Preparation of hexanoyl ethylene glycol chitosan/poloxamer composite hydrogel for drug release
-
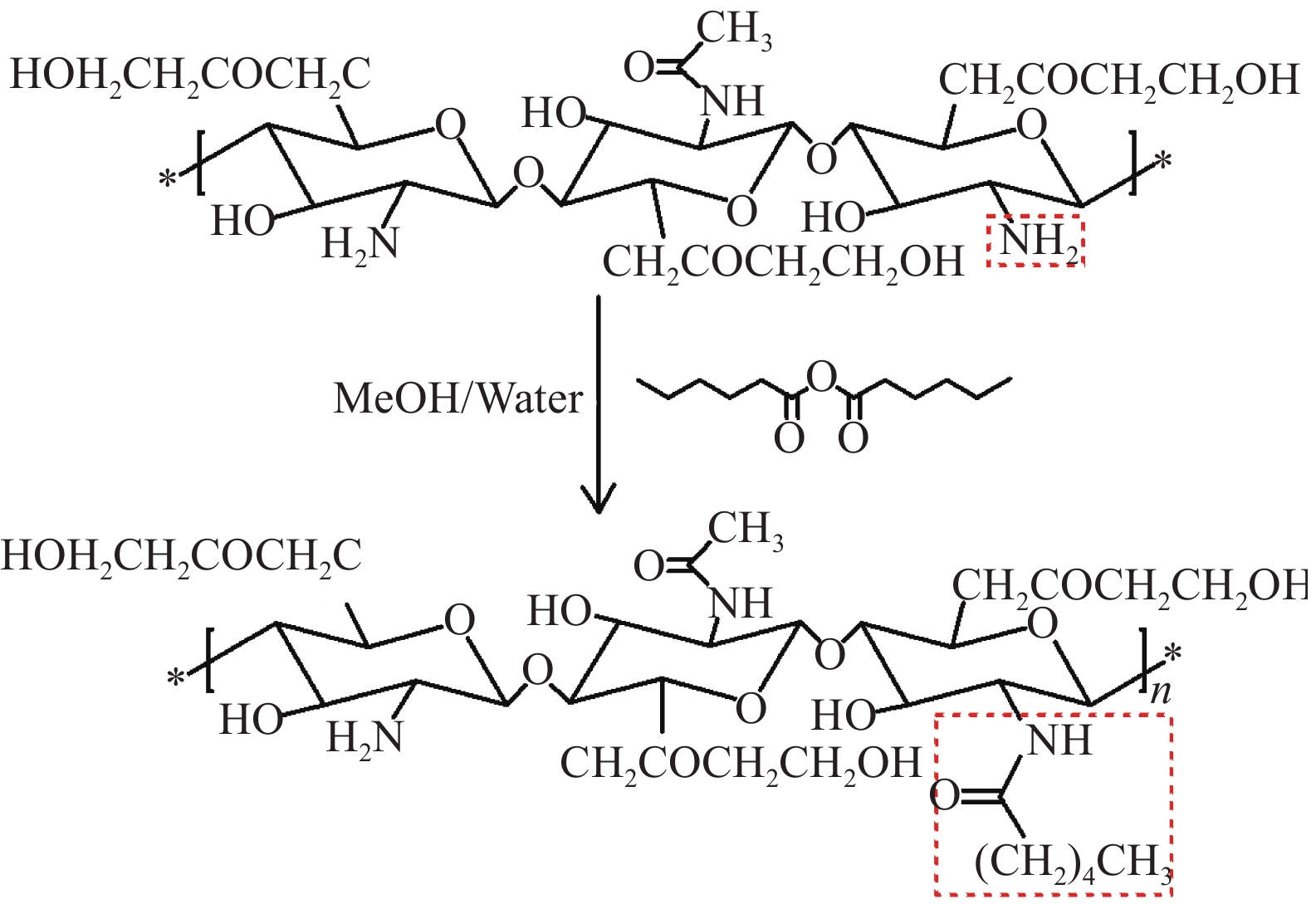
摘要: 为减少泊洛沙姆水凝胶的溶胶-凝胶转变温度对浓度的依赖性,以泊洛沙姆(P407)为基材,将己酰化乙二醇壳聚糖(HGC)与泊洛沙姆复合,制备了己酰化乙二醇壳聚糖/泊洛沙姆(HGC/P407)复合水凝胶,利用FTIR、SEM及试管反转法探讨了HGC/P407复合水凝胶的性能,并利用紫外-可见分光光度计(UV-vis)对HGC/P407复合水凝胶的体外药物缓释性能进行表征。结果表明,通过控制HGC的加入量,基于3%泊洛沙姆的HGC/P407复合水凝胶即可发生溶胶-凝胶转变现象,并使HGC/P407复合水凝胶的溶胶-凝胶转变温度处于32~37℃。HGC/P407复合水凝胶具有高度孔隙率,孔隙之间相互连通,孔径大小处于10~90 µm的范围之内。HGC/P407复合水凝胶对抗癌药物吉西他滨的释药量达到82.4%~90.6%,缓释时间可达80 h左右。HGC/P407复合水凝胶在可注射药物载体领域具有重要的应用前景。Abstract: In order to reduce the dependence of the sol-gel transition temperature of the poloxamer hydrogel on the concentration, the poloxamer (P407) was used as the substrate, and hexanoyl ethylene glycol chitosan (HGC) was compounded with poloxamer to prepare HGC/P407 composite hydrogel. FTIR, SEM and tube inversion method were used to investigate the properties of HGC/P407 composite hydrogel in different mass ratios, and the in vitro drug release performance of HGC/P407 composite hydrogel was characterized by UV-vis spectroscopy. The results show that sol-gel transformation can occur in HGC/P407 hydrogel based on 3% poloxam by controlling the addition of HGC, and the sol-gel transition temperature of HGC/P407 hydrogel is between 32℃ and 37℃. HGC/P407 composite hydrogel has high porosity with interconnected pores which size ranging from 10 to 90 µm. The release amount of the anticancer drug gemcitabine of HGC/P407 composite hydrogel is 82%~90.6%, and the sustained release time can reach about 80 h. HGC/P407 composite hydrogel has important application prospects in the field of injectable drug carriers.
-
Key words:
- hexanoyl glycol chitosan /
- poloxamer /
- composite hydrogel /
- drug release /
- injectability
-
表 1 HGC/泊洛沙姆407 (P407)复合水凝胶的配方
Table 1. The formula of HGC/poloxamer (P407) composite hydrogel
Samples Mass ratio Temprerature/℃ 30%HGC/P407 0.3∶1 65 50%HGC/P407 0.5∶1 50 70%HGC/P407 0.7∶1 37 100%HGC/P407 1.0∶1 32 表 2 HGC/P407复合水凝胶对吉西他滨的释放机制
Table 2. Release characteristics of encapsulated gemcitabine from HGC/P407 composite hydrogels
Samples K n Transport mechanism 70%HGC/P407 0.68 0.16 Pseudo-Fickian 100%HGC/P407 0.65 0.12 Pseudo-Fickian Notes: K ─ Rate constant; n ─ Release index. -
[1] BYEONGMOON J A, SUNG W K B, YOU H B. Thermosensitive sol-gel reversible hydrogels[J]. Advanced Drug Delivery Reviews,2012,64(1):154-162. [2] MEKONNEN G, EFREM G. Hydrogel-A promising technology for optimization of nutrients and water in agricultural and forest ecosystems[J]. International Journal of Environmental Sciences & Natural Resources,2020,23:106-111. [3] LI Y F, KILIAN K A. Bridging the gap: from 2D cell culture to 3D microengineered extracellular matrices[J]. Advanced Healthcare Materials,2016,4(18):2780-2796. [4] CONSTANTIN M, BUCATARIU S M, DOROFTEI F, et al. Smart composite materials based on chitosan microspheres embedded in thermosensitive hydrogel for controlled delivery of drugs[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2017,157:493-502. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.10.022 [5] GAO J, LIU R, WU J, et al. The use of chitosan based hydrogel for enhancing the therapeutic benefits of adipose-derived MSCs for acute kidney injury[J]. Biomaterials,2012,33(14):3673-3681. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2012.01.061 [6] SHARMA S, TIWARI S. A review on biomacromolecular hydrogel classification and its applications[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2020,162:737-747. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.06.110 [7] ZHENG X, DING Z, CHENG W, et al. Microskin-inspired injectable MSC-Laden hydrogels for scarless wound healing with hair follicles[J]. Advanced Healthcare Materials,2020,9(10):e2000041. doi: 10.1002/adhm.202000041 [8] CHEN Y, QIU Y, WANG Q, et al. Mussel-inspired sandwich-like nanofibers/hydrogel composite with super adhesive, sustained drug release and anti-infection capacity[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2020,399:125668. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.125668 [9] HSIEH H Y, LIN W Y, LEE A L, et al. Hyaluronic acid on the urokinase sustained release with a hydrogel system composed of poloxamer 407: HA/P407 hydrogel system for drug delivery[J]. Plos One,2020,15(3):e0227784. doi: 10.1371/journal.pone.0227784 [10] DENG Z X, WANG H, GUO B L, et al. Self-healing conductive hydrogels: preparation, properties and applications[J]. Nanoscale,2020,12(3). [11] AHMAD H, MOHAMMAD M R, MOHAMMAD A A, et al. A simple route to synthesize conductive stimuli-responsive polypyrrole nanocomposite hydrogel particles with strong magnetic properties and their performance for removal of hexavalent chromium ions from aqueous solution[J]. Journal of Magnetism & Magnetic Materials,2016,412:15-22. [12] GAO Y, REN F, DING B, et al. A thermo-sensitive PLGA-PEG-PLGA hydrogel for sustained release of docetaxel[J]. Journal of Drug Targeting,2011,19(7):516-527. doi: 10.3109/1061186X.2010.519031 [13] MAYOL L, QUAGLIA F, BORZACCHIELLO A, et al. A novel poloxamers/hyaluronic acid in situ forming hydrogel for drug delivery: Rheological, mucoadhesive and in vitro release properties[J]. European Journal of Pharmaceutics & Biopharmaceutics,2008,70(1):199-206. [14] NANJAWADE B K, MANVI F V, MANJAPPA A S. RETRACTED: In situ-forming hydrogels for sustained ophthalmic drug delivery[J]. Journal of Controlled Release,2007,122(2):119-134. doi: 10.1016/j.jconrel.2007.07.009 [15] HE Z X, WANG Z H, ZHANG H H, et al. Doxycycline and hydroxypropyl-β-cyclodextrin complex in poloxamer thermal sensitive hydrogel for ophthalmic delivery[J]. Acta Pharmaceutica Sinica B,2011,1(4):254-260. doi: 10.1016/j.apsb.2011.10.004 [16] WANG Q, HE Y, ZHAO Y, et al. A Thermosensitive heparin-poloxamer hydrogel bridge aFGF to treat spinal cord injury[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2017,9(8):6725. doi: 10.1021/acsami.6b13155 [17] ELENA G, DONATELLA P, MASSIMO F, et al. Mucosal applications of poloxamer 407-based hydrogels: An overview[J]. Pharmaceutics,2018,10(3):159. [18] POPESCU I, TERTOI M, SUFLET D M, et al. Alginate/poloxamer hydrogel obtained by thiolacrylate photopolymerization for the alleviation of the inflammatory response of human keratinocytes[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2021,180:418-431. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.03.082. [19] YU S H, ZHANG X Y, TAN G X, et al. A novel pH-induced thermosensitive hydrogel composed of carboxymethyl chitosan and poloxamer cross-linked by glutaraldehyde for ophthalmic drug delivery[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2017,155:208-217. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.08.073 [20] JOSÉ L S, CALPENA-CAMPMANY A C, SILVA-ABREU M, et al. Design and evaluation of a multifunctional thermosensitive poloxamer-chitosan-hyaluronic acid gel for the treatment of skin burns[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2020,142:412-422. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.09.113 [21] 李进, 候冰娜, 韩超越, 等. 可注射乙酰化乙二醇壳聚糖/泊洛沙姆复合水凝胶的制备及药物缓释研究[J]. 材料工程, 2020, 48(5):83-90.LI Jin, HOU Bingna, HAN Chaoyue, et al. Preparation of injectable N-acltyl glycol chitosan/poloxamer composite hydrogel for drug release[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering,2020,48(5):83-90(in Chinese). [22] WU W, LEE S Y, WU X, et al. Neuroprotective ferulic acid (FA)-glycol chitosan (GC) nanoparticles for functional restoration of traumatically injured spinal cord[J]. Biomaterials,2014,35(7):2355-2364. doi: 10.1016/j.biomaterials.2013.11.074 [23] LI Z Z, HYEEUN S, MYEONG O C, et al. Thermo-sensitive injectable glycol chitosan-based hydrogel for treatment of degenerative disc disease[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2018,184:342-353. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.01.006 [24] 李征征, 徐子扬, 高留意, 等. 温敏性乙二醇壳聚糖水凝胶的制备及药物缓释性能[J]. 高等学校化学学报, 2016, 37(12):2299-2305.LI Zhengzheng, XU Ziyang, GAO Liuyi, et al. Preparation and characterization of thermo-sensitive N-acetyl glycol chitosanhydrogel for sustained drug release[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2016,37(12):2299-2305(in Chinese). [25] WATT R P, KHATRI H, DIBBLE A R G. Injectability as a function of viscosity and dosing materials for subcutaneous administration[J]. International Journal of Pharmaceutics,2019,554:376-386. [26] LEI W, WANFU Z, QINGGUO W, et al. An injectable, dual responsive, and self-healing hydrogel based on oxidized sodium alginate and hydrazide-modified poly (ethyleneglycol)[J]. Molecules,2018,23(3):546. doi: 10.3390/molecules23030546 [27] HUAPING T, MARRA K G. Injectable, biodegradable hydrogels for tissue engineering applications[J]. Materials,2010,3(3):1746-1767. doi: 10.3390/ma3031746 [28] YANG X, ZHU Z, LIU Q, et al. Effects of PVA agar contents and irradiation doses on properties of PVA/ws-chitosan/glycerol hydrogels made by g-irradiation followed by freeze-thawing[J]. Radiation Physics & Chemistry,2008,77(8):954-960. [29] DINU M V, COCARTA A I, DRAGAN E S. Synthesis, characterization and drug release properties of 3D chitosan/clinoptilolite biocomposite cryogels[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2016,153:203-211. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2016.07.111 -






 下载:
下载: