Process optimization of typical composite cambered components with large thickness
-
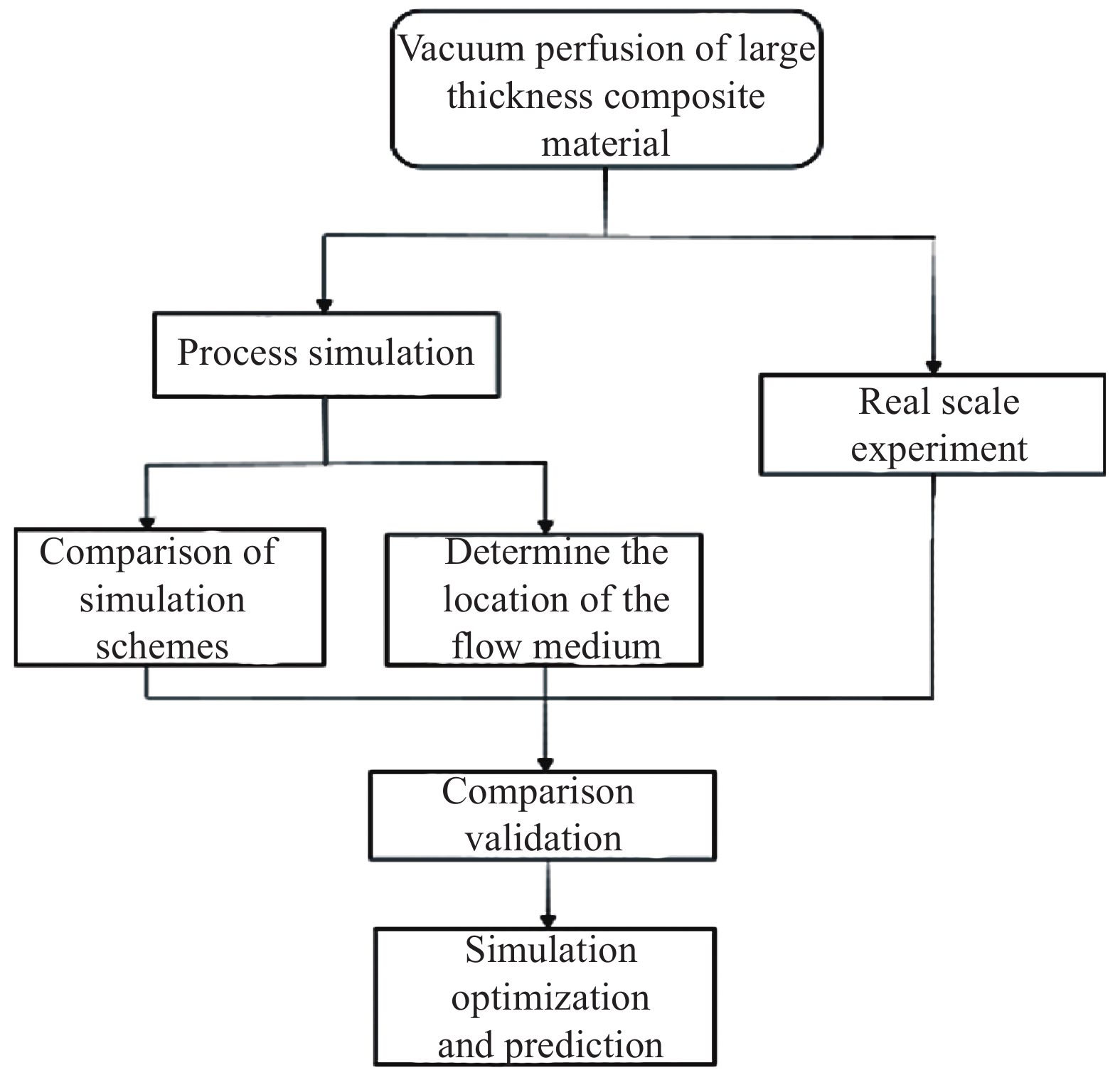
摘要: 大厚度复合材料的数值仿真存在缺乏实尺度验证、数值模型待优化等问题。本文针对真空辅助树脂传递模塑成型的大厚度复合材料曲面构件,通过大型风电叶片主梁的工艺仿真与实尺度实验验证,进行了工艺设计与工艺参数模型预测。首先对比研究了不同的工艺仿真方案;然后利用所选优化方案对树脂灌注方案进行工艺设计,并进行了实验验证;最后,提出了不同厚度制件的工艺参数预测模型。结果表明:所选优化方案可同时得到理想的计算效率和流动模拟结果;所设计工艺方案与实验吻合性良好;工艺参数预测模型所得结果与模拟结果基本一致。Abstract: There are critical limitations in numerical simulation of large-thickness composite materials, including lack of real-scale verifications and numerical model to be optimized. In this paper, the process design and model prediction of process parameters were carried out for the large-thickness composite curved cambered component formed by vacuum assisted resin transfer molding through process simulation and experimental verification. Firstly, different process simulation schemes were compared and studied. Then the optimum scheme was used to design the process of the resin infusion, and the experimental verification was carried out. Finally, the process parameter prediction model of different thickness parts was proposed. The results show that the optimal scheme can obtain ideal computational efficiency and flow simulation results simultaneously. The simulation results of the designed process scheme are in good agreement with the experiments. The results obtained by the process parameter prediction model are basically consistent with the simulation results.
-
Key words:
- real-scale /
- vacuum infusion /
- simulation /
- process optimization /
- process prediction model
-
表 1 实验材料
Table 1. Materials for experiment
Material Type Description Glass fiber HUD 1240 H=0.72 mm; K=4.6×10−12 m2; Kz=1.77×10−13 m2 Resin Epoxy resin Viscosity: 423-580 Pa·s Flow medium — Permeability: 5.5×10−9 m2 Consumable materials — Unidirectional permeable film; Peel ply Notes: H—Thickness of fiber; K—In-plane permeability of fiber; Kz—Thickness directional permeability. 表 2 大厚度复合材料曲面制件四种仿真模型对比
Table 2. Comparison of four simulation models of composite cambered component of large thickness
Model Dimension Meshing method Meshing type Element layers in thickness direction 1 2D Auto mesh Triangle 5 2 3D Laminate Tetrahedron 47 3 3D Laminate+layer mesh Tetrahedron 47/35/25/18/12/6 4 3D Layer mesh Tetrahedron 5 表 3 大厚度复合材料曲面制件模型3模拟结果对比(46 层)
Table 3. Comparison of simulation result of model 3 of composite cambered component of large thickness (46 layers)
Number of part 47 35 24 18 12 6 Filling time/s 5 928 6 240 6 281 6 297 6 350 6 151 Elements/thousand 2 150 1 600 1 130 780 550 270 CPU time/min 182 137 63 44 35 27 表 4 大厚度复合材料曲面制件模型3模拟结果对比(30层)
Table 4. Comparison of simulation results of model 3 of composite cambered component of large thickness (30 layers)
Number of laminate 31 26 21 16 11 6 Filling time/s 3 616 3 633 3 727 3 739 3 757 3 691 Element/thousand 1 420 1 190 960 730 500 270 CPU time/min 130 101 76 40 28 24 表 5 大厚度复合材料曲面制件不同模拟方案对比(46层)
Table 5. Comparison of different simulation schemes of composite cambered component of large thickness (46 layers)
Model 2 3 4 Filling time/s 6498 6151 6261 CPU time/min 170 27 44 -
[1] 杜善义. 先进复合材料与航空航天[J]. 复合材料学报, 2007, 24(1):12.DU Shanyi. Advanced composite materials and aerospace engineering[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2007,24(1):12(in Chinese). [2] DING A, LI S, WANG J, et al. A new path-dependent constitutive model predicting cure-induced distortions in composite structures[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2017,95:183-196. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2016.11.032 [3] DING A, LI S, WANG J, et al. A new analytical solution for spring-in of curved composite parts[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2017,142:30-40. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2017.01.024 [4] 张浩, 李书欣, 王继辉, 等. 基于新型测试装置的网孔板层开孔率对纤维厚度方向渗透率的影响[J]. 复合材料学报, 2020, 37(5):1175-1183.ZHANG Hao, LI Shuxin, WANG Jihui, et al. Influence of the ratio of hole area for mesh plate layer on through-thickness permeability based on a new designed test bench[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2020,37(5):1175-1183(in Chinese). [5] 张保丰, 杨汉嵩, 刘建秀. 风电叶片材料的研制[J]. 铸造技术, 2011, 32(12):1721-1723.ZHANG Baofeng, YANG Hansong, LIU Jianxiu. Development of wind turbine blade materials[J]. Foundry Technology,2011,32(12):1721-1723(in Chinese). [6] BICKERTON S, ADVANI S G. Experimental investigation and flow visualization of the resin-transfer mold-filling process in a non-planar geometry[J]. Composites ence & Technology,1997,57(1):23-33. [7] GRSSING H, STADLMAJER N, FAUSTER E, et al. Flow front advancement during composite processing: Predictions from numerical filling simulation tools in comparison with real-world experiments[J]. Polymer Composites,2016,37(9):2782-2793. doi: 10.1002/pc.23474 [8] DONG C H. Development of a process model for the vacuum assisted resin transfer molding simulation by the response surface method[J]. Composites: Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2006,37:1316-1324. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2005.08.012 [9] 李海晨, 王彪, 周振功. RTM工艺树脂流动过程数值模拟[J]. 复合材料学报, 2002, 19(2):18-23. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3851.2002.02.003LI Haichen, WANG Biao, ZHOU Zhengong. Numerical simulation of resin flow in RTM[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2002,19(2):18-23(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3851.2002.02.003 [10] KUANG T H, MATHIEU D, SURESH G A. Simulation based flow distribution network optimization for vacuum assisted resin transfer moulding process[J]. Modelling & Simulation in Materials ence&Engineering,2004,12(3):119-129. [11] 汤扬阁. 真空辅助成型工艺制作风机叶片工艺设计的充模模拟[D]. 呼和浩特: 内蒙古工业大学, 2013.TANG Yangge. Modeling and simulation of the VARI process for wind turbine blades process design[D]. Huhhot: Inner Mongolia University, 2013(in Chinese). [12] SIMACEK P, ADWANI S G. Modeling resin flow and fiber tow saturation induce by distribution media collapse in VARTM[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2007,67(13):2757-2769. doi: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2007.02.008 [13] 苏跃增, 纵海, 曹均助, 等. VARI工艺制备典型平面及曲面构件的流道设计模拟研究[J]. 材料工程, 2009 (A2):1-3. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4381.2009.12.001SU Yuezeng, ZONG Hai, CAO Junzhu, et al. Study on simulation of flow channel design in manufacturing typical plane and surface parts by using VARI process[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering,2009 (A2):1-3(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-4381.2009.12.001 [14] 成天建, 鲁先孝, 张兴刚. 复合材料增强纤维渗透率测量及VARI成型工艺仿真计算[J]. 工程塑料应用, 2011, 39(7):38-41. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3539.2011.07.010CHENG Tianjian, LU Xianxiao, ZHANG Xinggang. Research on composites reinforced fiber permeability measuring and VARI process simulation[J]. Engineering Plastics Application,2011,39(7):38-41(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-3539.2011.07.010 [15] 王德盼. 纤维增强复合材料VARTM工艺树脂充填模拟及实验研[D]. 南昌: 南昌大学, 2014.WANG Depan. Numerical simulation and experiment study on resin filling of fiber reinforced composites with VARTM process[D]. Nanchang: Nanchang University, 2014(in Chinese). [16] 孙玉敏, 段跃新, 李丹, 等. 风机叶片RTM工艺模拟分析及其优化[J]. 复合材料学报, 2005, 22(4):23-29. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3851.2005.04.005SUN Yumin, DUAN Yuexin, LI Dan, etl. Computer simulation analysis and optimization for wind turbine blade[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2005,22(4):23-29(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3851.2005.04.005 [17] VERLEYE B, ROOSE D, LOMOV S V, et al. Computation of permeability of textile reinforcement[C]. The 9th International Conference on Masterial Forming Esaform. 2006: 735-738. [18] KUPPUSAMY R R P, NEOGI S. Simulation of air entrapment and resin curing during manufacturing of composite cab front by resin transfer moulding process[J]. Archives of Metallurgy and Materials,2017,62(3):1839-1844. doi: 10.1515/amm-2017-0278 [19] 赖家美, 王德盼, 陈显明, 等. VARTM工艺中高渗透导流介质对树脂充填行为的影响[J]. 高分子材料科学与工程, 2014, 30(7):120-125.LAI Jiamei, WANG Depan, CHEN Xianming, et al. Effects of high-permeability medium on resin filling behavior in vacuum assisted resin transfer molding process[J]. Polymer Materials Science & Engineering,2014,30(7):120-125(in Chinese). [20] 王浩军, 王林文, 赵安安, 等. 复合材料带筋壁板预成型体压缩性与渗透性对树脂流动的影响[J]. 复合材料学报, 2019, 36(4):811-825.WANG Haojun, WANG Linwen, ZHAO An’an, et al. Effect of compaction and permeability of the composite stiffened panel preform on resin flow[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2019,36(4):811-825(in Chinese). [21] CLAUDIO D F, SUN Y, PHILIPPE C, et al. A dimensionless characteristic number for process selection and mold design in composites manufacturing: Part I—Theory[J]. Journal of Composite Science,2020,4(11):1-15. [22] LABAT L, BREARD J, PILLUT L S. Void formation prevision in LCM parts[J]. European Physical Journal Applied Phy-sics,2001,16(2):157-164. doi: 10.1051/epjap:2001104 [23] PATEL N, LEE L J. Modeling of void formation in liquid composite molding. Part Ⅱ: Model development and impregnation[J]. Polymer Composites,1996,17(1):104-114. doi: 10.1002/pc.10595 [24] PATEL N, LEE L J. Modeling of void formation in liquid composite molding:Part Ⅰ—Wettability analysis[J]. Polymer Composites,1996,17(1):96-103. doi: 10.1002/pc.10594 -






 下载:
下载: