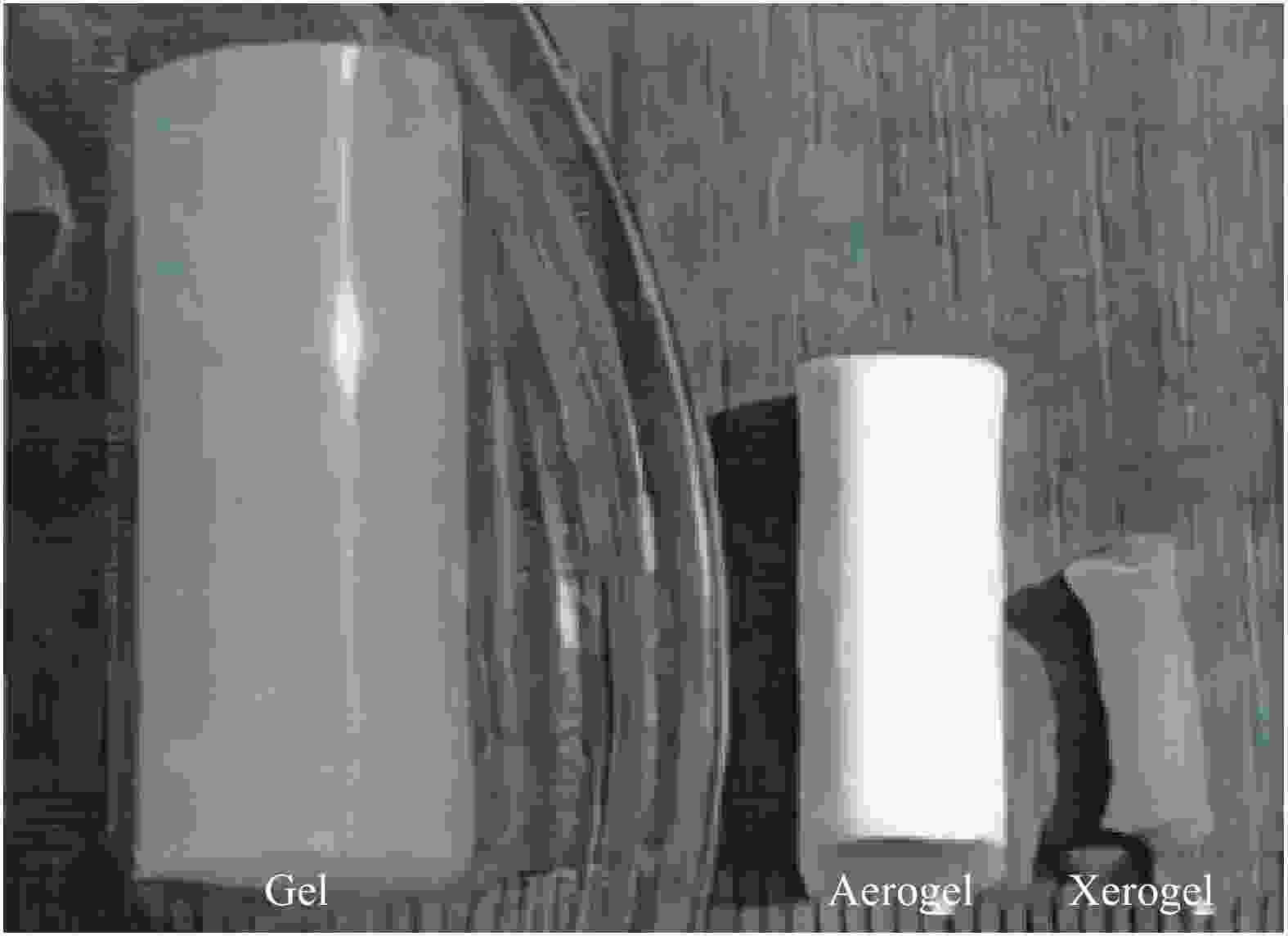
Research progress on preparation and flame retardant properties of organic-inorganic composite aerogel
-
摘要: 以有机高分子材料为基体,复合无机填料制备的气凝胶复合材料具有超轻、绝热、阻燃等优异特性,可广泛应用在建筑节能保温、电子工业、航空航天等领域。本文报道了有机-无机气凝胶复合材料的制备工艺过程和方法,对比了现有气凝胶材料制备方法的优缺点,并综述了当前研究热点的几种常见气凝胶复合材料:聚乙烯醇类、纤维素类、海藻酸盐类、果胶类有机相复合无机组份气凝胶材料的研究进展。总结了气凝胶复合材料的未来发展方向:亟需在气凝胶材料的机械性能优化方面做出改进,还需提高气凝胶复合材料耐水性能,研究无机填料对不同基体气凝胶阻燃等性能的影响规律,拓展生物质可降解高分子基气凝胶复合材料的种类,实现气凝胶材料的工业化应用。Abstract: Aerogel composites made from organic polymer materials and inorganic fillers have excellent properties such as ultralight, heat insulation and flame retardant, which can be widely used in building energy saving and heat preservation, electronics industry, aerospace and other fields. This paper reported the preparation of organic-inorganic aerogel composite materials processes and methods, compared the advantages and disadvantages of the existing aerogel materials preparation methods, and summarizes the current research hot spots of several common aerogel composite materials, including: poly (vinyl alcohol), cellulose, alginate and pectin as organic phase, inorganic components as filler. The future development of aerogel composites is summarized: the mechanical properties and water resistance of aerogel composites need to be improved, the influence of inorganic fillers on the properties of aerogels with different matrixes should be studied, the variety of biomass degradable aerogel composites should be expanded, and the industrial application of aerogel materials needs to be realized.
-
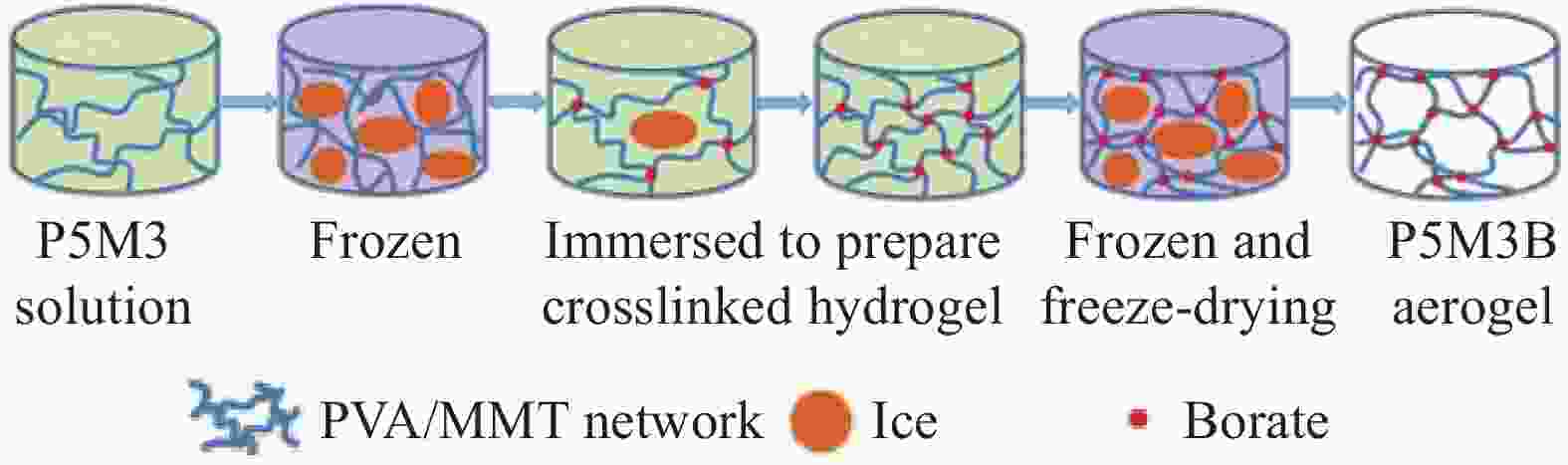
图 4 新型熔融交联法制备气凝胶[29]
Figure 4. Aerogels prepared by a new melting crosslinking method
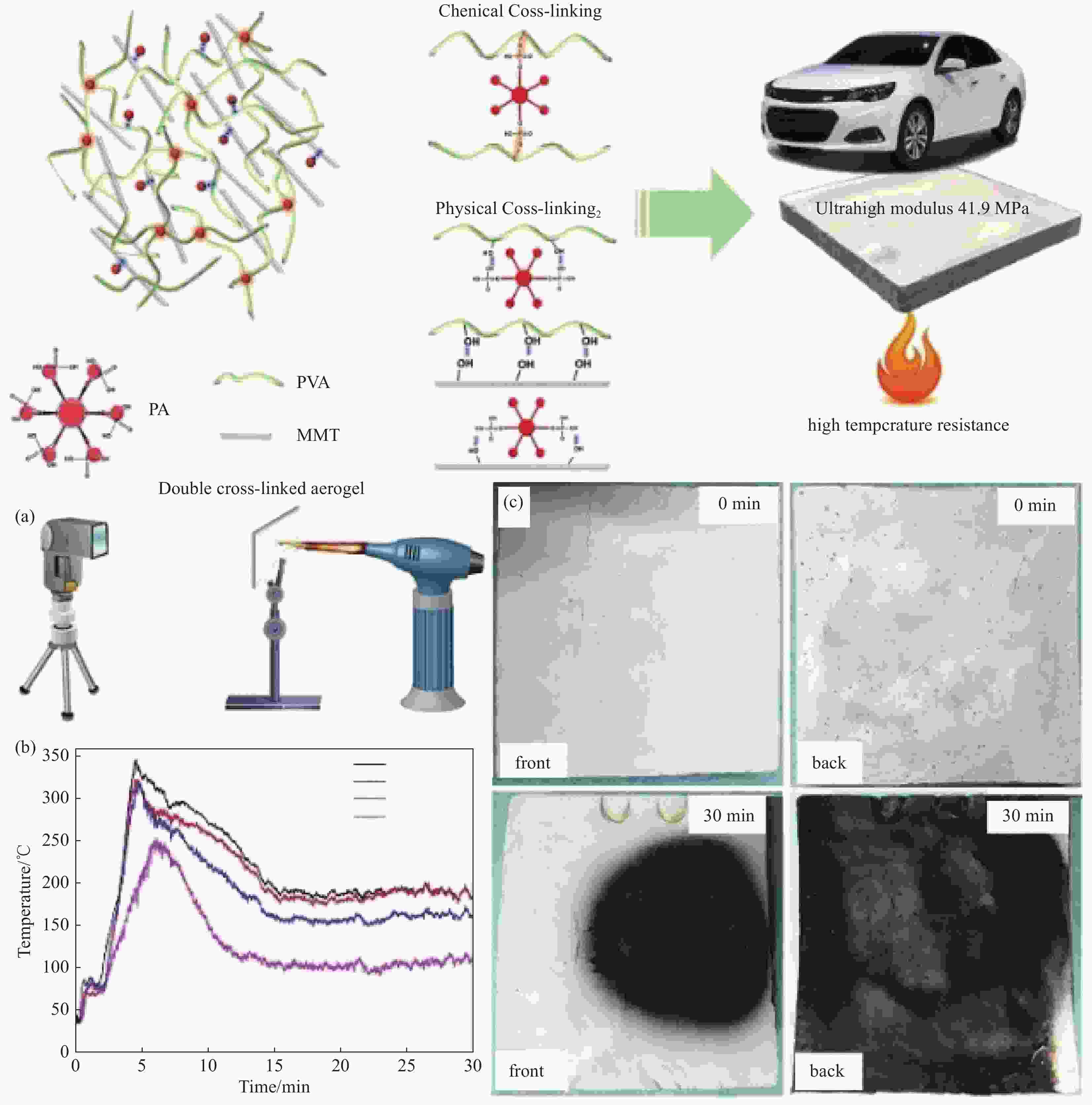
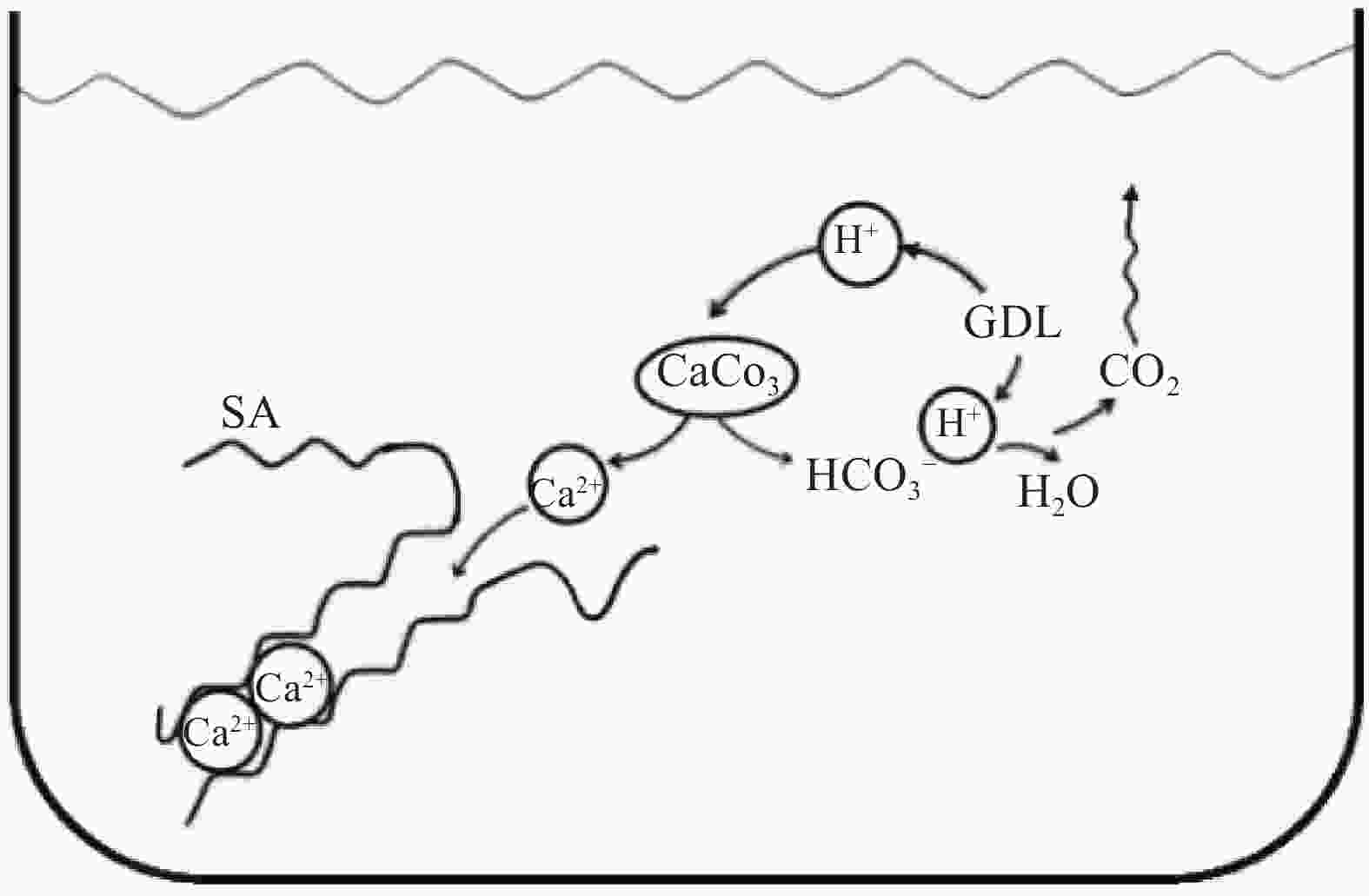
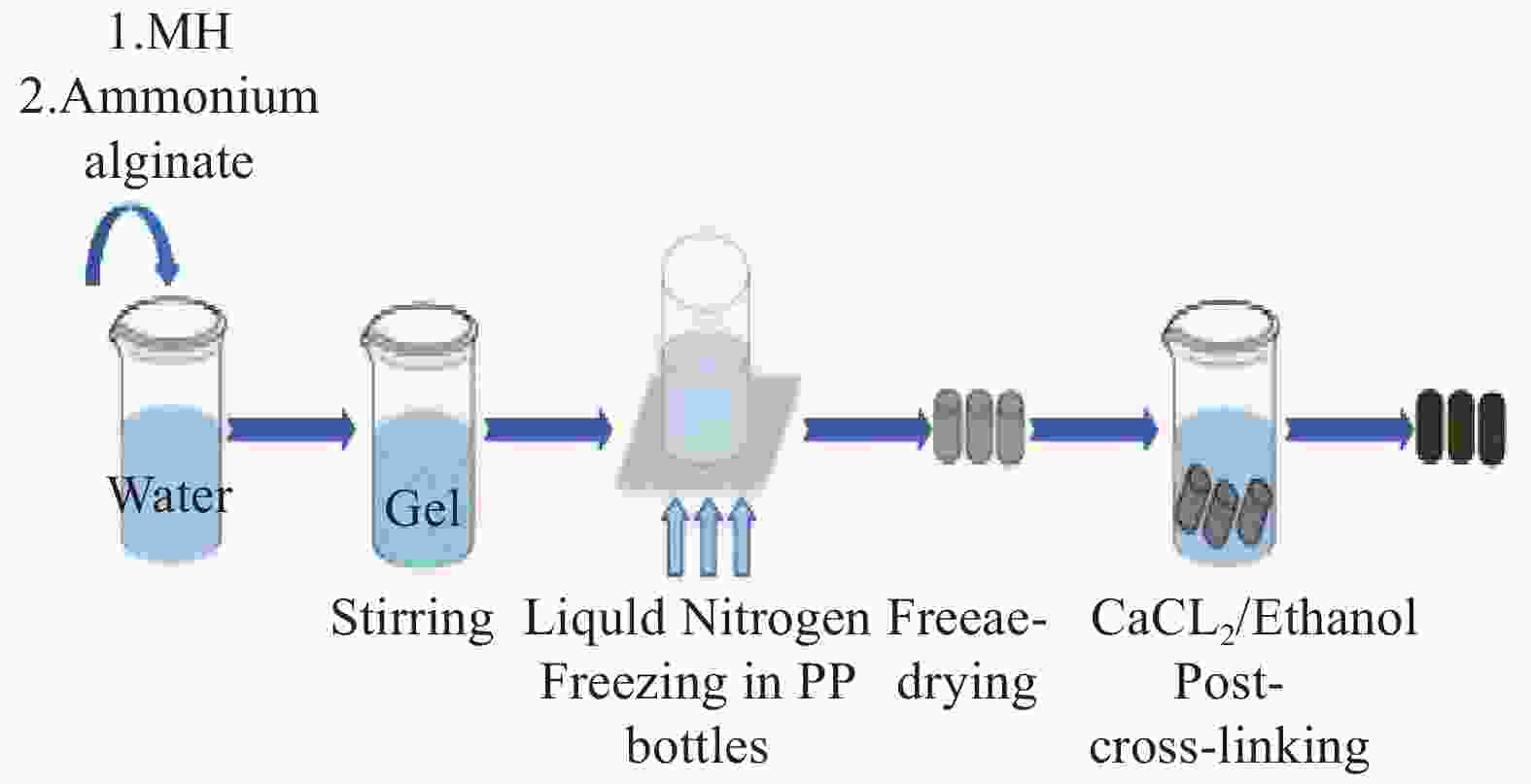
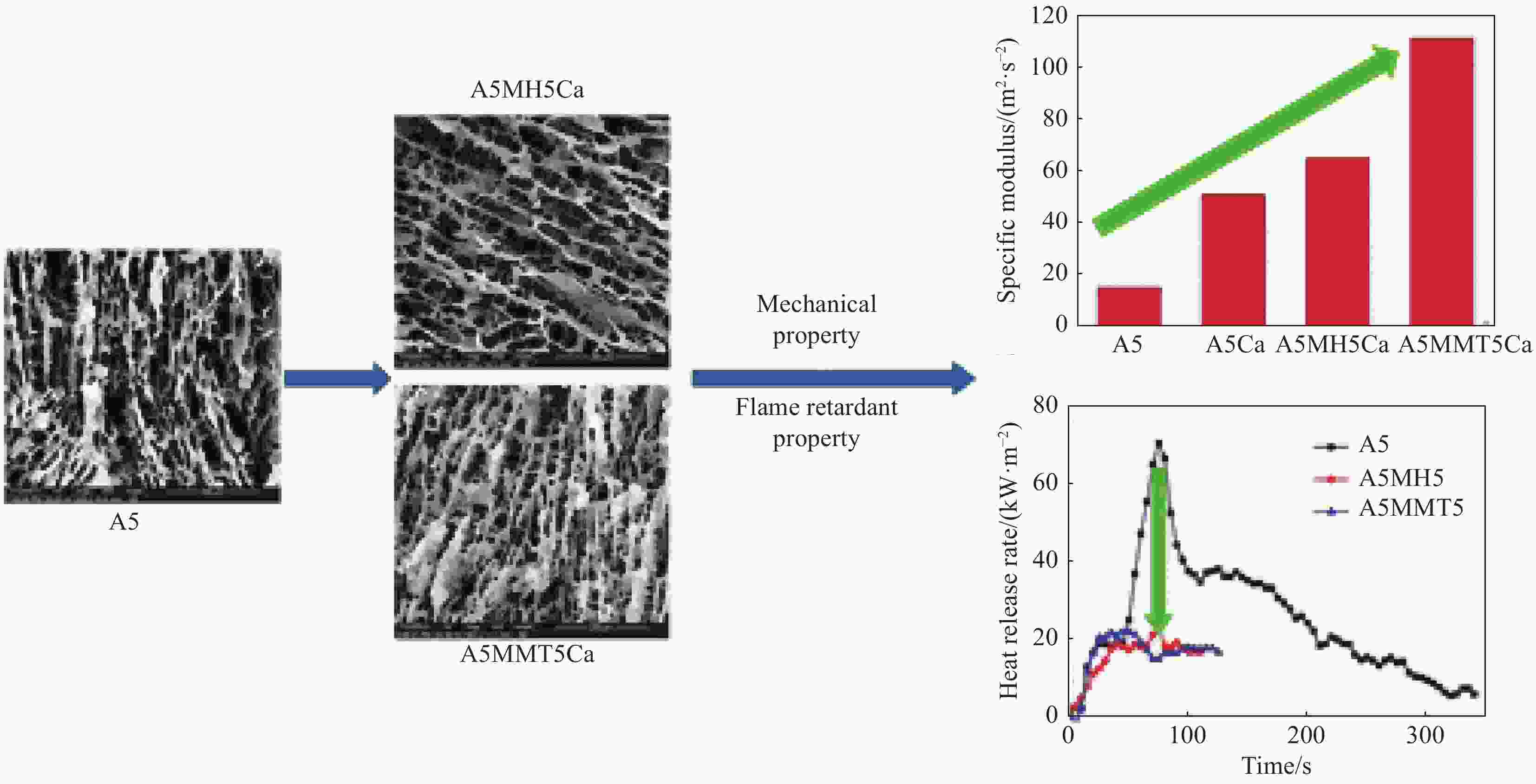
图 5 机械强度高、阻燃性能好的双交联气凝胶[30]
Figure 5. Double-cross-link aerogels with high mechanical strength and good flame-retardant properties
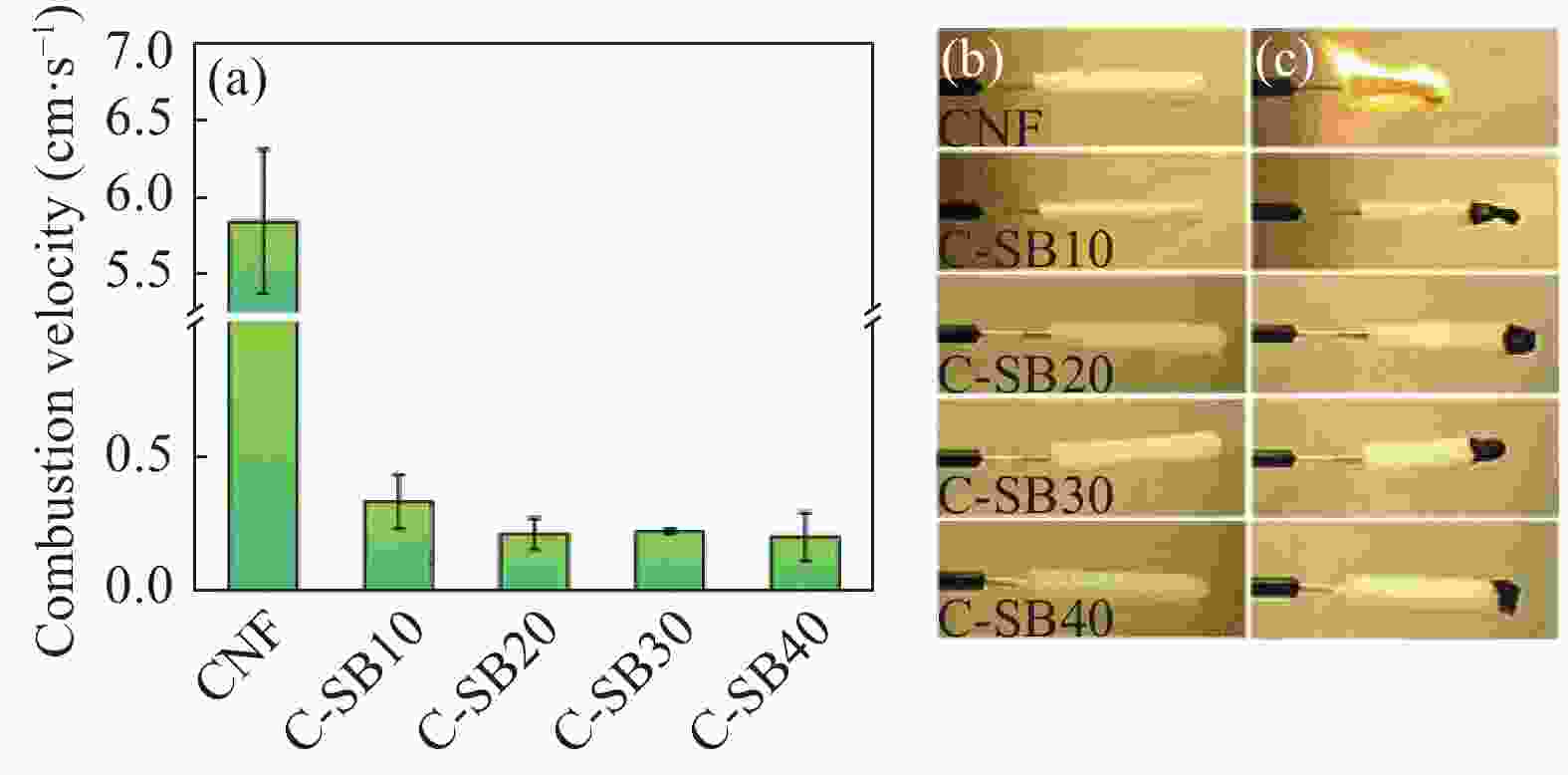
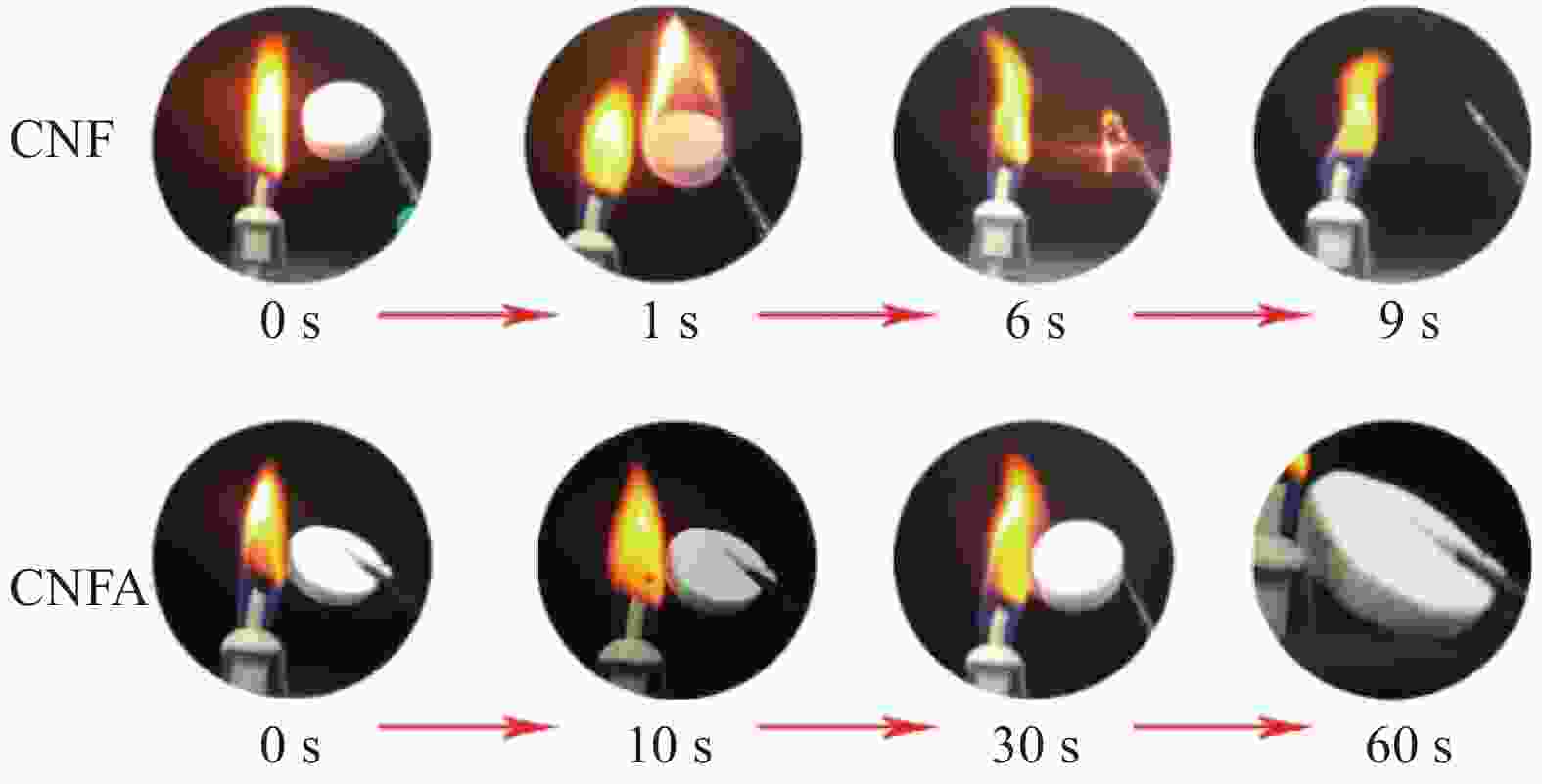
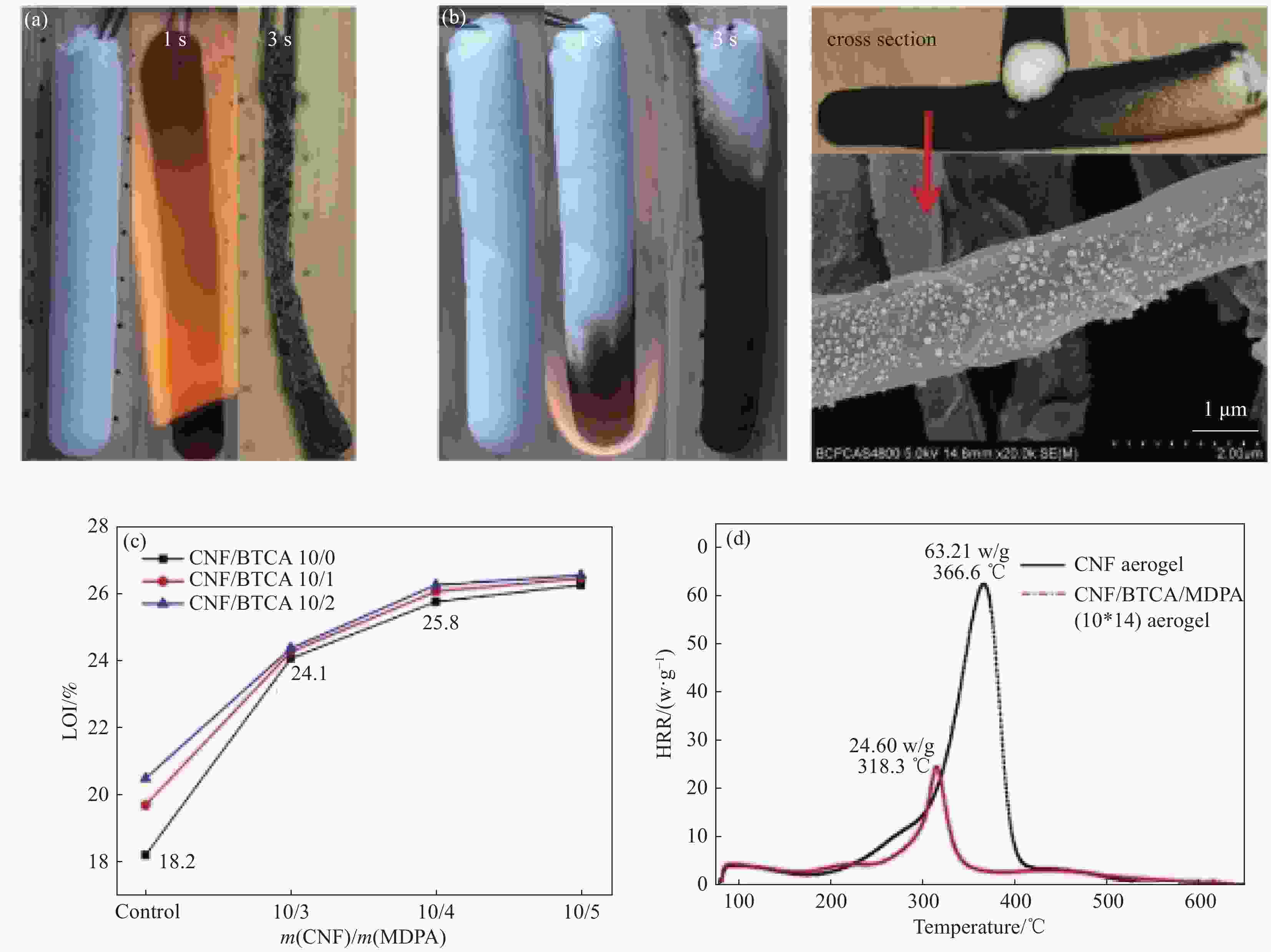
图 9 纯CNF气凝胶 (a) 和CNF/BTCA/MDPA气凝胶 (b) 垂直燃烧实验前后对比和各气凝胶试样的极限氧指数(LOI) (c) 和热释放速率(HRR) (d)[43]
Figure 9. Snapshots of the neat CNF aerogel (a) and CNF/BTCA/MDPA aerogel (b) before and after combustion test, limit oxygen index (LOI) values (c) and heat release rate (HRR) curves (d) of aerogel samples[43]
表 1 不同干燥方法的对比
Table 1. Comparation of different drying methods
Drying methods Supercritical drying Freeze-drying Atmospheric drying Advantage Good structure integrity,
high porosityEasy to operate,
high safetyLow energy consumption,
short production cycleShortage Complex preparation,
high riskExpensive equipment,
damaged porePoor structure integrity,
large pore size表 2 不同有机-无机复合气凝胶的关键指标
Table 2. The important parameters of different organic-inorganic aerogels
Sample Density/
(g·cm−3)Modulus
MPaLOI/% PHRR/
(kW·m−2)THR/
(MJ·m−2)TTI/s Residue/
%λ/
(W·(m·K)−1)FIGRA/
(W·s−1)P5C5[15] 0.086 ± 0.004 11.43 ± 0.13 − 137.1 16.3 5 76.4 − 6.9 P1C9 0.083 ± 0.001 4.92 ± 3.01 − 10.7 0.26 No flame 94.1 − 0.7 HNPA5[24] 0.081 0.34 − − − − − 0.044 ± 0.001 − SNPA5 0.090 1.02 − − − − − 0.050 ± 0.002 − 5P5C[26] 0.105 2.3 ± 0.5 − 182 9.0 − 61.9 − 2.0 5P5C2APP 0.115 0.8 ± 0.2 − 115 12.3 − 57.4 − 0.4 P/M/APP[27] 0.101 ± 0.001 0.91 ± 0.04 24.5 209.6 20.0 3 46.2 − 14.0*** P/M/PA-APP8 0.096 ± 0.002 1.78 ± 0.14 34.0 94.2 11.5 6 51.3 − 4.7*** P5[29] 0.075 ± 0.001 2.9 ± 0.4 19.5 366.6 22.2 3 1.5 − 18.3 P5 M3 0.076 ± 0.001 8.1 ± 1.1 22.5 227.3 15.2 1 39.6 − 15.1 P5 M3B 0.079 ± 0.001 30.7 ± 2.5 27.6 146.5 11.3 1 42.2 − 9.7 P5 M5[30] 0.078 13.9 ± 0.5 22.5 190.3 8.7 4 47.3 − 19.0*** P5PA1.5 M5 0.092 41.9 ± 1.8 38.3 83.8 4.9 6 56.0 0.073 0.7*** PVA-HAP-1[31] 0.112 ± 0.002 3.3 ± 0.5 21.0 ± 0.5 371 14.54 8 − 0.038 ± 0.002 19.1*** PVA-HAP-3 0.109 ± 0.001 6.4 ± 0.7 22.0 ± 0.5 129 3.51 5 − 0.034 ± 0.002 10.8*** P2L2[32] 0.040 ± 0.001 2.44 ± 0.12 24.5 ± 0.5 130.90 5.27 1 52.7 0.041 8.73*** P2L2F7 0.116 ± 0.002 11.56 ± 0.23 >60.0 57.64 2.94 3 78.3 0.049 3.84*** C0[42] 0.180 ± 0.005 − − 280* 13.2** 17 8.9 − − C4 0.450 ± 0.005 − − 22* 1.6** 26 63.4 − − A5[53] 0.047 ± 0.001 0.99 ± 0.06 − 64 13.2 96 3.3 − 2.6 A5C5 0.085 ± 0.001 5.8 ± 0.7 − 32 12.0 No flame 53.3 − 0.7 A5 MH5[54] 0.069 ± 0.001 4.92 ± 0.75 >60 24.63 1.79 No flame 66 − − A5 MH5Ca 0.110 ± 0.001 7.07 ± 1.12 >60 − − − − 0.039 − A5C5-6[57] 0.096 ± 0.002 17 ± 3 − 19.3 3.7 192 66.3 − − A5C5-8 0.090 ± 0.003 6.0 ± 0.4 − 20.0 4.6 153 58.6 − − P5[60] 0.06 ± <0.01 0.07 ± 0.01 − − − − − − − P5C5 0.10 ± <0.01 1.4 ± 0.3 − − − − − − − PE5[61] 0.050 1.4 ± 0.2 20.3 370.5 7.7 1 2.2 0.034 37.1 PE5PA2 0.068 3.6 ± 0.1 41.5 69.6 1.8 1 34.6 0.038 4.6 PA0.5PC4[62] − 4.7 − 35 ± 3 14.8 ± 1 41 ± 2 − 0.035 0.22 ± 0.01 PA2PC4 − 9.2 − 38 ± 3 3.1 ± 0.3 186 ± 5 − 0.038 0.18 ± 0.01 Notes: λ stands for the thermal conductivity. Because of different experimental equipment and methods, the units of some parameters differ. *: the PHRR in W/g; **: the THR in kJ/g; ***: the FIGRA in kW·(m−2·s). -
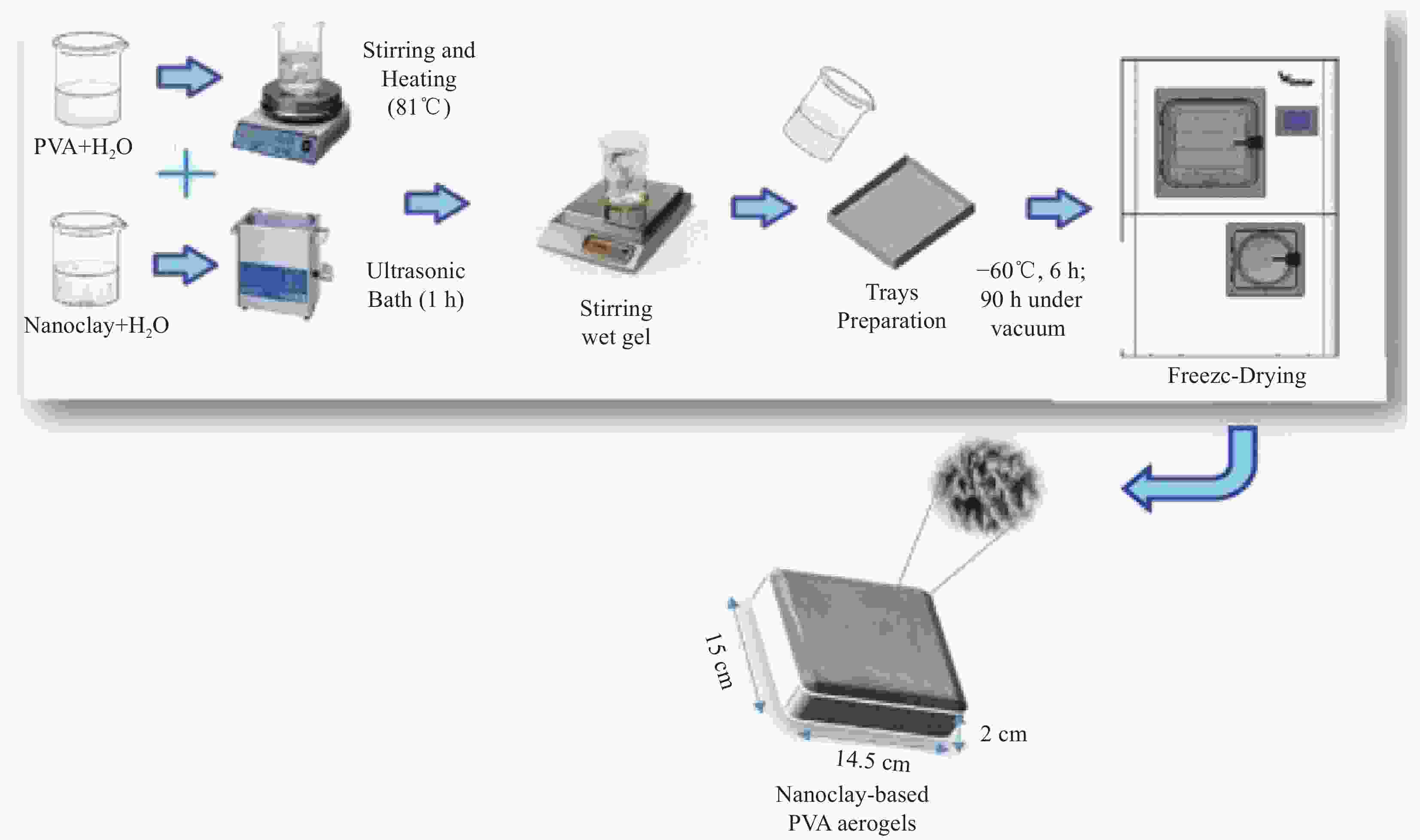
[1] KISTLER, S S. Coherent expanded aerogels and jellies[J], Nature, 1931, 127: 741-741. [2] HE Y L, XIE T. Advances of thermal conductivity models of nanoscale silica aerogel insulation material[J]. Applied Thermal Engineering,2015,81:28. doi: 10.1016/j.applthermaleng.2015.02.013 [3] XIA W, QU C, LIANG Z B, et al. High-performance energy storage and conversion materials derived from a single metal-organic framework/graphene aerogel composite[J]. Nano Letters,2017,17(5):2788. doi: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.6b05004 [4] KONG Y, SHEN X D, CUI S, et al. Preparation of monolith SiC aerogel with high surface area and large pore volume and the structural evolution during the preparation[J]. Ceramics International,2014,40(6):8265. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2014.01.025 [5] SI Y, YU J Y, TANG X M, et al. Ultralight nanofibre-assembled cellular aerogels with superelasticity and multifunctionality[J]. Nature Communications, 2014, 5: 5802. [6] CUCE E, CUCE P M, WOOD C J, et al. Toward aerogel based thermal superinsulation in buildings: A comprehensive review[J]. Renewable & Sustainable Energy Reviews,2014,34:273-299. [7] WANG X, LIU L, WANG X, et al. Preparation and performances of carbon aerogel microspheres for the application of supercapacitor[J]. Journal of Solid State Electrochemistry,2011,15(4):643-648. doi: 10.1007/s10008-010-1142-5 [8] NOCENTINI K, ACHARD P, BIWOLE P. Hygro-thermal properties of silica aerogel blankets dried using microwave heating for building thermal insulation[J]. Energy and Buildings,2018,158:14-22. doi: 10.1016/j.enbuild.2017.10.024 [9] HE S, YANG H, CHEN X. Facile synthesis of highly porous silica aerogel granules and its burning behavior under radiation[J]. Journal of Sol-Gel Science and Technology,2017,82(2):407-416. doi: 10.1007/s10971-017-4304-4 [10] GUO W W, NIE S B, EHSAN N K, et al. Construction of SiO2/UiO-66 core-shell microarchitectures through covalent linkage as flame retardant and smoke suppressant for epoxy resins[J]. Composites,2019:107261. [11] PEKALA R W, KONG F M. Resorcinol-formaldehyde aerogels and their carbonized derivatives[J]. Abstracts of Papers of the American Chemical Society,1989,197:113. [12] 沈晓冬, 吴晓栋, 孔勇, 等. 气凝胶纳米材料的研究进展[J]. 中国材料进展, 2018, 37(9):671-680, 692.SHEN Xiaodong, WU Xiaodong, KONG Yong, et al. Recent advances on aerogel based nano materials[J]. Materials China,2018,37(9):671-680, 692(in Chinese). [13] CHEN H B, WANG Y Z, MIGUEL Sánchez-Soto, et al. Low flammability, foam-like based on ammonium alginate and sodium montmorillonite clay[J], Polymer, 2012, 53, 5825-5831. [14] LI X L, CHEN M J, CHEN H B. Facile fabrication of mechanically-strong and flame retardant alginate/clay aerogels[J]. Composites Part B,2019:164. [15] CHEN H B, LIU B, HUANG W, et al. Fabrication and properties of irradiation-cross-linked poly(vinyl alcohol)/clay aerogel composites[J]. Acs Applied Materials & Interfaces,2014(6):16227-16236. [16] 沈军, 王珏, 吴翔. 气凝胶− 一种结构可控的新型功能材料[J]. 材料科学与工程, 1994(47):1-5.SHEN Jun, WANG Jue, WU Xiang. Aerogels-A type of structure controllable new functional materials[J]. Materials Science and Engineering,1994(47):1-5(in Chinese). [17] WANG L, SANCHEZ-SOTO M, MASPOCH M L. Polymer/clay aerogel composites with flame retardant agents: Mechanical, thermal and fire behavior[J]. Materials & Design,2013,52:609-614. [18] WANG Y T, LIAO S F, SHANG K, et al. Efficient approach to improving the flame retardancy of poly(vinyl alcohol)/clay aerogels: Incorporating piperazine-modified ammonium polyphosphate[J]. Acs Applied Materials & Interfaces,2015,7:1780-1786. [19] BANDI S, SCHIRALDI D A. Glass transition behavior of clay aerogel/poly (vinyl alcohol) composites[J]. Macromolecules,2006,39:6537-6545. doi: 10.1021/ma0611826 [20] BRINKER C J, SCHERER G W. Sol-gel science[M]. New York: Academic Press, 1990. [21] VALENTIN R, HORGA R, BONELLI B, et al. Acidity of alginate aerogels studied by FTIR spectroscopy of probe molecules[C]. Macromolecular Symposia, 2005, 230: 71-77. [22] 成一. 海藻酸钠基气凝胶的制备、补强与疏水改性[D]. 海口: 海南大学, 2012.CHENG Yi. Preparation, reinforcement and hydrophobic modification of sodium alginate aerogels[D]. Haikou: Hainan University, 2012(in Chinese). [23] ZUO L, ZHANG Y, ZHANG L, et al. Polymer/carbon-based hybrid aerogels: preparation, properties and applications[J]. Materials,2015,8(10):6806-6848. doi: 10.3390/ma8105343 [24] SIMÓN-HERRERO C, GOMEZ L, ROMERO A, et al. Nanoclay-based PVA aerogels: Synthesis and characterization[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research,2018,57(18):6218-6225. [25] KIM H, PARK J W, KIM H J, et al. Flame retardant nano-composites containing nano-fillers[J]. Tailored Nanostructures,2016,13(5):1-28. [26] WANG L, SÁNCHEZ-SOTO M, MASPOCH M L. Polymer/clay aerogel composites with flame retardant agents: Mechanical, thermal and fire behavior[J]. Materials & Design (1980-2015),2013,52:609-614. [27] WANG Y T, LIAO S F, SHANG K, et al. Efficient approach to improving the flame retardancy of poly(vinyl alcohol)/clay aerogels: Incorporating piperazine-modified ammonium polyphosphate[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2015,7(3):1780-1786. [28] CHEN H B, HOLLINGER E, WANG Y Z, et al. Facile fabrication of poly(vinyl alcohol) gels and derivative aerogels[J]. Polymer,2014,55(1):380-384. doi: 10.1016/j.polymer.2013.07.078 [29] SHANG K, YE D D, KANG A H, et al. Robust and fire retardant borate-crosslinked poly (vinyl alcohol)/montmorillonite aerogel via melt-crosslink[J]. Polymer,2017,131:111-119. doi: 10.1016/j.polymer.2017.07.022 [30] WANG H, CAO M, ZHAO H B, et al. Double-cross-linked aerogels towards ultrahigh mechanical properties and thermal insulation at extreme environment[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2020,399:125698. [31] GUO W W, LIU J J, ZHANG P, et al. Multi-functional hydroxyapatite/polyvinyl alcohol composite aerogels with self-cleaning, superior fire resistance and low thermal conductivity[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2018,158:128-136. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2018.01.020 [32] KANG A H, SHANG K, YE D D, et al. Rejuvenated fly ash in poly(vinyl alcohol)-based composite aerogels with high fire safety and smoke suppression[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2017,327:992-999. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2017.06.158 [33] EICHHORN S J, YOUNG R J, DAVIES G R. Modeling crystal and molecular deformation in regenerated cellulose fibers[J]. Biomacromolecules, 2005, 6(1): 507-513. [34] MACHADO M, SOUZA S M, FERREIRA M A, et al. Influence of cellulose fibers and fibrils on nanoscale friction in kraft paper[J]. Cellulose,2016,23:2653-2661. doi: 10.1007/s10570-016-0953-7 [35] BRINKMANN A, CHEN M, COUILLARD M, et al. Correlating cellulose nanocrystal particle size and surface area[J]. Langmuir,2016,32:6105-6114. doi: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.6b01376 [36] LI M C, WU Q L, SONG K L, et al. Cellulose nanoparticles: Structure-morphology-rheology relationships[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering, 2015, 3: 821–832. [37] VARANASI S, BATCHELOR W. Superior non-woven sheet forming characteristics of low-density cationic polymer-cellulose nanofiber colloids[J]. Cellulose,2014,21:3541-3550. doi: 10.1007/s10570-014-0370-8 [38] NUMATA Y, SAKATA T, FURUKAWA H, et al. Bacterial cellulose gels with high mechanical strength[J]. Materials Science & Engineering C-Materials for Biological Applications, 2015, 47: 57. [39] FAROOQ M, SIPPONEN M H, SEPPALA A, et al. Eco-friendly flame-retardant cellulose nanofibril aerogels by incorporating sodium bicarbonate[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2018,10(32):27407-27415. [40] FAN B, CHEN S J, YAO Q F, et al. Fabrication of cellulose nanofiber/AlOOH aerogel for flame retardant and thermal insulation[J]. Materials,2017,10(3):311. doi: 10.3390/ma10030311 [41] HAN Y Y, ZHANG X X, WU X D, et al. Flame retardant, heat insulating cellulose aerogels from waste cotton fabrics by in situ formation of magnesium hydroxide nanoparticles in cellulose gel nanostructures[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering,2015,3(8):1853-1859. [42] HE C, HUANG J Y, LI S H, et al. Mechanically resistant and sustainable cellulose-based composite aerogels with excellent flame retardant, sound-absorption, and superantiwetting ability for advanced engineering materials[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering,2017,6(1):927-936. [43] GUO L M, CHEN Z L, LYU S Y, et al. Highly flexible cross-linked cellulose nanofibril sponge-like aerogels with improved mechanical property and enhanced flame retardancy[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2018,179:333-340. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2017.09.084 [44] ABOU-OKEIL A, EL-SAWY S M, ABDEL-MOHDY F A. Flame retardant cotton fabrics treated with organophosphorus polymer[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2013,92:2293-2298. [45] GUO W W, WANG X, ZHANG P, et al. Nano-fibrillated cellulose-hydroxyapatite based composite foams with excellent fire resistance[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2018,195:71-78. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.04.063 [46] ROBITZER M, DAVID L, ROCHAS C, et al. Nanostructure of calcium alginate aerogels obtained from multistep solvent exchange route[J]. Langmuir,2008,24(21):12547-12552. doi: 10.1021/la802103t [47] ORIVE G, PONCE A, HERNANDEZ RM, et al. Biocompatibility of microcapsules for cell immobilization elaborated with different type of alginates[J]. Biomaterials,2002,23(18):3825-3831. [48] DRURY J L, MOONEY D J. Hydrogels for tissue engineering: scaffold design variables and applications[J]. Biomaterials,2003,24(24):4337-4351. [49] LAI H L, ABU’KHALIL A, CRAIG D, et al. The preparation and characterisation of drug-loaded alginate and chitosan sponges[J]. International Journal of Pharmaceutics,2003,251(1):175-181. [50] BABU V R, SAIRAM M, HOSAMANI K M, et al. Preparation of sodium alginate-methylcellulose blend microspheres for controlled release of nifedipine[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2006,69(2):241-250. [51] ARICA M Y, ARPA C, ERGENE A, et al. Ca-alginate as a support for Pb(II) and Zn(II) biosorption with immobilized Phanerochaete chrysosporium[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2003,52(2):167-174. [52] ZHANG J J, JI Q, SHEN X H, et al. Pyrolysis products and thermal degradation mechanism of intrinsically flame-retardant calcium alginate fibre[J]. Polymer Degradation and Stability,2011,96(5):936-942. [53] CHEN H B, WANG Y Z, SANCHEZ-SOTO M, et al. Low flammability, foam-like materials based on ammonium alginate and sodium montmorillonite clay[J]. Polymer,2012,53(25):5825-5831. doi: 10.1016/j.polymer.2012.10.029 [54] SHANG K, LIAO W, WANG J, et al. Nonflammable alginate nanocomposite aerogels prepared by a simple freeze-drying and post-cross-linking method[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2016,8(1):643-650. [55] RAVICHANDRAN J, SIVASANKAR B. Properties and catalytic activity of acid-modified montmorillonite and vermiculite[J]. Clays and Clay Miner 1997, 45, (6): 854–8. [56] BONGARTZ R, AG D, SELECI M, et al. Folic acid-modified clay: targeted surface design for cell culture applications[J]. Jounal of Materials Chemistry B 2013, 1: 522–528. [57] LI X L, CHEN M J, CHEN H B, Facile fabrication of mechanically-strong and flame retardant alginate/clay aerogels[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2019.164: 18-25. [58] DRAGET K I, SMIDSROD O, SKJAK-BRAK G. Alginates from algae. In E. J. Vandamme, S. De Baets, &A. Steinbuchel(Eds.), Biopolymers polysaccharides from eukaryotes[M]. Weinheim, Wiley-VCH. 2002: 215-244. [59] SOPHIE G, TATIANA B. Thermal conductivity /structure correlations in thermal super-insulating pectin aerogels[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2018,196:73-81. [60] CHEN H B, CHIOU B S, WANG Y Z, et al. Biodegradable pectin/clay aerogels[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2013,5(5):1715-1721. [61] 王涵, 刘晋旭, 李蒙恩, 赵海波, 王玉忠. 难燃生物质气凝胶的设计制备与性能研究[J]. 化学研究与应用, 2019, 31(7):1335-1341. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1656.2019.07.016WANG Han, LIU Jinxu, LI Mengen, et al. Fully biobased aerogels with high strength and flame retardancy[J]. Chemical Research and Application,2019,31(7):1335-1341(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1656.2019.07.016 [62] ZHAO H B, CHEN M J, et al. Thermal insulating and flame-retardant polyaniline/pectin aerogels[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering,2017,5(8):7012-7019. -





 下载:
下载: