Optimal design of laying sequence of composite gas cylinders based on impact damage
-
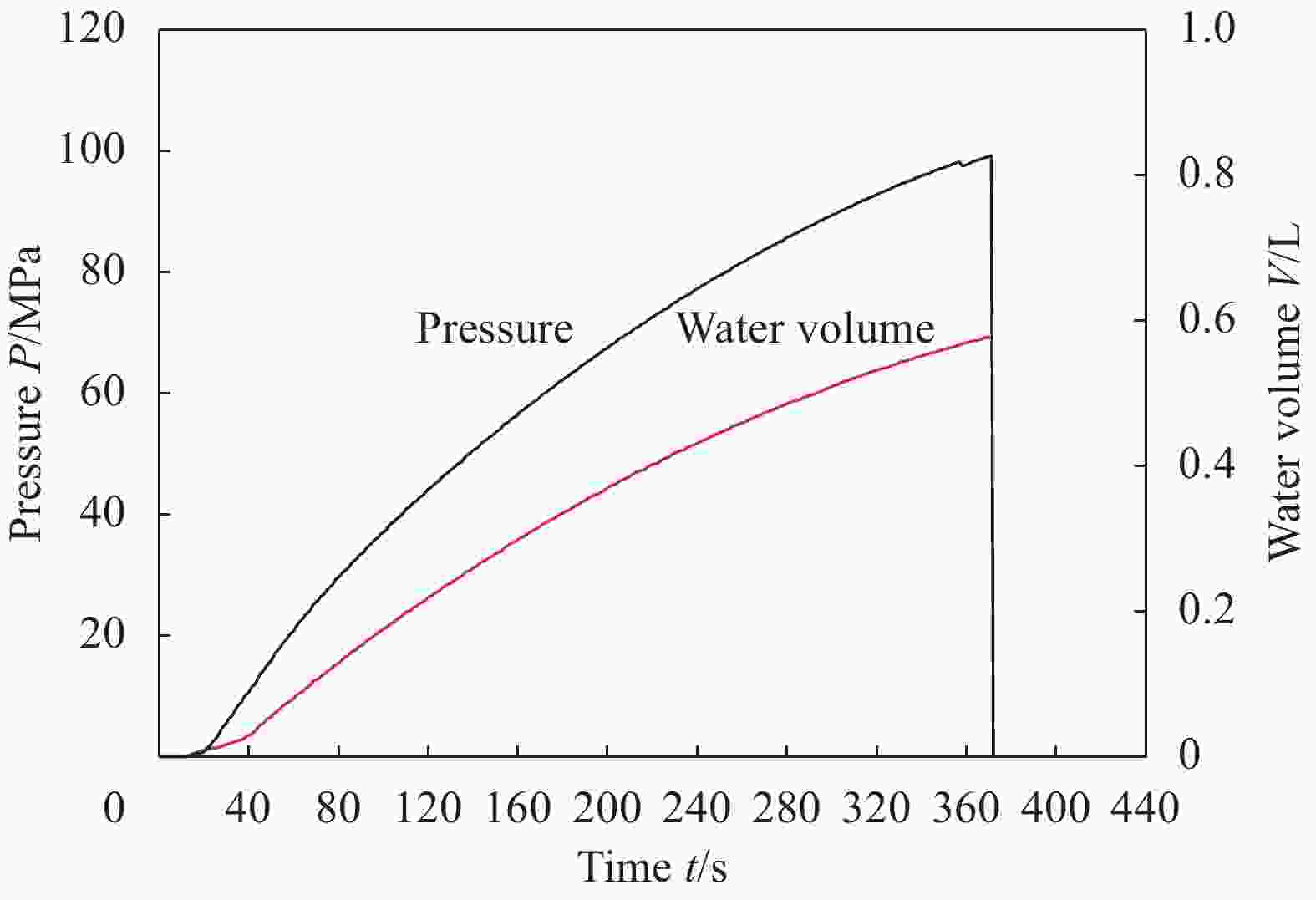
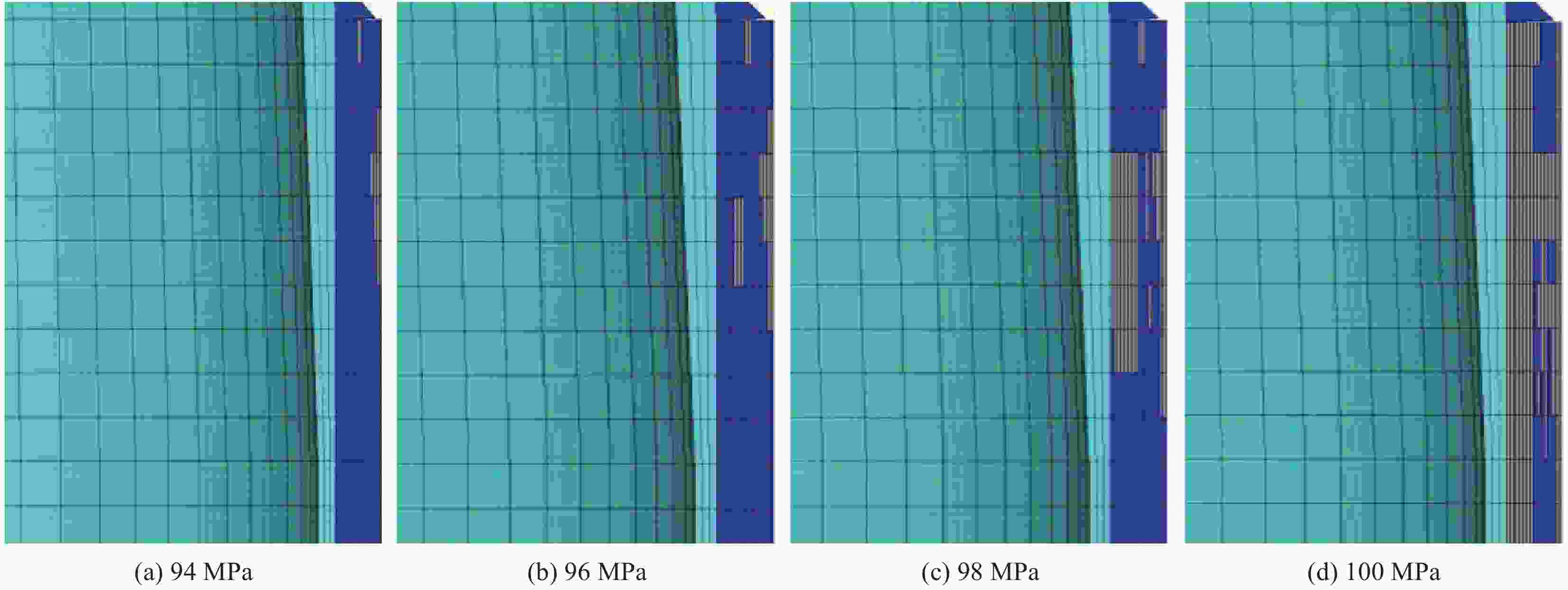
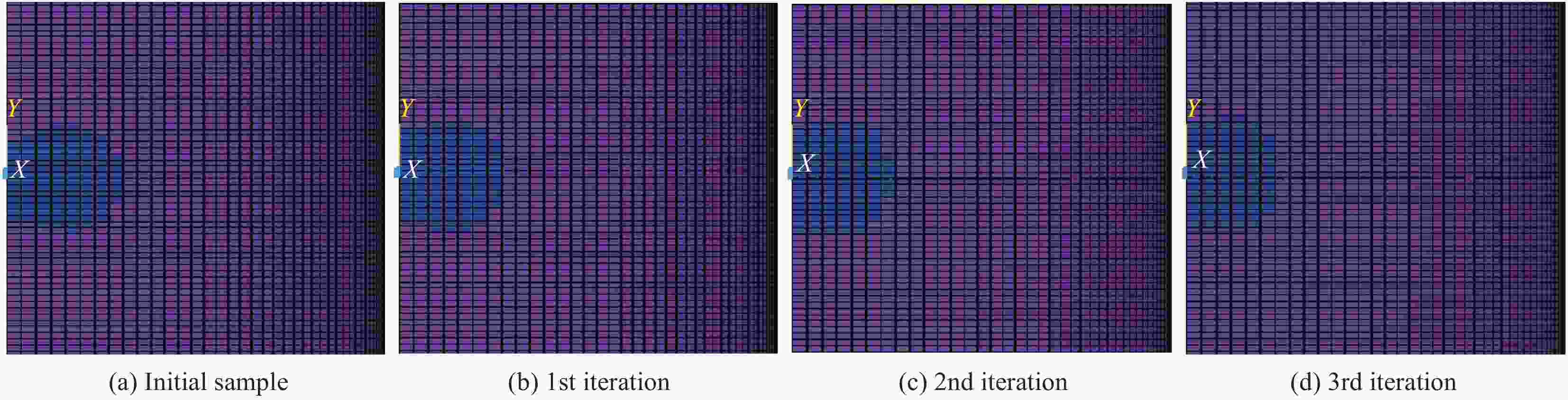
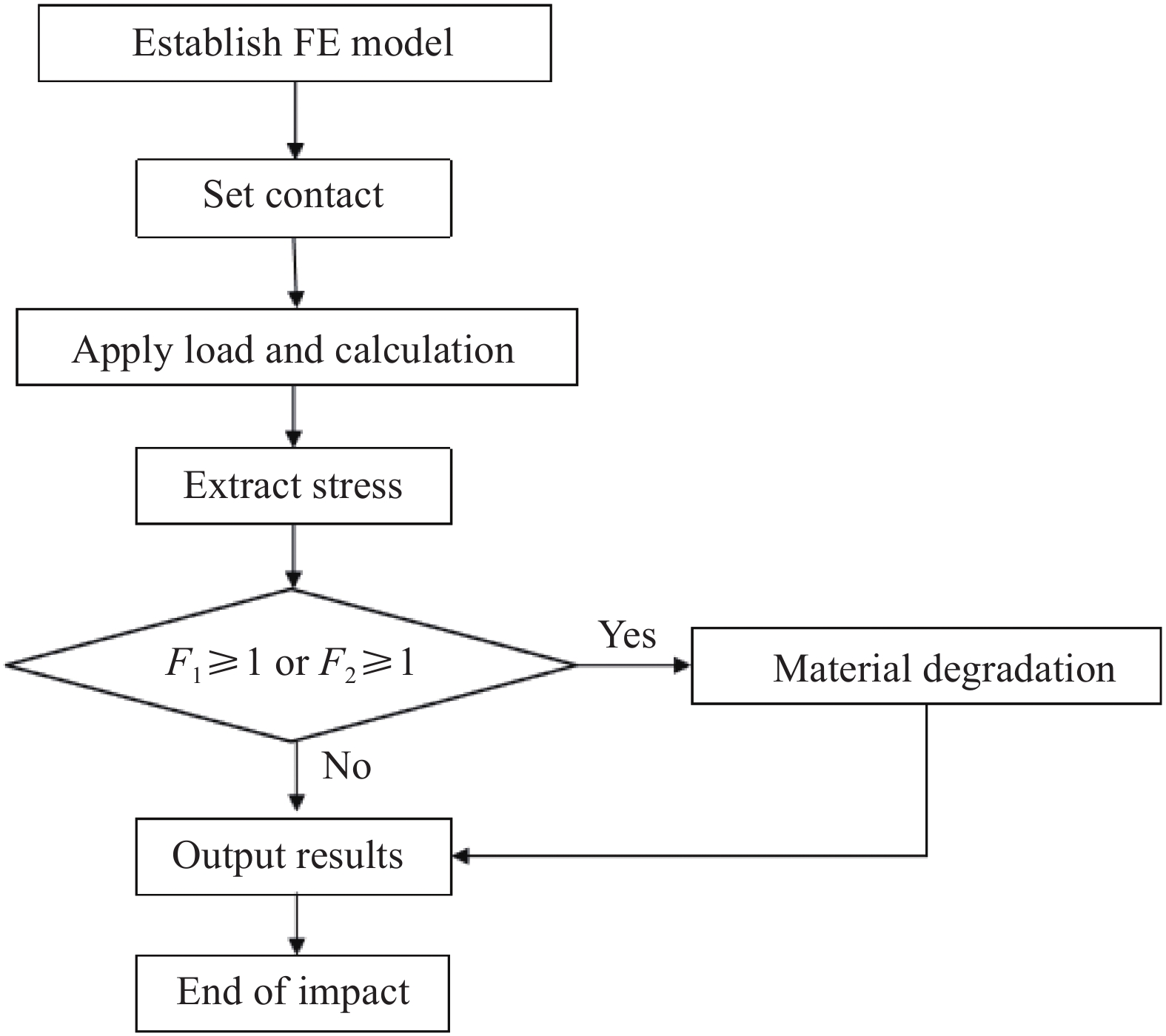
摘要: 基于瞬态动力学理论和遗传优化算法,以提高抗冲击损伤能力为优化目标对复合材料气瓶的铺层顺序进行优化。遗传算法利用MATLAB软件实现,复合材料气瓶冲击损伤分析采用ANSYS进行,通过两个软件之间的信息传递,实现优化计算。以铝内胆复合材料气瓶为算例进行优化,结果表明,在同一冲击能量下,优化后的气瓶基体破裂面积和基体破裂层数均大幅减小,剩余爆破压力显著提高。当冲击能量为60 J时,该气瓶表面基体破裂面积减少了8.8%,基体破裂层数减少了14.3%,剩余爆破压力值提高了9.6%。本文建立的优化算法可以用于复合材料气瓶铺层优化设计。Abstract: Based on the transient dynamics theory and genetic optimization algorithm, the layup sequence of composite gas cylinder was optimized with the optimization goal of improving the resistance to impact damage. The genetic algorithm was realized by MATLAB software, and the impact damage analysis of composite gas cylinders was carried out by ANSYS. Through the information transmission between the two software, the optimized process was realized. Taking an aluminum-lined composite gas cylinder as an example for optimization, the results show that under the same impact energy, the matrix rupture area and the number of matrix rupture layers of optimized gas cylinder are greatly reduced, and the remaining burst pressure is significantly increased. When the impact energy is 60 J, the rupture matrix area on the surface reduces 8.8%, the number of rupture layers in the matrix reduces 14.3%, and the remaining burst pressure value increases 9.6%. The optimization algorithm established in this paper can be used to optimize the design of composite gas cylinders.
-
Key words:
- composite materials /
- laying sequence /
- impact damage /
- genetic algorithm /
- burst pressure
-
表 1 Camanho参数退化
Table 1. Camanho parameter degradation
Failure mode Camanho degradation rule Matrix tensile or shear cracking $E_{yy}' = 0.2{E_{yy}}$;$G_{xy}' = 0.2{G_{xy}}$;$G_{yz}' = 0.2{G_{yz}}$ Matrix compression or shear cracking $E_{yy}' = 0.4{E_{yy}}$;$ G_{xy}' = 0.4{G_{xy} } $;$ G_{yz}' = 0.4{G_{yz} } $ Matrix fiber shearing $G_{xy}' = v_{xy}' = 0$ Fiber tensile fracture $E_{xx}' = 0.07{E_{xx}}$ Fiber compressive fracture $E_{xx}' = 0.14{E_{xx}}$ Notes: Exx, Eyy and Ezz—Young’s modulus of the composite layer in x, y, z direction, respectively; ν and G—Poisson’s ratio and shear modulus, respectively. 表 2 T700碳纤维环氧树脂基复合材料性能
Table 2. Mechanical properties of T700/epoxy composite
Exx/GPa Eyy/GPa Ezz/GPa νxy νyz νxz 154.1 11.41 11.41 0.49 0.33 0.49 Gxy/GPa Gyz/GPa Gxz/GPa Xt/MPa Yt/MPa Sxy/MPa 7.092 3.792 7.092 2360 66 129 Notes: Xt, Yt—Tensile strength in x, y direction, respectively; Sxy—Shear strength. -
[1] KIM S W, KIM E H, JEONG M S. Damage evaluation and strain monitoring for composite cylinders using tin-coated FBG sensors under low-velocity impacts[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering,2015,74:13-22. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2015.01.004 [2] CHOI B H, KWON I B. Damage mapping using strain distribution of an optical fiber embedded in a composite cylinder after low-velocity impacts[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering,2019,173:107009. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.107009 [3] 李小明, 邱桂杰, 刘锦霞. 某型复合材料气瓶优化设计[J]. 纤维复合材料, 2007, 3(1):21-23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6423.2007.01.006LI Xiaoming, QIU Guijie, LIU Jinxia. Optimal design of a certain type of composite gas cylinder[J]. Fiber Compo-site Materials,2007,3(1):21-23(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6423.2007.01.006 [4] 黄家康, 岳红军, 董永祺. 复合材料成型技术[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 1999.HUANG Jiakang, YUE Hongjun, DONG Yongqi. Composite material molding technology[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 1999(in Chinese). [5] 王晓宏, 张博明, 刘长喜, 等. 纤维缠绕复合材料压力容器渐进损伤分析[J]. 计算力学学报, 2009, 3:446-452.WANG Xiaohong, ZHANG Boming, LIU Changxi, et al. Progressive damage analysis of filament wound composite pressure vessels[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Mechanics,2009,3:446-452(in Chinese). [6] 王帅培, 王栋. 无人机复合材料尾翼结构的优化设计[J]. 机械研究与应用, 2020, 33(1):133-135, 141.WANG Shuaipei, WANG Dong. Optimal design of UAV composite tail wing structure[J]. Mechanical Research and Application,2020,33(1):133-135, 141(in Chinese). [7] 王慧敏. 复合纤维风机叶片铺层结构优化设计及应用[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古工业大学, 2014.WANG Huimin. Optimal design and application of compo-site fiber fan blade layer structure[D]. Huhhot: Inner Mongolia University of Technology, 2014(in Chinese). [8] RICHE R, HAFTKA R. Optimization of laminate stacking sequence for buckling load maximization by genetic algorithm[J]. AIAA Journal,1993,31(5):951-956. doi: 10.2514/3.11710 [9] NAGENDRA S, HAFTKA R, GURDAL Z. Stacking sequence optimization of simply supported laminates with stability and strain constraints[J]. 1992, 30(8): 2132-2137. [10] KIM C U, KANG J H, HONG C S, et al. Optimal design of filament wound structures under internal pressure based on the semi-geodesic path algorithm[J]. Composite Structures,2005,67(4):443-452. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2004.02.003 [11] KIM C U, HONG C S, KIM C G, et al. Optimal design of filament wound type 3 tanks under internal pressure using a modified genetic algorithm[J]. Composite Structures,2005,71(1):16-25. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2004.09.006 [12] LIU Pengfei, XU Ping, ZHENG Jinyang. Artificial immune system for optimal design of composite hydrogen storage vessel[J]. Computational Materials Science,2009,47(1):261-267. doi: 10.1016/j.commatsci.2009.07.015 [13] XU Ping, ZHENG Jinyang, CHEN Honggang, et al. Optimal design of high pressure hydrogen storage vessel using an adaptive genetic algorithm[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy,2010,35(7):2840-2846. doi: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2009.05.008 [14] JIAO Weicheng, NIU Yue, HAO Lifeng, et al. Optimal design of lightweight composite pressure vessel by using artificial immune algorithm[J]. Polymers & Polymer Composites,2014,22(3):323-328. [15] LIN DTW, HSIEH J C, CHINDAKHAM N, HAI P D. Optimal design of a composite laminate hydrogen storage vessel[J]. International Journal of Energy Research,2013,37(7):761-768. doi: 10.1002/er.2983 [16] 颜标, 郭凯特, 校金友. 考虑渐进损伤的纤维缠绕复合材料圆筒铺层顺序优化设计[J]. 固体火箭技术, 2020, 43(4):468-475.YAN Biao, GUO Kaite, XIAO Jinyou. Optimization design of fiber-wound composite cylinder layering sequence considering progressive damage[J]. Solid Rocket Technology,2020,43(4):468-475(in Chinese). [17] VAFAEESEFAT A. Optimization of composite pressure vessels with metal liner by adaptive response surface method[J]. Journal of Mechanical Science and Technology,2011,25(11):2811-2816. doi: 10.1007/s12206-011-0721-4 [18] HASHIN Z, ROTEM A. A fatigue failure criterion for fiber reinforced materials[J]. Journal of Composite Materials,1973,7(4):448-464. doi: 10.1177/002199837300700404 [19] WANG Zewu, ZHANG Guojin, LIU Peiqi, et al. Pregressive damage analysis of full-wrapped composite gas cylinder under overload condition and prediction of its bursting pressure[J]. Strength, Fracture and Complexity: An International Journal,2015,9(2):175-185. [20] CAMANHO P P, MATTHEWS F L. A progressive damage model for mechanically fastened joints in composite laminates[J]. Journal of Composite Materials,1999,33(24):2248-2280. doi: 10.1177/002199839903302402 -






 下载:
下载: