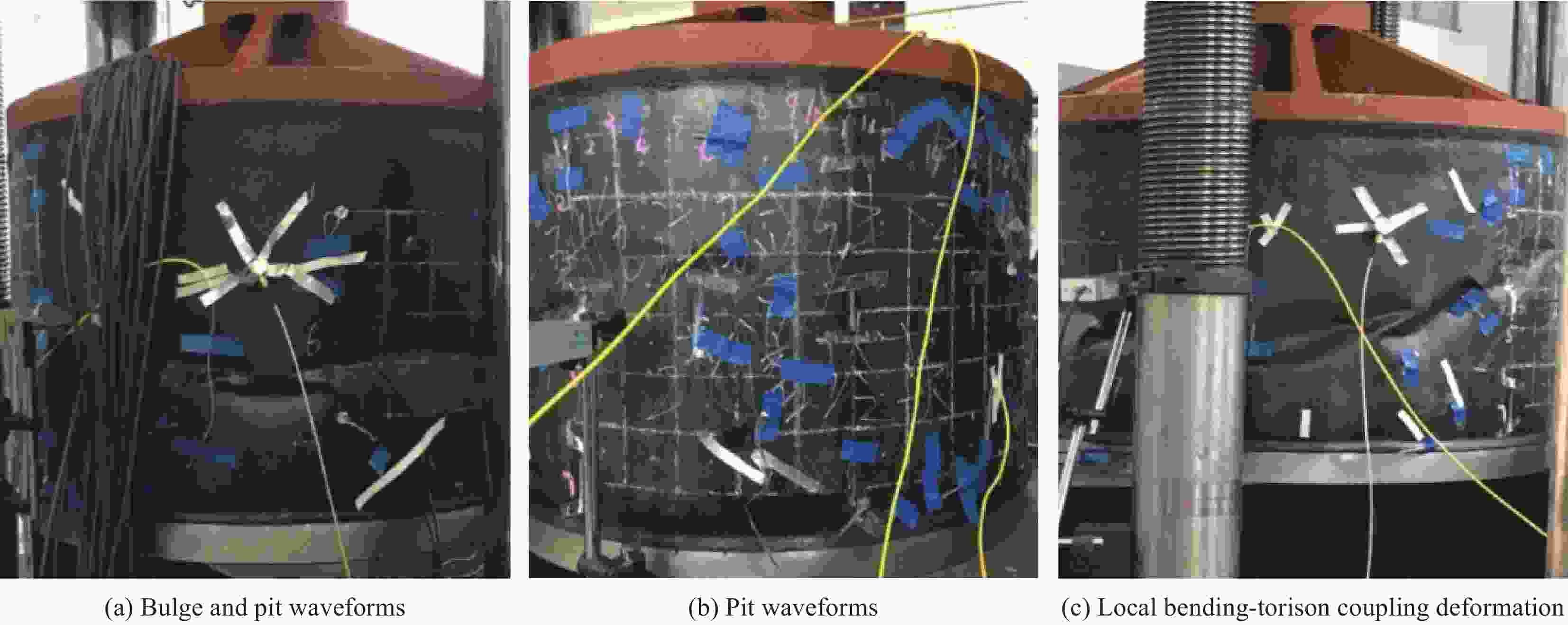
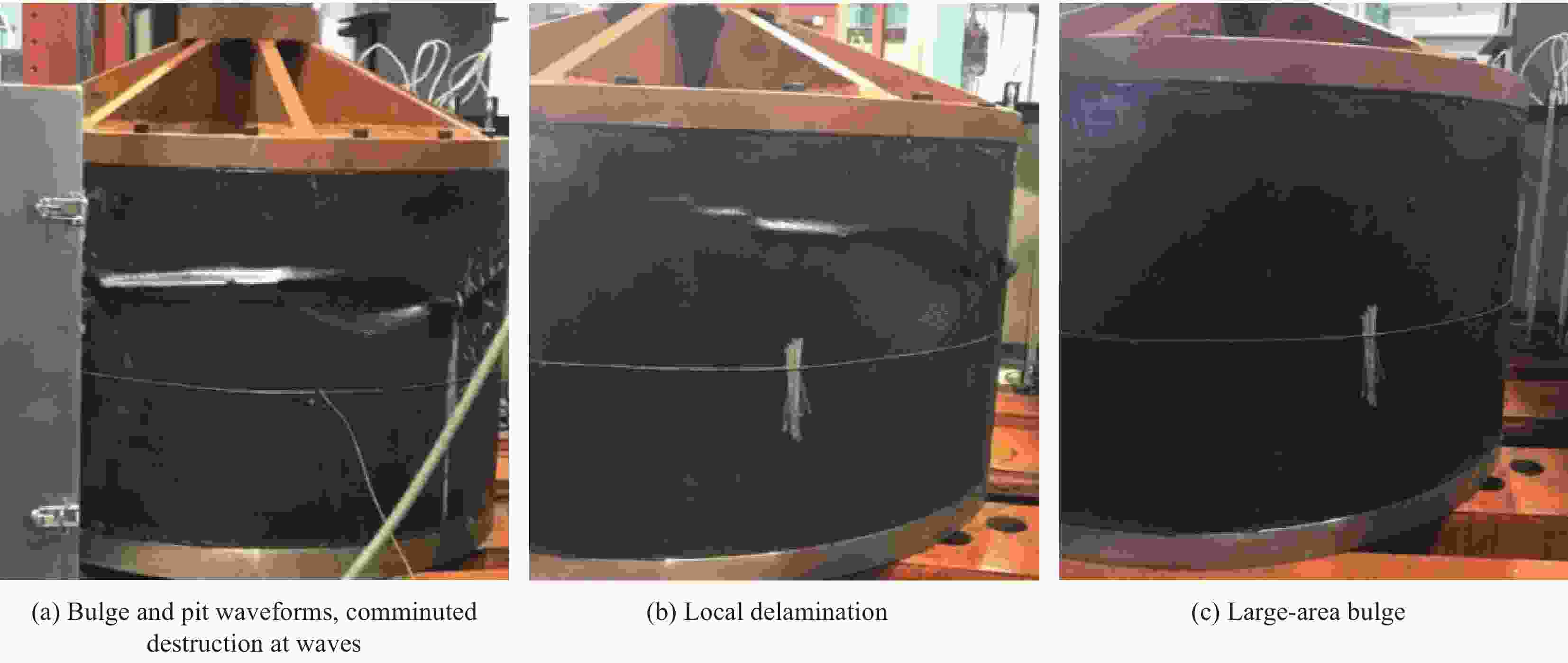
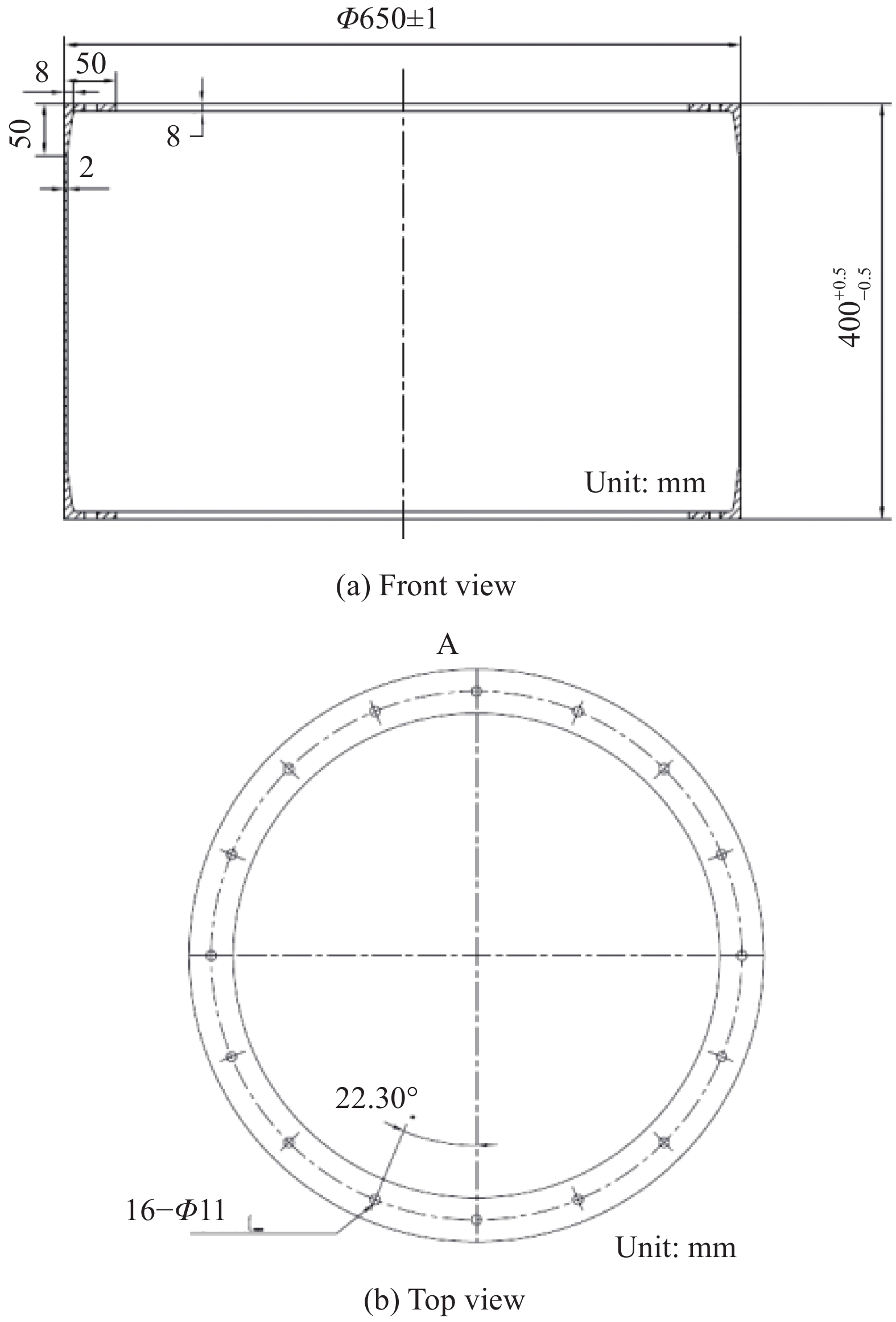
Load-bearing capability of laminated MT300/KH420 carbon fiber/polyimide resin composite cylindrical shell at high temperatures
-
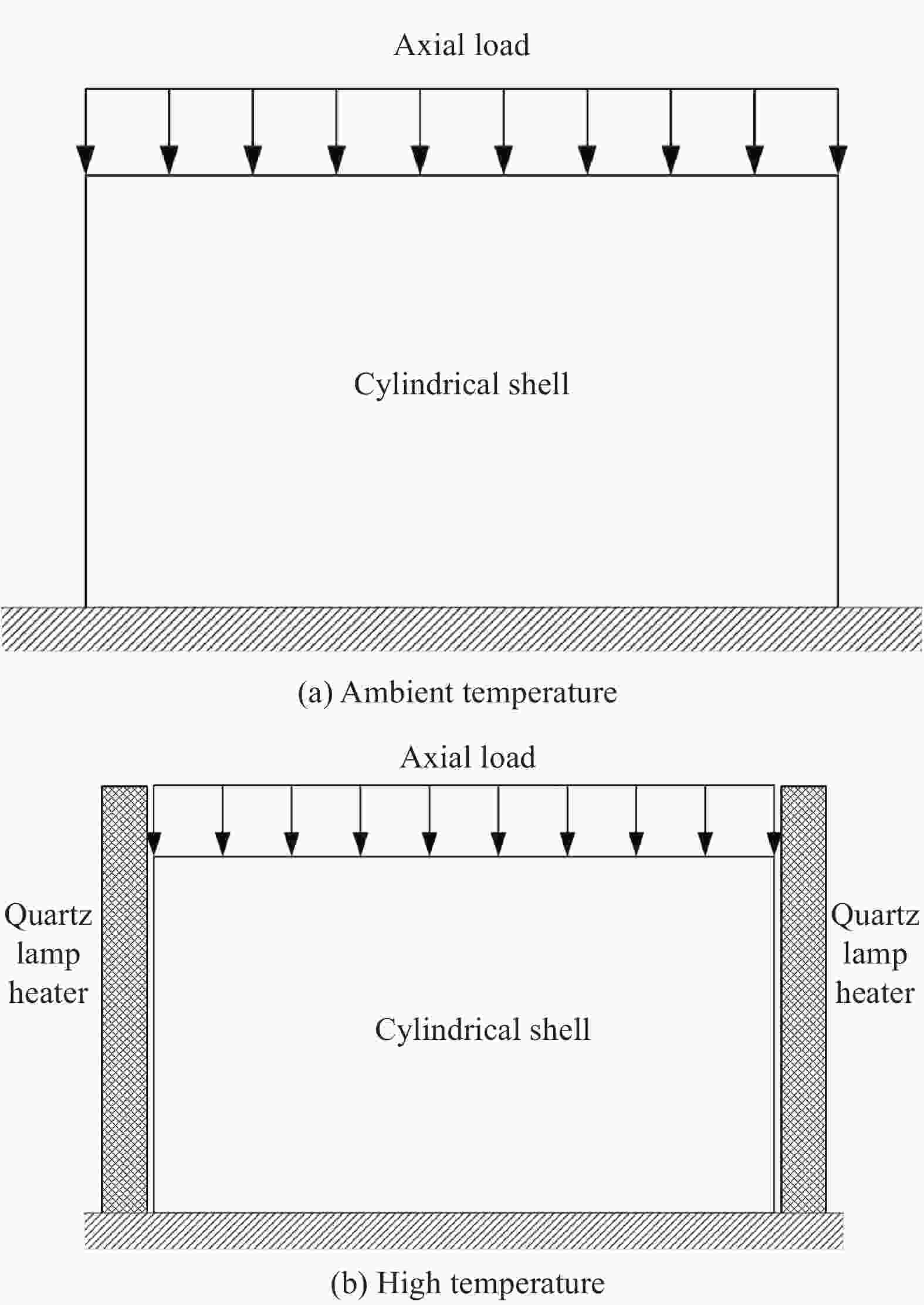
摘要: 基于Donnell-Mushtali近似理论及热弹性理论,考虑结构热变形和材料高温性能衰减等温度影响因素,对MT300/KH420碳纤维/聚酰亚胺树脂复合材料圆柱壳在常温、420℃及周向210~420℃不均匀温度场等热载工况下的承载性能进行了理论分析。并引入一阶屈曲模态缺陷作为几何初始扰动,利用ABAQUS,采用非线性显式动力学方法完成对MT300/KH420复合材料圆柱壳在以上热载工况下的轴压稳定性有限元仿真计算,计算结果与理论分析较为一致。设计并开展MT300/KH420复合材料圆柱壳力-热载荷联合轴压试验,获得圆柱壳在以上热载工况下的破坏载荷和破坏模式。研究表明:高温工况下,力学性能衰减和温场不均匀引起的结构热变形是影响MT300/KH420复合材料圆柱壳轴向失稳载荷的主要因素。Abstract: Based on Donnell-Mushtali approximate theory, combined with thermal elasticity theory, the axial load-bearing capability of MT300/KH420 carbon fiber/polyimide resin composite shell at ambient temperature, 420℃ and circumferential temperature distribution of 210–420℃ were evaluated by analytical methods, taking into consideration of the thermal deformation of structure, material’s degradation and other terms at high temperatures. In addition, the FEM analysis model was established by ABAQUS, which introduced the 1st buckling mode generated by buckle analysis as the original imperfection, and then studied the axial stability characteristics of MT300/KH420 composite shells by non-linear explicit dynamic method. The instability load and buckling mode are both presented which agree with the results obtained by analytical method. Furthermore, a thermal-mechanical joint axial compression test was designed and implemented, thus the failure loads and modes were obtained at above thermal fields. The results indicate that the material’s degradation and asymmetry deformation caused by non-uniform thermal fields are principal factors which impact the load-bearing capability of MT300/KH420 composite shells at high temperatures.
-
表 1 材料性能参数
Table 1. Material property parameters
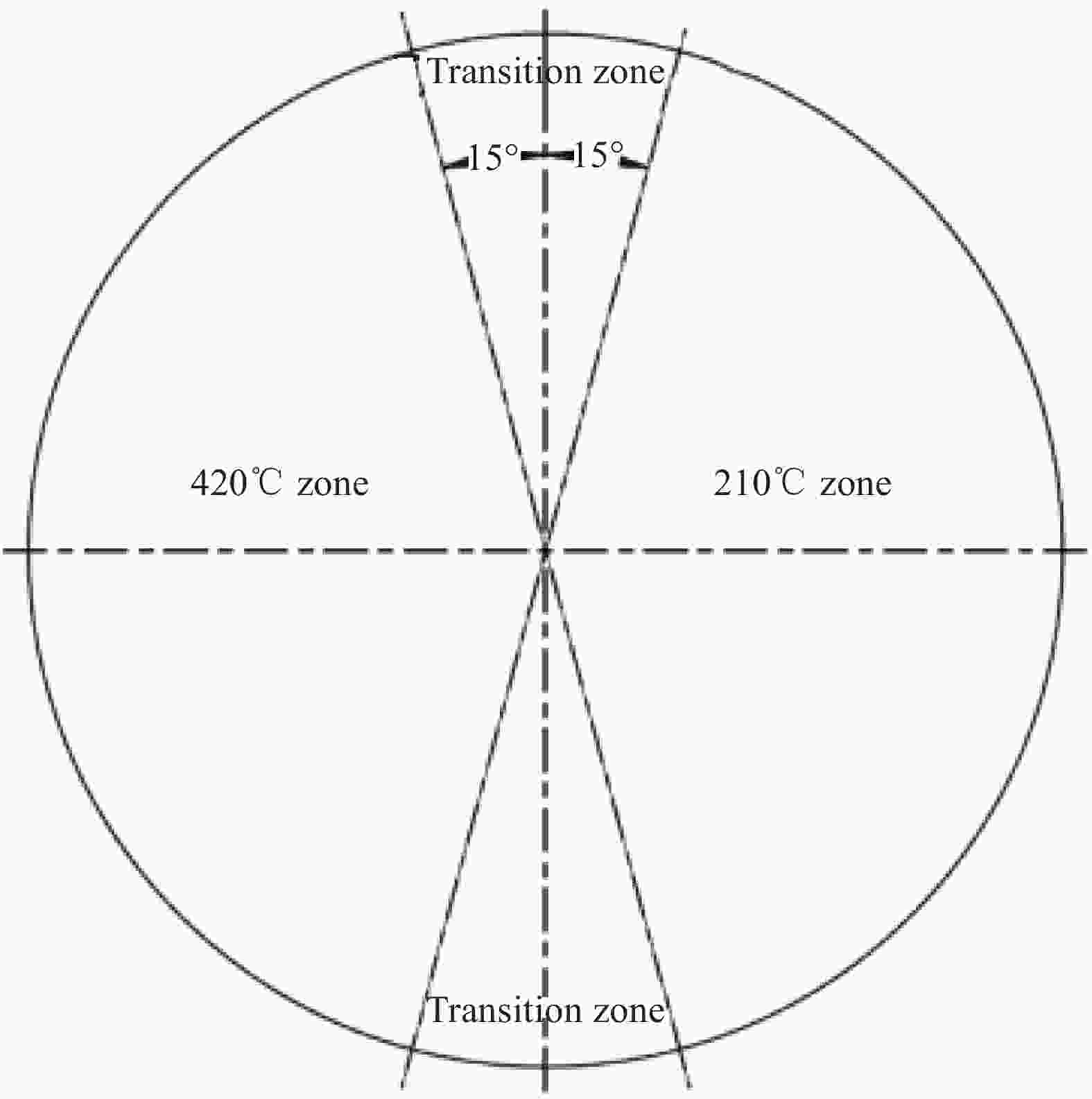
Temperature/℃ Engineering constant Expansion coefficient ${E_x}$/MPa ${E_y}$/MPa ${E_{\rm{s}}}$/MPa ${\nu _x}$ ${\alpha _x}$/10−7 ${\alpha _y}$/10−5 Ambient temperature 110700 9120 3700 0.32 5.2 3.33 210 99630/90% 8208/90% 2960/80% 0.32 5.2 3.33 420 88560/80% 7296/80% 2220/60% 0.32 5.2 3.33 Notes: 55350/50% means ${E_x}$=55350 MPa,which is 50% of the value at ambient temperature; ${E_x}$, ${E_y}$, ${E_{\rm{s}}}$—Modulus in longitudinal, transverse and shear directions, respectively; ${\nu _x}$—Poisson’s ratio; ${\alpha _x}$, ${\alpha _y}$—Coefficients of thermal expansion in longitudinal and transverse directions, respectively. 表 2 MT300/KH420复合材料圆柱壳轴压稳定性理论分析结果
Table 2. Theoretical analysis results of axial stability characteristics of MT300/KH420 composite cylindrical shell
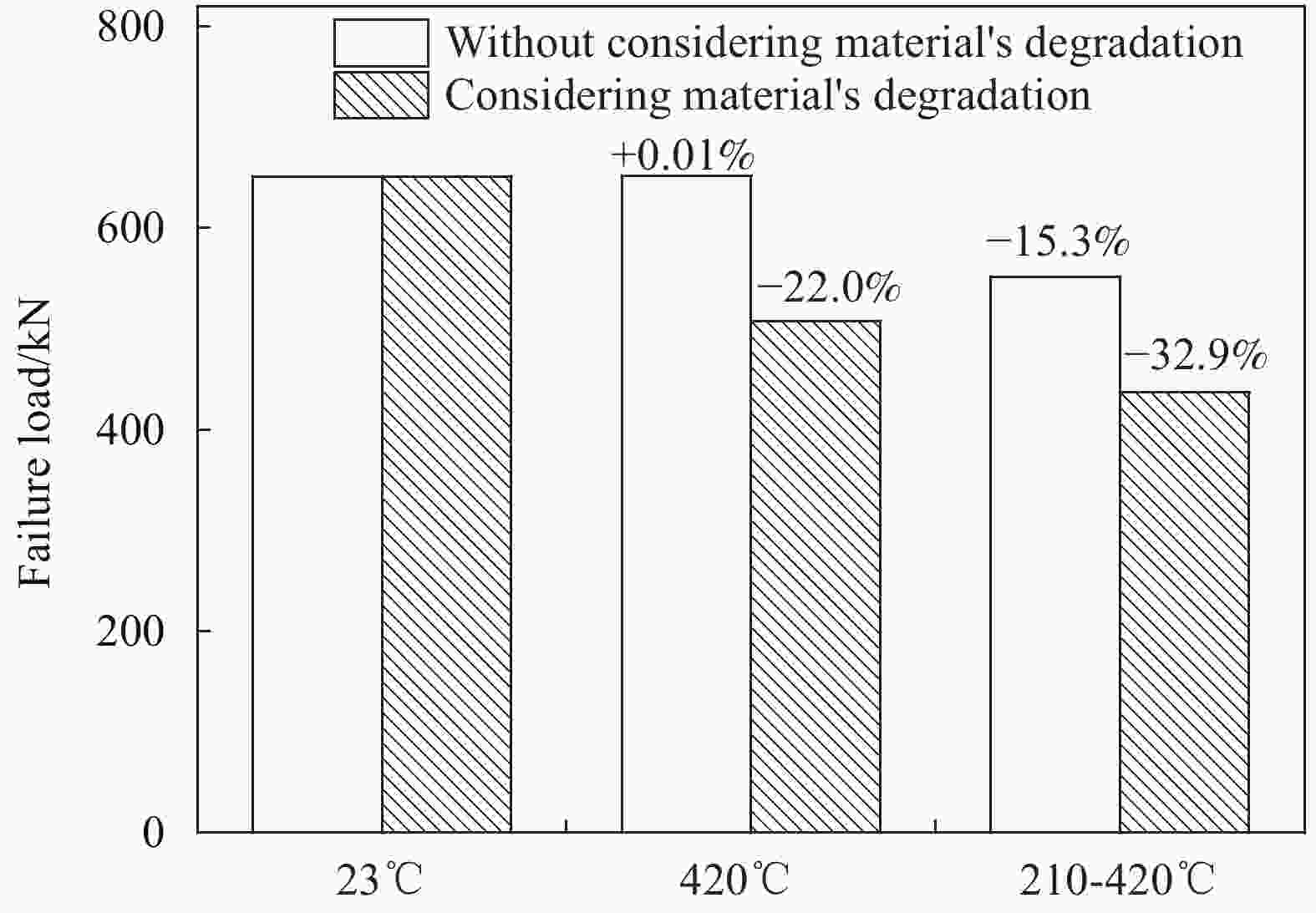
Material’s degradation Ambient temperature 420℃ 210–420℃ Without considering
material’s degradationBuckling load/kN 651.12 651.20 551.70 Change rate/% — 0.01 −15.3 Considering material’s degradation Buckling load/kN 651.12 507.80 437.06 Change rate/% — −22.0 −32.9 表 3 MT300/KH420复合材料圆柱壳轴压稳定性非线性显式动力学分析结果
Table 3. FEM analysis results of axial stability characteristics of MT300/KH420 composite cylindrical shell by non-linear explicit dynamic method
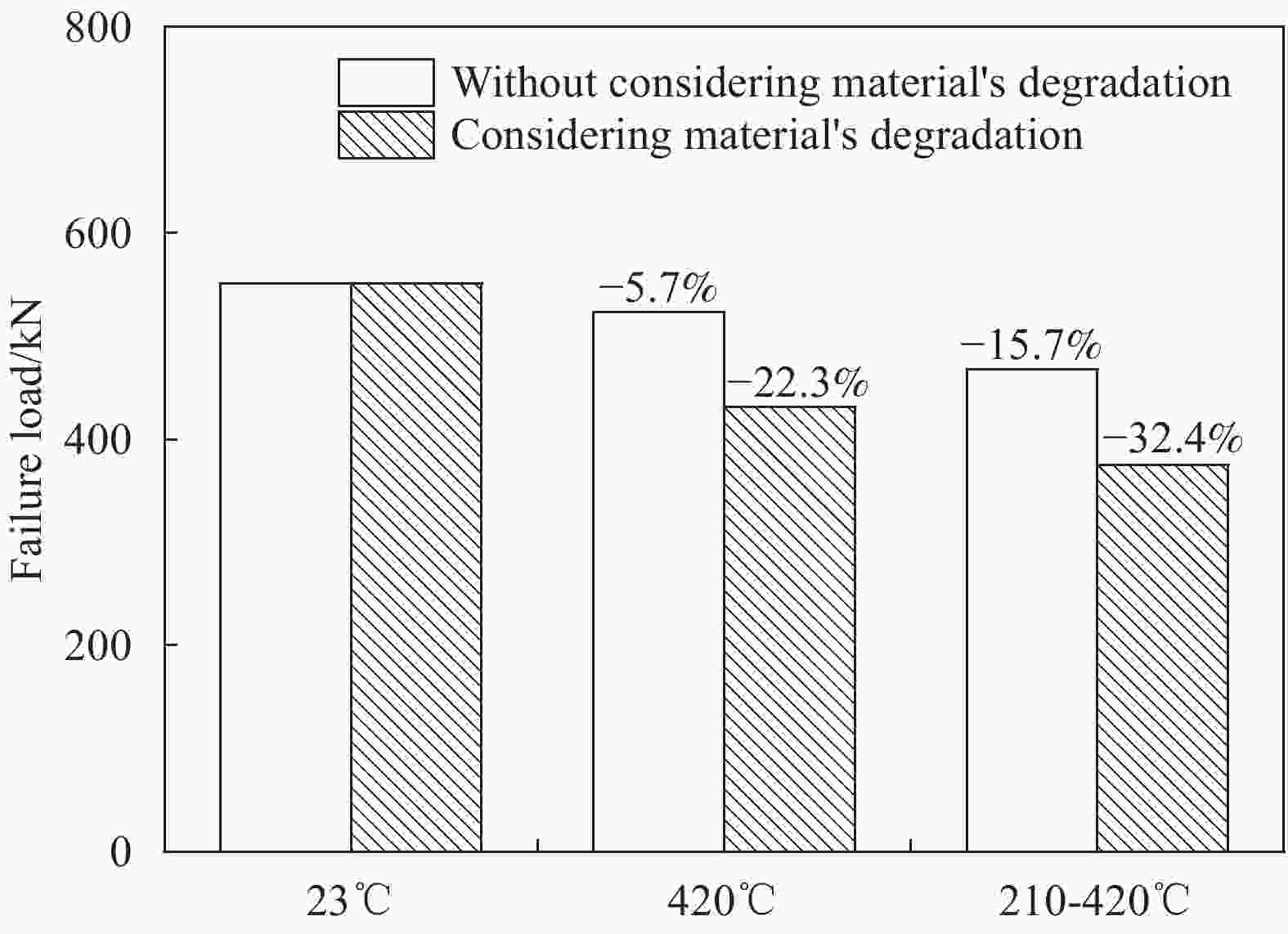
Material’s degradation Ambient temperature 420℃ 210–420℃ Without considering
material’s degradationBuckling load/kN 554.88 523.15 467.47 Change rate/% — −5.7 −15.7 Considering material’s degradation Buckling load/kN 554.88 431.26 375.26 Change rate/% — −22.3 −32.4 表 4 各载荷工况下MT300/KH420复合材料圆柱壳轴压破坏载荷
Table 4. Axial failure loads of MT300/KH420 composite cylindrical shell at different load conditions
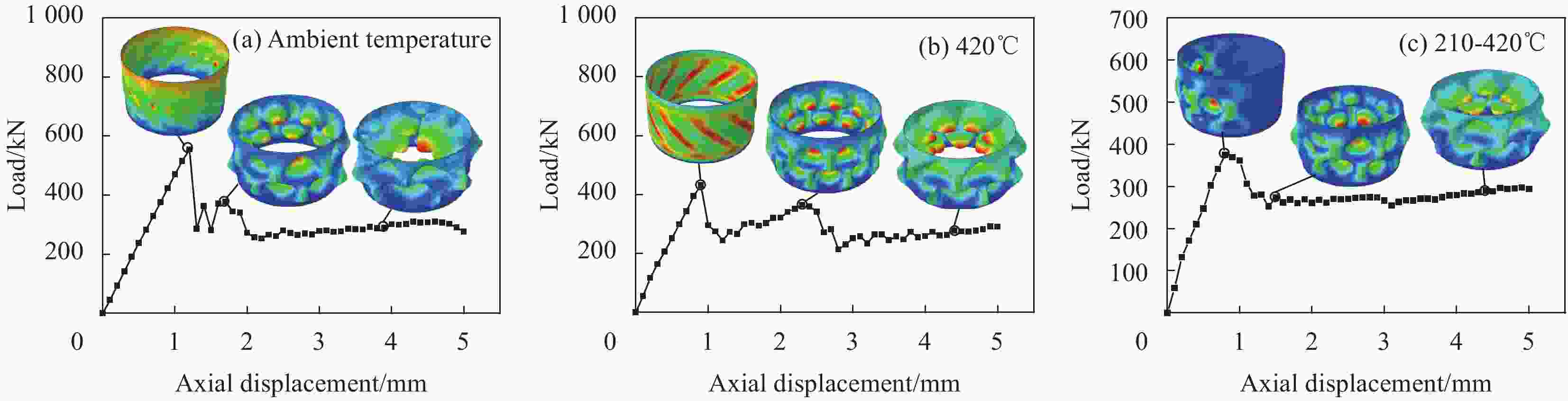
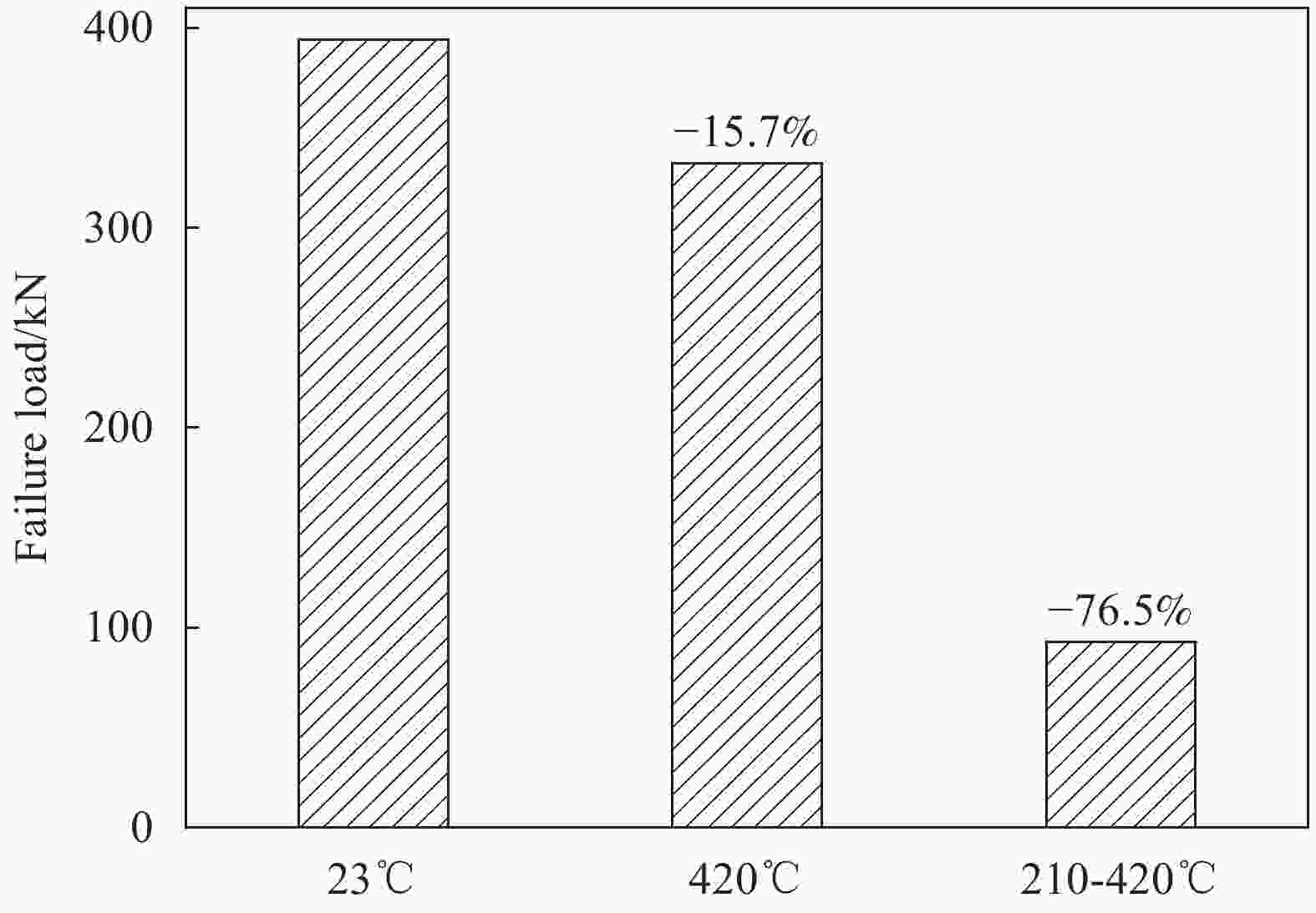
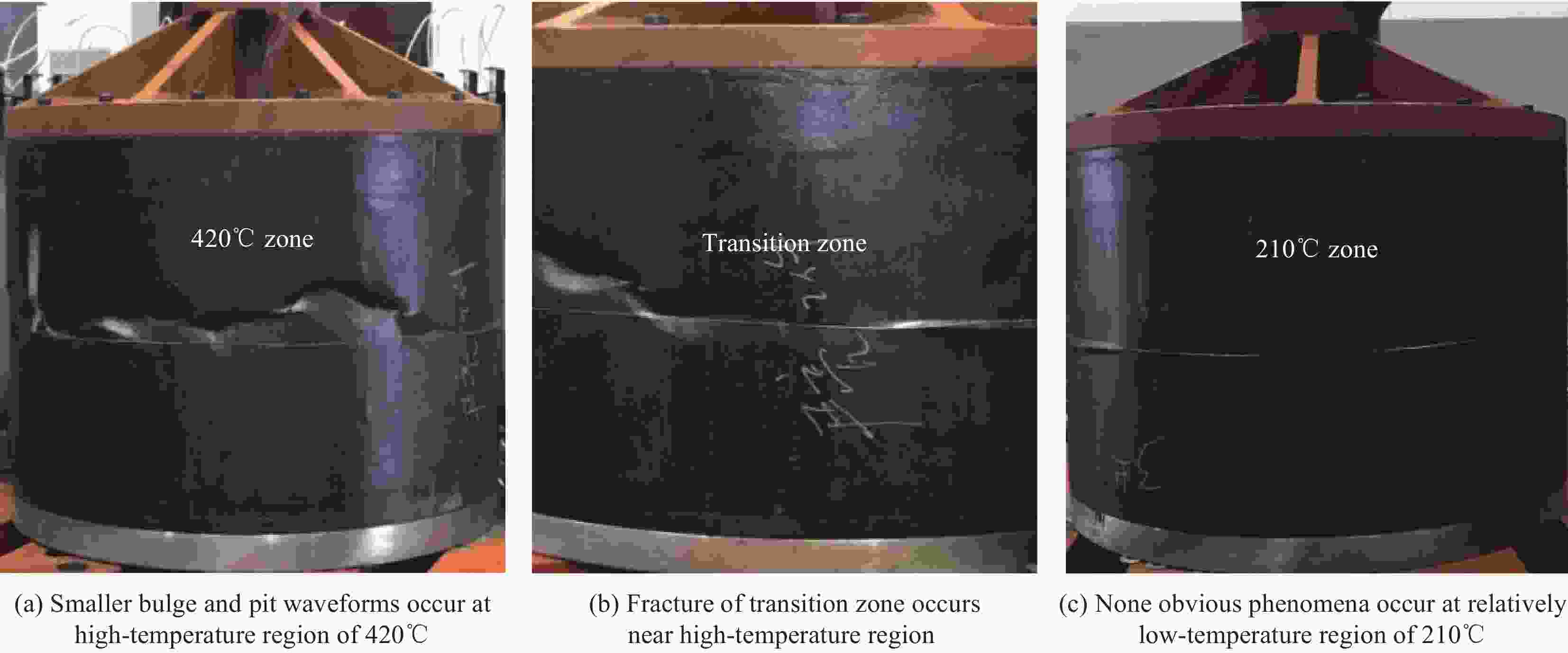
Buckling load Ambient temperature 420℃ 210–420℃ Load/kN 394.1 332.2 92.7 Change rate/% — −15.7 −76.5 表 5 MT300/KH420复合材料圆柱壳轴压稳定性理论及有限元分析与试验结果对比
Table 5. Results comparison of analytical methods, FEM analysis and experimental study of axial stability characteristics of MT300/KH420 composite cylindrical shell
Analysis method Ambient temperature 420℃ 210–420℃ Theoretical analysis Buckling load/kN 651.12 507.80 437.06 Change rate/% — −22.0 −32.9 FEM analysis Buckling load/kN 554.88 431.26 375.26 Change rate/% — −22.3 −32.4 Experimental study Buckling load/kN 394.1 332.2 92.7 Change rate/% — −15.7 −76.5 -
[1] GANAPATHI M, ANIRUDH B, ADITYA N D, et al. Thermal buckling behaviour of variable stiffness laminated composite plates[J]. Materials Today Communications,2018,16(5):142-151. [2] 沈惠申. 湿热环境中复合材料层合圆柱薄壳的屈曲和后屈曲[J]. 应用数学和力学, 2020, 22(3):228-238.SHEN H S. Buckling and postbuckling of laminated thin cylindrical shells under hygrothermal environments[J]. Applied Mathematics and Mechanics,2020,22(3):228-238(in Chinese). [3] BIRMAN V, BERT C W. Buckling and post-buckling of composite plates and shells subjected to elevated temperature[J]. Journal of applied mechanics,1993,60(2):514-519. doi: 10.1115/1.2900823 [4] ESLAMI M R. Buckling of composite cylindrical shells under mechanical and thermal loads[J]. Journal of Thermal Stresses,2010,33(11):527-545. [5] MA S F, WILCOX M W. Thermal buckling of antisymmetric angle-ply laminated cylindrical shells[J]. Composites Engineering,1991,1(3):183-192. doi: 10.1016/0961-9526(91)90018-N [6] HOUDAYFA O, ABDELOUAHAB T, ADEL B, et al. Thermal buckling behavior of laminated composite plates: A finite-element study[J]. Frontiers of Mechanical Engineering,2014,9(1):41-49. doi: 10.1007/s11465-014-0284-z [7] SHEN H S. Boundary layer theory for the buckling and postbuckling of an anisotropic laminated cylindrical shell Part Ⅰ: Prediction under axial compression[J]. Composite Structures,2008,82(3):346-361. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2007.01.024 [8] SHEN H S. Boundary layer theory for the buckling and postbuckling of an anisotropic laminated cylindrical shell Part Ⅱ: Prediction under external pressure[J]. Composite Structures,2008,82(3):362-370. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2007.01.018 [9] SHEN H S. Boundary layer theory for the buckling and postbuckling of an anisotropic laminated cylindrical shell Part Ⅲ: Prediction under torsion[J]. Composite Structures,2008,82(3):371-381. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2007.01.013 [10] SHEN H S. Thermal postbuckling behavior of anisotropic laminated cylindrical shells with temperature-dependent properties[J]. AIAA Journal,2008,46(1):185-93. doi: 10.2514/1.31192 [11] SHEN H S, XIANG Y. Thermal buckling and postbuckling behavior of FG-GRC laminated cylindrical shells with temperature-dependent material properties[J]. Meccania,2019,54:283-297. doi: 10.1007/s11012-019-00945-0 [12] PATEL B P. Thermal postbuckling characteristics of laminated conical shells with temperature-dependent materials properties[J]. AIAA Journal,2005,43(6):1380-1388. doi: 10.2514/1.13259 [13] THANGARATNAM R K. Thermal buckling of laminated composite shells[J]. AIAA Journal,1990,28(5):859-860. doi: 10.2514/3.25130 [14] 李钟海, 程小全, 汪源龙, 等. 复合材料柱面壳压缩性能分析[J]. 复合材料学报, 2011, 28(1):206-210.LI Z H, CHENG X Q, WANG Y L, et al. Compressive properties analysis of composite cylindrical shells[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2011,28(1):206-210(in Chinese). [15] TRABELSI S, FRIKHA A, ZGHAL S, et al. A modified FSDT-based four nodes finite shell element for thermal buckling analysis of functionally graded plates and cylindrical shells[J]. Engineering Structures,2019,178:444-459. doi: 10.1016/j.engstruct.2018.10.047 [16] ROSS B, HOFF N J, HORTON W H. The buckling behavior of uniformly heated thin circular cylindrical shells[J]. Experimental Mechanics, 1966, 6: 529–537. [17] XU J F, ZHAO Q, QIAO P Z. A critical review on buckling and post-buckling analysis of composite structures[J]. Frontiers in Aerospace Engineering,2013,2(3):157-168. [18] 张志民. 复合材料结构力学[M]. 北京: 北京航空航天大学出版社, 1993.ZHANG Z M. Structural mechanics of composite material[M]. Beijing: Beihang University Press, 1993(in Chinese). [19] 张骏华. 复合材料结构设计指南[M]. 北京: 宇航出版社, 1999.ZHANG J H. Guide for structural design of composite materials[M]. Beijing: China Astronautic Publishing House, 1999(in Chinese). [20] 高艺航, 石玉红, 王鲲鹏, 等. 碳纤维增强聚酰亚胺树脂基复合材料MT300/KH420高温力学性能Ⅰ: 拉伸和层间剪切性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2016, 33(6):1206-1213.GAO Y H, SHI Y H, WANG K P, et al. High-temperature mechanical properties of carbon fiber reinforced polyimide resin matrix composites MT300/KH420 Ⅰ: Tensile and interlaminar shear properties[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2016,33(6):1206-1213(in Chinese). [21] 高艺航, 石玉红, 王鲲鹏, 等. 聚酰亚胺树脂基MT300/KH420复合材料高温力学性能Ⅱ: 弯曲性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2016, 33(12):2699-2705.GAO Y H, SHI Y H, Wang K P, et al. High-temperature mechanical properties of polyimide resin matrix MT300/KH420 composites Ⅱ: Flexural properties[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2016,33(12):2699-2705(in Chinese). [22] 杨士勇, 范琳, 陈建升, 等. 高性能聚酰亚胺材料的研究进展[J]. 热固性树脂, 2008, 23(4):32-35.YANG S Y, FAN L, CHEN J S, et al. Research development of polyaimde with high performance[J]. Thermosetting Resin,2008,23(4):32-35(in Chinese). [23] SCHULTZ M R, NEMETH M P. Buckling imperfection sensitivity of axially compressed orthotropic cylinders[C]//51st AIAA/ASME/ASCE/AHS/ASC Structures, Structural Dynamics, and Materials Conference. Florida: AIAA, 2010. [24] 徐荣章, 关志东, 刘璐, 等. 屈曲模态对含缺陷复材加筋板后屈曲的影响[J]. 北京航空航天大学学报, 2014, 40(9):1299-1304.XU R Z, GUAN Z D, LIU L, et al. Effect of buckling mode on performance of post-buckled composite stringer-stiffened panels with debond[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Aeronautics and Astronautics,2014,40(9):1299-1304(in Chinese). [25] 郝鹏, 王博, 李刚, 等. 基于缺陷敏感性分析的加筋圆柱壳结构设计[J]. 应用力学学报, 2013, 30(3):344-349. doi: 10.11776/cjam.30.03.B080HAO P, WANG B, LI G, et al. Structural design of stiffened shells based on imperfectionsensitivity analysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Applied Mechanics,2013,30(3):344-349(in Chinese). doi: 10.11776/cjam.30.03.B080 [26] 殷毓基, 梁珂, 孙秦, 等. 基于非线性有限元降阶方法的网格加筋筒壳结构屈曲承载特性研究[J]. 宇航总体技术, 2019, 3(1):17-22.YIN Y J, LIANG K, SUN Q, et al. Buckling load-carrying capability analysis of grid-stiffened cylinders using a nonlinear finite element reduced-order method[J]. Astronautical Systems Engineering Technology,2019,3(1):17-22(in Chinese). -






 下载:
下载: