Thermal scale effect analysis of enhanced Reddy’s laminated composite based on new modified couple stress theory
-
摘要: 基于新修正偶应力理论,提出复合材料增强型Reddy层合板热尺度效应模型。该模型只含有一个材料长度参数
$\ell $ ,同时将首次引入厚度方向的旋转变量。通过虚功原理推导出平衡方程,并且利用纳维方法,分析热载作用下细观复合材料层合/夹层方板的位移和应力。数值计算表明:该模型能够很好地捕捉板的热尺度效应,随着材料长度参数增大,板的热尺度效应就会增强,另外随着板的跨厚比增加,板的热尺度效应会减弱,但减弱程度会下降。-
关键词:
- 增强型Reddy层合板 /
- 夹层板 /
- 热尺度效应 /
- 偶应力 /
- 材料长度参数
Abstract: Based on new modified couple stress theory, a model of thermal scale effect was proposed for the laminated composite plates of enhanced Reddy theory. The model contained only one materials length parameter$\ell $ , and the rotation variable was introduced through thickness direction for the first time. The equilibrium equations for the model were presented from the principle of virtual work, and displacements and stresses of micro-laminated composite/sandwich plates were analyzed by using Navier’s method under thermal loading. Numerical results show that the model can capture the thermal scale effect of plates well. As the material length parameter increases, the scale effects of plates are enhanced. Meanwhile, the scale effects are weakened with increasing of span-thickness ratio of plates, but there is a decline in the weakening extend. -
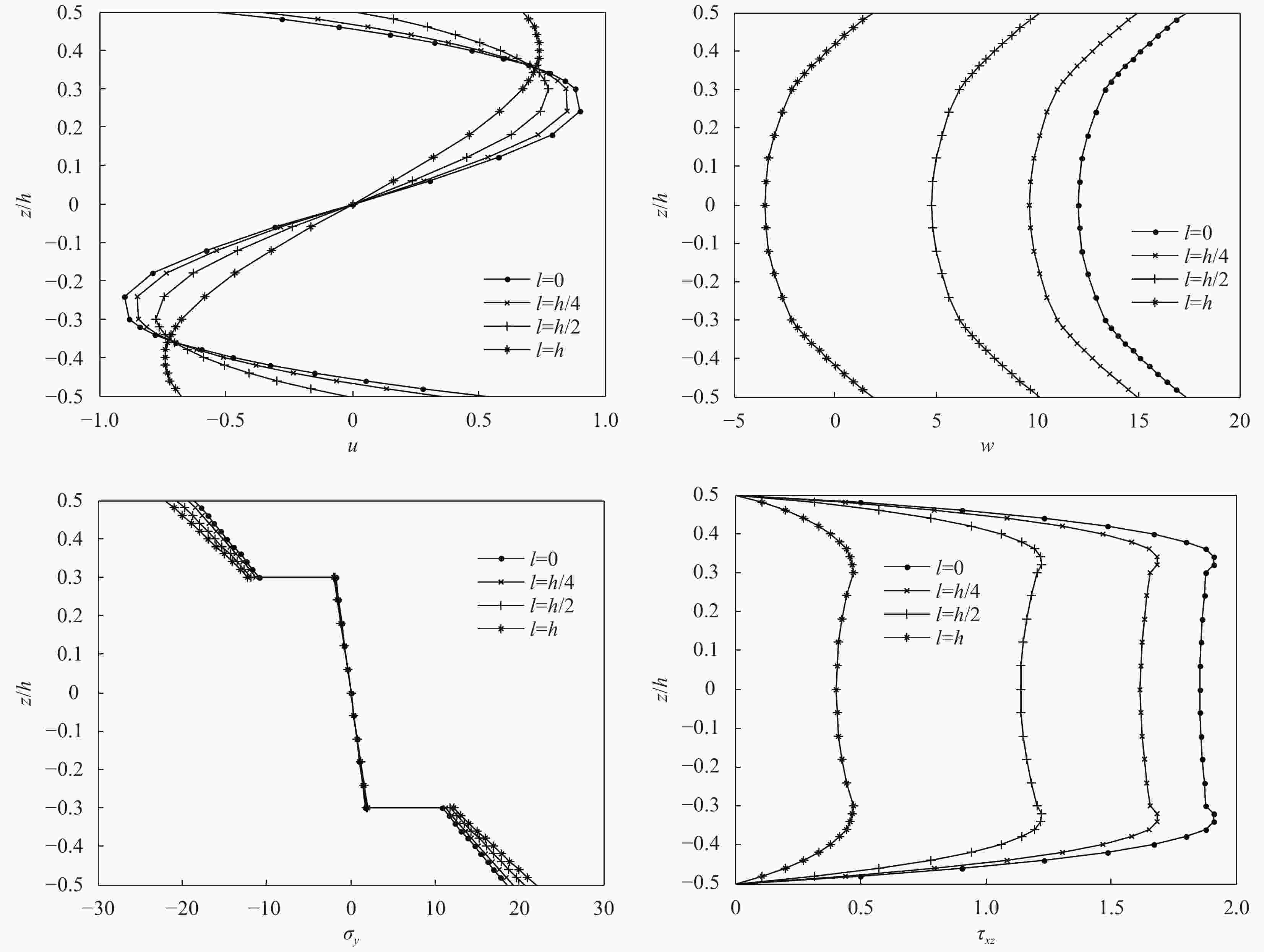
表 1 热载作用下细观层合板[0°/90°/0°]位移与应力的对比(括号内数值为
$\eta $ )Table 1. Comparison of displacements and stresses of micro-composite laminated plates [0°/90°/0°] under thermal loading (There is
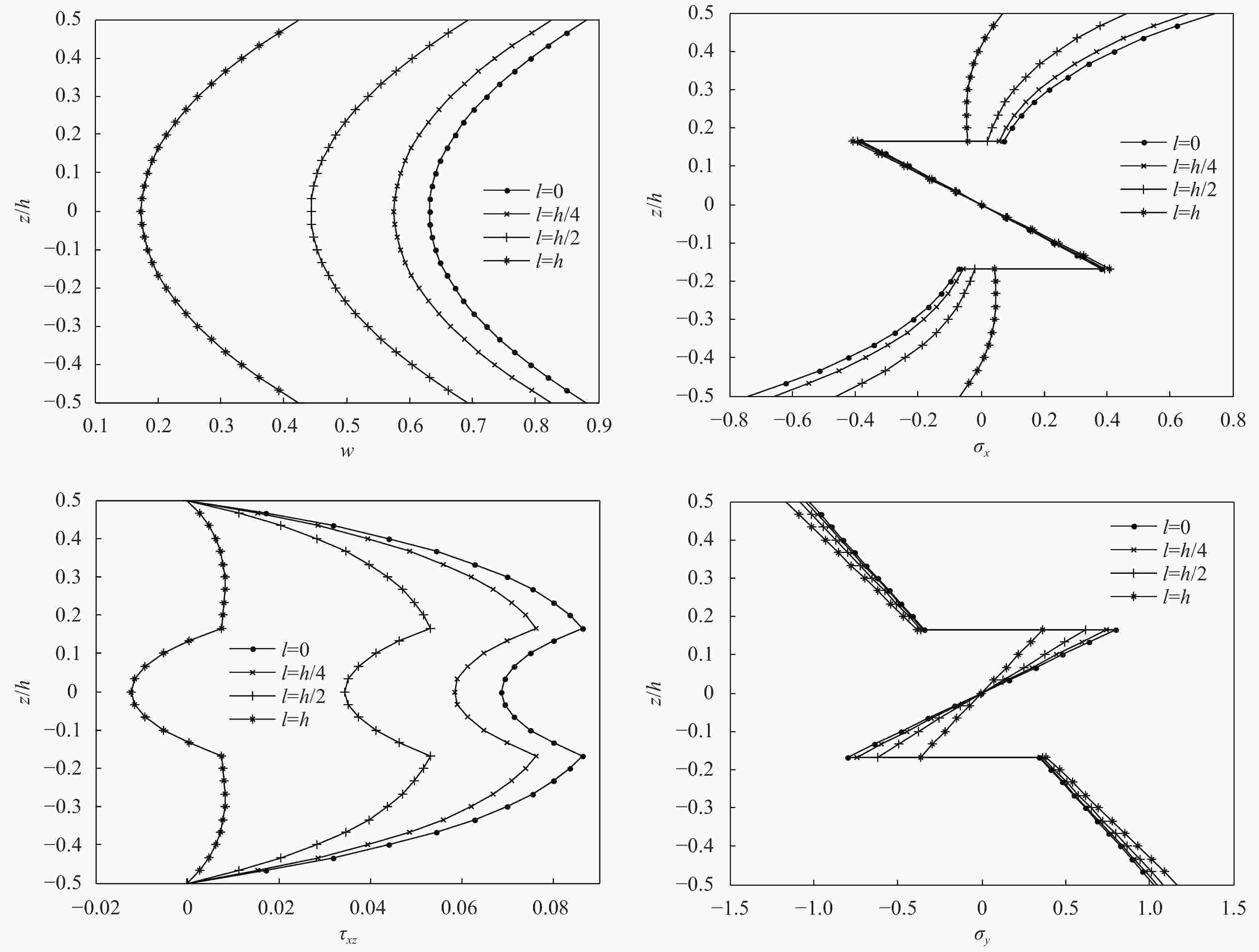
$\eta $ in the bracket)${a/h}$ ${\ell /h}$ $\bar u\left( {0,\dfrac{b}{2}, - \dfrac{h}{2}} \right)$ $\bar v\left( {\dfrac{a}{2},0, - \dfrac{h}{2}} \right)$ $\bar w\left( {\dfrac{a}{2},\dfrac{b}{2},0} \right)$ ${\bar \sigma _x}\left( {\dfrac{a}{2},\dfrac{b}{2},\dfrac{h}{2}} \right)$ ${\bar \sigma _y}\left( {\dfrac{a}{2},\dfrac{b}{2}, - \dfrac{h}{2}} \right)$ ${\bar \tau _{x{\textit{z}}}}\left( {0,\dfrac{b}{2},0} \right)$ ${\bar \tau _{y{\textit{z}}}}\left( {\dfrac{a}{2},0,0} \right)$ ${\bar \tau _{xy}}\left( {0,0, - \dfrac{h}{2}} \right)$ 5 0 0.1511/0.1327 0.3139/0.2866 0.6315/0.5410 0.7447/0.7837 1.0272/0.8050 0.0686/0.0696 −0.0802/−0.0644 0.1461/0.1317 1/4 0.1430(5.36) 0.2971(5.35) 0.5754(8.88) 0.6599(11.39) 1.0444(1.67) 0.0583(15.01) −0.0864(7.73) 0.1383(5.34) 1/2 0.1240(17.94) 0.2575(17.97) 0.4433(29.80) 0.4615(38.03) 1.0849(5.62) 0.0344(49.84) −0.1009(25.81) 0.1199(17.93) 1 0.0864(42.82) 0.1769(43.64) 0.1735(72.53) 0.0678(90.90) 1.1670(13.61) −0.0123(117.9) −0.1302(62.34) 0.0827(43.39) 10 0 0.3149/0.2625 0.4161/0.3542 2.2205/1.8368 0.7658/0.7511 1.1139/0.8722 0.0469/0.0454 −0.0576/−0.0444 0.1148/0.0969 1/4 0.3019(4.13) 0.3989(4.13) 2.1114(4.91) 0.6996(8.64) 1.1236(0.87) 0.0422(10.02) −0.0594(3.13) 0.1101(4.09) 1/2 0.2689(14.61) 0.3554(14.59) 1.8354(17.34) 0.5319(30.54) 1.1482(3.08) 0.0302(35.61) −0.0639(10.94) 0.0981(14.55) 1 0.1896(39.79) 0.2507(39.75) 1.1709(47.27) 0.1295(83.09) 1.2072(8.38) 0.0013(97.23) −0.0747(29.69) 0.0692(39.72) 20 0 0.6403/0.5232 0.6941/0.5714 8.3894/6.8426 0.7779/0.7392 1.1420/0.8954 0.0255/0.0244 −0.0318/−0.0243 0.1048/0.0860 1/4 0.6162(3.76) 0.6680(3.76) 8.0583(3.95) 0.7172(7.8) 1.1497(0.67) 0.0233(8.63) −0.0325(2.2) 0.1009(3.72) 1/2 0.5538(13.51) 0.6005(13.49) 7.2014(14.16) 0.5603(27.97) 1.1699(2.44) 0.0174(31.76) −0.0343(7.86) 0.0907(13.45) 1 0.3954(38.25) 0.4291(38.18) 5.0251(40.1) 0.1619(79.19) 1.2209(6.91) 0.0025(90.2) −0.0390(22.64) 0.0648(38.17) Notes: ${a/h}$—Span-thickness ratio of micro-composite laminated plates; ${\ell /h}$—Length-thickness ratio of micro-composite laminated plates. 表 2 热载作用下细观夹层板[0°/core/0°]位移与应力的对比(括号内数值为
$\eta $ )Table 2. Comparison of displacements and stresses of micro-composite sandwich plates [0°/core/0°] under thermal loading (There is
$\eta $ in the bracket )${a/h}$ ${\ell /h}$ $\bar u\left( {0,\dfrac{b}{2}, - \dfrac{h}{2}} \right)$ $\bar v\left( {\dfrac{a}{2},0, - \dfrac{h}{2}} \right)$ $\bar w\left( {\dfrac{a}{2},\dfrac{b}{2},0} \right)$ ${\bar \sigma _x}\left( {\dfrac{a}{2},\dfrac{b}{2},\dfrac{h}{2}} \right)$ ${\bar \sigma _y}\left( {\dfrac{a}{2},\dfrac{b}{2}, - \dfrac{h}{2}} \right)$ ${\bar \tau _{x{\textit{z}}}}\left( {0,\dfrac{b}{2},0} \right)$ ${\bar \tau _{y{\textit{z}}}}\left( {\dfrac{a}{2},0,0} \right)$ ${\bar \tau _{xy}}\left( {0,0, - \dfrac{h}{2}} \right)$ 4 0 0.5384/0.3310 10.5594/9.3526 12.0011/8.7933 29.3719/27.0127 18.5871/17.5300 1.8548/1.2821 −1.5962/−1.4914 5.4476/4.7534 1/4 0.3579(33.53) 9.8409(6.8) 9.6279(19.77) 25.5814(12.91) 19.2884(3.77) 1.6175(12.79) −1.7410(9.07) 5.0063(8.1) 1/2 −0.0140(102.6) 8.4783(19.71) 4.7786(60.18) 17.8069(39.37) 20.6277(10.98) 1.1402(38.53) −2.0107(25.97) 4.1549(23.73) 1 −0.6743(225.2) 7.1226(32.54) −3.4920(129.1) 4.3304(85.26) 22.0484(18.62) 0.4040(78.22) −2.2279(39.58) 3.1653(41.9) 8 0 1.2860/0.6431 9.4853/8.2103 24.2632/18.8468 29.6706/26.9638 23.7887/20.4417 1.4998/1.1408 −1.3898/−1.2466 2.6437/2.1730 1/4 1.1531(10.33) 9.1360(3.68) 22.4860(7.32) 28.3031(4.61) 23.9660(0.75) 1.4253(4.97) −1.4111(1.53) 2.5253(4.48) 1/2 0.8237(35.95) 8.2853(12.65) 18.0807(25.48) 24.9140(16.03) 24.3989(2.57) 1.2411(17.25) −1.4629(5.26) 2.2357(15.43) 1 0.0586(95.44) 6.4712(31.78) 7.8705(67.56) 17.0682(42.47) 25.3314(6.49) 0.8193(45.37) −1.5731(13.19) 1.6026(39.38) 12 0 2.1399/0.9690 8.3364/6.7533 36.4750/25.6378 30.4641/25.4640 25.5342/23.1161 1.1282/0.8838 −1.0635/−0.9493 1.7142/1.2636 1/4 2.0200(5.6) 8.1096(2.72) 34.8332(4.5) 29.6502(2.67) 25.6144(0.31) 1.0949(2.95) −1.0704(0.65) 1.6575(3.31) 1/2 1.7053(20.31) 7.5184(9.81) 30.5234(16.32) 27.5143(9.68) 25.8236(1.13) 1.0074(10.71) −1.0882(2.32) 1.5092(11.96) 1 0.8724(59.23) 6.0002(28.02) 19.1150(47.59) 21.8667(28.22) 26.3635(3.25) 0.7769(31.14) −1.1341(6.64) 1.1245(34.4) Notes: ${a/h}$—Span-thickness ratio of micro-composite sandwich plates; ${\ell /h}$—Length-thickness ratio of micro-composite sandwich plates -
[1] WHITNEY J M. The effect of transverse shear deformation on the bending of laminated plates[J]. Journal of Compo-site Materials,1969,3(3):534-547. doi: 10.1177/002199836900300316 [2] REDDY J N. A simple higher-order theory for laminated composite plates[J]. Journal of Applied Mechanics,1984,51 (4):745-752. doi: 10.1115/1.3167719 [3] LI X Y, LIU D. Generalized laminated theories based on double superposition hypothesis[J]. International Journal for Numerical Methods in Engineering,1997,40:1197-1212. doi: 10.1002/(SICI)1097-0207(19970415)40:7<1197::AID-NME109>3.0.CO;2-B [4] DISCIUVA M. Multilayered anisotropic plate models with continuous interlaminar stresses[J]. Composite Structures,1992,22:149-167. doi: 10.1016/0263-8223(92)90003-U [5] DISCIUVA M. Bending. vibration and buckling of simply supported thick multilayered orthotropic plates: An evaluation of a new displacement model[J]. Journal of Sound and Vibration,1986,105:425-442. doi: 10.1016/0022-460X(86)90169-0 [6] MATSUNAGA H. A comparison between 2-D single-layer and 3-D layer-wise theories for computing inter-laminar stresses of laminated composite and sandwich plates subjected to thermal loading[J]. Composite Structures,2004,64:161-177. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2003.08.001 [7] 吴振, 赵彧. 增强型Reddy层合梁理论与热应力分析[J]. 复合材料学报, 2012, 29(4):246-250.WU Zhen, ZHAO Yu. Enhanced Reddy’s beam theory and thermal stress analysis[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2012,29(4):246-250(in Chinese). [8] FLECK N A, MULLER G M, ASHBY M F. Stain gradient plasticity: Theory and experiment[J]. Acta Metallurgica et Materialia,1994,42(2):475-487. doi: 10.1016/0956-7151(94)90502-9 [9] LLOYD D J. Particle reinforced aluminum and magnesium matrix composites[J]. International Materials Reviews,1994,39:1-23. doi: 10.1179/imr.1994.39.1.1 [10] MINDLINR D, ESHEL N N. On first strain-gradient theories in linear elasticity[J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures,1968,4:109-124. doi: 10.1016/0020-7683(68)90036-X [11] MINDLINR D. Second gradient of strain and surfacetension in linear elasticity[J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures,1965,1(4):417-438. doi: 10.1016/0020-7683(65)90006-5 [12] TOUPIN R A. Elastic materials with couple stresses[J]. Archive for Rational Mechanics and Analysis,1962,11:385-414. doi: 10.1007/BF00253945 [13] KOITER W T. Couple stresses in the theory of elasticity. I and II[J]. Proceedings of the Koninkliske Nederlandse Akademie van Wetenschappen, 1964, 67: 17-44. [14] MINDLIN R D. Microstructure in linear elasticity[J]. Archive for Rational Mechanics and Analysis,1964,16:51-78. doi: 10.1007/BF00248490 [15] YANG F, CHONG A C M, LAM D C C, TONG P. Couple stress based strain gradient theory for elasticity[J]. International Journal of Solids and Structures,2002,39:2731-2743. doi: 10.1016/S0020-7683(02)00152-X [16] CHEN Wanji, LI Li, MA Xu. A modified couple stress model for bending analysis of composite laminated beams with first order shear deformation[J]. Composite Structures,2011,93:2723-2732. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2011.05.032 [17] CHEN Wanji, SI Junling. A model of composite laminated beam based on the global-local theory and new modified couple-stress theory[J]. Composite Structures,2013,103:99-107. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2013.03.021 [18] WU Zhen, YANG Zhichun, CHEN Wanji. Size-dependent vibration analysis of multi-layer composite micro-beam based on new modified couple stress theory[J]. International Journal for Multi-scale Computational Engineering,2017,15:459-476. doi: 10.1615/IntJMultCompEng.2017020796 [19] 张大千, 王良秀. 基于新修正偶应力理论的Mindlin层合板热稳定性分析[J]. 计算力学学报, 2019, 36(6):763-767. doi: 10.7511/jslx20181027001ZHANG Daqian, WANG Liangxiu. Thermal bucking analysis of composite laminated Mindlin plate founded in the new modified couple stress theory[J]. Chinese Journal of Computational Mechanics,2019,36(6):763-767(in Chinese). doi: 10.7511/jslx20181027001 [20] THANH C L, FERREIRA A J M, WAHAB M A. A refined size-dependent couple stress theory for laminated composite micro-plates using isogeometric analysis[J]. Thin-Walled Structures,2019,145:106427. doi: 10.1016/j.tws.2019.106427 -







 下载:
下载: