Performance and mechanism of the amino methylene phosphonic acid chelating resin (D418) for the efficient removal of Cu(II)
-
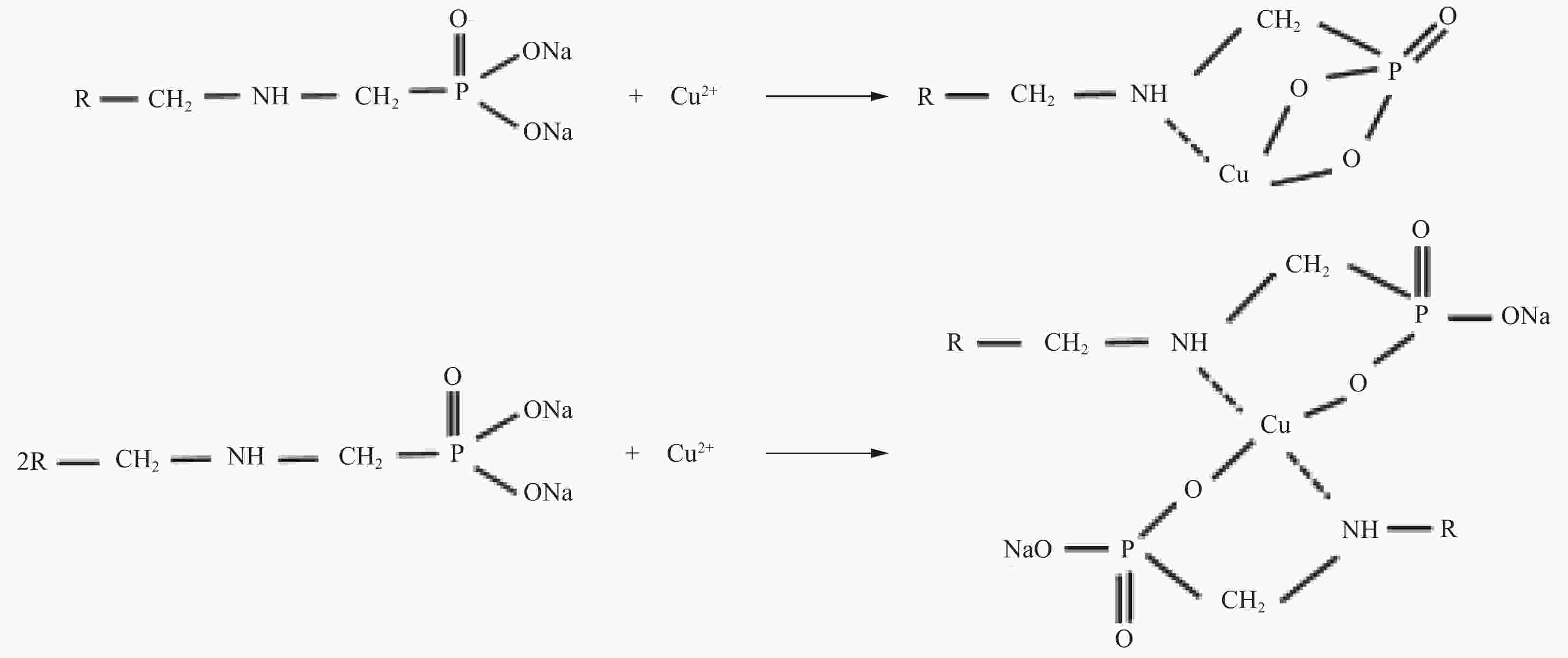
摘要: 为阐明氨基磷酸螯合树脂(D418)在水体中高效去除Cu(II)的作用机制,通过吸附实验系统考察了pH、离子强度、接触时间、温度等因素对D418树脂去除Cu(II)的影响,并通过吸附动力学模型、等温吸附模型和位点能量分布理论分析其去除机制。研究结果表明:Cu(II)溶液初始pH=9.00时,Cu(II)最大去除率达到97.20%,且Zeta电位变化对Cu(II)去除率影响符合Boltzmann模型。离子强度在0~0.10 mol/L增加,有利于促进D418树脂去除Cu(II)。根据线性相关系数大小比较,D418树脂吸附Cu(II)过程最符合颗粒内扩散模型和Sips模型。以Sips模型计算热力学参数和吸附位点能量分布,D418树脂对Cu(II)的去除为自发进行的吸热过程。Cu(II)先占据D418树脂高能量位点,再占据低能量位点。基于XPS和FTIR数据分析,D418树脂去除Cu(II)的机制主要是静电吸引、化学沉淀和内层络合作用。Abstract: In order to elucidate the adsorption mechanism of the amino methylene phosphonic acid chelating resin (D418) with high efficiency for removal of Cu(II) from wastewater, the influence of pH, ionic strength, contact time and temperature were detailly investigated by adsorption experiment. Meanwhile, adsorption kinetics, adsorption isotherms and site energy distribution theory were used to explain the removal mechanism of Cu(II) on the D418 resin. The results demonstrate that the optimal removal rate of Cu(II) on the D418 resin reaches to 97.20% at the initial pH=9.00, and the change of zeta potential on the influence of removal rate is well compatible with Boltzmann model. Furthermore, the removal efficiency of Cu(II) increases with the ionic strength at the range of 0-0.10 mol/L. According to the comparisons of the linear correlation coefficient values, the data of the adsorption kinetics fits well to the intra-particle diffusion while isotherm model data fits well to the Sips model. Based on the Sips model, the isotherm parameters and the energy distributions of adsorption sites were also conducted, and the result shows that the process of the Cu(II) adsorption on the D418 resin is spontaneous and endothermic. Cu(II) is preferentially adsorbed to the high- energy sites and to the low-energy sites. Based on the XPS and FTIR analysis, the adsorption mechanism of the Cu(II) ions is mainly attributed to the electrostatic interaction, the chemical precipitation and the inner-sphere complexation.
-
Key words:
- Cu(II) /
- chelate resins /
- adsorption /
- model /
- site energy distribution
-
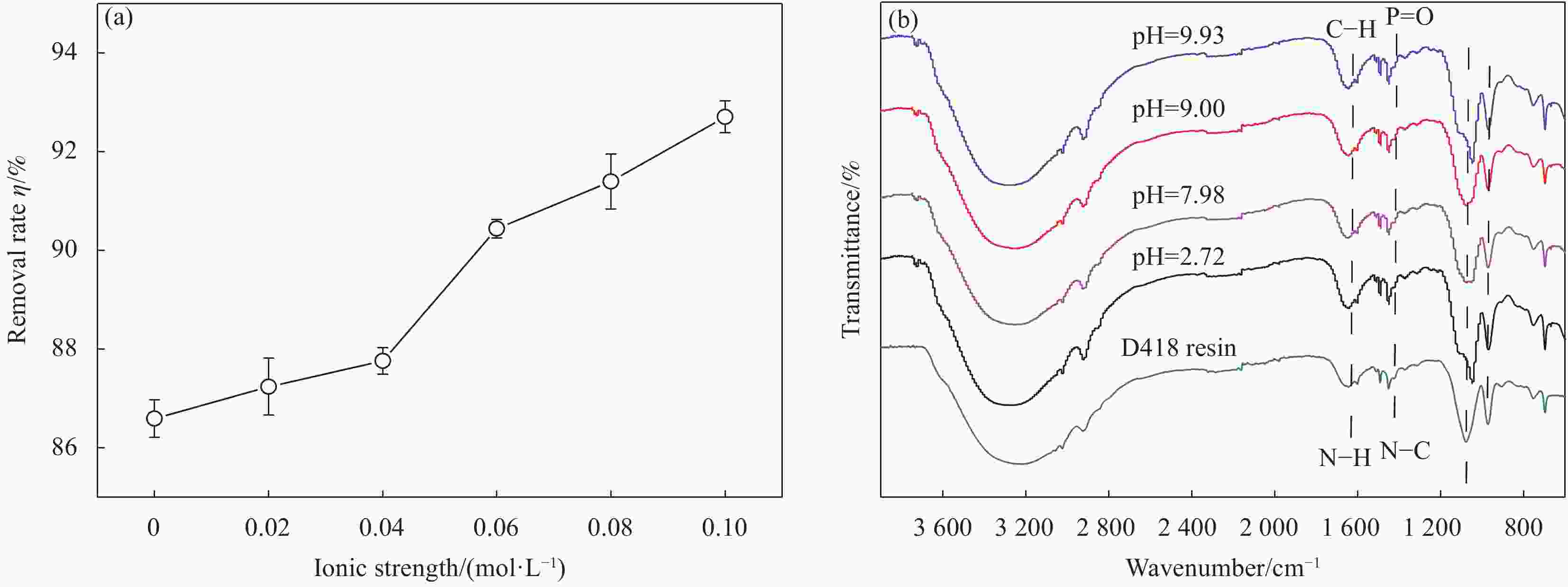
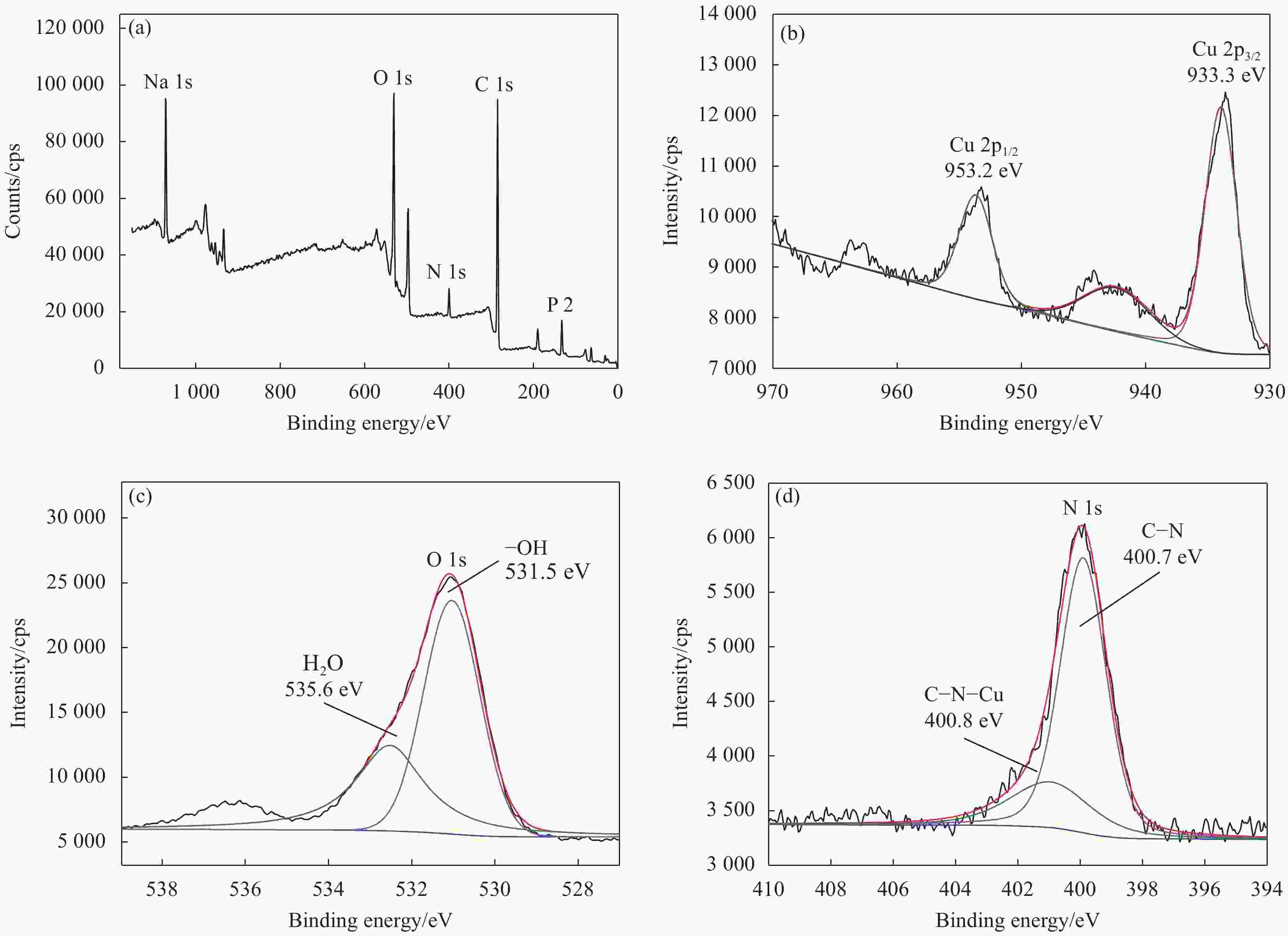
图 2 溶液初始pH对Cu(II)去除率η的影响(ρ0=20 mg/L, I=0 mol/L, T=298 K, m=0.1 g, V=50 mL) (a)、Cu(II)在水溶液中分布形态(T=298 K) (b)、不同pH条件下D418树脂的zeta电位 (c)、Zeta电位变化对η的影响 (d)
Figure 2. Effect of initial pH on Cu(II) removal rate η (ρ0=20 mg/L, I=0 mol/L, T=298 K, m=0.1 g, V=50 mL) (a), speciation diagram for the Cu(II)–H2O system(T=298 K) (b), zeta potential of D418 resin at different pH values (c), effect of zeta potential on η (d)
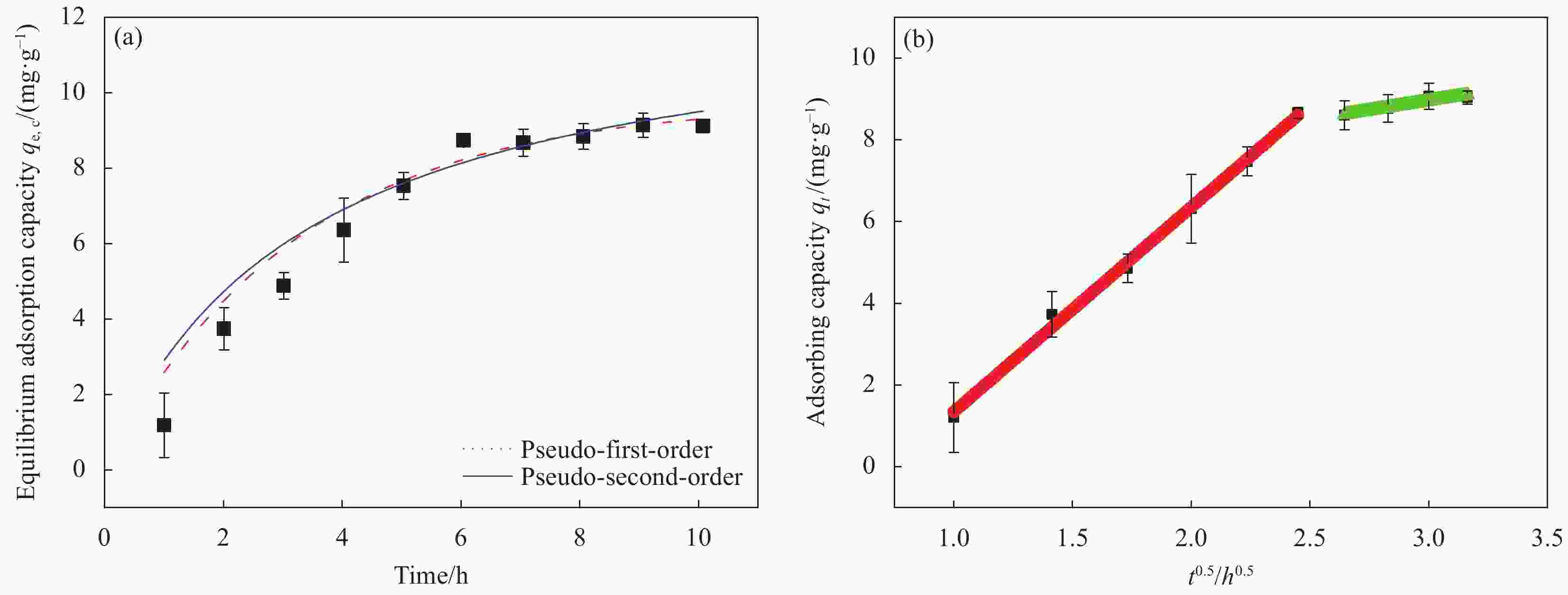
表 1 D418树脂吸附Cu(II)的动力学参数和拟合的线性相关系数
Table 1. Kinetic parameters and correlation coefficient for Cu(II) adsorption onto D418 resin
Kinetic model Parameter Result Pseudo-first order qe,c/(mg·g−1) 9.75 k1/h−1 0.3070 R2 0.8908 Pseudo-second order qe,c/(mg·g−1) 12.57 k2/(g·(mg·h)−1) 0.0239 R2 0.8349 Intra-particlediffusion kp1; kp2/(mg·(g·h0.5)−1) 5.0101; 0.9932 C1; C2 −3.672; 6.1511 R2; R2 0.9948; 0.8795 Notes: qe,c—Adsorbed amount of Cu(II) at a given time and the equilibrium concentration; k1, k2 and kp—Rate constants for the pseudo-first order, pseudo-second order and intraparticle diffusion, respectively; R2—Coefficient of determination; C—Dsorption constant. 表 2 D418树脂吸附Cu(II)的等温模型参数
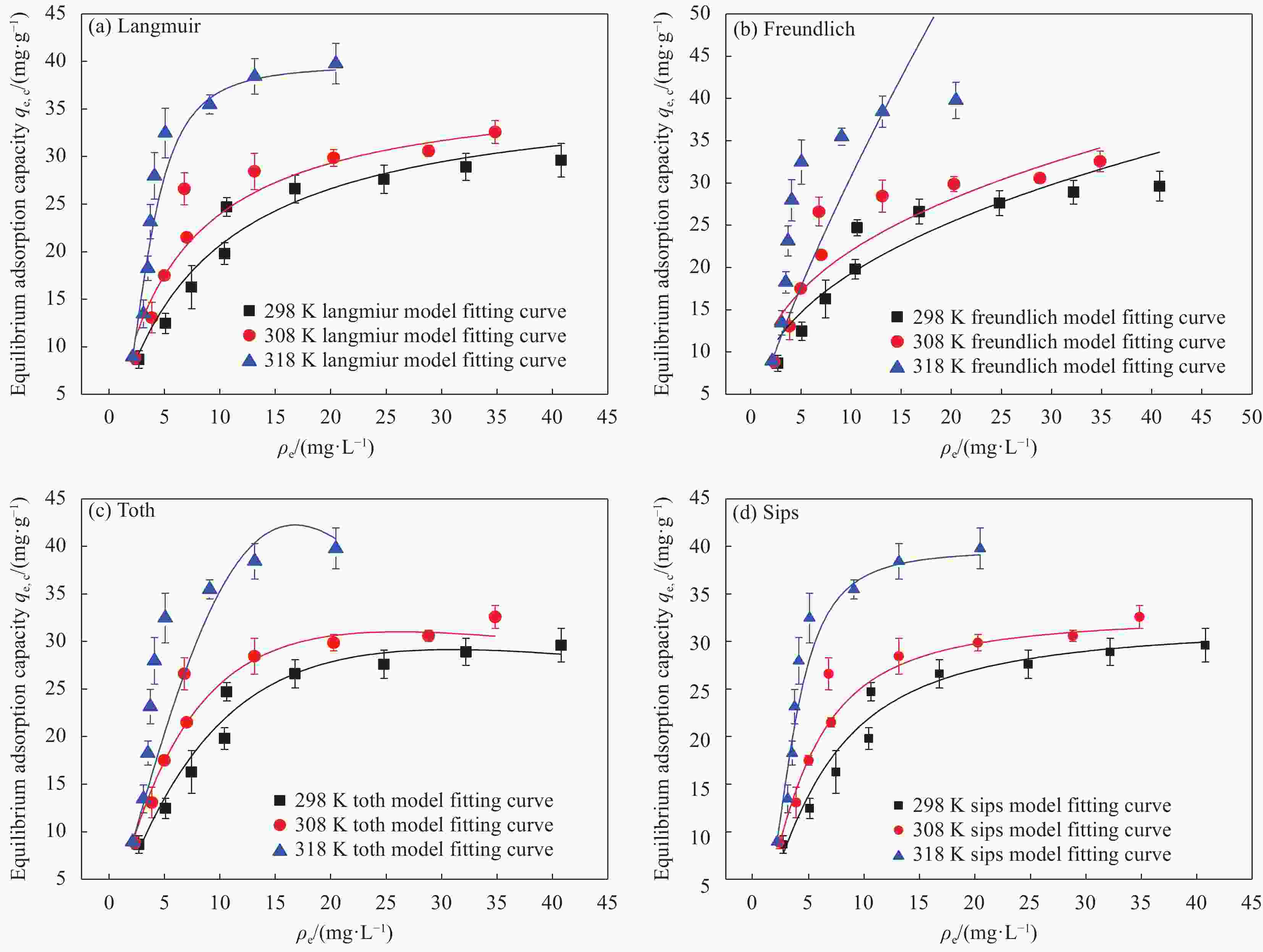
Table 2. Isotherm parameters of Cu(II) adsorption onto D418 resin at varying temperatures
Model and parameter 298 K 308 K 318 K Langmuir nonlinear fit ${q_{\rm{e,c}}} = \dfrac{{{\rm{4}}{\rm{.63}}{\rho _{\rm{e}}}}}{{1 + 0.1{\rm{238}}{\rho _{\rm{e}}}}}$ ${q_{\rm{e,c}}} = \dfrac{{{\rm{6}}{\rm{.55}}{\rho _{\rm{e}}}}}{{1 + 0.{\rm{1734}}{\rho _{\rm{e}}}}}$ ${q_{\rm{e,c}}} = \dfrac{{{\rm{1}}{\rm{.82}}{\rho _{\rm{e}}}}}{{1 + 0.{\rm{0458}}{\rho _{\rm{e}}}}}$ R2 0.9284 0.9615 0.9866 Freundlich nonlinear fit ${q_{\rm{e,c}}} = 14.96{\rho _{\rm{e}}}^{0.3272}$ ${q_{\rm{e,c}}} = 1{\rm{6}}{\rm{.01}}{\rho _{\rm{e}}}^{0.327{\rm{8}}}$ ${q_{\rm{e,c}}} = 1{\rm{5}}{\rm{.84}}{\rho _{\rm{e}}}^{0.3{\rm{420}}}$ R2 0.8272 0.8745 0.8414 Toth nonlinear fit ${q_{\rm{e,c}}} = \dfrac{{{\rm{380}}{\rm{.05}}{\rho _{\rm{e}}}}}{{{{\left( {{\rm{43}}{\rm{.4256}} + {\rho _{\rm{e}}}^{{\rm{1}}{\rm{.2572}}}} \right)}^{{\rm{1}}{\rm{.2572}}}}}}$ ${q_{\rm{e,c}}} = \dfrac{{{\rm{226}}{\rm{.93}}{\rho _{\rm{e}}}}}{{{{\left( {{\rm{24}}{\rm{.3591}} + {\rho _{\rm{e}}}^{{\rm{1}}{\rm{.2572}}}} \right)}^{{\rm{1}}{\rm{.2572}}}}}}$ ${q_{\rm{e,c}}} = \dfrac{{{\rm{2}}{\rm{.83}} \times {\rm{1}}{{\rm{0}}^{\rm{7}}}{\rho _{\rm{e}}}}}{{{{\left( {{\rm{1820}}{\rm{.9799}} + {\rho _{\rm{e}}}^{2.1442}} \right)}^{2.1442}}}}$ R2 0.9349 0.9770 0.9346 Sips nonlinear fit $q_{\rm{e,c}}^{} = \dfrac{{{\rm{2}}{\rm{.49}}{\rho _{\rm{e}}}^{{\rm{1}}{\rm{.4237}}}}}{{1 + {\rm{0}}{\rm{.0780}}{\rho _{\rm{e}}}^{{\rm{1}}{\rm{.4237}}}}}$ ${q_{\rm{e,c}}} = \dfrac{{{\rm{3}}{\rm{.18}}{\rho _{\rm{e}}}^{{\rm{1}}{\rm{.5502}}}}}{{1 + {\rm{0}}{\rm{.0974}}{\rho _{\rm{e}}}^{{\rm{1}}{\rm{.5502}}}}}$ ${q_{\rm{e,c}}} = \dfrac{{{\rm{1}}{\rm{.1814}}{\rho _{\rm{e}}}^{{\rm{2}}{\rm{.4557}}}}}{{1 + {\rm{0}}{\rm{.0458}}{\rho _{\rm{e}}}^{{\rm{2}}{\rm{.4557}}}}}$ R2 0.9386 0.9826 0.9866 表 3 不同种类螯合树脂对Cu(II)的去除效果
Table 3. Cu(II) adsorption by different chelating resins
Number Sorbent Reaction condition Adsorption capacity/(mg·g-1) Reference 1 R-AC pH=5.0, C0=3 mmol/L, T=298 K 77.31 [4] 2 MMARS pH=5.0, C0=0.1 mmol/L, T=283 K, t=720 min 28.99 [6] 3 DTC pH=7-9, ρ0 =16 mg/L, T=293 K 10.25 [7] 4 PS-AMPY pH=5.0, C0=1 mmol/L, T=318 K, t=480 min 78.08 [27] 5 PSA pH=4.0, C0= 0.1 mmol/L, T=298 K, t=72 h 16.13 [28] 6 Si-AMPY-1 pH=4.0-5.0, C0=1.0 mmol/L, T=328 K, t=90 min 28.16 [29] 7 PV-g-PS pH=5.0, C0=4.0 mmol/L, T=298 K, t=240 min 53.12 [30] 8 D418 resin pH=5.68, ρ0=100 mg/L, T=318 K, t=360 min 39.76 Present study 表 4 D418树脂吸附Cu(II)的热力学参数
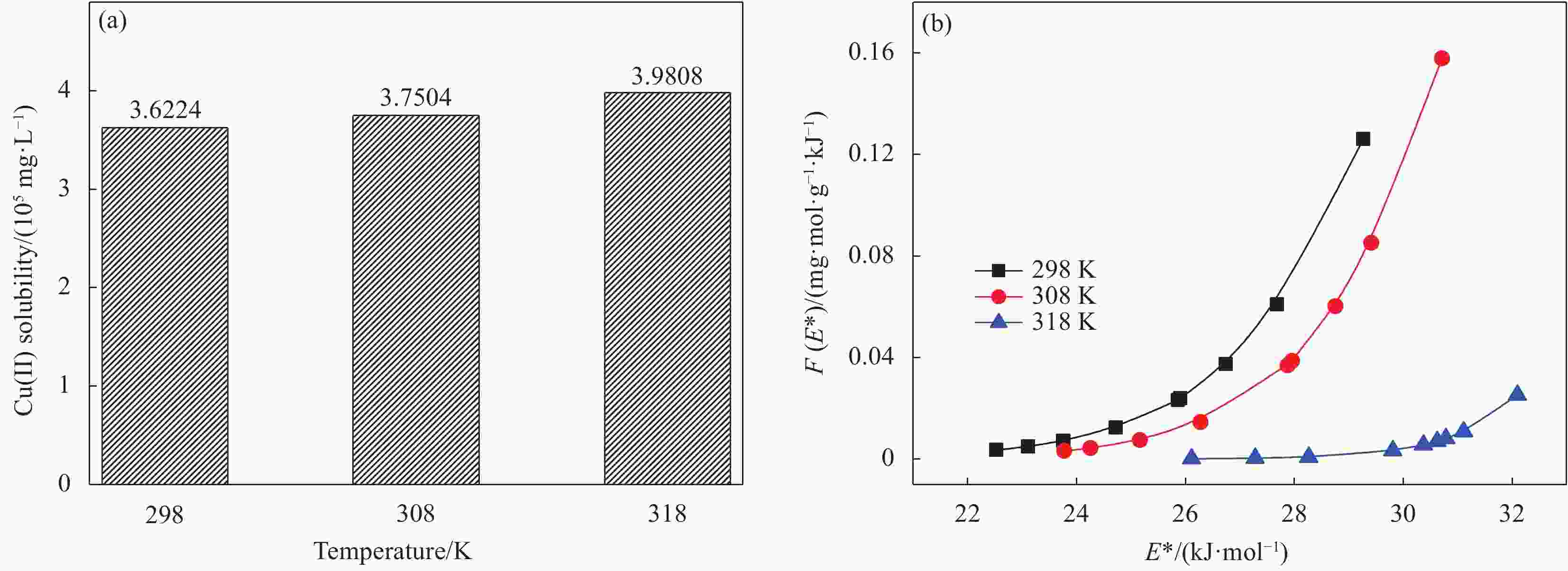
Table 4. Thermodynamic parameters for the adsorption of Cu(II) onto D418 resin
T/K ΔG/(kJ·mol−1) ΔH/( kJ·mol−1) ΔS/(J·mol−1·K) 298 −46.88 — — 308 −53.91 597.02 2 144.60 318 −89.77 — — Notes: T—Temperature; ΔG—Gibbs free energy; ΔH—Change in enthalpy during adsorption; ΔS—Adsorption process entropy change. -
[1] LIU S, WANG J, HUANG W, et al. Adsorption of phenolic compounds from water by a novel ethylenediamine rosin-based resin: Interaction models and adsorption mechanisms[J]. Chemosphere,2019,214:821-829. doi: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2018.09.141 [2] LI L, LIU F, JING X, et al. Displacement mechanism of binary competitive adsorption for aqueous divalent metal ions onto a novel IDA-chelating resin: Isotherm and jinetic modeling[J]. Water Research,2011,45(3):1177-1188. doi: 10.1016/j.watres.2010.11.009 [3] MONIER M, AYAD D M, WEI Y, et al. Adsorption of Cu(II), Co(II), and Ni(II) ions by modified magnetic chitosan chelating resin[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2010,177(1-3):962-970. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.01.012 [4] LING C, LIU F Q, XU C, et al. An integrative technique based on synergistic coremoval and sequential recovery of copper and tetracycline with dual-functional chelating resin: Roles of amine and carboxyl groups[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2013,5(22):11808-11817. [5] ZHU C, LIU F, XU C, et al. Enhanced removal of Cu(II) and Ni(II) from saline solution by novel dual-primary-amine chelating resin based on anion-synergism[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2015,287:234-242. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2015.01.054 [6] ZHU Z, ZHANG M, WANG W, et al. Efficient and synergistic removal of tetracycline and Cu(II) using novel magnetic multi-amine resins[J]. Scientific Reports,2018,8(1):4762. doi: 10.1038/s41598-018-23205-9 [7] YAN P, YE M, GUAN Z, et al. Synthesis of magnetic dithiocarbamate chelating resin and its absorption behavior for ethylenediaminetetraacetic acid copper[J]. Process Safety and Environmental Protection,2019,123:130-139. doi: 10.1016/j.psep.2018.12.026 [8] YAN B, NIU C H. Modeling and site energy distribution analysis of levofloxacin sorption by biosorbents[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2017,307:631-642. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2016.08.065 [9] YAN B, NIU C H. Adsorption behavior of norfloxacin and site energy distribution based on the Dubinin-Astakhov isotherm[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2018,631:1525-1533. [10] HE J, GUO J, ZHOU Q, et al. Adsorption characteristics of nitrite on natural filter medium: Kinetic, equilibrium, and site energy distribution studies[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety,2019,169:435-441. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2018.11.039 [11] ZHOU Y Y, HE Y Z, HE Y Z, et al. Analyses of tetracycline adsorption on alkali-acid modified magnetic biochar: Site energy distribution consideration[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2019,650:2260-2266. doi: 10.1016/j.scitotenv.2018.09.393 [12] TRAN H N, LIN C C, WOO S H, et al. Efficient removal of copper and lead by Mg/Al layered double hydroxides intercalated with organic acid anions: Adsorption kinetics, isotherms, and thermody-namics[J]. Applied Clay Science,2018,154:17-27. doi: 10.1016/j.clay.2017.12.033 [13] ZHOU C, JIA D, LIU M, et al. Removal of glyphosate from aqueous solution using nanosized copper hydroxide modified resin: Equilibrium isotherms and kinetics[J]. Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data,2017,62(10):3585-3592. [14] BARANIK A, SITKO R, GAGOR A, et al. Graphene oxide decorated with cerium(IV) oxide in determination of ultratrace metal ions and speciation of selenium[J]. Analytical Chemistry,2018,90(6):4150-4159. doi: 10.1021/acs.analchem.8b00137 [15] KARIMIPOUR A, ESFEM H, SAFAEI M R, et al. Mixed convection of copper-water nanofluid in a shallow inclined lid driven cavity using the lattice Boltzmann method[J]. Physica A: Statistical Mechanics and Its Applications,2014,402:150-168. doi: 10.1016/j.physa.2014.01.057 [16] VILLAR L D, GARCIA O. Solubilization profiles of metal ions from bioleaching of sewage sludge as a function of pH[J]. Biotechnology Letters,2002,24(8):611-614. doi: 10.1023/A:1015010417315 [17] OHSHIMA H. Approximate expressions for the surface charge density/surface potential relationship and double-layer potential distribution for a spherical or cylindrical colloidal particle based on the modified Poisson-Boltzmann equation[J]. Colloid and Polymer Science,2018,296(4):647-652. doi: 10.1007/s00396-018-4286-y [18] AL-DEGS Y S, EL-BARGHOUTHI M I, EL-SHEIKH A H, et al. Effect of solution pH, ionic strength, and temperature on adsorption behavior of reactive dyes on activated carbon[J]. Dyes Pigments,2008,77:16-23. doi: 10.1016/j.dyepig.2007.03.001 [19] GOLDBERG S. Inconsistency in the triple layer model description of ionic strength dependent boron adsorption[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science,2005,285(2):509-517. doi: 10.1016/j.jcis.2004.12.002 [20] KHAMIRCHI R, HOSSEINI-BANDEGHARAEI A, ALAHABADI A, et al. Adsorption property of Br-PADAP-impregnated multiwall carbon nanotubes towards uranium and its performance in the selective separation and determination of uranium in different environmental samples[J]. Ecotoxicology and Environmental Safety,2018,150:136-143. doi: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2017.12.039 [21] HAI N T, SHENG J Y, AHMAD H B, et al. Mistakes and inconsistencies regarding adsorption of contaminants from aqueous solutions: A critical review[J]. Water Research,2017,120(1):88-116. [22] BLANCO S P D M, SCHEUFELE F B, MODENES A N, et al. Kinetic, equilibrium and thermodynamic phenomenological modeling of reactive dye adsorption onto polymeric adsorbent[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2017,307:466-475. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2016.08.104 [23] TRAN H N, YOU S J, CHAO H P. Fast and efficient adsorption of methylene green 5 on activated carbon prepared from new chemical activation method[J]. Journal of Environmental Management,2017,188:322-336. doi: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2016.12.003 [24] VILARDI G, Di PALMA L, VERDONE N. Heavy metals adsorption by banana peels micro-powder: Equilibrium modeling by non-linear models[J]. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering,2018,26(3):455-464. doi: 10.1016/j.cjche.2017.06.026 [25] SYAFIUDDIN A, SALMIATI S, JONBI J, et al. Application of the kinetic and isotherm models for better understanding of the behaviors of silver nanoparticles adsorption onto different adsorbents[J]. Journal of Environmental Management,2018,218:59-70. [26] KUMAR K V, SERRANO-RUIZ J C, SOUZA H K S, et al. Site energy distribution function for the sips isotherm by the condensation approximation method and its application to characterization of porous materials[J]. Journal of Chemical & Engineering Data,2011,56(5):2218-2224. [27] QIU X, HU H, YANG J, et al. Removal of trace copper from simulated nickel electrolytes using a new chelating resin[J]. Hydrometallurgy,2018,180:121-131. doi: 10.1016/j.hydromet.2018.07.015 [28] QIU H, LING C, YUAN R, et al. Bridging effects behind the coadsorption of copper and sulfamethoxazole by a polyamine-modified resin[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2019,362:422-429. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.01.043 [29] WANG C, HU H, QIU X, et al. Synthesis of novel silica-supported chelating resin containing tert-butyl 2-picolyamino-N-acetate and its properties for selective adsorption of copper from simulated nickel electrolyte[J]. Transactions of Nonferrous Metals Society of China,2018,28(12):2553-2565. doi: 10.1016/S1003-6326(18)64902-7 [30] CHEN Y, ZHAN W, YANG X, et al. Efficient removal of heavy metal ions from aqueous solution by a novel poly(1-vinylimidazole) chelate resin[J]. Polymer Bulletin,2019,76(3):1081-1097. doi: 10.1007/s00289-018-2426-7 [31] TRAN H N, YOU S J, CHAO H P. Thermodynamic parameters of cadmium adsorption onto orange peel calculated from various methods: A comparison study[J]. Journal of Environmental Chemical Engineering,2016,4(3):2671-2682. doi: 10.1016/j.jece.2016.05.009 [32] WANG X, SATO T, XING B. Sorption and displacement of pyrene in soils and sediments[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2005,39(22):8712-8718. [33] SHEN X, GUO X, ZHANG M, et al. Sorption mechanisms of organic compounds by carbonaceous materials: Site energy distribution consideration[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2015,49(8):4894-4902. [34] LIU F F, FAN J L, WANG S G, et al. Adsorption of natural organic matter analogues by multi-walled carbon nanotubes: Comparison with powdered activated carbon[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2013,219:450-458. doi: 10.1016/j.cej.2013.01.026 [35] BERGER J M, WINAND R. Solubilities, densities and electrical conductivities of aqueous copper(I) and copper(II) chlorides in solutions containing other chlorides such as iron, zinc, sodium and hydrogen chlorides[J]. Hydrometallurgy,1984,12(1):61-81. doi: 10.1016/0304-386X(84)90048-3 [36] HUANG Z, HUANG Z, FENG L, et al. Modified cellulose by polyethyleneimine and ethylenediamine with induced Cu(II) and Pb(II) adsorption potentialities[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2018,202:470-478. doi: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2018.08.136 -





 下载:
下载: