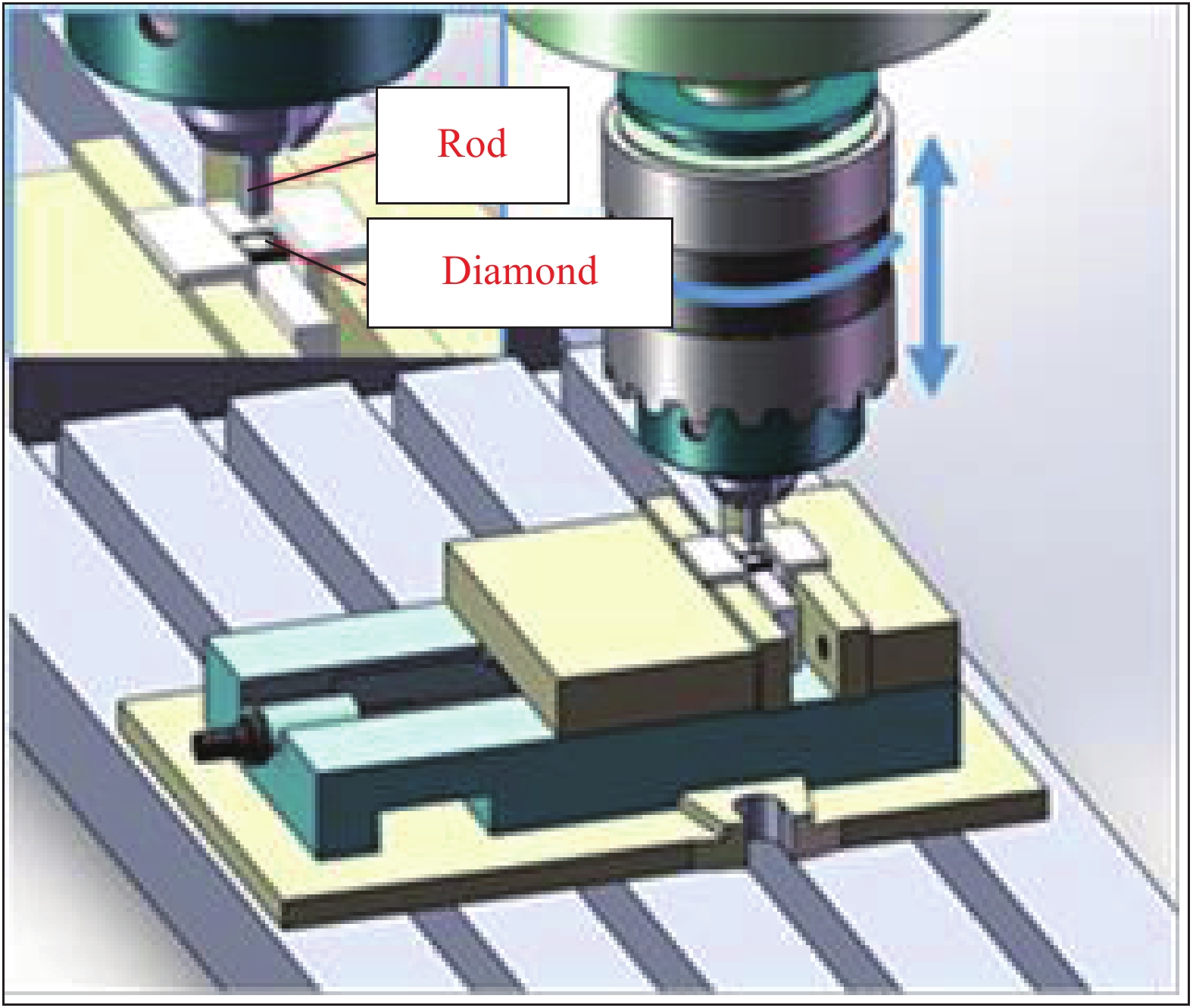
Fabrication of Ti layer on diamond surface with rotary friction extrusion heating method
-
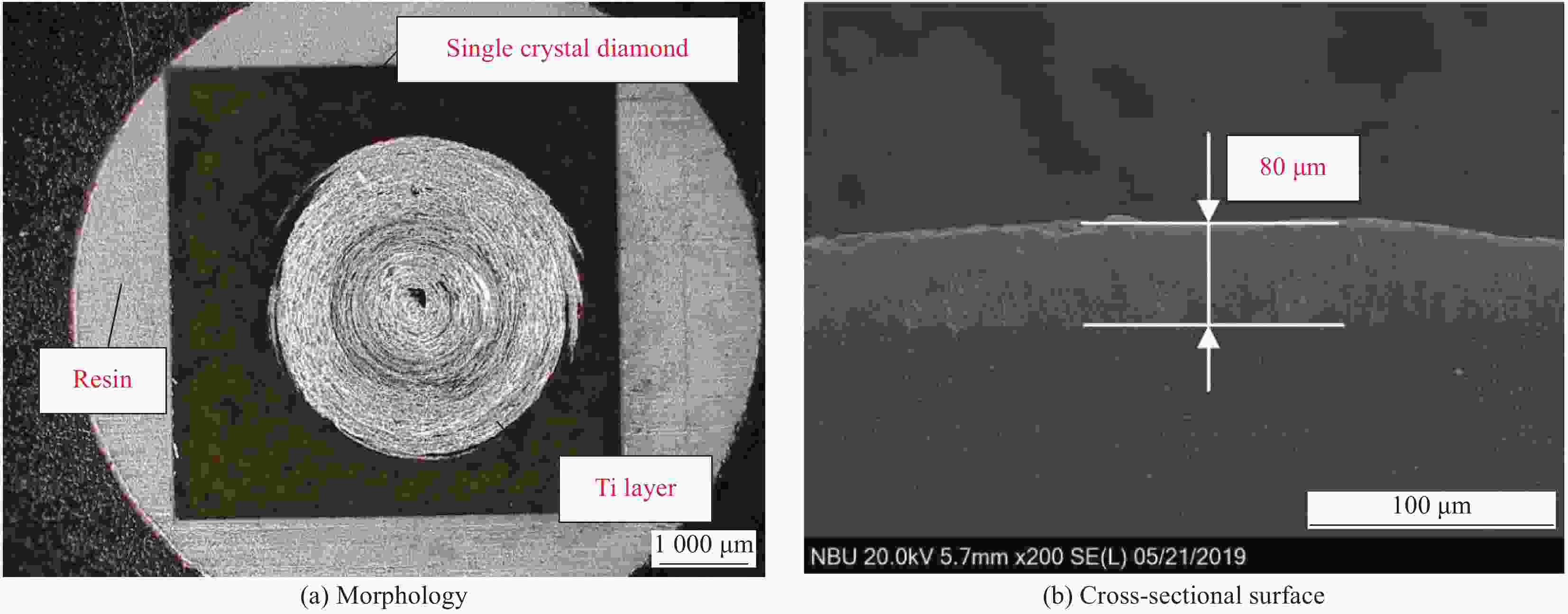
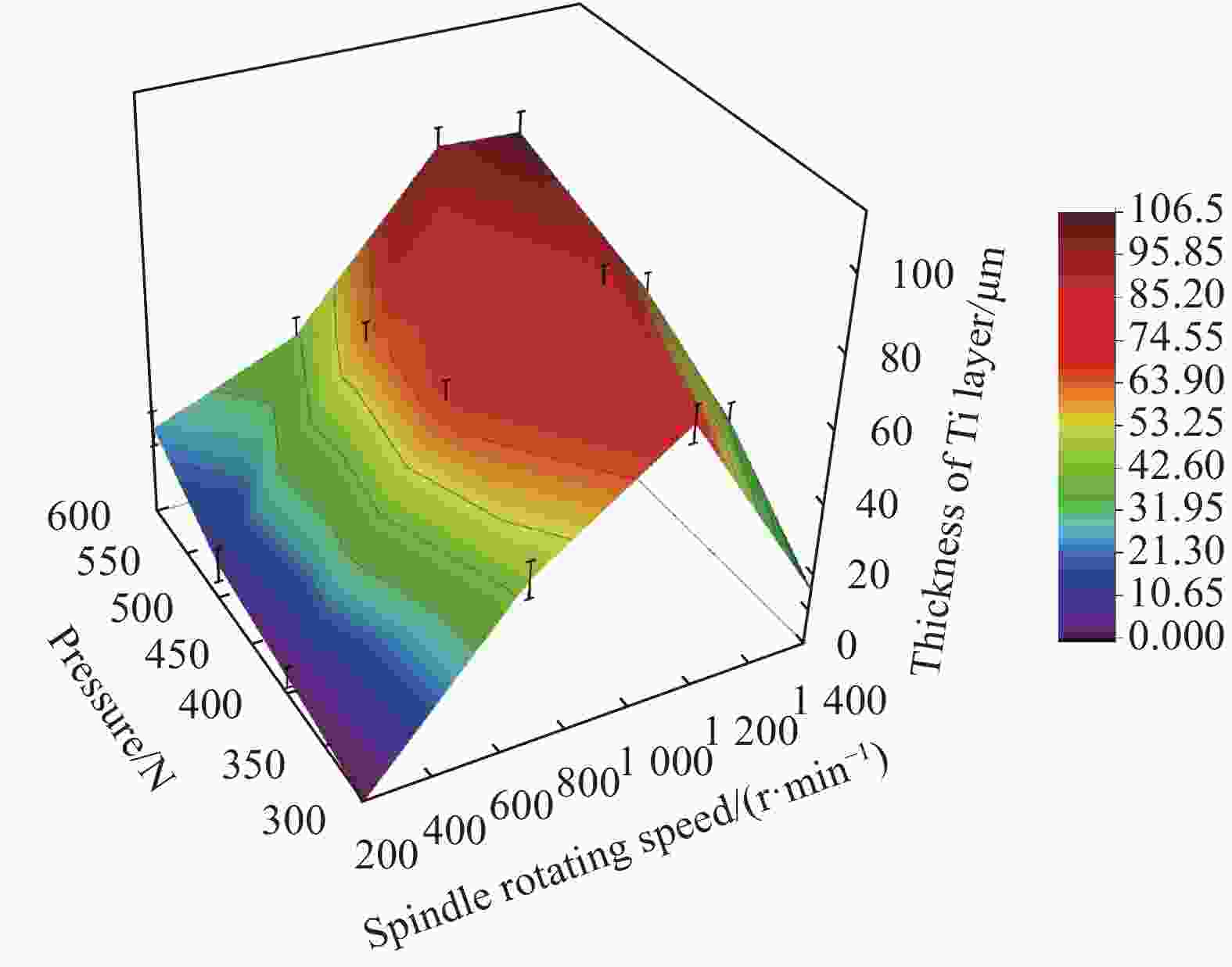
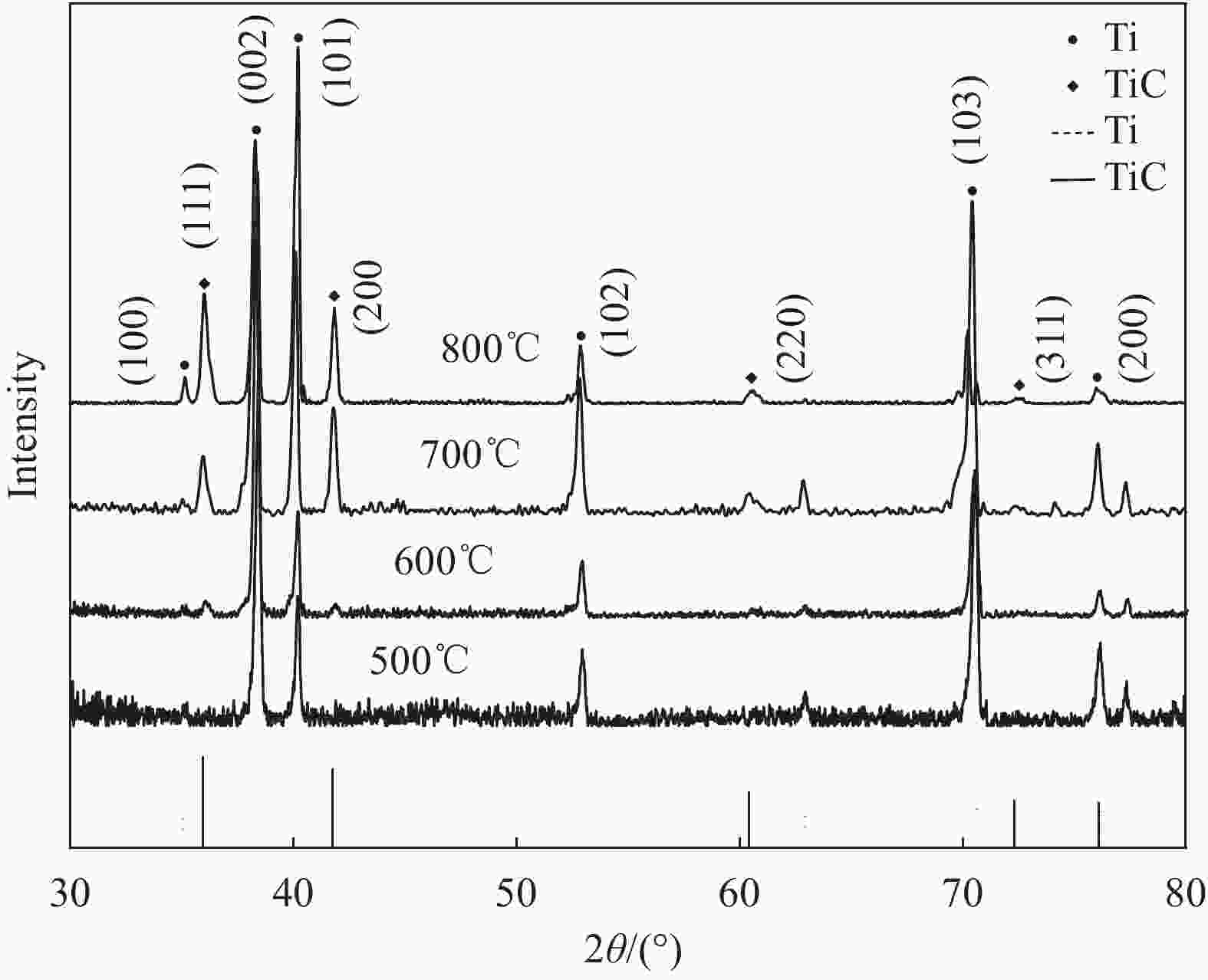
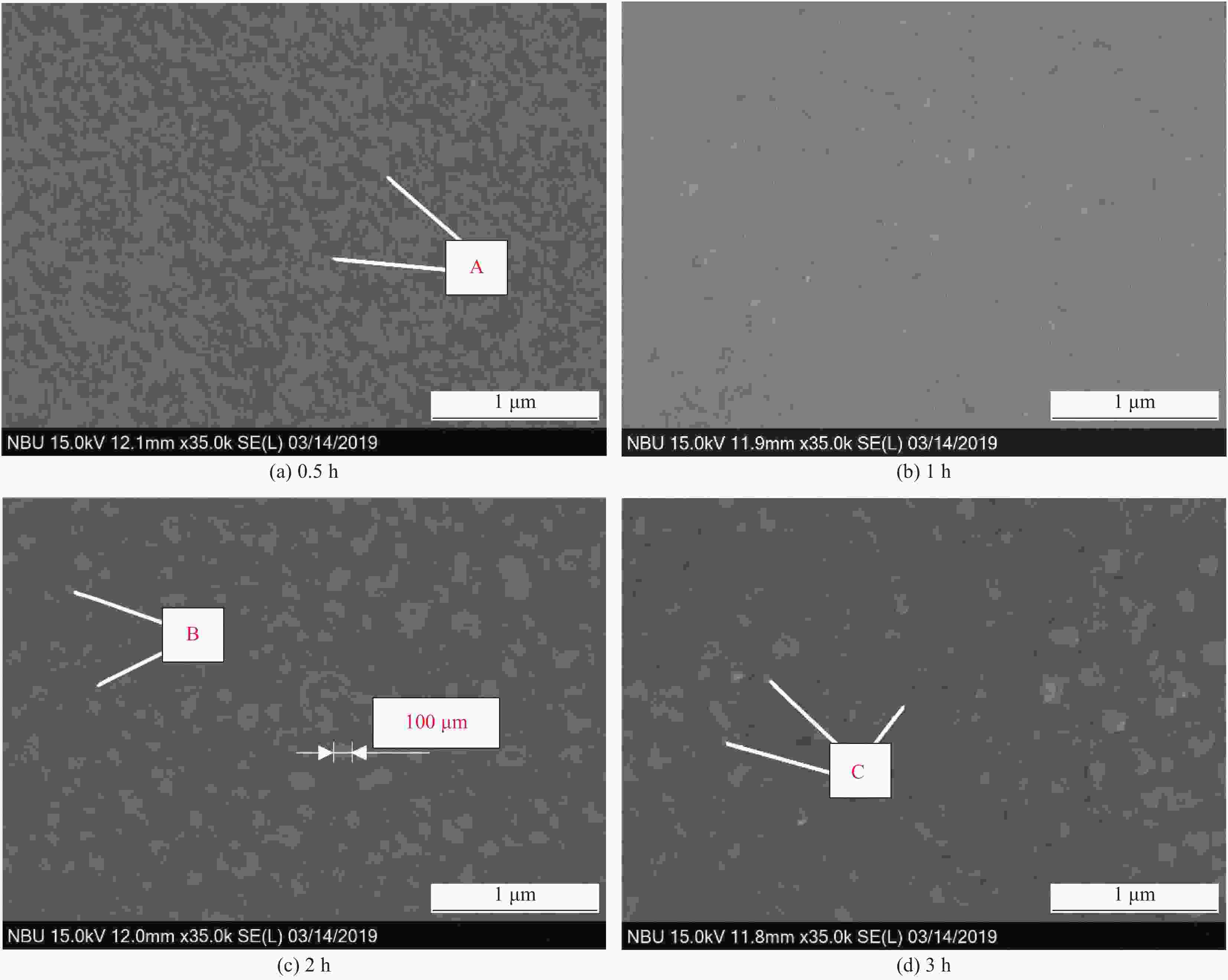
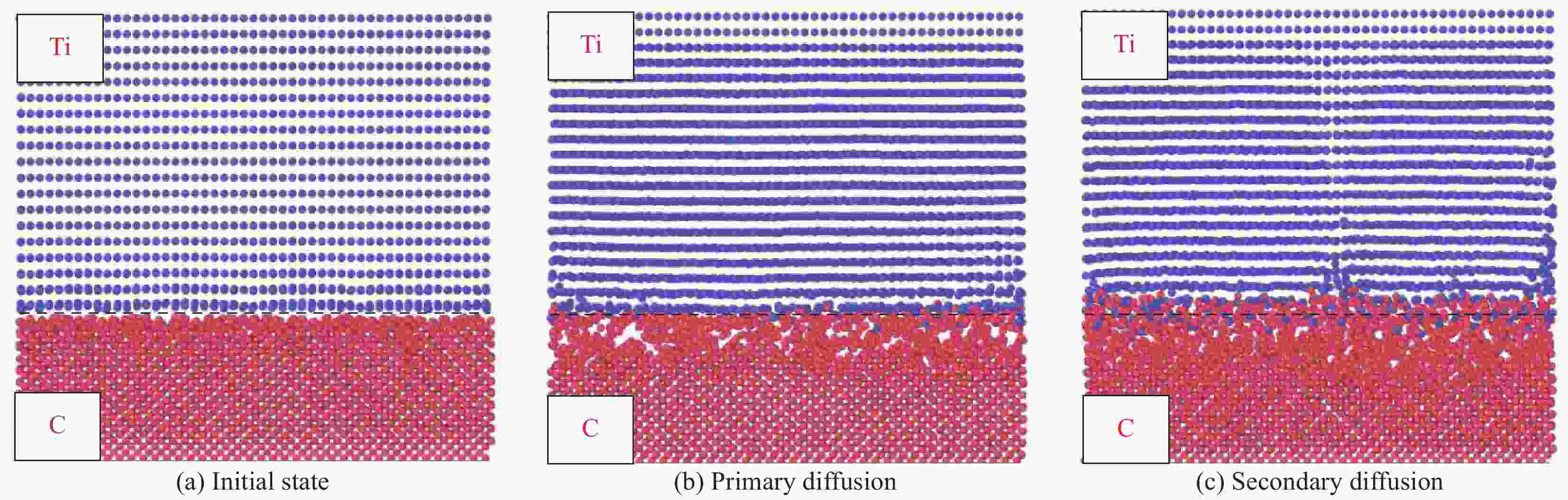
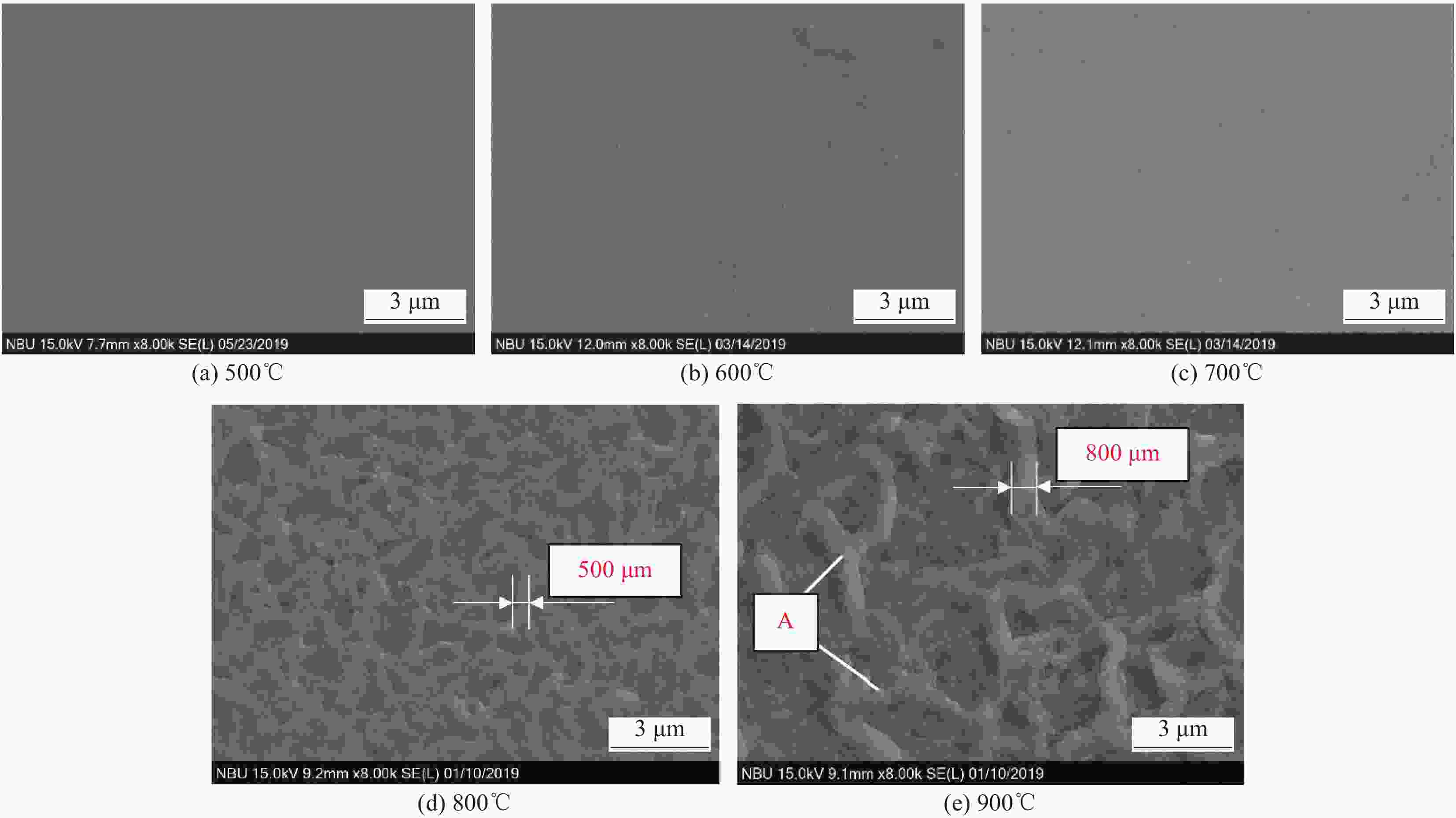
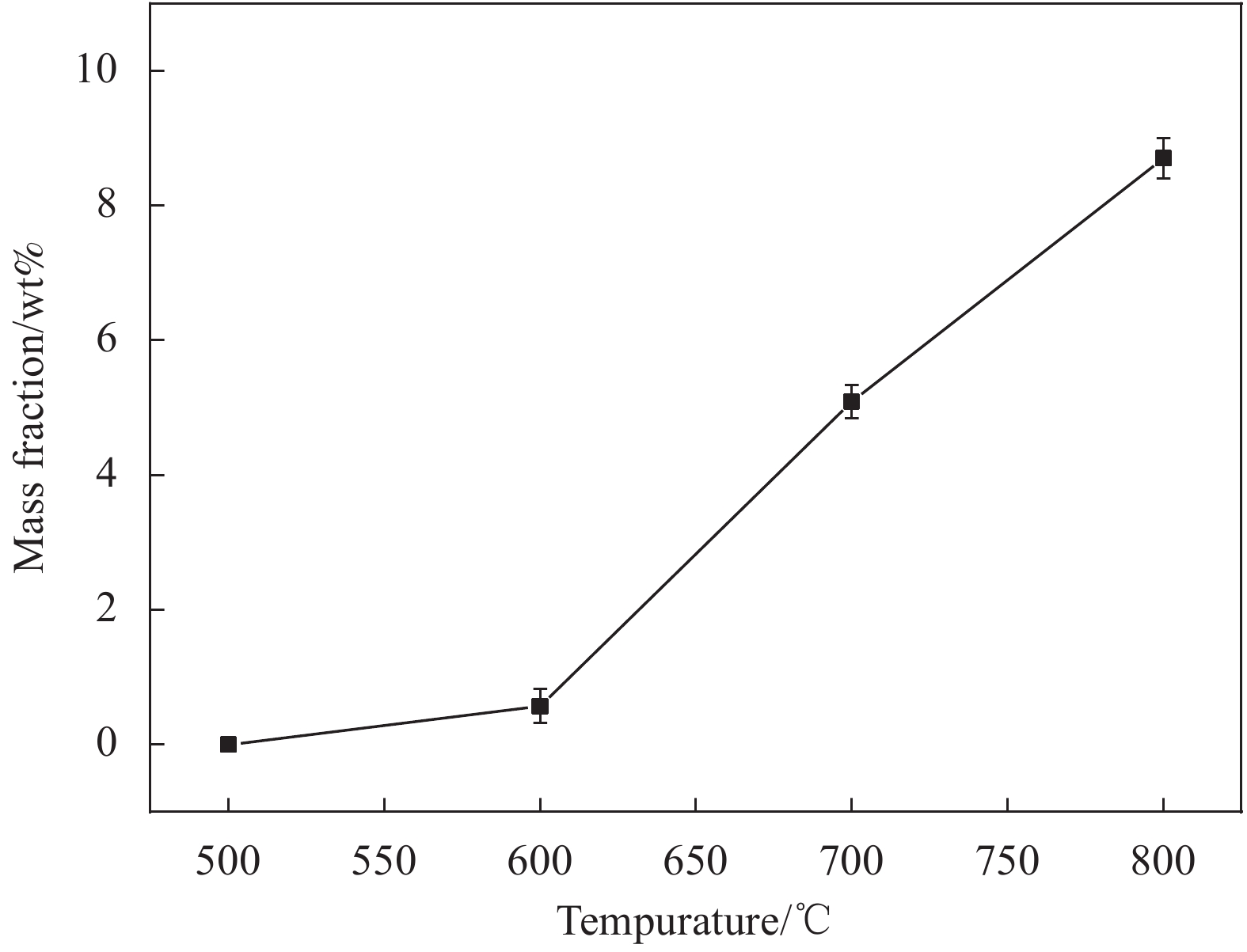
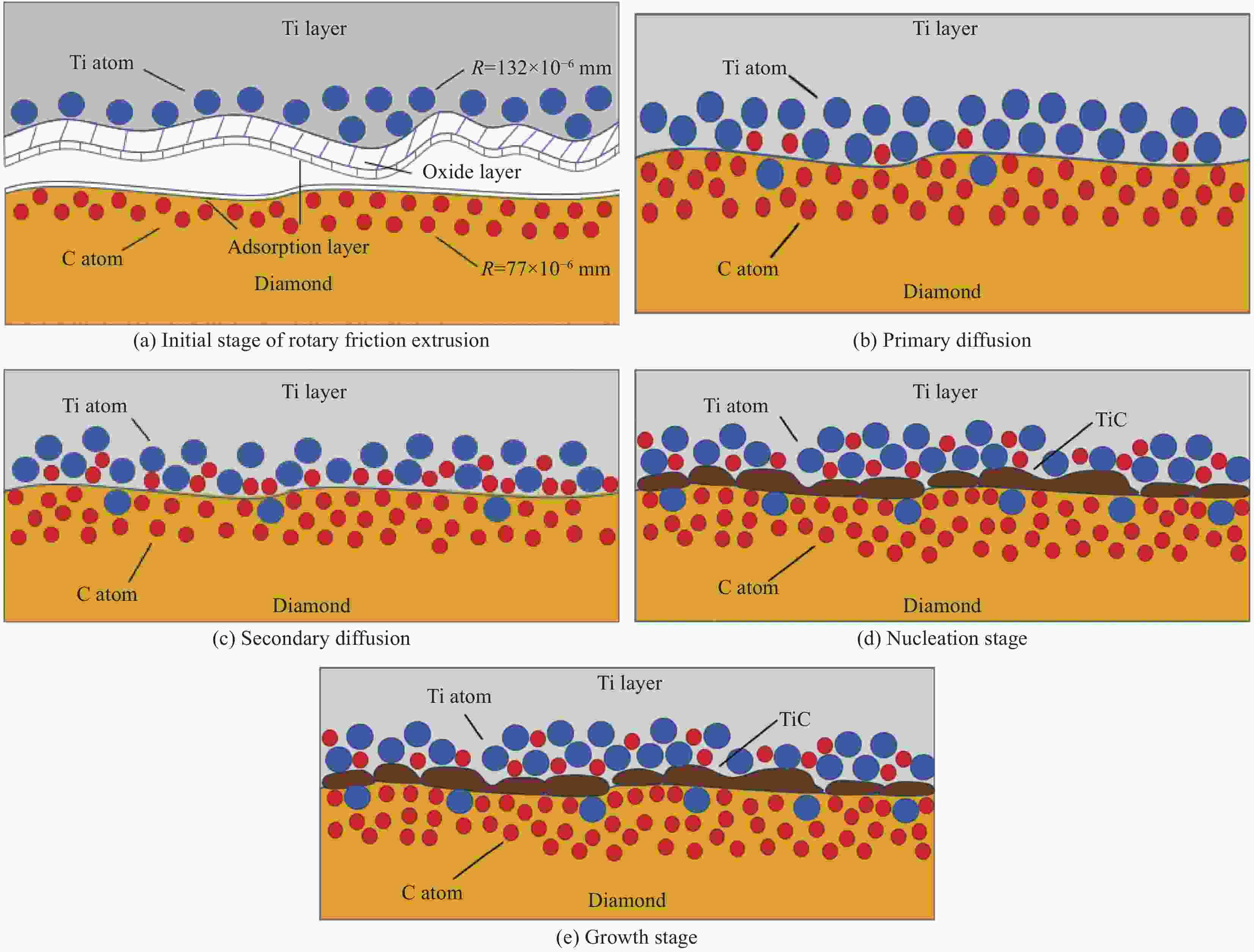
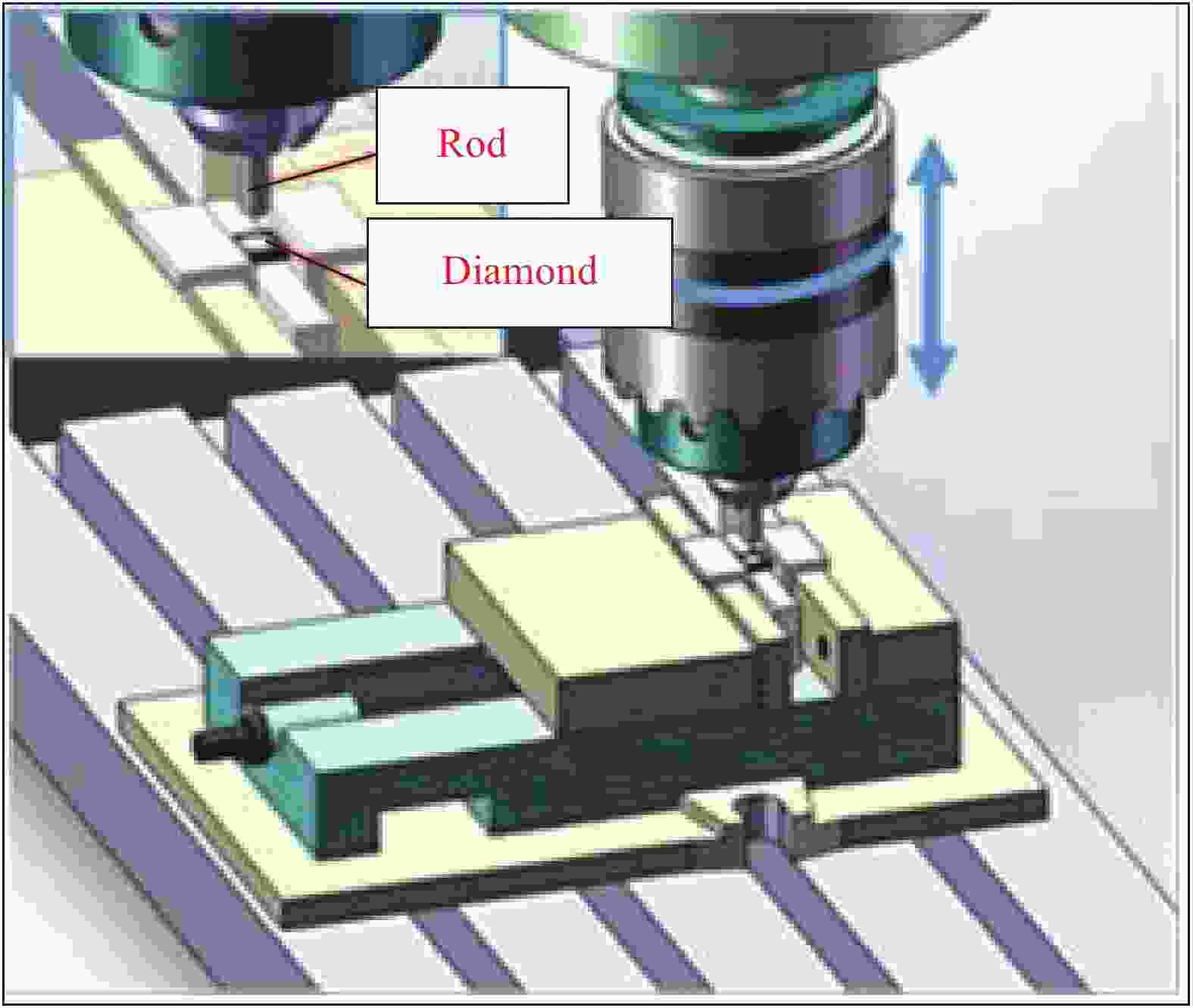
摘要: 为了实现金刚石表面金属化,提出了一种旋转摩擦挤压加温法在人造单晶金刚石表面制备Ti涂层。利用SEM和XRD,分析了Ti涂层内表面的微观形貌和界面间的物相组成,并采用能谱仪进行了元素分析,研究了扩散退火温度和保温时间对Ti涂层内表面物相组成的影响,并分析了金刚石/Ti涂层的界面形成机制。研究结果表明:经过旋转摩擦挤压涂覆,在金刚石表面形成了均匀、致密的Ti涂层。经过600℃保温0.5 h的扩散退火,Ti涂层内表面生成了点状的TiC晶粒,实现了金刚石与Ti涂层的化学结合。随着扩散退火温度的升高与保温时间的延长,TiC晶粒形貌由点状生长为棒状,界面TiC含量随扩散退火温度提高而增加。旋转摩擦挤压加温法在金刚石表面形成Ti涂层可分为五个阶段,即旋转摩擦挤压初始阶段、初级扩散阶段、二级扩散阶段、TiC成核阶段和TiC生长阶段。Abstract: In order to realize metallization of the diamond surface, a rotary friction extrusion heating method is proposed to fabricate Ti layer on the surface of artificial single crystal diamond. The micromorphology of the inner surface of Ti layer and the phase composition of the interface between the diamond and Ti layer were analyzed with a scanning electron microscope and an X-ray diffractometer, and element analysis was carried out with an energy disperse spectrometer. The effect of diffusion annealing temperature and holding time on phase composition of the inner surface of Ti layer was studied. The formation mechanism of the diamond/Ti layer interface was analyzed. The research results show that a uniform and dense Ti layer is formed on the diamond surface after rotary friction extrusion. After diffusion annealing at 600°C for 0.5 h, dot-shaped TiC grains were formed on the inner surface of Ti layer, and the chemical combination between diamond and Ti layer was realized. With the increase of diffusion annealing temperature and holding time, the morphology of TiC grains grows from dot-shaped to rod-shaped. The mass fraction of TiC of the interface increases with the increase of diffusion annealing temperature. The formation of Ti layer on the diamond surface with rotary friction extrusion heating method can be divided into five stages: initial stage, primary diffusion stage, secondary diffusion stage, TiC nucleation stage and TiC growth stage.
-
Key words:
- rotary friction extrusion /
- diffusion annealing /
- metallizing /
- diamond /
- Ti /
- coating
-
表 1 扩散退火前后Ti涂层内表面的EDS能谱分析
Table 1. EDS spectra analysis of inner surface of Ti layer before and after diffusion annealing
Mass fraction of Ti/wt% Mass fraction of C/wt% Before diffusion annealing 99.03 0.97 After diffusion annealing at 500℃ 93.83 6.17 After diffusion annealing at 600℃ 90.66 9.34 After diffusion annealing at 700℃ 88.94 11.06 After diffusion annealing at 800℃ 85.20 14.80 表 2 棒状物质的EDS能谱分析
Table 2. EDS spectra analysis of rod-shaped substance
Mass fraction/wt% Atomic fraction/at% C 18.85 51.9 Ti 81.15 48.1 表 3 旋转摩擦挤压加温法与一些常见金刚石表面金属化方法对比
Table 3. A comparison between the rotary friction extrusion heating method and some common diamond surface metallization methods
Metallization
methodElectroless plating
and electroplating
methodPhysical vapor
deposition
(PVD)Chemical vapor
deposition
(CVD)Salt bath method
and powder coating
sintering methodVacuum micro-
evaporation
plating methodRotary friction
extrusion
heating methodCoating composition Ni or Ni-W, Ni-Co alloy Ti, Mo, W, Cr Ti, Mo, W, Cr
and corresponding carbideTi, Mo, etc. and corresponding
carbidesTi, Mo, etc. and corresponding carbides Ti, TiC Combination forms Physical Physical Chemical Chemical Chemical Chemical Bond strength Low Low High High High High Plating temperature <373 K <673 K >1123 K 1123-1373 K 973-1093 K >873 K Process cost High High High High, Medium High Low Environmental pollution High Low Medium High, Medium Medium Low Technical difficulty High High High High, Medium High Low Diamond thermal damage No No Severe Severe No No -
[1] 龙伟民. 超硬工具钎焊技术[M]. 郑州: 河南科学技术出版社, 2017: 1-4.LONG Weimin. Brazing technology of superhard tools[M]. Zhengzhou: Henan Science and Technology Press, 2017: 1-4(in Chinese). [2] COE S E, SUSSMANN R S. Optical, thermal and mechanical properties of CVD diamond[J]. Diamond and Related Materials,2000,9(9):1726-1729. [3] KHMELNITSKY R A, EVLASHIN S A, MARTOVITSKY V P, et al. Heteroepitaxy of Ni-based alloys on diamond[J]. Crystal Growth and Design,2016,16(3):1420-1427. doi: 10.1021/acs.cgd.5b01520 [4] HUANG Q, YU D, XU B, et al. Nanotwinned diamond with unprecedented hardness and stability[J]. Nature,2014,510(7504):250-253. doi: 10.1038/nature13381 [5] QU X H, ZHANG L, WU M, et al. Review of metal matrix composites with high thermal conductivity for thermal management applications[J]. Progress in Natural Science: Materials International,2011,21(3):189-197. doi: 10.1016/S1002-0071(12)60029-X [6] JAMES M C, FOGARTY F, ZULKHARNAY R, et al. A review of surface functionalisation of diamond for thermionic emission applications[J]. Carbon,2021,171:532-550. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2020.09.019 [7] DONG Y, ZHANG R, ZHOU L, et al. Formation mechanism and properties of thickness-controllable tungsten layer on diamond surface by salt bath plating[J]. Materials Science Forum,2018,933:264-273. doi: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/MSF.933.264 [8] 郭宏, 王光宗, 贾成厂, 等. 高压熔渗金刚石/铜复合材料的低温导热特性[J]. 复合材料学报, 2014, 31(3):550-555.GUO Hong, WANG Guangzong, JIA Chengchang, et al. Low-temperature heat conduction characteristics of diamond/Cu composite by high pressure infiltration[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2014,31(3):550-555(in Chinese). [9] WEI C, CHENG J, LI J, et al. Tungsten-coated diamond powders prepared by microwave-heating salt-bath plating[J]. Powder Technology,2018,338:274-279. doi: 10.1016/j.powtec.2018.07.035 [10] 王海鹏, 彭坤. 基体中Ti元素含量对金刚石/Cu-Ti复合材料热导率的影响[J]. 复合材料学报, 2018, 35(4):910-919.WANG Haipeng, PENG Kun. Influence of minor Ti addition in matrix on the thermal conductivity of diamond/Cu-Ti composites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2018,35(4):910-919(in Chinese). [11] 王艳辉, 王明智, 关长斌, 等. Ti镀层对金刚石-铜基合金复合材料界面结构和性能的作用[J]. 复合材料学报, 1993, 10(2):107-112. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3851.1993.02.001WANG Yanhui, WANG Mingzhi, GUAN Changbin, et al. Influence of Ti coating on interface structure and properties of diamond-copper base alloy composites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,1993,10(2):107-112(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3851.1993.02.001 [12] ZUO Z, HU B, CHEN H, et al. Effect of activators on the properties of nickel coated diamond composite powders[J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology,2017,33(11):1409-1415. [13] 罗莉, 周强, 杨树忠, 等. 金刚石表面镀钛及其在胎体中结合状态的研究[J]. 金刚石与磨料磨具工程, 2018, 38(5):6-11.LUO Li, ZHOU Qiang, YANG Shuzhong, et al. Study on the titanium plating on diamond surface and its bonding state in the matrix[J]. Diamond & Abrasives Engineering,2018,38(5):6-11(in Chinese). [14] 温立民. 铝铜异种金属的冷压焊和摩擦焊及其接头性能的研究[D]. 成都: 华南理工大学, 2006: 8-11.WEN Limin. Research on cold press welding and friction welding of aluminum and copper dis-similar metals and their joint performance[D]. Chengdu: South China University of Technology, 2006: 8-11(in Chinese). [15] 高志潘. 表面科学与工程[M]. 上海: 华东理工大学出版社, 2006: 10-20.GAO Zhipan. Surface science and engineering[M]. Shanghai: East China University of Science and Technology Press, 2006: 10-20(in Chinese). [16] 靳正国, 郭瑞松, 师春生, 等. 材料科学基础[M]. 天津: 天津大学出版社, 2008: 229, 234-236.JIN Zhengguo, GUO Ruisong, SHI Chunsheng, et al. Fundamentals of materials science[J]. Tianjin: Tianjin University Press, 2008: 229, 234-236(in Chinese). [17] 温诗铸, 黄平. 摩擦学原理[M]. 北京: 清华大学出版社, 2012: 241-243.WEN Shizhu, HUANG Ping. Principles of tribology[M]. Beijing: Tsinghua University Press, 2012: 241-243(in Chinese). [18] 杜随更. 摩擦焊接工艺新发展(一)[J]. 焊接技术, 2000, 29(3):49. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-025X.2000.03.028DU Suigeng. New development of friction welding technology(1)[J]. Welding Technology,2000,29(3):49(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-025X.2000.03.028 [19] 丁大伟, 陈燕, 傅玉灿. 含硼金刚石钎焊界面分析及磨粒强度研究[J]. 金刚石与磨料磨具工程, 2015, 35(5):9-14.DING Dawei, CHEN Yan, FU Yucan. Investigation of grain strength and interfacial microstructure in the brazed joint of boron-doped diamond[J]. Diamond & Abrasives Engineering,2015,35(5):9-14(in Chinese). [20] ZHANG Y, ZHANG H L, WU J H, et al. Enhanced thermal conductivity in copper matrix composites reinforced with titanium-coated diamond particles[J]. Scripta Materialia,2011,65(12):1097-1100. doi: 10.1016/j.scriptamat.2011.09.028 [21] 丁大伟, 陈燕, 傅玉灿. 镀钛金刚石钎焊界面微区结构分析[J]. 南京航空航天大学学报, 2016, 48(6):879-883.DING Dawei, CHEN Yan, FU Yucan. Brazing interface microstructure analysis of Ti-coated diamond[J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Aeronautics & Astronautics,2016,48(6):879-883(in Chinese). [22] LEROY W P, DETAVERNIER C, MEIRH-AEGHE R L V, et al. Thin film solid-state reactions forming carbides as contact materials for carbon-containing semiconductors[J]. Journal of Applied Physics,2007,101(5):1-10. [23] 郭志猛, 宋月清, 陈宏霞, 等. 超硬材料与工具[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 1996: 17.GUO Zhimeng, SONG Yueqing, CHEN Hongxia, et al. Superhard materials and tools[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 1996: 17(in Chinese). [24] LI W C, LIANG C, LIN S T. Epitaxial interface of nanocrystalline TiC formed between Cu-10Sn-15Ti alloy and diamond[J]. Diamond & Related Materials,2002,11(7):1366-1373. [25] 黄继武, 李周. 多晶材料 X 射线衍射: 实验原理、方法与应用[M]. 北京: 冶金工业出版社, 2012: 96-97.HUANG Jiwu, LI Zhou. X-ray diffraction of polycrystalline materials: Experimental principles, methods and applications[M]. Beijing: Metallurgical Industry Press, 2012: 96-97(in Chinese). -





 下载:
下载: