Preparation of dual-network MXene hydrogels and their electromagnetic and UV shielding properties
-
摘要: MXene因其高导电性、丰富的活性位点(如—OH、—F、—O)、电化学行为和优异的亲水性使其在柔性可穿戴材料中显示出了特有的优势。然而,兼具优异力学强度和高电磁屏蔽效能的水凝胶还有待进一步研究;同时,透明水凝胶往往缺乏过滤紫外线的能力,这极大限制了材料的应用。本文以丙烯酰胺(AAm)共聚甲基丙烯酸羟乙酯(HEMA)化学交联为第一网络,聚丙烯酸(PAA)-Fe3+金属离子络合为第二网络,二维MXene作为导电纳米填料,制备了独特双屏蔽机制 PAAm-PHEMA/PAA-Fe3+-MXene水凝胶。MXene和Fe3+的存在使得该水凝胶同时兼具电磁和紫外屏蔽特性。通过 FTIR、SEM和EDS确认了水凝胶三维网络结构。所制备的双网络水凝胶具有高力学强度(320.1 kPa)、高拉伸性(1786%)和良好的导电性(3.8 S/m)。此外,该水凝胶还表现出了优异的紫外线屏蔽能力,在365和550 nm的特征波长下的透射率分别为0%和79.2%。同时,该水凝胶在X波段内可以获得超过 36 dB 的出色电磁屏蔽(EMI)效能以及对各种基材强黏附性、快速自愈合能力和高度形状适应性。本文提供了一种灵活且可高度可调的双屏蔽机制水凝胶网络设计和大规模简易制备新思路,在柔性可穿戴材料方面展示出了巨大的应用前景。Abstract: MXenes show unique advantages in electromagnetic shielding materials due to their high electrical conductivity, abundant active sites (such as —OH, —F, —O), electrochemical behavior, and excellent hydrophilicity. However, hydrogels with both excellent mechanical strength and high electromagnetic shielding efficiency remain to be further studied. Meanwhile, transparent hydrogels often lack the ability to filter ultraviolet light, which greatly limits the application of hydrogel materials. In this work, PAAm-PHEMA/PAA-Fe3+-MXene hydrogels with double shielding mechanism were prepared by using acrylamide (AAm) copolymer hydroxyethyl methacrylate (HEMA) chemical cross-linking as the first network, and polyacrylic acid (PAA)-Fe3+ metal ion complexation as the second network, and two-dimensional MXene as conductive nanofillers. The presence of MXene and Fe3+ makes the hydrogel possess both electromagnetic and UV shielding properties. The structure and three-dimensional network of the composite hydrogel were confirmed by FTIR, SEM and EDS. The as-prepared double-network hydrogel exhibits high mechanical strength (320.1 kPa), high stretchability (1786%), and good electrical conductivity (3.8 S/m). In addition, the composite hydrogel also exhibits excellent UV shielding ability, with transmittances of 0% and 79.2% at characteristic wavelengths of 365 and 550 nm, respectively. At the same time, the composite hydrogel can obtain excellent electromagnetic-interference (EMI) shielding effect of more than 36 dB in the X-band, strong adhesion to various substrates, rapid self-healing performance and high shape adaptability. This work provides a flexible and highly tunable dual-shielding mechanism hydrogel network design and large-scale facile fabrication of new ideas, showing great application prospects in flexible wearable materials.
-
Keywords:
- conductive hydrogel /
- double network /
- MXene /
- electromagnetic shielding /
- UV shield
-
-
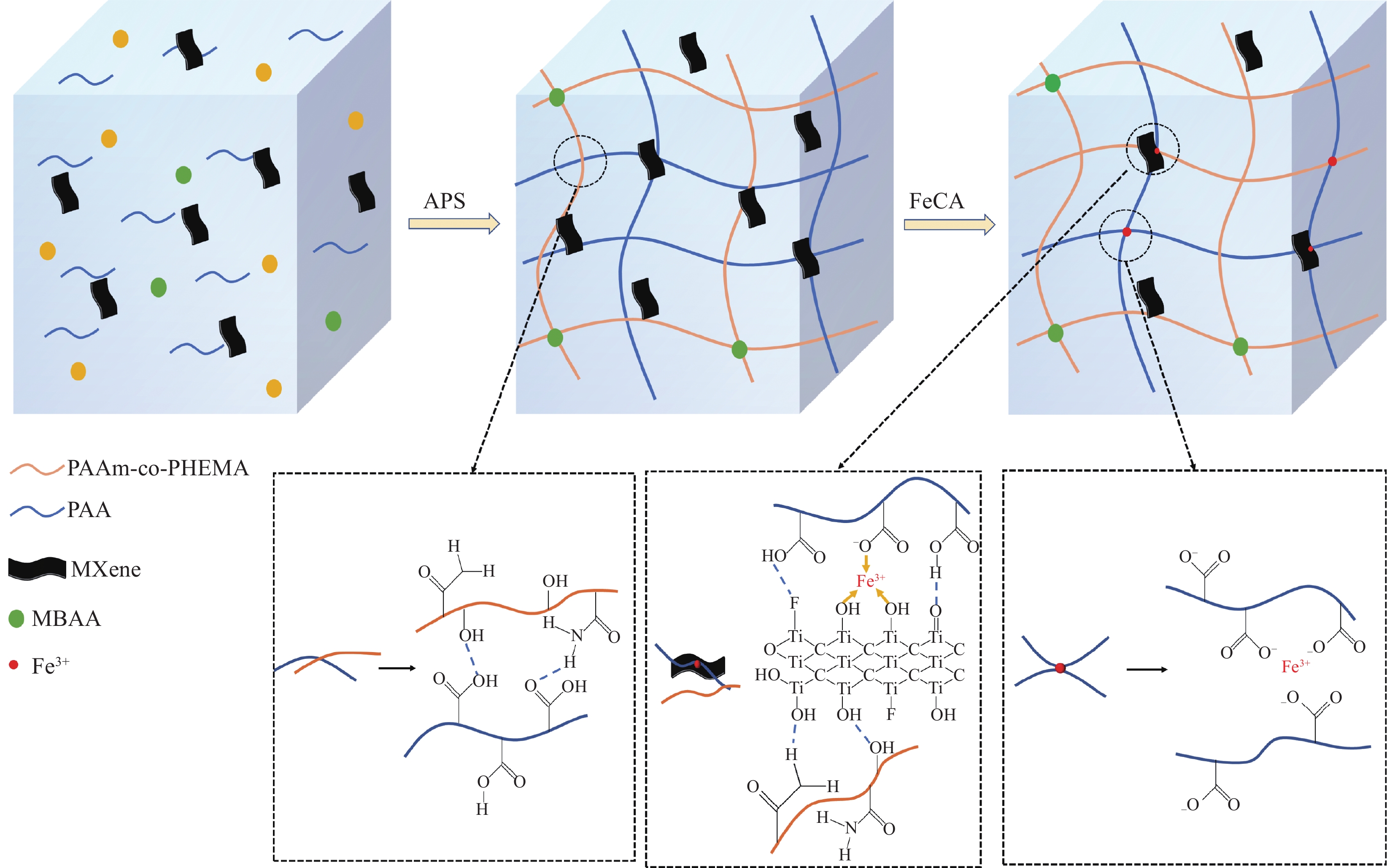
图 1 坚韧和黏性聚丙烯酰胺(PAAm)-聚甲基丙烯酸羟乙酯 (PHEMA)/聚丙烯酸 (PAA)-Fe3+-MXene水凝胶的的设计策略
Figure 1. Design strategies for tough and sticky PAAm-PHEMA/PAA-Fe3+-MXene hydrogels
AAm—Acrylamide; HEMA—Hydroxyethyl methacrylate; PAA—Polyacrylic acid; MBAA—N, N'-methylenebis(2-propenamide); APS—Ammonium persulphate; CA—Citric Acid
图 2 (a) Ti3AlC2(MAX)粉末的SEM图像;(b) HCl/LiF蚀刻的最小强度分层(MILD)-Ti3C2Tx粉末;((c), (d)) MXene的SEM图像和TEM图像;((e), (f)) 分层的Ti3C2Tx 纳米片的AFM图像和高度分布;((g), (h)) 分层的 Ti3C2Tx 纳米片的XPS、XRD图谱
Figure 2. (a) SEM image of Ti3AlC2 (MAX) powder; (b) HCl/LiF etched minimally intensive layer delamination (MILD)-Ti3C2Tx powder; ((c), (d)) SEM image and TEM image of MXene; ((e), (f)) AFM image and height distribution of layered Ti3C2Tx nanosheets; ((g), (h)) XPS spectra and XRD patterns of highly distributed layered Ti3C2Tx MXene nanosheets
图 3 (a) PAAm-PHEMA/PAA-Fe3+-MXene水凝胶的FTIR图谱;(b) 冷冻干燥后的SEM图像;(c) 冷冻干燥后的PAAm-PHEMA/ PAA-Fe3+-MXene水凝胶的元素分布扫描;((d), (e)) PAAm-PHEMA/PAA-Fe3+-MXene水凝胶不同添加量下的拉伸应力-应变曲线;(f) PAAm-PHEMA/PAA-Fe3+-MXene水凝胶的不同应变(100%、200%、400%和 600%)下加载-卸载循环期间的耗散能量;(g) 8次连续加载-卸载循环的应力-应变曲线;(h) PAAm-PHEMA/PAA-Fe3+-MXene水凝胶的自愈合拉伸应力-应变曲线;(i) PAAm-PHEMA/PAA-Fe3+-MXene水凝胶的流变行为;(j) 拉伸试验中1000%伸长率的高拉伸性
Figure 3. (a) FTIR spectra of PAAm-PHEMA/PAA-Fe3+-MXene hydrogel; (b) SEM image after freeze-drying; (c) Elemental distribution scan of the freeze-dried PAAm-PHEMA/PAA-Fe3+-MXene hydrogel; ((d), (e)) Tensile stress-strain curves of PAAm-PHEMA/PAA-Fe3+-MXene hydrogels with different loadings; (f) PAAm-PHEMA/PAA-Fe3+-MXene hydrogels loaded under different strains (100%, 200%, 400% and 600%)-energy dissipated during unloading cycles; (g) Stress-strain curves for eight consecutive loading-unloading cycles; (h) Self-healing tensile stress-strain curves of PAAm-PHEMA/PAA-Fe3+-MXene hydrogels; (i) Rheological behavior of PAAm-PHEMA/PAA-Fe3+-MXene hydrogels; (j) 1000% elongation in tensile test high stretchability
G'—Energy storage modulus; G''—Loss modulus; w—Angular velocity
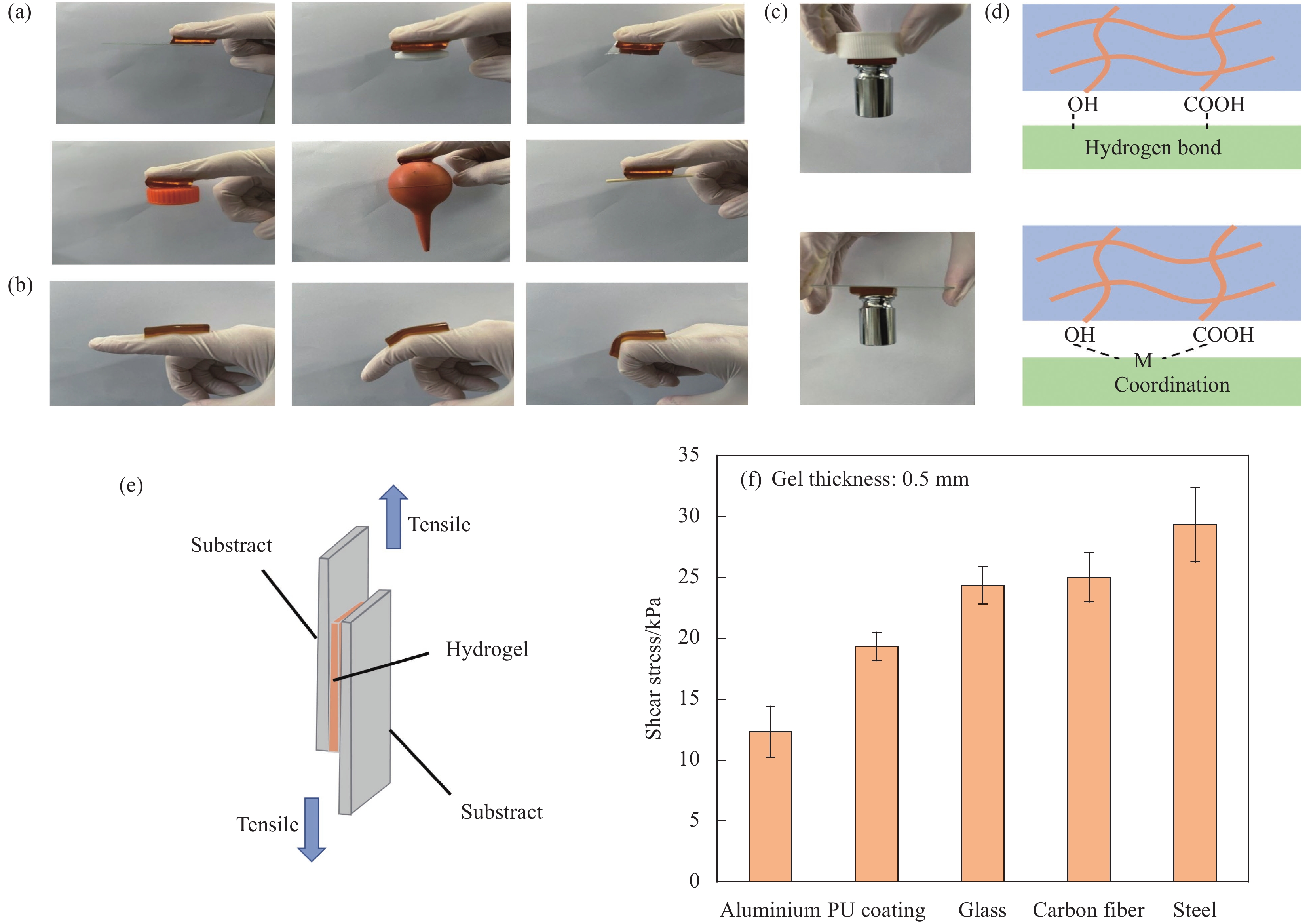
图 4 (a) PAAm-PHEMA/PAA-Fe3+-MXene水凝胶可黏附各种固体材料,包括聚四氟乙烯(PTFE)、聚乙烯(PE)、玻璃、天然橡胶(NR)、铁;(b) 在手指活动过程中的黏附性;(c) PAAm-PHEMA/PAA-Fe3+-MXene水凝胶对100 g砝码良好的黏附性;(d) 黏附机制;(e) 水凝胶黏附测量的示意图;(f) 水凝胶对各种基材的黏合强度
Figure 4. (a) PAAm-PHEMA/PAA-Fe3+-MXene hydrogel adheres to various solid materials including polytetrafluoroethylene (PTFE), polyethylene (PE), glass, natural rubber (NR), iron; (b) On adhesion during finger movement; (c) Good adhesion of PAAm-PHEMA/PAA-Fe3+-MXene hydrogel to 100 g weight; (d) Adhesion mechanism; (e) Schematic illustration of hydrogel adhesion measurement; (f) Adhesion strength of hydrogel to various substrates
PU—Polyurethane; M—Metal ion
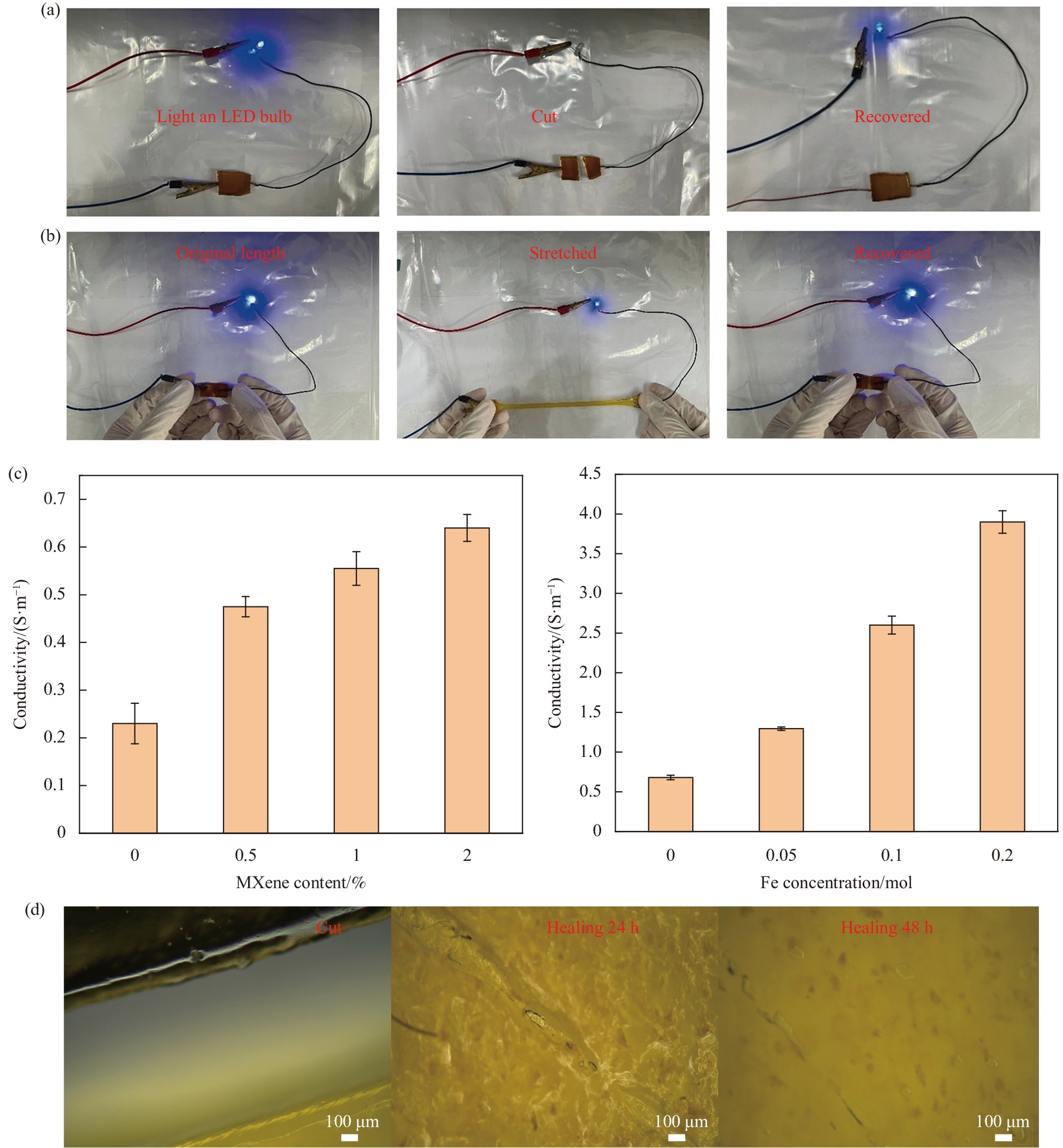
图 5 (a) PAAm-PHEMA/PAA-Fe3+-MXene水凝胶在切割前后电导率的即时恢复;(b) PAAm-PHEMA/PAA-Fe3+-MXene水凝胶在拉伸过程中LED小灯泡的变化;(c) PAAm-PHEMA/PAA-Fe3+-MXene水凝胶在不同MXene含量和不同Fe3+浓度浸泡下的电导率;(d) 愈合过程的超景深光学显微镜图像,其中水凝胶上 100 μm宽的划痕随时间而变化
Figure 5. (a) Immediate recovery of conductivity of PAAm-PHEMA/PAA-Fe3+-MXene hydrogel before and after cleavage; (b) LED light bulb change of PAAm-PHEMA/PAA-Fe3+-MXene hydrogel during stretching; (c) PAAm-PHEMA/PAA-Fe3+-MXene conductivity of MXene hydrogels soaked with different MXene contents and different Fe3+ concentrations; (d) Optical microscope images of the healing process with 100 μm wide scratches on the hydrogel as a function of time
图 6 ((a), (b)) PAAm-PHEMA/PAA-Fe3+-MXene水凝胶的紫外-可见光谱透射率图及在550和365 nm处的相应透射率;(c) PAAm-PHEMA/PAA-Fe3+-MXene水凝胶在切断后不同愈合时间的紫外-可见光谱透射率图;(d) PAAm-PHEMA/PAA-Fe3+-MXene水凝胶的紫外线阻挡能力的图像;((e), (f)) 展示出强紫外吸收和对可见光的高透明度
Figure 6. ((a), (b)) UV-Vis spectral transmittance plot of PAAm-PHEMA/PAA-Fe3+-MXene hydrogel and corresponding transmittance at 550 and 365 nm; (c) UV-Vis spectral transmittance of PAAm-PHEMA/PAA-Fe3+-MXene hydrogels at different healing time after cutting; (d) Images of the UV blocking ability of PAAm-PHEMA/PAA-Fe3+-MXene hydrogels; ((e), (f)) Showing strong UV absorption and high transparency to visible light
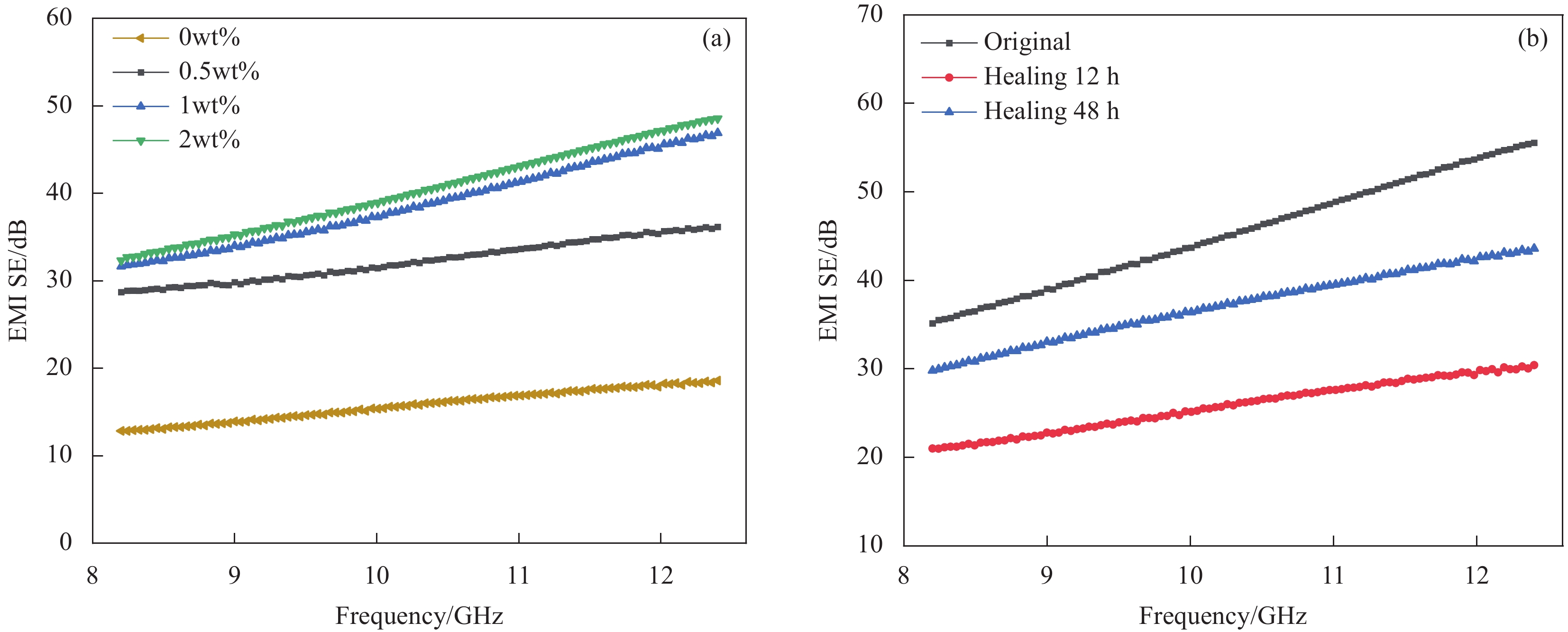
图 7 (a) 不同 MXene含量的PAAm-PHEMA/PAA-Fe3+-MXene水凝胶的电磁屏蔽(EMI)曲线;(b) PAAm-PHEMA/PAA-Fe3+-MXene水凝胶不同愈合时间的EMI曲线
Figure 7. (a) EMI curves of PAAm-PHEMA/PAA-Fe3+-MXene hydrogels containing different MXene contents; (b) EMI curves of PAAm-PHEMA/PAA-Fe3+-MXene hydrogels with different healing time
EMI SE—Electromagnetic-interference shielding effect
-
[1] 胡魁, 王映月, 王昊昱, 等. 高强度耐低温纳米纤维素/聚乙烯醇导电复合水凝胶的制备及其在柔性传感中的应用[J]. 复合材料学报, 2022, 40(2):1060-1070. DOI: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20220322.003 HU Kui, WANG Yingyue, WANG Haoyu, et al. Preparation of high-strength and low-temperature-resistant nanocellulose/polyvinyl alcohol conductive composite hydrogel and its application in flexible sensing[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2022,40(2):1060-1070(in Chinese). DOI: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20220322.003
[2] MA C, MA M G, SI C, et al. Flexible MXene-based composites for wearable devices[J]. Advanced Functional Materials,2021,31(22):2009524. DOI: 10.1002/adfm.202009524
[3] WANG S X, LIU Q R, FENG S J, et al. A water-retaining, self-healing hydrogel as ionic skin with a highly pressure sensitive properties[J]. Journal of the Taiwan Institute of Chemical Engineers,2019,104:318-329. DOI: 10.1016/j.jtice.2019.09.005
[4] 李晓彬. 自修复的MXene复合水凝胶的制备与传感性能研究[D]. 北京: 北京化工大学, 2021. LI Xiaobin. Preparation and sensing properties of self-healing MXene composite hydrogels[D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Chemical Technology, 2021(in Chinese).
[5] LIM H R, KIM H S, QAZI R, et al. Advanced soft materials, sensor integrations, and applications of wearable flexible hybrid electronics in healthcare, energy, and environment[J]. Advanced Materials,2020,32(15):1901924. DOI: 10.1002/adma.201901924
[6] IQBAL A, SAMBYAL P, KOO C M. 2D MXenes for electromagnetic shielding: A review[J]. Advanced Functional Materials,2020,30(47):2000883. DOI: 10.1002/adfm.202000883
[7] LI S, ZHOU X, DONG Y, et al. Flexible self-repairing materials for wearable sensing applications: Elastomers and hydrogels[J]. Macromolecular Rapid Communications,2020,41(23):2000444. DOI: 10.1002/marc.202000444
[8] MIAO M, LIU R, THAIBOONROD S, et al. Silver nanowires intercalating Ti3C2Tx MXene composite films with excellent flexibility for electromagnetic interference shielding[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry C,2020,8(9):3120-3126. DOI: 10.1039/C9TC06361G
[9] YUN T, KIM H, IQBAL A, et al. Electromagnetic shielding of monolayer MXene assemblies[J]. Advanced Materials,2020,32(9):1906769. DOI: 10.1002/adma.201906769
[10] XIA Y, GAO W, GAO C. A review on graphene-based electromagnetic functional materials: Electromagnetic wave shielding and absorption[J]. Advanced Functional Materials,2022,32(42):2204591. DOI: 10.1002/adfm.202204591
[11] ALHABEB M, MALESKI K, ANASORI B, et al. Guidelines for synthesis and processing of two-dimensional titanium carbide (Ti3C2Tx MXene)[J]. Chemistry of Materials,2017,29(18):7633-7644. DOI: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.7b02847
[12] TONDERA C, AKBAR T F, THOMAS A K, et al. Highly conductive, stretchable, and cell-adhesive hydrogel by nanoclay doping[J]. Small,2019,15(27):e1901406. DOI: 10.1002/smll.201901406
[13] HIRSCH M, CHARLET A, AMSTAD E. 3D printing of strong and tough double network granular hydrogels[J]. Advanced Functional Materials,2020,31(5):2005929.
[14] 张光照. 基于脲基嘧啶酮四重氢键超分子水凝胶的设计及其刺激响应性能研究[D]. 广州: 华南理工大学, 2019. ZHANG Guangzhao. Design and stimuli-responsive properties of supramolecular hydrogels based on ureidopyrimidinone quadruple hydrogen bonds[D]. Guangzhou: South China University of Technology, 2019(in Chinese).
[15] JEON I, CUI J, ILLEPERUMA W R, et al. Extremely stretchable and fast self-healing hydrogels[J]. Advanced Materials,2016,28(23):4678-4683. DOI: 10.1002/adma.201600480
[16] 鲁程程, 于振坤, 杨园园, 等. 聚丙烯酸-Al3+/壳聚糖复合双网络水凝胶的制备与性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2021, 39(12):5901-5911. DOI: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20211119.004 LU Chengcheng, YU Zhenkun, YANG Yuanyuan, et al. Preparation and properties of polyacrylic acid-Al3+/chitosan composite double network hydrogels[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2021,39(12):5901-5911(in Chinese). DOI: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20211119.004
[17] LIPATOV A, ALHABEB M, LUKATSKAYA M R, et al. Effect of synthesis on quality, electronic properties and environmental stability of individual monolayer Ti3C2 MXene flakes[J]. Advanced Electronic Materials,2016,2(12):1600255. DOI: 10.1002/aelm.201600255
[18] ZHAO H, HAO S, FU Q, et al. Ultrafast fabrication of lignin-encapsulated silica nanoparticles reinforced conductive hydrogels with high elasticity and self-adhesion for strain sensors[J]. Chemistry of Materials,2022,34(11):5258-5272. DOI: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.2c00934
[19] GE G, ZHANG Y Z, ZHANG W, et al. Ti3C2Tx MXene-activated fast gelation of stretchable and self-healing hydrogels: A molecular approach[J]. ACS Nano,2021,15(2):2698-2706. DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.0c07998
[20] DENG Y, SHANG T, WU Z, et al. Fast gelation of Ti3C2Tx MXene initiated by metal ions[J]. Advanced Materials,2019,31(43):1902432. DOI: 10.1002/adma.201902432
[21] CHEN W, BU Y, LI D, et al. Development of high-strength, tough, and self-healing carboxymethyl guar gum-based hydrogels for human motion detection[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry C,2020,8(3):900-908. DOI: 10.1039/C9TC05797H
[22] WANG Y, HUANG F, CHEN X, et al. Stretchable, conductive, and self-healing hydrogel with super metal adhesion[J]. Chemistry of Materials,2018,30(13):4289-4297. DOI: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.8b01260
[23] QIAO H, QI P, ZHANG X, et al. Multiple weak H-bonds lead to highly sensitive, stretchable, self-adhesive, and self-healing ionic sensors[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2019,11(8):7755-7763. DOI: 10.1021/acsami.8b20380
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 王新羽,刘婷婷,赵小宇. 改性碳纳米管/PVDF膜的制备及性能研究. 绿色环保建材. 2020(10): 14-15 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 关集俱,刘德利,王勇,冯伯华,许雪峰. 碳纳米管/油酸复合物制备的纳米流体导电与润湿性能. 复合材料学报. 2020(10): 2582-2589 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(2)
-




 下载:
下载: