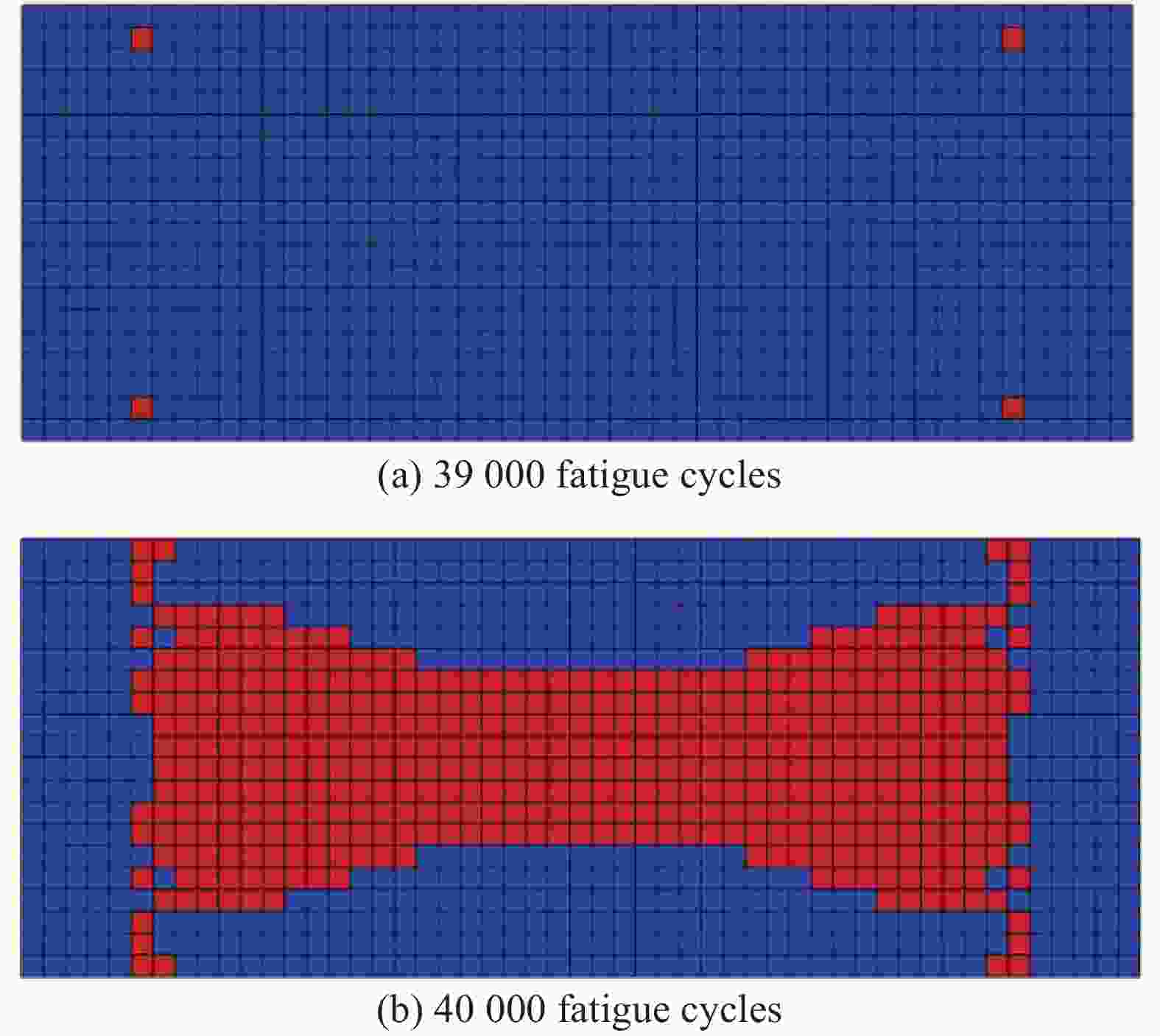
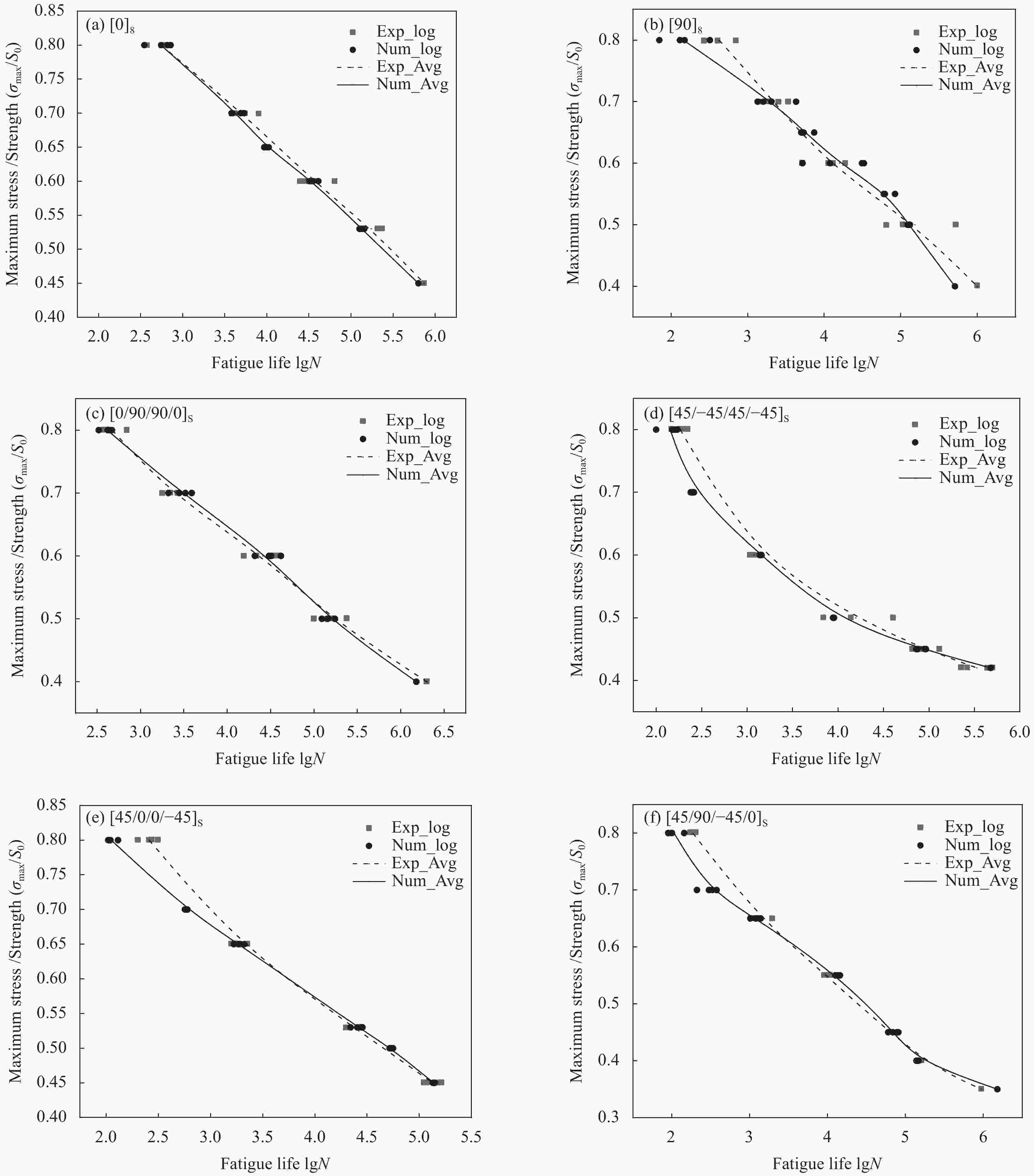
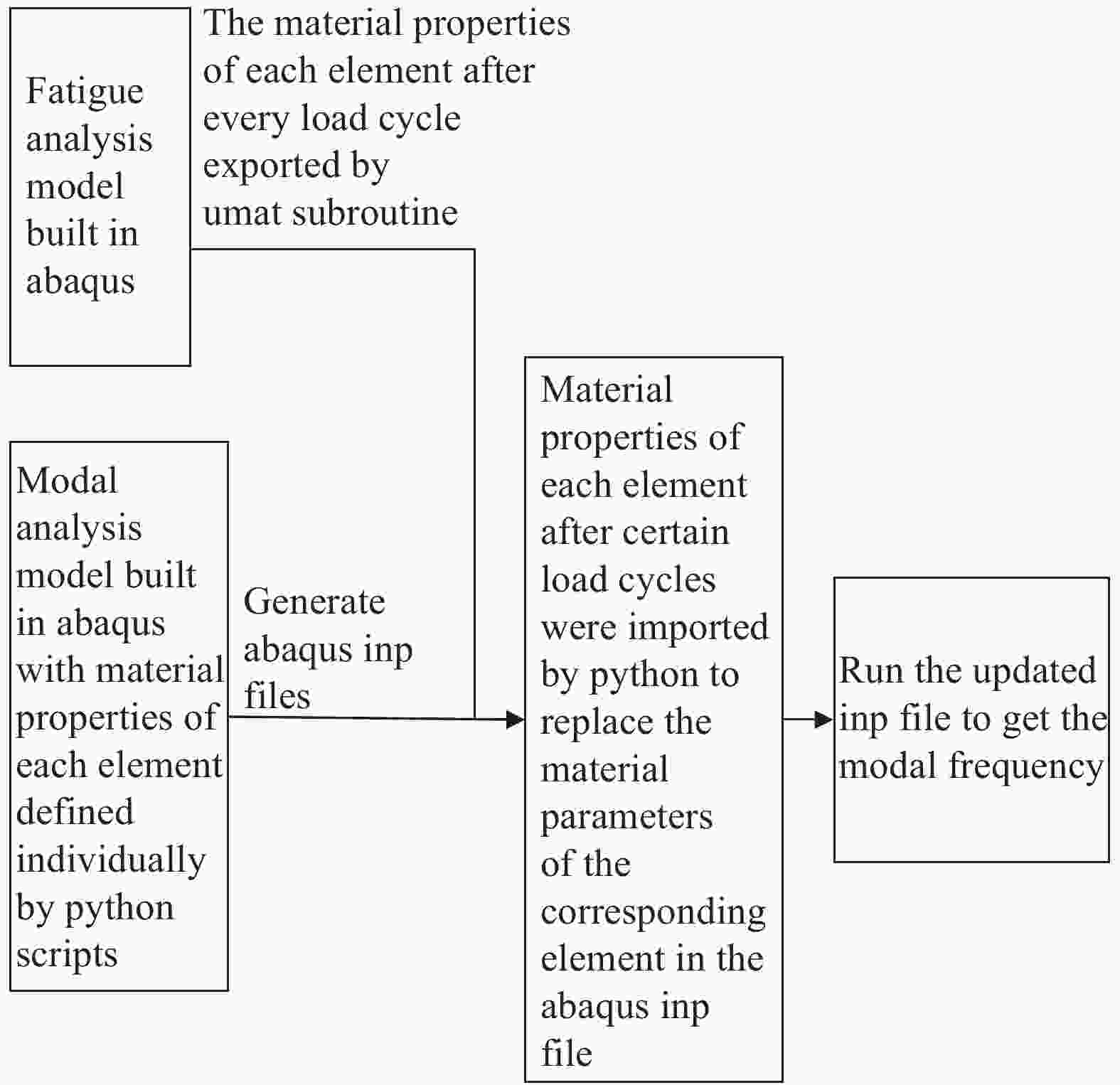
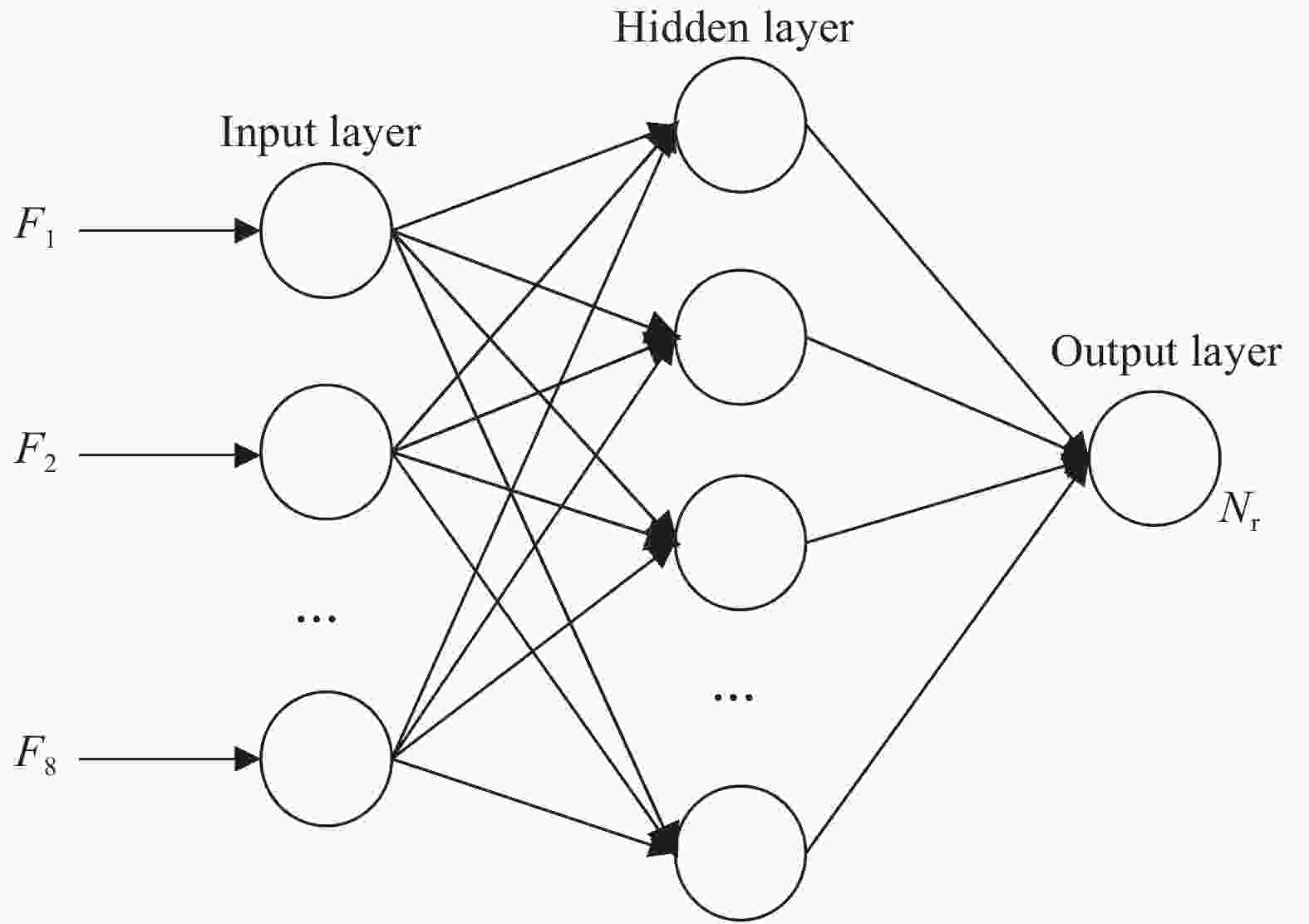
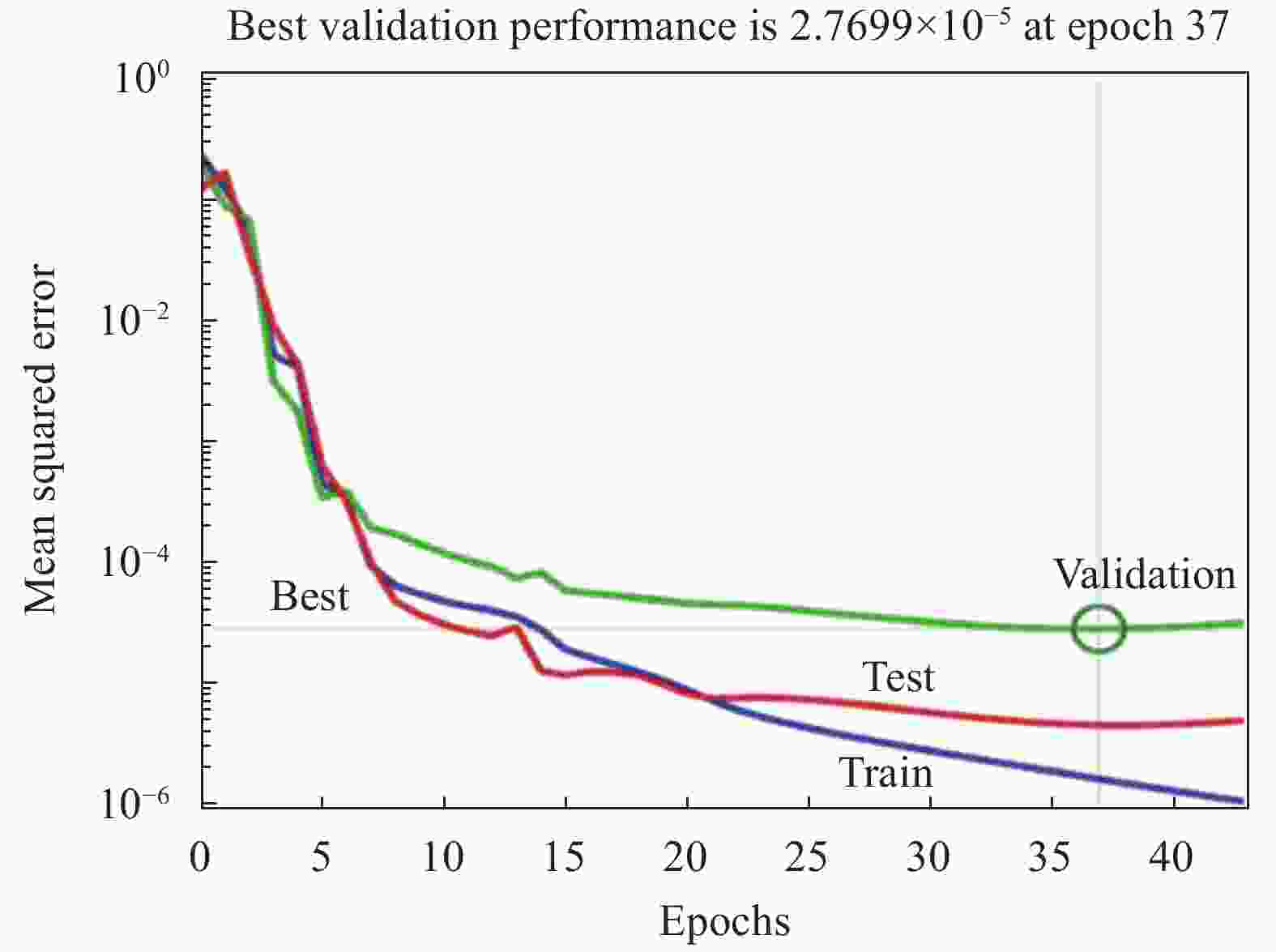
Prediction of remaining fatigue life of glass fiber reinforced polymer laminates based on frequency change
-
摘要: 复合材料结构在疲劳过程中的累积损伤将导致结构刚度下降,并进一步引起结构的动态参数如频率发生衰减。因此,可以将结构疲劳状态与结构频率联系起来,基于频率预测结构的剩余疲劳寿命。本文首先基于复合材料在纵向、横向和面内剪切三个方向的疲劳特性,结合ABAQUS与Umat子程序开发了三维有限元模型模拟复合材料层合板中的疲劳损伤演变,并构建了不同疲劳状态下对应的模态分析模型,由此获得了疲劳过程中的频率衰减曲线。之后,基于疲劳过程的频率变化量训练了人工神经网络,用于预测玻璃纤维增强复合材料层合板的剩余疲劳寿命。特别地,在当前的数值模型中为每个单元分配了符合高斯正态分布的材料属性,以模拟实际情况下复合材料性能的离散性。结果表明,疲劳模型数值模拟结果与已有文献的疲劳实验数据吻合,基于频率变化量训练的人工神经网络可以成功预测玻璃纤维增强复合材料试件的剩余疲劳寿命。Abstract: The cumulative damage in the composite structures during the fatigue process will lead to decrease in the stiffness of structures. This will further cause the changes in the dynamic parameters of the structure, such as the frequencies. Therefore, the fatigue status can be related to the frequencies of structures, and inversely, the frequencies can be used to predict the fatigue life of the structures. In this paper, by incorporating Umat subroutines in ABAQUS, a three-dimensional finite element model was developed to simulate the evolution of fatigue damage in glass fiber reinforced polymer (GFRP) laminates. The fatigue characteristics of composite materials in the longitudinal, transverse and in-plane shear directions have been considered in the model. The fatigue state of the glass fiber reinforced polymer laminates was exported from the fatigue model and then was imported into a second model to apply modal analysis for obtaining the frequencies which are corresponding to the fatigue status. An artificial neural network was trained based on the frequency data during the fatigue process, with the frequency shifts as the input and the remaining fatigue life as the output. The training data for ANN was generated from the finite element (FE) models, based on which the remaining fatigue life of the GFRP laminates was predicted. In particular, to consider the discreteness of material properties of fiber reinforced polymer (FRP) composite materials, each element in the finite element model (FEM) was individually assigned the material properties randomly distributed in the Gaussian normal distribution. The results show that the numerical simulation results of the present fatigue model are consistent with the fatigue test data in the existing literature. The trained artificial neural network can successfully predict the remaining fatigue life of the GFRP laminates.
-
Key words:
- composite materials /
- fatigue life /
- frequency shift /
- artificial neural network /
- discreteness /
- finite element model
-
表 1 材料参数突降方案
Table 1. Degradation scheme of material parameters
Failure mode Parameter degradation scheme Fiber tensile failure ${E_{11}}$, ${E_{{\rm{22}}}}$, ${G_{1{\rm{2}}}}$, ${G_{{\rm{13}}}}$, ${G_{{\rm{23}}}}$, ${\nu_{1{\rm{2}}}}$, ${\nu_{{\rm{13}}}}$, ${\nu_{{\rm{23}}}}$ reduced to 0.07 times the initial value Fiber compressive failure ${E_{11}}$, ${E_{{\rm{22}}}}$, ${G_{1{\rm{2}}}}$, ${G_{{\rm{13}}}}$, ${G_{{\rm{23}}}}$, ${\nu_{1{\rm{2}}}}$, ${\nu_{{\rm{13}}}}$, ${\nu_{{\rm{23}}}}$ reduced to 0.14 times the initial value Matrix tensile failure ${E_{{\rm{22}}}}$, ${G_{1{\rm{2}}}}$, ${G_{{\rm{23}}}}$ reduced to 0.2 times the initial value Matrix compression failure ${E_{{\rm{22}}}}$, ${G_{1{\rm{2}}}}$, ${G_{{\rm{23}}}}$ reduced to 0.4 times the initial value Fiber/matrix shear failure ${G_{1{\rm{2}}}}$. ${\nu_{1{\rm{2}}}}$ reduced to 0.2 times the initial value Delamination failure ${E_{{\rm{33}}}}$, ${G_{{\rm{13}}}}$, ${G_{{\rm{23}}}}$, ${\nu_{{\rm{13}}}}$, ${\nu_{{\rm{23}}}}$ reduced to 0.2 times the initial value Notes: E11, E22, E33—Young’s moduli; G12, G13, G23—Shear moduli; ν11, ν12, ν23—Poisson’s ratios. 表 2 GFRP层合板试件的铺层角度与静拉伸强度[7]
Table 2. Layup and static tensile strength of GFRP laminate specimens[7]
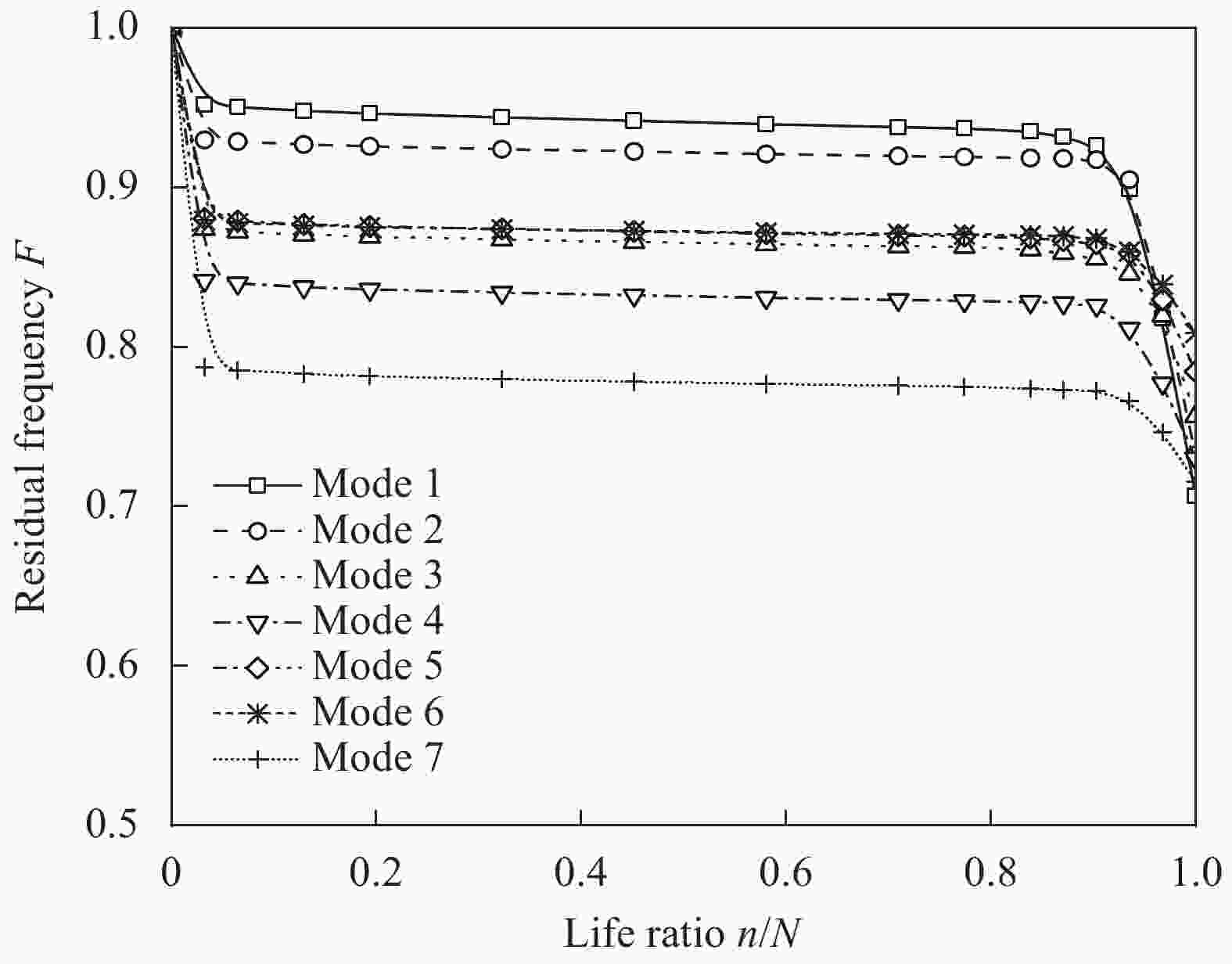
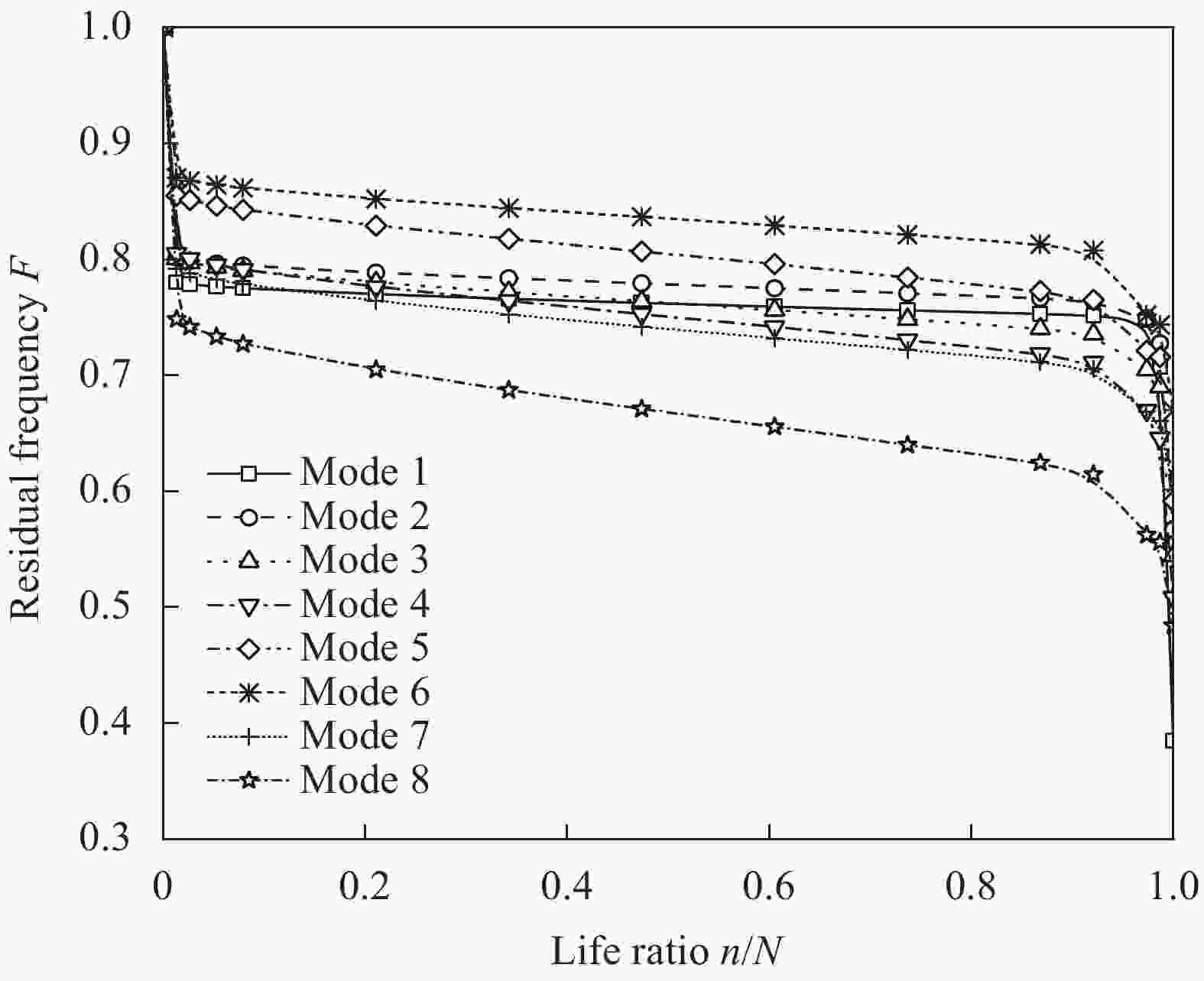
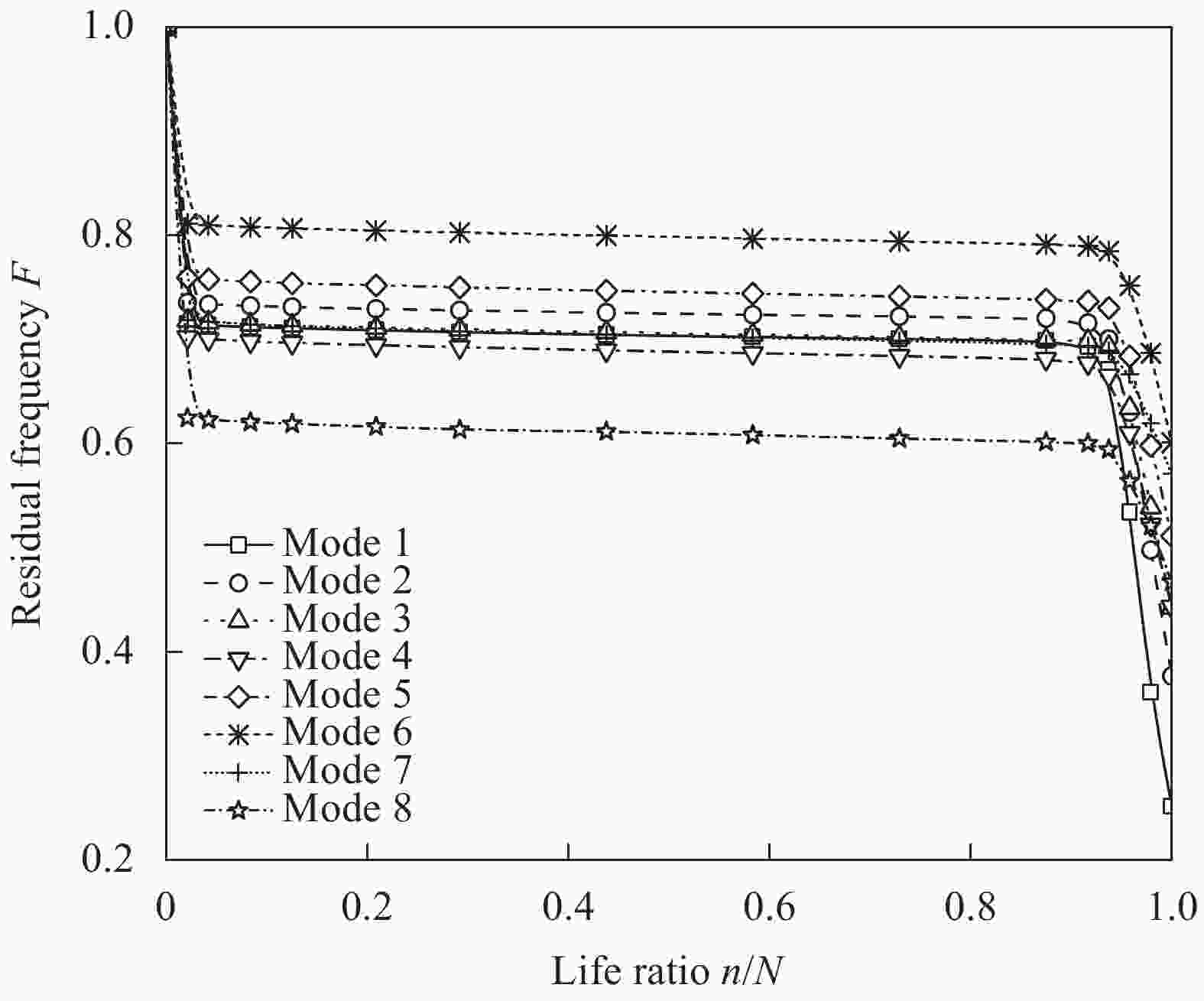
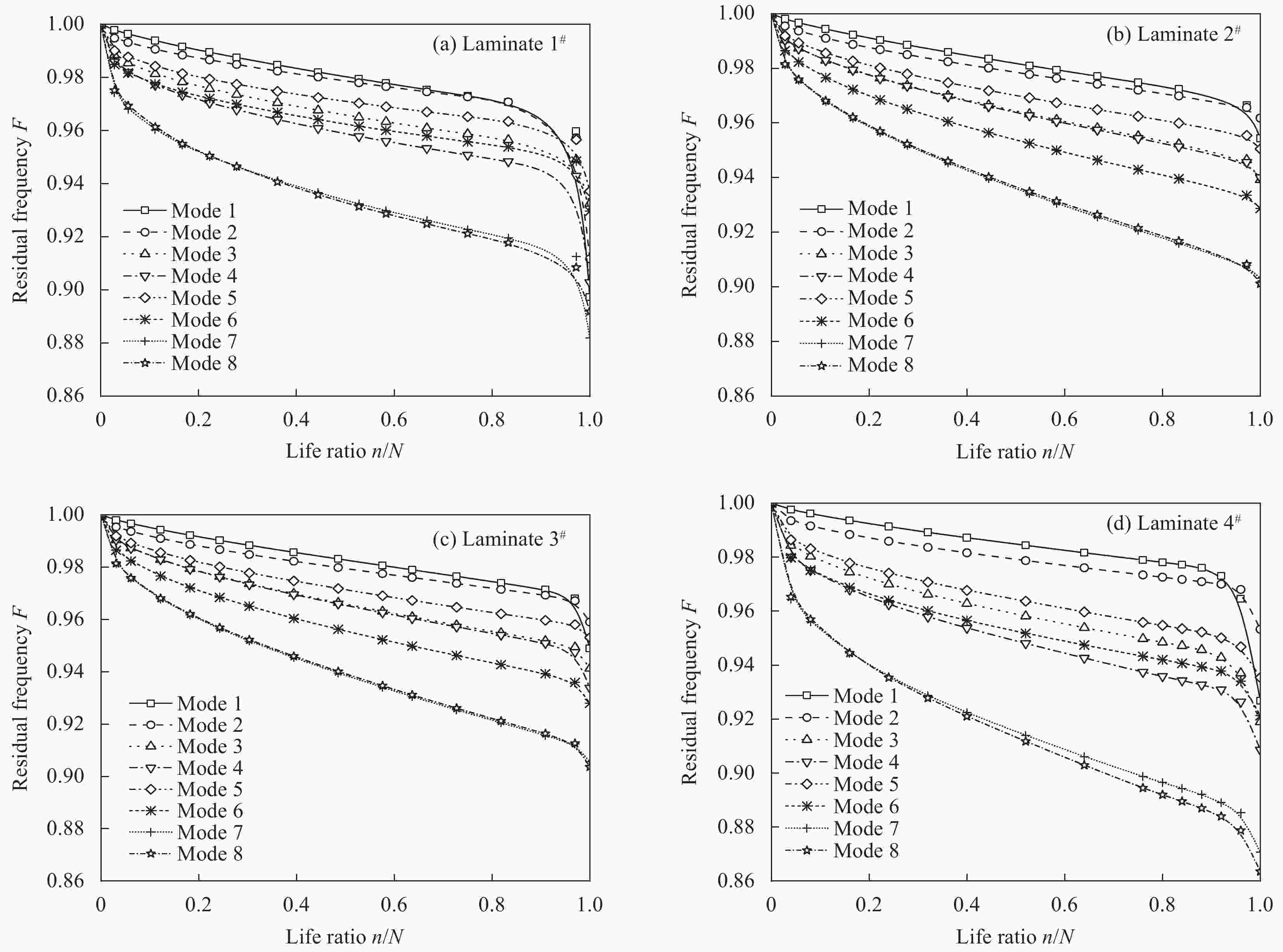
Sample No. Stacking sequence Strength/MPa A [0]8 900 B [90]8 36 C [0/90/90/0]S 470 D [45/−45/45/−45]S 118 E [45/0/0/−45]S 592 F [45/90/−45/0]S 372 表 3 GFRP层合板剩余刚度-剩余强度关联模型参数[7]
Table 3. Parameters for the correlated model of the remaining stiffness-remaining strength[7] for GFRP laminate
Parameter Magnitude Longitudinal $u$ 0.8 $v$ 60 $a$ 0.25 E11rc/E110 0.95 Transverse $w$ 1.2s2−1.85s+0.85 $u$ 0.6 $v$ 2 $a$ 80 E22rc/E220(E33rc/E330) 0.9 Shear $w$ 1.57s2−2.43s+1.12 $u$ 0.5 $v$ 0.3 $a$ 15 G12rc/G120 0.3 $w$ 10.86s2−16.2s+7.3 Note: E11rc/E110, E22rc/E220 (E33rc/E330), G12rc/G120—Ratio of critical residual stiffness to initial stiffness along longitudinal, transverse and shear direction, respectively. 表 4 不同分网下GFRP层合板的模态频率
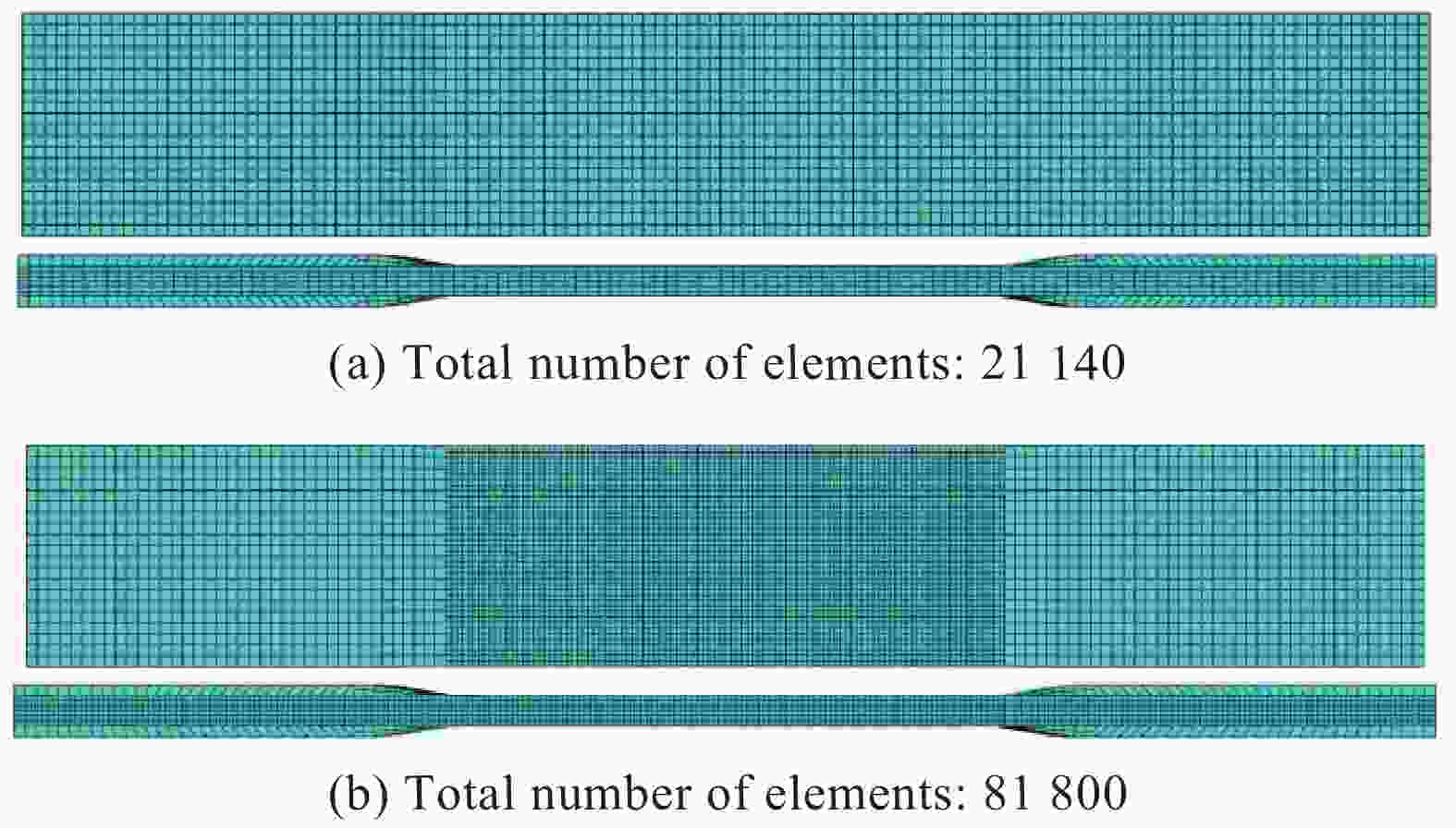
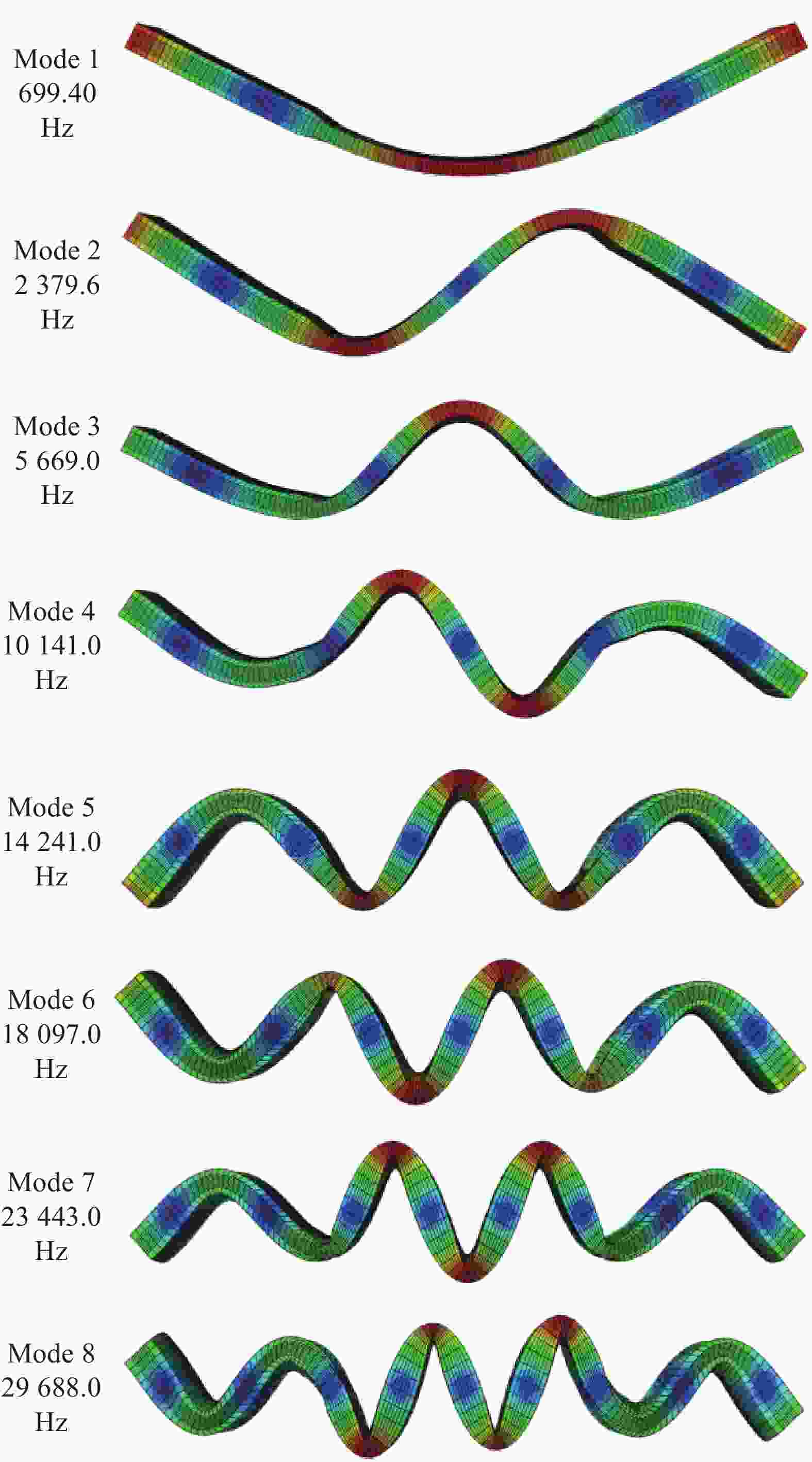
Table 4. Modal frequencies of GFRP laminate under different mesh densities
Mode No. 1# mesh density-21140 elements/Hz 2# mesh density -81800 elements/Hz Discrepancy between 1# and 2# mesh density/% 1 699.4 699.32 0.01 2 2379.6 2378.4 0.05 3 5669 5664.8 0.07 4 10141 10136 0.05 5 14241 14240 0.01 6 18097 18091 0.03 7 23443 23426 0.07 8 29688 29676 0.04 表 5 铝片的材料参数
Table 5. Material parameters of aluminum
Material Elastic
modulus/MPaPoisson's
ratioDensity/
(g·cm−3)Aluminum 70000 0.32 2.7 表 6 [0]8层合板0.6应力水平下最终寿命
Table 6. Fatigue life of [0]8 laminate under 0.6 stress level
Number 1# 2# 3# 4# Fatigue life 36000 36000 33000 25000 表 7 神经网络预测3#GFRP层合板剩余疲劳寿命结果
Table 7. Neural network prediction of the remaining fatigue life of GFRP laminate 3#
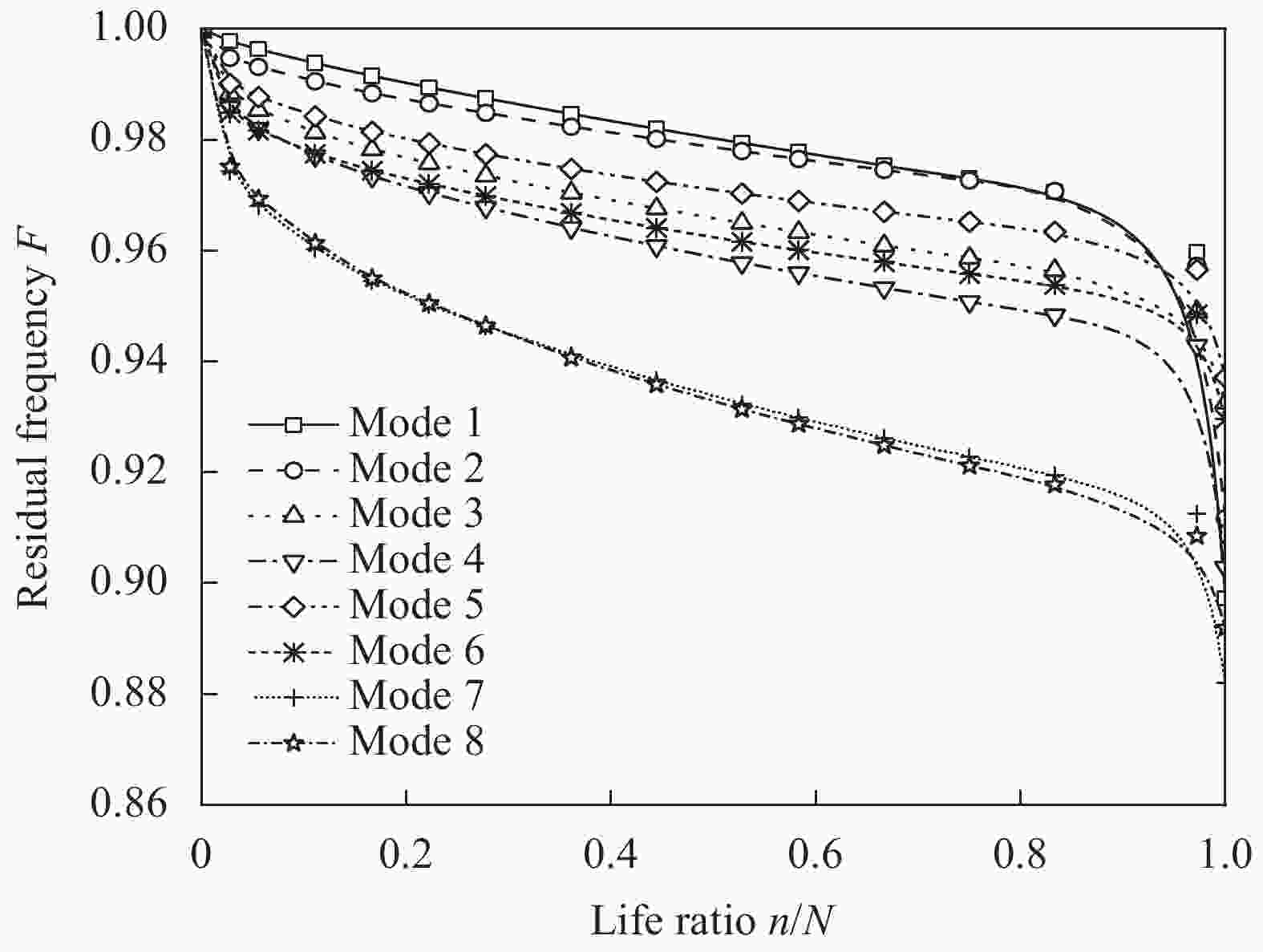
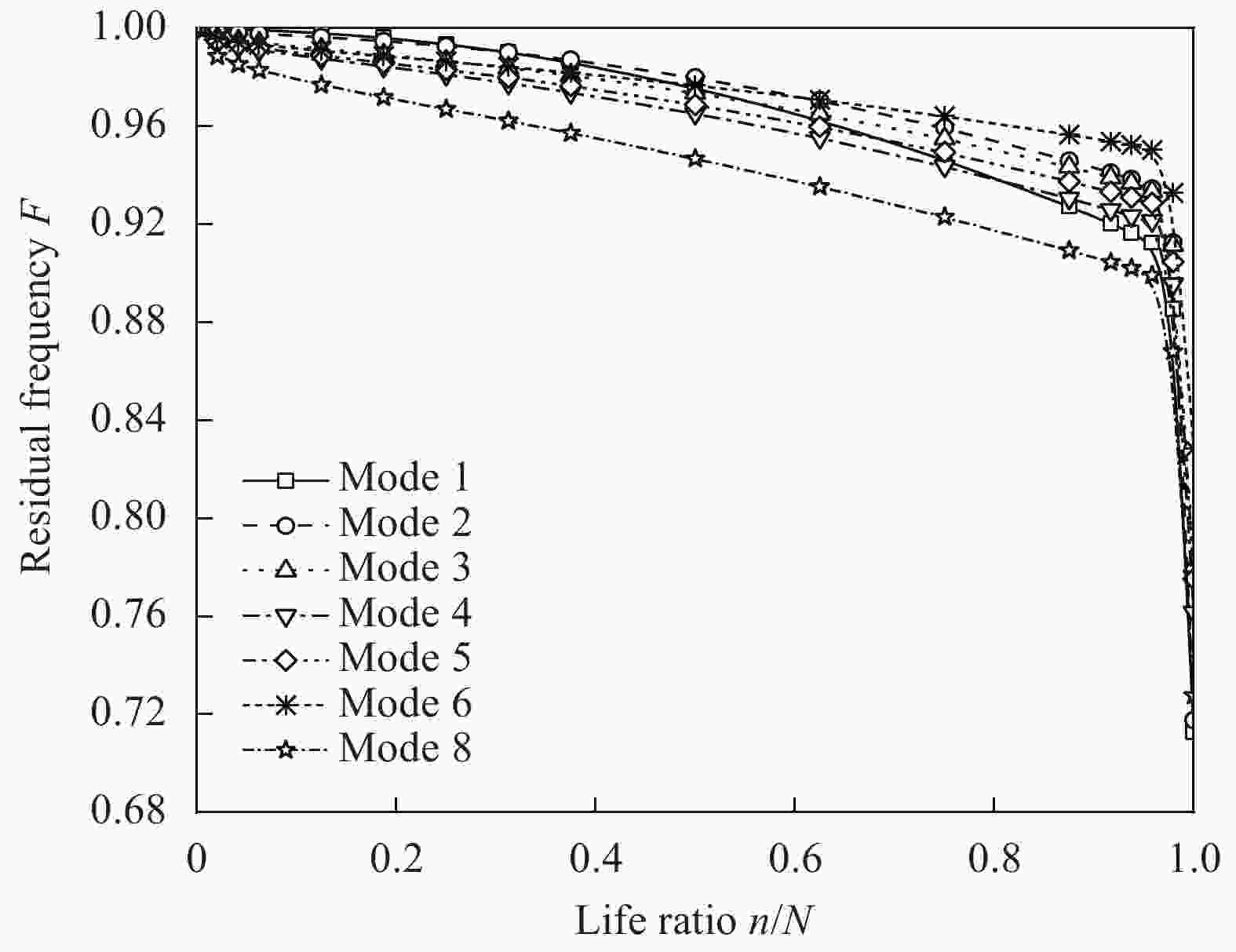
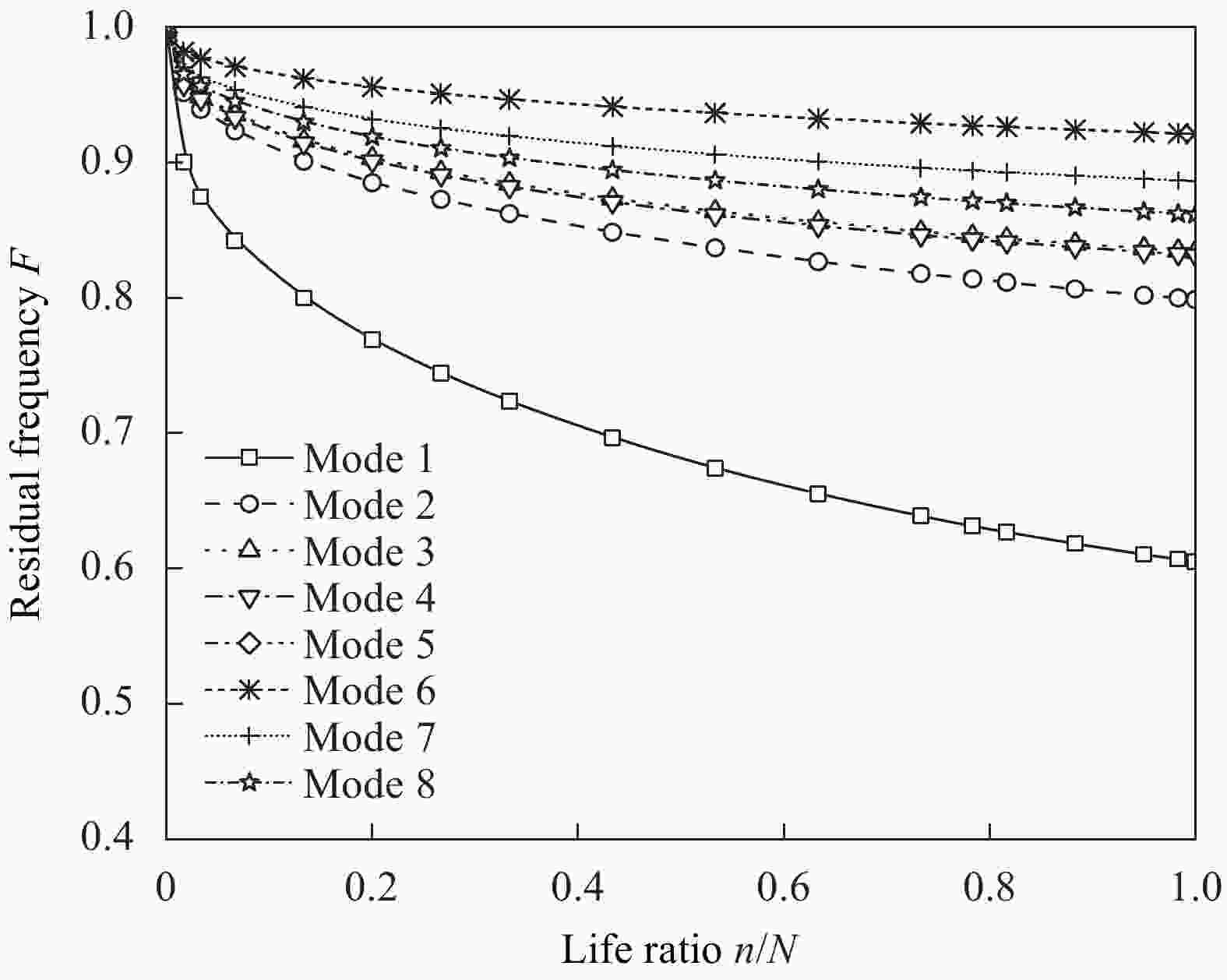
Abaqus simulation actual value Nr/% Neural network algorithm prediction ${N_{\rm{r}}}'$/% Prediction error ${N_{\rm{r}}}$−${N_{\rm{r}}}'$/% 100.00 99.88 0.12 96.97 97.16 −0.19 93.94 94.36 −0.42 87.88 88.59 −0.71 81.82 82.90 −1.08 75.76 77.02 −1.26 69.70 71.29 −1.59 60.61 62.61 −2.01 51.52 53.92 −2.41 42.42 45.05 −2.62 36.36 39.01 −2.64 27.27 30.18 −2.91 18.18 21.38 −3.20 9.09 13.29 −4.19 3.03 6.12 −3.09 0 0 0 -
[1] NADERI M, MALIGNO A R. Fatigue life prediction of carbon/epoxy laminates by stochastic numerical simulation[J]. Composite Structures,2012,94(3):1052-1059. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2011.11.013 [2] ELLYIN F, EL-KADI H. A fatigue failure criterion for fiber reinforced composite laminae[J]. Composite Structures,1990,15(1):61-74. doi: 10.1016/0263-8223(90)90081-O [3] PLUMTREE A, CHENG G X. A fatigue damage parameter for off-axis unidirectional fibre-reinforced composites[J]. International Journal of Fatigue,1999,21(8):849-856. doi: 10.1016/S0142-1123(99)00026-2 [4] SHOKRIEH M M, TAHERI-BEHROOZ F. A unified fatigue life model based on energy method[J]. Composite Structures,2006,75(1):444-450. [5] VARVANI-FARAHANI A, HAFTCHENARI H, PANBECHI M. An energy-based fatigue damage parameter for off-axis unidirectional FRP composites[J]. Composite Structures,2006,79(3):381-389. [6] SHOKRIEH M M. Progressive fatigue damage modeling of composite materials, Part Ⅰ: Modeling[J]. Journal of Composite Materials,2000,34(13):1056-1080. [7] LIAN W, YAO W. Fatigue life prediction of composite laminates by FEA simulation method[J]. International Journal of Fatigue,2010,32(1):123-133. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2009.01.015 [8] ABO-ELKHIER M, HAMADA A A, BAHEI EL-DEEN A. Prediction of fatigue life of glass fiber reinforced polyester composites using modal testing[J]. International Journal of Fatigue,2014,69:28-35. doi: 10.1016/j.ijfatigue.2012.10.002 [9] 李丹卉. 拉-拉循环载荷下复合材料固有频率疲劳衰减规律研究[D]. 南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2019.LI D H. Research on natural frequency fatigue attenuation law of composite material under tension-tension cyclic load[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2019(in Chinese). [10] 卢翔, 李顶河, 冯振宇, 等. 复合材料层合板刚度降理论模型研究[J]. 中国民航大学学报, 2008(2):21-24. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5590.2008.02.007LU X, LI D H, FENG Z Y, et al. Research on theoretical model of stiffness reduction of composite laminated plates[J]. Journal of Civil Aviation University of China,2008(2):21-24(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-5590.2008.02.007 [11] HAHN H T. On the behavior of composite laminates after initial failures[J]. Journal of Composite Materials,1974,8(3):288-305. [12] 王德, 金平, 刘鹏, 等. 基于刚度退化的复合材料层合板疲劳损伤模型的研究进展[J]. 材料导报, 2012, 26(23):120-123. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-023X.2012.23.026WANG D, JIN P, LIU P, et al. Research progress on fatigue damage model of composite laminates based on stiffness degradation[J]. Materials Reports,2012,26(23):120-123(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-023X.2012.23.026 [13] 姚卫星, 宗俊达, 廉伟. 监测复合材料结构剩余疲劳寿命的剩余刚度方法[J]. 南京航空航天大学学报, 2012, 44(5):677-682. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-2615.2012.05.012YAO W X, ZONG J D, LIAN W, et al. Residual stiffness method for monitoring remaining fatigue life of composite structure[J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics,2012,44(5):677-682(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-2615.2012.05.012 [14] 郭霞, 迟海, 贺俊智, 等. 纤维增强复合材料胶接结构疲劳特性试验研究[J]. 实验力学, 2019, 34(6):1077-1084.GUO X, CHI H, HE J Z, et al. Experimental research on fatigue characteristics of fiber reinforced composite material bonded structure[J]. Journal of Experimental Mechanics,2019,34(6):1077-1084(in Chinese). [15] MOON T, KIM H, HWANG W. Natural-frequency reduction model for matrix-dominated fatigue damage of composite laminates[J]. Composite Structures,2003,62(1):19-26. doi: 10.1016/S0263-8223(03)00080-1 [16] 刘英芝. 复合材料层合板疲劳行为研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2015.LIU Y Z. Research on fatigue behavior of composite laminate[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2015(in Chinese). [17] 王乐. 复合材料单向板刚度退化及数值仿真分析研究[D]. 南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2016.WANG L. Research and numerical simulation on composite unidirectional laminates stiffness reduction[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2016(in Chinese). [18] LIU K, TSAI S W. A progressive quadratic failure criterion for a laminate[J]. Composites Science and Technology,1998,58(7):1023-1032. doi: 10.1016/S0266-3538(96)00141-8 [19] HASHIN Z. A fatigue failure criterion for fiber reinforced materials[J]. Journal of Composite Materials,1973,7(4):448-464. [20] SIMS D, BROGDON V. Fatigue behaviour of composites under different loading modes. Fatigue of filamentary materials[J]. Fatigue Behavior of Composites under Different Loading Modes,1977,636:185-205. [21] FRANCIS P H. Biaxial fatigue loading of notched composites[J]. Journal of Composite Materials,1977,11(4):488-501. [22] PHILIPPIDIS T P, VASSILOPOULOS A P. Complex stress state effect on fatigue life of GFRP laminates[J]. International Journal of Fatigue,2002,24(8):825-830. [23] SHOKRIEH M M. Progressive fatigue damage modeling of composite materials, Part II: Material characterization and model verification[J]. Journal of Composite Materials,2000,34(13):1081-1161. [24] TSERPES K I, PAPANIKOS P, LABEAS G, et al. Fatigue damage accumulation and residual strength assessment of CFRP laminates[J]. Composite Structures,2004,63(2):219-230. [25] CHANG F, CHANG K. A progressive damage model for laminated composites containing stress concentrations[J]. Journal of Composite Materials,1987,21(9):834-855. doi: 10.1177/002199838702100904 [26] 廉伟, 姚卫星. 复合材料层压板剩余刚度-剩余强度关联模型[J]. 复合材料学报, 2008(5):151-156. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3851.2008.05.025LIAN W, YAO W X. Residual stiffness-residual strength correlation model of composite laminates[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2008(5):151-156(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3851.2008.05.025 [27] CAMANHO P P, MATTHEWS F L. A progressive damage model for mechanically fastened joints in composite laminates[J]. Journal of Composite Materials,1999,33(24):2248-2280. doi: 10.1177/002199839903302402 [28] 华宏星, 陈小琳, 石银明. 运用神经网络识别复合材料板刚度[J]. 复合材料学报, 2000, 17(1):108-110. doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3851.2000.01.024HUA H X, CHEN X L, SHI Y M. Composite plate stiffness identification using neural networks[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2000,17(1):108-110(in Chinese). doi: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-3851.2000.01.024 [29] TALREJA R R. Fatigue of composite materials[M]. Boca Raton: CRC Press, 1987. [30] HECHT-NIELSEN R. Theory of the backpropagation neural network[C]. International Joint Conference on Neural Networks. New York: IEEE Press, 2002: 593-605. [31] 薛掌安, 邓海亮. BP神经网络在复合材料研究中的应用[J]. 材料导报, 2009, 23(S1):250-253.XUE Z A, DENG H L. Application of BP neural network in composite materials research[J]. Materials Reports,2009,23(S1):250-253(in Chinese). -





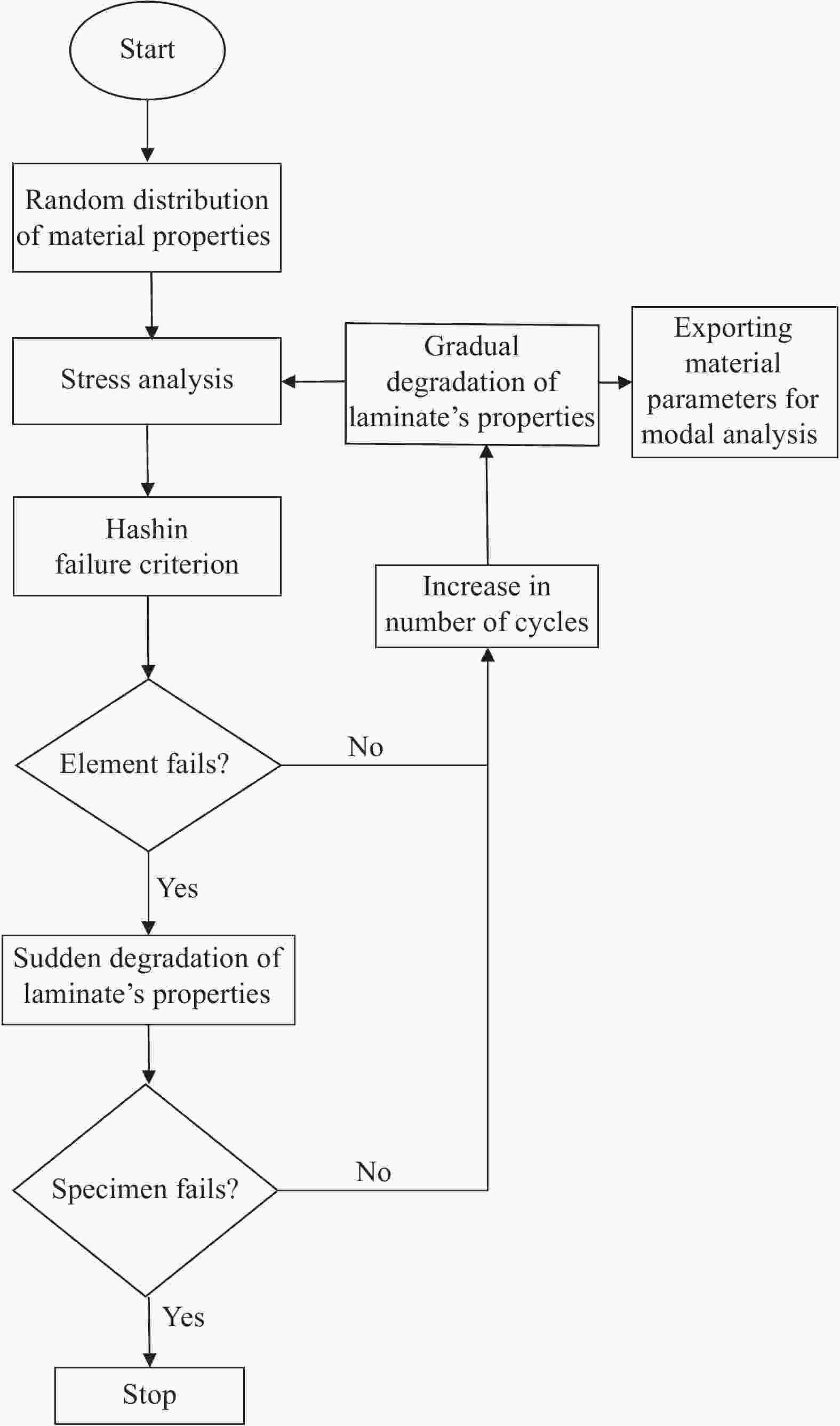
 下载:
下载: