Research progress of antibacterial finishing of textiles based on graphene oxide and its composite materials
-
摘要: 作为石墨烯的含氧衍生物,氧化石墨烯(GO)因其优异的物理、化学性能而受到广泛关注。本文首先分析了GO的抗菌机制,其次总结了GO与金属粒子、金属氧化物和有机物的抗菌复合材料的研究进展,然后探讨了基于GO及其复合材料的纺织品抗菌整理方法及其优缺点,最后提出了GO及其复合材料在纺织品抗菌整理方面的研究方向。Abstract: Graphene oxide (GO), as an oxygen-containing derivative of graphene, has attracted wide attention for its excellent physical and chemical properties. In this paper, the antibacterial mechanism of graphene oxide was analyzed; the research progress of antibacterial composite materials of graphene oxide and metal particles, metal oxides and organics were summarized; and the antibacterial finishing methods and their advantages and disadvantages of textiles based on graphene oxide and its composite materials were discussed again. Finally, the research trends of graphene oxide and its composite materials in textile antibacterial finishing were further analyzed.
-
Key words:
- graphene oxide /
- composites material /
- textiles /
- antibacterial finishing /
- nanoparticles
-
表 1 GO、GO-CS、GO-Ag 和 GO-CS-Ag 纳米复合材料对革兰氏阳性和革兰氏阴性菌株的最低抑菌浓度值[28]
Table 1. MIC values of GO、GO-CS、GO-Ag and GO-CS-Ag nanocomposite againstgram-positive and gram-negative bacterial strains
Microorganisms MIC (mean±SD)/(μg·mL−1) GO GO-CS GO-Ag GO-CS-Ag S. aureus 50±0.32 45±0.30 20±0.33 10±0.32 S. mutans 45±0.21 40±0.25 25±0.35 10±0.35 E. coli 35±0.36 30±0.24 15±0.41 8±0.41 K. pneumonia 35±0.32 30±0.36 15±0.42 8±0.42 P. aeruginosa 35±0.47 30±0.41 14±0.36 7±0.32 S. typhi 30±0.30 25±0.21 15±0.21 8±0.38 Notes:MIC—Minimum inhibitory concentration; SD—Standard deviation; All experiments were performed in triplicates and reported as mean±SD. Antibacterial activity of GO = GO-CS, GO-Ag and GO-CS-Ag were significantly different from each other at p ≤ 0.05. 表 2 GO复合材料纺织品抗菌整理方法
Table 2. Summary of antibacterial finishing methods for textiles based on GO composite materials
Antibacterial finishing method Basic rules Advantages Disadvantages Electrospinning Jet spinning of polymer solution or melt in strong electric field Controllable process, many kinds of spinnable materials, low cost and simple preparation devices Graphene oxide is easy to agglomerate and it is difficult to spin uniformly Dipping Finishing agent is formulated into a solution, soaked into the fabric, pressed, and baked Less impact on the mechanical properties of the fabric Consumption of antibacterial materials is large, the bonding fastness is low, and the uniformity is difficult to control Coating method Antibacterial material is diluted and added with additives, and then evenly coated on the surface of the fabric Simple method and has low requirements for fabric quality Thickness of the fabric increases after coating, which has a greater impact on the feel and breathability of the fabric Electrostatic layer-by-layer self-assembly method Two materials with opposite charges are alternately deposited on the surface of the fabric in a polyelectrolyte solution Poor stability High adsorption capacity and controllable thickness of finished fabric Chemical grafting First, the graphene oxide is chlorinated, and then other materials are covalently grafted onto the graphene oxide Short occurrence time and strong combination High requirements for reactant functional groups In situ reduction Fabric is coated with graphene oxide, and the graphene oxide is reduced and compounded in a reducing solution High binding fastness Has eestrictions on reactive functional groups -
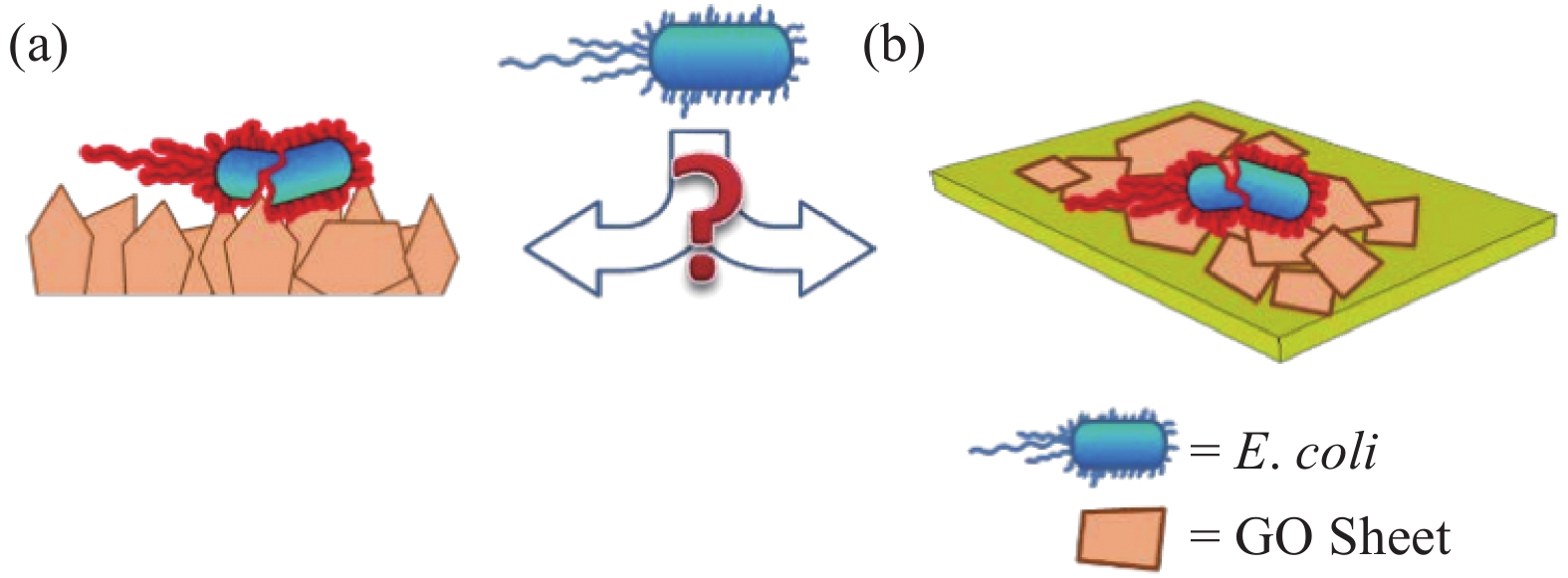
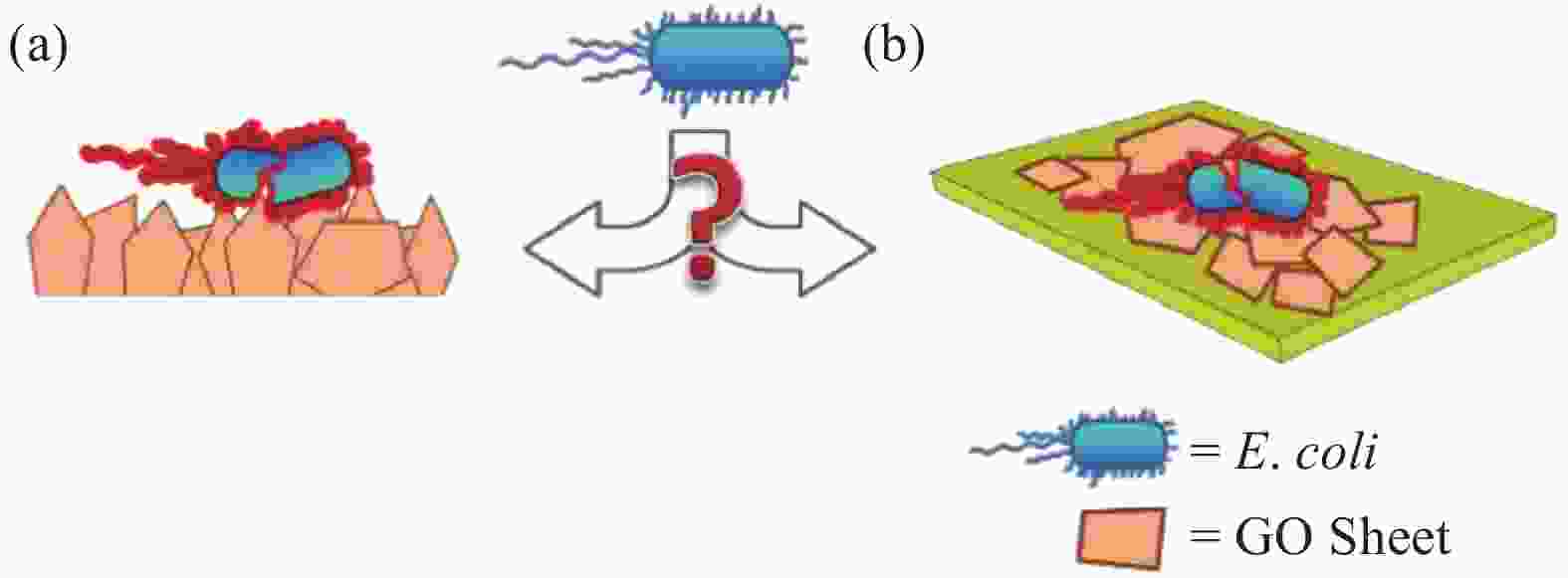
[1] 刘荣清, 张敢. 石墨烯材料的特性及其在纺织上的应用[J]. 纺织导报, 2017(6):48-50. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3025.2017.06.014LIU Rongqing, ZHANG Gan. Characteristics of graphene materials and their applications in textiles[J]. China Textile Leader,2017(6):48-50(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-3025.2017.06.014 [2] NAKAJIMA T, MABUCHI A, HAGIWARA R. A new structure model of graphite oxide[J]. Carbon,1988,26(3):357-361. doi: 10.1016/0008-6223(88)90227-8 [3] SI Y C, SAMULSKI E T. Synthesis of water soluble graphene[J]. Nano Letters,2008,8(6):1679. [4] NURHAFIZAH M D, AZIZ A A, SURIANI A B, et al. Low-temperature exfoliated graphene oxide incorporated with different types of natural rubber latex: Electrical and morphological properties and its capacitance performance[J]. Ceramics International,2020,46(5):5610-5622. [5] MAHANTA N K, ABRAMSON A R. Thermal conductivity of graphene and graphene oxide nanoplatelets[C]. 13th InterSociety Conference on Thermal and Thermomechanical Phenomena in Electronic Systems, 2012: 1-6. [6] WANG C, LUO S, LIU C, et al. WO3 quantum dots enhanced the photocatalytic performances of graphene oxide/TiO2 films under flowing dye solution[J]. Inorganic Chemistry Communications,2020,115:107875. [7] LIU Y, JING W, YANG G, et al. Antibacterial graphene oxide coatings on polymer substrate[J]. Applied Surface Science,2018,436:624-630. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.12.006 [8] GHOLIBEGLOO E, KARBASI A, POURHAJIBAGHER M, et al. Carnosine-graphene oxide conjugates decorated with hydroxyapatite as promising nanocarrier for ICG loading with enhanced antibacterial effects in photodynamic therapy against Streptococcus mutans[J]. Journal of Photochemistry & Photobiology, B: Biology,2018,181:14. [9] 张晓, 杨蓉, 王琛, 等. 功能化氧化石墨烯的细胞相容性(英文)[J]. 物理化学学报, 2012, 28(6):1520-1524. doi: 10.3866/PKU.WHXB201203131ZHANG Xiao, YANG Rong, WANG Chen, et al. Cell biocompatibuity of functionalized graphene oxide[J]. Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica,2012,28(6):1520-1524(in Chinese). doi: 10.3866/PKU.WHXB201203131 [10] 徐静, 闻宏亮, 欧阳建波, 等. 氧化石墨烯-壳聚糖复合材料对甲烯蓝的吸附动力学[J]. 上海大学学报(自然科学版), 2013, 19(4):400-404.XU Jing, WEN Hongliang, OUYANG Jianbo, et al. Adsorption kinetics of methylene blue on graphene oxide-chitosan composite[J]. Journal of Shanghai University (Natural Science),2013,19(4):400-404(in Chinese). [11] SIVARAMAPANICKER S, XING M, YANLI Z. Graphene oxide wrapping on squaraine-loaded mesoporous silica nanoparticles for bioimaging[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society,2012,134(42):17346. [12] 赵银桃, 赵飞格, 秦泗霞, 等. 氧化石墨烯改性涤棉织物的制备及性能[J]. 印染助剂, 2019, 36(7):13-16. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-0439.2019.07.003ZHAO Yintao, ZHAO Feige, QIN Sixia, et al. Preparation and properties of graphene oxide modified polyester-cotton fabric[J]. Textile Auxiliaries,2019,36(7):13-16(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-0439.2019.07.003 [13] 苗广远, 韩伟伟, 柴梦倩, 等. 氧化石墨烯在纯棉织物上的抗菌应用[J]. 纺织导报, 2016(12):58-61.MIAO Guangyuan, HAN Weiwei, CHAI Mengqian, et al. The antibacterial application of graphene oxide on cotton fabric[J]. China Textile Leader,2016(12):58-61(in Chinese). [14] SHAOBIN L. Antibacterial activity of graphite, graphite oxide, graphene oxide, and reduced graphene oxide: Membrane and oxidative stress[J]. Acs Nano,2011,5(9):6971-6980. [15] GURUNATHAN S, HAN J, ABDAL DAYEM A, et al. Oxidative stress-mediated antibacterial activity of graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide in pseudomonas aeruginosa[J]. International journal of nanomedicine,2012,7:5901-5914. [16] LIU S, HU M, ZENG T H, et al. Lateral dimension-dependent antibacterial activity of graphene oxide sheets[J]. Langmuir,2012,28(33):12364-12372. doi: 10.1021/la3023908 [17] 姜国飞, 刘芳, 随林林, 等. 石墨烯及其复合材料在抗菌方面应用研究进展[J]. 石油学报(石油加工), 2017, 33(5):1017-1028.JIANG Guofei, LIU Fang, SUI Linlin, et al. Progress in the application of graphene and its composites in antibacterial[J]. Acta Petrolei Sinica (Petroleum Processing Section),2017,33(5):1017-1028(in Chinese). [18] MANGADLAO J D, SANTOS C M, FELIPE M J, et al. On the antibacterial mechanism of graphene oxide (GO) langmuir-blodgett films[J]. Chem Commun (Camb),2015,51(14):2886-2889. doi: 10.1039/C4CC07836E [19] CHEN J, PENG H, WANG X, et al. Graphene oxide exhibits broad-spectrum antimicrobial activity against bacterial phytopathogens and fungal conidia by intertwining and membrane perturbation[J]. Nanoscale,2014,6(3):1879-1889. doi: 10.1039/C3NR04941H [20] LI Y, YUAN H, VON DEM BUSSCHE A, et al. Graphene microsheets enter cells through spontaneous membrane penetration at edge asperities and corner sites[J]. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences of the United States of America,2013,110(30):12295-12300. doi: 10.1073/pnas.1222276110 [21] TU Y, LV M, XIU P, et al. Erratum: Destructive extraction of phospholipids from Escherichia coli membranes by graphene nanosheets[J]. Nature Nanotechnology,2013,8(12):968. doi: 10.1038/nnano.2013.275 [22] ASHRAF G M, KHAN A A P, ASIRI A M, et al. Graphene oxide based metallic nanoparticles and their some biological and environmental application[J]. Current Drug Metabolism,2017,18(11):1020-1029. [23] DE MORAES A C M, ANDRADE P F, DE FARIA A F, et al. Fabrication of transparent and ultraviolet shielding composite films based on graphene oxide and cellulose acetate[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers, 2015, 123: 217-227. [24] DAS M R, SARMA R K, SAIKIA R, et al. Synthesis of silver nanoparticles in an aqueous suspension of graphene oxide sheets and its antimicrobial activity[J]. Colloids and Surfaces. B, Biointerfaces,2010,83(1):16-22. [25] LIU L, LIU J, WANG Y, et al. Facile synthesis of monodispersed silver nanoparticles on graphene oxide sheets with enhanced antibacterial activity[J]. New Journal of Chemistry,2011,35:1418-1423. doi: 10.1039/c1nj20076c [26] FARIA A F D, MARTINEZ D S T, MEIRA S M M, et al. Anti-adhesion and antibacterial activity of silver nanoparticles supported on graphene oxide sheets[J]. Colloids and Surfaces, B: Biointerfaces,2014,113:115-124. doi: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2013.08.006 [27] POUNRAJ S, SOMU P, PAUL S. Chitosan and graphene oxide hybrid nanocomposite film doped with silver nanoparticles efficiently prevents biofouling[J]. Applied Surface Science,2018,452:487-497. doi: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.05.009 [28] KHAWAJA H, ZAHIR E, ASGHAR M A, et al. Graphene oxide, chitosan and silver nanocomposite as a highly effective antibacterial agent against pathogenic strains[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects,2018,555:246-255. [29] 田惠博, 张强, 闫岩, 等. Ag/石墨烯复合涂层的制备及抗菌性能[J]. 吉林大学学报(理学版), 2020, 58(2):403-409.TIAN Huibo, ZHANG Qiang, YAN Yan, et al. Preparation and antibacterial properties of Ag/graphene composite coating[J]. Journal of Jilin University: Science Edition,2020,58(2):403-409(in Chinese). [30] JIN J, FEI D, ZHANG Y, et al. Functionalized titanium implant in regulating bacteria and cell response[J]. International Journal of Nanomedicine,2019,14:1433-1450. doi: 10.2147/IJN.S193176 [31] DENG W, WU Z, YANG F, et al. Gold nanoparticles decorated graphene oxide/nanocellulose paper for NIR laser-induced photothermal ablation of pathogenic bacteria[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers: Scientific and Technological Aspects of Industrially Important Polysaccharides,2018,198:206-214. [32] 刘璐. 医用钛表面氧化石墨烯薄膜水热处理及性能研究[D]. 上海: 上海师范大学, 2019.LIU Lu. Preparation and performance study of graphene oxide film on medical titanium surface[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Normal University, 2019(in Chinese). [33] ANDRETTA M T, CHANDRA R S, MOTLHALETSI M R. Zeolitic imidazolate framework-8-encapsulated nanoparticle of Ag/Cu composites supported on graphene oxide: Synthesis and antibacterial activity[J]. ACS omega,2020,5(17):9626-9640. [34] HATAMIE S, AHADIAN M M, ZOMOROD M S, et al. Antibacterial properties of nanoporous graphene oxide/cobalt metal organic framework[J]. Materials Science & Engineering C,2019,104:109862. [35] 伍兰天. GO、GQDs与金属氧化物复合材料的制备、表征及其抗菌性能与应用的研究[D]. 镇江: 江苏科技大学, 2019.WU Lantian. Study on preparation, characterization, antibacterial performance and application of GO, GQDs and metal oxide composite materials[D]. Zhenjiang: Jiangsu University of Science and Technology, 2019(in Chinese). [36] ZHONG L, YUN K. Graphene oxide-modified ZnO particles: Synthesis, characterization, and antibacterial properties[J]. International Journal of Nanomedicine,2015,10(Spec Iss):79-92. [37] ASHRAF M A, YANG Y, FAKHRI A. Synthesis of NiS–MoO3 nanocomposites and decorated on graphene oxides for heterogeneous photocatalysis, antibacterial and antioxidant activities[J]. Ceramics International,2020,46(6):8379-8384. [38] XIE Y Y, HU X H, ZHANG Y W, et al. Development and antibacterial activities of bacterial cellulose/graphene oxide-CuO nanocomposite films[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2019,229:115456. [39] GAO N, CHEN Y, JIANG J. Ag@Fe2O3-GO nanocomposites prepared by a phase transfer method with long-term antibacterial property[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2013,5(21):11307-11314. [40] LIM H N, HUANG N M, LOO C H. Facile preparation of graphene-based chitosan films: Enhanced thermal, mechanical and antibacterial properties[J]. Journal of Non-Crystalline Solids,2012,358(3):525-530. doi: 10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2011.11.007 [41] JIANG Y, GONG J L, ZENG G M, et al. Magnetic chitosan-graphene oxide composite for anti-microbial and dye removal applications[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2016,82:702-710. doi: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2015.11.021 [42] 吴云波. CH/PVA/GO共混膜的制备及其对铜绿假单胞菌生物被膜形成抑制研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江工商大学, 2019.WU Yunbo. Preparation of CH/PVA/GO blend film and its inhibition of pseudomonas aeruginosa biofilm formation[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang Gongshang University, 2019(in Chinese). [43] 孔令春. 纳米金属氧化物抗菌材料的制备及其抑菌性能研究[D]. 曲阜: 曲阜师范大学, 2007.KONG Lingchun. Preparation of nanometer metal oxide antibacterial material and research on its antibacterial performance[D]. Qufu: Qufu Normal University, 2007(in Chinese). [44] 杨娟, 苗志明, 李怡, 等. 季铵盐修饰磁性氧化石墨烯气凝胶的制备及抗菌性的研究[J]. 化工中间体, 2015, 11(10):61-62.YANG Juan, MIAO Zhiming, LI Yi, et al. Preparation of quaternary ammonium salt modified magnetic graphene oxide aerogel and its antibacterial properties[J]. Chemical Intermediate,2015,11(10):61-62(in Chinese). [45] 叶小莉, 施庆珊, 谭绍早. 氧化石墨烯/十二烷基二甲基苄基氯化铵复合物的制备和抗菌性能研究[J]. 工业微生物, 2016, 46(4):49-52. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6678.2016.04.010YE Xiaoli, SHI Qingshan, TAN Shaozao. Preparation of graphene oxide/dodecyl dimethyl benzyl ammonium chloride complex and its antibacterial properties[J]. Industrial Microbiology,2016,46(4):49-52(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-6678.2016.04.010 [46] 余坤明. 氧化石墨烯在静电纺丝及棉织物功能整理中的应用及性能研究[D]. 苏州: 苏州大学, 2018.YU Kunming. Research on application and properties of graphene oxide in electrospinning and functional finishing of cotton fabric[D]. Suzhou: Soochow University, 2018(in Chinese). [47] LIU Y, PARK M, SHIN H K, et al. Facile preparation and characterization of poly (vinyl alcohol)/chitosan/graphene oxide biocomposite nanofibers[J]. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry,2014,20(6):4415-4420. doi: 10.1016/j.jiec.2014.02.009 [48] KARIMI L, YAZDANSHENAS M E, KHAJAVI R, et al. Using graphene/TiO2 nanocomposite as a new route for preparation of electroconductive, self-cleaning, antibacterial and antifungal cotton fabric without toxicity[J]. Cellulose,2014,21(5):3813-3827. doi: 10.1007/s10570-014-0385-1 [49] 史飞龙. 多组分改性氧化石墨烯的制备及应用[D]. 石家庄: 河北科技大学, 2019.SHI Feilong. Preparation and application of multi-component modified graphene oxide[D]. Shijiazhuang: Hebei University of Science & Technology, 2019(in Chinese). [50] 李婉迪. 纳米TiO2/SiO2/氧化石墨烯复合涂层涤棉织物的制备及性能研究[D]. 上海: 东华大学, 2016.LI Wandi. Preparation and performance of nano TiO2/SiO2/graphene oxide composite coated polyester-cotton fabric[D]. Shanghai: Donghua University, 2016(in Chinese). [51] 姜国飞, 李旭飞, 刘芳, 等. 纳米ZnO-氧化石墨烯及ZnO-氧化石墨烯/水性聚氨酯复合涂层的抗菌性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2018, 35(7):1930-1938.JIANG Guofei, LI Xufei, LIU Fang, et al. Antibacterial properties of nano ZnO-graphene oxide and ZnO-graphene oxide/waterborne polyurethane composite coating[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2018,35(7):1930-1938(in Chinese). [52] 赵兵. 氧化石墨烯/壳聚糖/银纳米线功能化棉纤维: 中国, CN201710836978.5[P]. 2017-09-17.ZHAO Bing. GO/chitosan/silver nanowires functionalized cotton fiber: China, CN201710836978.5[P]. 2017-09-17(in Chinese). [53] 彭勇刚, 纪俊玲, 汪媛, 等. 一种基于氧化石墨烯的染色、抗菌整理剂及其制备方法和应用: 中国, CN201210548529.8[P]. 2013-03-27.PENG Yonggang, JI Junling, WANG Yuan, et al. A dyeing antibacterial finishing agent based on GO and its preparation method and application: China, CN201210548529.8[P]. 2013-03-27(in Chinese). [54] MIRJALILI M. Preparation of electroconductive, magnetic, antibacterial, and ultraviolet-blocking cotton fabric using reduced graphene oxide nanosheets and magnetite nanoparticles[J]. Fibers and Polymers,2016,17(10):1579-1588. doi: 10.1007/s12221-016-6689-z -





 下载:
下载: