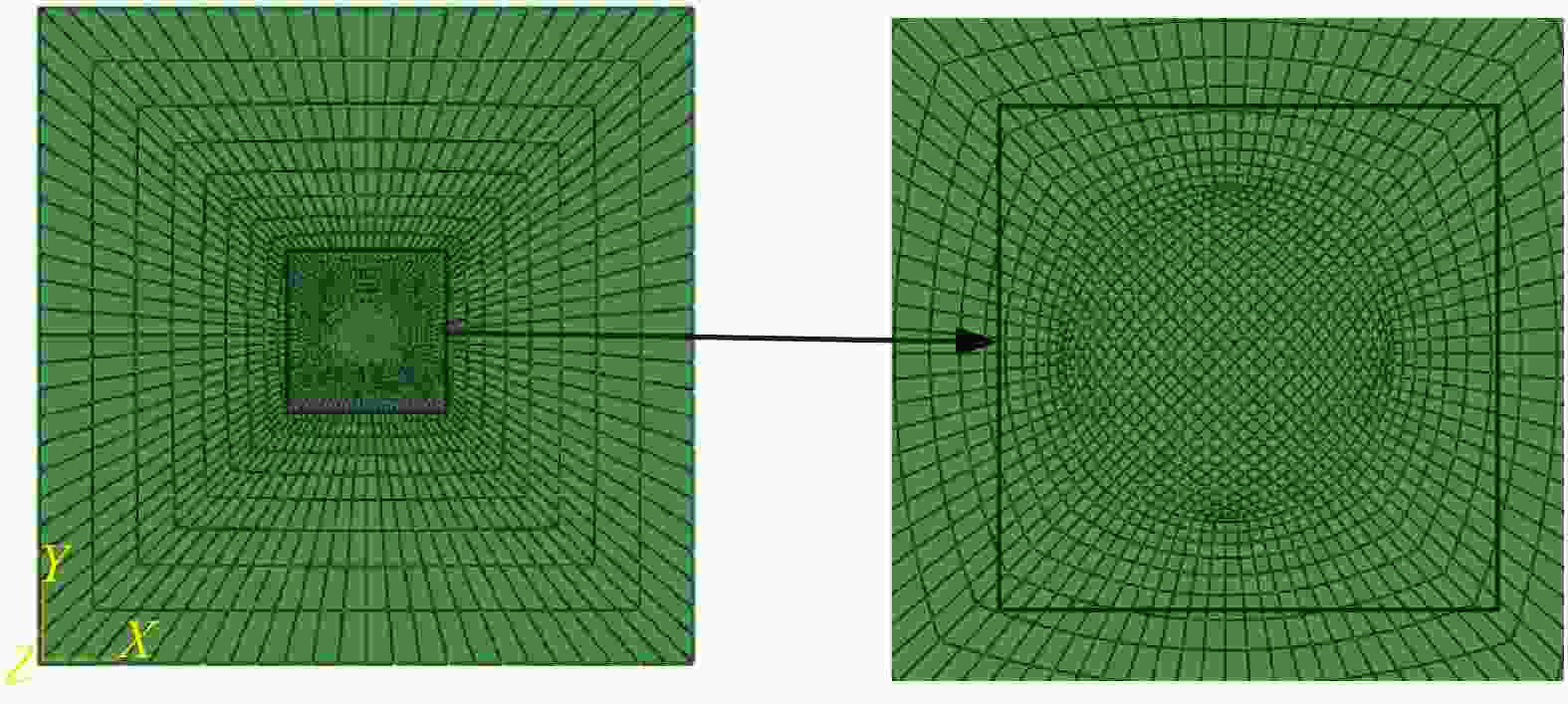
Numerical simulation of spherical fragment penetrating UHMWPE soft body armor based on ABAQUS
-
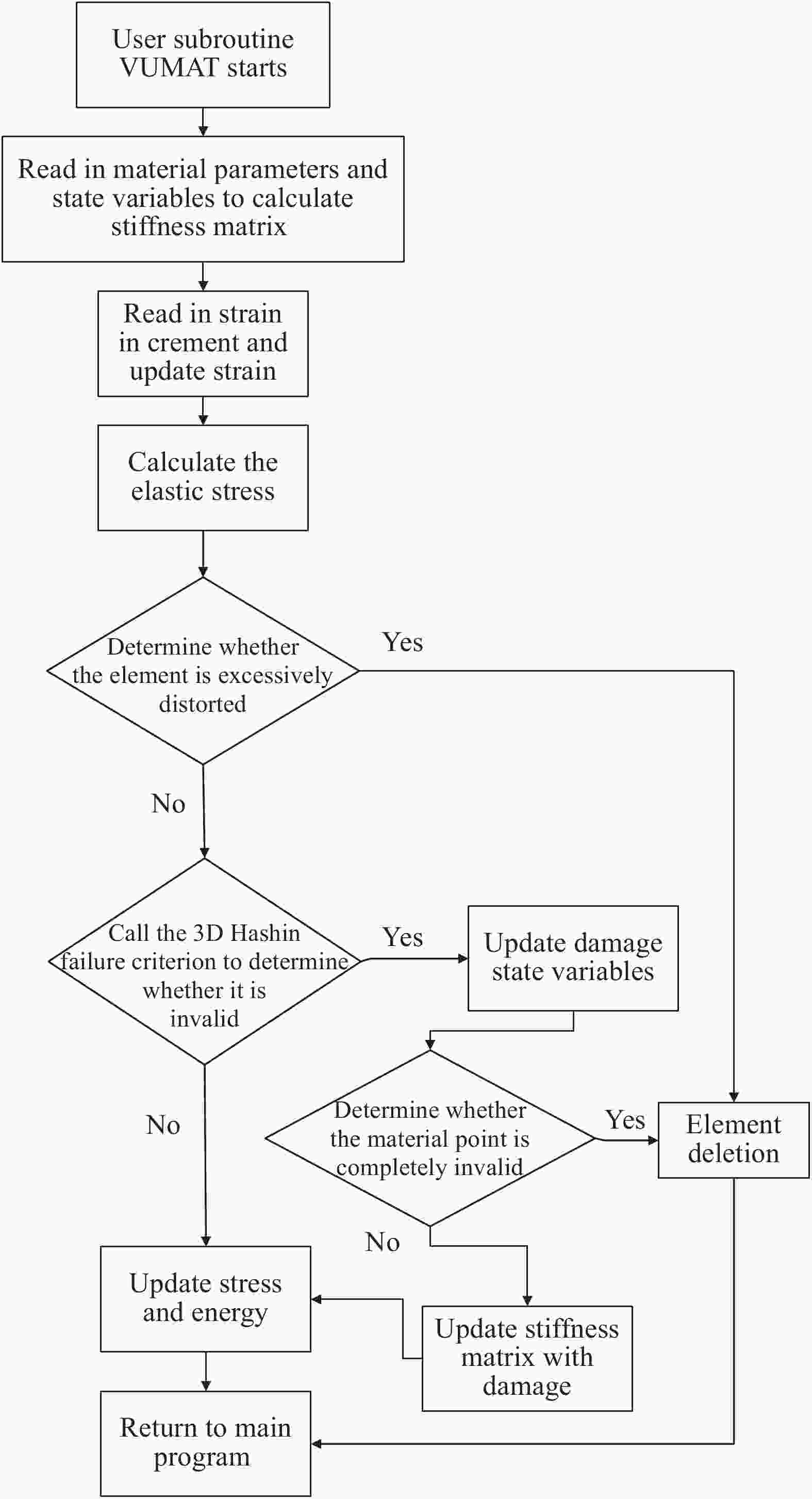
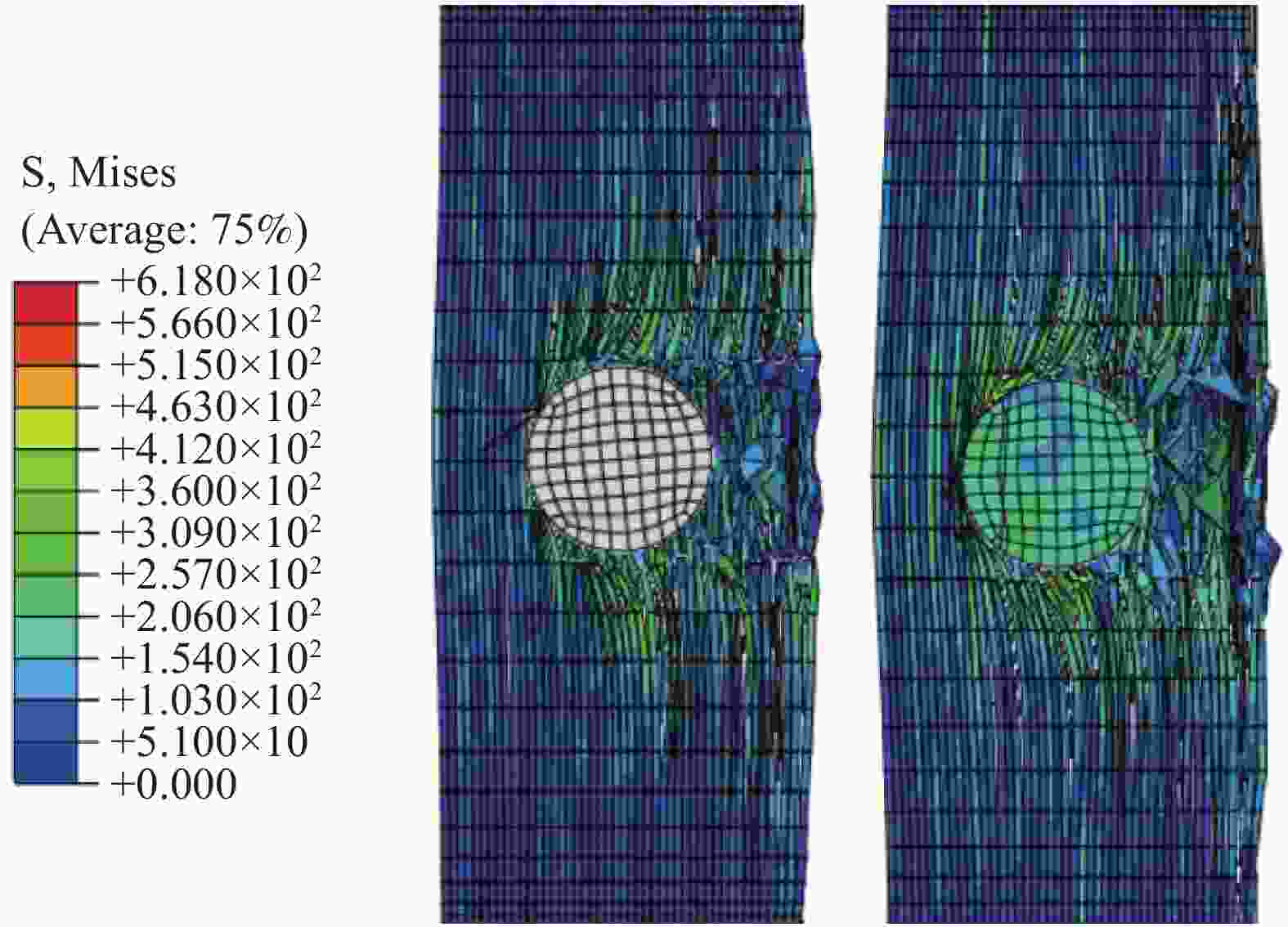
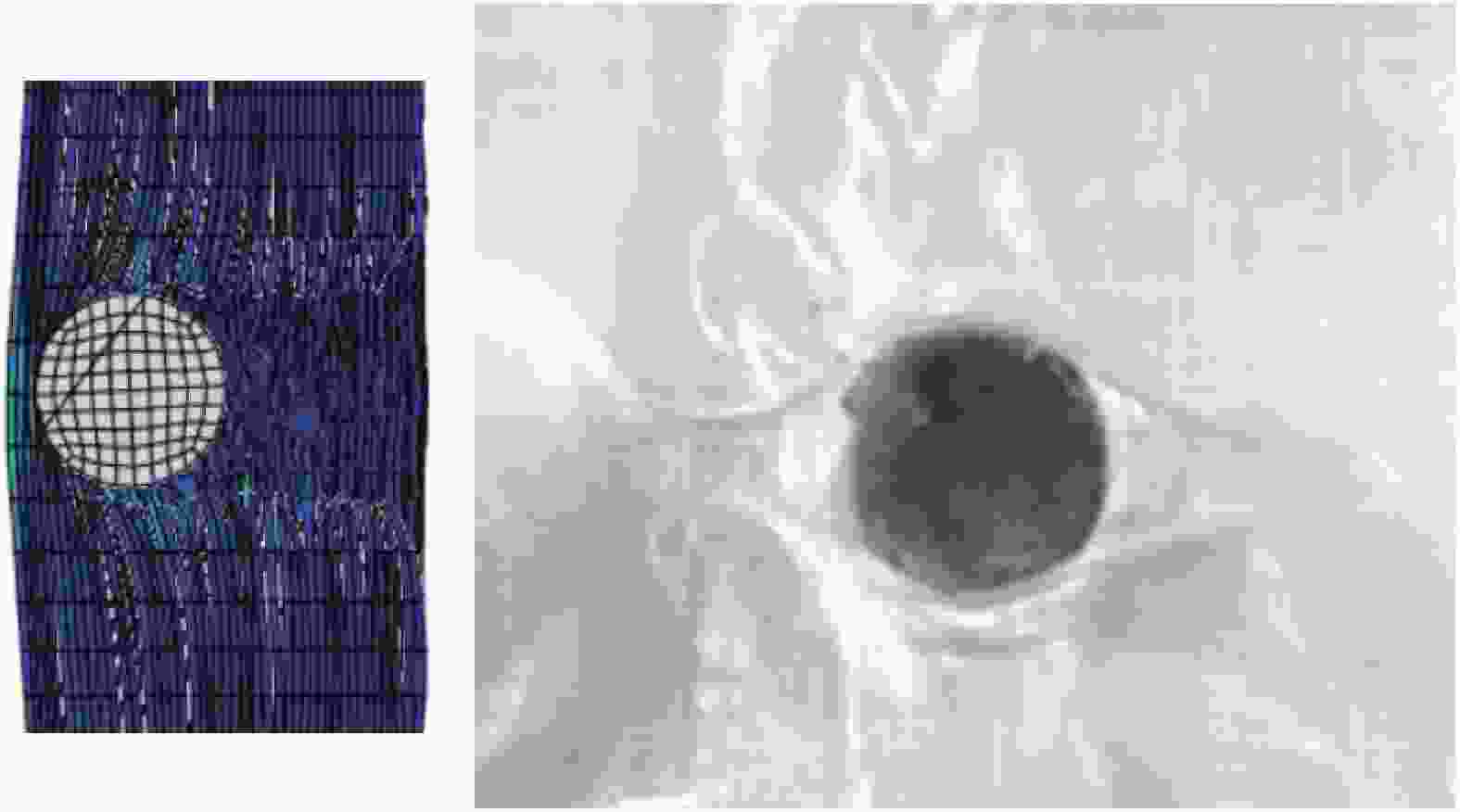
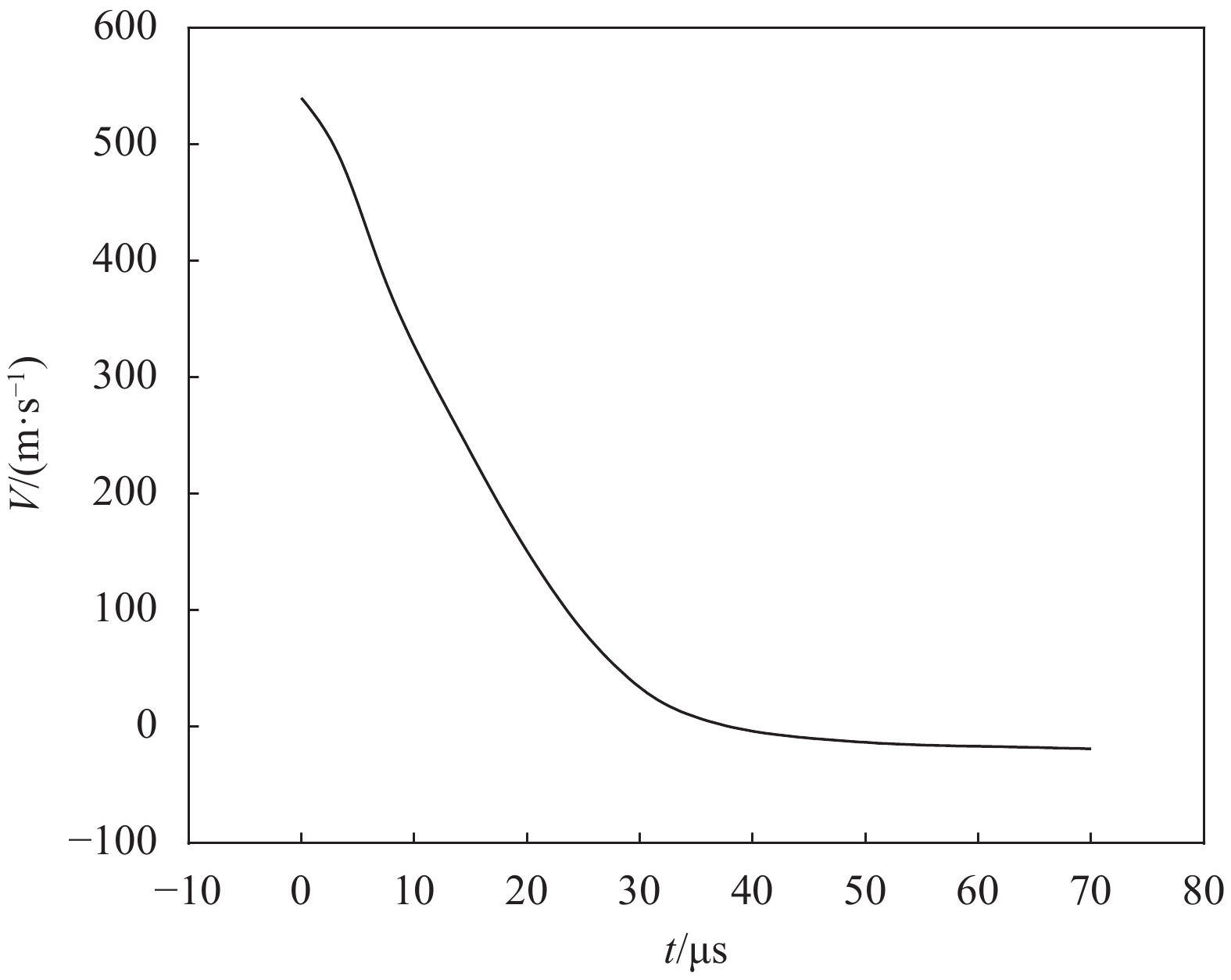
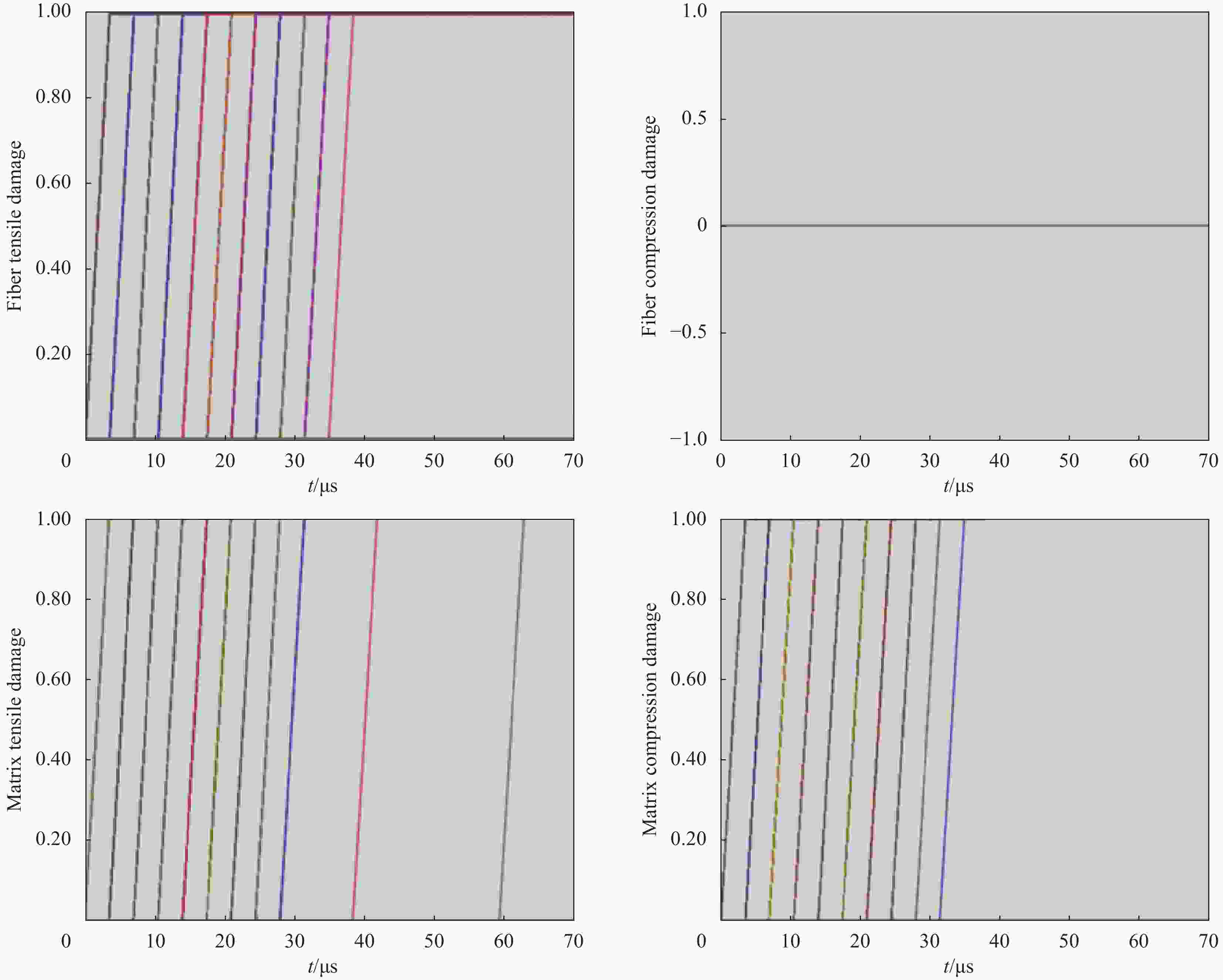
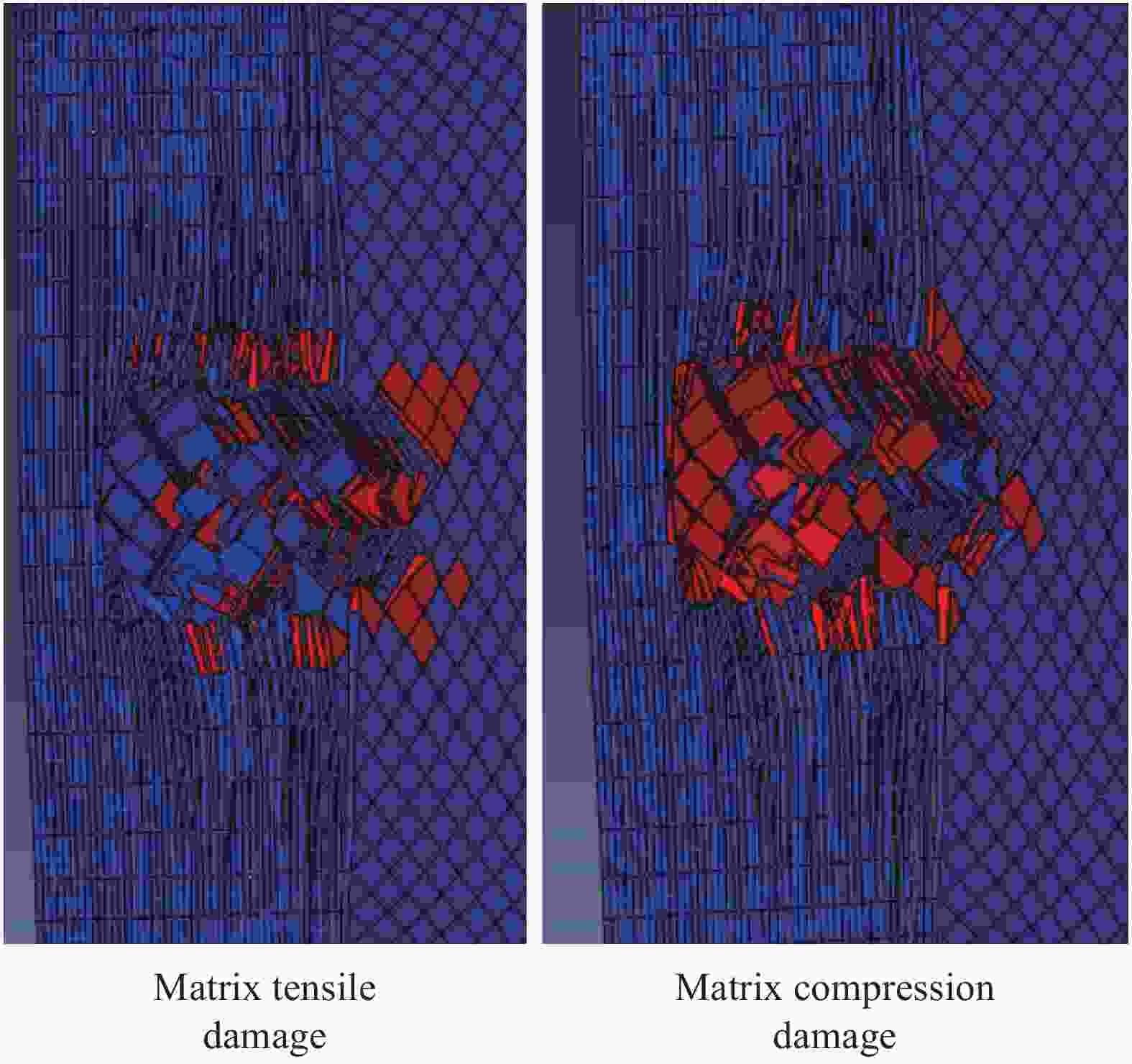
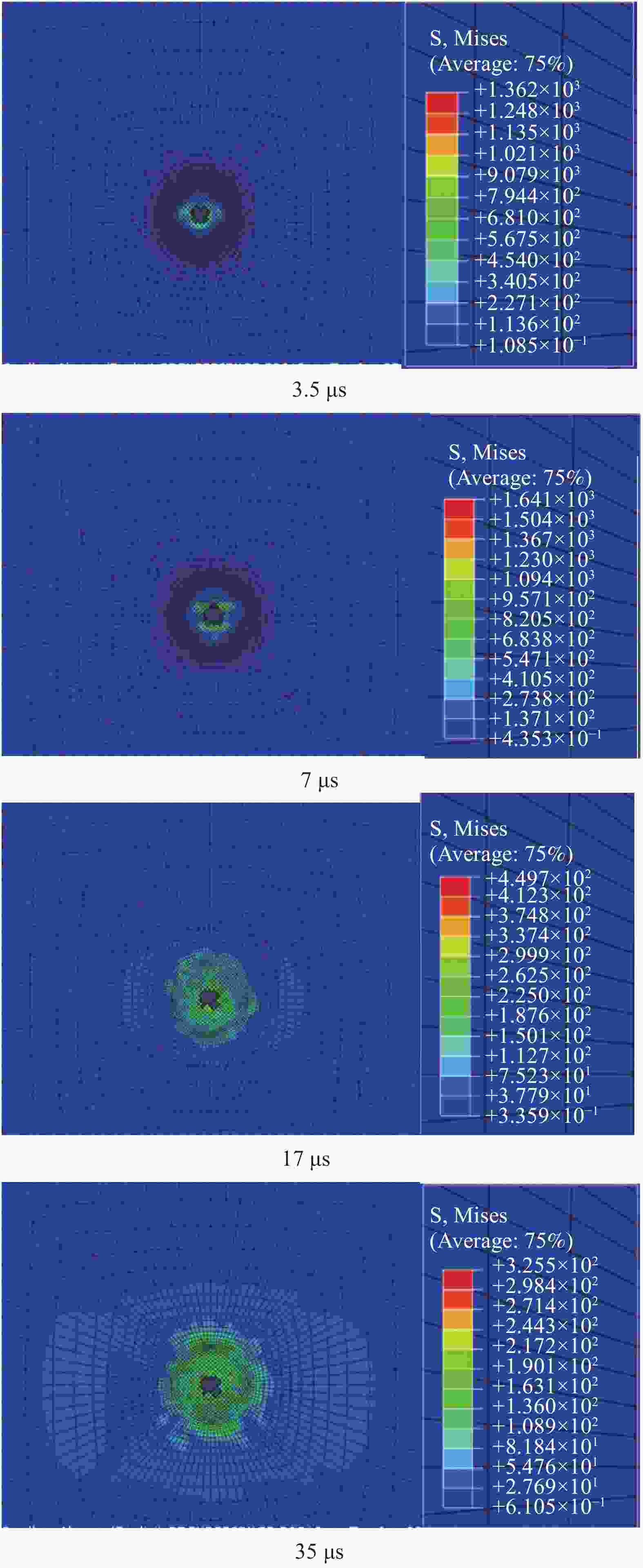
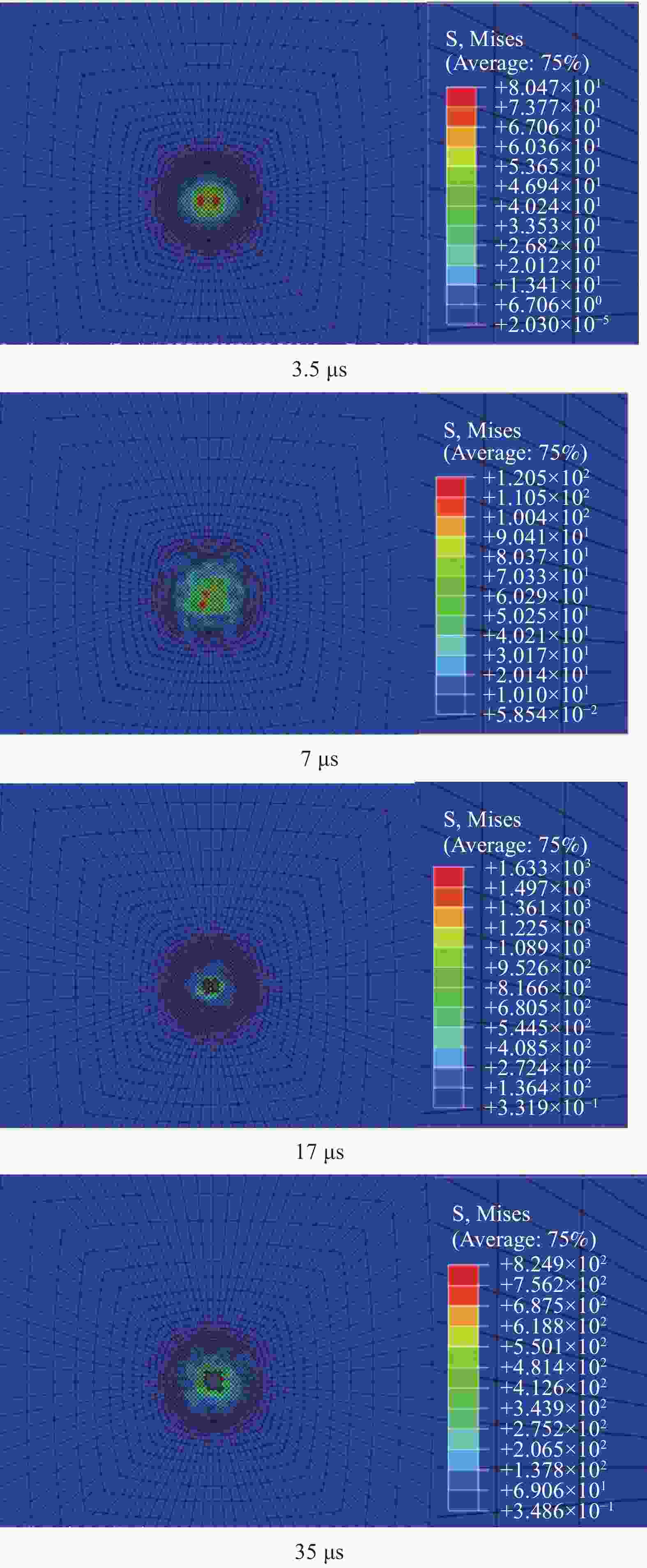
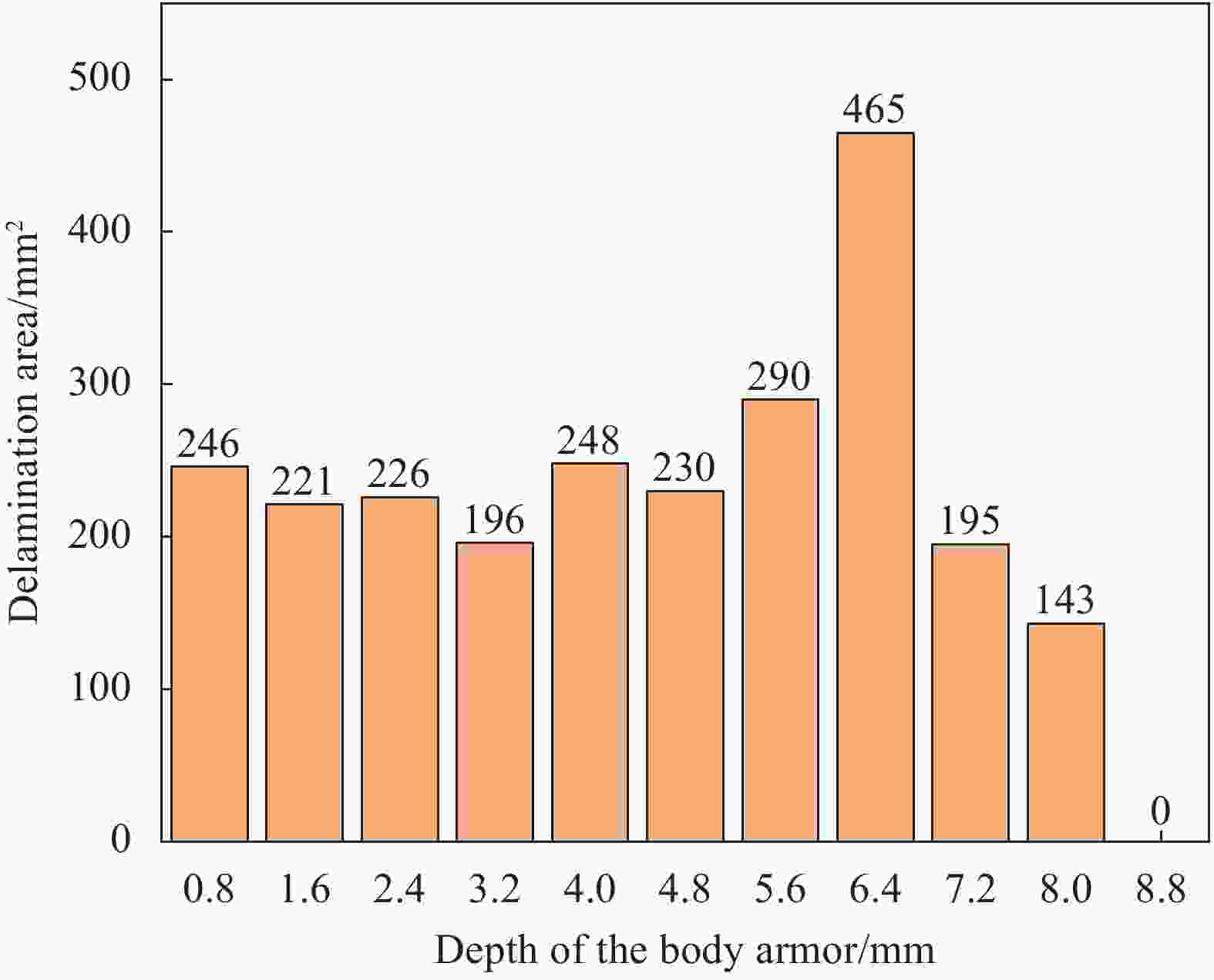
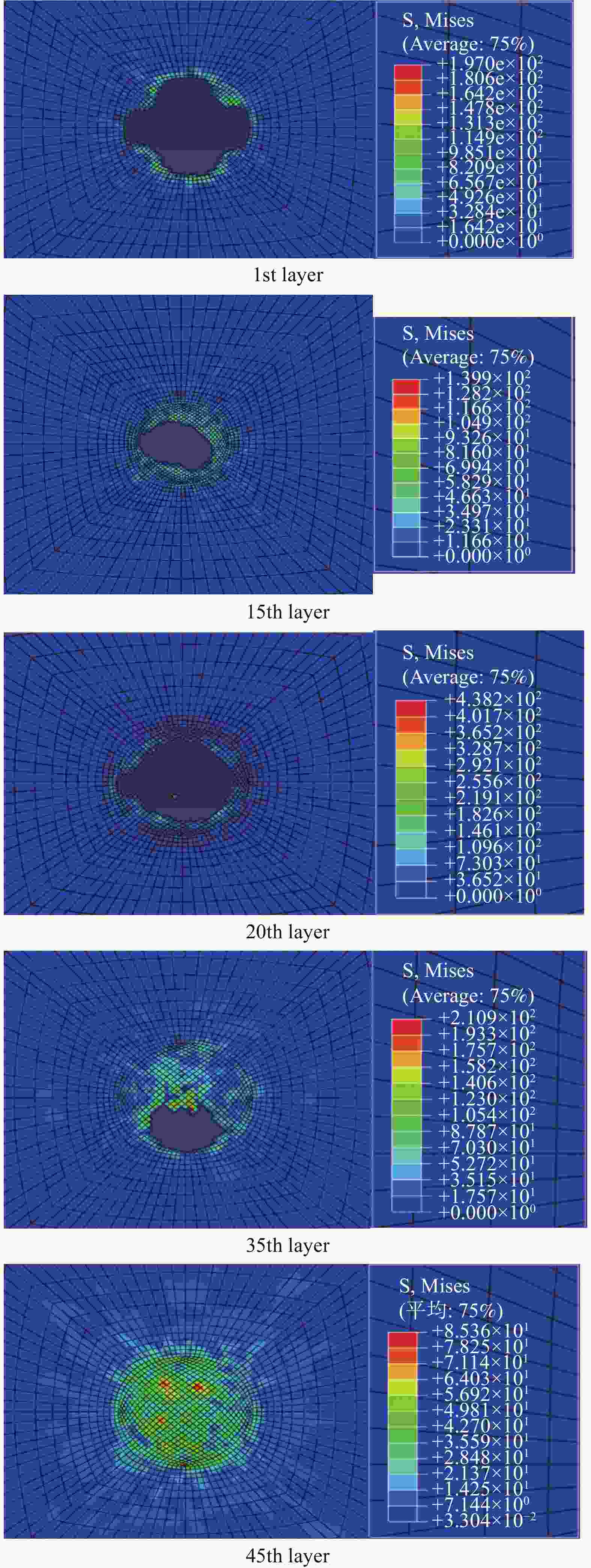
摘要: 为准确模拟破片侵彻防弹衣的过程,揭示破片与软质防弹衣相互作用机制,本文基于ABAQUS用户子程序VUMAT编写了适用于模拟软质防弹衣材料力学性能的本构模型,建立了球形破片侵彻软质防弹衣的有限元模型,数值模拟结果与实验吻合较好。本构模型中材料失效模式数据表明,无纬布主要发生纤维拉伸、基体拉伸和压缩失效;在钢球侵彻防弹衣的初期,无纬布上的应力云图一般呈现较规则的圆形或椭圆形,然后再慢慢向四周扩散;钢球侵彻软质防弹衣的过程中伴随有较明显的纤维层间分层失效,未穿透的纤维层中也出现了分层的现象,分层面积从迎弹面到背弹面先减小后增大再减小。
-
关键词:
- 超高分子量聚乙烯(UHMWPE) /
- 球形破片 /
- VUMAT /
- 侵彻 /
- 防弹衣
Abstract: To accurately simulate the process of fragment penetrating bulletproof vests and reveal the interaction mechanism, a constitutive model suitable for simulating the mechanical properties of soft bulletproof vests was developed based on the user subroutine VUMAT of ABAQUS, and the finite element model of spherical fragment penetrating soft bulletproof vest was established. The numerical simulation results are in good agreement with the experimental results. The material failure mode data in the constitutive model show that the unidirectional fiber cloth mainly fails in fiber tension, matrix tension and compression. In the initial stage of steel sphere penetrating bullet proof vest, the stress contours on the unidirectional fiber cloth generally present a regular circle or ellipse, and then slowly diffuse around. In the penetrating process, there is obvious fiber delamination failure. Moreover, the delamination phenomenon also appears in the fiber layer which is not pierced. The delamination area decreases first, then increases, and then decreases from the attack surface to the back surface. -
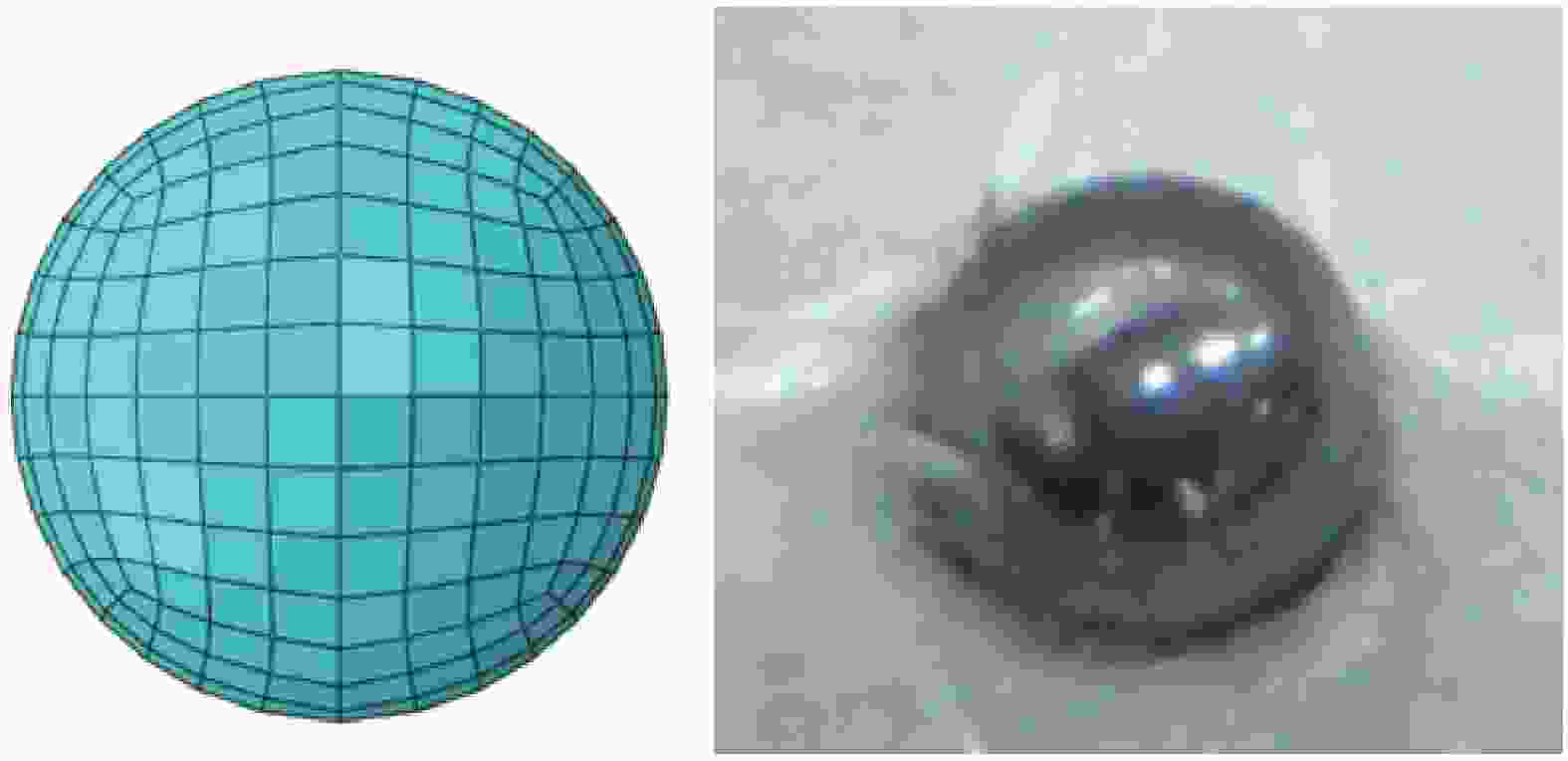
表 1 钢球材料参数
Table 1. Material parameters of steel sphere
Material ρ/(g·cm−3) E/GPa ν Steel 7.83 211 0.27 Notes: ρ—Density; E—Elastic modulus; ν—Poisson's ratio. 表 2 UHMWPE软质防弹衣材料参数[6]
Table 2. Material parameters of UHMWPE soft bulletproof vest
Model parameter ρ/(g·cm−3) ${E_1}$/GPa ${E_2}$/GPa ${E_3}$/GPa ${v_{12}}$ ${v_{13}}$ ${v_{23}}$ 0.97 80 30 20 0.18 0.18 0.11 Model parameter ${G_{12}}$/GPa ${G_{23}}$/GPa ${G_{13}}$/GPa XC/MPa XT/MPa YC/MPa YT/MPa 20 10 20 4500 4500 700 700 Model parameter ZC/MPa ZT/MPa S12/MPa S23/MPa S13/MPa 700 700 400 400 400 Notes: ${E_1}$, ${E_2}$, ${E_3}$—Elastic modulus in x, y, and z directions, respectively; ${v_{12}}$, ${v_{13}}$, ${v_{23}}$—Poisson's ratios; ${G_{12}}$, ${G_{23}}$, ${G_{13}}$—Shear modulus; XC, XT, YC, YT, ZC, ZT—Compressive and tensile strengths in x, y, z directions; S12, S23, S13—Shear strengths. 表 3 内聚力单元材料参数[29]
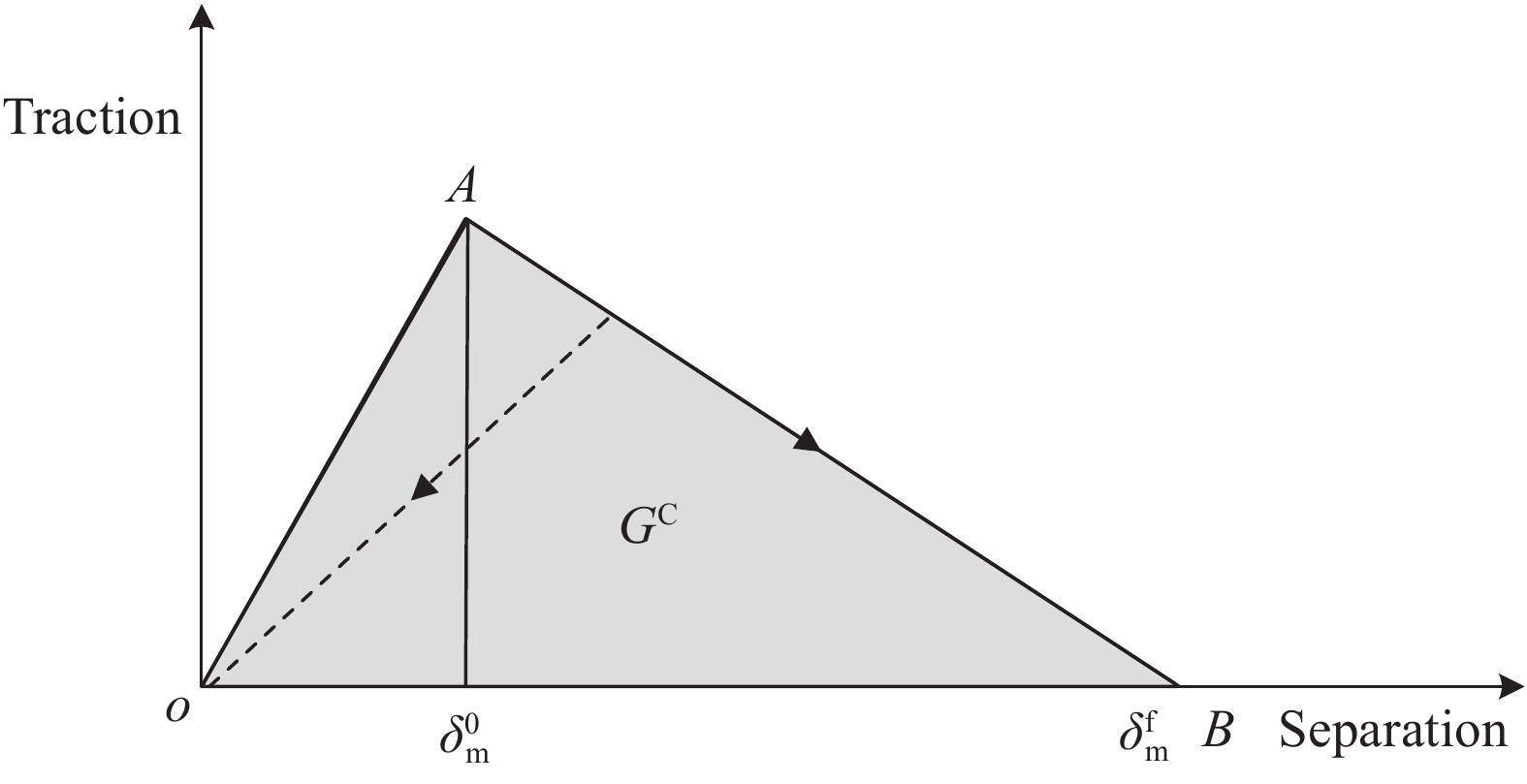
Table 3. Material parameters of cohesive element
Model parameter ρ/(g·cm−3) En/MPa Gs/MPa σn/MPa σs/MPa GⅠ C/(J·m−2) GⅡ C/(J·m−2) GⅢ C/(J·m−2) 2 9700 6500 55 120 280 495 495 Notes:En—Elastic modulus; Gs—Shear modulus; σn, σs—Normal and tangential strengths; GⅠ C, GⅡ C, GⅢ C—Critical energy release rates in mode I, mode II and mode III. 表 4 实验和数值仿真中UHMWPE软防护破坏层数对比(钢球着靶速度区间为617~650 m/s)
Table 4. Comparison of the computed and the experimentally observed number of UHMWPE soft bulletproof vest failure layers(Impact velocity of steel sphere is 617-650 m/s)
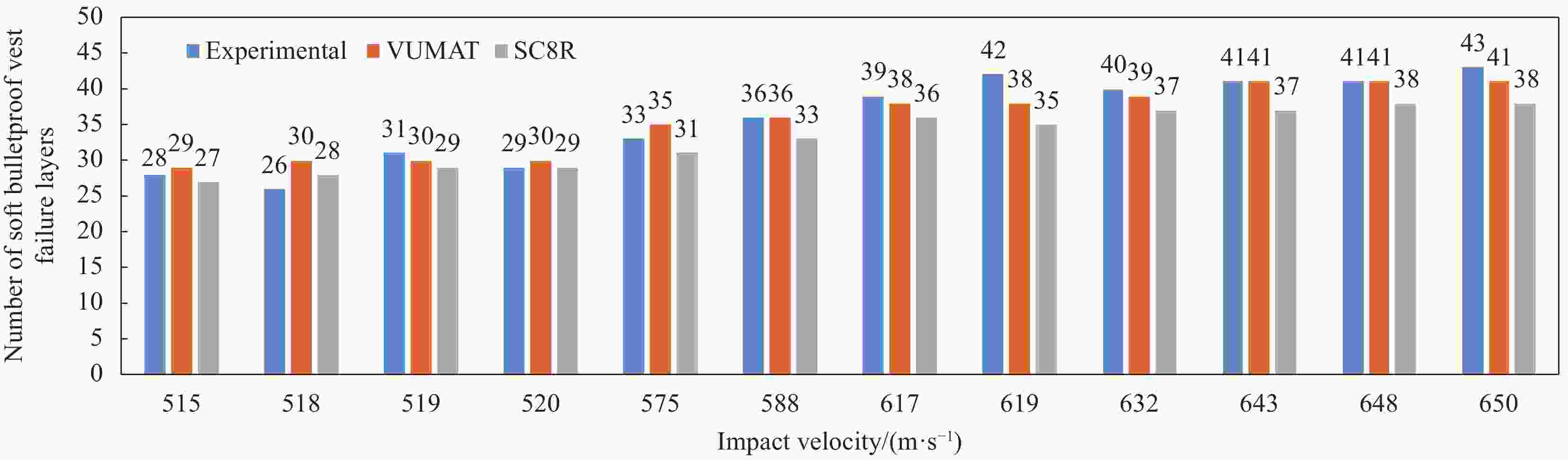
Impact velocity/(m·s−1) Coordinates of impact point/cm Number of penetrating layers Experimental value 1 650 (17,16.5) 43 Experimental value 2 643 (15,15.5) 41 Experimental value 3 619 (14,16.5) 42 Experimental value 4 648 (14.5,16) 41 Experimental value 5 617 (14,15.5) 39 Experimental value 6 632 (14,15.5) 40 Simulation value 630 (15,15) 40 Note: Take the sitting corner of the front of the body armor as the origin of the coordinates. 表 5 实验和数值仿真中UHMWPE软防护破坏层数对比(钢球着靶速度区间为515~588 m/s)
Table 5. Comparison of the computed and the experimentally observed number of UHMWPE soft bulletproof vest failure layers(Impact velocity of steel sphere is 515-588 m/s)
Impact velocity/(m·s−1) Coordinates of impact point/cm Number of penetrating layers Experimental value 1 588 (16.5,16.5) 36 Experimental value 2 575 (17,15.5) 33 Experimental value 3 519 (17,15.5) 31 Experimental value 4 520 (17,16.5) 29 Experimental value 5 518 (17,15.5) 26 Experimental value 6 515 (16.5,16.5) 28 Simulation value 540 (15,15) 33 Note: Take the sitting corner of the front of the body armor as the origin of the coordinates. -
[1] 邹渝, 李曙光, 肖南. 单兵防弹衣对穿甲破片的防护效应研究[J]. 医疗卫生装备, 2015, 36(11):36-38.ZOU Yu, LI Shuguang, XIAO Nan. Study on protective effect of individual bullet-proof cloth against armor-piercing fragments[J]. Chinese Medical Equipment Journal,2015,36(11):36-38(in Chinese). [2] 顾冰芳, 龚烈航, 徐国跃. UHMWPE纤维复合材料防弹机理和性能[J]. 纤维复合材料, 2006(1):20-23. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6423.2006.01.007GU Bingfang, GONG Liehang, XU Guoyue. Ballistic resistance mechanism and performance of UHMWPE compo-sites[J]. Fiber Composites,2006(1):20-23(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-6423.2006.01.007 [3] ZHENG Xiaotao, WU Kewei, WANG Jiqiang, et al. Mechanical characteristics of medical grade UHMWPE under dynamic compression[J]. Journal of Materials Science Materials in Medicine,2019,30(5):50. [4] LI Chen, KANG Zheng, QIN Fang. Effect of strain rate on the dynamic tensile behaviour of UHMWPE fibre laminates[J]. Polymer Testing,2017,63:54-64. [5] 肖文莹, 郭万涛, 李想. 超高分子量聚乙烯纤维增强防弹复合材料研究进展[J]. 材料开发与应用, 2019, 34(2):131-138.XIAO Wenying, GUO Wantao, LI Xiang. Research progress of UHMWPE fiber reinforced bulletproof composites[J]. Development and Application of Materials,2019,34(2):131-138(in Chinese). [6] 黄拱武. 弹体撞击带纤维软防护明胶靶标的数值仿真研究[D]. 南京: 南京理工大学, 2013.HUANG Gongwu. Numerical simulation of soft fiber protection gelatin target in projectile impact zone[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Science and Technology, 2013(in Chinese). [7] 罗少敏. 小质量物体高速撞击陶瓷复合靶板毁伤效应研究[D]. 南京: 南京理工大学, 2013.LUO Shaomin. Study on damage effect of ceramic composite target impacted by small mass at high speed[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Science and Technology, 2013(in Chinese). [8] 董萍, 徐诚, 陈菁. 非贯穿侵彻超高分子量聚乙烯纤维软体防弹衣数值模拟[J]. 计算机辅助工程, 2013, 22(1):46-49, 53.DONG Ping, XU Cheng, CHEN Jing. Numerical simulation of non-penetrating penetration of UHMWPE soft body armor[J]. Computer Aided Engineering,2013,22(1):46-49, 53(in Chinese). [9] 孙非, 马力, 朱一辉, 等. 手枪弹对带UHMWPE软防护明胶靶标冲击效应的数值分析[J]. 振动与冲击, 2018, 37(13):20-26.SUN Fei, MA Li, ZHU Yihui, et al. Numerical analysis for impact effects of a pistol bullet on a gelatin target covered with UHMWPE fiber amor[J]. Journal of Vibration and Shock,2018,37(13):20-26(in Chinese). [10] 张启宽. 步枪弹对带复合防护人体靶标作用的数值模拟[D]. 南京: 南京理工大学, 2012.ZHANG Qikuan. Numerical simulation of the effect of bullet on human body target with compound protection[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Science and Technology, 2012(in Chinese). [11] 包阔, 张先锋, 谈梦婷, 等. 子弹撞击碳化硼陶瓷复合靶试验与数值模拟研究[J]. 爆炸与冲击, 2019, 39(12):57-68.BAO Kuo, ZHANG Xianfeng, TAN Mengting, et al. Experimental and numerical simulation of impact of bullet on boron carbide ceramic composite target[J]. Explosion and Shock Waves,2019,39(12):57-68(in Chinese). [12] 江怡, 黄健, 陈威, 等. 防弹复合结构抗侵彻性能分析[J]. 计算机仿真, 2019, 36(12):10-14, 30.JIANG Yi, HUANG Jian, CHEN Wei, et al. Analysis of anti penetration performance of bulletproof composite structure[J]. Computer Simulation,2019,36(12):10-14, 30(in Chinese). [13] LI X G, GAO X L, KLEIVEN S. Behind helmet blunt trauma induced by ballistic impact: A computational model[J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering, 2016, 91: 56-67. [14] GILSON L, RABET L, IMAD A, et al. Experimental and numerical assessment of non-penetrating impacts on a composite protection and ballistic gelatine[J]. International Journal of Impact Engineering,2020,136:103417. [15] WEN Y, XU C, WANG S, et al. Analysis of behind the armor ballistic trauma[J]. Journal of the Mechanical Behavior of Biomedical Materials,2015,45:11-21. [16] ZHANG R, QIANG L S, HAN B, et al. Ballistic performance of UHMWPE laminated plates and UHMWPE encapsulated aluminum structures: Numerical simulation[J]. Composite Structures,2020,252:112686. [17] LUO S M, XU C , CHEN A, et al. Experimental investigation of the response of gelatine behind the soft body armor[J]. Forensic Science International,2016,266:8-13. [18] GOPINATH G, ZHENG J Q, BATRA R C. Effect of matrix on ballistic performance of soft body armor[J]. Composite Structures,2012,94(9):2690-2696. [19] ROBERTS J C, MERKLE A C, BIERMANN P J, et al. Computational and experimental models of the human torso for non-penetrating ballistic impact[J]. Journal of Biomechanics,2005,40(1):125-136. [20] 陈滨琦. 基于多尺度方法的复合材料层合板结构失效机理研究[D]. 南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2016.CHEN Bingqi. Study on failure mechanism of composite laminates based on multi-scale method[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2016(in Chinese). [21] 张嘉睿, 吴富强, 姚卫星. 复合材料冲击损伤数值仿真模型评估[J]. 航空工程进展, 2019, 10(6):767-779.ZHANG Jiarui, WU Fuqiang, YAO Weixing. Evaluation of numerical simulation model for impact damage of compo-site materials[J]. Advances in Aeronautical Science and Engineering,2019,10(6):767-779(in Chinese). [22] 程之遥, 张健. 基于内聚力模型的层合板屈曲行为分析[J]. 西安理工大学学报, 2020, 36(4): 581-586CHENG Zhiyao, ZHANG Jian. Buckling behavior analysis of laminated plates based on cohesive force model[J]. Journal of Xi’an University of Technology, 2020, 36(4): 581-586(in Chinese). [23] ENGENHARIA F D, BRANCH C M. Numerical simulation of mixed-mode progressive delamination in composite materials[J]. Journal of Composite Materials, 2003, 37(16): 1415-1438. [24] 汪品红. 基于Abaqus子程序的高分子材料本构关系实现[J]. 计算机辅助工程, 2013, 22(S2):408-410.WANG Pinhong. Implementation of polymers constitutive relationship based Abaqus subroutine[J]. Computer Aided Engineering,2013,22(S2):408-410(in Chinese). [25] 伊鹏跃, 于哲峰, 汪海. 复合材料层压板低速冲击刚度退化仿真方案研究[J]. 力学季刊, 2012, 33(3):469-475. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-0053.2012.03.018YI Pengyue, YU Zhefeng, WANG Hai. Stiffness degradation methodology for low-velocity impact simulation in composite laminate[J]. Chinese Quarterly of Mechanics,2012,33(3):469-475(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.0254-0053.2012.03.018 [26] 刘勇, 陈世健, 高鑫, 等. 基于Hashin准则的单层板渐进失效分析[J]. 装备环境工程, 2010, 7(1):34-39. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9242.2010.01.009LIU Yong, CHEN Shijian, GAO Xin, et al. Progressive failure analysis of monolayer composite based on Hashin criterion[J]. Equipment Environmental Engineering,2010,7(1):34-39(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-9242.2010.01.009 [27] SPRING D W, PAULINO G H. A growing library of three-dimensional cohesive elements for use in ABAQUS[J]. Engineering Fracture Mechanics, 2014, 126: 190-216. [28] SUPRATIK M, HALLETT S R. An augmented cohesive element for coarse meshes in delamination analysis of composites[J]. Composite Structures, 2020, 254: 112890. [29] 王念. 复合材料层合板冲击损伤及损伤容限研究[D]. 南京: 南京航空航天大学, 2014.WANG Nian. Impact damage and damage tolerance of com posite laminates[D]. Nanjing: Nanjing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics, 2014(in Chinese). -





 下载:
下载: