Progress in intrinsic thermally conductive polymers
-
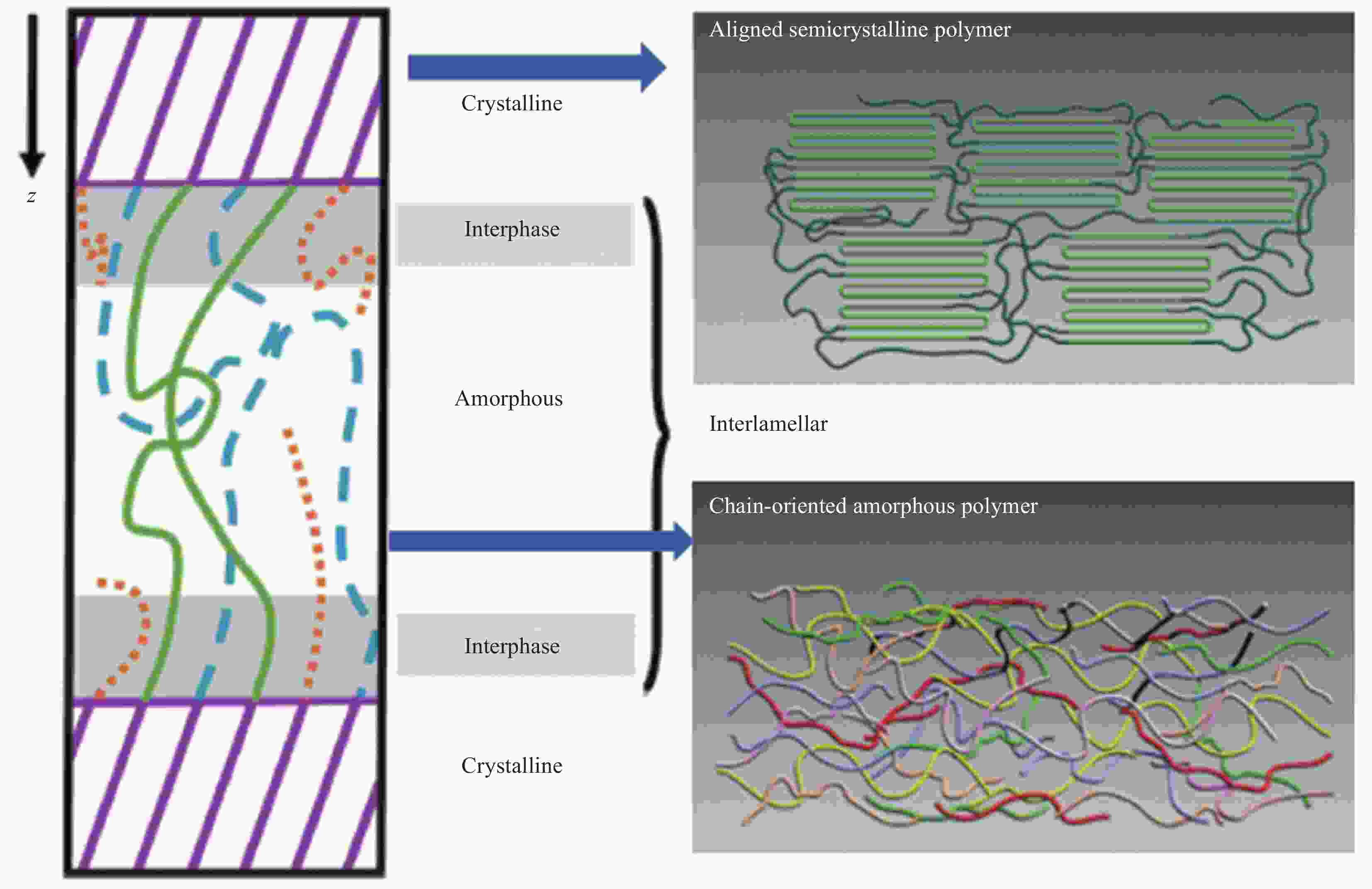
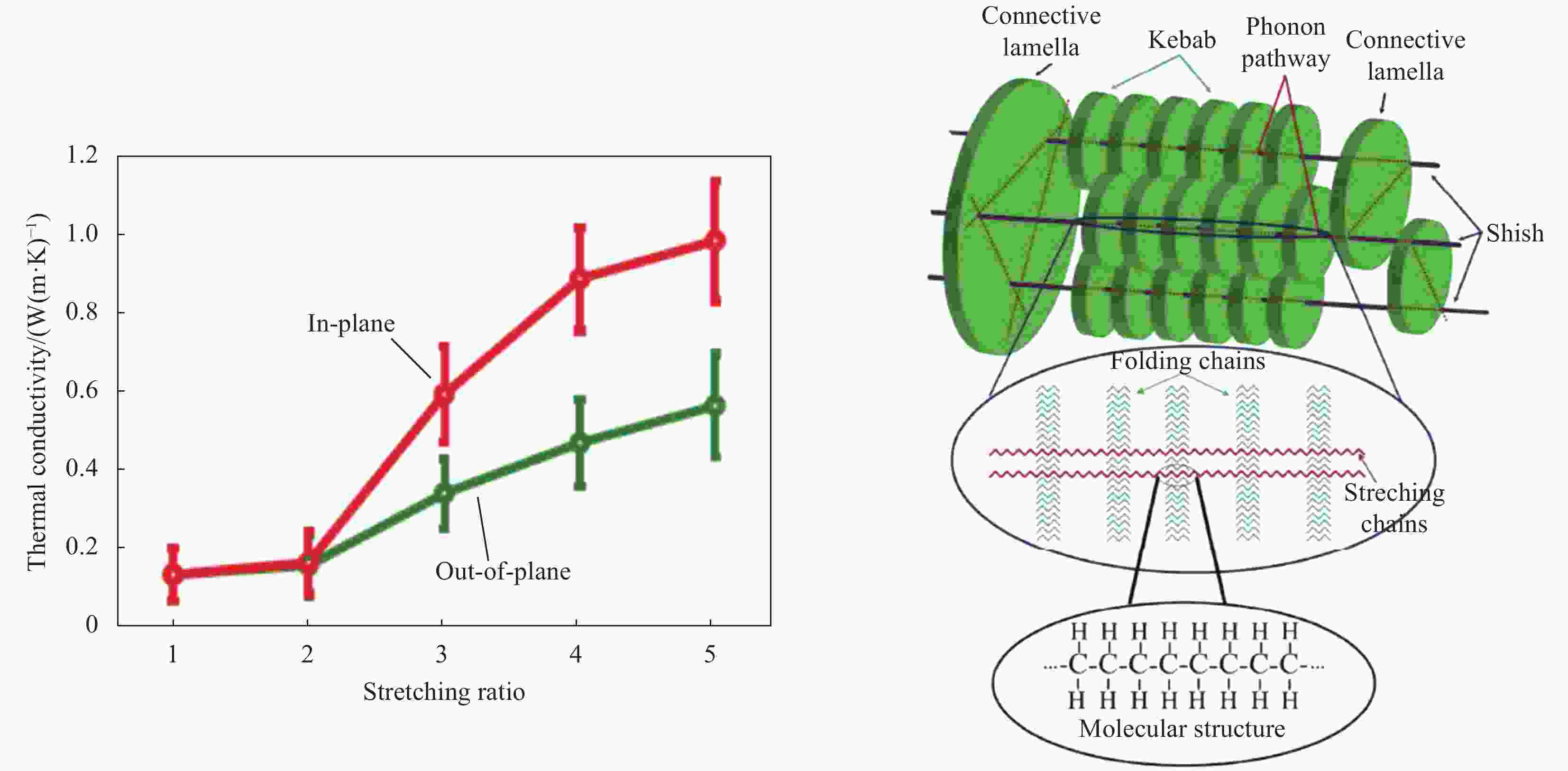
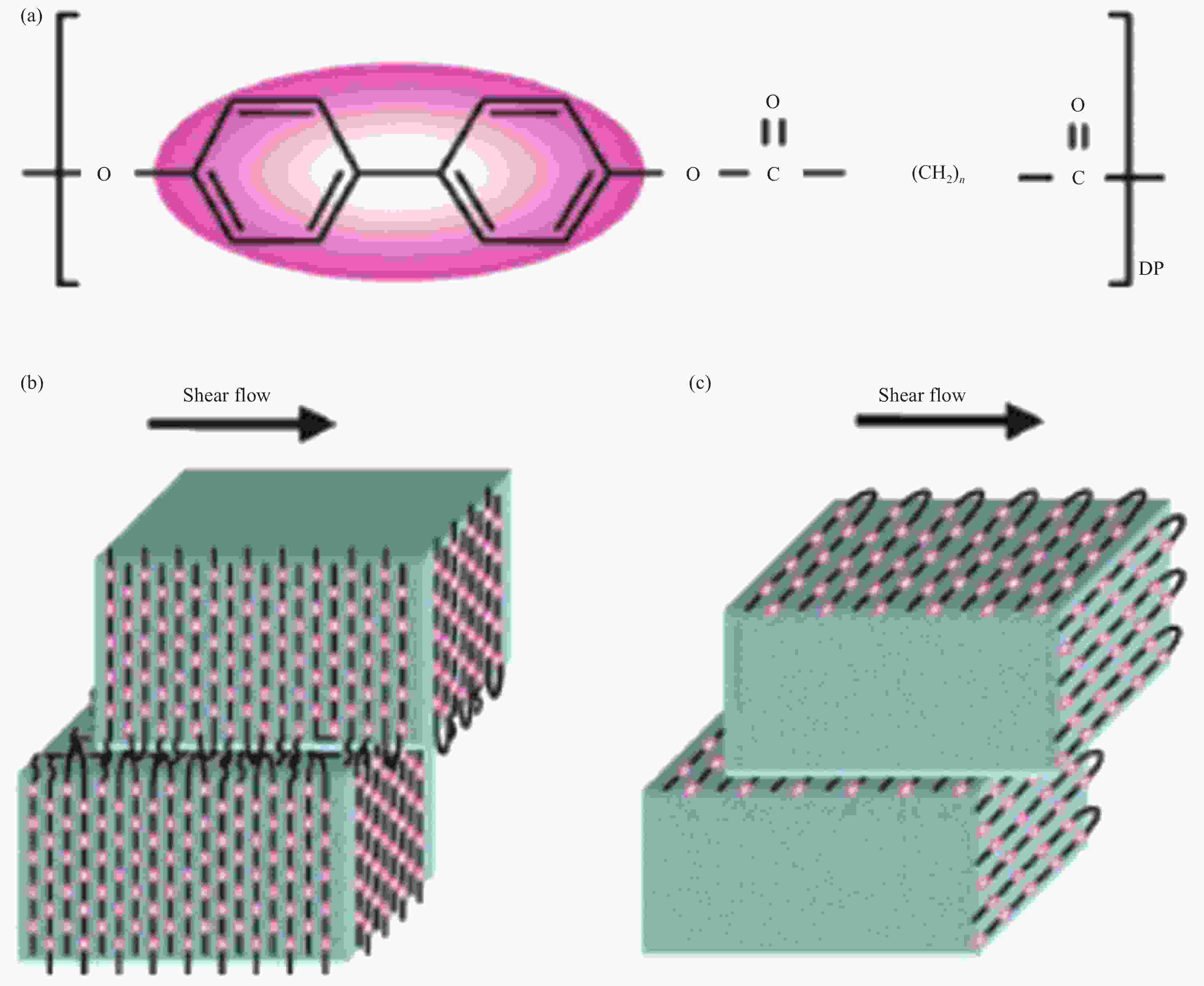
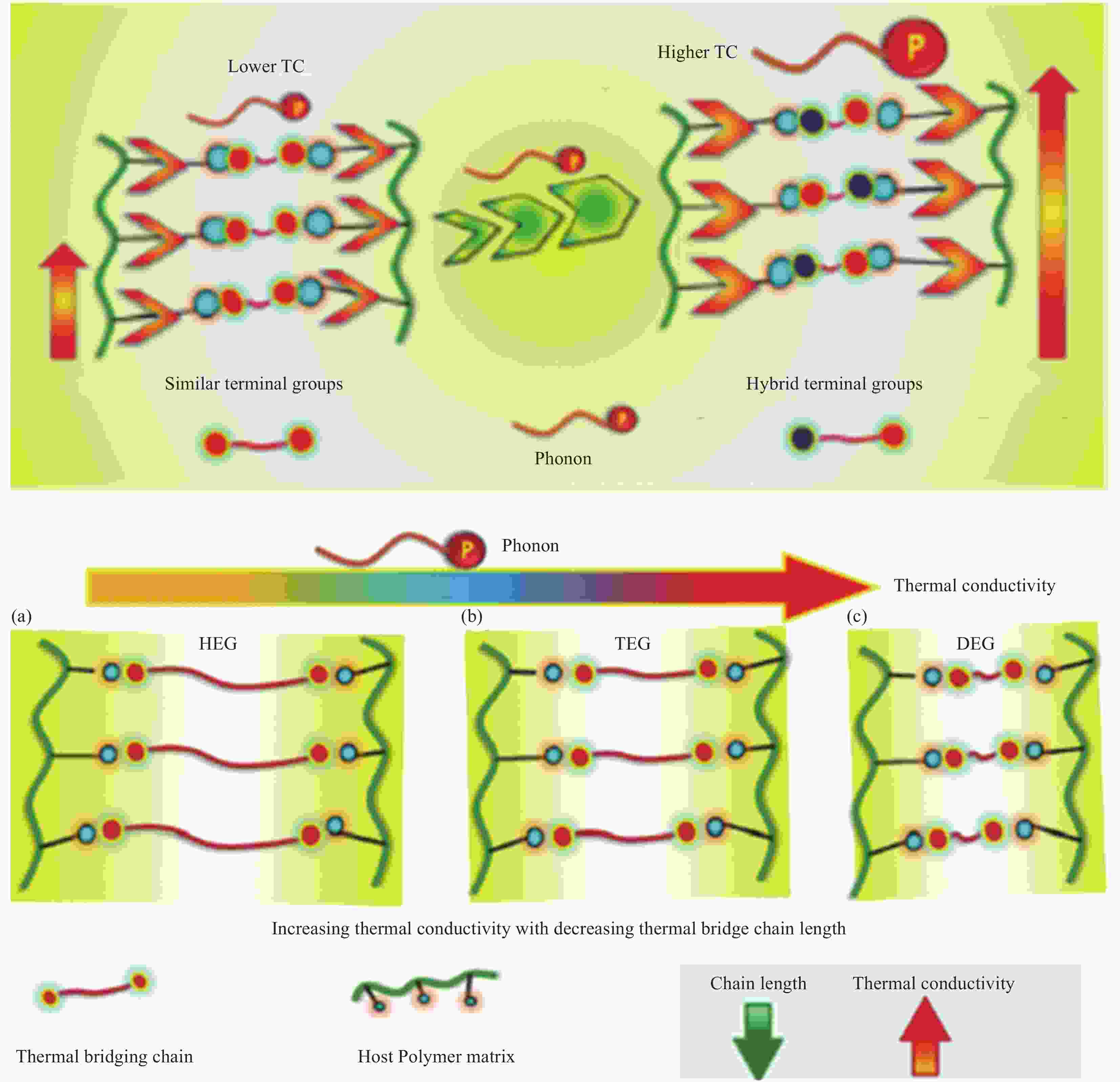
摘要: 导热高分子复合材料因轻质、设计自由度大及易加工等优势获得了广泛的工业应用,但也面临着热导率k与介电强度Eb之间无法协同提高的严峻问题,严重影响和限制了其在高压电力绝缘设备领域的工业应用。而基于提高无序结构聚合物的结构有序性而获得本征导热高分子(ITCP)的策略,不但同步提高Eb及k,还保留了其自身卓越的综合性能。本文讨论了本征聚合物的导热机制,系统分析了本征k的影响因素,综述了两类不同结构ITCP的研究进展,探讨了聚合物微结构、取向、氢键作用、液晶基元及固化剂、加工方式等因素对本征k的影响机制,阐述了提高聚合物有序结构及本征k的途径。最后总结了当前ITCP研究中存在的问题及未来研究方向,综合性能优异的ITCP在高密度封装微电子、高电压及大功率电力设备等领域具有重要用途,代表了导热高分子的未来发展方向。Abstract: Thermally conductive polymer composites have been widely applied in various industries due to lightweight, flexible design and easy-processing. However, the thermal conductivity k and dielectric breakdown strength Eb of polymer composites cannot be synergistically enhanced, thereby seriously affecting and limiting their applications in the high-voltage power equipment. The intrinsic thermally conductive polymers (ITCP) resulting from the developed ordered structures based on pristine discorded structures, not only reserve inherent excellent overall properties, but also exhibit a concurrent enhancement in both Eb and k. This paper discussed the heat conduction mechanism and analyzed the factors influencing k of intrinsic polymers, and summarized the latest advances in ITCP. Furthermore, the factors influencing k, such as polymer structure, orientation, hydrogen bonding, mesomorphic unit and curing agents, processing methods, were analyzed, as well as the strategies to improve the ordered arrangement and k of polymer microstructures. Finally, this paper summarized the existing questions in the study of ITCP and pointed out the future research direction of ITCP. The ITCP show important applications in high-density electronic packaging and high-voltage power equipment, representing the future development direction of thermally conductive polymer composites.
-
Key words:
- polymers /
- intrinsic thermal conductivity /
- ordered structure /
- orientation /
- hydrogen bond /
- liquid crystal units
-
表 1 不同结构的 ITCP
Table 1. Various ITCP with different structures
Catagory Processing method Polymers Thermal conductivity/(W(m·K)−1) Note Reference Thermoplas-
ticsTensile orientation PE nano-fiber 104 Draw ratio 400 [5] PE film 1.2, 0.5 (vertical) Draw ratio 5 [21] UHMWPE 60 Kudat flow, Draw ratio 110 [20] Spin orientation PEO nano-fiber 13-29 Electrospinning [18] PE nano-fiber 9.3 Electrospinning 45 kV [19] Hydrogen bond PAA/PVA 0.35 φPVA=0.4 [27] PAA/PAP, PAP/PVA 1.1, 0.5 φPAP=0.3 [29] PVA/alanine, ethanol amine 0.55, 0.52 Micromolecular crystal [26] Shear orientation Bulk PE 3.3 Solid extrusion [22] PB-n 1.2 (vertical) Injecting molding [23] Polyhexylthiophene 3.8 Spin coating [24] Liquid crystal molecules PVA, LCM 1.2 Self-assembled LCM in PVA [30] PVA, liquid crystal organosilicon 0.74 [31] OCVD Polythiophene 2.2 Bottom-up growth [32] Nano template Polythiophene fiber (amorphous) 4.4 Electropolymerization [6] Electrostatic interaction PAA 1.2 Adjusting pH by sodium hydroxide [33] Cross-linked
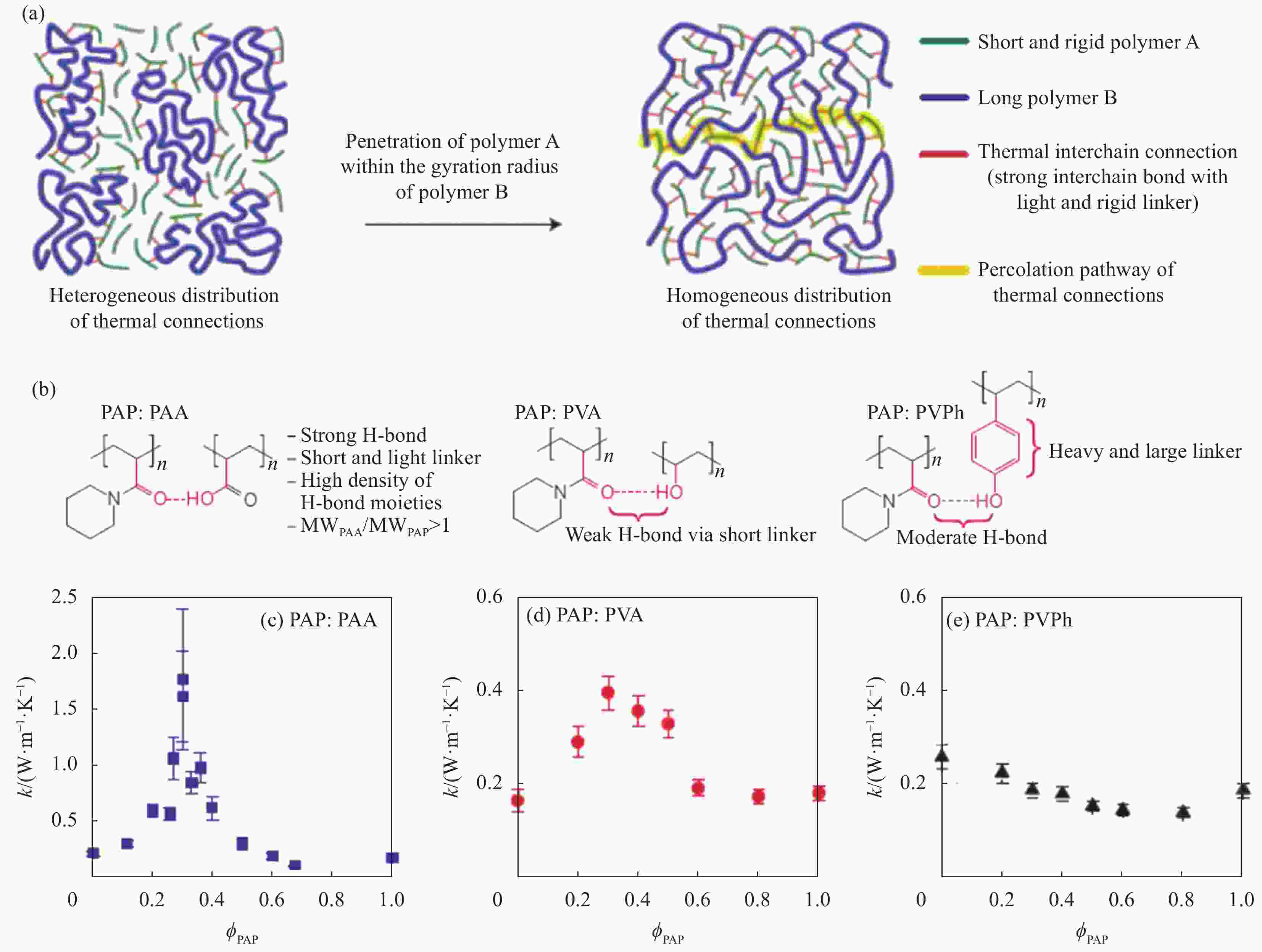
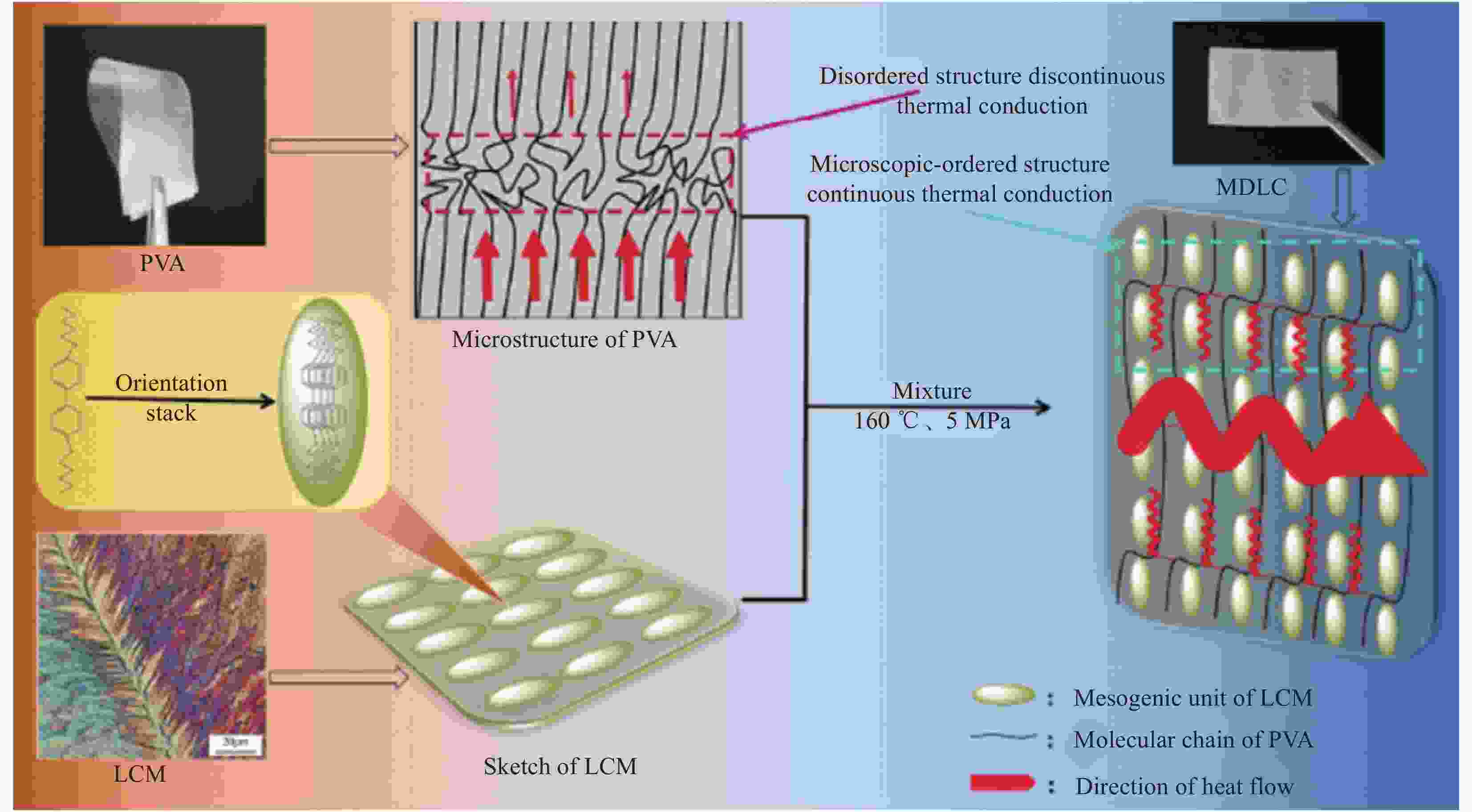
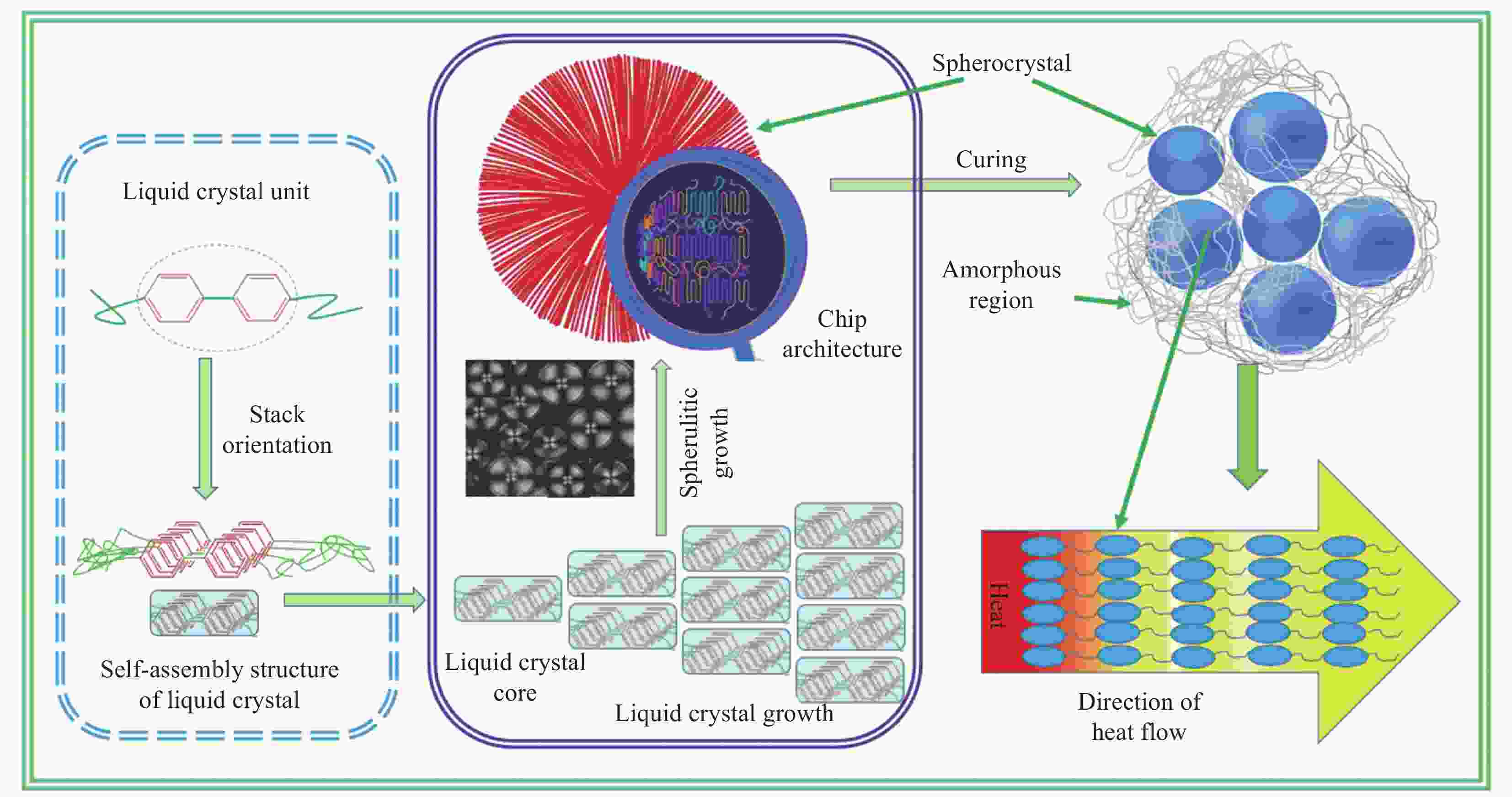
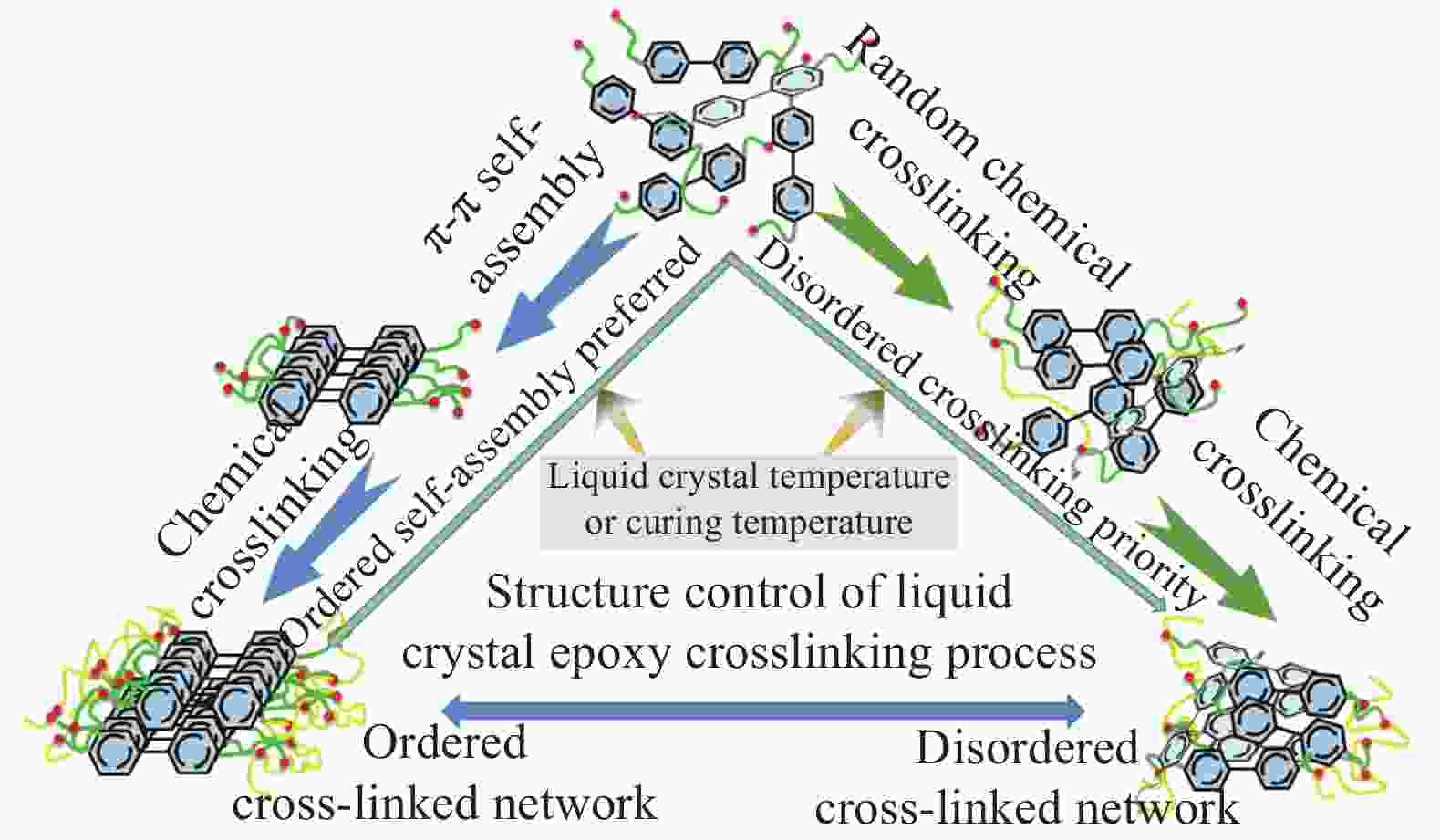
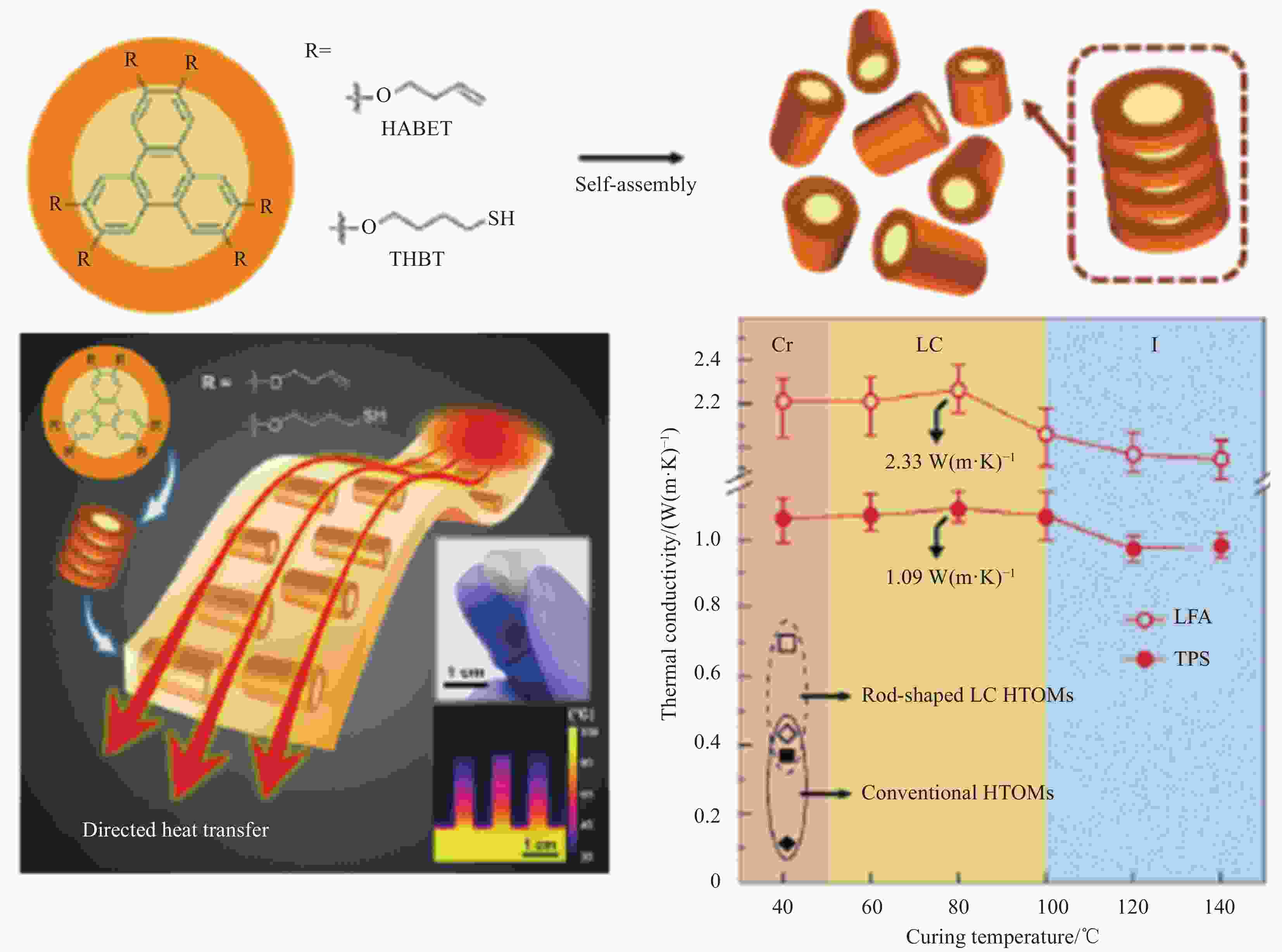
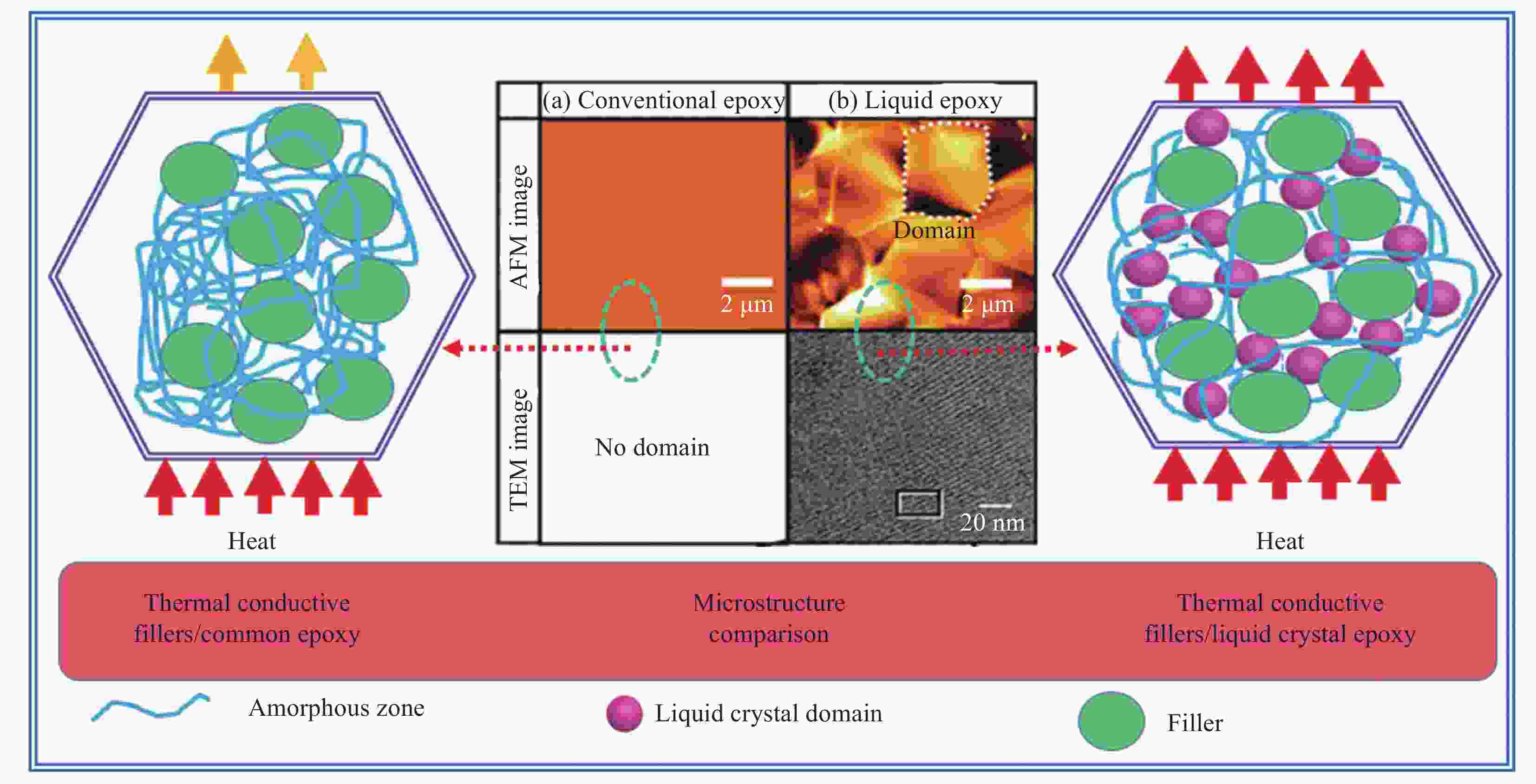
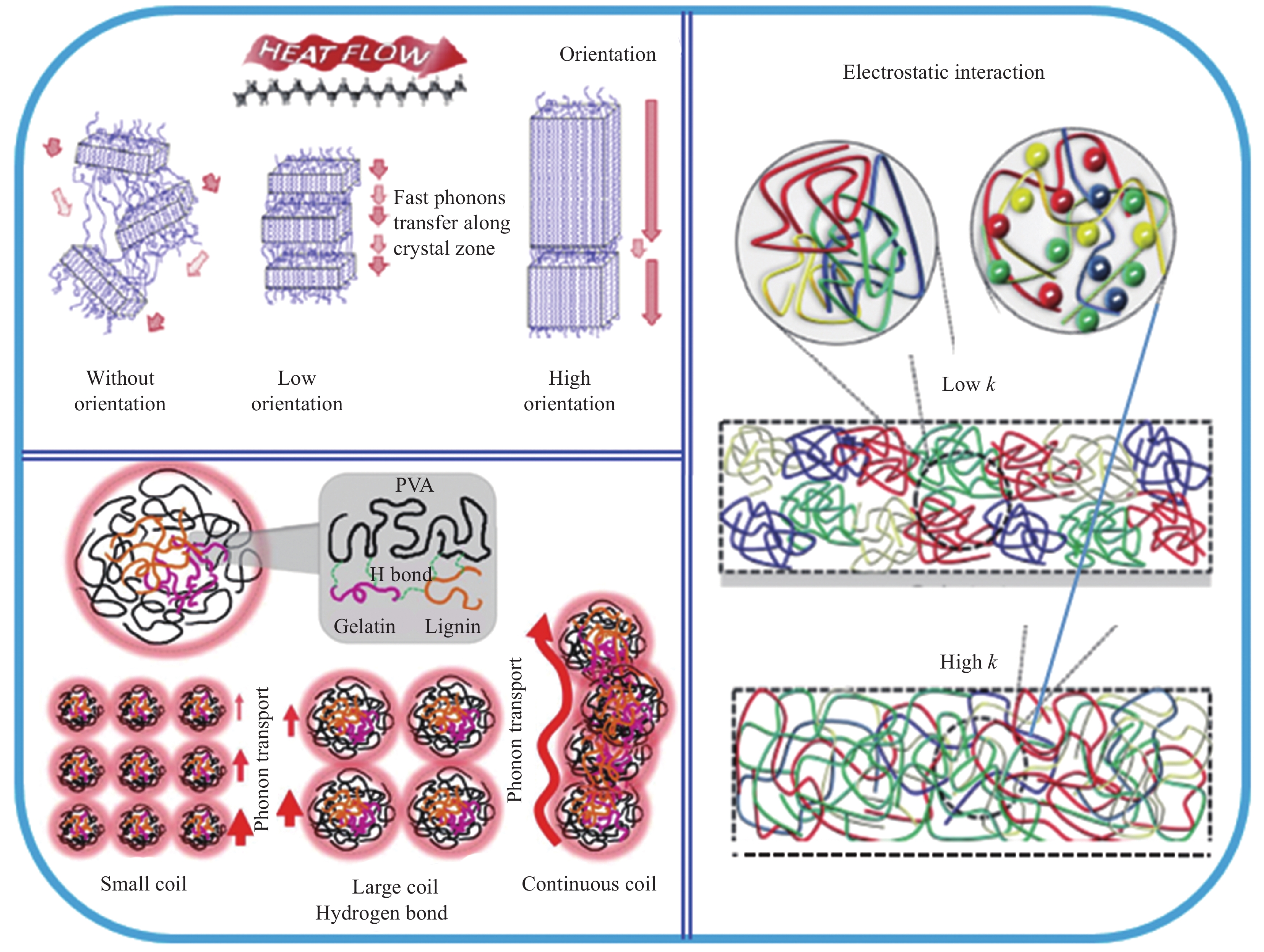
polymersAdjusting LC dispersion in the disordered cross-linked network Biphenyl liquid crystal epoxy 1.2 DDM curing [39] Liquid crystal epoxy 1.25 DETDA [41] Liquid crystal epoxy 1.16 DDM [44] Biphenyl liquid crystal epoxy 0.48 Cationic curing agent [46] Liquid crystal epoxy 0.4 Ursol curing agent [47] Liquid crystal epoxy 0.8 DDM, 2 T magenitic [49] Organosilicone LCM 0.81-0.83 LC curing agent [38] LC with C=C and —SH 3 Orientation, photocuring [48] T6EE9 3.56 (vertical) Electric field induced orientation, photocuring [50] Notes: PE—Polyethylene; UHMWPE—Ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene; PEO—Polyethylene oxide; PAA—polyacrylic acid; PVA—Polyvinyl alcohol; PAP—Propargyl alcohol propoxylate; PB-n—Polybutylene; LCM—Liquid crystal molecule; LC—Liquid crystal; DDM—4,4'-Methylenedianiline; T6EE9—Highly conjugated diphenylacetylene sulfur-ene liquid crystal monomer; φPVA—Mole fraction of PVA; φPAP—Mole fraction of PAP. -
[1] 周文英, 党智敏, 丁小卫, 等. 聚合物基导热复合材料[M]. 北京: 国防工业出版社, 2017.ZHOU W Y, DANG Z M, DING X W, et al. Heat conductive polymer composites[M]. Beijing: National Defense Industry Press, 2017(in Chinese). [2] CHEN H Y, GINZBURG V V, YANG J, et al. Thermal conductivity of polymer-based composites: Fundamentals and applications[J]. Progress in Polymer Science,2016,59:41-85. doi: 10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2016.03.001 [3] XU X F, CHEN J, ZHOU J, et al. Thermal conductivity of polymers and their nanocomposites[J]. Advanced Materials,2018,30(17):1705544. doi: 10.1002/adma.201705544 [4] HUANG C L, QIAN X, YANG R G. Thermal conductivity of polymers and polymer nanocomposites[J]. Materials Science & Engineering R: Reports,2018,132:1-22. [5] GUO Y, RUAN K, SHI X, et al. Factors affecting thermal conductivities of the polymers and polymer composites: A review[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2020,193:108134. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2020.108134 [6] CHAUDHRY A U, MABROUK A N, ABDALA A. Thermally enhanced polyolefin composites: Fundamentals, progress, challenges, and prospects[J]. Science and Technology of Advanced Materials,2020,21(1):737-766. doi: 10.1080/14686996.2020.1820306 [7] PRADHAN S S, UNNIKRISHNAN L, MOHANTY S, et al. Thermally conducting polymer composites with EMI shielding: A review[J]. Journal of Electronic Materials,2020,49(3):1749-1764. doi: 10.1007/s11664-019-07908-x [8] ZHAN H, NIE Y, CHEN Y, et al. Thermal transport in 3D nanostructures[J]. Advanced Functional Materials,2020,30(8):1903841. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201903841 [9] FENG C P, CHEN L B, TIAN G L, et al. Robust polymer-based paper-like thermal interface materials with a through-plane thermal conductivity over 9 W·m−1·K−1[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2020,392:123784. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.123784 [10] SHEN S, HENRY A, TONG J, et al. Polyethylene nanofibres with very high thermal conductivities[J]. Nature Nanotechnology,2010,5(4):251-255. doi: 10.1038/nnano.2010.27 [11] SINGH V, BOUGHER T L, WEATHERS A, et al. High thermal conductivity of chain-oriented amorphous polythiophene[J]. Nature Nanotechnology,2014,9(5):384-390. doi: 10.1038/nnano.2014.44 [12] LUO D, HUANG C L, HUANG Z. Decreased thermal conductivity of polyethylene chain influenced by short chain branching[J]. Journal of Heat Transfer-Transactions of the ASME,2018,140(3):31302. doi: 10.1115/1.4038003 [13] ZHANG T, LUO T F. Role of chain morphology and stiffness in thermal conductivity of amorphous polymers[J]. Journal of Physical Chemistry B,2016,120(4):803-812. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.5b09955 [14] LIU J, JU S H, DING Y F, et al. Size effect on the thermal conductivity of ultrathin polystyrene films[J]. Applied Physics Letters,2014,104(15):153110. doi: 10.1063/1.4871737 [15] MA H, TIAN Z T. Effects of polymer chain confinement on thermal conductivity of ultrathin amorphous polystyrene films[J]. Applied Physics Letters,2015,107(7):73111. doi: 10.1063/1.4929426 [16] SANTOS W N D, SOUSA J A D, GREGORIO R. Thermal conductivity behaviour of polymers around glass transition and crystalline melting temputeratures[J]. Polymer Testing,2013,32(5):987-994. doi: 10.1016/j.polymertesting.2013.05.007 [17] DINPAJOOH M, NITZAN A. Thermal conduction in polymer chains with controlled end-end distance[J]. Journal of Chemical Physics,2020,153(16):164903. doi: 10.1063/5.0023085 [18] ZAO J H, JIANG J W, WEI N, et al. Thermal conductivity dependence on chain length in amorphous polymers[J]. Journal of Applied Physics,2013,113(18):184304. doi: 10.1063/1.4804237 [19] WANG X J, HO V, SEGALMAN R A, et al. Thermal conductivity of high-modulus polymer fibers[J]. Macromolecules,2013,46(12):4937-4943. doi: 10.1021/ma400612y [20] CHOY C L, FEI Y, XI T G. Thermal conductivity of gel-spun polyethylene fibers[J]. Journal of Polymer Science Part B: Polymer Physics,1993,31(3):365-370. doi: 10.1002/polb.1993.090310315 [21] XU X F, ZHOU J, CHEN J. Thermal transport in conductive polymer-based materials[J]. Advanced Functional Materials,2020,30(8):1904704. doi: 10.1002/adfm.201904704 [22] CHOY C L, WONG Y W, LAU K W E, et al. Thermal conductivity and thermal expansivity of thermotropic liquid crystalline polymers[J]. Journal of Polymer Science Part B: Polymer Physics,1995,33(14):2055-2064. doi: 10.1002/polb.1995.090331407 [23] LU C H, CHIANG S W, DU H D, et al. Thermal conductivity of electrospinning chain-aligned polyethylene oxide[J]. Polymer,2017,115:52-59. doi: 10.1016/j.polymer.2017.02.024 [24] MA J, ZHANG Q, MAYO A, et al. Thermal conductivity of electrospun polyethylene nanofibers[J]. Nanoscale,2015,7(40):8-11. [25] KUNITSKI M, EICHE N, HUBER P, et al. Double-slit photoelectron interference in strong-field ionization of the neon dimer[J]. Nature Communications,2019,10(1):1-7. doi: 10.1038/s41467-018-07882-8 [26] ZHANG R C, HUANG Z H, SUN D, et al. New insights into thermal conductivity of uniaxially stretched high density polyethylene films[J]. Polymer,2018,154:42-47. doi: 10.1016/j.polymer.2018.08.078 [27] HUANG Y F, WANG Z G, YU W C, et al. Achieving high thermal conductivity and mechanical reinforcement in ultrahigh molecular weight polyethylene bulk material[J]. Polymer,2019,180:121760. doi: 10.1016/j.polymer.2019.121760 [28] YOSHIHARA S, EZAKI T, NAKAMURAA M, et al. Enhanced thermal conductivity of thermoplastics by lamellar crystal alignment of polymer matrices[J]. Macromolecular Chemistry and Physics,2012,213(21):2213-2219. doi: 10.1002/macp.201200317 [29] FENG X H, LIU G Q, XU S, et al. 3-Dimensional anisotropic thermal transport in microscale poly(3-hexylthiophene) thin films[J]. Polymer,2013,54(7):1887-1895. doi: 10.1016/j.polymer.2013.01.038 [30] ZHANG L, RUESCH M, ZHANG X L, et al. Tuning thermal conductivity of crystalline polymer nanofibers by interchain hydrogen bonding[J]. RSC Advances,2015,5(107):87981-87986. doi: 10.1039/C5RA18519J [31] MEHRA N, LI Y, ZHU J. Small organic linkers with hybrid terminal groups drive efficient phonon transport in polymers[J]. Journal of Physical Chemistry C,2018,122(19):10327-10333. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.8b01991 [32] XIE X, LI D Y, TSAI T H, et al. Thermal conductivity, heat capacity, and elastic constants of water-soluble polymers and polymer blends[J]. Macromolecules,2016,49(3):972-978. doi: 10.1021/acs.macromol.5b02477 [33] MATHUE V, SHARMA K. Thermal response of polystyrene/poly methyl methacrylate (PS/PMMA) polymeric blends[J]. Heat and Mass Transfer,2016,52(12):2901-2911. doi: 10.1007/s00231-016-1779-4 [34] KIM G H, LEE D L, SHANKER A, et al. High thermal conductivity in amorphous polymer blends by engineered interchain interactions[J]. Nature Nanotechnology,2014,14(3):295-300. [35] LI C G, LI Y, GONG C D, et al. High thermal conductivity of liquid crystalline monomer poly(vinyl alcohol) dispersion films containing microscopic-ordered structure[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science,2021,138(6):49791. doi: 10.1002/app.49791 [36] LI Y, PAN P, LIU C, et al. Influence of chain interaction and ordered structures in polymer dispersed liquid crystalline membranes on thermal conductivity[J]. Journal of Polymer Engineering,2020,40(7):573-581. doi: 10.1515/polyeng-2020-0004 [37] XU Y, WANG X X, ZHOU J, et al. Molecular engineered conjugated polymer with high thermal conductivity[J]. Science Advances,2018,4(3):eaar3031. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.aar3031 [38] SHANKER A, LI C, KIM G H, et al. High thermal conductivity in electrostatically engineered amorphous polymers[J]. Science Advances,2017,3(7):e1700342. doi: 10.1126/sciadv.1700342 [39] KATO T, NAGAHARA T, AGAIR Y, et al. Relation between thermal conductivity and molecular alignment direction of free-standing film aligned with rubbing method[J]. Journal of Polymer Science Part B: Polymer Physics,2005,43(24):3591-3599. doi: 10.1002/polb.20628 [40] YU S, PARK C, HONG S M, et al. Thermal conduction behaviors of chemically cross-linked high-density polyethylenes[J]. Thermochimica Acta,2014,583:67-71. doi: 10.1016/j.tca.2014.03.018 [41] LI S H, YU X X, BAO H, et al. High thermal conductivity of bulk epoxy resin by bottom-up parallel-linking and strain: A molecular dynamics study[J]. Journal of Physical Chemistry C,2018,122(24):13140-13147. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.8b02001 [42] LIN Y, HUANG X Y, CHEN J, et al. Epoxy thermoset resins with high pristine thermal conductivity[J]. High Voltage,2017,2(3):139-146. doi: 10.1049/hve.2017.0120 [43] LI Y, LI C G, ZHANG L, et al. Effect of microscopic-ordered structures on intrinsic thermal conductivity of liquid-crystalline polysiloxane[J]. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics,2019,30(9):8329-8338. doi: 10.1007/s10854-019-01150-1 [44] AKATSUKA M, TAKEZAWA Y. Study of high thermal conductive epoxy resins containing controlled high-order structures[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science,2003,89(9):2464-2467. doi: 10.1002/app.12489 [45] YANG X, ZHU J, YANG D, et al. High efficiency improvement of thermal conductivities for epoxy composites from synthesized liquid crystal epoxy followed by doping BN fillers[J]. Journal of Applied Polymer Science,2020,185:107784. [46] YANG X T, ZHONG X, ZHANG J L, et al. Intrinsic high thermal conductive liquid crystal epoxy film simultaneously combining with excellent intrinsic self-healing performance[J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology,2020,68:209-215. [47] MO H, HUANG X, LIU F, et al. Nanostructured electrical insulating epoxy thermosets with high thermal conductivity, high thermal stability, high glass transition temperatures and excellent dielectric properties[J]. IEEE Transactions on Dielectrics and Electrical Insulation,2015,22(2):906-915. doi: 10.1109/TDEI.2015.7076791 [48] AKATSUKA M, TAKEZAWA Y, FARREN C. Development of epoxy resins with controlled high order structures having excellent heat release properties[J]. IEEJ Transactions on Fundamentals and Materials,2003,123(7):687-692. doi: 10.1541/ieejfms.123.687 [49] SONG S, KATAGI H, TAKEZAWA Y. Study on high thermal conductivity of mesogenic epoxy resin with spherulite structure[J]. Polymer,2012,53(20):4489-4492. doi: 10.1016/j.polymer.2012.07.065 [50] AKATSUKA M, TAKAZAWA Y, SUGAWARA K. Thermosetting resin compounds: US, 20060276568[P]. 2006-12-07. [51] ISLAM A M, LIM H, YOU N H, et al. Enhanced thermal conductivity of liquid crystalline epoxy resin using controlled linear polymerization[J]. ACS Macro Letters,2018,7(10):1180-1185. doi: 10.1021/acsmacrolett.8b00456 [52] KIM Y, YEO H, YOU N H, et al. Highly thermal conductive resins formed from wide-temperature-range eutectic mixtures of liquid crystalline epoxies bearing diglycidyl moieties at the side positions[J]. Polymer Chemistry,2017,8(18):2806-2814. doi: 10.1039/C7PY00243B [53] KANG D G, PARK M, KIM D Y, et al. Heat transfer organic materials: Robust polymer films with the outstanding thermal conductivity fabricated by the photopolymerization of uniaxially oriented reactive discogens[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2016,8(44):30492-30501. [54] HARADA M, OCHI M, TOBITA M, et al. Thermal-conductivity properties of liquid-crystalline epoxy resin cured under a magnetic field[J]. Journal of Polymer Science Part B: Polymer Physics,2003,41(14):1739-1743. doi: 10.1002/polb.10531 [55] GE S J, ZHAO T P, WANG M, et al. A homeotropic main-chain tolane type liquid crystal elastomer film exhibiting high anisotropic thermal conductivity[J]. Soft Matter,2017,13(32):5463-5468. doi: 10.1039/C7SM01154G [56] RASHIDI V, COYLE E J, SEBECK K, et al. Thermal conductance in cross-linked polymers: Effects of non bonding interactions[J]. Journal of Physical Chemistry B,2017,121(17):4600-4609. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcb.7b01377 [57] TONGPHENG B, YU J C, ANDERSSON O. Effects of cross-links, pressure and temperature on the thermal properties and glass transition behavior of polybutadiene[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics,2011,13(33):15047-15054. doi: 10.1039/c1cp20785g [58] XIONG X, YANG M, LIU C, et al. Thermal conductivity of cross-linked polyethylene from molecular dynamics simulation[J]. Journal of Applied Physics,2017,122(3):984-987. [59] 祝大同. 高导热性树脂开发与应用的新进展(2): 对高导热性基板材料制造新技术的综述[J]. 印制电路信息, 2012(11):15-20.ZHU D T. Development of research and application of resin with high thermal conductivity(2): Review of new technology of heat dissipation substrate material[J]. Printed Circuit Information,2012(11):15-20(in Chinese). -





 下载:
下载: