Effect of HCl concentration on P adsorption behavior of hydrated ferrous oxide composite adsorbents
-
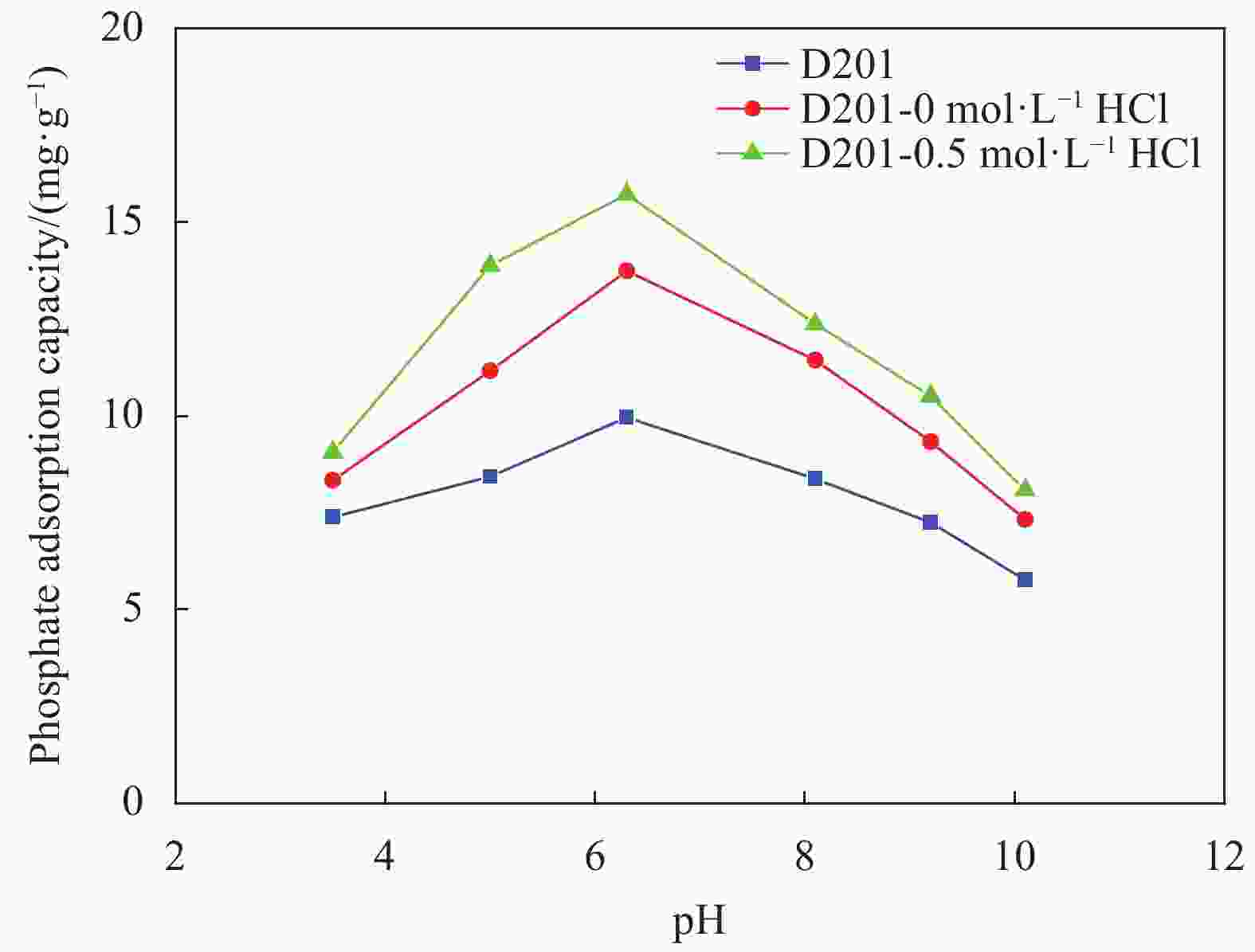
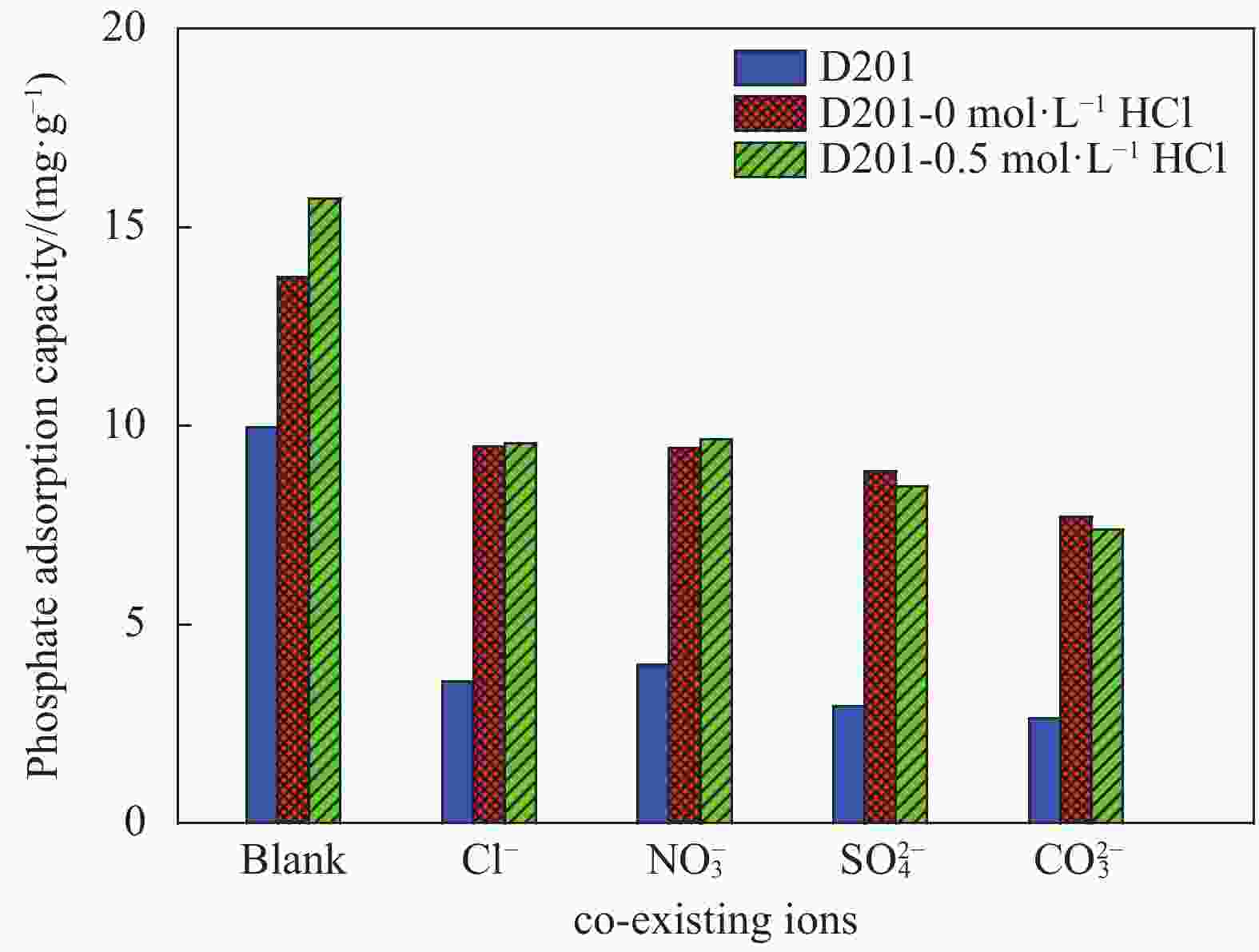
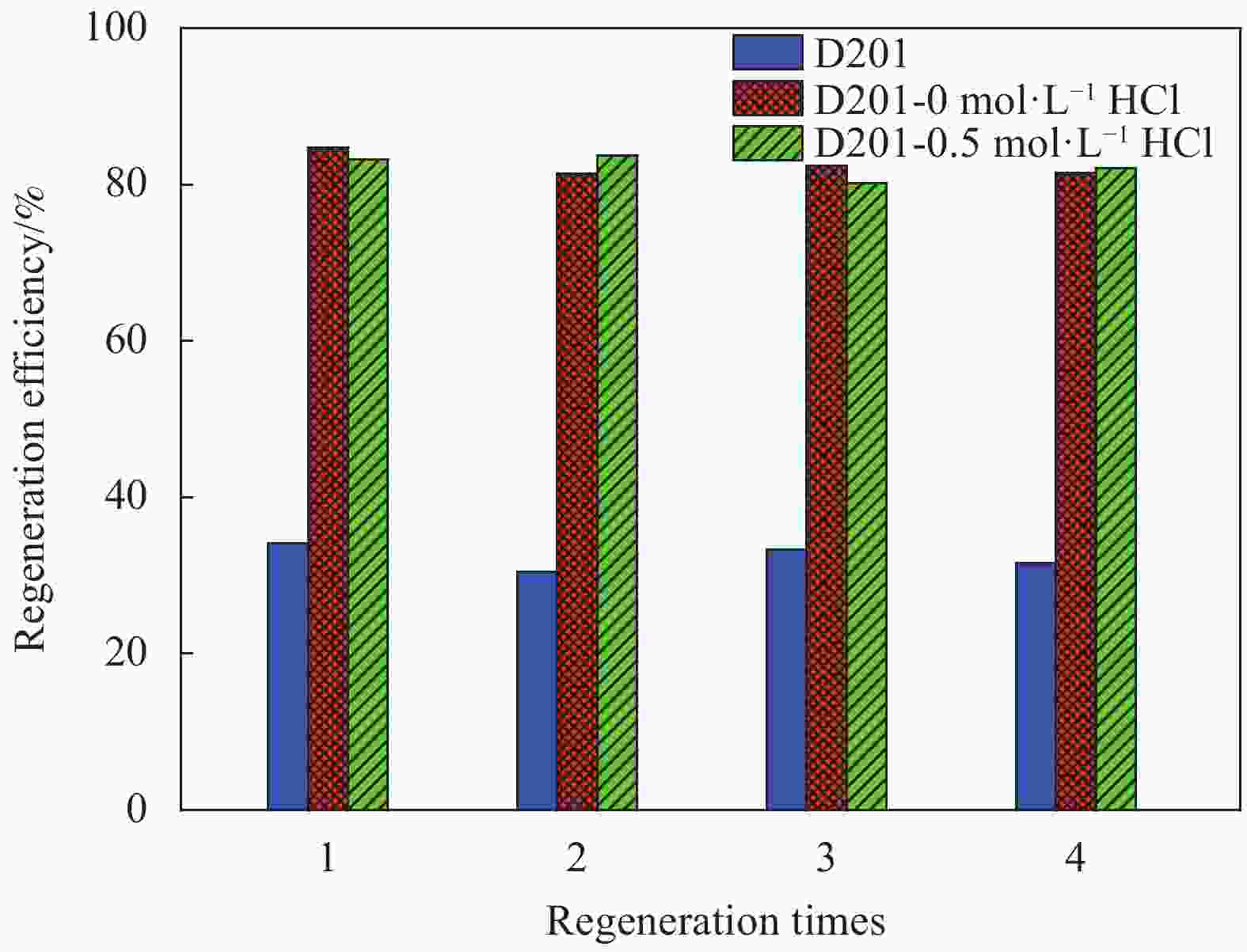
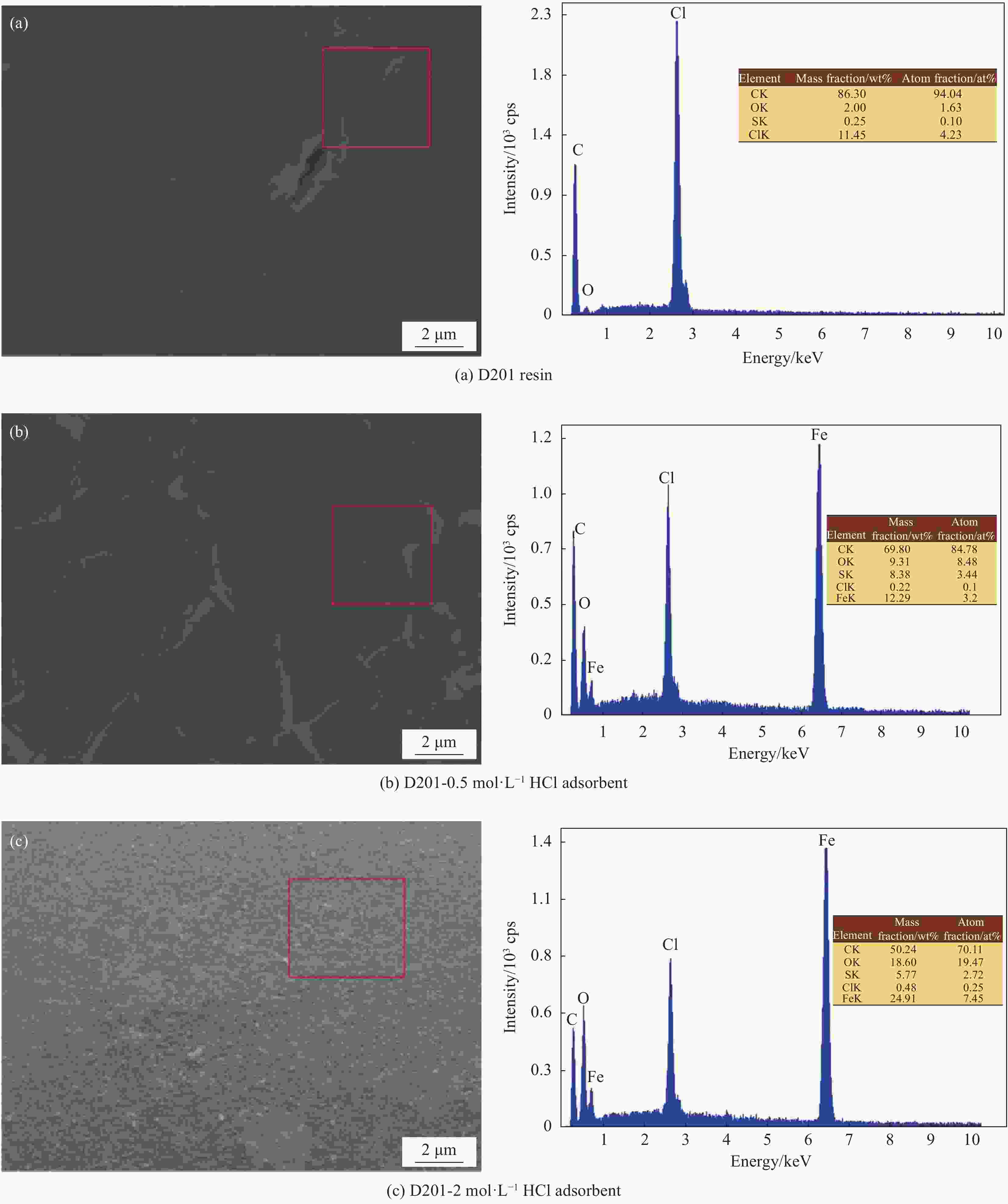
摘要: 为避免传统水合氧化铁(HFO)负载树脂复合吸附剂制备过程中大量使用HCl对设备防腐、安全及环保带来的问题,优化HFO复合吸附剂的制备工艺方法,改变负载液中HCl浓度制备得到多种HFO复合吸附剂,考察制备得到的HFO复合吸附剂对P的吸附动力学、吸附等温线、初始pH、共存离子影响、解吸再生方法等,评价负载液中HCl浓度对吸附剂吸附效能的影响。结果表明,负载液中HCl浓度由2 mol·L−1降低至0.5 mol·L−1,并不会显著降低HFO复合吸附剂的P吸附容量。HCl浓度为0.5 mol·L−1时制备得到的HFO复合吸附剂对P的最大吸附容量为29.67 mg·g−1,显著高于D201树脂载体(16.39 mg·g−1),其吸附动力学曲线更符合准一级吸附动力学模型,最佳的P吸附pH为6~8,在共存离子Cl−、NO3−、SO42−、CO32−浓度为1.0 g·L−1的条件下,吸附剂对P的吸附容量降低31.1%~53.0%。采用5wt%的NaOH溶液能有效实现吸附剂中P的解吸再生。
-
关键词:
- 吸附剂 /
- 水合氧化铁(HFO) /
- P /
- HCl /
- 树脂
Abstract: In order to reduce the amount of HCl used in the hydrated ferrous oxide (HFO) composite adsorbents preparation process, which frequently caused serious equipment corrosion, safe and environmental problems, several adsorbents were prepared with various HCl concentrations. The effectiveness of P adsorption by the adsorbents were investigated at various perspectives, including adsorption kinetics, adsorption isotherms, effect of pH, co-existing ions and desorption methods. Experimental results demonstrate that phosphate adsorption capacity of HFO composite adsorbents doesn’t decrease significantly with the decreasing HCl concentration (from 2 mol·L−1 to 0.5 mol·L−1). The maximum P adsorption capacity of HFO composite adsorbent prepared at 0.5 mol·L−1 HCl is 29.67 mg·g−1, which is higher than the corresponding value of D201 resin (16.39 mg·g−1). The adsorption kinetic curves of the adsorbents are fitted well with the pseudo first order adsorption kinetic equation. The optimal pH for P removal is 6-8. When the concentration of coexisting ions, such as Cl−, NO3−, SO42−, CO32−, in P solution is 1.0 g·L−1 respectively, the phosphate adsorption of HFO composite adsorbents decreases by 31.1%-53.0%. The adsorbed P on HFO composite adsorbents could be well desorbed with 5wt% NaOH solution.-
Key words:
- adsorbent /
- hydrated ferrous oxide (HFO) /
- P /
- HCl /
- resin
-
表 1 不同HCl浓度制备的水合氧化铁(HFO)复合吸附剂
Table 1. Hydrated ferrous oxide (HFO) composite adsorbents prepared with different HCl concentrations
HCl concentration/(mol·L−1) Adsorbent 0 D201-0 mol·L−1 HCl 0.5 D201-0.5 mol·L−1 HCl 1.0 D201-1 mol·L−1 HCl 2.0 D201-2 mol·L−1 HCl 表 2 D201树脂与HFO复合吸附剂的P吸附动力学拟合结果
Table 2. Kinetic fitting results of P adsorption by D201 resin and HFO composite adsorbents
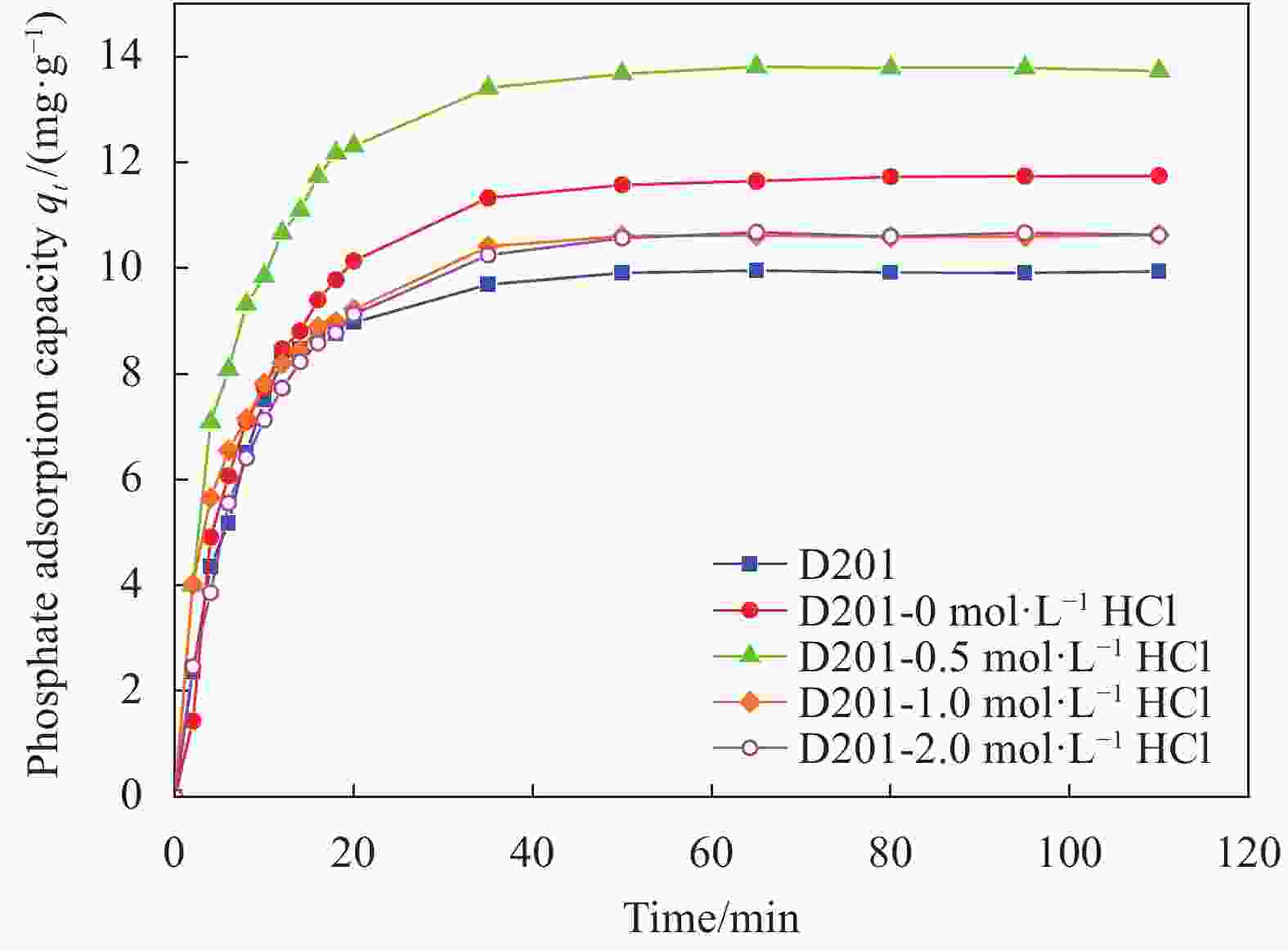
Adsorbent Pseudo-first-order Pseudo-second-order Intra-particle diffusion k1/min−1 qe/(mg·g−1) R2 k2/min−1 qe/(mg·g−1) R2 C kdif/(mg·g−1·min−1/2) R2 D201 0.106 9.872 0.997 0.018 10.878 0.967 3.765 0.785 0.634 D201-0 mol·L−1 HCl 0.110 11.610 0.990 0.011 12.964 0.964 3.588 1.007 0.713 D201-0.5 mol·L−1 HCl 0.144 13.497 0.995 0.015 14.773 0.985 5.431 1.052 0.664 D201-1 mol·L−1 HCl 0.155 10.266 0.995 0.022 11.180 0.959 4.363 0.784 0.679 D201-2 mol·L−1 HCl 0.152 10.532 0.954 0.013 11.714 0.992 3.392 0.897 0.726 Notes: k1—Pseudo-first-order kinetic constant; k2—Pseudo-second-order kinetic constant; qe—Phosphate adsorption capacity in equilibrium; kdif—Intra-particle diffusion rate constant; C—Reaction constant. 表 3 D201树脂与HFO复合吸附剂的等温吸附模型拟合参数
Table 3. Isothermal adsorption model fitting parameters of D201 resin and HFO composite adsorbents
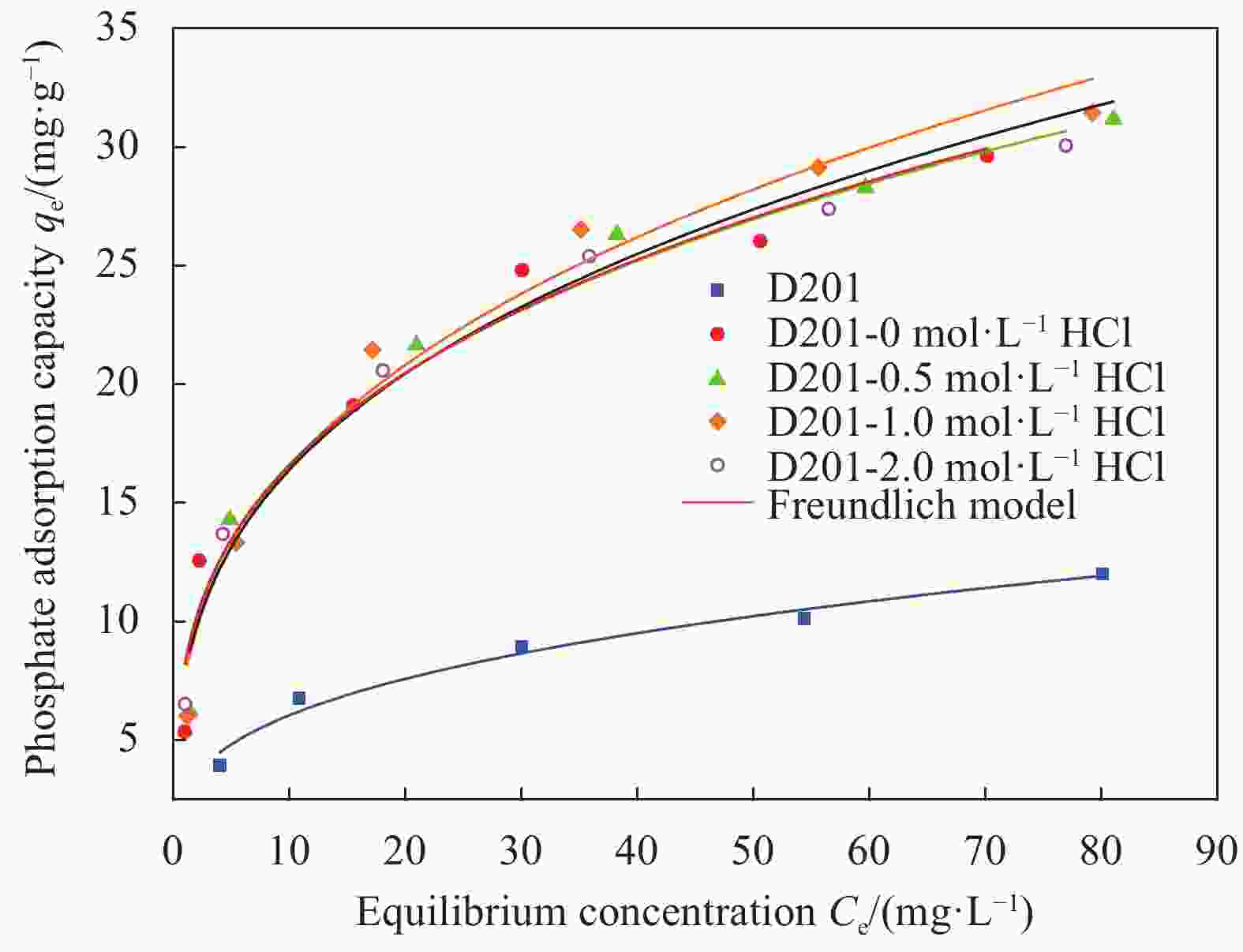
Adsorbent Langmuir model Freundlich model qm/(mg·g-1) b/(L·mg-1) R2 n K/(mg 1-1/n·L1/n·g-1) R2 D201 16.39 0.075 0.851 3.066 2.855 0.971 D201-0 mol·L-1HCl 26.67 0.316 0.914 3.329 8.321 0.981 D201-0.5 mol·L-1HCl 29.67 0.235 0.931 3.301 8.263 0.951 D201-1 mol·L-1HCl 29.85 0.192 0.927 3.141 7.876 0.970 D201-2 mol·L-1HCl 28.57 0.221 0.921 3.014 7.704 0.971 Notes: qm—Maximum adsorption capacity; b, K and n—Isotherm constants. -
[1] 项学敏, 刘颖, 周集体, 等. 水合氧化铁对废水中磷酸根的吸附-解吸性能研究[J]. 环境科学, 2008, 29(11):69-73.XIANG Xuemin, LIU Ying, ZHOU Jiti, et al. Sorption-desorption of phosphate in wastewater by hydrous iron oxide[J]. Environmental Science,2008,29(11):69-73(in Chinese). [2] 葛磊, 王静, 陈欢, 等. 活性炭负载水合氧化铁对草甘膦吸附性能的研究[J]. 环境工程学报, 2009, 3(10):1745-1748.GE Lei, WANG Jing, CHEN Huan, et al. Adsorption of glyphosate from aqueous solution by hydrous ferric oxide preloaded into active carbon[J]. Chinese Journal of Environmental Engineering,2009,3(10):1745-1748(in Chinese). [3] 莫德清, 段钧元, 王曦兢. 水合氧化铁对含磷废水的吸附特性研究[J]. 环境科学与技术, 2012, 35(12J):66-69.MO Deqing, DUAN Junyuan, WANG Xijing. Study on phosphate contained wastewater adsorption by hydrous iron oxide[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2012,35(12J):66-69(in Chinese). [4] DEY S, GOSWAMI S, GHOSH U C. Hydrous ferric oxide (HFO) a scavenger for fluoride from contaminated water[J]. Water Air& Soil Pollution,2004,158(1):311-323. [5] LI Y, LI Z, XU F, et al. Superconducting magnetic separation of phosphate using freshly formed hydrous ferric oxide sols[J]. Environmental Technology,2017,38(1-4):377-384. [6] 张庆建, 张炜铭, 潘丙才, 等. 载铁复合环境材料的制备及对水体中砷的深度净化[J]. 离子交换与吸附, 2009, 25(3):282-288.ZHANG Qingjian, ZHANG Weiming, PAN Bingcai, et al. Preparation of iron-loaded hybrid materials for trace arsenic removal from waters[J]. Ion Exchange and Adsorption,2009,25(3):282-288(in Chinese). [7] GUPTA V K, SAINI V K, JAIN N. Adsorption of As(III) from aqueous solutions by iron oxide-coated sand[J]. Journal of Colloid & Interface Science,2005,288(1):55-60. [8] BOUJELBEN N, BOUZID J, ELOUEAR Z. Adsorption of nickel and copper onto natural iron oxide-coated sand from aqueous solutions: Study in single and binary systems[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2009,163(1):376-382. doi: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2008.06.128 [9] JEON C S, BAEK K, PARK J K, et al. Adsorption characteristics of As(v) on Iron-coated zeolite[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2009,163(2-3):804-808. [10] KUNDU S, GUPTA A K. Arsenic adsorption onto iron oxide-coated cement (IOCC): Regression analysis of equilibrium data with several isotherm models and their optimization[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2006,122(1-2):93-106. [11] CUMBAL L, SENGUPTA A K. Arsenic removal using polymer-supported hydrated iron(III) oxide nanoparticles: Role of Donnan membrane effect[J]. Environmental Science& Technology,2005,39(17):6508-6515. [12] ZHAO X, LV L, PAN B, et al. Polymer-supported nanocomposites for environmental application: A review[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2011,170(2-3):381-394. [13] PAN B, WU J, PAN B, et al. Development of polymer-based nanosized hydrated ferric oxides (HFOs) for enhanced phosphate removal from waste effluents[J]. Water Research,2009,43(17):4421-4429. [14] SENDROWSKI A, BOYER T H. Phosphate removal from urine using hybrid anion exchange resin[J]. Desalination,2013,322(4):104-112. [15] LI H, SHAN C, ZHANG Y, et al. Arsenate adsorption by hydrous ferric oxide nanoparticles embedded in cross-linked anion exchanger: Effect of the host pore structure[J]. Acs Applied Materials & Interfaces,2016,8(5):3012-3020. [16] HUA M, YANG B, SHAN C, et al. Simultaneous removal of As(V) and Cr(VI) from water by macroporous anion exchanger supported nanoscale hydrous ferric oxide composite[J]. Chemosphere,2017,171(3):126-133. [17] 中国石油和化学工业联合会. 离子交换树脂预处理方法: GB/T 5476—2013[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2013.China Petroleum and Chemical Industry Federation. Methods for pretreating ion exchange resins: GB/T 5476—2013[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2013(in Chinese). [18] DEMARCO M J, SENGUPTA A K, GREENLEAF J E. Arsenic removal using a polymeric/inorganic hybrid sorbent[J]. Water Research,2003,37(1):164-176. [19] 国家环境保护局标准处. 水质总磷的测定. 钼酸铵分光光度法: GB/T 11893—1989[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 1989.Standards Division, Ministry of Environmental Protection of the People’s Republic of China. Water quality-Determination of total phosphorus-Ammonium molybdate spectrophotrometric method: GB/T 11893—1989[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 1989 (in Chinese). [20] 唐振平, 毕玉玺, 刘迎九, 等. 氧化石墨烯/有机改性膨润土复合材料的制备及其对Cd(Ⅱ)的吸附[J]. 复合材料学报, 2018, 35(11):284-292.TANG Zhenping, BI Yuxi, LIU Yingjiu, et al. Preparation of graphene oxide/organo-modified bentonite composites and their adsorption on Cd(II)[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2018,35(11):284-292(in Chinese). [21] 谢发之, 李振宇, 李海斌, 等. 水合氧化铁负载D418树脂对磷的吸附性能研究[J]. 环境污染与防治, 2019, 41(2):175-179.XIE Fazhi, LI Zhenyu, LI Haibin, et al. Phosphorus adsorption capacity of D418 resin loaded with hydrated ferric oxide[J]. Environmental Pollution & Control,2019,41(2):175-179(in Chinese). [22] 郑晓英, 李楠, 邱丽佳, 等. 羟基铁对污水厂二级处理出水中低浓度磷的深度处理性能[J]. 净水技术, 2019, 28(3):70-75.ZHENG Xiaoying, LI Nan, QIU Lijia, et al. Advanced phosphorus removal from low phosphorus concentration water by iron hydroxyl[J]. Water Purification Technology,2019,28(3):70-75(in Chinese). -





 下载:
下载: