Study on impermeability of polymer modified repair mortar based on low field nuclear magnetic resonance technology
-
摘要:
:1H低场核磁共振是通过氢原子能量变化分析水的分布和含量,一种快速、有效、无损的测试技术。通过三轴1H低场核磁共振获得了不同应力状态下可再分散乳胶粉(简称聚合物)改性修补砂浆中可蒸发水的横向弛豫时间(T2)和渗水量,据此分析了砂浆的抗渗性,并通过孔结构与微观形貌揭示了聚合物对砂浆可蒸发水横向弛豫特征的影响机制。研究表明:渗透压是修补砂浆横向弛豫时间和渗水量的主要影响因素,聚合物降低了不同渗透压下修补砂浆毛细孔和凝胶孔水的含量,6 MPa时渗水量降低57.3%,显著提升了修补砂浆的抗渗性能;聚合物提高了修补砂浆的韧性,三轴荷载作用下砂浆由交叉裂缝破坏变为压缩破坏,避免了砂浆在轴压作用下产生的抗渗性能突破。聚合物膜的阻隔和填充作用使砂浆孔隙率降低了3.28%,减弱了凝胶孔和毛细孔中的传输能力,从而降低了修补砂浆的横向弛豫强度和渗水量,提高了其抗渗性能。相较于传统的抗渗性检测方法,1H低场核磁共振可以表征水分的渗透过程,是一种切实可行的抗渗性检测方法。
Abstract:Low field 1H-nuclear magnetic resonance (NMR) is a quick, effective and nondestructive measuring technique to investigate the distribution and content of water by H-atom energy changes. Transverse relaxation time (T2) and seepage amount of redispersible polymer powder (polymer)-modified repair mortars were obtained by triaxial low field 1H-NMR, that was wont to analyze the permeability of the repair mortars. The mechanism of polymer influence on the transverse relaxation characteristics of repair mortars was explained by pore structure and micromorphology analysis. It’s shown that: Osmotic pressure is the main factor affecting the transverse relaxation time and seepage amount of mortar. Polymer reduces the water content in capillary and gel pores of repair mortar under different osmotic pressures, and the water seepage decreases by 57.3% at 6MPa, which significantly improves the impermeability of repair mortar. The polymer improves the toughness of the repair mortar, which makes the cross-cracking damage of mortar change into compression deterioration under three-axis loading conditions, thus avoiding the breakthrough of impermeability of the mortar under axial compression. The blocking and filling effect of polymer film reduces the porosity of mortar by 3.28%, and weakens the transmission ability in gel pores and capillary pores. Therefore, the transverse relaxation strength and water seepage of repair mortar are reduced, enhancing its impermeability. Compared with the traditional impermeability testing methods, low field 1H-NMR can characterize the water infiltration process and the seepage amount at different osmotic pressures, which is a practical impermeability testing method.
-
Keywords:
- low field NMR /
- transverse relaxation time /
- seepage amount /
- polymer /
- repair mortar /
- impermeability
-
-
表 1 水泥的化学组成
Table 1 Chemical compositions of cement
SiO2 Al2O3 Fe2O3 CaO MgO SO3 Na2O f-CaO Loss 20.6 4.57 3.29 63.27 2.59 2.11 0.55 0.76 2.15 表 2 水泥物理力学性能
Table 2 Physical and mechanical properties of cement
Setting time/min Flexural strength/MPa Compressive strength/MPa Initial set Final set 3 d 7 d 28 d 3 d 7 d 28 d 128 196 5.3 6.4 8.5 26 35.9 45.6 表 3 聚合物改性修补砂浆配合比
Table 3 Mix proportion of polymer modified repair mortar
Specimen No. Cement/g Sand/g Superplasticizer/g Defoamer/g Water/g Polymer/g K0 100 200 0.2 0.5 35 0 K3 100 200 0.2 0.5 35 3 K6 100 200 0.2 0.5 35 6 K9 100 200 0.2 0.5 35 9 K12 100 200 0.2 0.5 35 12 K15 100 200 0.2 0.5 35 15 表 4 不同渗透时间修补砂浆渗水量
Table 4 Seepage amount of repaired mortar at different times
5 min 10 min 15 min 20 min 25 min 30 min K0 0.4% 0.71% 1.02% 1.29% 1.54% 1.72% K9 0.05% 0.13% 0.18% 0.22% 0.24% 0.27% 表 5 不同渗透压修补砂浆渗水量
Table 5 Seepage amount of repaired mortar at different infiltration times
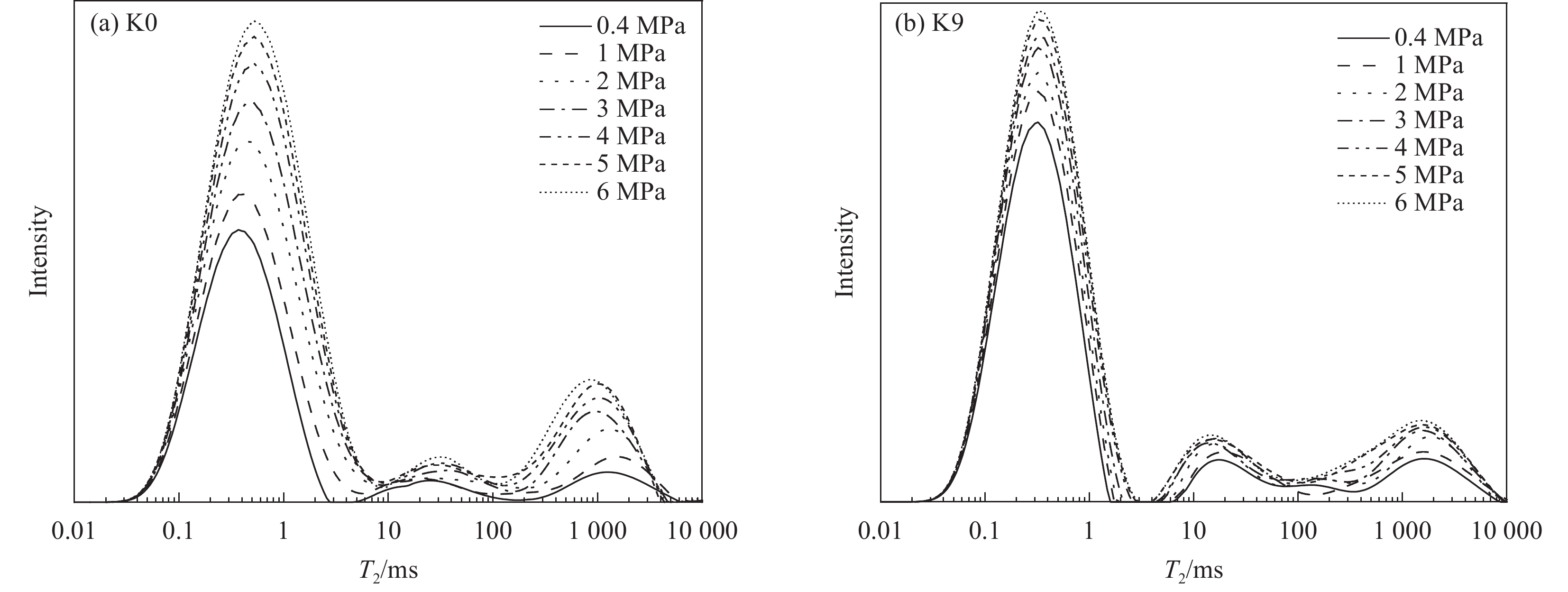
1 MPa 2 MPa 3 MPa 4 MPa 5 MPa 6 MPa K0 1.59% 3.1% 3.9% 4.26% 4.68% 5.34% K9 0.57% 0.97% 1.48% 1.79% 2.02% 2.28% 表 6 不同轴压修补砂浆渗水量
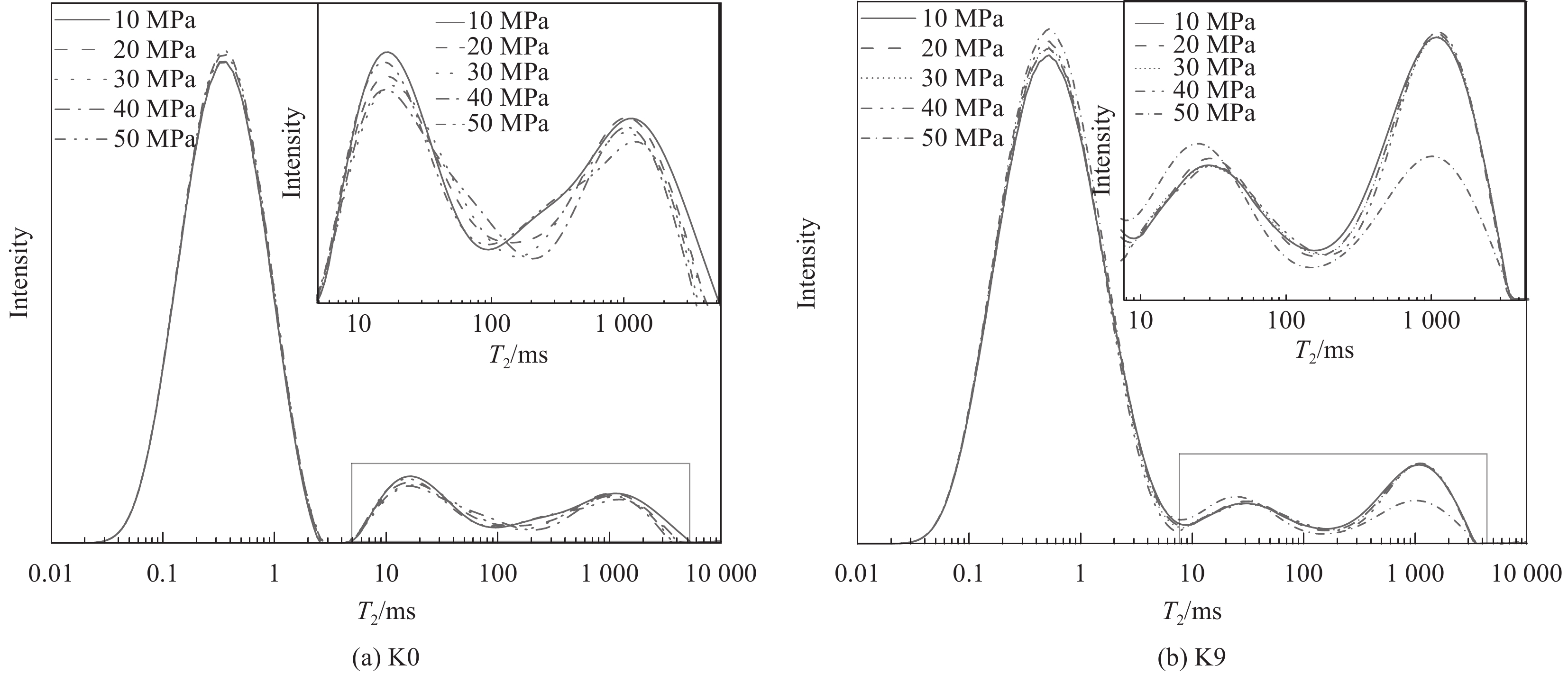
Table 6 Seepage amount of repairing mortar under different coaxial pressure
20 MPa 30 MPa 40 MPa 50 MPa K0 0.03% −0.03% −0.11% −0.38% K9 −0.08% −0.13% −0.12% −0.03% 表 7 聚合物掺量对修补砂浆孔隙率的影响
Table 7 Influence of polymer content on porosity of repair mortar
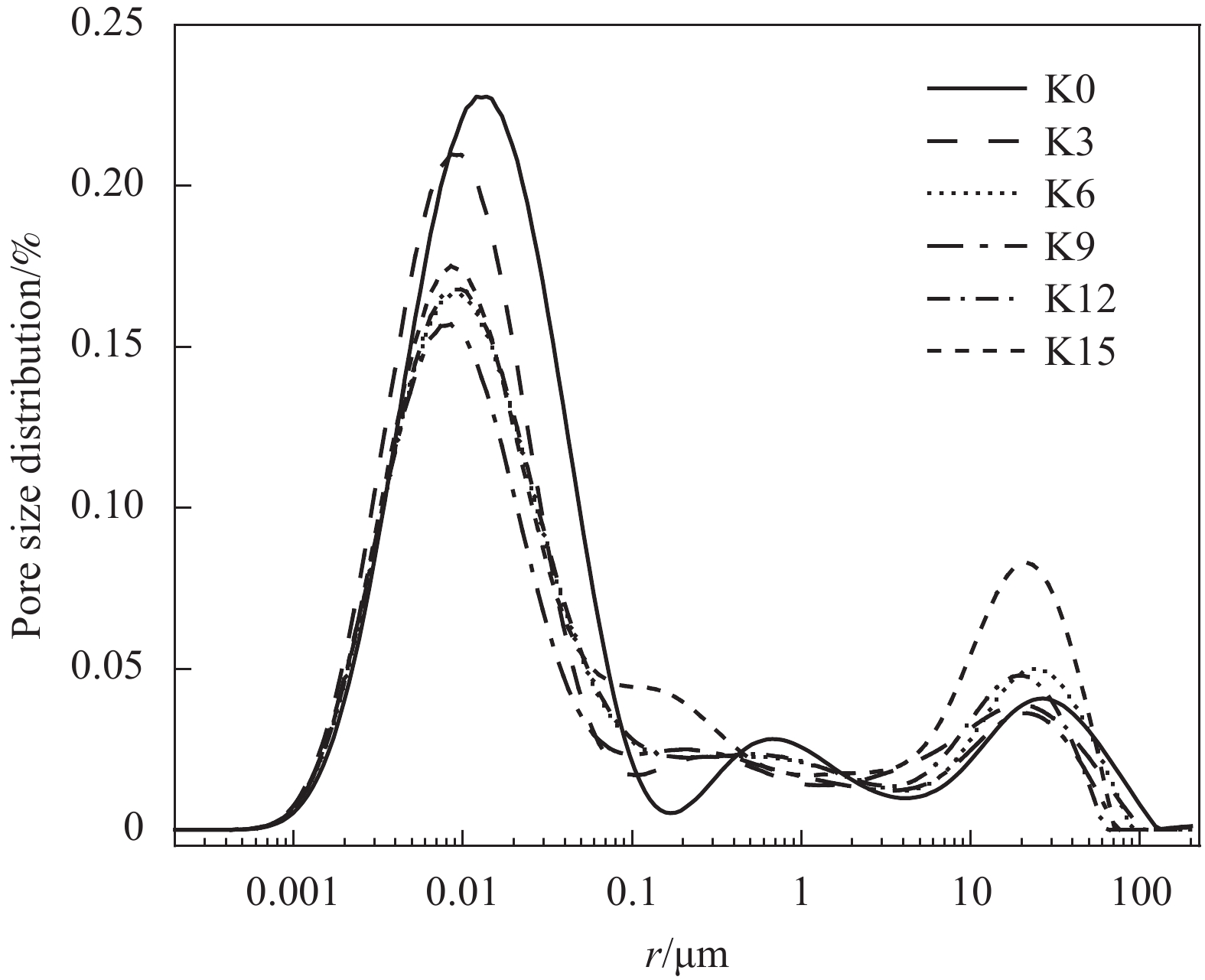
K0 K3 K6 K9 K12 K15 Porosity/% 10.73 9.25 8.53 7.45 8.49 9.84 -
[1] 陈立军, 王永平, 尹新生, 等. 混凝土孔径尺寸对其抗渗性的影响[J]. 硅酸盐学报, 2005, (4): 500-505. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:0454-5648.2005.04.017 CHEN Lijun, WANG Yongping, YIN Xinsheng, et. al. Effect of aperture size on impermeability of concrete[J]. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2005, (4): 500-505(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:0454-5648.2005.04.017
[2] 于琦, 万小梅, 赵铁军, 等. 碱激发矿渣混凝土抗氯离子渗透性及电测试验方法研究[J]. 材料导报, 2022, 36(5): 100-105. DOI: 10.11896/cldb.20120067 YU Qi, WAN Xiaomei, ZHAO Tiejun, et. al. Investigation on resistance of chloride penetration of alkali activated slag concrete and related electrical test methods[J]. Materials Review, 2022, 36(5): 100-105(in Chinese). DOI: 10.11896/cldb.20120067
[3] Valckenborg R M E, Pel L, Hazrati K. Pore water distribution in mortar during drying as determined by NMR[J]. Materials and Structures, 2001, 34(244): 599-604.
[4] Heijden G, Bijnen R, Pel L, et. al. Moisture transport in heated concrete, as studied by NMR, and its consequences for fire spalling[J]. Cement & Concrete Research, 2007, 37(6): 894-901.
[5] Bohris A J, Goerke U, Mcdonald P J, et. al. A broad line NMR and MRI study of water and water transport in Portland cement pastes[J]. Magnetic Resonance Imaging, 1998, 16(5-6): 455-461. DOI: 10.1016/S0730-725X(98)00072-1
[6] Zhang A, Yang W, Ge Y, et. al. Study on the hydration and moisture transport of white cement containing nanomaterials by using low field nuclear magnetic resonance[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2020, 249: 118788. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.118788
[7] 程福周, 雷学文, 孟庆山, 等. 基于核磁共振技术的疏浚淤泥固化土孔隙水含量及分布研究[J]. 长江科学院院报, 2016, 33(10): 116-120. CHENG Fuzhou, Lei Xuewen, Meng Qingshan, et. al. Pore water content of solidified dredging silt and its distribution based on nuclear magnetic resonance[J]. Journal of Yangtze River Scientific Research Institute, 2016, 33(10): 116-120(in Chinese).
[8] Chen Shi, Xiwen Zou, Liu Yang, Ping Wang, et. al. Influence of humidity on the mechanical properties of polymer-modified cement-based repair materials[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2020, 261(2): 119928.
[9] 阎培渝, 岳蕾, 代丹, 等. 无固化剂环氧树脂乳液对油井水泥早期水化的影响[J]. 硅酸盐学报, 2017, 45(5): 608-613. YAN Peiyu, YUE Lei, DAI Dan, et. al. Influence of epoxy resin emulsion without curing agent on hydration of oil well cement in early age[J]. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2017, 45(5): 608-613(in Chinese).
[10] Peng Y, Zhao G, Qi Y, et. al. In-situ assessment of the water-penetration resistance of polymer modified cement mortars by μ-XCT, SEM and EDS[J]. Cement and Concrete Composites, 2020, 114: 103821. DOI: 10.1016/j.cemconcomp.2020.103821
[11] Nirrupama K I, Gujar P, Ashwin K N, et. al. Interfacial adhesion mechanism between organic polymer coating and hydrating cement paste[J]. Cement and Concrete Composites, 2020, 115.
[12] 梅军鹏, 徐智东, 李海南, 等. 纳米粒子/聚合物对水泥基材料强度和抗渗性的影响[J]. 功能材料, 2021, 52(12): 12184-12189. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9731.2021.12.028 MEI Junpeng, XU Zhidong, LI Hainan, et. al. Effects of nanoparticle/polymer composites on strength and impermeability of cement-based materials[J]. Journal of Functional Materials, 2021, 52(12): 12184-12189(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9731.2021.12.028
[13] 李国忠, 张水. 聚合物水泥基灌浆材料的性能研究[J]. 建筑材料学报, 2010, 13(6): 744-748. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9629.2010.06.008 LI Guozhong, ZHANG Shui. Study on the property of polymer cement-based grouting material[J]. Journal of Building Materials, 2010, 13(6): 744-748(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9629.2010.06.008
[14] 全国水泥标准化技术委员会. 水泥胶砂强度检验方法(ISO法)[J]. 2021. National Technical Committee for Cement Standardisa tion. Test method of cement mortar strength (ISO method)[J]. 2021(in Chinese).
[15] 李文郁, 尹健昊, 王健, 等. 低场核磁共振技术在水泥基材料中的理论模型及应用[J]. 硅酸盐学报, 2022, 50(11): 2992-3008. LI Wenyu, YIN Jianhao, WANG Jian, et. al. Principles and applications of low-field nuclear magnetic resonance in cementitious materials[J]. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2022, 50(11): 2992-3008(in Chinese).
[16] 杨正宏, 高双双, 于龙, 等. 养护温度对陶粒内水分向水泥浆体中迁移行为的影响[J]. 建筑材料学报, 2020, 23(1): 138-144. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9629.2020.01.021 YANG Zhenghong, YU Long, GAO Shuangshuan, et. al. Effect of curing temperature on migration of water from ceramsite to cement paste[J]. Journal of Building Materials, 2020, 23(1): 138-144(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9629.2020.01.021
[17] 佘安明, 姚武. 基于低场核磁共振技术的水泥浆体孔结构与比表面积的原位表征[J]. 武汉理工大学学报, 2013, 35(10): 11-15. DOI: 10.3963/j.issn.1671-4431.2013.10.003 SHE An-ming, YAO Wu. Characterization of microstructure and specific surface area of pores in cement paste by low field nuclear magnetic resonance technique[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology, 2013, 35(10): 11-15(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3963/j.issn.1671-4431.2013.10.003
[18] Xue S, Meng F, Zhang P, et. al. Influence of water re-curing on microstructure of heat-damaged cement mortar characterized by low-field NMR and MIP[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2020, 262: 120532. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.120532
[19] 刘大智, 沈化荣, 储洪强, 等. 聚合物水泥砂浆的力学性能与微观机理研究[J]. 南京航空航天大学学报, 2010, 42(6): 802-805. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-2615.2010.06.025 Liu Dazhi, Shen Huarong, Chu Hongqiang, et. al. Mechanical properties and microscopic mechanism of polymer modified mortar[J]. Journal of Nanjing University of Aeronautics & Astronautics, 2010, 42(6): 802-805(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-2615.2010.06.025
[20] 王茹, 许运东. 养护温度对丁苯乳液/硫铝酸盐水泥砂浆物理力学性能的影响[J]. 硅酸盐学报, 2017, 45(2): 227-234. WANG Ru, XU Yundong. Influence of curing temperature on physical and mechanical properties of styrene-butadiene rubber latex/sulphoaluminate cement mortar[J]. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2017, 45(2): 227-234 (in Chinese).
[21] 王培铭, 赵国荣, 张国防. 可再分散乳胶粉在水泥砂浆中的作用机理[J]. 硅酸盐学报, 2018, 46(2): 256-262. WANG Peiming, ZHAO Guorong, ZHANG Guofang. Mechanism of redispersible polymer powder in cement mortar[J]. Journal of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2018, 46(2): 256-262 (in Chinese).
[22] Mehta P K, Monteiro P J M. Concrete: Microstructure, Properties, and Material[M]. McGraw-Hill Publishing, 01.
[23] Pang Bo, Jia Yantao, Pang Sze Dai, et. al. The interpenetration polymer network in a cement paste–waterborne epoxy system[J]. Cement and Concrete Research, 2021, 139: 106236. DOI: 10.1016/j.cemconres.2020.106236
[24] 高乙博, 罗健林, 李治庆, 等. 正交优化纤维聚合物修补防护砂浆配比及其综合性能实现机制[J]. 复合材料学报, 2023, 40(9): 5258-5275. GAO Yibo, LUO Jianlin, LI Zhiqing, et. al. Orthogonal optimization mix ratio of fiber polymer repair protect mortar and its comprehensive performance realization mechanism[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2023, 40(9: 5258-5275 (in Chinese)
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 柯俊,李志虎,秦玉林. 金属主簧-复合材料副簧复合刚度计算模型. 汽车实用技术. 2021(05): 39-43 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 曾婷,王咏莉,尹忠旺,苏婷慧,师志峰,饶猛. 端面凸轮下压机构支承轴承冲击失效分析及优化(英文). 机床与液压. 2017(24): 37-42 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(5)
-
目的
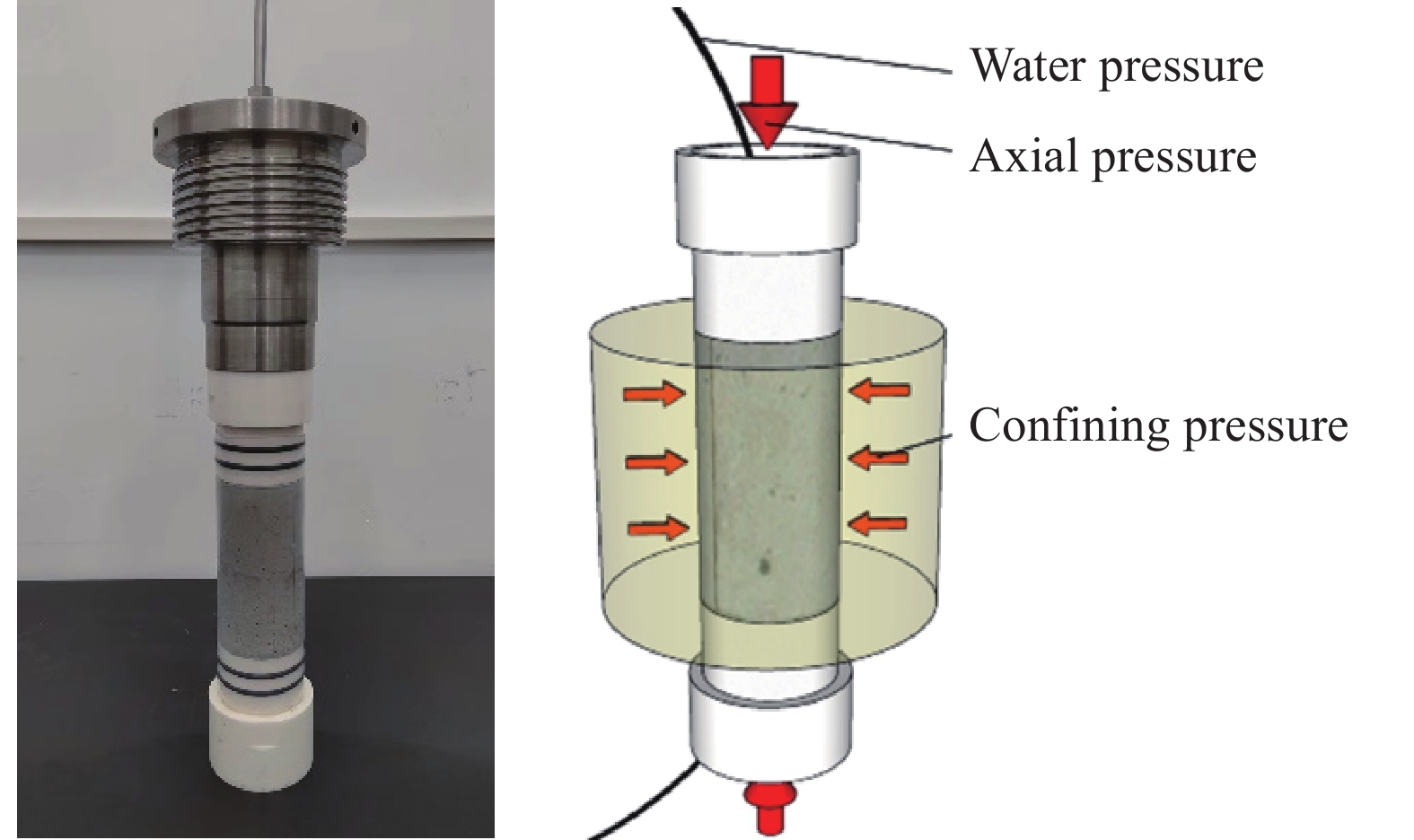
水泥基材料渗透性和耐久性密切相关。目前,水泥基材料的抗渗测试有抗水渗透试验和抗氯离子渗透试验两种方法。这两种方法仅能测得水或离子的渗透结果,无法全面分析渗透过程,因此难以提供足够的数据分析水泥基材料抗渗性能。聚合物改性水泥基材料是一种有机-无机复合材料,具有高韧性、强粘结力和优异的抗渗性能。深入了解水在修补材料中的渗透过程,对揭示聚合物改性机理至关重要。H低场核磁共振是通过氢原子能量变化分析水的分布和含量,可快速、高效、无损的测试水在修补材料的渗透过程。相较于传统的抗渗性检测方法,H低场核磁共振可以表征水分的渗透过程和渗水量,是一种切实可行的抗渗性检测方法。
方法首先设计胶砂比为1:2,水灰比为0.35的修补砂浆,研究了0、3%、6%、9%、12%、15%水泥质量的聚合物对修补砂浆的抗折强度、抗压强度和粘结强度的影响。通过1H低场核磁共振技术测试了渗透压力、渗透时间和轴压对聚合物修补砂浆中可蒸发水的横向弛豫时间和渗水量的影响,并以此表征修补砂浆的抗渗性。最后,通过孔结构和微观形貌分析了聚合物对修补砂浆横向弛豫时间和渗水量的影响机理。
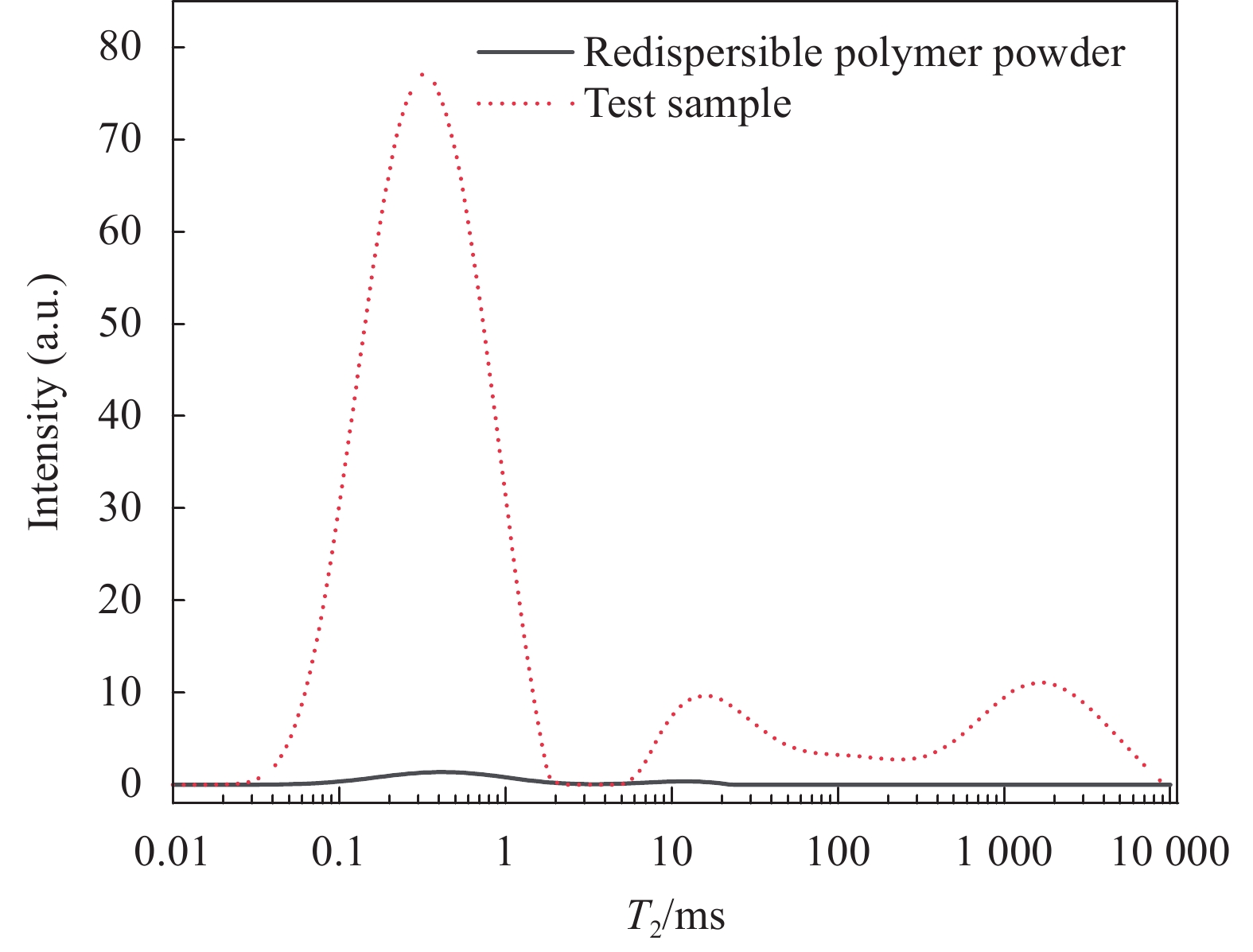
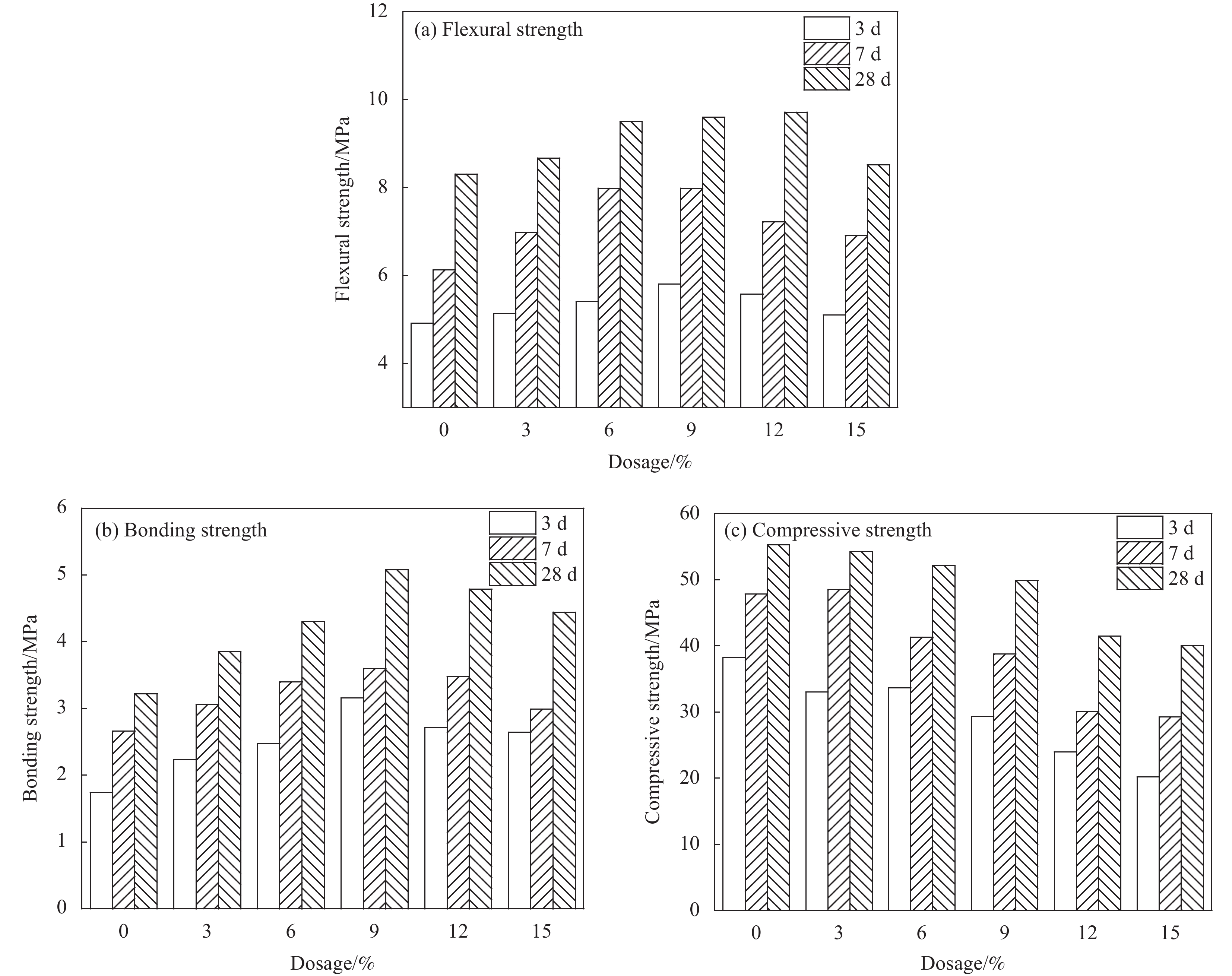
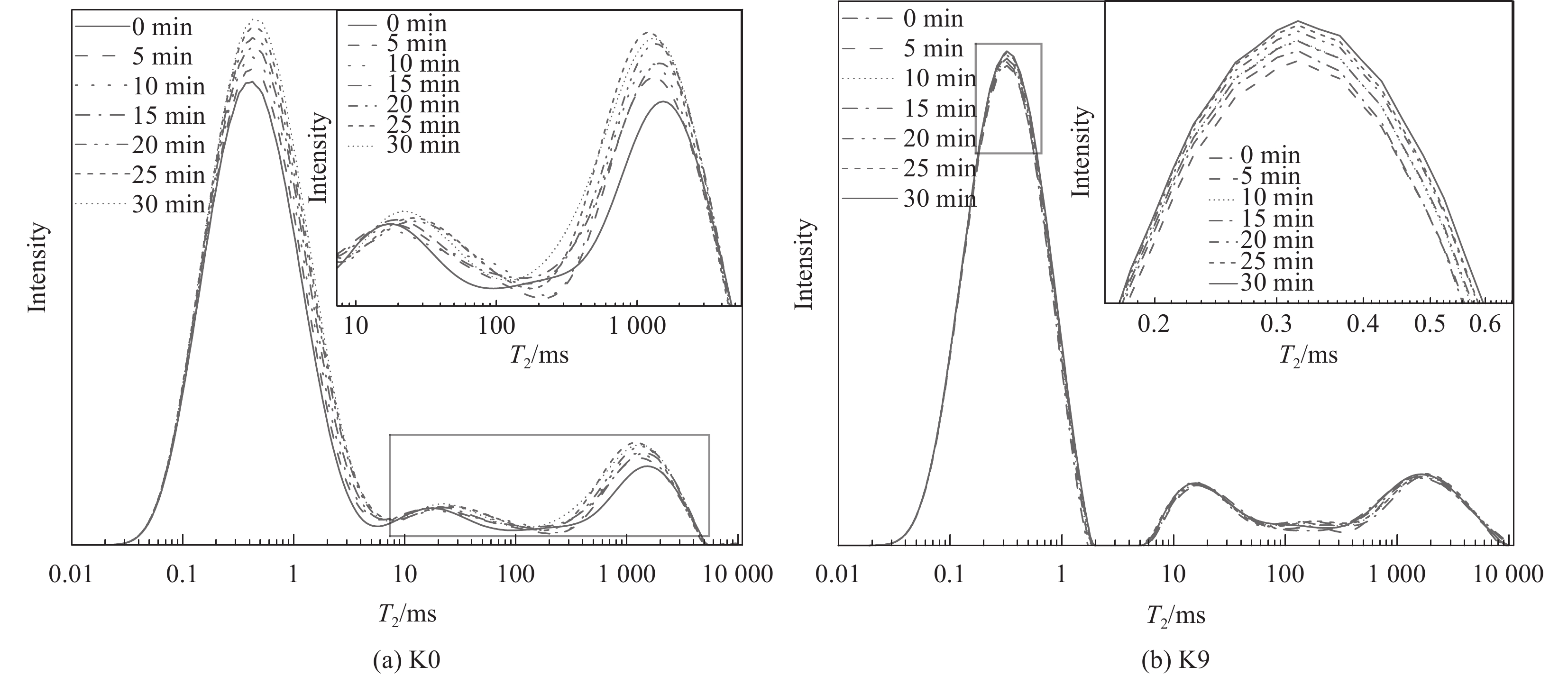
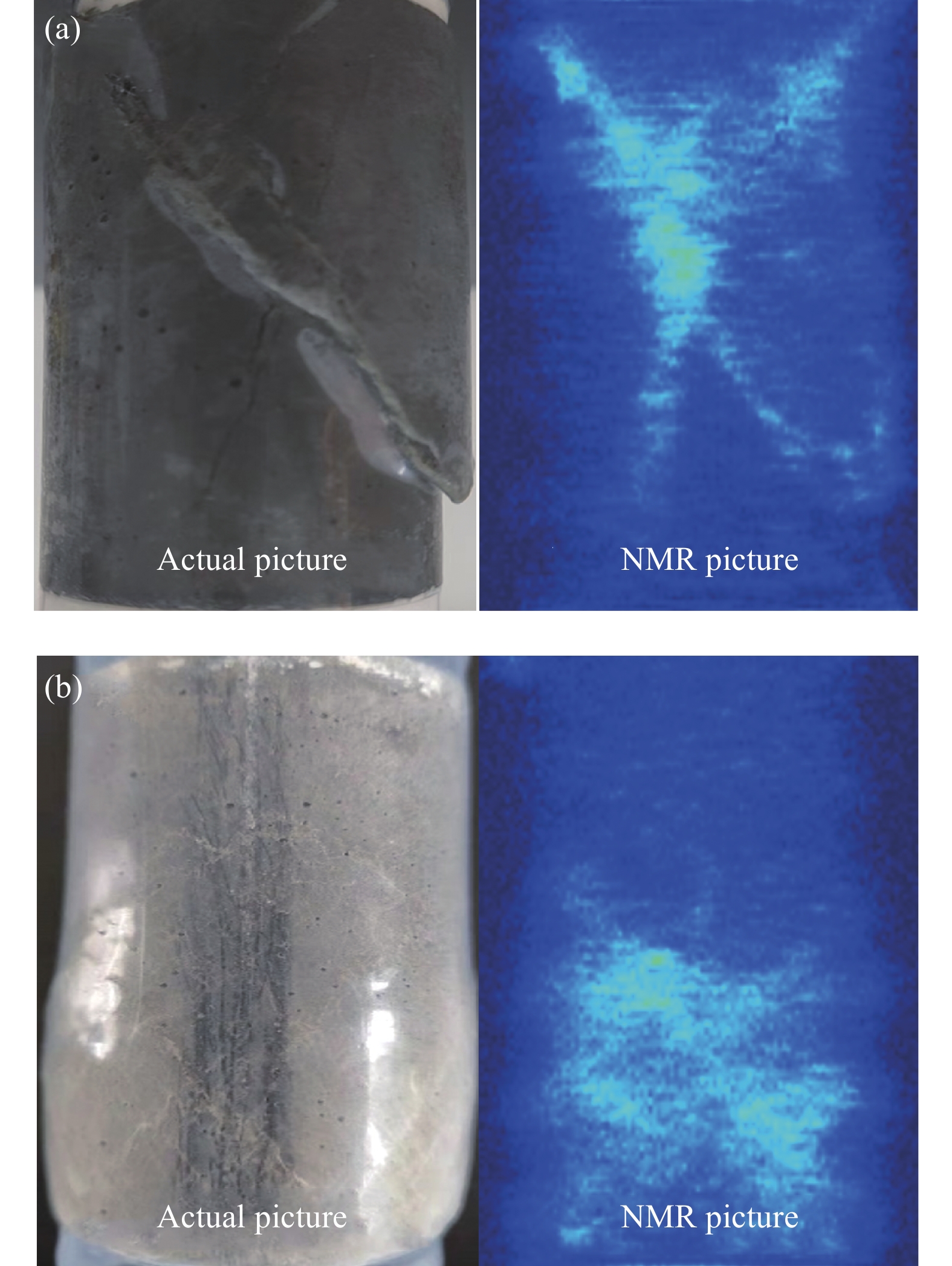
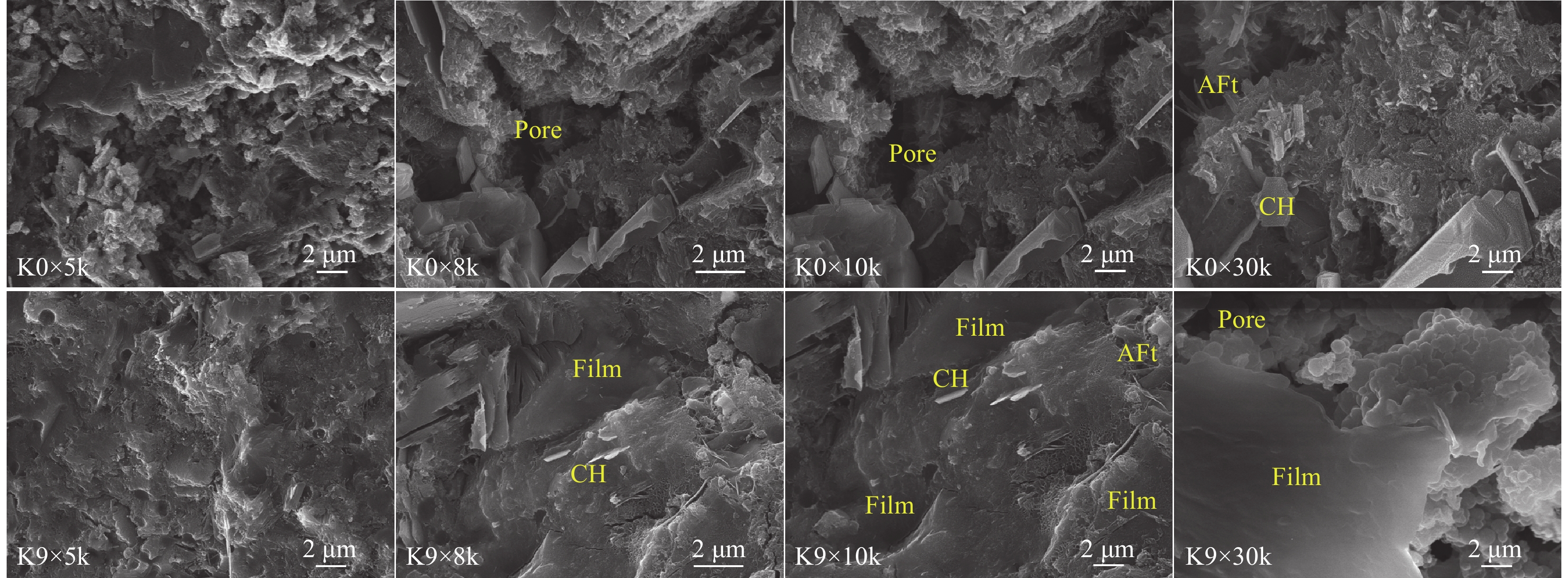
结果(1)聚合物提高了修补砂浆的力学性能,当掺量为9%时,砂浆的抗折强度和粘结强度分别增加了16.99%和57.45%,改善了修补砂浆的韧性和界面性能。(2)通过横向弛豫时间分布和渗水量可以有效的表征聚合物改性修补砂浆抗渗性能。随渗透压渗透时间的增加,水逐渐向修补砂浆凝胶孔隙和毛细孔隙中渗透,聚合物明显降低两者的增长趋势。(3)轴向压力作用下,修补砂浆中的孔隙被压缩,横向弛豫时间分布一个峰的峰值略有增加。当轴压增大到50MPa时,对照组试样横向弛豫时间分布突变,产生交叉裂缝破坏。聚合物改性修补砂浆产生明显的压缩变形未产生明显裂纹,试样的横向弛豫时间分布没有突变。(4)聚合物成膜后粘附在水化产物表面,分割、填充了水泥基材料的孔隙,孔隙率最大降低了3.28%,改善了修补砂浆的微观结构。
结论渗透压力是修补砂浆横向弛豫时间和渗水量的主要影响因素,聚合物降低了不同渗透压下修补砂浆毛细孔和凝胶孔水的含量,6MPa时渗水量降低57.3%,显著提升了修补砂浆的抗渗性能。聚合物提高了修补砂浆的韧性,三轴荷载作用下砂浆由交叉裂缝破坏变为压缩破坏,避免了砂浆在轴压作用下产生的抗渗性能突破。聚合物膜的阻隔和填充作用减弱了凝胶孔和毛细孔中的传输能力,从而降低了修补砂浆的横向弛豫强度和渗水量,提高了其抗渗性能。相较于传统的抗渗性检测方法,H低场核磁共振可以表征水分的渗透过程,是一种切实可行的抗渗性检测方法。





 下载:
下载: