Preparation of CaC2O4-direct claret B/chitosan composite materials and adsorption properties for ethyl violet
-
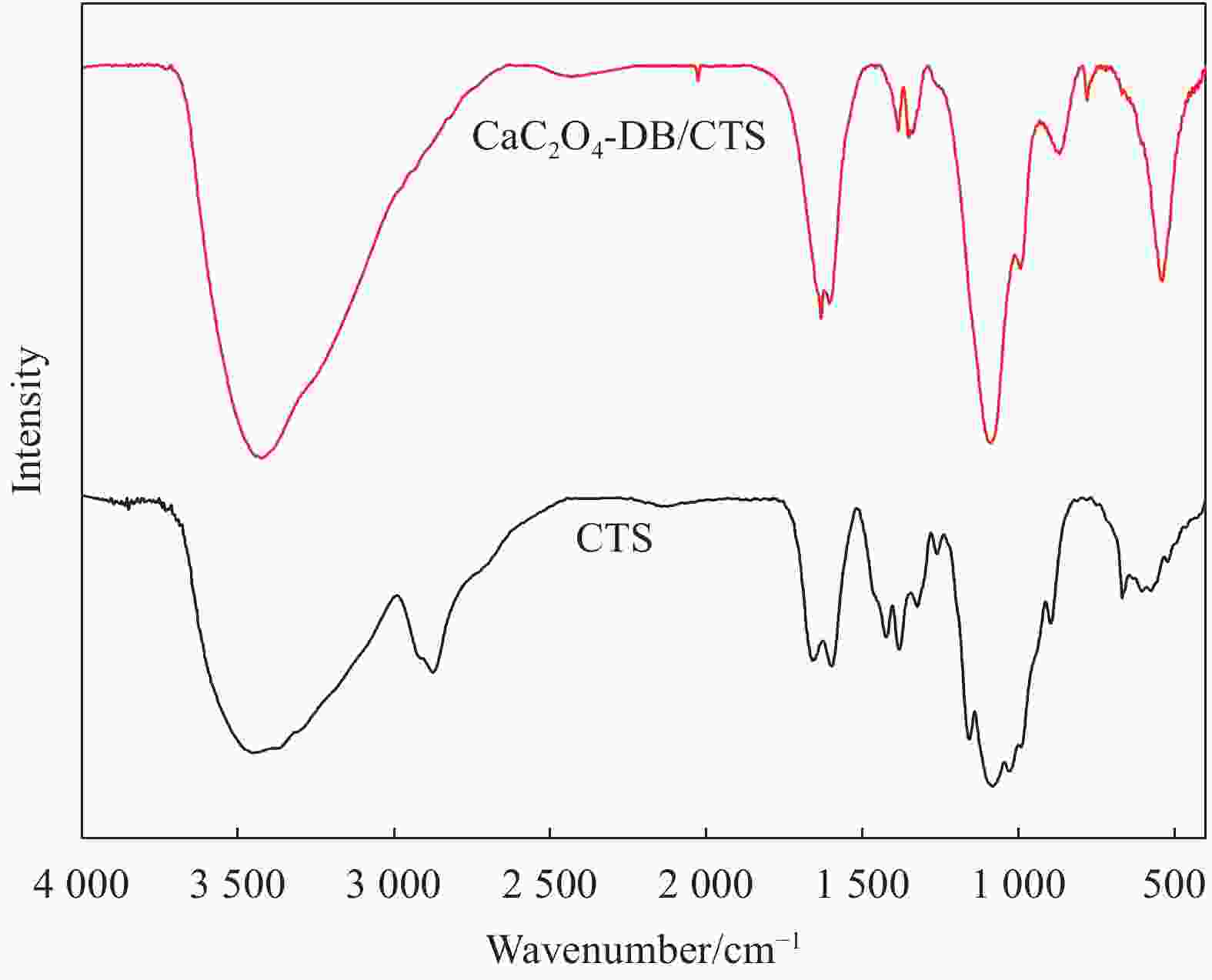
摘要: 以壳聚糖(CTS)和草酸钙-直接枣红B(CaC2O4-DB)杂化材料为原料,采用共混原位固载法制备草酸钙-直接枣红B/壳聚糖(CaC2O4-DB/CTS)复合材料。利用SEM、BET和FTIR对 CTS 和CaC2O4-DB/CTS的形貌及结构等进行表征分析,CaC2O4-DB的固载并未改变CTS的形貌结构,仅增加其比表面积和结合位点。详细考察了吸附时间、乙基紫 (Ethyl violet,EV)初始浓度、溶液pH及温度等因素对CaC2O4-DB/CTS吸附EV的影响,初步探讨了CaC2O4-DB/CTS对EV的吸附动力学和吸附热力学行为。结果表明,CaC2O4-DB/CTS吸附EV在3 h内达到吸附平衡,且pH=8、投加量为6 g/L时,25℃的100 mg/L EV溶液(化学需氧量(COD)为187 mg/L)染料去除率高达95%,COD去除率达90%以上。该吸附过程是自发进行的,符合Langmuir等温线模型和准二级动力学模型,其吸附过程由颗粒内扩散和化学吸附共同控制。Abstract: A composite adsorbent of CaC2O4-DB/CTS was prepared using chitosan (CTS) and the hybrid materials of CaC2O4 and direct claret B (CaC2O4-DB/CTS) by the method of blending in-situ immobilization. CTS and CaC2O4-DB/CTS were characterized by SEM, BET and FTIR. The immobilization of CaC2O4-DB only increases the specific surface area and binding sites without changing the morphology and structure of CTS. The effects of adsorption time, the initial concentration of ethyl violet (EV), pH and temperature of the solution on the adsorption properties of CaC2O4-DB/CTS composite material were investigated in detail, and the adsorption kinetics and thermodynamic behavior of EV on CaC2O4-DB/CTS were preliminarily discussed. The results show that the removal rate of dye and chemical oxygen demand (COD) reach 95% and 90% for 100 mg/L EV solution (COD is 187 mg/L), respectively, under conditions of room temperature, CaC2O4-DB/CTS dosage of 6 g/L, adsorption time of 3 h and pH=8. The adsorption behavior of EV by the adsorbent is spontaneous and in accordance with Langmuir model and the quasi-second-order kinetic model. The adsorption process is controlled by intra-particle diffusion and the chemical adsorption.
-
Key words:
- chitosan /
- composite materials /
- adsorption /
- kinetics /
- thermodynamics /
- ethyl violet
-
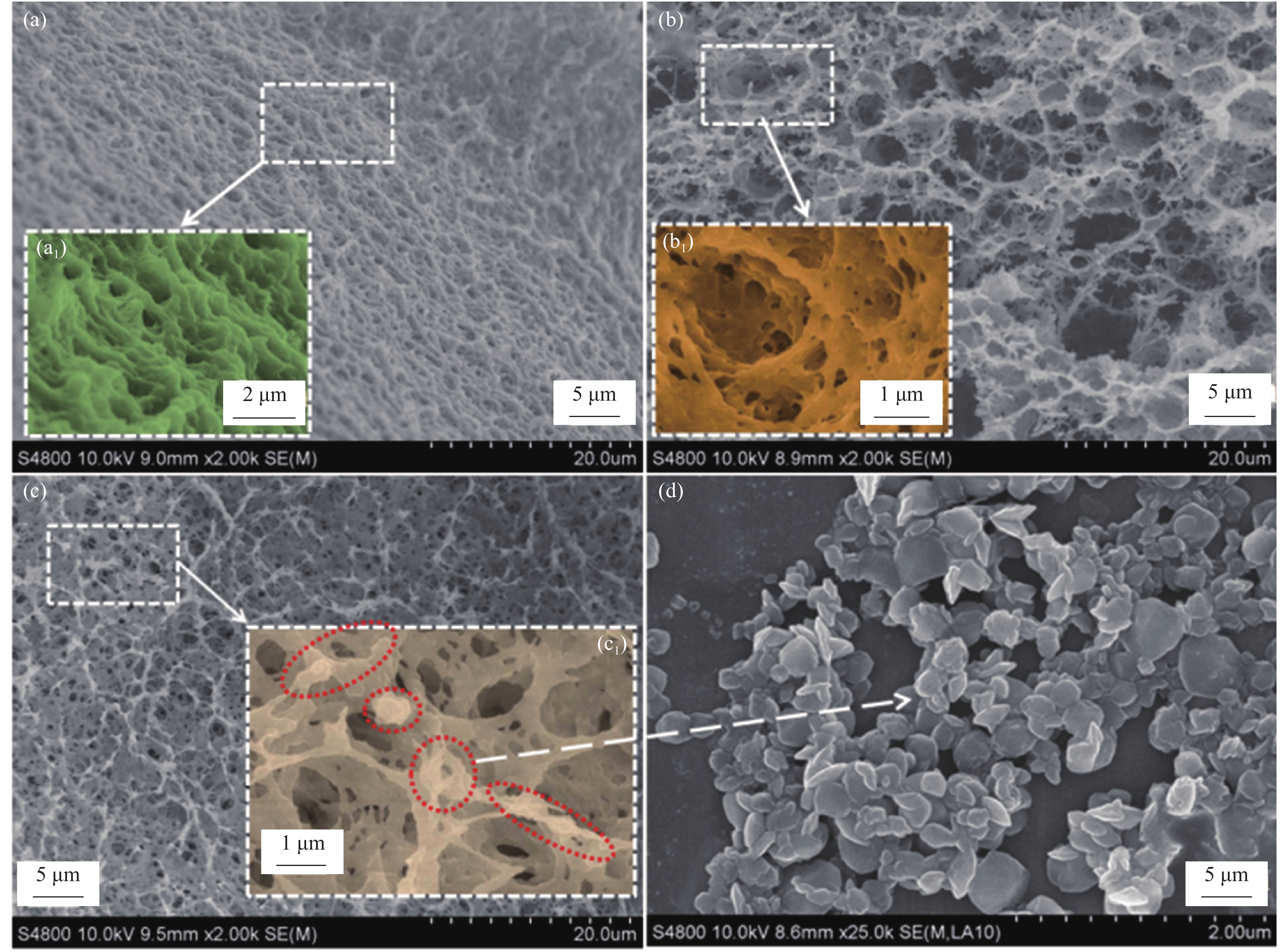
图 1 各种材料SEM图像:(a) 壳聚糖(CTS)材料表面;(b) CTS材料切面;(c) CaC2O4-直接枣红B(DB)/CTS材料表面;(a1) CTS材料表面局部放大图;(b1) CTS材料切面局部放大图;(c1) CaC2O4-DB/CTS材料切面;(d) CaC2O4-DB材料
Figure 1. SEM images of chitosan (CTS) ((a), (b)), CaC2O4-direct claret B (DB)/CTS (c) and CaC2O4-DB (d), area of CaC2O4-DB materials (a1), CTS materials (b1), CaC2O4-DB/CTS materials (c1)
表 1 动边界模型拟合参数
Table 1. Parameters of moving boundary model Rate controlling step
Moving boundary model Rate controlling step k R2 Liquid film diffusion 0.01217 0.9643 Intraparticle diffusion 0.00280 0.9341 Chemical reaction 0.00196 0.9319 Notes: k—Constant of rate; R2—Fitting coefficients. 表 2 CaC2O4-DB/CTS吸附EV各吸附动力学方程的参数
Table 2. Kinetics parameters of kinetic models for the adsorption of EV on CaC2O4-DB/CTS
First-order kinetic model Second-order kinetic model Elovich model qe/(mg·g−1) K1/min−1 R2 qe/(mg·g−1) K2/(g·mg−1·min−1) R2 qe/(mg·g−1) α/(g·mg −1·min−1) R2 13.22 0.0204 0.9682 32.15 0.0311 0.9995 30.63 109.57 0.9858 Notes:qe—Equilibrium adsorption capacity; qt—Adsorption capacity at time t; kl—Rate constant of the pseudo-first-order model; k2—Rate constant of the pseudo-second-order model; β—Desorption constant. 表 3 CaC2O4-DB/CTS对EV吸附颗粒内扩散模型参数
Table 3. Parameters of intra-particle kinetic model for the adsorption of EV on CaC2O4-DB/CTS
The first step >The second step >The third step >qt=1.765t1/2+14.51 >qt=0.942t1/2+19.45 >qt=0.209t1/2+28.19 kp C R2 kp C R2 kp C R2 1.765 14.51 0.9933 0.942 19.45 0.9915 0.209 28.19 0.9999 Notes:kp—Constant intra-particle diffusion rate; C—Constant of the reaction boundary layer effect. 表 4 CaC2O4-DB/CTS对EV等温吸附线参数
Table 4. Isotherm parameters for adsorption of EV on CaC2O4-DB/CTS
T/K Langmuir model Freundlich model D-R model qm/(mg·g−1) KL/(L·mg−1) R2 KF/(mg·g−1)·
(L·mg−1)1/nn R2 k/(mol2·kJ−2) R2 ε/(kJ·mol−1) 288.15 40.65 0.0768 0.9964 7.72 2.75 0.9842 0.4671 0.9429 5.17 298.15 45.25 0.0959 0.9952 8.85 2.64 0.9285 0.4046 0.9794 5.96 308.15 51.81 0.1092 0.9980 9.62 2.40 0.9458 0.3054 0.9883 7.92 Notes: T—Temperature; qm—Maximumadsorption capacity; KL —Langmuir characteristic constant; KF—Freundlich characteristic constant; n—Freundlich characteristic constant; k—Constant of adsorption energy; ε—Adsorption potential energy. 表 5 CaC2O4-DB/CTS材料吸附EV的热力学参数
Table 5. Isotherm parameters for adsorption of EV on CaC2O4-DB/CTS
C0/(mg·L−1) T/K ΔG/(kJ·mol−1) ΔH/(kJ·mol−1) ΔS/(J·(mol·K)−1) 125 288.15-308.15 −2.204 - −4.412 27.5228 0.1031 150 −1.598 - −3.393 22.5636 0.0839 175 −0.9234 - −2.810 24.5821 0.0887 Notes: C0—Initial concentration; ΔG—Gibbs free energy change; ΔH—Enthalpy change; ΔS—Entropy change. -
[1] YANG X Y, CHEN L H, LI Y, et al. Hierarchically porous materials: Synthesis strategies and structure design[J]. Che-mical Society Reviews,2017,46(2):481-558. doi: 10.1039/C6CS00829A [2] BHATNAGAR A, SILLANPAA M, WITEK A. Agricultural waste peels as versatile biomass for water purification-A review[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2015,270:244-271. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2015.01.135 [3] KAYAN A. Inorganic-organic hybrid materials and their adsorbent properties[J]. Advanced Composite and Hybrid Materials,2019,2:34. doi: 10.1007/s42114-018-0073-y [4] NF N T, KAMARUDDIN A F, WAN I. Advances in organic-inorganic hybrid sorbents for the extraction of organic and inorganic pollutants in different types of food and environmental samples[J]. Journal of Separation Science,2018,41:195-208. doi: 10.1002/jssc.201700689 [5] PARISA M P, SEYED J P. Review on recent progress in chitosan-based hydrogels for wastewater treatment application[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2018,201:264-279. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.08.070 [6] 牛耀岚. 新型壳聚糖纤维材料的制备及其对重金属离子的吸附研究[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学, 2017.NIU Yaolan. The preparation of chitosan-based fibrous materials and research of adsorption performance for metal ions[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiaotong University, 2017(in Chinese). [7] ZHANG Q S, ZHANG T T, HE T, et al. Removal of crystal violet by clay/PNIPAm nanocomposite hydrogels with various clay contents[J]. Applied Clay Science,2014,90:1-5. doi: 10.1016/j.clay.2014.01.003 [8] 赵丹华. CaF2-WAGGS杂化吸附材料的制备及应用研究[J]. 水处理技术, 2012, 8(8):51-54. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3770.2012.08.014ZHAO Danhua. Preparation of the calcium fluoride-weak acid green as hybrid absorption material and application to dye wastewater treatment[J]. Technology of Water Treatment,2012,8(8):51-54(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-3770.2012.08.014 [9] MOHAMMED E K, EI M N, BAHCINE B, et al. Study of removal of Congo red by local natural clay[J]. Scientific Study and Research,2016,17(3):295-307. [10] KANNAN K P, GEORGE T S, GURU K S. Extraction, purification and characterization of chitosan from endophytic fungi isolated from medicinal plants[J]. World Journal of Science and Technology,2011,1(4):43-48. [11] 马建青. 基于壳聚糖和石墨相氮化碳的净水材料制备及其机理研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2018.MA Jianqing. Preparation and mechanism study of water purification materials based on chitosan and graphitic carbon nitride[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2018(in Chinese). [12] MRIDUSMITA G, PRODEEP P. Enhanced adsorption of cationic dyes using sulfonic acid modified activated carbon[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering,2017,5:3508-3517. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2017.07.016 [13] FAN L, LU Y, YANG L Y, et al. Fabrication of polyethylenimine-functionalized sodium alginate/cellulose nanocrystal/polyvinyl alcohol core-shell microspheres ((PVA/SA/CNC)@PEI) for diclofenac sodium adsorption[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science,2019,554:48-58. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2019.06.099 [14] SAYED G O. Removal of methylene blue and crystal violet from aqueous solutions by palm kernel fiber[J]. Desalination,2011,272:225-232. doi: 10.1016/j.desal.2011.01.025 [15] 谭忠祥. 高堆积密度壳聚糖及其制备方法: 中国, ZL02110716.5[P]. 2002-8-21.TAN Zhongxiang. High bulk density chitosan and its preparation method: China, ZL02110716.5[P]. 2002-8-21(in Chinese). [16] HUI K S, CHO C Y N, KOT S C. Removal of mixed heavy metal ions in wastewater by zeolite 4A and residual products from recycled coal fly ash[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2005,127(13):89-101. [17] SILVIA P D, FABIANO B S, APARECIDO N M, et al. Kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic phenomenological modeling of reactive dye adsorption onto polymeric adsorbent[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2017,307:466-475. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2016.08.104 [18] LIU C, OMER A M, OUYANG X K. Adsorptive removal of cationic methylene blue dye using carboxymethyl cellulose/k-carrageenan/activated montmorillonite composite beads: Isotherm and kinetic studies[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2018,106:823-833. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2017.08.084 [19] KUMARI H J, KRISHNAMOORTHY P, ARUMUGAM T K, et al. An efficient removal of crystal violet dye from waste water by adsorption onto TLAC/Chitosan composite: A novel low-cost adsorbent[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2017,96:324-333. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2016.11.077 [20] SONG X, AN J L, HE C, et al. A bioinspired strategy towards super-adsorbent hydrogel spheres via self-sacrificing micro-reactors for robust wastewater remediation[J]. Jour-nal of Materials Chemistry,2019,7:21386-21403. doi: 10.1039/C9TA05550A [21] HO Y S, MCKAY G. Pseudo-second order model for sorption processes[J]. Process Biochemistry,1999,34(5):451-465. doi: 10.1016/S0032-9592(98)00112-5 [22] 万骏. 基于功能设计的水凝胶对水中磷酸盐去除研究[D]. 武汉: 华中科技大学, 2018.WAN Jun. Hydrogels based on functional design for phosphorous removal from water[D]. Wuhan: Huazhong University of Science and Technology, 2018(in Chinese). [23] HU X, ZHANG H, SUN Z R. Adsorption of low concentration ceftazidime from aqueous solutions using impregnated activated carbon promoted by iron copper and aluminum[J]. Applied Surface Science,2017,392:332-341. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2016.09.047 [24] AHMED M J. Adsorption of quinolone, tetracycline from aqueous solutions onto multi-walled carbon nanotubes with different oxygen contents[J]. Scientific Reports,2014,4(3):4326-4332. [25] KAUSHAL S, BADRU R, KUMAR S, et al. Efficient removal of cationic and anionic dyes from their binary mixtures by organic-inorganic hybrid material[J]. Journal of Inorganic and Organometallic Polymers and Materials,2018,28(3):968-977. doi: 10.1007/s10904-018-0817-8 [26] INYINBOR A A, ADEKOLA F A, OLATUNJI G A. Kinetics, isotherms and thermodynamic modeling of liquid phase adsorption of Rhodamine B dye onto Raphia hookerie fruit epicarp[J]. Water Resources and Industry,2016,15:14-27. doi: 10.1016/j.wri.2016.06.001 [27] SANGHWA O, KAWK M Y, SHIN W S. Competitive sorption of lead and cadmium onto sediments[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2009,152(23):376-388. [28] SCHEUFELE F B, MODENEDS A N, BORBA C E, et al. Monolayer-multilayer adsorption phenome-nological model: Kinetics, equilibrium and thermodynamics[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2016,284:1328-1341. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2015.09.085 [29] ISAH U A, ABDULRAHEEM G, BALA S, et al. Kinetics, equilibrium and thermodynamics studies of Reactive Blue 19 dye adsorption on coconut shell based activated carbon[J]. International Biodeterioration Biodegradation,2015,102:265-273. doi: 10.1016/j.ibiod.2015.04.006 [30] AHMAD A, MOHD-SETAPAR S H, AHMAD A, et al. Recent advances in new generation dye removal technologies: Novel search for approaches to reprocess wastewater[J]. RSC Advances,2015,5(39):30801-30818. doi: 10.1039/C4RA16959J [31] OEPEN B V, KORDEL W, KLEIN W. Sorption of nonpolar and polar compounds to soils: Processes, measurements and experience with the applicability of the modified OECD-Guideline 106[J]. Chemosphere,1991,22(3-4):285-304. doi: 10.1016/0045-6535(91)90318-8 [32] NOLLET H, ROELS M, LUTGEN P, et al. Removal of PCBs from wastewater using fly ash[J]. Chemosphere, 2003, 53: 655-665. [33] 国家环境保护局. 水质化学需氧量的测定−重铬酸盐法: GB/T 11914—1989[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 1989.National Environmental Protection Agency. Water quality-Determination of the chemical oxygen demand-Dichromate method: GB/T 11914—1989[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 1989(in Chinese). [34] 陈锦诗, 孙诗乐, 黄文海, 等. CaF2-CR杂化吸附材料对乙基紫的吸附性能研究[J]. 化学试剂, 2018, 40(10):937-942, 970.CHEN Jinshi, SUN Shile, HUANG Wenhai, et al. Adsorption of ethylene violet on hybrid adsorption material of CaF2-CR[J]. Chemical Reagents,2018,40(10):937-942, 970(in Chinese). -






 下载:
下载: