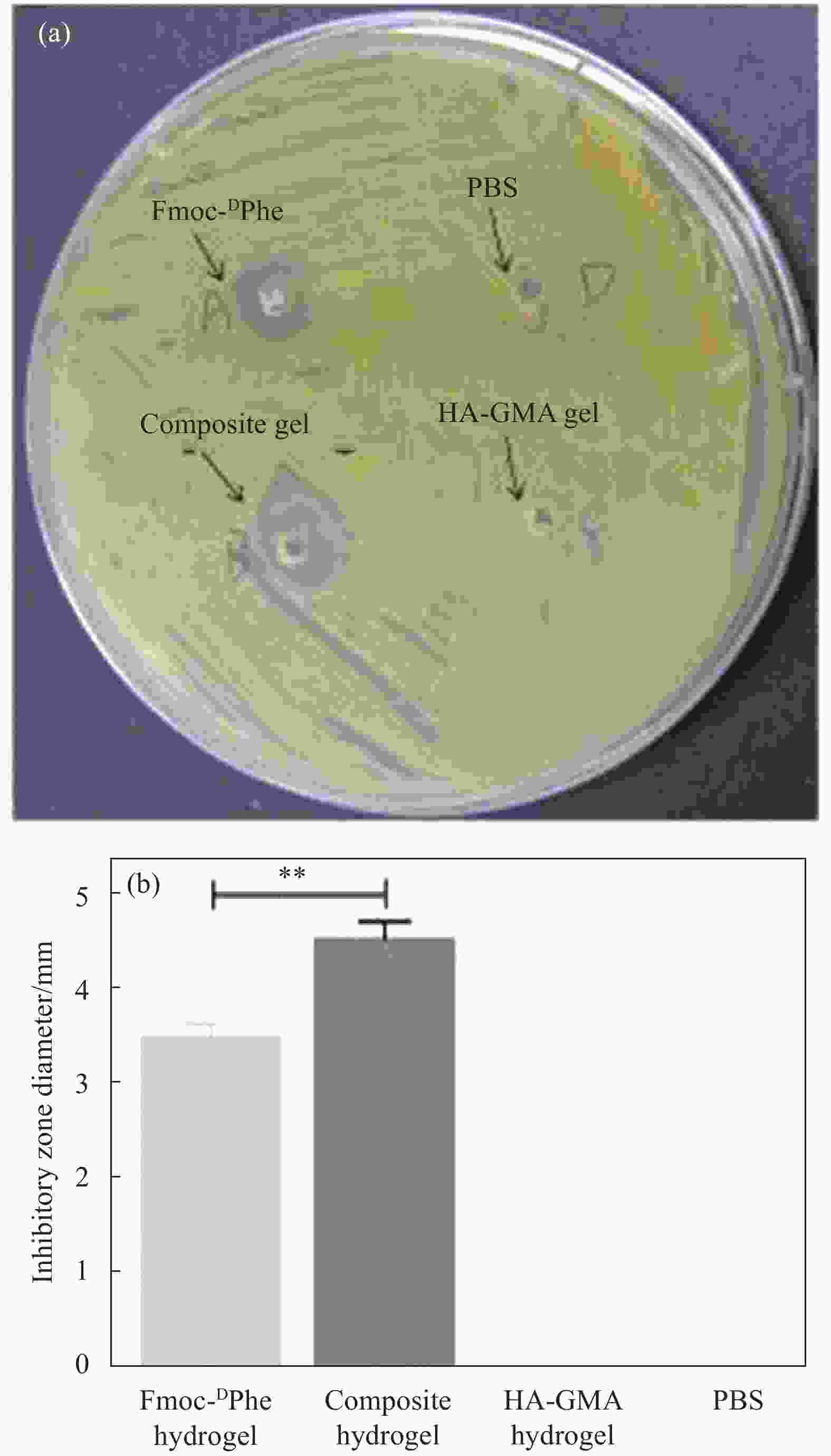
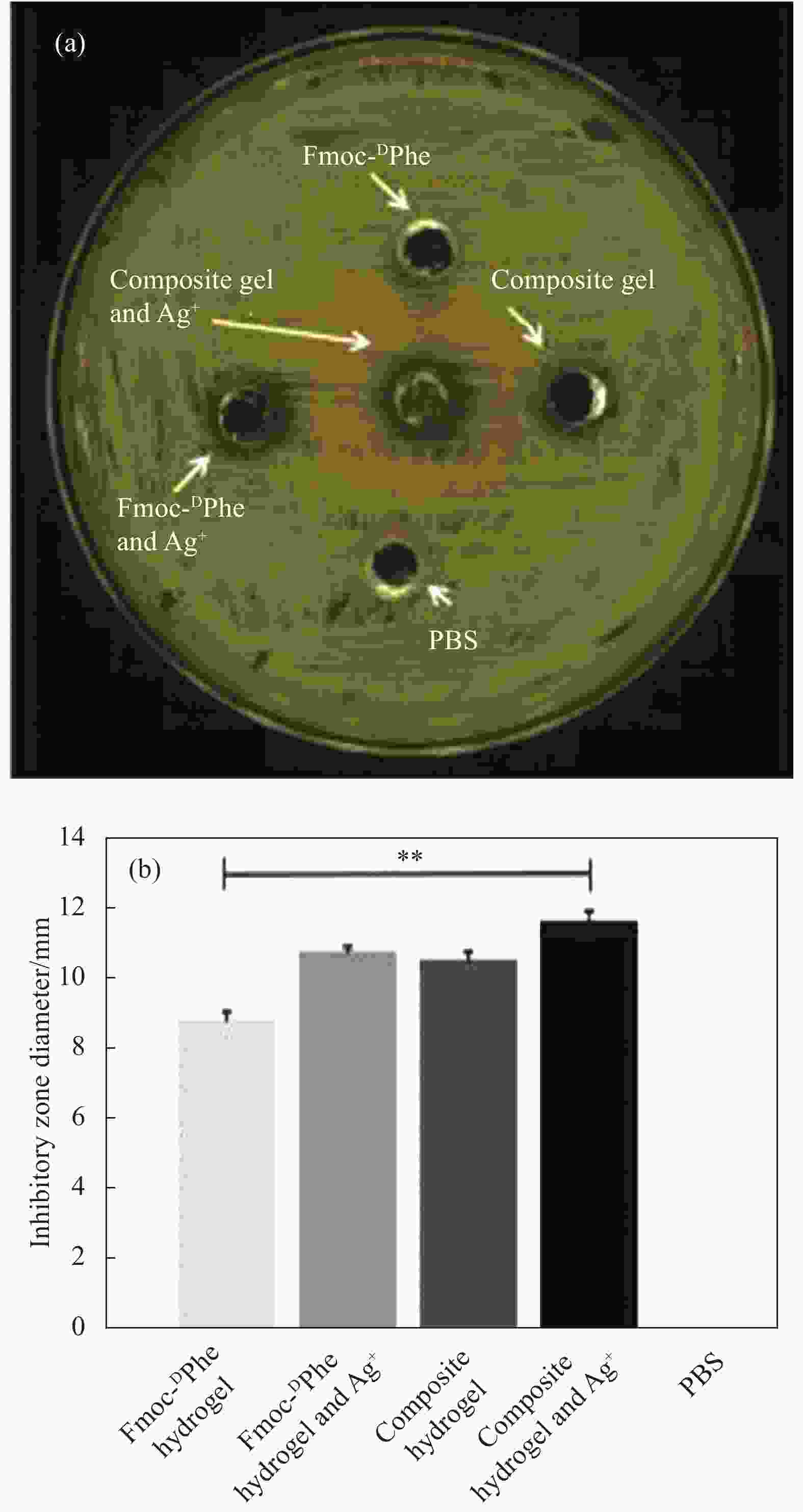
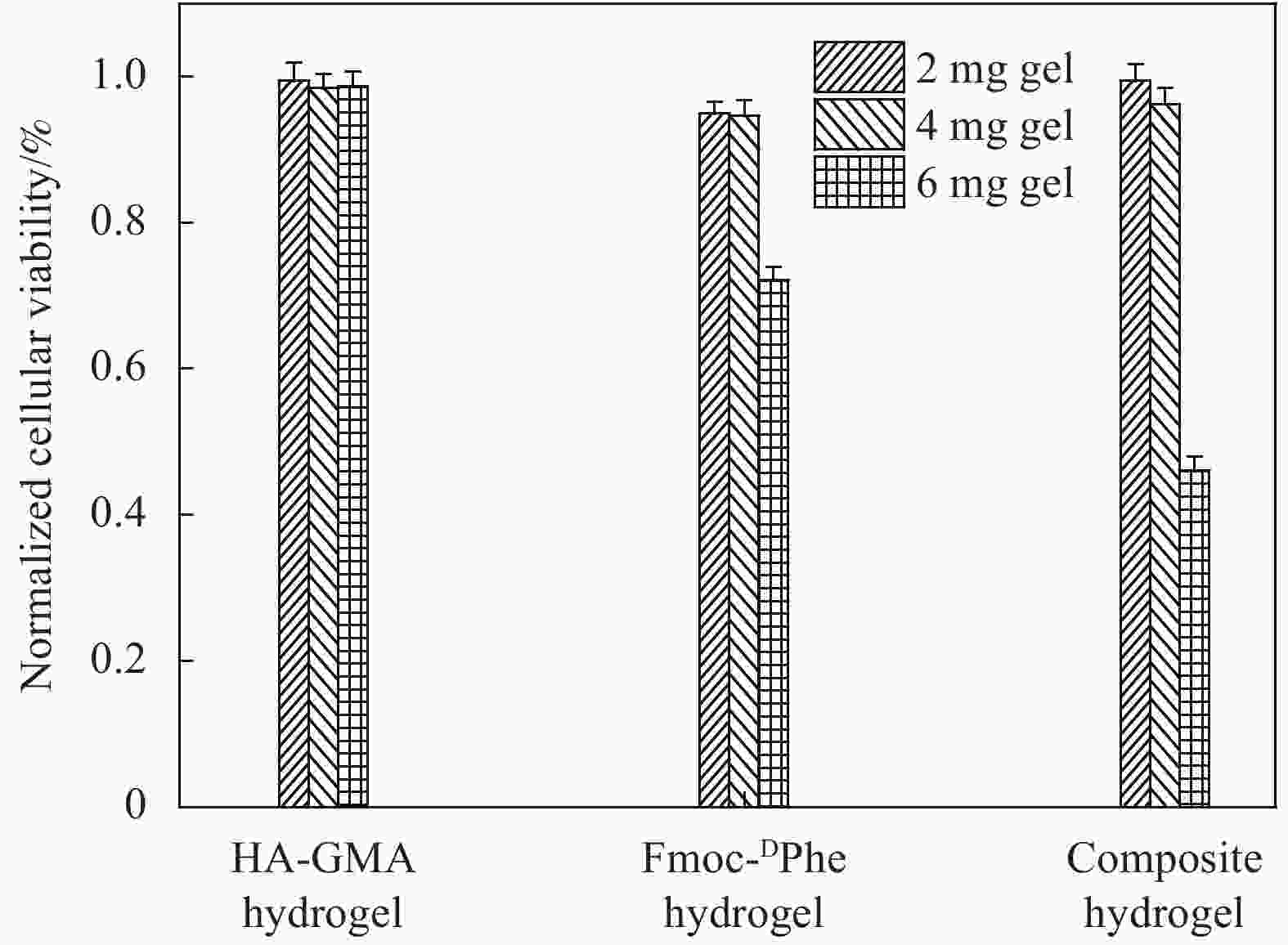
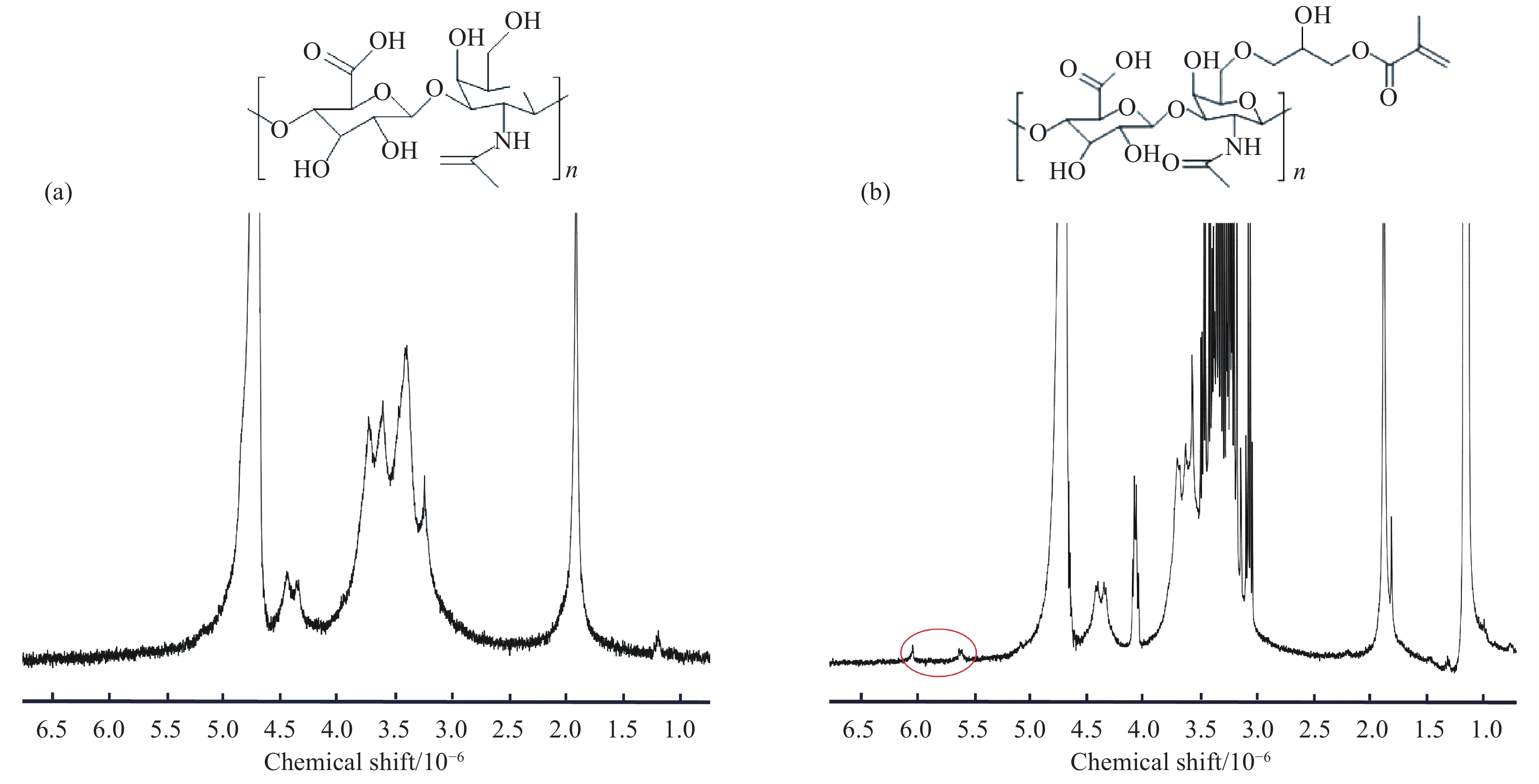
将N-芴甲氧羰基-D-苯丙氨酸(Fmoc-DPhe)和甲基丙烯酸缩水甘油酯(Glycidyl methacrylate,GMA)修饰的透明质酸(HA-GMA)在磷酸缓冲液中共混加热,冷却后Fmoc-DPhe分子先自组装形成超分子水凝胶,超分子水凝胶中的HA-GMA再经光照引发交联制备双网络复合水凝胶。研究该双网络水凝胶的力学性能、光学性质、微观形貌、药物缓释能力和抑菌性能。研究结果表明,双网络水凝胶比HA-GMA单网络水凝胶的力学性能强一倍左右且HA-GMA网络存在于双网络水凝胶中;光学性质显示双网络水凝胶中存在Fmoc-DPhe网络;微观形貌表明有两种水凝胶网络均存在于复合水凝胶中。当复合水凝胶包裹小分子模拟药物后,复合水凝胶达到模拟药物最大累积释放量的时间要比Fmoc-DPhe单网络水凝胶的长6 h;针对革兰氏阳性细菌的抑菌能力研究显示,双网络水凝胶的抑菌效果也比Fmoc-DPhe单网络水凝胶的更好。
-
关键词:
- D型Fmoc-苯丙氨酸 /
- 透明质酸 /
- 复合水凝胶 /
- 药物释放 /
- 抑菌性能
Abstract:N-fluoren-methoxycarbonyl-D-Phenylalanine (Fmoc-DPhe) and glycidyl methacrylate (GMA)-modified hyaluronic acid (HA-GMA) were mixed and heated in phosphoric acid buffer. After cooling, Fmoc-DPhe molecules were self-assemble into supermolecular hydrogel followed by forming double network hydrogel with HA-GMA under UV light irradiation. The mechanical properties, optical properties, microstructure, drug release and bacteriostatic properties of the composite hydrogel were studied. The results show that the double-network hydrogels are about twice as strong as those of HA-GMA single-network hydrogel, and the HA-GMA network exists in the double-network hydrogels. Optical properties show the existence of Fmoc-DPhe network in the double network hydrogels. The microstructure indicates that there are two kinds of hydrogel networks in the composite hydrogel. Moreover, after loading the drug, the double-network hydrogel takes 6 hours longer to reach the maximum drug accumulation rate than the Fmoc-DPhe single-network hydrogel. The antibacterial activity of the double-network hydrogel against gram-positive bacteria is also better than that of the Fmoc-DPhe single-network hydrogel.
-
Key words:
- Fmoc-DPhe /
- hyaluronic acid /
- composite hydrogel /
- drug-release /
- antibacterial activity
-
表 1 压缩实验测试水凝胶的压缩强度和压缩应变
Table 1. Fracture stresses and strains of hydrogels under compression
Hydrogel Fmoc-DPhe hydrogel HA-GMA hydrogel Composite hydrogel Fracture stress/kPa 6.9 0.6 36.1 Fracture strain/% 47.11 53.86 48.93 -
[1] XU Hua, WANG Tingting, YANG Chengbiao, et al. Supramolecular nanofibers of curcumin for highly amplified radiosensitization of colorectal cancers to ionizing radiation[J]. Advanced Functional Materials,2018,28(14):1-11. [2] WANG Yan, ZHANG Wensi, GONG Coucong, et al. Recent advances in the fabrication, functionalization, and bioapplications of peptide hydrogels[J]. Soft Matter,2020,16(44):10029-10045. doi: 10.1039/D0SM00966K [3] HABIBI Neda, KAMALY Nazila, MEMIC Adnan, et al. Self-assembled peptide-based nanostructures: Smart nanomaterials toward targeted drug delivery[J]. Nano Today,2016,11(1):41-60. doi: 10.1016/j.nantod.2016.02.004 [4] MUKHERJEE Nabanita, ADAK Anindyasundar, GHOSH Surajit. Recent trends in the development of peptide and protein-based hydrogel therapeutics for the healing of CNS injury[J]. Soft Matter,2020,16(44):10046-10064. doi: 10.1039/D0SM00885K [5] DAS A K, GAVEL P K. Low molecular weight self-assembling peptide-based materials for cell culture, antimicrobial, anti-inflammatory, wound healing, anticancer, drug delivery, bioimaging and 3D bioprinting applications[J]. Soft Matter,2020,16(44):10065-10095. doi: 10.1039/D0SM01136C [6] DIAFERIA Carlo, MORELLI Giancarlo, ACCARDO Antonella. Fmoc-diphenylalanine as a suitable building block for the preparation of hybrid materials and their potential applications[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry B,2019,7(34):5142-5155. doi: 10.1039/C9TB01043B [7] DIAFERIA Carlo, GHOSH Moumita, SIBILLANO Teresa, et al. Fmoc-FF and hexapeptide-based multicomponent hydrogels as scaffold materials[J]. Soft Matter,2019,15(3):487-496. doi: 10.1039/C8SM02366B [8] HUANG Renliang, QI Wei, FENG Libin, et al. Self-assembling peptide-polysaccharide hybrid hydrogel as a potential carrier for drug delivery[J]. Soft Matter,2011,7(13):6222-6230. doi: 10.1039/c1sm05375b [9] 顾其胜, 严凯. 透明质酸与临床医学[M]. 上海: 第二军医大学出版社, 2003.GU Qisheng, YAN kai. Hyaluronic acid and clinical medicine[M]. Shanghai: The Second Military Medical University Press, 2003(in Chinese). [10] PATIL Rahul, KANSARA Vrushti, RAY Debes, et al. Slow degrading hyaluronic acid hydrogel reinforced with cationized graphene nanosheets[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2019, 141: 232-239. [11] TAM Nicky W., CHUNG Dudley, BALDWIN Samuel J., et al. Material properties of disulfide-crosslinked hyaluronic acid hydrogels influence prostate cancer cell growth and metabolism[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry B,2020,8(42):9718-9733. doi: 10.1039/D0TB01570A [12] SEI K H, JUNG K P, TAKASHI T, et al. Synthesis and degradation test of hyaluronic acid hydrogels[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2007,40(4):374-380. [13] ANTUNES Jéssica, GASPAR Vítor M, FERREIRA Luís, et al. In-air production of 3D co-culture tumor spheroid hydrogels for expedited drug screening[J]. Acta Biomaterialia,2019,94:392-409. doi: 10.1016/j.actbio.2019.06.012 [14] FAN Changjiang, LING Yang, DENG Wenshuai, et al. A novel cell encapsulatable cryogel (CECG) with macro-porous structures and high permeability: A three-dimensional cell culture scaffold for enhanced cell adhesion and proliferation[J]. Biomedical Materials,2019,14(5):055006. doi: 10.1088/1748-605X/ab2efd [15] 刘东, 赵孔银, 宋欢语, 等. 硅酸钙-海藻酸钙复合水凝胶膜的制备及表征[J]. 复合材料学报, 2017, 34(11):2401-2406.LIU Dong, ZHAO Kongyin, SONG Huanyu, et al. Preparation and characterization of calcium silicate-calcium alginate compsite hydrogel film[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica.,2017,34(11):2401-2406(in Chinese). [16] FAN Yuchao, YUE Zhilian, LUCARELLI Enrico, et al. Hybrid printing using cellulose nanocrystals reinforced GelMA/HAMA hydrogels for improved structural integration[J]. Advanced Healthcare Materials,2020,9(24):2001410. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202001410 [17] 施小宁, 陈晖, 张浩波, 等. 基于酵母发酵致孔的小麦麸质蛋白/聚丙烯酸钠复合多孔水凝胶的合成及溶胀性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2018, 35(6):1386-1394.SHI Xiaoning, CHEN Hui, ZHANG Haobo, et al. Synthesis, characterization, and swelling behaviors of wheat gluten/poly(sodium acrylate) porous composite hydrogel produced by yeast fermentation[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2018,35(6):1386-1394(in Chinese). [18] ZHANG Yuankai, ZHANG Han, ZOU Qianli, et al. An injectable dipeptide-fullerene supramolecular hydrogel for photodynamic antibacterial therapy[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry B,2018,6(44):7335-7342. doi: 10.1039/C8TB01487F [19] GONG Xiao, BRANFORD-WHITE Christopher, TAO Lei, et al. Preparation and characterization of a novel sodium alginate incorporated self-assembled Fmoc-FF composite hydrogel[J]. Materials Science and Engineering C,2016,58:478-486. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2015.08.059 [20] AVIV Moran, HAIPERIN-STERNFELD Michal, GRIGORIANTS Irena, et al. Improving the mechanical rigidity of hyaluronic acid by integration of a supramolecular peptide matrix[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2018,10(49):41883-41891. [21] FAN Changjiang, LIAO Liqiong, ZHANG Chao, et al. A tough double network hydrogel for cartilage tissue engineering[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry B,2013,1(34):4251-4258. doi: 10.1039/c3tb20600a [22] HOLMES Róisín, YANG Xuebin, DUNNE Aishling, et al. Thiol-ene photo-click collagen-peg hydrogels: Impact of water-soluble photoinitiators on cell viability, gelation kinetics and rheological properties[J]. Polymers,2017,9(6):226. [23] CHEN Jiahui, TAO Na, FANG Shiqi, et al. Incorporation of Fmoc-Y nanofibers into mechanical properties and the controlled release of small molecules[J]. New Journal of Chemistry,2018,42(12):9651-9657. doi: 10.1039/C8NJ00729B [24] 中国人民共和国国家标准. 塑料压缩性能试验方法: GB/T 1041—92[S]. 北京: 国家技术监督局, 1992.National Standard of the People’s Republic of China. Plastics-Determination of compressive properties: GB/T 1041—92[S]. Beijing: The State Bureau of Quality and Technical Supervision, 1992(in Chinese). [25] 段红梅, 汪希铭, 黄子欣, 等. 纤维基介孔SiO2药物载体的构建及其释药性能[J]. 纺织学报, 2020, 41(7):15-22.DUAN Hongmei, WANG Ximing, HUANG Zixin, et al. Construction and drug release properties of fiber-based mesoporous SiO2 drug carrier[J]. Journal of Textile Research,2020,41(7):15-22(in Chinese). [26] ROY Subhasish, BANERJEE Arindam. Amino acid based smart hydrogel: Formation, characterization and fluorescence properties of silver nanoclusters within the hydrogel matrix[J]. Soft Matter,2011,7(11):5300-5308. doi: 10.1039/c1sm05034f [27] GAHANE A Y, RANJAN P, SINGH V, et al. Fmoc-phenylalanine displays antibacterial activity against Gram-positive bacteria in gel and solution phases[J]. Soft Matter,2018,14(12):2234-2244. doi: 10.1039/C7SM02317K [28] CAO Zhongming, LUO Yue, LI Zhaoyang, et al. Antibacterial hybrid hydrogels[J]. Macromolecular Bioscience,2020,21:2000252. [29] YUAN Shuaishuai, LI Zhihong, ZHAO Jie, et al. Enhanced biocompatibility of biostable poly(styrene-b-isobutylene-b-styrene elastomer via poly(dopamine)-assisted chitosan/hyaluronic acid immobilization[J]. RSC Advances,2014,4(59):31481-31488. doi: 10.1039/C4RA04523H [30] SONG Jingwen, YUAN Chengqian, JIAO Tifeng, et al. Multifunctional antimicrobial biometallohydrogels based on amino acid coordinated self-assembly[J]. Small,2020,16(8):1907309. -






 下载:
下载: