Robustness analysis of dynamic properties of polyurethane damping materials based on multi-index control
-
摘要: 强震或强风下,建筑结构中的隔震或消能装置受力大、变形大,这就要求阻尼材料的阻尼系数高,适用温度与室外环境匹配,具有大阻尼温域。目前,聚氨酯阻尼材料难以同时满足上述诸多指标性能,因而无法广泛应用于建筑结构减震领域。本文选择了玻璃纤维、石墨烯、四脚状氧化锌晶须及受阻酚小分子四种增强填料,以同时提高聚氨酯材料的阻尼性能、力学性能并改变其温度特性。通过正交试验设计了不同用量的聚氨酯复合阻尼材料,并进行基本物理力学性能和动态力学性能试验。根据动态热机械分析(DMA)试验结果,利用田口法进行损耗因子峰值tanδmax、大阻尼温域ΔT0.5和玻璃化转变温度Tg三个动态力学性能指标的信噪比分析和方差分析,以获得各指标的稳健性。依据各指标的重要性进行权重赋值,由层次分析法(AHP)构建多指标赋权评价方法,得到优化方案。并通过验证试验可知,优化后聚氨酯材料tanδmax为1.24,ΔT0.5为57℃,Tg为21.8℃,与初始组相比,其tanδmax提高了16.98%,ΔT0.5拓宽了46.91%。Abstract: The isolation devices and dampers in architectural structure have large force and deformation under strong earthquake or wind, which requires high damping coefficient of damping material, suitable temperature matching with outdoor environment, and large damping temperature range. Currently, polyurethane damping materials are difficult to satisfy the above-mentioned performance indexes simultaneously, therefore they can not be widely used in structure engineering. In this paper, glass fiber, graphene, tetra-needle like ZnO whiskers (T-ZnOw) and hindered phenol were selected to improve the damping, mechanical properties and temperature properties. Through orthogonal design, polyurethane with different additions were prepared. And the robustness of loss peak value (tanδmax), damping temperature range (ΔT0.5) and glass transition temperature (Tg) were analyzed based on the dynamic thermomechanical analysis (DMA) test. According to the degree of importance of each index, weight assignment was carried out. The optimization scheme was obtained based on analytic hierarchy process (AHP), which is a multi-index weighting evaluation method. The validation test shows that tanδmax is 1.24, ΔT0.5 is 57℃, and Tg is 21.8℃.Compared with the initial group, the improvement rate of tanδmax reaches 16.98 %, and the improvement rate of ΔT0.5 reaches 46.91 %.
-
Key words:
- polyurethane /
- Taguchi method /
- robustness analysis /
- variance analysis /
- damping performance
-
表 1 因素水平
Table 1. Factor level
Experimental
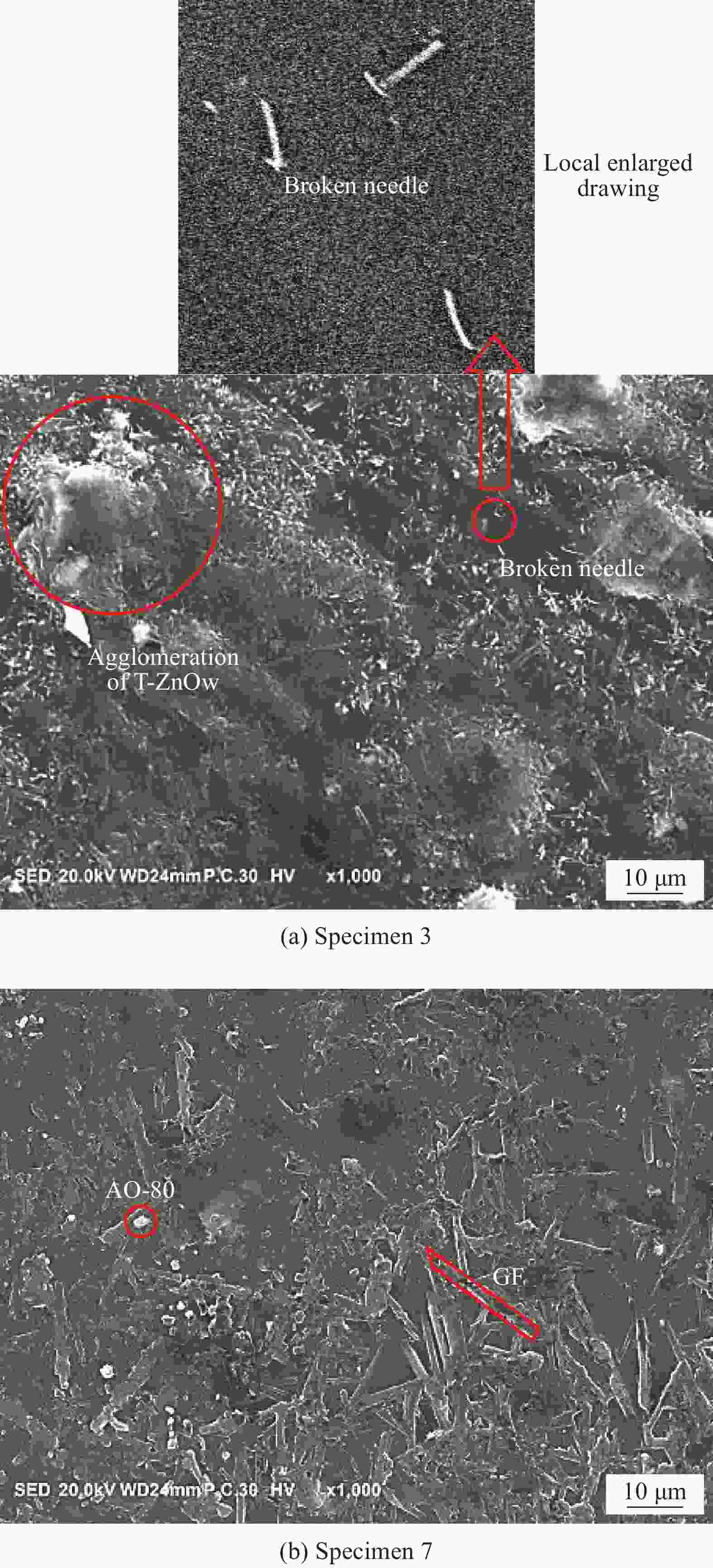
factorFactor Content Level 1 Level 2 Level 3 GF A 10 12 15 T-ZnOw B 0.3 0.5 0.7 Graphene C 0.1 0.2 0.3 AO-80 D 10 14 18 Notes: Dosage in the table is 100 phr of polyurethane-epoxy; GF—Glass fiber; T-ZnOw—Tetra-needle like ZnO whiskers. 表 2 高阻尼聚氨酯材料
$ {\rm{L}}_{9}\left({3}^{4}\right) $ 正交表Table 2.
$ {\rm{L}}_{9}\left({3}^{4}\right) $ orthogonal table of high damping polyurethane materialsNumber Specimen A B C D 1 A1B1C1D1 10 0.3 0.1 10 2 A1B2C2D2 10 0.5 0.2 14 3 A1B3C3D3 10 0.7 0.3 18 4 A2B1C2D3 12 0.3 0.2 18 5 A2B2C3D1 12 0.5 0.3 10 6 A2B3C1D2 12 0.7 0.1 14 7 A3B1C3D2 15 0.3 0.3 14 8 A3B2C1D3 15 0.5 0.1 18 9 A3B3C2D1 15 0.7 0.2 10 Notes: A, B, C and D—Factors; 1, 2 and 3—Factor level in Table 1. 表 3 聚氨酯阻尼材料样品的基本物理力学性能指标
Table 3. Basic physical mechanical properties of polyurethane damping material specimens
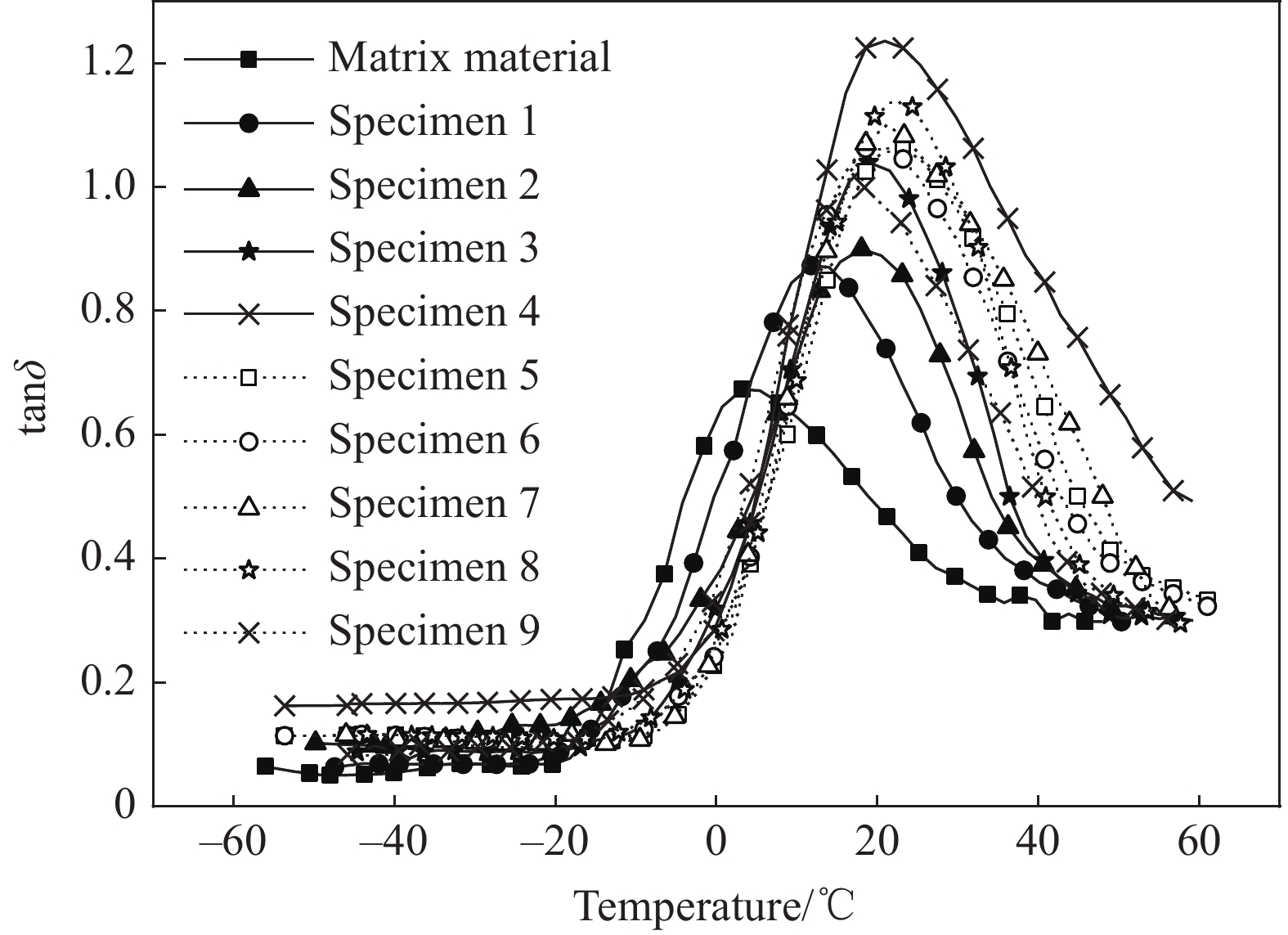
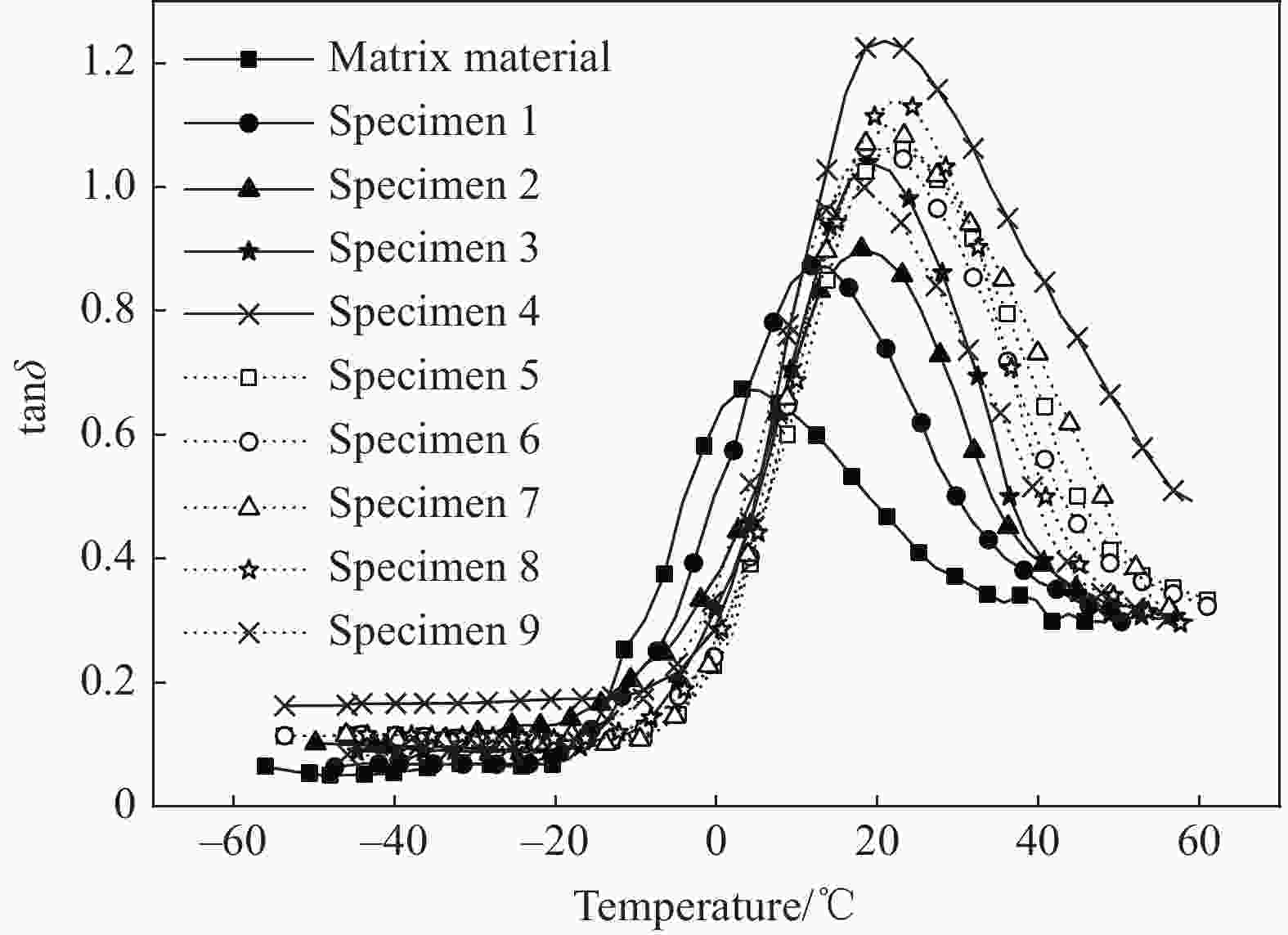
表 4 聚氨酯阻尼材料DMA试验结果及其信噪比(S/N)
Table 4. Results and signal-to-noise ratio (S/N) of DMA test for polyurethane damping materials
Number Specimen tanδmax ΔT0.5 Tg Value S/N/dB Value/℃ S/N/dB Value /℃ S/N/dB 1 A1B1C1D1 0.87 −1.21 30 29.54 11.8 18.3 2 A1B2C2D2 0.9 −0.92 38.2 31.64 18 6.0 3 A1B3C3D3 1.04 0.34 42 32.46 18.9 0.8 4 A2B1C2D3 1.25 1.94 52.8 34.45 22 6.0 5 A2B2C3D1 1.06 0.51 40 32.04 21.2 1.6 6 A2B3C1D2 1.06 0.51 38.8 31.78 18.9 0.8 7 A3B1C3D2 1.1 0.83 41.4 32.34 21.1 0.8 8 A3B2C1D3 1.14 1.14 39.7 31.98 22 6.0 9 A3B3C2D1 1 0 36.2 31.17 16 12.0 Average — 0.35 — 32.03 — 5.8 表 5 聚氨酯阻尼材料损耗因子峰值tanδmax信噪比
Table 5. Noise-signal ratio for loss peak value tanδmax of polyurethane damping materials
Name Level 1/dB Level 2/dB Level 3/dB DIF A:GF −0.59 0.98 0.66 1.57 B:T-ZnOw 0.52 0.24 0.28 0.28 C:Graphene 0.14 0.34 0.56 0.42 D:AO-80 −0.23 0.14 1.14 1.37 Average(S/N)=0.35 — Notes: DIF—Difference between the maximum and minimum signal-to-noise ratio; GF—Glass fiber. 表 6 聚氨酯阻尼材料tanδmax信噪比方差分析
Table 6. Variance analysis of signal-to-noise ratio of tanδmax of polyurethane damping materials
Name Freedom Sum of square Variance F A 2 1.39 0.70 21.22 B 2 0.05 0.02 0.69 C 2 0.09 0.04 1.31 D 2 1 0.50 15.27 Error 0 0 — — Sum 8 2.52 — — (Error) (4) (0.13) (0.03) — Notes: Meanings of the values in the table are given in Ref. [12]; F—Ratio of the two mean square (effect term/error term). 表 7 聚氨酯阻尼材料大阻尼温域ΔT0.5因素信噪比
Table 7. Noise-signal ratio for damping temperature range ΔT0.5 of polyurethane damping materials
Name Level 1/dB Level 2/dB Level 3/dB DIF A 31.22 32.76 31.83 1.54 B 32.11 31.89 31.81 0.3 C 31.10 32.42 32.28 1.32 D 30.92 31.92 32.96 2.04 Average(S/N)=32.03 — 表 8 聚氨酯阻尼材料ΔT0.5信噪比方差分析
Table 8. Variance analysis of signal-to-noise ratio of ΔT0.5 of polyurethane damping materials
Name Freedom Sum of square Variance F A 2 1.203 0.60 24.90 B 2 0.048 0.02 1.00 C 2 1.052 0.53 21.77 D 2 2.081 1.04 43.09 Error 0 0 — — Sum 8 4.38 — — (Error) (2) (0.048) (0.02) — 表 9 聚氨酯阻尼材料玻璃化转变温度Tg因素信噪比
Table 9. Noise-signal ratio for glass transition temperature Tg of polyurethane damping materials
Name Level 1/dB Level2 /dB Level 3/dB DIF A 8.37 2.81 6.3 5.56 B 8.37 4.54 4.57 3.87 C 8.37 8.03 1.08 7.3 D 10.63 2.56 4.29 6.34 Average(S/N)=5.83 — 表 10 聚氨酯阻尼材料Tg信噪比方差分析
Table 10. Variance analysis of signal-to-noise ratio of Tg of polyurethane damping materials
Name Freedom Sum of square Variance F A 2 15.79 7.90 1.63 B 2 9.7 4.85 1.00 C 2 33.85 16.93 3.49 D 2 36.1 18.1 3.72 Error 0 0 — — Sum 8 95.44 — — (Error) (2) (9.7) (4.85) — 表 11 AHP赋权法综合评估结果
Table 11. Comprehensive evaluation results of AHP weighting method
Factor tanδmax ΔT0.5/℃ Tg/℃ Weight coefficient Criteria weight 0.143 0.286 0.571 Scheme A2B1C3D3 0.571 0.286 0.143 0.347 A2B1C2D3 0.286 0.571 0.286 0.449 A1B1C1D1 0.143 0.143 0.571 0.204 Notes: Meanings of the values in the table are given in Ref. [12]; AHP—Analytic Hierarchy Process. 表 12 高阻尼聚氨酯材料阻尼性能试验验证
Table 12. Experimental verification of damping performance of polyurethane damping materials
Quality characteristic
targetInitial
groupOptimization group Improvement/
dBImprovement
rate/%Predicted Measured tanδmax 1.06 — 1.24 0.18 16.98 S/N of tanδmax 0.51 2.01 1.87 1.36 266.67 ΔT0.5/℃ 38.8 — 53 14.2 36.60 S/N of ΔT0.5 31.78 34.96 34.48 2.7 8.50 Tg/℃ 18.9 — 21.8 −0.7 −3.70 S/N of Tg 0.83 6.02 5.11 — — -
[1] 张志, 许勇. 岳耀, 等. AO-60/丁腈橡胶-环氧化天然橡胶-天然橡胶复合材料的制备及其阻尼性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2019, 36(8):1796-1803.ZHANG Zhi, XU Yong, YUE Yao, et al. Preparation and damping properties of hindered phenol AO-80/nitrile butadiene rubber-epoxidized natural rubber-natural rubber composites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2019,36(8):1796-1803(in Chinese). [2] 许俊红, 李爱群, 苏毅, 等. 开环式聚降冰片烯共混黏弹性阻尼材料的动态阻尼力学热分析[J]. 高分子材料科学与工程, 2015, 31(7):51-56.XU Junhong, LI Aiqun, SU Yi, et al. Dynamic damping mechanical analysis of viscolastic damping material mixed norsorex by ring-opening metathesis polymerization[J]. Polymer Materials Science Engineering,2015,31(7):51-56(in Chinese). [3] WANG Yueqiong, LIAO Lusheng, LIN Hongtu, et al. Damping properties of natural rubber/epoxidized natural rubber composites with different fillers[J]. Advances in Engineering Research,2018,120:772-775. [4] SHI X, LI Q, FU G, et al. The effects of a polyol on the damping properties of EVM/PLA blends[J]. Polymer Testing,2015,33:1-6. [5] 李翰模, 杨一林, 李志鹏, 等. 基于网络结构设计制备宽温域高阻尼聚氨酯弹性体[J]. 高分子材料科学与工程, 2017, 33(6):146-151.LI Hanmo, YANG Yilin, LI Zhipeng, et al. Preparation of high damping polyurethane with wide temperature range based on network structure designing[J]. Polymer Materials Science & Engineering,2017,33(6):146-151(in Chinese). [6] MOUSA A. Thermal properties of carboxylated nitrile rubber/nylon-12 composites-filled lignocellulose[J]. Journal of Thermoplastic Composite Materials,2014,27(2):167-179. doi: 10.1177/0892705712475017 [7] LEE K S, CHOI J I, KIM S K, et al. Damping and mechanical properties of composite composed of polyurethane matrix and preplaced aggregates[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2017,3(233):68-75. [8] KHIMI S R, PICKRING K L. The effect of silane coupling agent on the dynamic mechanical properties of iron sand/natural rubber magnetorheological elastomers[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering,2016,90:115-125. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2015.11.042 [9] LEE D J, KIM M K, WALSH J, et al. Experimental characterization of temperature dependent dynamic properties of glass fiber reinforced polyurethane foams[J]. Polymer Texting,2019,74:30-38. doi: 10.1016/j.polymertesting.2018.12.013 [10] ATIQAH A, JAWAID M, SAPUAN S M, et al. Thermal properties of sugar palm/glass fiber reinforced thermoplastic polyurethane hybrid composites[J]. Composite Structures,2018,202:954-958. doi: 10.1016/j.compstruct.2018.05.009 [11] LIU Gang, TANG Shawei, REN Wenchao, et al. Effect of thermal cycling on the damping behavior in alumina borate whisker with and without Bi2O3 coating reinforced pure aluminum composites[J]. Materials and Design,2014,3(34):244-249. [12] ADEYINKA Idowu, PRANJAL Nautiyal, LUIZA Fontoura, et al. Multi-scale damping of graphene foam-based polyurethane composites synthesized by electrostatic spraying[J]. Polymer Composites,2019,40:1862-1870. doi: 10.1002/pc.24948 [13] HUNG Puiyan, KINTAK Lau, KUN Qiao, et al. Property enhancement of CFRP composites with different graphene oxide employment methods at a cryogenic temperature[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science & Manufacturing,2019,120:56-63. doi: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2019.02.012 [14] YANG Dawei, ZHAO Xiuying, CHAN Tung, et al. Investigation of the damping properties of hindered phenol AO-80/polyacrylate hybrids using molecular dynamics simulations in combination with experimental methods[J]. Journal of Materials Science,2016,51(12):5760-5774. doi: 10.1007/s10853-016-9878-7 [15] ZHU H, HU Y M, ZHU W D, et al. Multi-objective design optimization of an engine accessory drive system with a robustness analysis[J]. Applied Mathematical Modelling,2020,77:1564-1581. doi: 10.1016/j.apm.2019.09.016 [16] CHAN KY, YIU C K F, NORDHOLM S. Microphone configuration for beamformer design using the Taguchi method[J]. Measurement,2017,10(25):58-66. [17] 王卫红, 王园. 基于PCA-AHP-IE的多指标评价模型研究与应用[J]. 浙江工业大学学报, 2019, 47(6):591-596.WANG Weihong, WANG Yuan. Research and application of multi-criteria evaluation model based on PCA-AHP-IE[J]. Journal of Zhejiang University of Technology,2019,47(6):591-596(in Chinese). [18] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局. 硫化橡胶或热塑性橡胶压入硬度试验方法第1部分: 邵氏硬度计法: GB/T 531.1—2008[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2008.General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China. Rubber, vulcanized or thermoplastic-Determination of indentation hardness-Part 1: Duromerer method (Shore hardness): GB/T 531.1—2008[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2008(in Chinese). [19] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局. 硫化橡胶或热塑性橡胶拉伸应力应变性能的测定: GB/T 528—2009[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2009.General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China. Rubber, vulcanized or thermoplastic-Determination of tensile stress-strain properties: GB/T 528—2009[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2009(in Chinese). [20] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局. 硫化橡胶或热塑性橡胶撕裂强度的测定: 裤形、直角形和新月形试样: GB/T 529.1—2008[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2008.General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China. Rubber, vulcanized or thermoplastic-Determination of tear strength (Trouser, angle and crescent test pieces): GB/T 529.1—2008[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2008(in Chinese). [21] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局. 硫化橡胶或热塑性橡胶 压缩永久变形的测定 第1部分: 在常温及高温条件下: GB/T 7759.1—2015[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2015.General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China. Rubber, vulcanized or thermoplastic-Determination of compression set-Part 1: At ambient or elevated temperatures: GB/T 7759.1—2015[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2015(in Chinese). [22] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局. 《硫化橡胶或热塑性橡胶动态性能的测定 第1部分: 通则》: GB/T 9870.1—2006[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2006.General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China. Rubber, vulcanized or thermoplastic-Determination of dynamic properties-Part 1: General guidance: GB/T 9870.1—2006[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2006(in Chinese). [23] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局. 《橡胶支座第3部分: 建筑隔震橡胶支座》: GB 20688.3—2006[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2006.General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People’s Republic of China. Rubber bearing-Part 3: Elastomeric seismic-Protection isolators for buildings: GB 20688.3—2006[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2006(in Chinese). -





 下载:
下载: