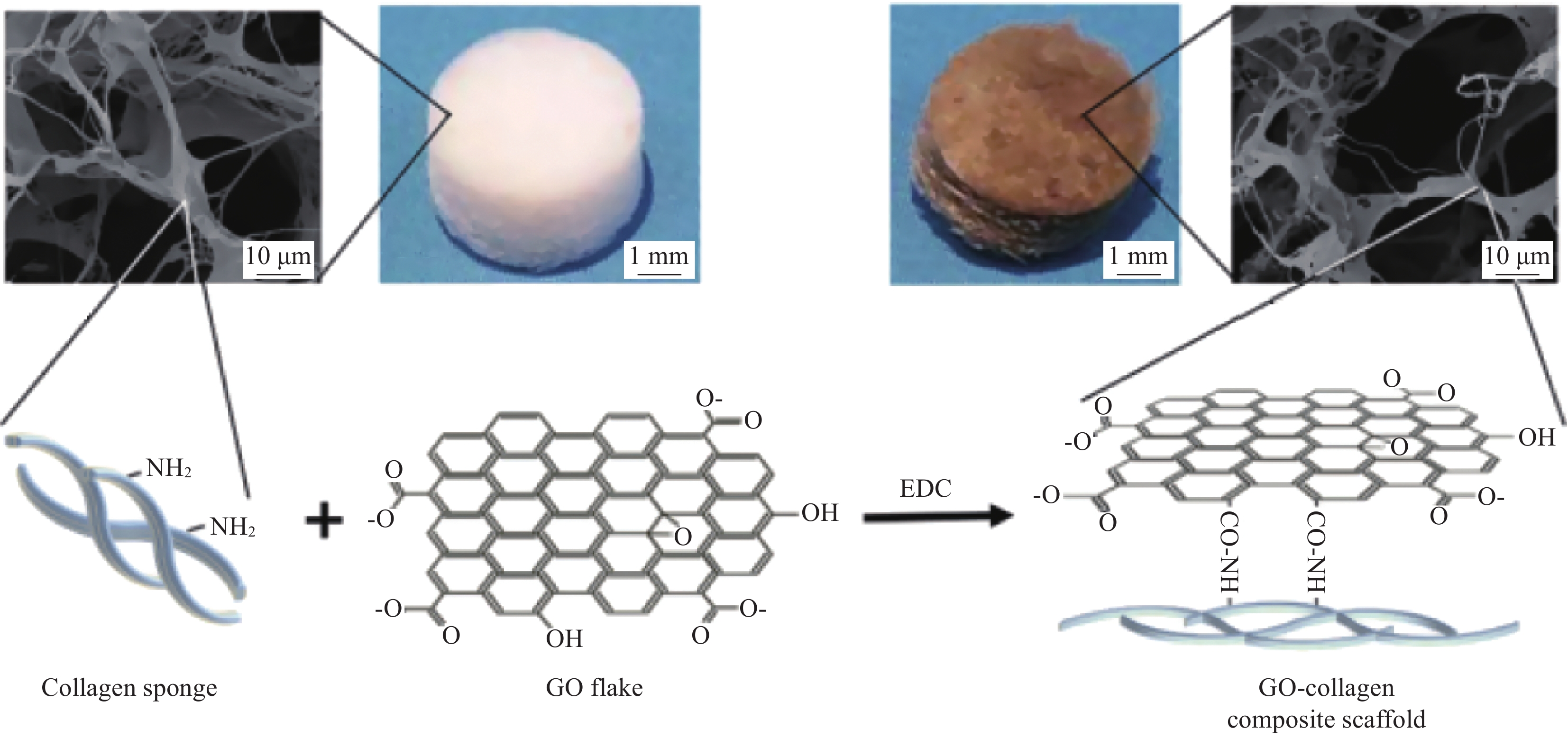
Progress on properties and interface of collagen-based nanocomposites
-
摘要: 胶原蛋白(COL)是一种绿色可再生的有机天然高分子材料,具有优异的生物相容性、可生物降解性和低抗原性等特点,将具有独特功能特性的无机纳米材料引入其中,可以开发出兼具二者优异性能的新型COL基纳米复合材料。然而,无机纳米材料与有机COL之间的界面结合特性会显著影响所制备复合材料的性能。因而,有必要研究纳米材料与COL之间的界面结合特性。本文系统回顾了未改性/有机化改性纳米材料对COL基纳米复合材料性能影响的研究现状,重点阐述了通过现代仪器分析表征方法和分子动力学模拟两种方法对纳米材料与COL之间的界面研究进展,对比了两种方法的优缺点,展望了COL基纳米复合材料性能及界面研究未来可能的发展趋势,指出在COL中引入新型纳米材料制备绿色化、多功能化、高性能化、应用多元化的COL基纳米复合材料及利用多种现代仪器分析方法和计算机模拟相结合的手段进行界面研究是未来的主要研究方向。Abstract: Collagen (COL) is a green and renewable organic natural polymer material with excellent biocompatibility, biodegradability and low antigenicity. A series of novel collagen-based nanocomposites combining excellent properties of two components could be developed by introducing inorganic nanomaterials with unique functional characteristics into collagen matrix. However, the interface interaction characteristics between inorganic nanomaterials and organic COL have a significant effect on the properties of the corresponding nanocomposites. Therefore, it is necessary to investigate the interface interaction between nanomaterials and COL. This paper systematically reviewed the main research status of the effect of unmodified/modified nanomaterials on the properties of COL-based nanocomposite, and summarized the progress of the interface research between nanomaterials and COL through methods of modern instrumental analysis and molecular dynamics simulation. Moreover, the advantages and disadvantages of the two methods were compared. Finally, the possible future research trend of the interface interaction between nanomaterials and COL matrix was prospected. It is pointed out that the introduction of nanomaterials into the COL matrix to prepare environmentally friendly, multi-functional, high-performance, and widely used COL-based nanocomposites, and the combination of modern instrument analysis methods and computer simulation methods to conduct interface research will be the main research directions in the future.
-
Key words:
- composites /
- collagen /
- nanomaterials /
- interfacial /
- molecular dynamics
-
图 9 不同COL和SiO2浓度的SiNR-COL复合水凝胶的储能模量(G′);采用单因素方差分析和Dunnett法计算同一胶原浓度下水凝胶G′的方差,*P < 0.05;箭头表示同一胶原浓度下水凝胶G′最小时对应的SiO2浓度[44]
Figure 9. Storage modulus (G′) of SiNR-collagen composite hydrogels with various COL and SiO2 concentrations; Variance of the G′ value between the hydrogels with same collagen concentration was determined by one-way analysis of variance with Dunnett post hoc test, *P < 0.05; Arrows indicate the SiNR concentration for minimal G′ value[44]
表 1 现代仪器分析方法在界面研究中的应用
Table 1. Application of modern instrument analysis in interface research
Characterization Information SEM, TEM Microstructure of interfacial phase FTIR, UV-vis, Raman spectra Composition and chemical structure of interfacial phase Turbidimetric method Aggregation at the interface phase XPS Binding energy, element composition and chemical bond XRD Phase analysis of interfacial phase DSC, TGA Thermal properties of interfacial phase Rheometer, DMA Viscoelasticity (storage modulus and loss modulus) of interfacial phase AFM Nanoscale imaging and mechanical properties of interface morphology 表 2 分子动力学模拟中的相关计算参数及应用
Table 2. Calculation parameters and their application in molecular dynamics simulation
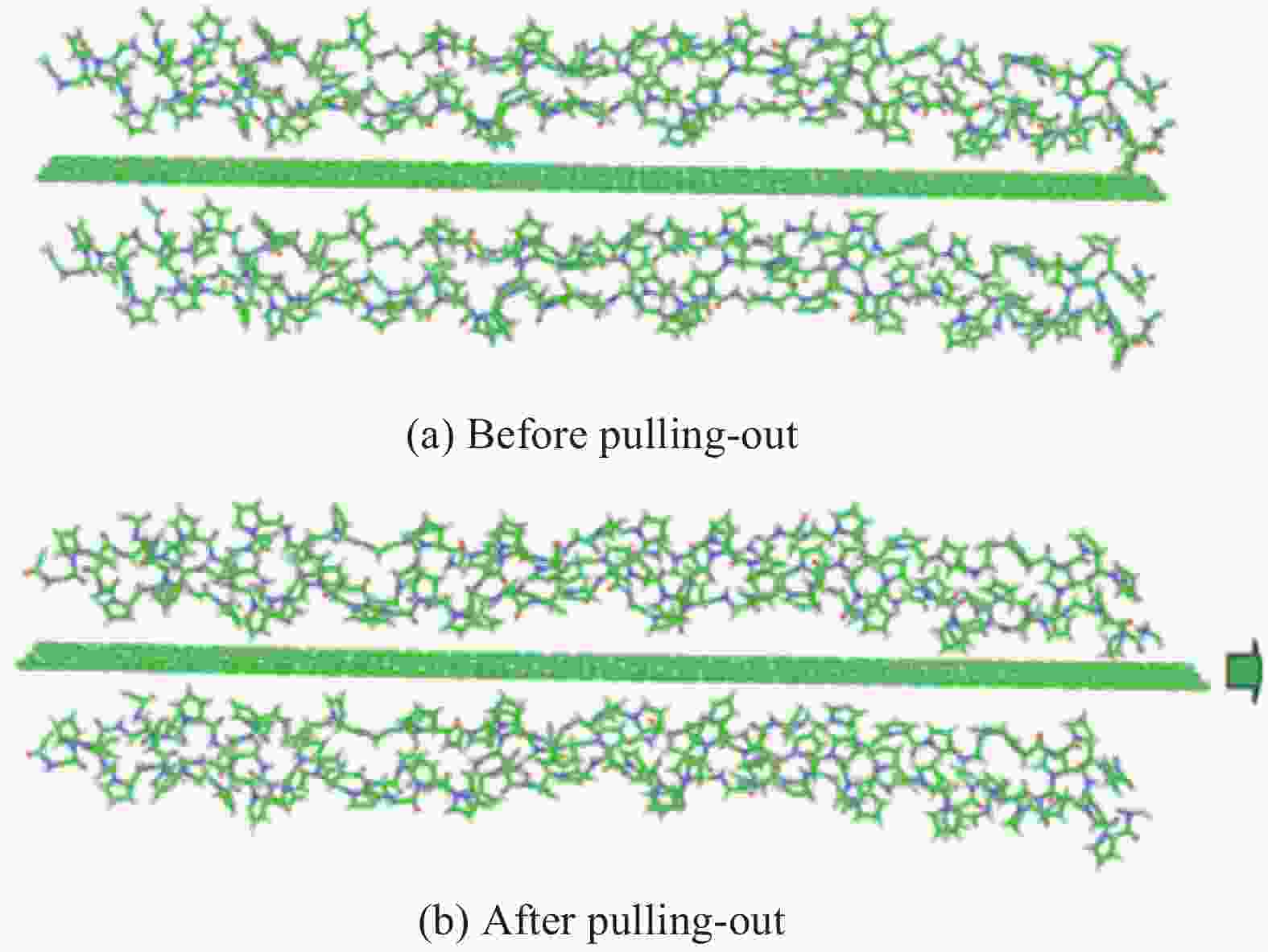
Calculation parameter Application Radius of gyration, root mean square deviation Conformational change of collagen Radial distribution function, interaction energy Type and size of interface interaction Pull-out studies, adhesion energy, surface free energy Bonding performance of interface -
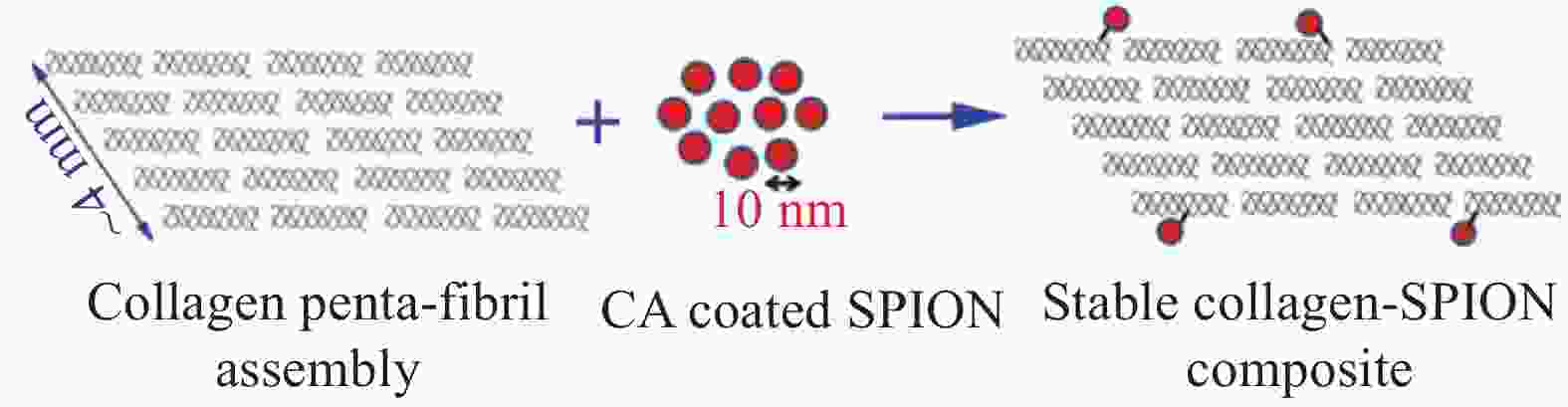
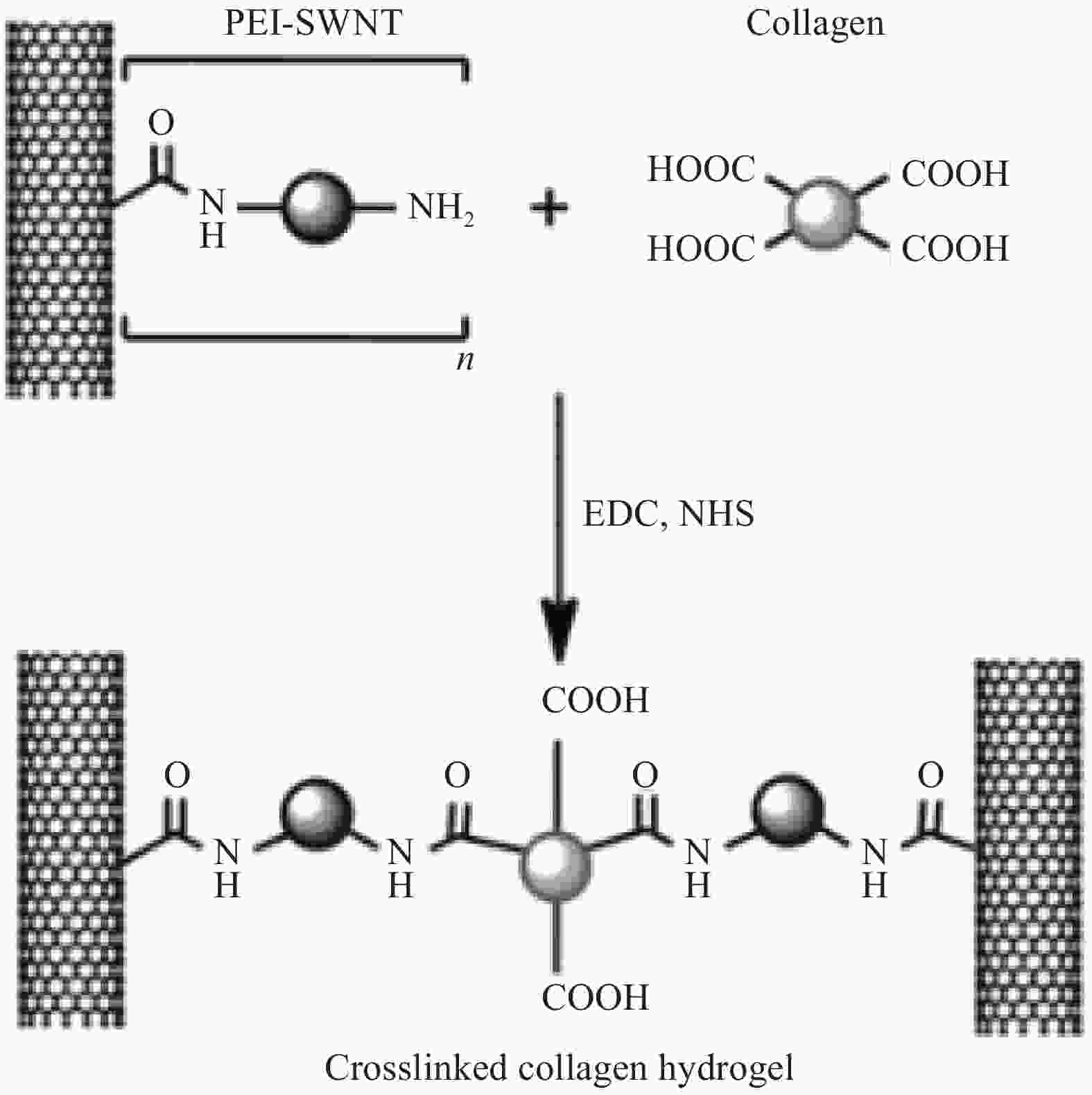
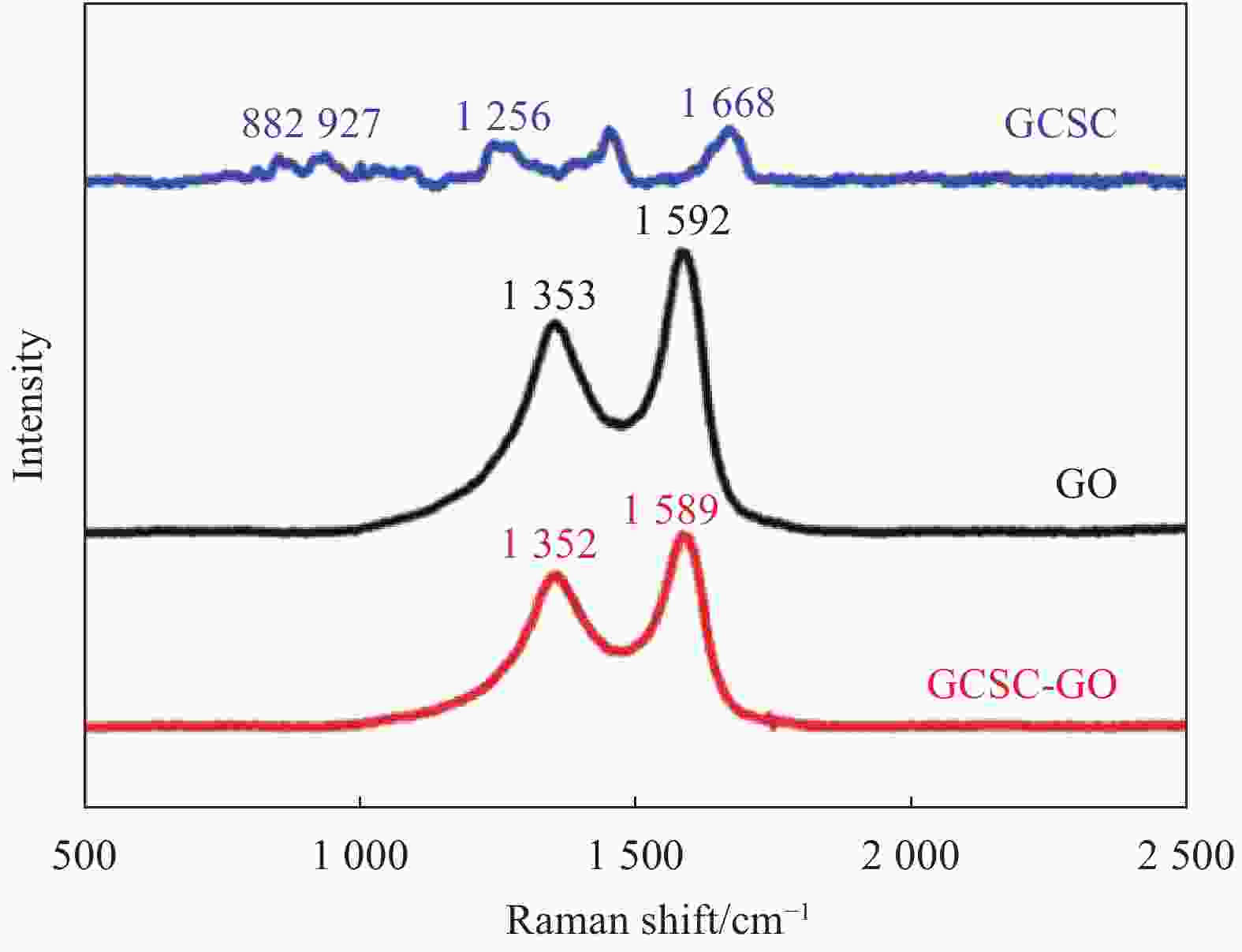
[1] LEE C H, SINGLA A, LEE Y. Biomedical applications of collagen[J]. International Journal of Pharmaceutics,2001,221(1-2):1-22. [2] SHEKHTER A B, FAYZULLIN A L, VUKOLOVA M N, et al. Medical applications of collagen and collagen-based materials[J]. Current Medicinal Chemistry,2017,25(3):506-516. [3] SIONKOWSKA A, ADAMIAK K, MUSIAL K, et al. Collagen based materials in cosmetic applications: A review[J]. Materials,2020,13(19):4217. doi: 10.3390/ma13194217 [4] CAO S, SONG J Z, LI H, et al. Improving characteristics of biochar produced from collagen-containing solid wastes based on protease application in leather production[J]. Waste Management,2020,105:531-539. doi: 10.1016/j.wasman.2020.02.043 [5] QI Y P, MAI S, YE Z, et al. Biomimetic fabrication and characterization of collagen/strontium hydroxyapatite nanocomposite[J]. Materials Letters,2020,274:127982. doi: 10.1016/j.matlet.2020.127982 [6] 王蕊, 冯莉莉, 张引引, 等. 纳米材料的制备和应用[J]. 化学世界, 2017, 58(7):433-441.WANG Rui, FENG Lili, ZHANG Yinyin, et al. Outline of preparation and application of nano-scale materials[J]. Chemical World,2017,58(7):433-441(in Chinese). [7] AIDUN A, SAFAEI FIROOZABADY A, MOHARRAMI M, et al. Graphene oxide incorporated polycaprolactone/chitosan/collagen electrospun scaffold: Enhanced osteogenic properties for bone tissue engineering[J]. Artificial Organs,2019,43(10):264-281. [8] 董雨菲, 马建中, 刘超, 等. SiO2的功能化改性及其与聚合物基体的界面研究进展[J]. 材料导报, 2019, 33(11):1910-1918. doi: 10.11896/cldb.18040152DONG Yufei, MA Jianzhong, LIU Chao, et al. Research progress on functional modification of SiO2 and its interface with polymer matrix[J]. Materials Reports,2019,33(11):1910-1918(in Chinese). doi: 10.11896/cldb.18040152 [9] WU Y K, MA J Z, LIU C, et al. Surface modification design for improving the strength and water vapor permeability of waterborne polymer/SiO2 composites: Molecular simulation and experimental analyses[J]. Polymers,2020,12(1):170. doi: 10.3390/polym12010170 [10] ZHOU C L, TAO M, LIU J, et al. Effects of interfacial interaction on corrosion resistance of polybenzoxazine/SiO2 nanocomposite coat-ings[J]. ACS Applied Polymer Materials, 2019, 1(3): 381-391. [11] 何金良, 彭思敏, 周垚, 等. 聚合物纳米复合材料的界面特性[J]. 中国电机工程学报, 2016, 36(24):6596-6605, 6911.HE Jinliang, PENG Simin, ZHOU Yao, et al. Interface properties of polymer nanocomposites[J]. Proceedings of The Chinese Society for Electrical Engineering,2016,36(24):6596-6605, 6911(in Chinese). [12] 吴英柯, 马建中, 鲍艳. 聚合物基纳米复合材料的界面作用研究进展[J]. 材料导报, 2018, 32(3):434-442.WU Yingke, MA Jianzhong, BAO Yan. Advances in interfacial interaction within polymer matrix nanocomposites[J]. Materials Reports,2018,32(3):434-442(in Chinese). [13] TÜRK S, ALTMSOY I, ÇELEBI EFE G, et al. 3D porous collagen/functionalized multiwalled carbon nanotube/chitosan/hydroxyapatite composite scaffolds for bone tissue engineering[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: C,2018,92:757-768. doi: 10.1016/j.msec.2018.07.020 [14] DERKU B, EMREGÜL E, YLMAZ M S. Investigation of the use of collagen-gelatin-gold nanoparticle nanocomposite system as an aptasensor matrix[J]. Hacettepe Journal of Biology and Chemistry,2018,4(46):523-531. doi: 10.15671/HJBC.2018.260 [15] LIU C, HUANG X, ZHOU J F, et al. Lightweight and high-performance electromagnetic shielding nanocomposites based on surface coating of Cu@Ag nanoflakes on dielectric nanofibrous collagen network[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry C,2015,4(5):914-920. [16] JIANG Y P, LI J X, LI B, et al. Study on a novel multifunctional nanocomposite as flame retardant of leather[J]. Polymer Degradation and Stability,2015,115:110-116. doi: 10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2015.02.018 [17] AHMADIAN S, GHORBANI M, MAHMOODZADEH F. Silver sulfadiazine-loaded electrospun ethyl cellulose/polylactic acid/collagen nanofibrous mats with antibacterial properties for wound healing[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2020,162:1555-1565. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.08.059 [18] KHOLKHOEV B C, BUINOV A S, MAKOTCHENKO V G, et al. Electrically conductive composites of collagen and graphene[J]. Russian Chemical Bulletin,2018,67(7):1316-1318. doi: 10.1007/s11172-018-2218-0 [19] SUBAGIO A, UMIATI N A K, GUNAWAN V. Growth of collagen-nanosilver (Co-AgNP) biocomposite film with electrospinning method for wound healing applications[J]. Journal of Physics: Conference Series,2020,1524(1):12032. [20] BAIA L, BAIA M, DANCIU V, et al. Type I collagen-TiO2 aerogel based biocomposites[J]. Journal of Optoelectronics & Advanced Materials,2008,10(4):933-936. [21] KANG S, PARK J B, LEE T J, et al. Covalent conjugation of mechanically stiff graphene oxide flakes to three-dimensional collagen scaffolds for osteogenic differentiation of human mesenchymal stem cells[J]. Carbon,2015,83:162-172. doi: 10.1016/j.carbon.2014.11.029 [22] LIU S K, ZHOU C C, MOU S, et al. Biocompatible graphene oxide-collagen composite aerogel for enhanced stiffness and in situ bone regeneration[J]. Materials Science & Engineering C,2019,105:110137. [23] 李青, 全仁夫, 陈利红, 等. 负载纳米氧化锌丝素胶原蛋白支架修复皮肤创面[J]. 中国组织工程研究, 2018, 22(14):2157-2161. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0784LI Qing, QUAN Renfu, CHEN Lihong, et al. Acceleration of wound healing by a porous collagen/silk fibroin scaffold carrying zinc oxide nanoparticles[J]. Chinese Journal of Tissue Engineering Research,2018,22(14):2157-2161(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.2095-4344.0784 [24] FAN X L, CHEN K K, HE X C, et al. Nano-TiO2/collagen-chitosan porous scaffold for wound repairing[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2016,5:94. [25] NEASCU I A, MELENTE A E, HOLBAN A M, et al. Novel hydrogels based on collagen and ZnO nanoparticles with antibacterial activity for improved wound dressings[J]. Romanian Biotechnological Letters,2019,24(2):317-323. doi: 10.25083/rbl/24.2/317.323 [26] RYAN A J, KEARNEY C J, SHEN N, et al. Electroconductive biohybrid collagen/pristine graphene composite biomaterials with enhanced biological activity[J]. Advanced Materials,2018:1706442. [27] SUN T W, ZHU Y J, CHREN F. Hydroxyapatite nanowire/collagen elastic porous nanocomposite and its enhanced performance in bone defect repair[J]. RSC Advances,2018,8(46):26218-26229. doi: 10.1039/C8RA03972K [28] 程国君, 陈晨, 李世迁, 等. CaCO3/SiO2纳米粒子的表面改性及其对天然胶乳膜抗紫外光老化性能的影响[J]. 辐射研究与辐射工艺学报, 2019, 37(6):12-21.CHENG Guojun, CHEN Chen, LI Shiqian, et al. Surface modification of CaCO3/SiO2 nanoparticles and its effect on the UV aging resistance of natural rubber latex film[J]. Journal of Radiation Research and Radiation Processing,2019,37(6):12-21(in Chinese). [29] SEKAR V, BASKARALINGAM V. Antibiofilm, anti cancer and ecotoxicity properties of collagen based ZnO nanoparticles[J]. Advanced Powder Technology,2018,29(10):2331-2345. doi: 10.1016/j.apt.2018.06.013 [30] YE X Y, ZHOU Y M, CHEN J, et al. Synthesis and infrared emissivity study of collagen-g-PMMA/Ag@TiO2 composite[J]. Materials Chemistry and Physics,2007,106(2/3):447-451. [31] THANIKAIVELAN P, NARAYANAN N T, PRADHAN B K, et al. Collagen based magnetic nanocomposites for oil removal applications[J]. Scientific Reports,2012,2:230. doi: 10.1038/srep00230 [32] MACDONALD R A, LAURENZI B F, VISWANATHAN G, et al. Collagen-carbon nanotube composite materials as scaffolds in tissue engineering[J]. Journal of Biomedical Materials Research Part A,2010,74(3):489-496. [33] HOMENICK C M, SHEARDOWN H, ADRONOV A. Reinforcement of collagen with covalently-functionalized single-walled carbon nanotube crosslinkers[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry,2010,20(14):2887-2894. doi: 10.1039/b925799c [34] CHEN Y H, ZHENG Z W, ZHOU R P, et al. Developing a strontium-releasing graphene oxide-/collagen-based organic-inorganic nanobiocomposite for large bone defect regeneration via MAPK signaling pathway[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2019,11(17):15986-15997. [35] LOHRASBI S, MIRZAEI E, KARIMIZADE A, et al. Collagen/cellulose nanofiber hydrogel scaffold: Physical, mechanical and cell biocompatibility properties[J]. Cellulose,2020,27(2):927-940. doi: 10.1007/s10570-019-02841-y [36] MA J Z, DONG Y F, BAO Y, et al. Tunable microstructure of polyacrylate/ZnO nanorods composite emulsion and its film-forming properties[J]. Progress in Organic Coatings,2019,135:382-391. doi: 10.1016/j.porgcoat.2019.05.044 [37] 李春哲. 浅谈现代仪器分析的发展趋势和前景[J]. 石化技术, 2017, 24(12):280. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0235.2017.12.229LI Chunzhe. The development trend and prospect of modern instrument analysis[J]. Petrochemical Industry Technology,2017,24(12):280(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-0235.2017.12.229 [38] YE X Y, ZHOU Y M, SUN Y Q, et al. Structure and infrared emissivity of collagen/SiO2 composite[J]. Applied Surface Science,2008,254(18):5975-5980. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2008.03.186 [39] WEI B M, ZHONG H Y, WANG L J, et al. Facile preparation of a collagen-graphene oxide composite: A sensitive and robust electrochemical aptasensor for determining dopamine in biological samples[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2019,135:400-406. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2019.05.176 [40] BETTINI S, BONFRATE V, MADAGHIELE M, et al. On demand release of hydrosoluble drugs from a paramagnetic porous collagen-based scaffold[J]. Chemistry-A European Journal,2017,23:1338-1345. doi: 10.1002/chem.201603210 [41] KUBOKI Y, TERADA M, KITAGAWA Y, et al. Interaction of collagen triple-helix with carbon nanotubes: Geometric property of rod-like molecules[J]. Biomedical Materials and Engineering,2009,19(1):3-9. doi: 10.3233/BME-2009-0557 [42] 王变红, 刘长营, 呼峰, 等. 纳米级钛颗粒对牙周组织细胞的影响[J]. 北京口腔医学, 2019, 27(3):137-142.WANG Bianhong, LIU Changying, HU Feng, et al. Effects of nano titanium particles on periodontal tissue cells[J]. Beijing Journal of Stomatology,2019,27(3):137-142(in Chinese). [43] NOJIRI T, CHEN C Y, KIM D M, et al. Establishment of perpendicular protrusion of type I collagen on TiO2 nanotube surface as a priming site of peri-implant connective fibers[J]. Journal of Nanobiotechnology,2019,17(1):34. doi: 10.1186/s12951-019-0467-1 [44] SHI Y P, HÉLARY C, CORADIN T. Exploring the cell protein-mineral interfaces: Interplay of silica (nano)rods@collagen biocomposites with human dermal fibroblasts[J]. Materials Today Bio,2019,1:100004. doi: 10.1016/j.mtbio.2019.100004 [45] ANDONEGI M, PEÑALBA M, CABA K D L, et al. ZnO nanoparticle-incorporated native collagen films with electroconductive properties[J]. Materials Science & Engineering C,2020,108:110394. [46] DU J H, DING C K, CAO Y M, et al. Effects of the aspect ratio of multi-walled carbon nanotubes on the structure and properties of regenerated collagen fibers[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2019,126:595-602. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2018.12.144 [47] TUCKERMAN M E, MARTYNA G J. Understanding modern molecular dynamics: Techniques and applications[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry B,2000,104(2):159-178. doi: 10.1021/jp992433y [48] SHAW D E, DROR R O, SALMON J K, et al. Millisecond-scale molecular dynamics simulations on anton[C]//Proceedings of the Conference on High Performance Computing Networking, Storage and Analysis. New York: Association for Computing Machinery, 2009: 1-11. [49] GAO D G, CHENG Y M, WANG P P, et al. An eco-friendly approach for leather manufacture based on P(POSS-MAA)-aluminum tanning agent combination tannage[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production,2020,257:120546. doi: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2020.120546 [50] GOPALAKRISHNAN R, BALAMURUGAN K, SINGAM E R, et al. Adsorption of collagen onto single walled carbon nanotubes: A molecular dynamics investigation[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics,2011,13(28):13046-13057. doi: 10.1039/c1cp20107g [51] BURGOT J L. The notion of activity in chemistry[M]. Switzerland: Springer International Publishing, 2017: 329-335. [52] 高建静. 烷基糖苷衍生物/Ag-TiO2/大豆磷脂纳米复合加脂剂的研究[D]. 西安: 陕西科技大学, 2019.GAO Jianjing. Research of alkyl polyglucoside derivative/Ag-TiO2/soybean phospholipids nanocompo-site fatliquor[D]. Xi’an: Shaanxi University of Science & Technology, 2019(in Chinese). [53] EBRAHIMI S, MONTAZERI A, RAFII-TABAR H. Molecular dynamics study of the interfacial mechanical properties of the graphene-collagen biological nanocomposite[J]. Computational Materials Science,2013,69:29-39. doi: 10.1016/j.commatsci.2012.11.030 [54] EBRAHIMI S, GHAFOORI-TABRIZIB K, RAFII-TABAR H. Molecular dynamics simulation of the adhesive behavior of collagen on smooth and randomly rough TiO2 and Al2O3 surfaces[J]. Computational Materials Science,2013,71:172-178. doi: 10.1016/j.commatsci.2013.01.017 [55] HEIDARI H, SHAMLOO A. The effect of rippled graphene sheet roughness on the adhesive characteristics of a collagen–graphene system[J]. International Journal of Adhesion & Adhesives,2016,64:9-14. [56] TANG M, GANDHI N S, BURRAGE K, et al. Interaction of gold nanosurfaces/nanoparticles with collagen-like peptides[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics,2019,21(7):3701-3711. doi: 10.1039/C8CP05191G [57] XUE Z Y, YANG M, XU D. Nucleation of biomimetic hydroxyapatite nanoparticles on the surface of type I collagen: Molecular dynamics investigations[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C,2019,123(4):2533-2543. doi: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.8b10342 -






 下载:
下载: