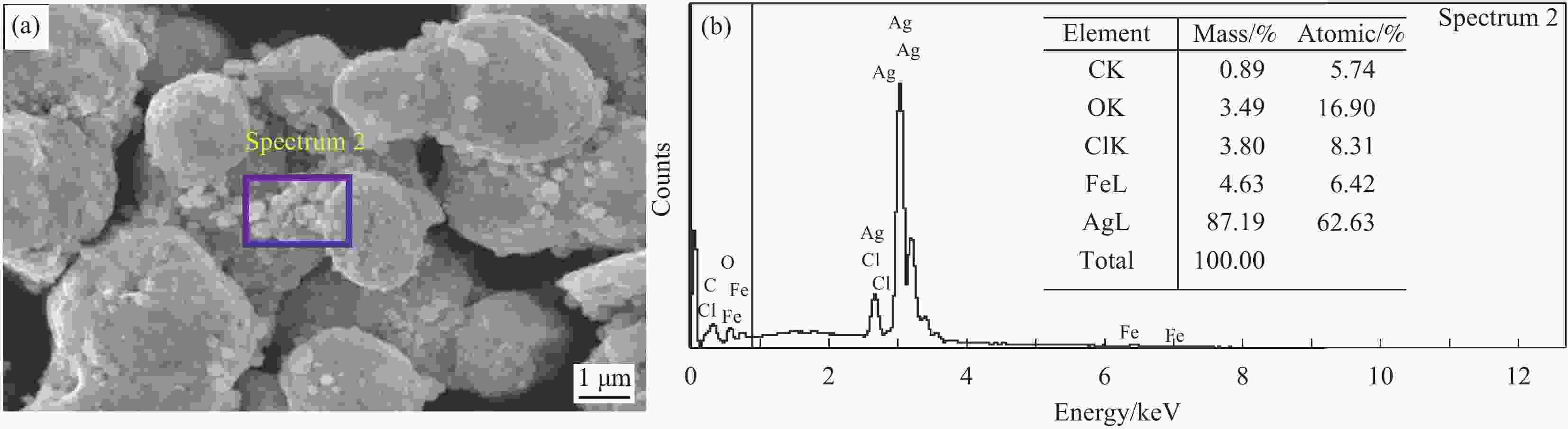
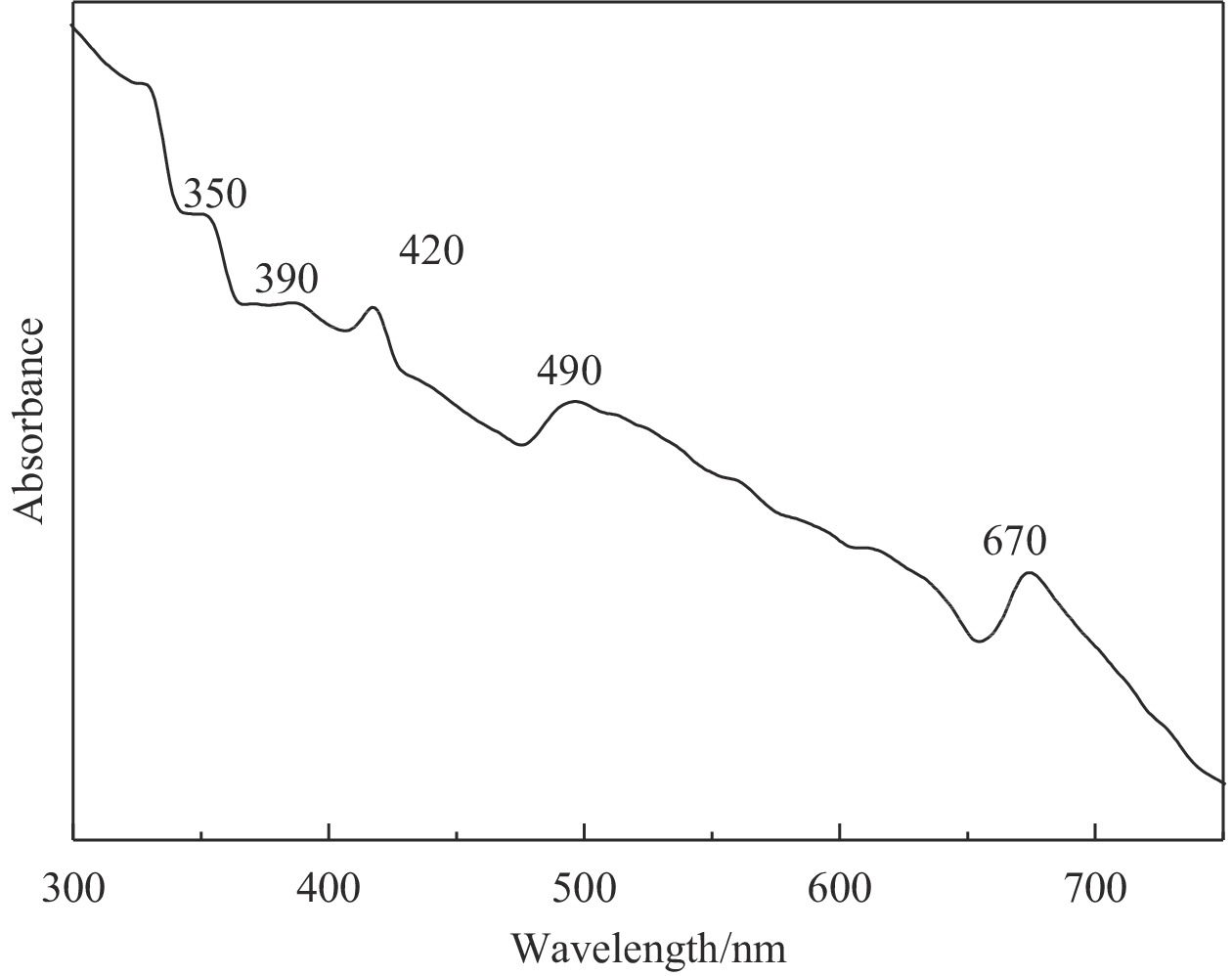
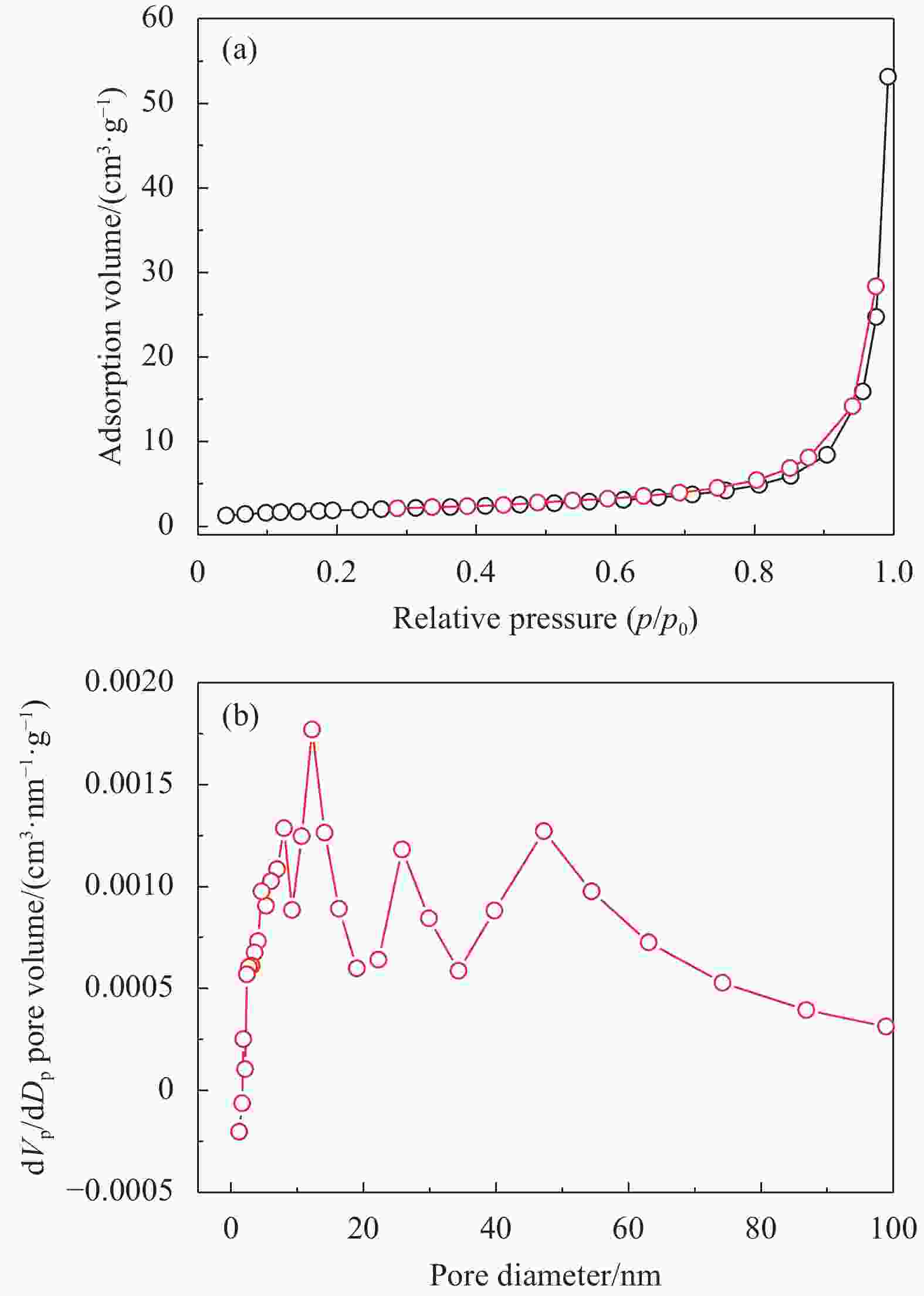
Adsorption and photocatalytic degradation of dyes and heavy metals in printing and dyeing wastewater by Ag@AgCl-Fe3O4/rGO composites
-
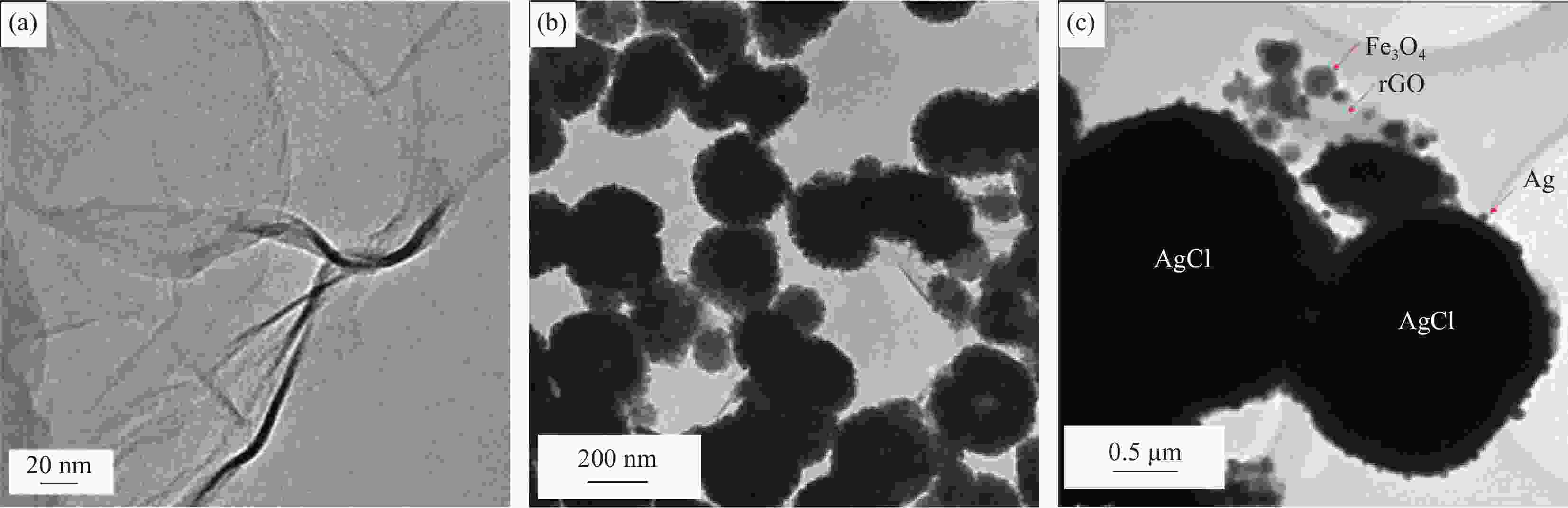
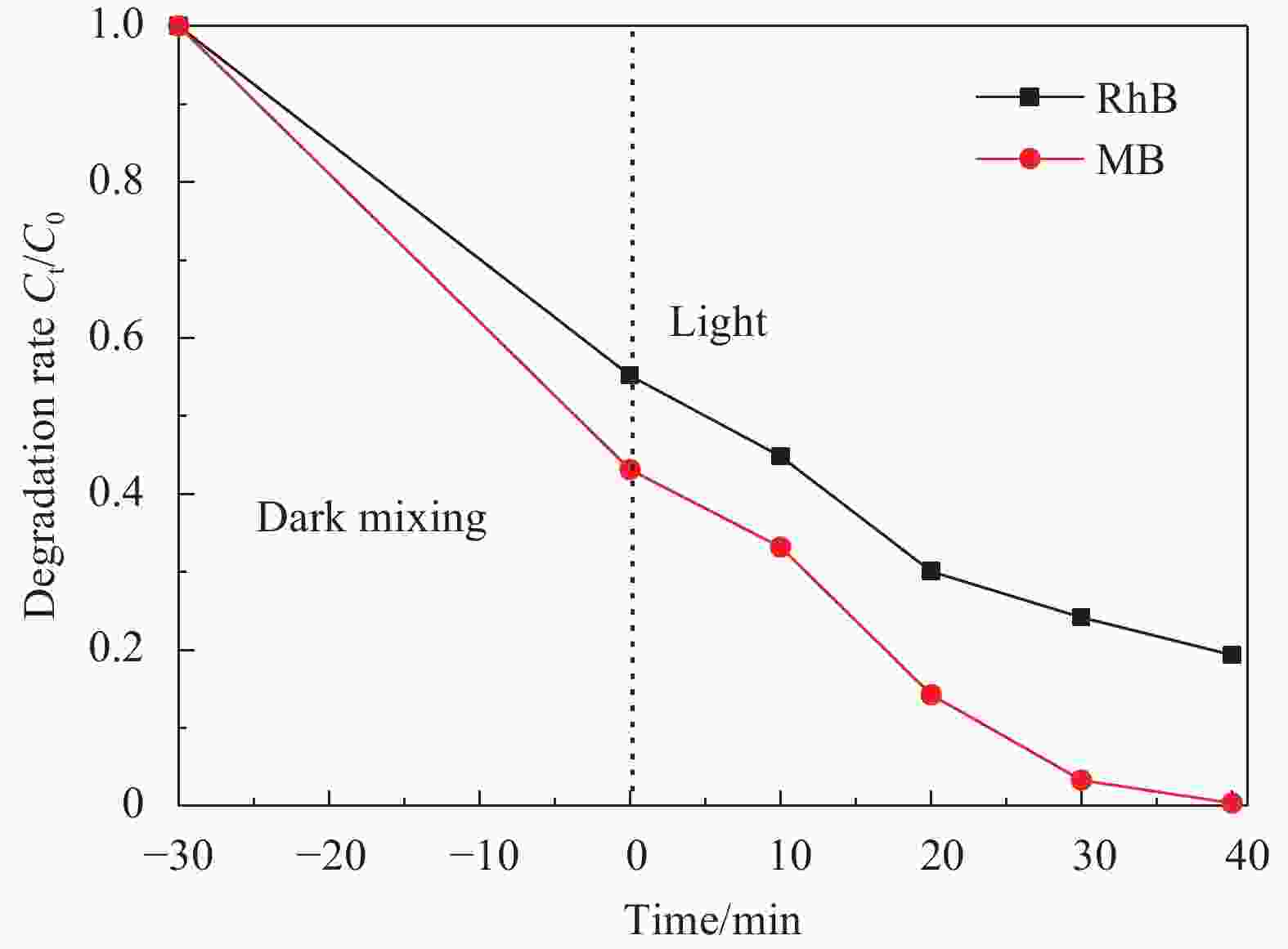
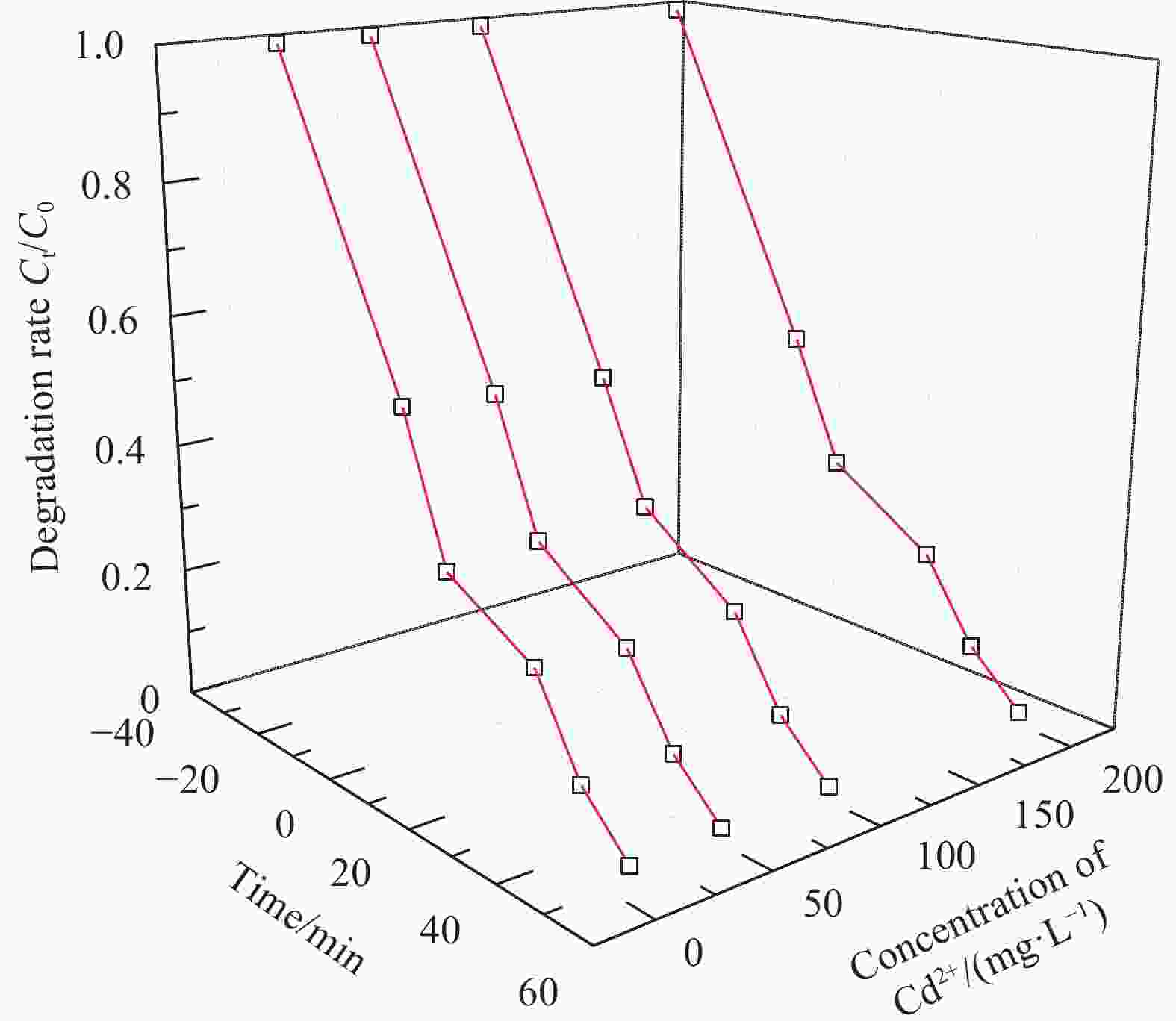
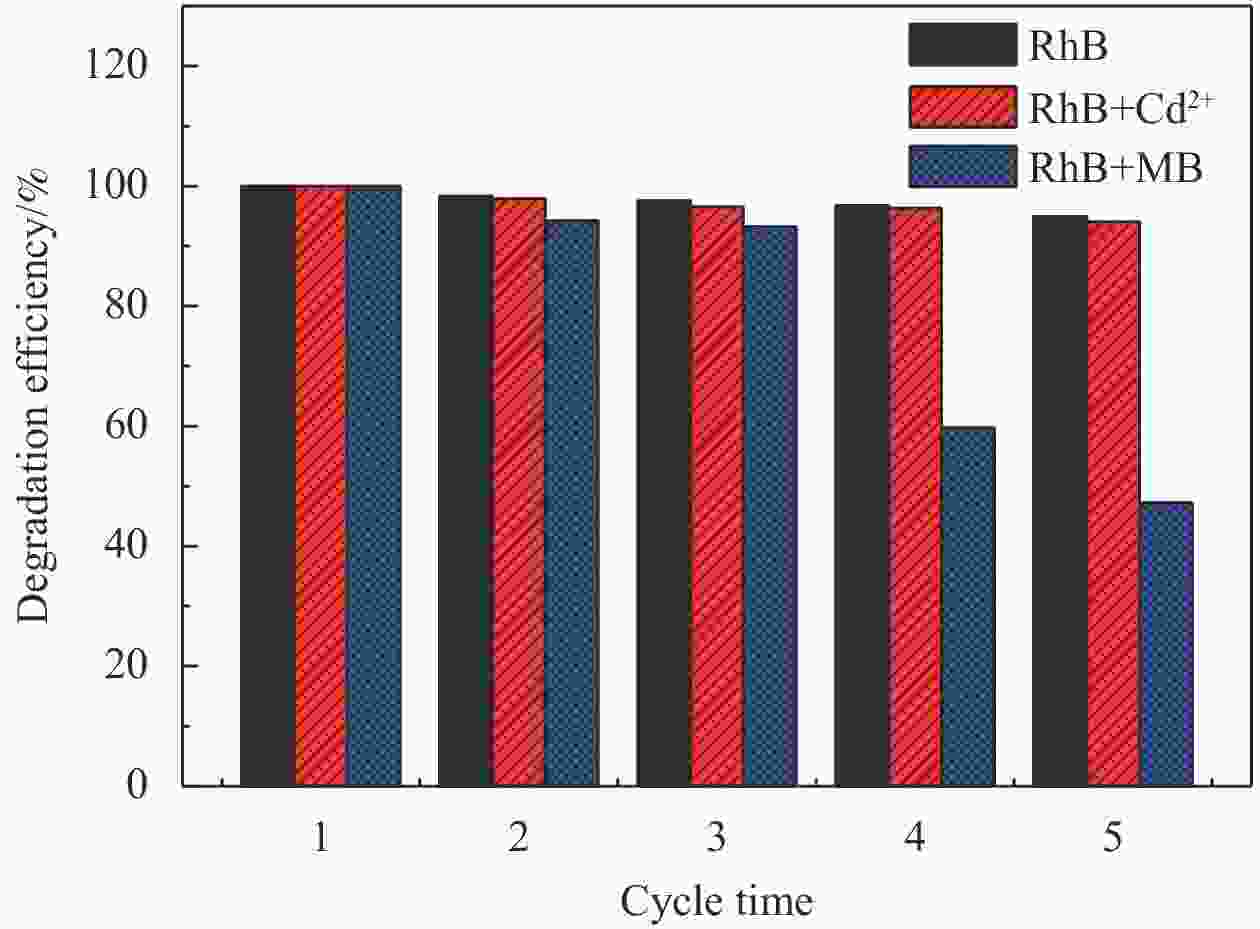
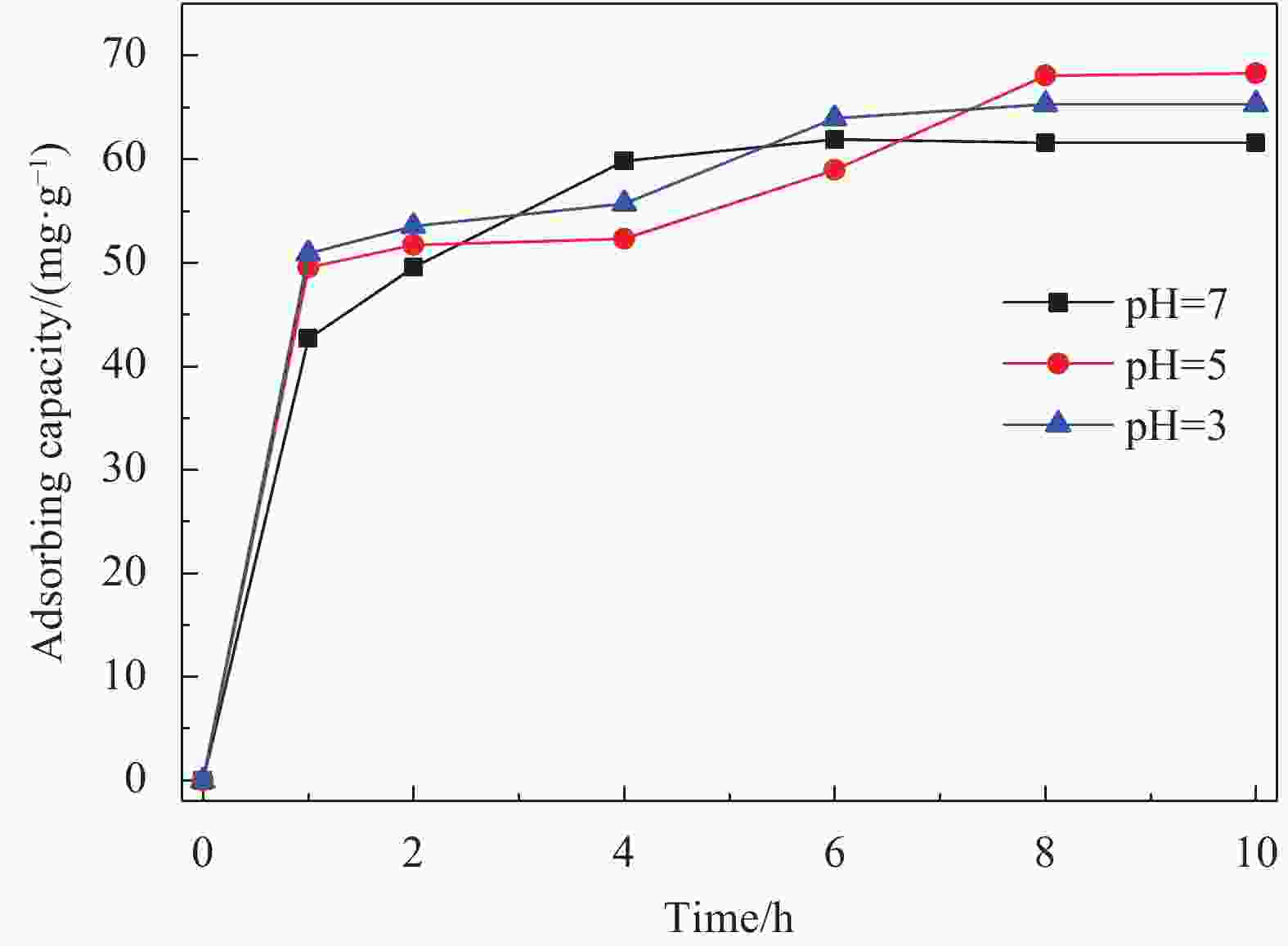
摘要: 依次利用溶剂热法和原位沉积法制备了Ag@AgCl-Fe3O4/还原氧化石墨烯(rGO)复合材料,并对其进行结构和形貌表征。分别以罗丹明B(RhB)和Cd2+为研究对象,探讨了Ag@AgCl-Fe3O4/rGO复合材料吸附和可见光光催化印染废水中重金属离子和芳香族染料的性能,考察了Ag@AgCl-Fe3O4/rGO复合材料中rGO含量、与RhB共存的亚甲基蓝(MB)和Cd2+对RhB降解效果的影响;同时研究了溶液的初始pH值及与Cd2+共存的MB对Cd2+吸附效果的影响。结果表明:Ag@AgCl-Fe3O4/rGO复合材料对RhB的吸附量为47%,可见光照50 min的光催化降解率可达98%;Ag@AgCl-Fe3O4/rGO复合材料的吸附-光催化降解活性随rGO含量的增加而提高;废水中与RhB共存的MB使Ag@AgCl-Fe3O4/rGO复合材料对RhB的降解效率和循环性能受到一定抑制,而与RhB共存的Cd2+对RhB的降解效率和循环性能几乎没有影响。Ag@AgCl-Fe3O4/rGO复合材料对Cd2+也有良好的吸附性能,具有一定的pH值依赖性,在pH值为5时,复合材料对Cd2+的吸附量可达68 mg/g,但废水中MB染料的存在会抑制复合材料对Cd2+的吸附。Abstract: The Ag@AgCl-Fe3O4/reduced graphene oxide (rGO) composites were obtained by solvothermal and in-situ precipitation method. The structure and morphology of the Ag@AgCl-Fe3O4/rGO composites were characterized. The effects of rGO content, other organic dyes (such as methylene blue (MB)) and heavy metal ions (such as Cd2+) co-existing with Rhodamine B (RhB) on the degradation of RhB were investigated, and the effects of initial pH value and other organic dyes (such as MB) co-existing with Cd2+ on the adsorption of Cd2+ were also studied. The results show that about 47% of RhB can be absorbed to Ag@AgCl-Fe3O4/rGO composites in the dark and the degradation of RhB could reach 98% within 50 min visible-light irradiation, and the adsorption-photocatalytic activity of the Ag@AgCl-Fe3O4/rGO composites increases with the increasing rGO content. The degradation efficiency on RhB and the good cycle performance of the catalyst will be suppressed by the coexisted MB, but are almost unaffected by the coexisted Cd2+. For the Cd2+ solution system, the adsorption amount of Cd2+ on Ag@AgCl-Fe3O4/rGO composites varies with the pH value and the adsorption capacity at pH=5 can be up to 68 mg/g. However, the adsorption of Cd2+ will be restrained by the presence of MB in wastewater.
-
Key words:
- graphene /
- Fe3O4 /
- Ag@AgCl /
- adsorption /
- photocatalytic degradation
-
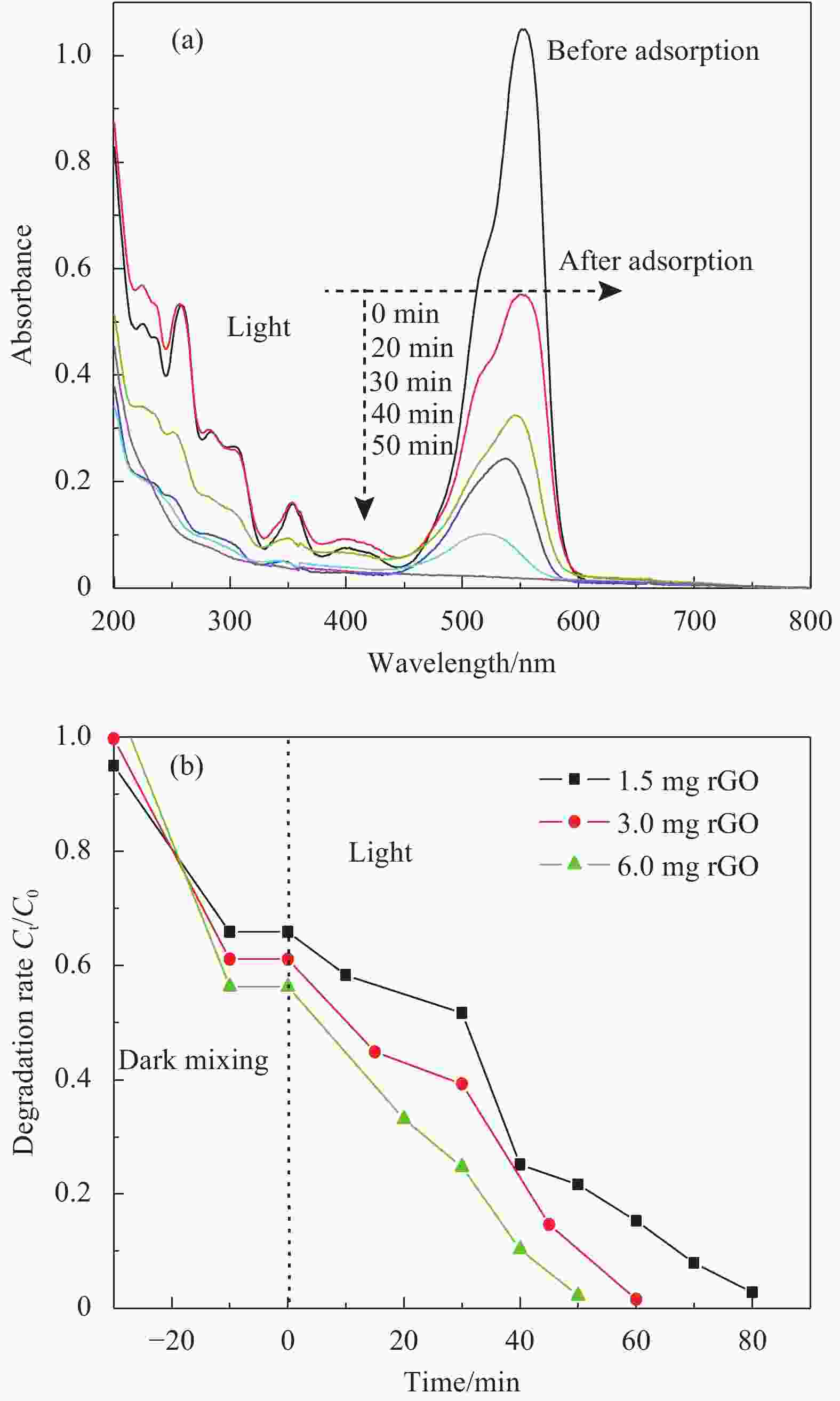
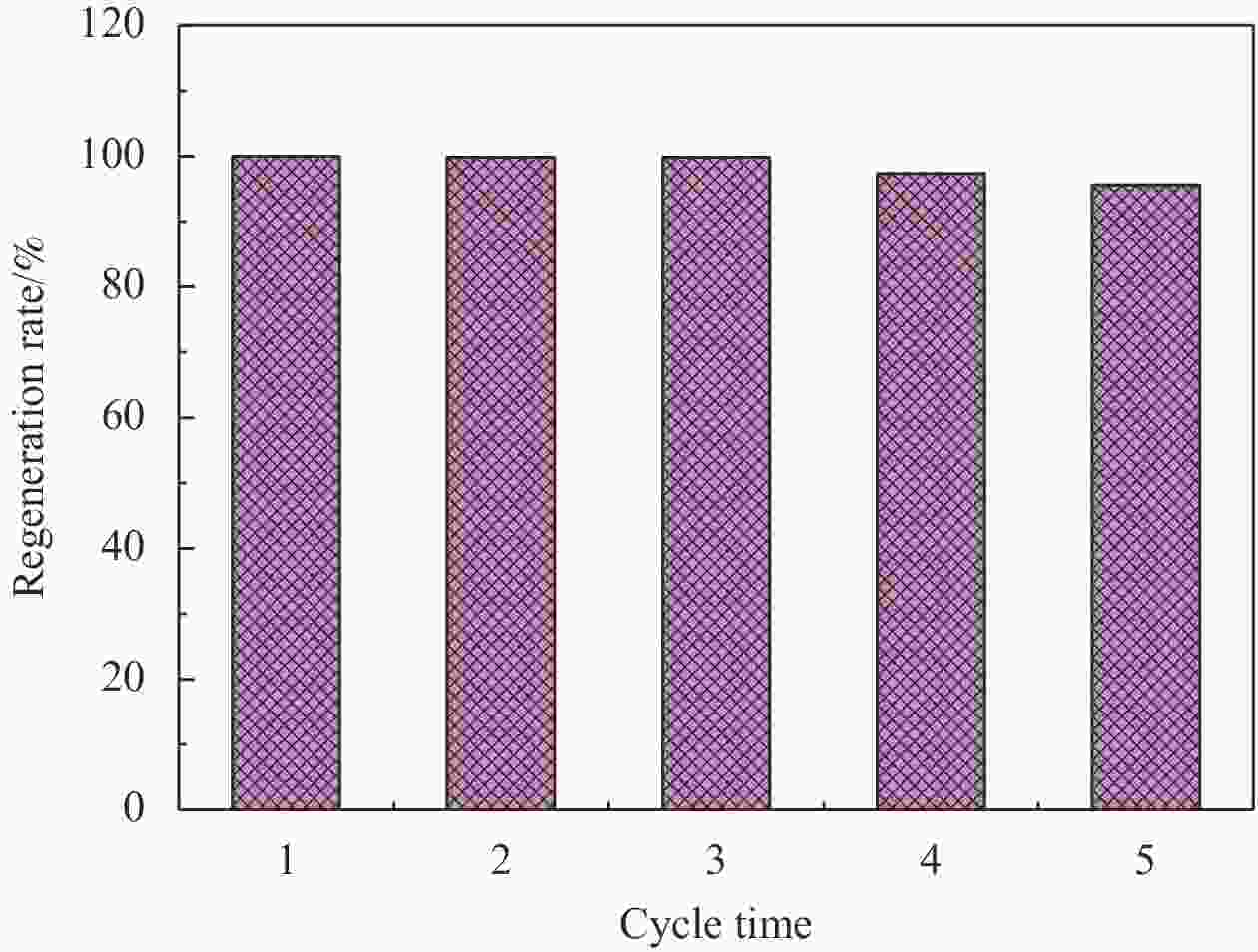
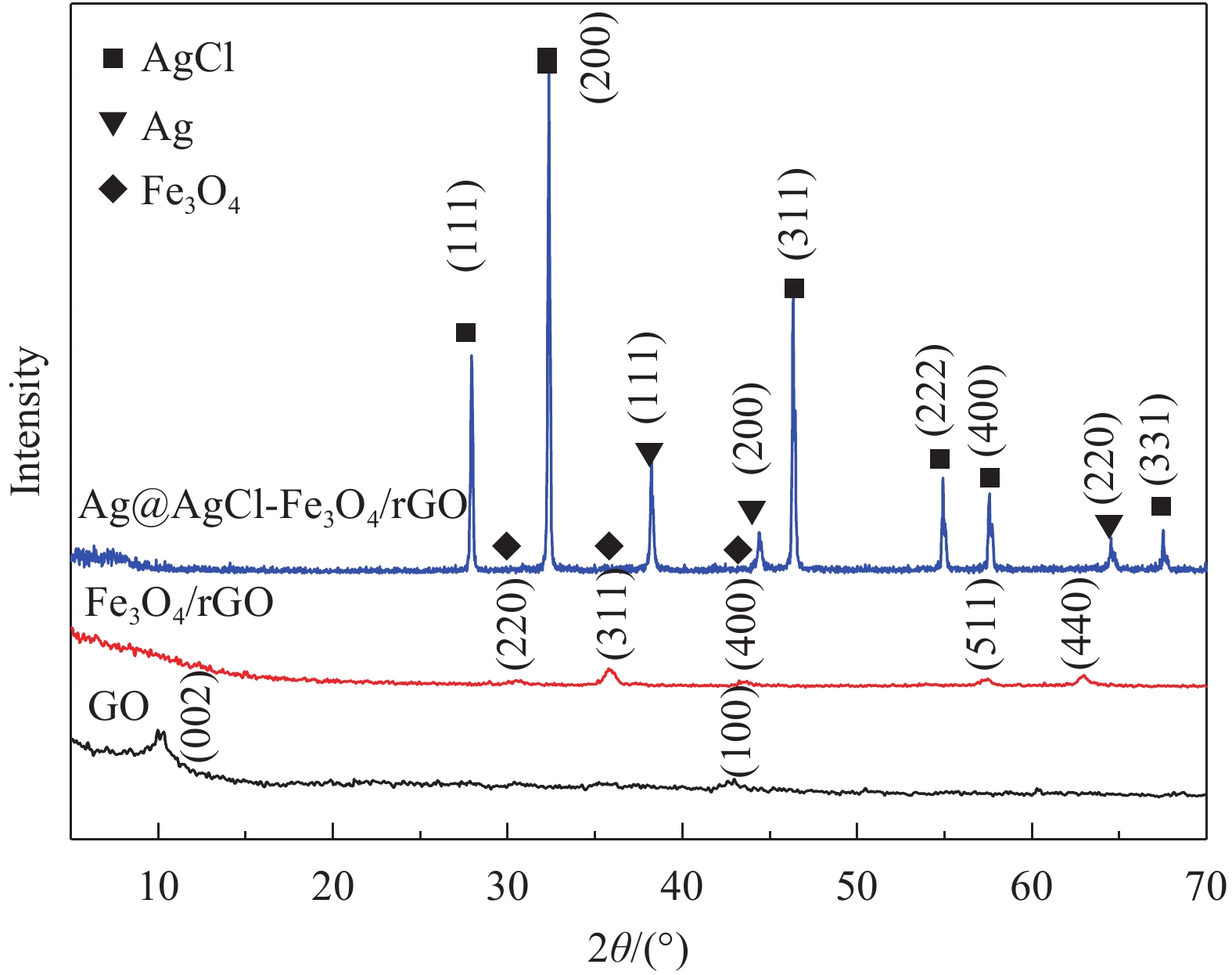
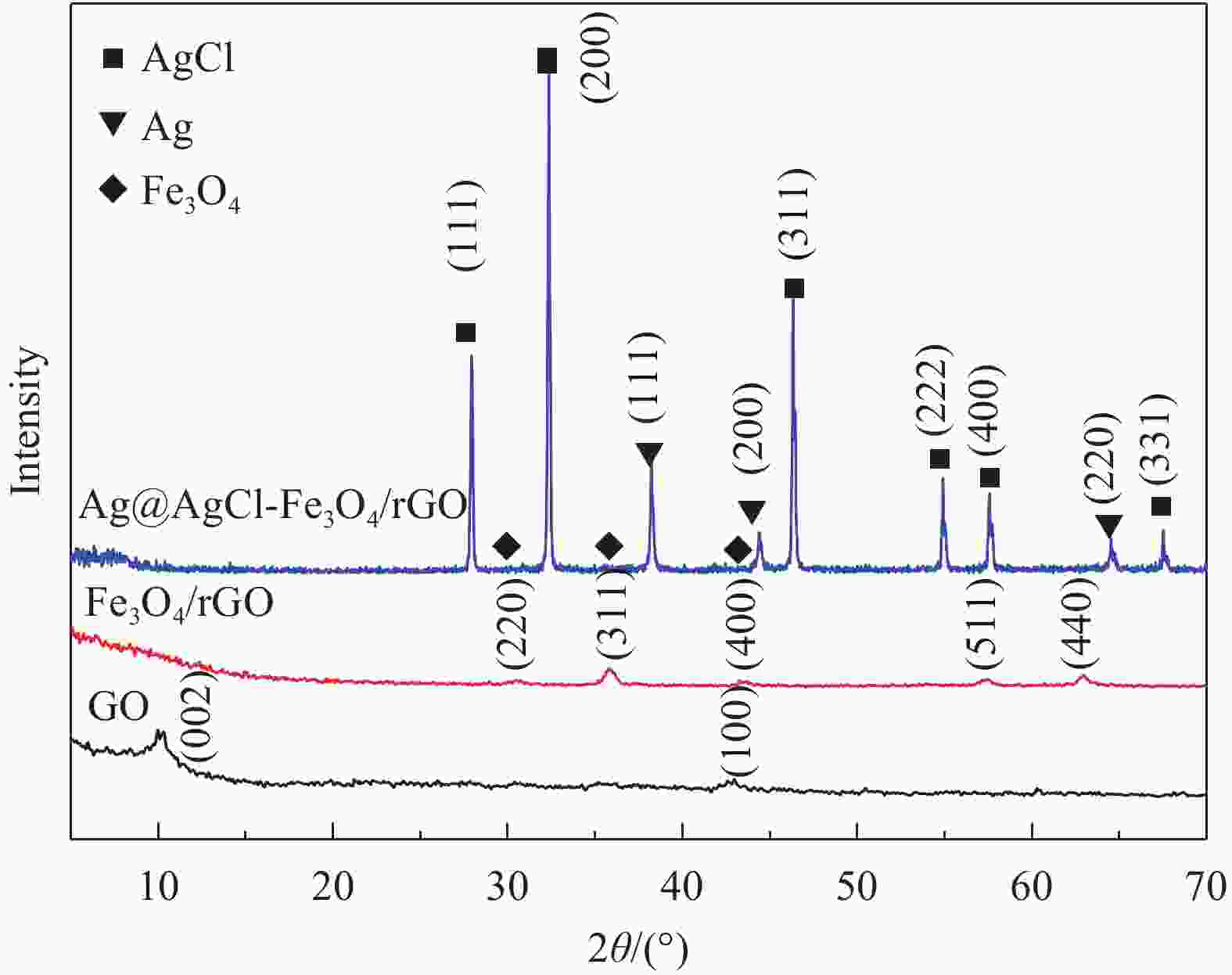
图 7 Ag@AgCl-Fe3O4/rGO复合材料光催化降解RhB的时间相关UV-vis图谱(a); rGO含量对Ag@AgCl-Fe3O4/rGO复合材料光催化降解性能的影响(b)
Figure 7. Temporal evolution UV-vis absorption spectra of photocatalytic degradation of RhB by Ag@AgCl-Fe3O4/rGO composite (a); Effect of rGO content on adsorption-photocatalytic degradation properities of Ag@AgCl-Fe3O4/rGO composites (b)
-
[1] LI Y, ZHAO K Y, YANG W, et al. Efficient removal of Cd2+ ion from water by calcium alginate hydrogel filtration membrane[J]. Water Science & Technology,2017,75(10):2322-2330. [2] LAM S M, SIN J C, MOHAMED A R. A review on photocatalytic application of g-C3N4/semiconductor (CNS) nanocomposites towards the erasure of dyeing wastewater[J]. Materials Science in Semiconductor Processing,2016,6(47):62-84. [3] WANG L, LI Z, CHEN J, et al. Enhanced photocatalytic degradation of methyl orange by porous graphene/ZnO nanocomposite[J]. Environmental Pollution,2019,249:801-811. doi: 10.1016/j.envpol.2019.03.071 [4] AI J P, HU L L, ZHOU Z H, et al. Surfactant-free synthesis of a novel octahedral ZnFe2O4/graphene composite with high adsorption and good photocatalytic activity for efficient treatment of dye wastewater[J]. Ceramics International,2020,46(8):11786-11798. doi: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.01.213 [5] XIE Y, CHEN C L, LU X R, et al. Porous NiFe-oxide nanocubes derived from prussian blue analogue as efficient adsorbents for the removal of toxic metal ions and organic dyes[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2019,379:120786. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.120786 [6] ZHAO G X, HUANG X B, TANG Z W, et al. Polymer-based nanocomposites for heavy metal ions removal from aqueous solution: A review[J]. Polymer Chemistry,2018,9(26):3562-3582. doi: 10.1039/C8PY00484F [7] LIU J Y, HU C W, HUANG Q G. Adsorption of Cu2+, Pb2+, and Cd2+ onto oiltea shell from water[J]. Bioresource Technology,2019,271:487-491. doi: 10.1016/j.biortech.2018.09.040 [8] AN C H, WANG S T, SUN Y G, et al. Plasmonic silver incorporated silver halides for efficient photocatalysis[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A,2016,4(12):4336-4352. doi: 10.1039/C5TA07719B [9] GAO W Y, RAN C X, WANG M Q, et al. The role of reduction extent of graphene oxide in the photocatalytic performance of Ag/AgX (X=Cl, Br)/rGO composites and the pseudo-second-order kinetics reaction nature of the Ag/AgBr system[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics,2016,18(27):18219-18226. doi: 10.1039/C6CP03110B [10] MA X L, TANG Y X, TAO H J, et al. Uniform spatial distribution of a nanostructured Ag/AgCl plasmonic photocatalyst and its segregative membrane towards visible light-driven photodegradation[J]. CrystEngComm,2016,18(20):3725-3733. doi: 10.1039/C6CE00499G [11] WU W B, WU J C, ZHANG T Y, et al. Controllable synthesis of Ag/AgCl@MIL-88A via in situ growth method for morphology-dependent photocatalytic performance[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry C,2019,7(18):5451-5460. doi: 10.1039/C9TC00398C [12] GHALY H A, EL-KALLINY A S, GAD-ALLAH T A, et al. Stable plasmonic Ag/AgCl-polyaniline photoactive composite for degradation of organic contaminants under solar light[J]. RSC Advances,2017,7(21):12726-12736. doi: 10.1039/C6RA27957K [13] LIANG C, NIU C G, WEN X J, et al. Effective removal of colourless pollutants and organic dyes by Ag@AgCl nanoparticle-modified CaSn(OH)6 composite under visible light irradiation[J]. New Journal of Chemistry,2017,41(13):5334-5346. doi: 10.1039/C7NJ00162B [14] ZHAO X R, XU X, TENG J, et al. Three-dimensional porous graphene oxide-maize amylopectin composites with controllable pore-sizes and good adsorption-desorption properties: Facile fabrication and reutilization, and the adsorption mechanism[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety,2019,176:11-19. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2019.03.069 [15] ZARE-DORABEI R, FERDOWSI S M, BARZIN A, et al. Highly efficient simultaneous ultrasonic-assisted adsorption of Pb(II), Cd(II), Ni(II) and Cu (II) ions from aqueous solutions by graphene oxide modified with 2,2′-dipyridylamine: Central composite design optimization[J]. Ultrasonics Sonochemistry,2016,32:265-276. doi: 10.1016/j.ultsonch.2016.03.020 [16] HUANG D, WU J Z, WANG L, et al. Novel insight into adsorption and co-adsorption of heavy metal ions and an organic pollutant by magnetic graphene nanomaterials in water[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2019,358:1399-1409. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2018.10.138 [17] XIA D H, AN T C, LI G Y, et al. Synergistic photocatalytic inactivation mechanisms of bacteria by graphene sheets grafted plasmonic AgAgX (X=Cl, Br, I) composite photocatalyst under visible light irradiation[J]. Water Research,2016,99(1):149-161. [18] JANG S, LEE S M, YOU J S, et al. Facile fabrication and photocatalytic activity of Ag/AgI/rGO films[J]. Korean Journal of Chemical Engineering,2019,36(12):2104-2109. doi: 10.1007/s11814-019-0396-6 [19] 黄冬根, 莫壮洪, 全水清, 等. 石墨烯/纳米TiO2复合材料的制备及光催化还原性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2016, 33(1):155-162.HUANG D G, MOZ H, QUAN S Q, et al. Preparation and photocatalytic reduction performance of graphene/nanoTiO2 composites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2016,33(1):155-162(in Chinese). [20] LI C B, XU Q, XU S X, et al. Synergy of adsorption and photosensitization of graphene oxide for improved removal of organic pollutants[J]. RSC Advances,2017,7(26):16204-16209. doi: 10.1039/C7RA01244F [21] ZHANG L Y, ZHANG W L, ZHOU Z Q, et al. γ-Fe2O3 nanocrystals-anchored macro/meso-porous graphene asa highly efficient adsorbent toward removal of methylene blue[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science,2016,476:200-205. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2016.05.025 [22] HOU X H, LIU J J, GUO W, et al. A novel 3D-structured flower-like bismuth tungstate/mag-graphene nanoplates composite with excellent visible-light photocatalytic activity for ciprofloxacin degradation[J]. Catalysis Communications,2019,121:27-31. doi: 10.1016/j.catcom.2018.12.006 [23] SUN L L, WU W, TIAN Q Y, et al. In situ oxidation and self-assembly synthesis of dumbbell-like α-Fe2O3/Ag/AgX (X=Cl, Br, I) heterostructures with enhanced photocatalytic properties[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering,2016,4(3):1521-1530. [24] NIE T T, HAO P L, ZHAO Z D, et al. Effect of oxidation-induced aging on the adsorption and co-adsorption of tetracycline and Cu2+ onto biochar[J]. The Science of the Total Environment,2019,673:522-532. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2019.04.089 [25] TABRIZIAN P, MA W, BAKR A, et al. pH-sensitive and magnetically separable Fe/Cu bimetallic nanoparticles supported by graphene oxide (GO) for high-efficiency removal of tetracyclines[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science,2019,534:549-562. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2018.09.034 [26] MARCANO D C, KOSYNKIN D V, BERLIN J M, et al. Improved synthesis of graphene oxide[J]. ACS Nano,2010,4(8):4806-4814. doi: 10.1021/nn1006368 [27] CHEN F H, WANG Y W, CHEN Q T, et al. Multifunctional nanocomposites of Fe3O4-graphene-Au for the repeated use in simultaneous adsorption, in-situ SERS detection and catalytic reduction of 4-nitrophenol in water[J]. Materials Research Express,2014,1(4):045049. doi: 10.1088/2053-1591/1/4/045049 [28] XU Y G, HUANG S Q, XIE M, et al. Core-shell magnetic Ag/AgCl@Fe2O3 photocatalysts with enhanced photoactivity for eliminating bisphenol A and microbial contamination[J]. New Journal of Chemistry,2016,40(4):3413-3422. doi: 10.1039/C5NJ02898A [29] 黄文鑫, 魏虎, 蒋彩云, 等. Bi2MoO6/Bi2S3异质结光催化降解四环素-铜复合物[J]. 环境科学, 2020, 41(12): 5488-5499.HUANG W X, WEI H, JIANG C Y, et al. Photocatalytic degradation of tetracycline and copper complex by Bi2MoO6/Bi2S3 heterojunction[J]. Environmental Science, 2020, 41(12): 5488-5499(in Chinese). [30] HU X L, LIU X, TIAN J, et al. Towards full-spectrum (UV, visible, and near-infrared) photocatalysis: Achieving an all-solid-state Z-scheme between Ag2O and TiO2 using reduced graphene oxide as the electron mediator[J]. Catalysis Science & Technology,2017,7(18):4193-4205. [31] MAHDIZADEH A, FARHADI S, ZABARDASTI A. Microwave-assisted rapid synthesis of grapheneanalogue hexagonal boron nitride (h-BN) nanosheets and their application for the ultrafast and selective adsorption of cationic dyes from aqueous solutions[J]. RSC Advance,2017,7(85):53984-53995. doi: 10.1039/C7RA11248C [32] JI X, GUO Y, HUA S G, et al. Interaction-determined sensitization photodegradation of dye complexes by boron nitride under visible light irradiation: Experimental and theoretical studies[J]. New Journal of Chemistry,2020,44(28):9238-9247. [33] LI W C, LAW F Y, CHAN Y H M. Biosorption studies on copper (II) and cadmium (II) using pretreated rice straw and rice husk[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research,2017,24:8903-8915. doi: 10.1007/s11356-015-5081-7 [34] 常帅帅. 微波生物炭制备及其对铜、铅和镉吸附行为和机理研究[D]. 济南: 山东建筑大学, 2020.CHANG S S. Preparation of microwave biochar and its adsorption behavior and mechanism for copper, lead and cadmium[D]. Ji’nan: Shandong Jianzhu University, 2020(in Chinese). [35] DEHGHANA S, JAFARI A J, FARZADKIA M, et al. Visible-light-driven photocatalytic degradation of metalaxyl by reduced graphene oxide/Fe3O4/ZnO ternary nanohybrid: Influential factors, mechanism and toxicity bioassay[J]. Journal of Photochemistry and Photobiology A: Chemistry,2019,375:280-292. doi: 10.1016/j.jphotochem.2019.01.024 [36] GAN W, FU X C, ZHANG J. Ag@AgCl decorated graphene-like TiO2 nanosheets with nearly 100% exposed (001) facets for efficient solar light photocatalysis[J]. Materials Science and Engineering B,2018,229:44-52. doi: 10.1016/j.mseb.2017.12.021 [37] XIONG T, ZHANG H J, ZHANG Y X, et al. Ternary Ag/AgCl/BiOIO3 composites for enhanced visible-light-driven photocatalysis[J]. Chinese Journal of Catalysis,2015,36(12):2155-2163. doi: 10.1016/S1872-2067(15)60980-9 -





 下载:
下载: