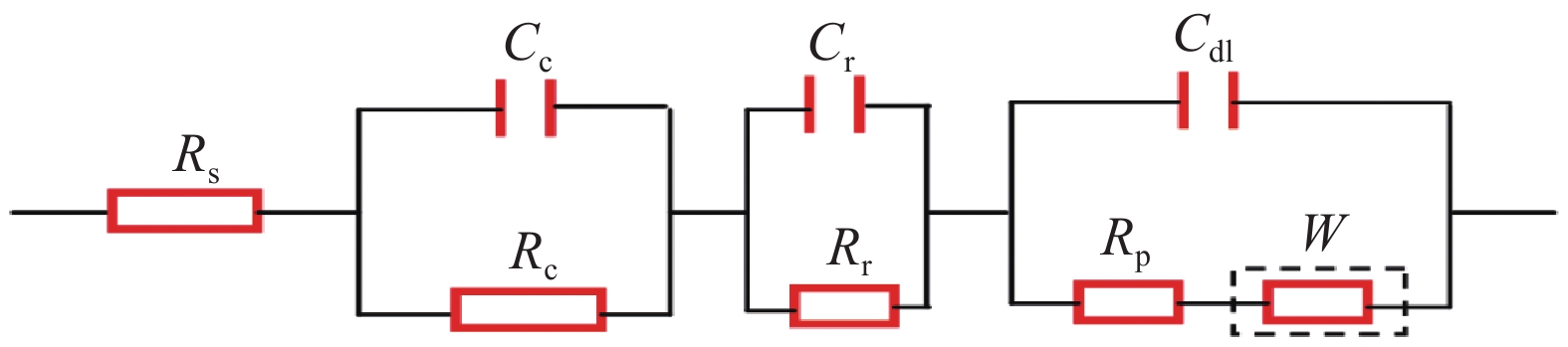
Weibull durability life prediction method of reinforced concrete in environment of coupled salt solution
-
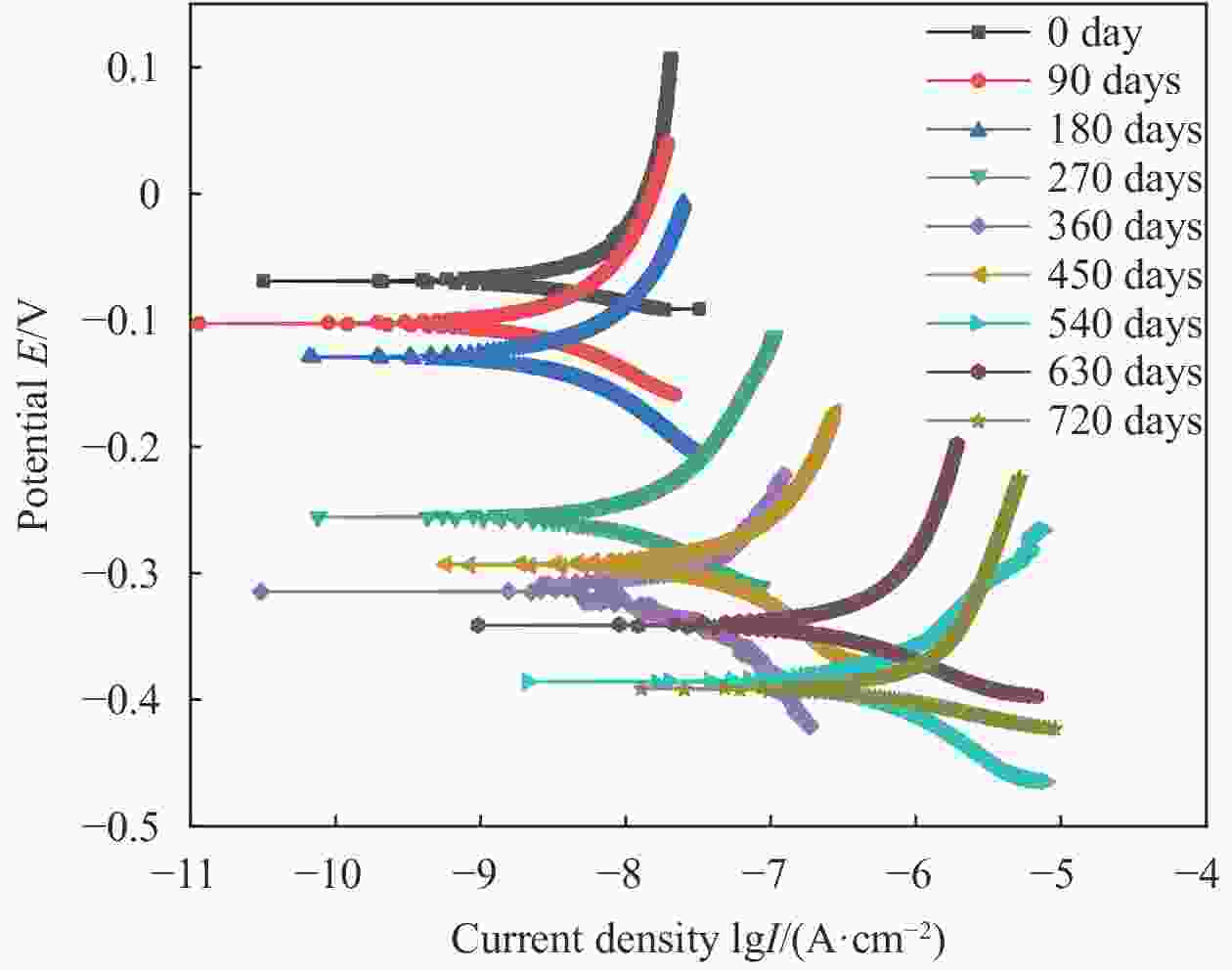
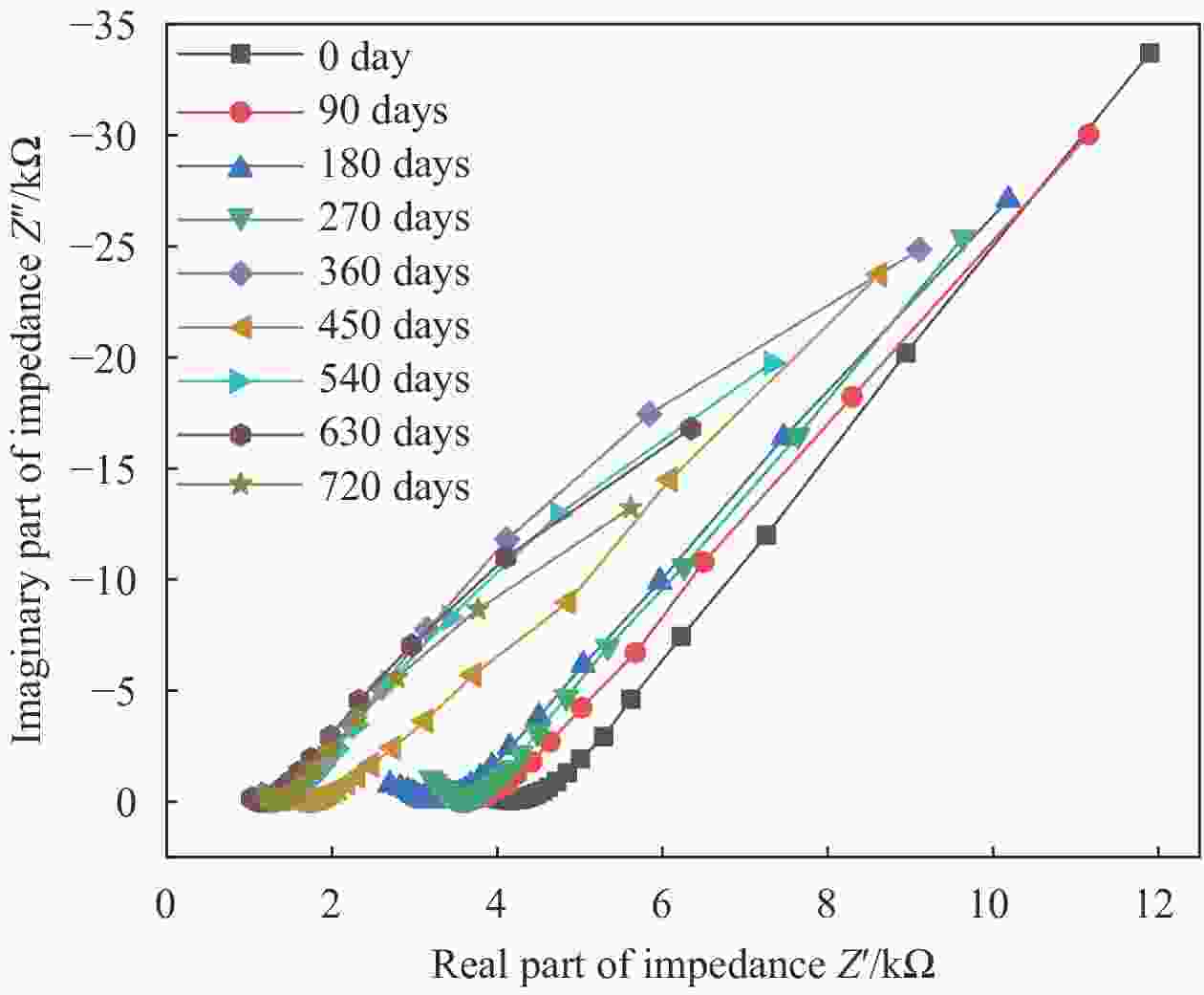
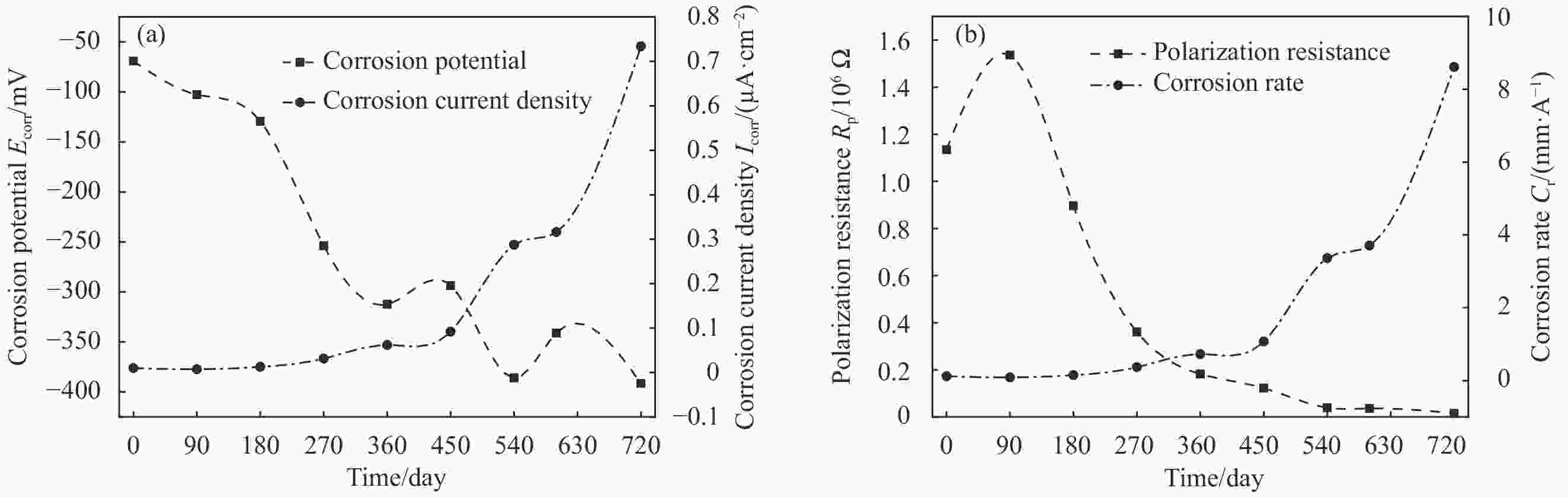
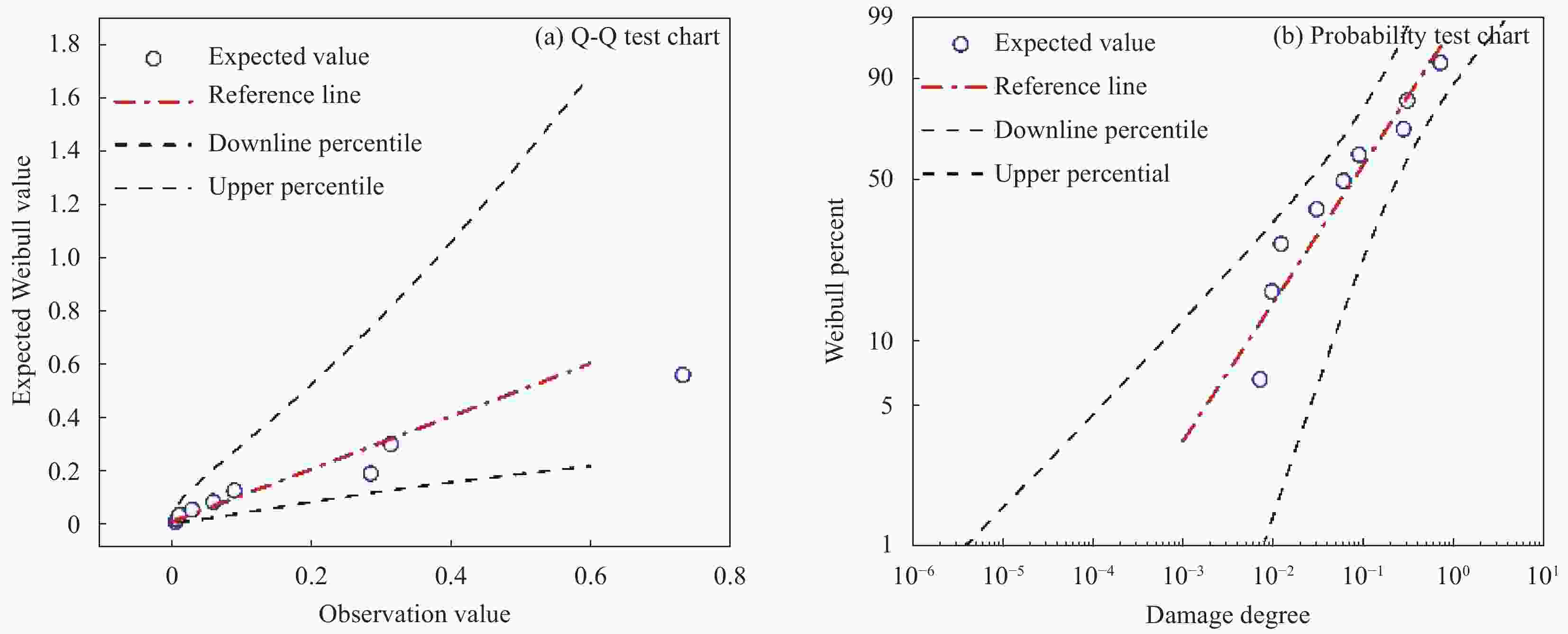
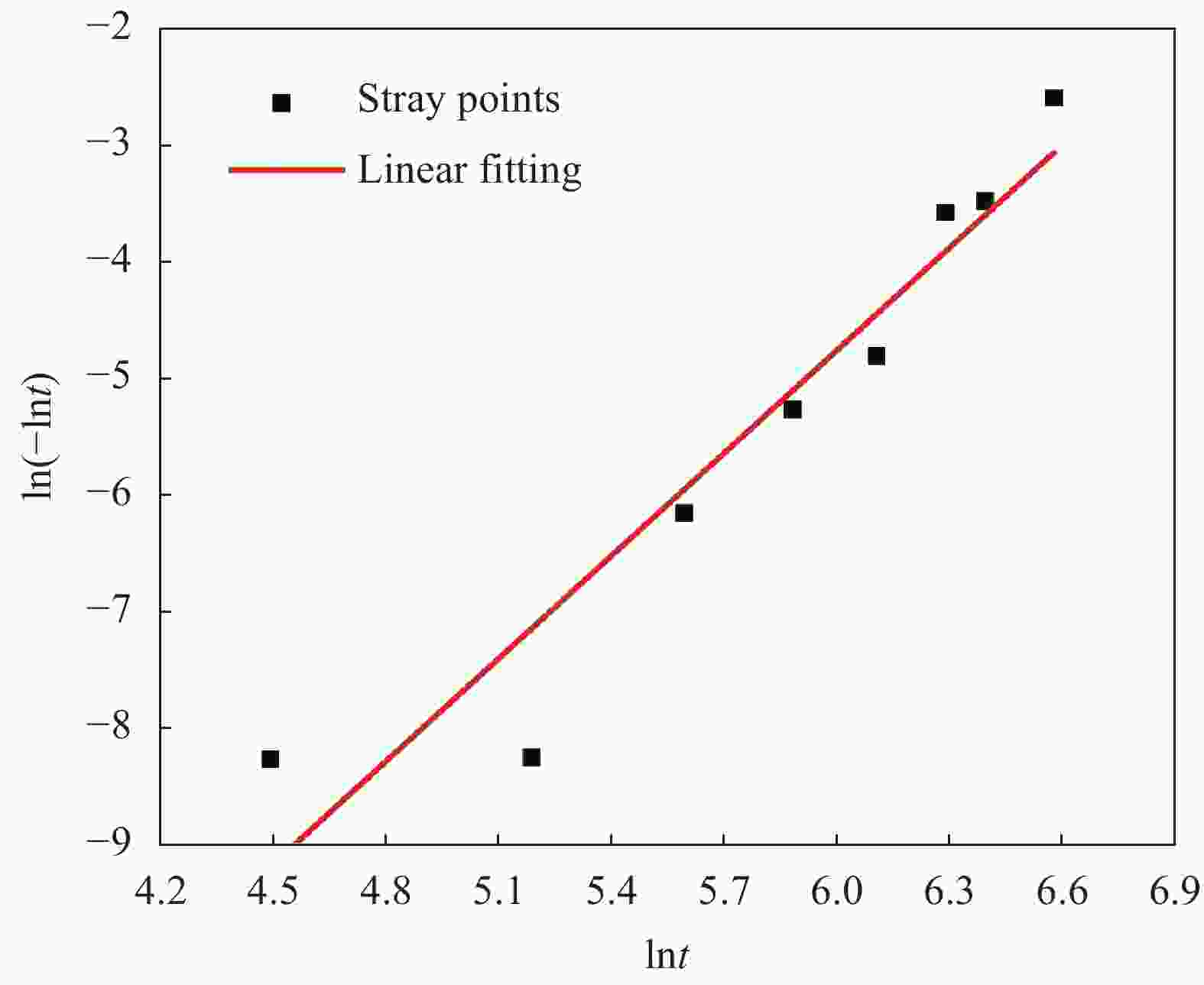
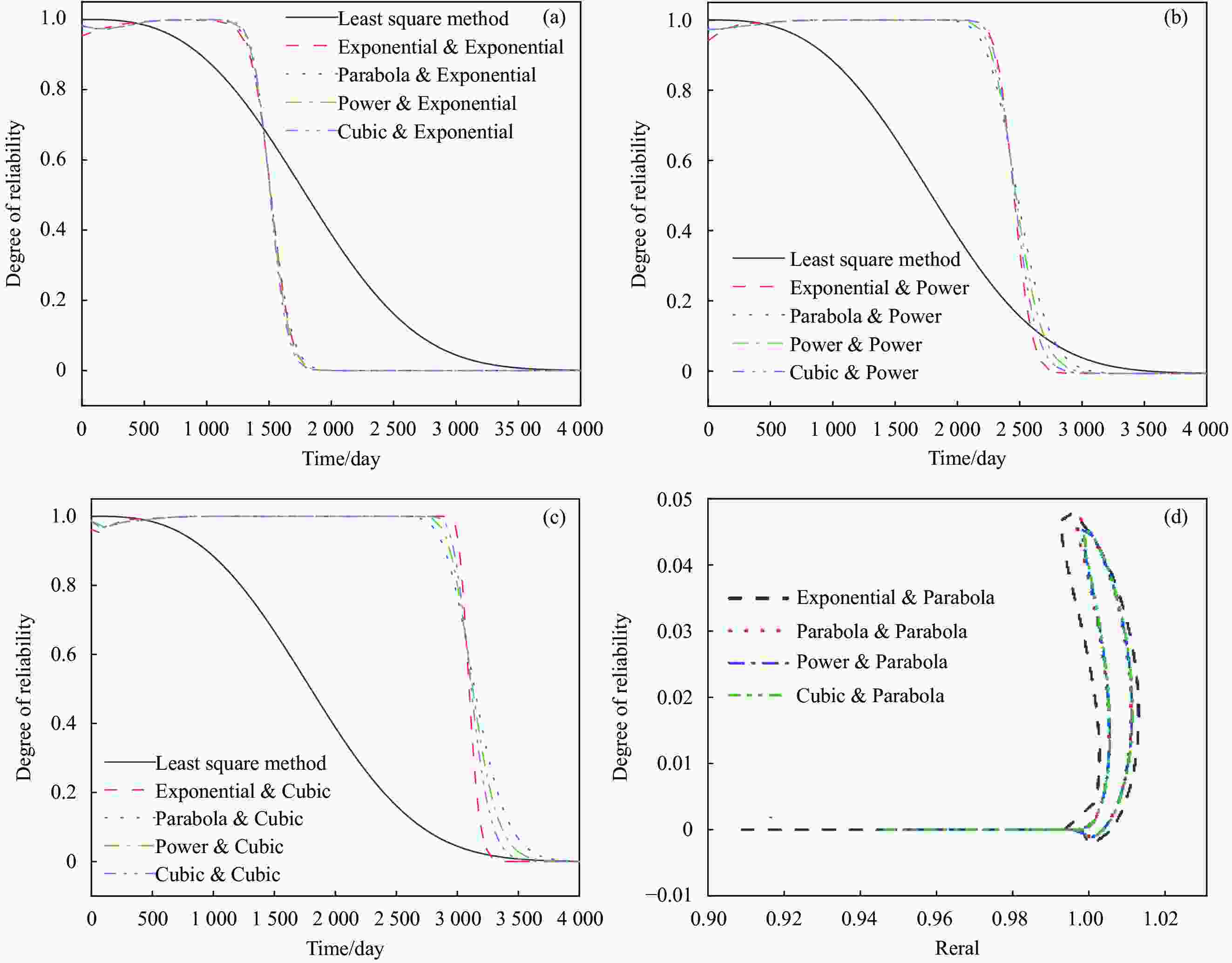
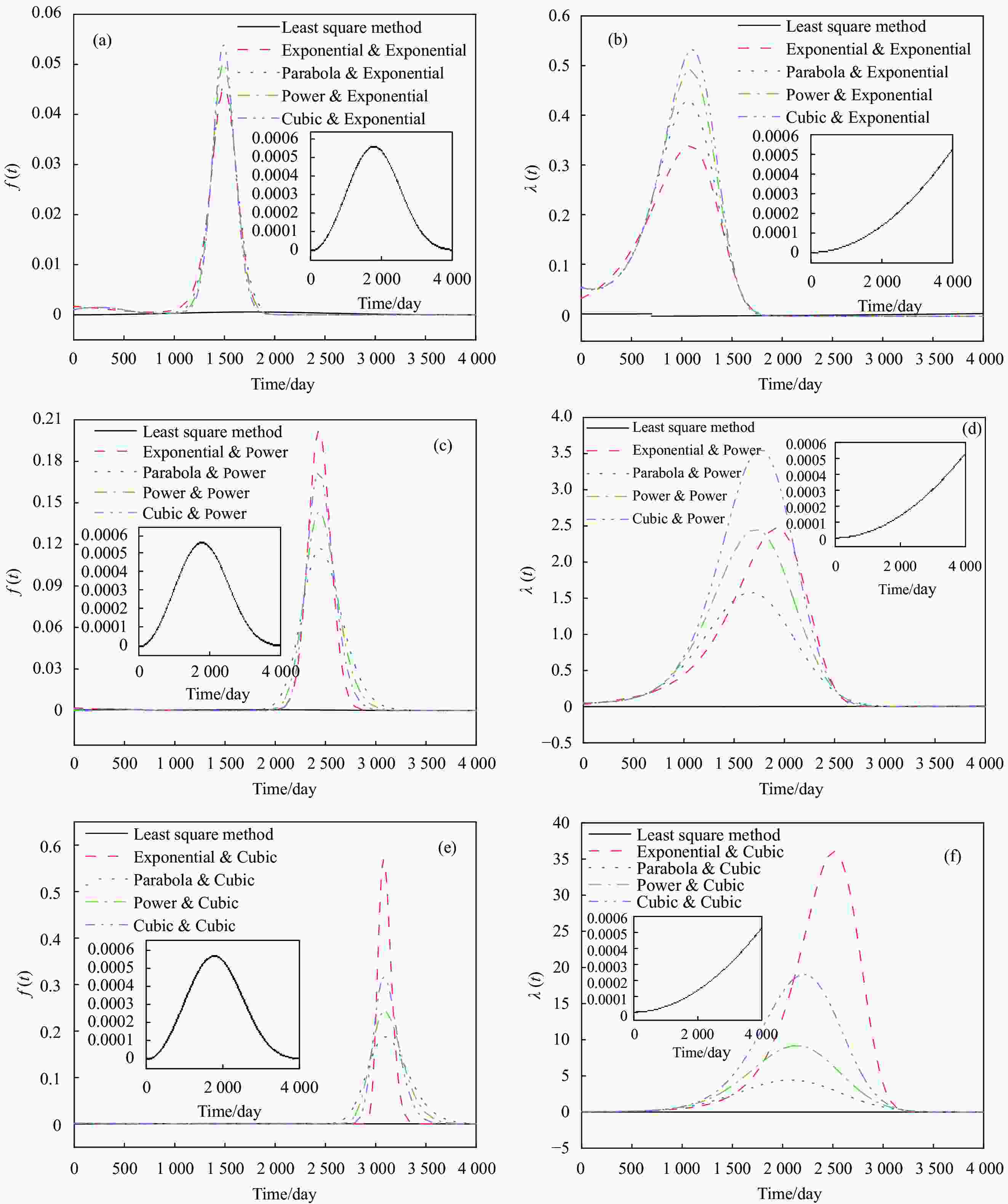
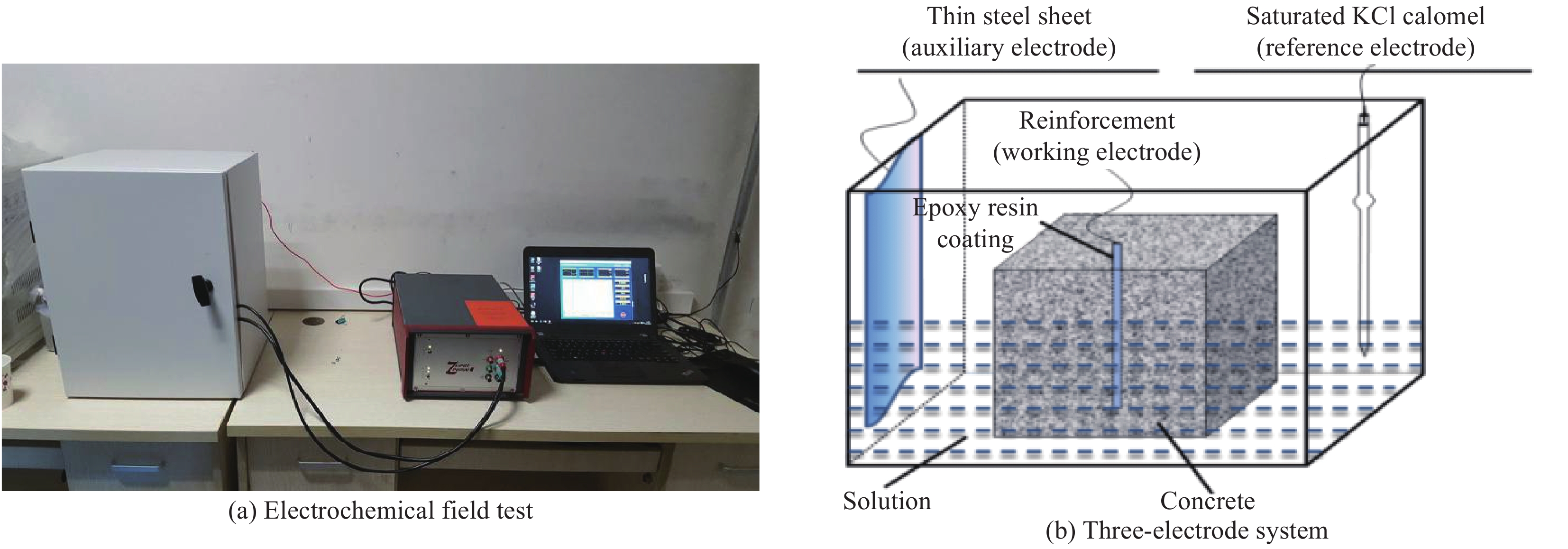
摘要: 根据兰州地铁沿线站台服役环境,配置含有SO42−、Cl−、Mg2+的耦合盐溶液,将钢筋/混凝土试件置于耦合盐溶液中每隔90天利用电化学工作站进行无损检测,选择Weibull分布建模,通过最小二乘法和BLUE法得到退化分布的固定参数估计值和动态参数估计值。结果表明:耦合盐溶液环境中腐蚀离子通过扩散、渗透及电化学迁移等方式到达钢筋表面,导致钢筋附近pH值降低,钝化膜由完整状态过渡到局部破损状态。可靠度曲线均呈现出三阶段变化特点,动态参数估计值中三次型尺度参数的可靠性寿命最接近固定参数值可靠性寿命,失效率最大;指数型尺度参数可靠性寿命最短,失效率最小;幂次型介于两者之间。且动态参数函数必须满足一阶导数及函数值为正的要求,否则可靠度计算结果为复数。尺度参数的函数形式对可靠度曲线影响大于形状参数的函数形式对可靠度曲线的影响。尺度参数函数类型一定时,形状参数函数类型对寿命结果影响较大,尺度参数函数类型变化时,可靠性曲线均发生较大变化。Abstract: According to the service environment of the platform along Lanzhou Metro Line, coupled salt solutions containing SO42−, Cl− and Mg2+ were allocated. The reinforced concrete specimens were placed in a coupled salt solution for nondestructive testing every 90 days. Weibull distribution model was selected. Fixed and dynamic parameter estimates of the degradation distribution were obtained by least square method and BLUE method. The results show that the corrosion ions in coupled salt solution reach the surface of steel bar by diffusion, permeation and electrochemical migration. The pH value near the steel bar decreases, and the passivation film transits from undamaged state to partial damaged state. The polarization curve moves towards the direction of negative potential and increasing corrosion current density, and the AC impedance graph shows a double capacitive reactance arc, while the low-frequency impedance arc radius gradually decreases and contracts to the real part of the impedance. The reliability curves show three-stage variation characteristics. Among the dynamic parameter estimates, the reliability life of the cubic scale parameter is the closest to that of the fixed parameter value, the failure rate is the largest, the reliability life of the exponential scale parameter is the shortest, the failure rate is the smallest, the power type is between the two, and the dynamic parameter function must be between them. The first derivative and the value of the function must be positive. Otherwise, the result of the reliability calculation is complex. The influence of the scale parameter function form on reliability curve is greater than that of the shape parameter function form on reliability curve. When the scale parameter function type is fixed, the shape parameter function type has great influence on the life result. However, the reliability curve changes obviously with the scale parameter function type altering.
-
Key words:
- Weibull distribution /
- parameter estimation /
- least square method /
- reinforced concrete /
- reliability /
- life prediction
-
表 1 兰州地铁1号线部分站台地下水、土壤中主要腐蚀性离子浓度及腐蚀程度
Table 1. Concentration and degree of corrosive ions in underground water and soil of some platforms of subway line 1 in Lanzhou
Subway site Location Corrosive ion concentration/(mg·L−1) Corrosion
evaluationDurability environment
categorySO42− Mg2+ Cl− pH Eastern market station Ground water 4250.7 595.6 1613.0 7.3 Strong corrosion Ⅴ-E Soil 696.4 48.6 205.6 7.7 Medium corrosion Ⅳ-D Jiaojia bay station Ground water 1657.0 255.3 762.2 7.3 Strong corrosion Ⅴ-E Soil 1248.8 54.7 195.0 7.8 Medium corrosion Ⅳ-D Gongxingdun station Ground water 4202.6 619.9 1595.0 7.4 Strong corrosion Ⅴ-E Soil 552.3 48.6 262.3 7.6 Medium corrosion Ⅳ-D Note:“Ⅳ-D”—Severe chloride environment; “Ⅴ-E”—Very severely chemical corrosion environment. 表 2 混凝土配合比设计
Table 2. Design of concrete mix proportion
Cement/
(kg·m−3)Fly ash/
(kg·m−3)Aggregate/
(kg·m−3)Sand/
(kg·m−3)Water/
(kg·m−3)Corrosion inhibito/
(kg·m−3)Water to binder
ratio (W/B)Compressive
strength/MPaSlump/
mm340 102 1100 720 141.5 36 0.32 48.3 175 表 3 腐蚀电位与钢筋锈蚀程度的对应关系[22]
Table 3. Corresponding relationship between corrosion potential and corrosion degree of reinforcement[22]
American standard (ASTM C876—15[24]) Standard of Chinese metallurgical ministry Potential range Corrosion discriminant Potential range Corrosion discriminant >−200 mV 5% probability of corrosion >−250 mV No rust −200–−350 mV 50% probability of corrosion −250–−400 mV May be corroded <−350 mV 95% probability of corrosion <−400 mV Rust 表 4 腐蚀电流密度Icorr与钢筋锈蚀程度的对应关系[23]
Table 4. Corresponding relationship between corrosion current density
Icorr and corrosion degree of reinforcement[23] Icorr/(μA·cm−2) Icorr<0.2 0.2<Icorr<0.5 0.5<Icorr<1.0 1.0<Icorr<10 Icorr>10 Corrosion
statusPassivation
stateLow corrosion
condition stateModerate corrosion
condition stateHigher corrosion
condition stateHighly corrosive
condition state表 5 钢筋/混凝土耐久性参数拟合汇总
Table 5. Summary of durability parameter fitting of reinforced concrete
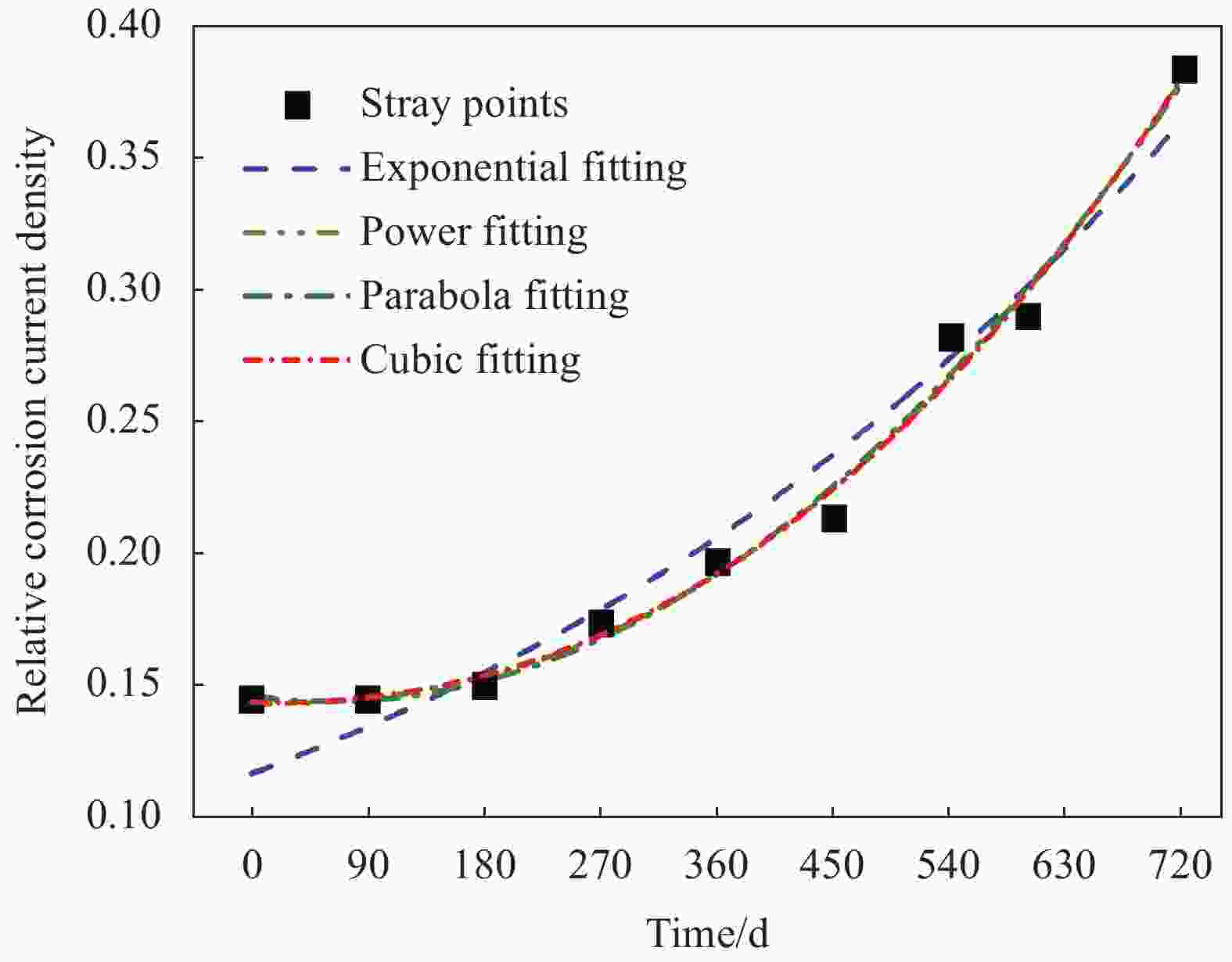
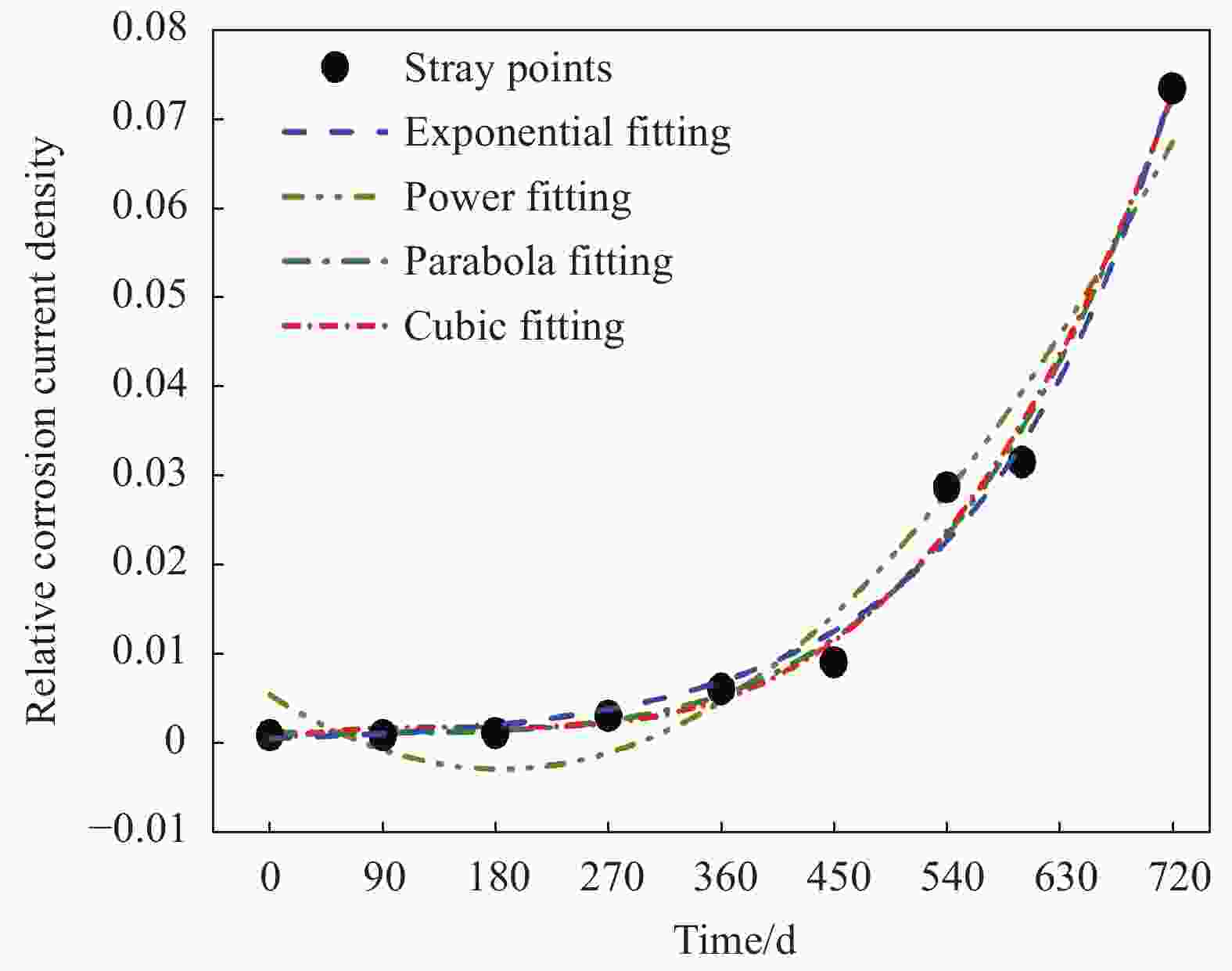
Serial number Function form Indicator Parameter R2 a b c d Exponential y=abt U 0.1165 1.0016 — — 0.9599 V 6.71×10−4 1.0066 — — 0.9884 Power y=a+btc U 0.143 7.73×10−8 2.2707 — 0.9889 V 0.0013 1.58×10−13 4.0799 — 0.9887 Parabola y=a+bt+ct2 U 0.1459 −6.52×10−5 5.40×10−7 — 0.9898 V 0.0055 −8.98×10−5 2.44×10−7 — 0.9604 Cubic y=a+bt+ct2+dt3 U 0.1436 −1.26×10−5 3.48×10−7 1.77×10−10 0.9903 V 4.01×10−4 3.03×10−5 −1.94×10−7 4.05×10−10 0.9885 -
[1] 刘松玉, 李洪江, 童立元, 等. 城市地下结构污染腐蚀耐久性的若干问题[J]. 岩土工程学报, 2016, 38(s2):7-17.LIU S Y, LI H J, TONG L Y, et al. Some problems on polluted erosive durability of urban underground structures[J]. Journal of Geotechnical Engineering,2016,38(s2):7-17(in Chinese). [2] 陈晓斌, 唐孟雄, 马昆林. 地下混凝土结构硫酸盐及氯盐侵蚀的耐久性实验[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2012, 43(7):2803-2812.CHEN X B, TANG M X, MA K L. Underground concrete structure exposure tosulfate and chloride invading environment[J]. Journal of Central South University (Natural Science Edition),2012,43(7):2803-2812(in Chinese). [3] CUI Z, ALIPOUR A. Concrete cover cracking and service life prediction of reinforced concrete structures in corrosive environments[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2018,159:652-671. doi: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.03.224 [4] DUAN A, DAI J, JIN W. Probabilistic approach for durability design of concrete structures in marine environments[J]. Cement and Concrete Research,2015,27(2):A4014007. [5] MITSUYOSHI A, DAN M, FRANGOR P, et al. Reliability-based durability design and service life assessment of reinforced concrete deck slab of jetty structures[J]. Structure and Infrastructure Engineering,2017,13(4):468-477. doi: 10.1080/15732479.2016.1164725 [6] 金伟良, 钟小平. 结构全寿命的耐久性与安全性、适用性的关系[J]. 建筑结构学报, 2009, 30(6):1-7.JIN W L, ZHONG X P. Relationship of structural durability with structural safety and serviceability in whole life cycle[J]. Journal of Architectural Structure,2009,30(6):1-7(in Chinese). [7] 潘洪科, 牛季收, 杨林德, 等. 地下工程砼结构基于碳化作用的耐久性劣化模型[J]. 工程力学, 2008, 25(7):172-178.PAN H K, NIU J S, YANG L D, et al. The durability deterioration model based on carbonation for underground concrete structures[J]. Engineering Mechanics,2008,25(7):172-178(in Chinese). [8] 潘洪科, 边亚东, 杨林德. 钢筋混凝土结构基于耐久性劣化度的可靠性分析[J]. 建筑结构学报, 2011, 32(1):105-109.PAN H K, BIAN Y D, YANG L D. Reliability analysis of reinforced concrete structure based on durability and deterioration grade[J]. Journal of Building Structure,2011,32(1):105-109(in Chinese). [9] LIM S, AKIYAMA M, FRANGOPOL D M, et al. Assessment of the structural performance of corrosion-affected RC members based on experimental study and probabilistic modeling[J]. Engineering Structures,2016,127:189-205. [10] ZHANG M, SONG H, LIM S, et al. Reliability estimation of corroded RC structures based on spatial variability using experimental evidence, probabilistic analysis and finite element method[J]. Engineering Structures,2019,192:30-52. [11] 刘海, 姚继涛, 牛荻涛. 钢筋混凝土结构基于锈胀开裂寿命准则的耐久性设计方法[J]. 西安建筑科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2009, 41(1):25-31.LIU H, YAO J T, NIU D T. Durability design of RC structures based on the life criterion of cover cracking[J]. Journal of Xi’an University of Architecture and Technology (Natural Science Edition),2009,41(1):25-31(in Chinese). [12] 王显利, 郑建军. 钢筋混凝土结构锈胀开裂及裂缝扩展试验研究[J]. 大连理工大学学报, 2009, 49(2):246-253.WANG X L, ZHENG J J. Experimental study of corrosion-induced crack initiation and propagation of reinforced concrete structures[J]. Journal of Dalian University of Technology,2009,49(2):246-253(in Chinese). [13] 唐孟雄, 陈晓斌. 基于扩孔理论的混凝土钢筋锈胀开裂分析[J]. 中南大学学报(自然科学版), 2010, 41(3):1172-1177.TANG M X, CHEN X B. Analysis of rebar rust cover cracking in reinforced concrete with cylindrical cavity expansion theory[J]. Journal of Central South University (Natural Science Edition),2010,41(3):1172-1177(in Chinese). [14] 毛江鸿, 金伟良, 李志远, 等. 氯盐侵蚀钢筋混凝土桥梁耐久性提升及寿命预测[J]. 中国公路学报, 2016, 29(1):61-66. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2016.01.008MAO J H, JIN W L, LI Z Y, et al. Durability improvement and service life prediction of reinforced concrete bridge under chloride attack[J]. Journal of China Highway,2016,29(1):61-66(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-7372.2016.01.008 [15] 陈梦成, 袁素叶. 多重因素下混凝土氯离子扩散CA模型及寿命预测[J]. 铁道建筑, 2016(9):134-138. doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1995.2016.09.34CHEN M C, YUAN S Y. Cellular automata model chloride ions diffusion in concrete influenced by multi-factors and life prediction of concrete[J]. Railway construction,2016(9):134-138(in Chinese). doi: 10.3969/j.issn.1003-1995.2016.09.34 [16] 关博文, 杨涛, 於德美, 等. 干湿循环作用下钢筋混凝土氯离子侵蚀与寿命预测[J]. 材料导报, 2016, 30(20):152-157.GUAN B W, YANG T, YU D M, et al. Chloride erosion life prediction of steel reinforced concrete under dry and wet cycles[J]. Materials Reports,2016,30(20):152-157(in Chinese). [17] GHAVIJORBOZEH R, HAMADANI A Z. Application of the mixed Weibull distribution in machine reliability analysis for a cell formation problem[J]. International Journal of Quality & Reliability Management,2017,34(1):128-142. [18] LOWE P, LEWIS W. Reliability analysis based on the Weibull distribution: An application to maintenance float factors[J]. International Journal of Production Research,1983,21(4):461-470. doi: 10.1080/00207548308942382 [19] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 混凝土耐久性设计标准: GB/T 50476—2019[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2019.Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development People’s Republic of China. Standard for design of concrete structure durability: GB/T 50476—2019[S], Beijing: China Building Industry Press, 2019(in Chinese). [20] 朱彬荣. 基于概率方法的西部地区混凝土结构材料服役寿命预测[D]. 兰州: 兰州理工大学, 2017.ZHU B R. Service life prediction for concrete structure materials in western region of China based on probabilistic method[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University of Technology, 2017(in Chinese). [21] 李岩, 蔡跃波, 葛燕, 等. 用交流阻抗谱研究活性砂浆胶结材料的电化学行为[J]. 硅酸盐学报, 2013, 41(2):199-204.LI Y, CAI Y B, GE Y, et al. Electrochemical performance of active mortar cementitious materials via AC impedance spectroscopy[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society,2013,41(2):199-204(in Chinese). [22] 乔国富. 混凝土结构钢筋腐蚀的电化学特征与监测传感器系统[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2008.QIAO G F. Electrochemical characteristics and monitoring sensor system of the corrosion of the steel bar in concrete structure[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2008(in Chinese). [23] ERDOGDU S, BREMNER T W, KONDRATOVA I L. Accelerated testing of plain and epoxy-coated reinforcement in simulated seawater and chloride solutions[J]. Cement and Concrete Research,2001,31(6):861-867. doi: 10.1016/S0008-8846(01)00487-2 [24] ASTM International. Standard test method for corrosion potentials of uncoated reinforcing steel in concrete: ASTM C876—15[S]. West Conshohocken: ASTM International, 2015. [25] 郭飞, 费庆国, 李彦斌, 等. 基于Weibull模型的C/C复合材料销钉剪切强度分布及本构关系[J]. 复合材料学报, 2019, 36(2):461-468.GUO F, FEI Q G, LI Y B, et al. Shear strength distribution and constitutive model of C/C composite on Weibull model[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2019,36(2):461-468(in Chinese). [26] 韩旭旭, 张程煜, 陈博, 等. 2D-SiCf/SiC复合材料抗拉强度统计分布规律[J]. 复合材料学报, 2019, 36(2):434-440.HAN X X, ZHANG C Y, CHEN B, et al. Statistical distribution of tensile strength of a 2D-SiCf/SiC composite[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2019,36(2):434-440(in Chinese). -





 下载:
下载: