Low-velocity impact performance of grid-honeycomb hybrid core sandwich structure
-
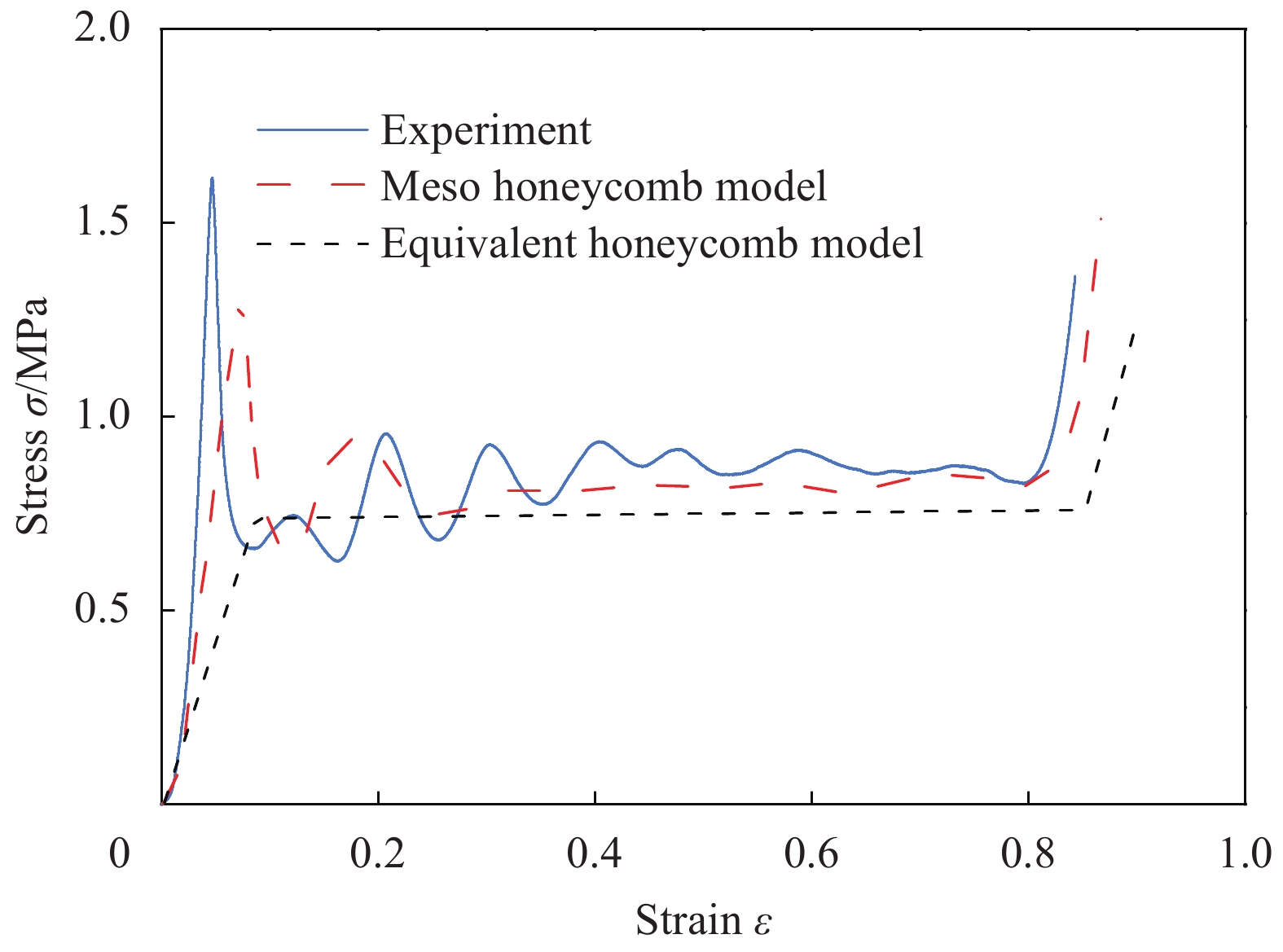
摘要: 针对传统复合材料夹芯结构抗冲击性能差的缺陷,提出一种格栅-蜂窝混式芯体,并对其低速冲击性能进行了研究。采用半球头式落锤冲击实验平台对碳纤维铝蜂窝夹芯结构的低速冲击响应进行研究;其次基于蜂窝非线性本构与完美界面假设,建立了碳纤维铝蜂窝夹芯板低速冲击仿真模型,实验与仿真结果吻合良好;最后对不同冲击位置和冲击角度下格栅-蜂窝混式芯体夹芯板的破坏模态及力学响应进行研究。结果表明:不同冲击位置及不同角度冲击下结构损伤模态及吸能模式存在巨大差异;格栅-蜂窝混式芯体可以显著提高结构的抗低速冲击性能,对于冲击损伤具有良好的限制作用。Abstract: A grid-honeycomb hybrid core was proposed and investigated to address the disadvantage of poor impact resistance of traditional composite sandwich structures. The impact test system of hemisphere-head drop hammer was used to study the low-speed impact response of the carbon fiber aluminum honeycomb sandwich structure. Based on the nonlinear constitutive and perfect interface assumption, the low-speed impact simulation model of the carbon fiber aluminum honeycomb sandwich panel was established and investigated. Research shows that the experimental and simulation results are in good agreement. Finally, the failure mode and mechanical response of grid-reinforced honeycomb hybrid core sandwich panels under different impact positions and impact angles were studied. The results show that there are huge differences in structural damage modes and energy absorption modes under different impact positions and different impact angles. The grid-honeycomb hybrid core can significantly improve the low-speed impact resistance of the structure, and has a good limiting effect on impact damage.
-
表 1 碳纤维单向布材料属性
Table 1. Carbon fiber single layer material parameters
ρ/(kg·m−3) E11/GPa E22=E33/GPa ν12,ν13 ν23 G12=G13/GPa 1560 108 8 0.32 0.3 4 G23/GPa Xt/GPa Xc/GPa Yt/MPa Yc/GPa S12=S23=S13/MPa 3 2.1 0.72 25 0.12 40 Notes: ρ—Density; E1, E2, E3—Young’s moduli; ν12,ν23,ν13 —Possion’s ratios; G12, G23, G13—Shear moduli; Xt, Yt—Tensile strength; Xc, Yc—Compression strength; S12, S23, S13—Shear strength. 表 2 铝蜂窝等效模型参数
Table 2. Equivalent cellular model parameters of aluminum honeycomb
Symbol Property Value ρ/(kg·m−3) Nominal density 62 Eaau/MPa W direction elastic modulus 8.2 Ebbu/MPa L direction elastic modulus 8.2 Eccu/GPa T direction elastic modulus 0.39 Gabu/MPa W-L direction shear modulus 2.83 Gbcu/MPa L-T direction shear modulus 15.6 Gcau/GPa L-W direction shear modulus 0.31 TSEF Tensile strain at element failure 0.3 SSEF Shear strain at element failure 0.3 VF Densification relative volume 0.15 MU Material viscosity coefficient 0.05 表 3 铝格栅材料参数
Table 3. Aluminum grid material parameters
Symbol Property Value ρ/(kg·m−3) Density 2710 E/GPa Elastic modulus 69 ν Poisson’s ratio 0.33 SIGY/GPa Yield strength 0.29 ETAN/GPa Tangent modulus 0.689 表 4 传统蜂窝夹芯板与格栅增强蜂窝夹芯板上面板末层损伤云图
Table 4. Damage cloud maps of the end layer of the honeycomb sandwich panel and grid reinforced honeycomb sandwich panel
Impact energy/J Impact angle/(°) Sandwich panel type Impact location Fiber tensile damage Fiber compression damage Matrix tensile damage Matrix compression damage 50 0 Honeycomb sandwich panel 




50 0 Grid reinforced honeycomb sandwich panel 




50 0 Grid reinforced honeycomb sandwich panel 




50 0 Grid reinforced honeycomb sandwich panel 




-
[1] 沈真. 碳纤维复合材料在飞机结构中的应用[J]. 高科技纤维与应用, 2010, 35(4):1-4, 24.SHEN Zhen. Application of carbon fiber composites in aircraft structures[J]. Hi-Tech Fiber & Application,2010,35(4):1-4, 24(in Chinese). [2] KIM J S, LEE S J, SHIN K B. Manufacturing and structural safety evaluation of a composite train carbody[J]. Composite Structures,2007,78(4):468-476. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2005.11.006 [3] RADFORD D W. Development of composite chassis for motorsports[J]. Comprehensive Composite Materials II,2018,3:350-419. [4] SHEN W, LUO B, YAN R, et al. The mechanical behavior of sandwich composite joints for ship structures[J]. Ocean Engineering,2017,144:78-89. doi: 10.1016/j.oceaneng.2017.08.039 [5] SHI S S, SUN Z, HU X Z, et al. Flexural strength and energy absorption of carbon-fiber-aluminum-honeycomb composite sandwich reinforced by aluminum grid[J]. Thin-Walled Structures,2014,84:416-422. doi: 10.1016/j.tws.2014.07.015 [6] SUN Z, SHI S S, GUO X, et al. On compressive properties of composite sandwich structures with grid reinforced honeycomb core[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering,2016,94:245-252. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2016.03.054 [7] MCSHANE G J, RADFORD D D, DESHPANDE V S, et al. The response of clamped sandwich plates with lattice cores subjected to shock loading[J]. European Journal of Mechanics A/Solids,2006,25(2):215-229. doi: 10.1016/j.euromechsol.2005.08.001 [8] WU Y H, LIU Q, FU J, et al. Dynamic crash responses of bio-inspired aluminum honeycomb sandwich structures with CFRP panels[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering,2017,121:122-133. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2017.03.030 [9] HE W T, YAO L, MENG X J, et al. Effect of structural parameters on low-velocity impact behavior of aluminum honeycomb sandwich structures with CFRP face sheets[J]. Thin-Walled Structures,2019,137:411-432. doi: 10.1016/j.tws.2019.01.022 [10] 王堃, 孙勇, 彭明军, 等. 基于ANSYS的铝蜂窝夹芯板低速冲击仿真模拟研究[J]. 材料导报, 2012, 26(08):157-160.WANG Kun, SUN Yong, PENG Mingjun, et al. Simulation of low-velocity impact of aluminium honeycomb sandwich panels with ANSYS[J]. Materials Reports,2012,26(08):157-160(in Chinese). [11] AUDIBERT C, ANDRÉANI A S, LAINÉ É, et al. Discrete modelling of low-velocity impact on Nomex® honeycomb sandwich structures with CFRP skins[J]. Composite Structures,2019,207:108-118. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2018.09.047 [12] CASTANIÉ B, BOUVET C, AMINANDA Y, et al. Modelling of low-energy/low-velocity impact on Nomex honeycomb sandwich structures with metallic skins[J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering,2008,35(7):620-634. doi: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2007.02.008 [13] 顾卫平, 骆卫东, 童文, 等. 复合材料蜂窝夹层板低速冲击损伤模拟及实验研究[J]. 机械科学与技术, 2013, 32(7):1017-1021.GU Weiping, LUO Weidong, TONG Wen, et al. Numerical simulation and experiment on low velocity impacting damage of composite honeycomb sandwich[J]. Mechanical Science and Technology for Aerospace Engineering,2013,32(7):1017-1021(in Chinese). [14] 徐小刚, 黄海, 贾光辉. 蜂窝夹芯板超高速碰撞仿真[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2007(1):18-21.XU Xiaogang, HUANG Hai, JIA Guanghui. Simulation of hypervelocity impact to honeycomb sandwich[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics,2007(1):18-21(in Chinese). [15] KAMRAN M, WU F, XUE P, et al. New Numerical modeling for impact dynamics behavior of composite honeycomb sandwich structures[J]. Journal of Aerospace Engineering,2020,33(4):04020016. doi: 10.1061/(ASCE)AS.1943-5525.0001129 [16] LI R F, KARDOMATEAS G A, SIMITSES G J. Pointwise impulse (blast) response of a composite sandwich plate including core compressibility effects[J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures,2009,46(10):2216-2223. doi: 10.1016/j.ijsolstr.2009.01.036 [17] LI G, MUTHYALA V D. Impact characterization of sandwich structures with an integrated orthogrid stiffened syntactic foam core[J]. Composites Science & Technology,2008,68(9):2078-2084. [18] 蓝友泽, 朱亮, 徐志伟. 复合材料机翼格栅结构低速冲击损伤仿真研究[J]. 复合材料学报, 2013, 30(2):165-172.LAN Youze, ZHU Liang, XU Zhiwei. Simulation research on impact damages under low velocities of composite grid structures for aircraft wing[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2013,30(2):165-172(in Chinese). [19] LI J H, JOHN H, GONG S Q, et al. Quasi-static compression and low-velocity impact behavior of tri-axial bio-composite structural panels using a spherical head[J]. Materials,2017,10(2):185. [20] 富明慧, 徐欧腾, 陈誉. 蜂窝芯层等效参数研究综述[J]. 材料导报, 2015, 29(05):127-134.FU Minghui, XU Outeng, CHEN Yu. An overview of equivalent parameters of honeycomb cores[J]. Materials Reports,2015,29(05):127-134(in Chinese). [21] GIBSON L J, ASHBY M F. The Mechanics of two-dimensional cellular materials[J]. Proceedings of the Royal Society of London,1982,382(1782):43-59. [22] GIBSON L J, ASHBY M F. Cellular solids: structure and properties[M]. 2nd ed. New York: Cambridge University Press, 1997: 93-174. [23] ASTM International. Standard test method for measuring the resistance of a fiber reinforced polymer matrix composite to a drop-weight impact event: ASTM D7136/D7136M—2015[S]. West Conshohocken: ASTM, 2015. [24] MENNA C, ZINNO A, ASPRONE D, et al. Numerical assessment of the impact behavior of honeycomb sandwich structures[J]. Composite Structures,2013,106:326-339. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2013.06.010 [25] TARAGHI I, FEREIDOON A. Non-destructive evalua-tion of damage modes in nanocomposite foam-core sandwich panel subjected to low-velocity impact[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering,2016,103:51-59. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2016.08.009 [26] ZINNO A, PROTA A, MAIO E D, et al. Experimental characterization of phenolic-impregnated honeycomb sandwich structures for transportation vehicles[J]. Composite Structures,2011,93(11):2910-2924. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2011.05.012 -






 下载:
下载: