Experimental study on fracture performance of coal gangue coarse aggregate concrete reinforced by multi-factor synergy
-
摘要: 煤矸石资源化利用符合我国绿色发展理念,但煤矸石骨料强度低、吸水率大等原因导致煤矸石混凝土的实际工程应用受到限制。为了研究不同骨料强化方法对煤矸石混凝土的损伤和断裂特性的影响,本文通过水泥浆包裹法(GC)、水玻璃浸泡法(SC)、水泥浆-碳化协同强化法(GT)和水泥浆-水玻璃协同强化法(GS)四种强化处理方法对煤矸石骨料进行强化处理。以碎石混凝土(NC)和无强化的煤矸石混凝土(MC)作为对照组,结合数字图像相关(DIC)技术,对强化后的煤矸石混凝土断裂性能进行了试验研究。结果表明:四种强化方式均可以延缓裂缝的产生与发展,提高煤矸石混凝土的抗断裂能力,其中协同强化效果最为明显,GS、GT组与MC组相比,试件的起裂韧度与失稳韧度分别提高了9.09%、13.64%和25.0%、36.21%;断裂能分别提高了12.63%、17.94%。GT组断裂性能提高幅度最大,与NC组相当。这为煤矸石混凝土的实际工程应用提供了理论依据。Abstract: The resource utilization of coal gangue is in line with the concept of green development in China, but the practical engineering application of coal gangue concrete is limited due to the low strength and high water absorption of coal gangue aggregate. In order to study the effects of different aggregate strengthening methods on the damage and fracture characteristics of coal gangue concrete, four strengthening treatment methods were used to strengthen coal gangue aggregates by four strengthening methods: cement slurry wrapping method (GC), water glass immersion method (SC), cement slurry-carbonization synergistic strengthening method (GT) and cement slurry-water glass synergistic strengthening method (GS). The fracture properties of the strengthened gangue concrete were studied by using crushed stone concrete (NC) and non-reinforced coal gangue concrete (MC) as the control group, combined with digital image correlation (DIC) technology. The results show that the four strengthening methods can delay the occurrence and development of cracks and improve the fracture resistance of gangue concrete, among which the synergistic strengthening effect is the most obvious, compared with the MC group, the cracking toughness of the specimen in the GS and GT groups are increased by 9.09% and 13.64%, and the instability toughness are increased by 25.0% and 36.21%. The fracture energies increase by 12.63% and 17.94%, respectively. The GT group has the largest improvement in fracture performance, which is comparable to that of the NC group. This provides a theoretical basis for the practical engineering application of coal gangue concrete.
-
Keywords:
- coal gangue /
- concrete /
- aggregate strengthening /
- digital speckle /
- fracture property
-
-
表 1 粗骨料的不同强化方式
Table 1 Methods of strengthening coarse aggregates
Species Reinforcement methods Specific practice NC Control group Natural gravel MC Control group Untreated coal gangue GC Cement slurry coating method The cement slurry with a water-cement ratio of 0.35 is prepared to evenly wrap the coal gangue coarse aggregate, wherein the mass ratio of the coal gangue coarse aggregate to the cement slurry is 1:3, and it is moistened and cured for 28 days after hardening. SC Water glass immersion method The coal gangue coarse aggregate was soaked in a water glass solution with a modulus of 3.0 and a concentration of 15% for 1 hour, and then dried naturally. GS Coating - water glass synergistic strengthening method First, prepare a water glass solution with a modulus of 3.0 and a concentration of 15%, pour the cement slurry coal gangue aggregate cured to 28 days old into the configured water glass solution and soak it for 1 hour, and dry it naturally. GT Coating and carbonization synergistic strengthening method The cement coarse aggregate cured to 28 days old is placed in a carbonization box for one week of carbonization curing, and the carbonization environment is temperature: (20±2)℃; Humidity: (70±5)%; CO2 concentration: (20±2)%. Notes: NC is natural crushed stone concrete; MC is unreinforced coal gangue concrete; GC is coal gangue concrete reinforced by aggregate wrapped in grout; SC is coal gangue concrete strengthened by soaking the aggregate in water glass; GS is a coal gangue concrete with aggregate co-reinforced slurry-water glass; GT is a coal gangue concrete whose aggregate is coated with slurry and carbonization. 表 2 天然粗骨料及强化前后煤矸石骨料的基本物理力学性能
Table 2 Basic physical and mechanical properties of natural coarse aggregate and coal gangue aggregate before and after reinforcement
Species Apparent density/(kg·m−3) Water absorption/% Crushing index/% NC 2713 1.1 6.7 MC 2523 10.6 17.3 GC 2554 10.2 13.3 SC 2561 8.6 15.4 GS 2581 7.8 12.7 GT 2594 8.1 12.3 表 3 混凝土配合比及28 d立方体抗压强度
Table 3 Concrete fit ratio and 28 d cube compressive strength
Specimen number Cement Water Sand Crushed stone
qualityQuality of coal
gangueWater reducing
agentCompressive
strength /MPaNC 312 175 863 1054 0 1.6 39.7 MC 312 175 829 0 1013 2.5 32.5 GC 312 175 834 0 1020 2.5 35.6 SC 312 175 836 0 1021 2.5 36.1 GS 312 175 839 0 1043 2.5 37.0 GT 312 175 842 0 1029 2.5 38.1 表 4 双K断裂参数计算结果
Table 4 Calculation results of double K fracture parameters
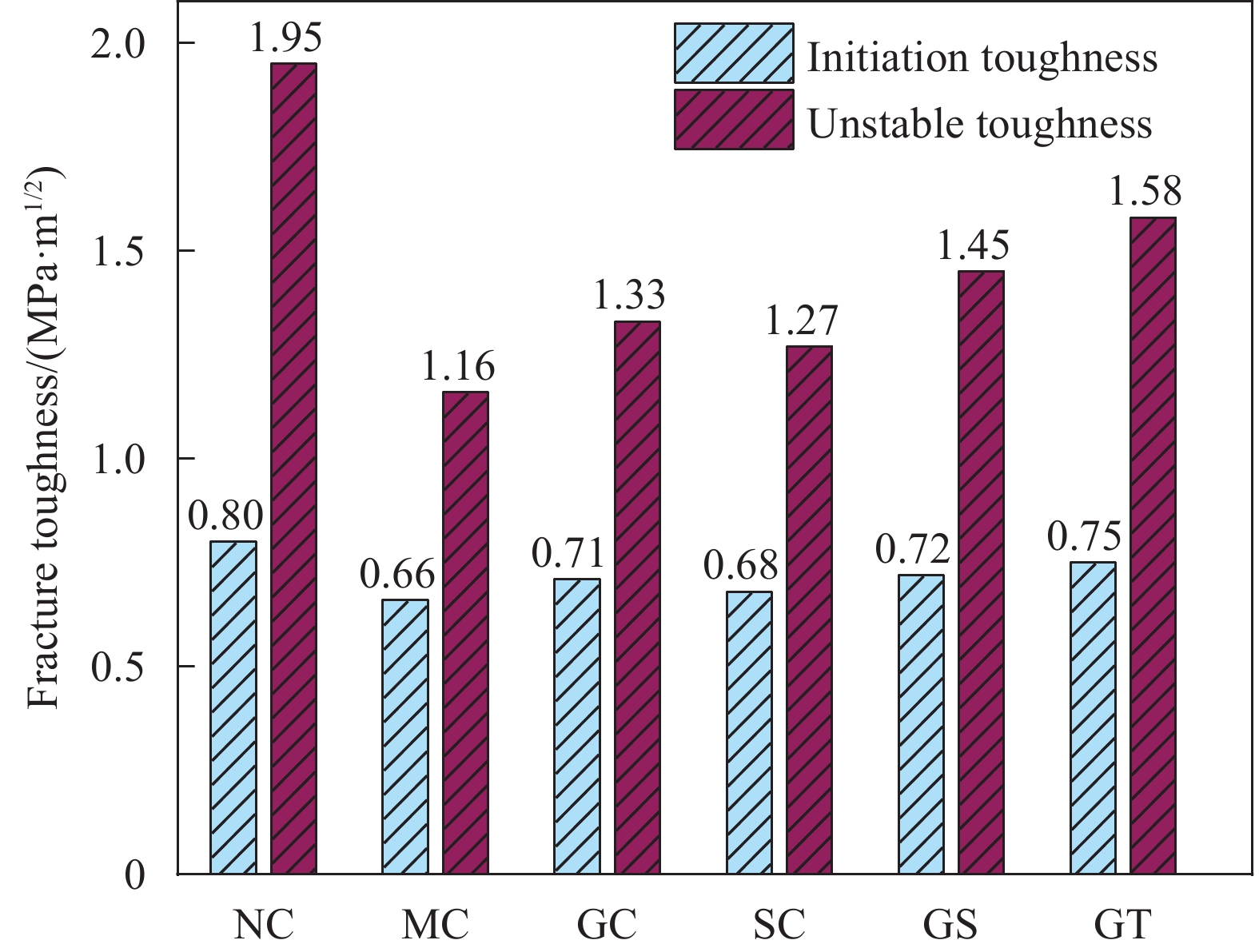
Number Pini/kN Pmax/kN CMODc/mm E/GPa KiniIc/(MPa·m1/2) KunIc/(MPa·m1/2) NC 2.58 2.94 0.0798 32.4 0.80 1.95 MC 2.07 2.59 0.0538 22.4 0.66 1.16 GC 2.29 2.73 0.0584 25.2 0.71 1.33 SC 2.15 2.66 0.0556 24.7 0.68 1.27 GS 2.34 2.78 0.0591 28.7 0.72 1.45 GT 2.45 2.85 0.0608 31.7 0.75 1.58 Notes: Pini and Pmax are the initiation load and peak load; CMODc is the critical opening displacement; E is the calculated modulus of elasticity for concrete; KiniIc and KunIc are initiation toughness and unstable toughness. 表 5 混凝土断裂能计算
Table 5 Concrete fracture energy calculation
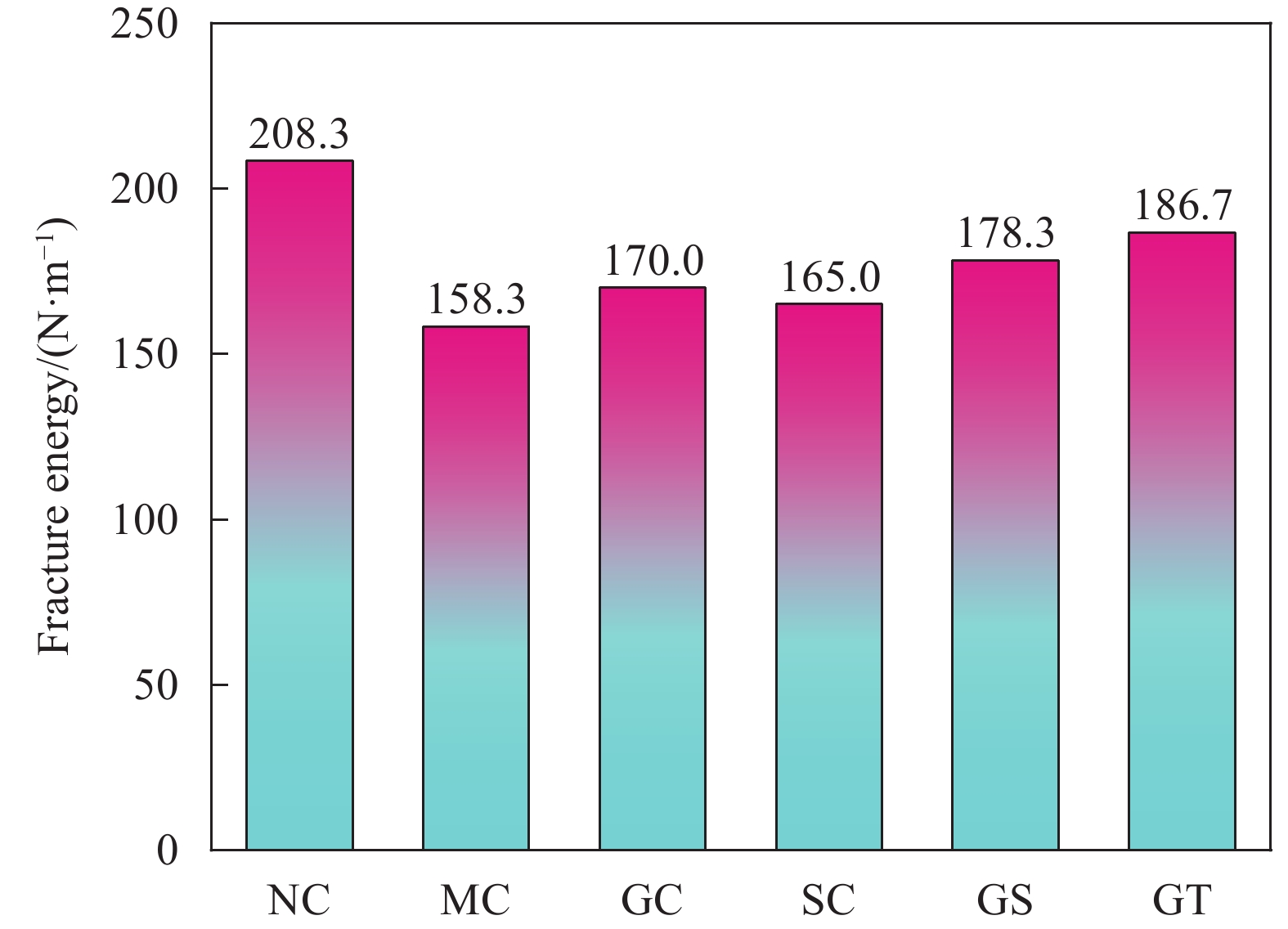
Number W0/J W1/J Alig/mm2 GF/(N·m−1) NC 0.88 0.37 6000 208.3 MC 0.67 0.28 6000 158.3 GC 0.73 0.29 6000 170.0 SC 0.70 0.29 6000 165.0 GS 0.77 0.30 6000 178.3 GT 0.81 0.31 6000 186.7 Notes: W0 is the work done by the external force of the concrete specimen; W1 is the work done by the gravity of the concrete specimen itself; Alig is the area of the fracture zone of the concrete specimen; GF is the fracture energy of the concrete specimen -
[1] 刘泽, 段开瑞, 周梅, 等. 煤矸石在土木工程材料中的应用研究进展[J]. 材料导报, 2024, 38(10): 88-99. LIU Ze, DUAN Kairui, ZHOU Mei, et al. Re search progress on the application of coal gan gue in civil engineering materials[J]. Material Herald, 2024, 38(10): 88-99(in Chinese).
[2] 冷发光. 煤矸石综合利用的研究与应用现状[J]. 四川建筑科学研究, 2000, 26(2): 3. LENG Faguang. Sichuan Building Science Research, 2000, 26(2): 3 (in Chinese).
[3] 罗畅, 刘萍, 贾毅超, 等. 煤矸石综合利用知识图谱可视化分析[J]. 化工矿物与加工, 2022, 51(9): 1-5. LUO Chang, LIU Ping, JIA Yichao, et al. Visualization analysis of knowledge graph of comprehensive utilization of coal gangue[J]. Chemical Minerals & Processing, 2022, 51(9): 1-5(in Chinese).
[4] 于乐乐, 王爱国, 仲小凡, 等. 煤矸石骨料混凝土力学和耐久性能研究进展[J/OL]. 材料导报, 1-19 2024-07-19]. YU Lele, WANG Aiguo, ZHONG Xiaofan, et al. Research progress on the mechanics and durability of coal gangue aggregate concrete [J/OL]. Material Herald, 1-19[2024-07-19] (in Chinese).
[5] GUO J M and ZHU L L. Experimental Research on Durabilities of Coal Gangue Concrete[J]. Advanced Materials Research, 2011, 1368(306-307): 1569-1575.
[6] GUAN X, QIU J S, SONG H T, et al. Stress–strain behaviour and acoustic emission characteristic of gangue concrete under axial compression in frost environment[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2019, 220: 476-488. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.06.008
[7] WANG Z S and ZHAO N. Influence of coal gangue aggregate grading on strength properties of concrete[J]. Wuhan University Journal of Natural Sciences, 2015, 20(1): 66-72. DOI: 10.1007/s11859-015-1060-6
[8] 杨尚谕, 周梅, 张玉琢, 等. 自燃煤矸石粗集料取代率对混凝土断裂韧性的影响[J]. 建筑材料学报, 2020, 23(4): 858-864. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9629.2020.04.018 YANG Shangyu, ZHOU Mei, ZHANG Yuzhuo, et al. Effect of the substitution rate of crude aggregates of spontaneously ignited coal gangue on the fracture toughness of concrete[J]. Journal of Building Materials, 2020, 23(4): 858-864(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9629.2020.04.018
[9] XU SL, REINHARDT HW. Determination of double-K criterion for crack propagation in quasi-brittle fracture, Part: Analytical evaluating and practical measuring methods for three point bending noSChed beams[J]. International Journal of Fracture, 1999, 98(2): 151-177. DOI: 10.1023/A:1018740728458
[10] 李永靖, 程耀辉, 文成章, 等. 基于Weibull分布的煤矸石对混凝土断裂损伤特性的影响[J]. 长江科学院院报, 2024, 41(3): 134-141+147. DOI: 10.11988/ckyyb.20221336 LI Yongjing, CHENG Yaohui, WEN Chengzhang, et al. Effect of coal gangue on fracture damage characteristics of concrete based on Weibull distribution[J]. Proceedings of the Yangtze Academy of Sciences, 2024, 41(3): 134-141+147(in Chinese). DOI: 10.11988/ckyyb.20221336
[11] WANG J , ZHANG J , CAO D, et al. Comparison of recycled aggregate treatment methods on the performance for recycled concrete[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2020, 234: 117366.
[12] 应敬伟, 蒙秋江, 肖建庄. 再生骨料CO2强化及其对混凝土抗压强度的影响[J]. 建筑材料学报, 2017, 20(2): 277-282. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9629.2017.02.021 YING Jingwei, MENG Qiujiang, XIAO Jianzhuang. The strengthening of CO2 from recycled aggregates and its influence on the compressive strength of concrete[J]. Journal of BuildingMaterials, 2017, 20(2): 277-282(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9629.2017.02.021
[13] LI L, XUAN D X, Adebayo O S, et al. Development of nano-silica treatment methods to enhance recycled aggregate concrete[J]. Cement and Concrete Composites, 2021, 118(republish).
[14] 宋学锋, 白超. 化学强化剂对再生骨料及再生混凝土性能的影响研究[J]. 硅酸盐通报, 2019, 38(6): 1748-1754. SONG Xuefeng, BAI Chao. Research on the influence of chemical enhancers on the properties of recycled aggregates and recycled concrete[J]. Silicate bulletin, 2019, 38(6): 1748-1754(in Chinese).
[15] Murzakarimova A. A Review of Improvement of Interfacial Transition Zone and Adherent Mortar in Recycled Concrete Aggregate[J]. Buildings, 2022, 12.
[16] LEI B, XIONG Q H, TANG Z, et al. Effect of Recycled Aggregate Modification on the Properties of Permeable Asphalt Concrete[J]. Sustainability, 2022, 14(17): 10495-10495. DOI: 10.3390/su141710495
[17] 中华人民共和国行业标准. 普通混凝土 配合比设计规程: JGJ55-2011[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2011. Industry standard of the People's Republic of China. Specification for mix proportion design of ordinary concrete: JGJ55- 2011[S]. Beijing: China Architecture and Building Press, 2011. (in Chinese)
[18] Tada H, Paris P C, Irwin G R. The Stress Analysis of Cracks Handbook, 3rd ed[J]. New York: American Society of Mechanical Engineers Press, 2000: 58.
[19] 李少伟, 周梅, 张莉敏. 自燃煤矸石粗骨料特性及其对混凝土性能的影响[J]. 建筑材料学报, 2020, 23(2): 334-340+380. LI Shaowei, ZHOU Mei, ZHANG Limin. Characteristics of coarse aggregate of spontaneously combusted coal gangue and its effect on concrete properties[J]. Journal of Building Materials, 2020, 23(2): 334-340+380(in Chinese).
[20] 冯春花, 陈钰, 黄益宏, 等. 煤矸石骨料及其改性技术研究进展[J]. 硅酸盐通报, 2023, 42(1): 133-143. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1625.2023.1.gsytb202301013 FENG Chunhua, CHEN Yu, HUANG Yihong, et al. Research progress on coal gangue aggregate and its modification technology[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2023, 42(1): 133-143 (in Chinese). DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-1625.2023.1.gsytb202301013
[21] 温久然, 刘小婷, 刘开平, 等. 黏土质煤矸石强化技术研究[J]. 硅酸盐通报, 2020, 39(1): 233-241. WEN Jiuran, LIU Xiaoting, LIU Kaiping, et al. Study on clay coal gangue strengthening technology[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2020, 39(1): 233-241(in Chinese).
-
目的
煤矸石资源化利用符合我国绿色发展理念,但煤矸石骨料强度低、吸水率大等原因导致煤矸石混凝土的实际工程应用受到限制。为了提高煤矸石在工程中的利用率,扩大其在工程中的应用范围,改善煤矸石混凝土脆性破坏的特征,降低工程中使用煤矸石混凝土带来的安全隐患,有必要对煤矸石进行强化,提高煤矸石粗骨料混凝土的断裂性能。
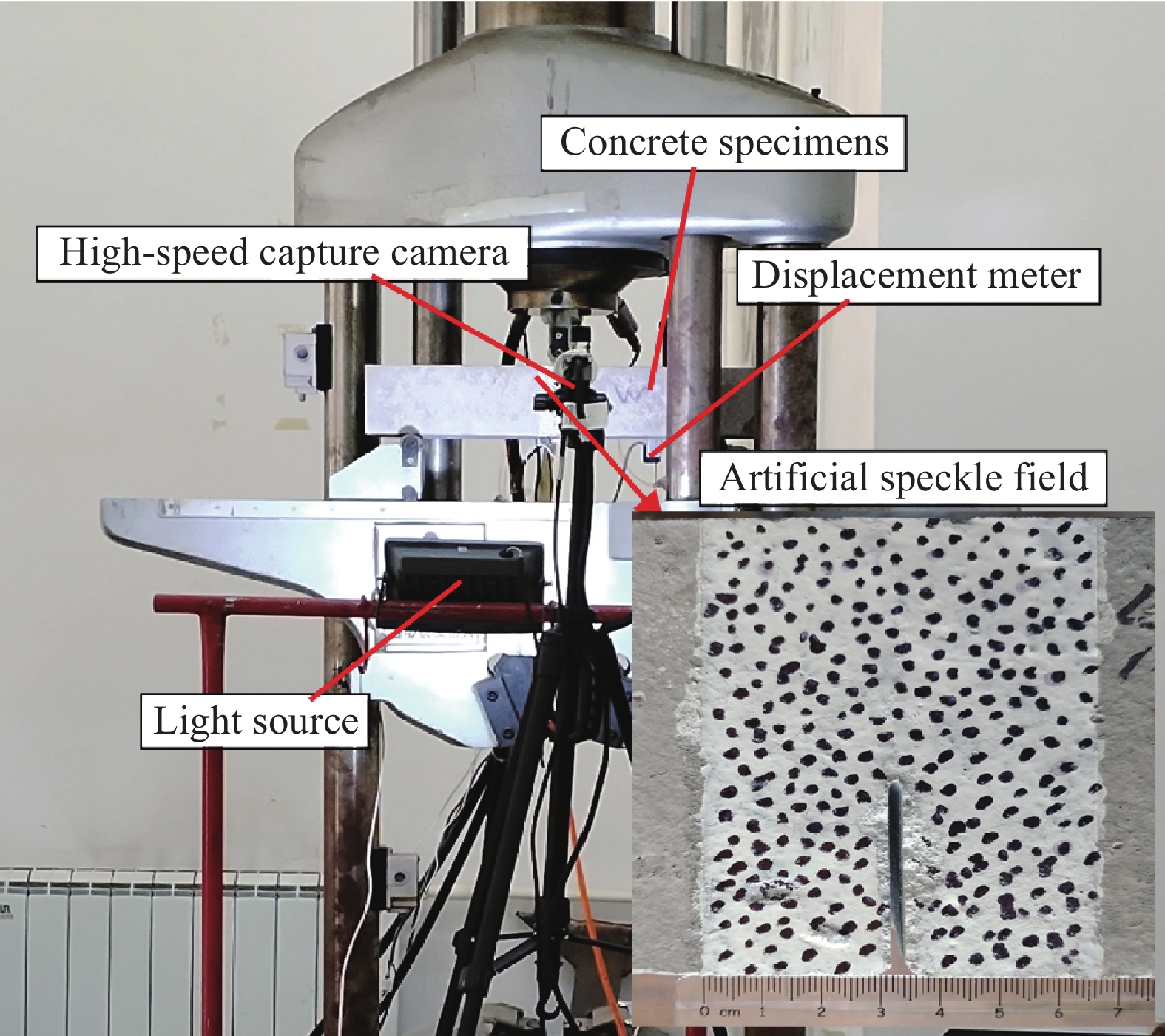
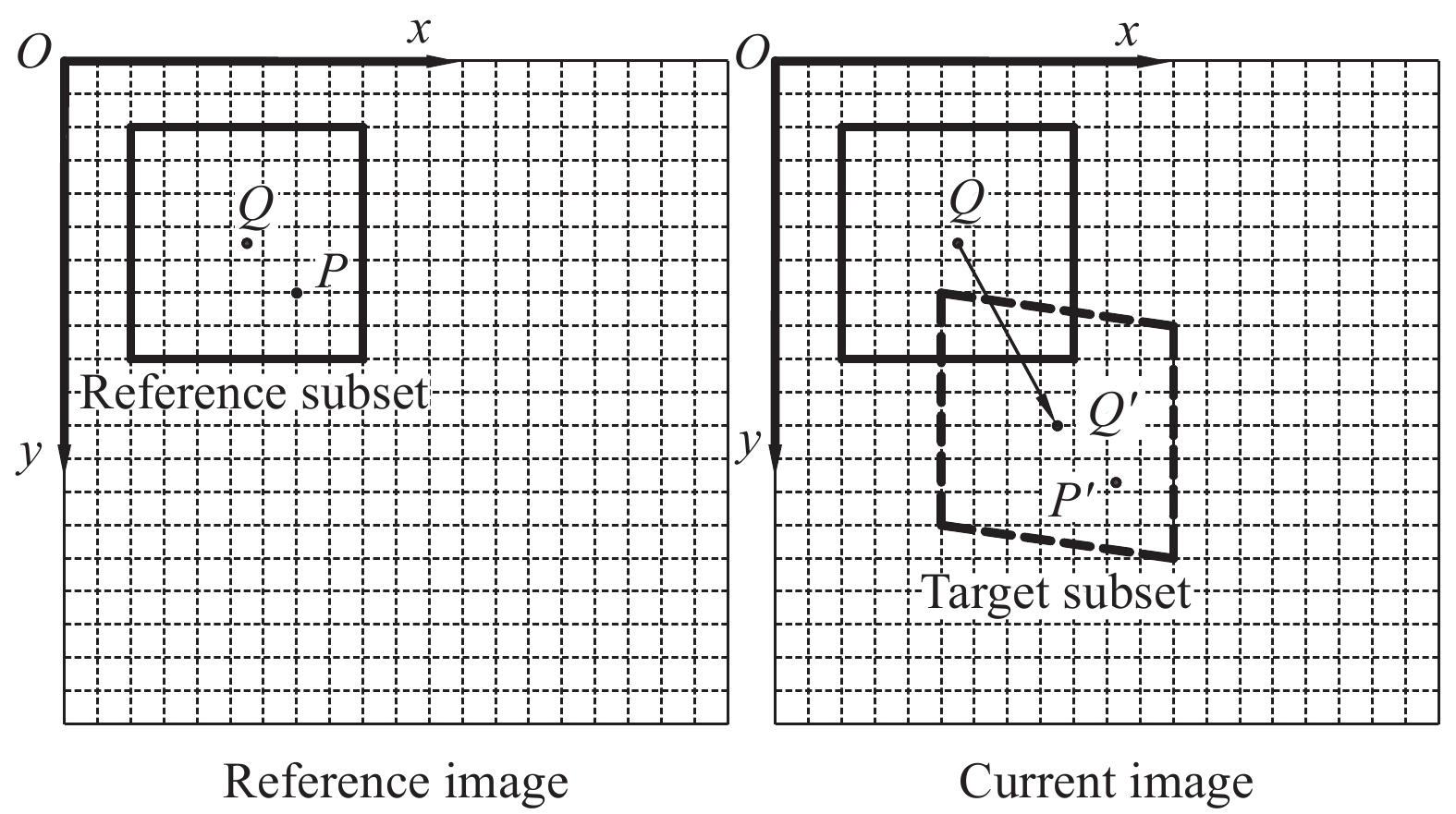
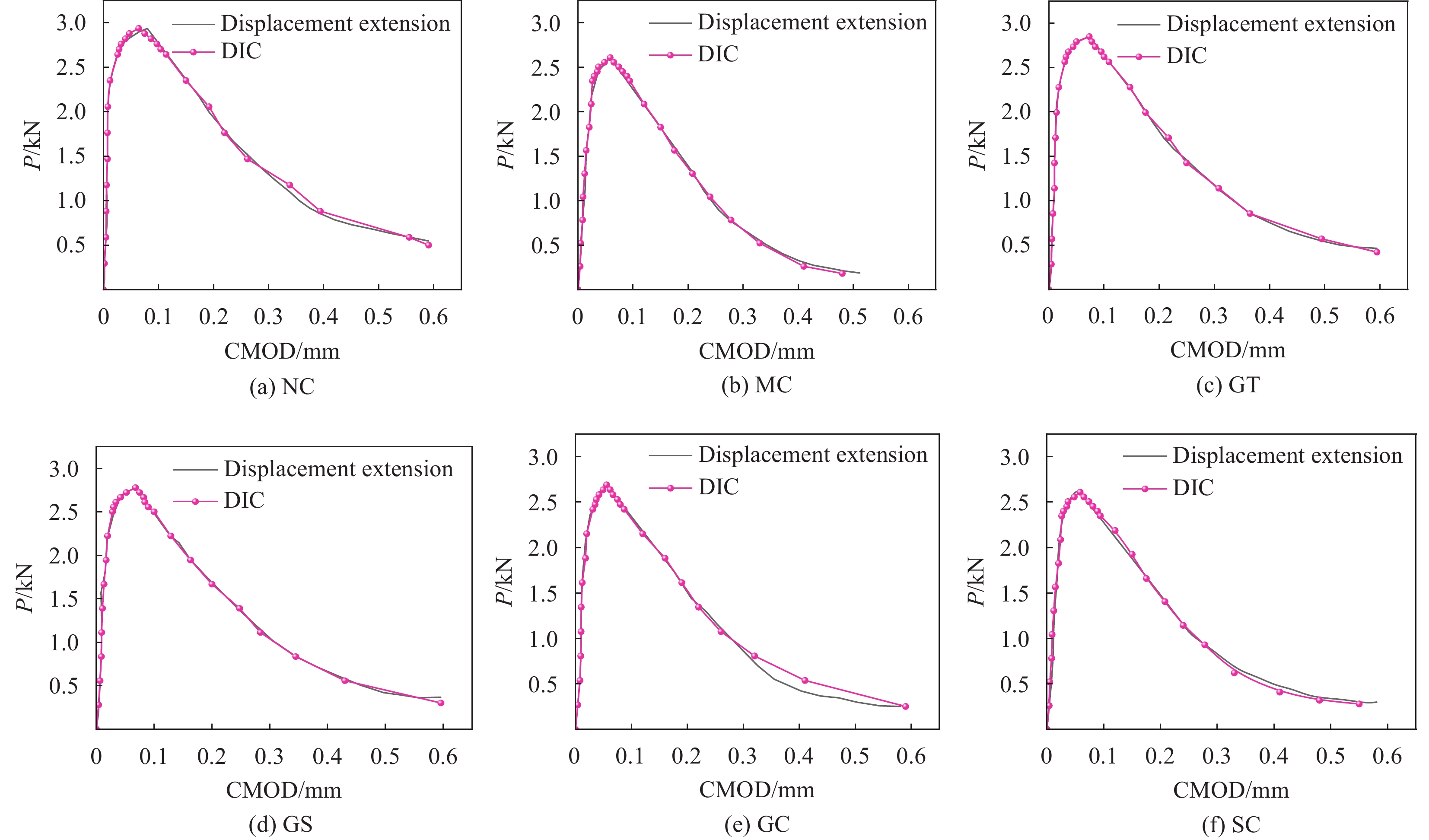
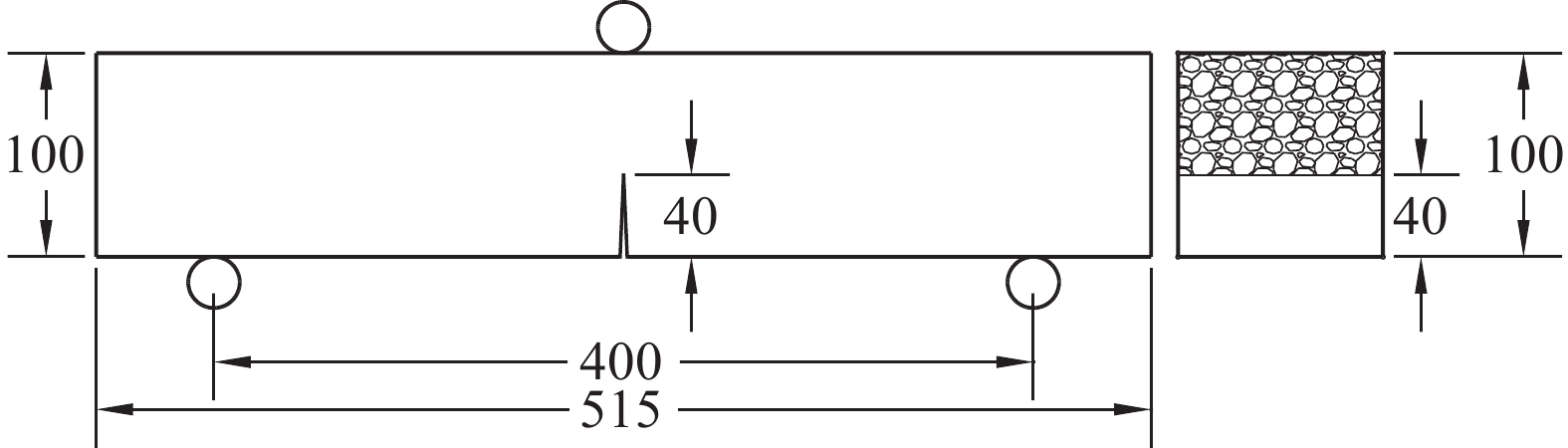
方法本文通过水泥浆包裹法(GC)、水玻璃浸泡法(SC)、水泥浆-碳化协同强化法(GT)和水泥浆-水玻璃协同强化法(GS)四种强化处理方法对煤矸石骨料进行强化处理。以碎石混凝土(NC)和无强化的煤矸石混凝土(MC)作为对照组,结合数字散斑DIC技术对各种骨料的混凝土进行断裂试验研究,以探求骨料强化对煤矸石混凝土断裂性能的影响。用6种骨料制作515mm×100mm×100mm的三点弯曲试件,每组3个,试件浇筑时在中间部位用高40mm、厚度3.5mm的T型钢板预留出预制裂缝。试件标准养护28d后在预制裂缝左右各3cm范围内制作人工散斑场,加载设备采用位移加载的方式,加载速度为0.1mm/min。加载时采用数字散斑仪器、位移计、夹式引伸计对试件进行数据采集。对采集到的数据采用双断裂模型进行计算,得到混凝土各项断裂参数。最后通过DIC软件分析的模拟值与位移计、引伸计所测得的试验值进行对比,来验证DIC技术的准确性。
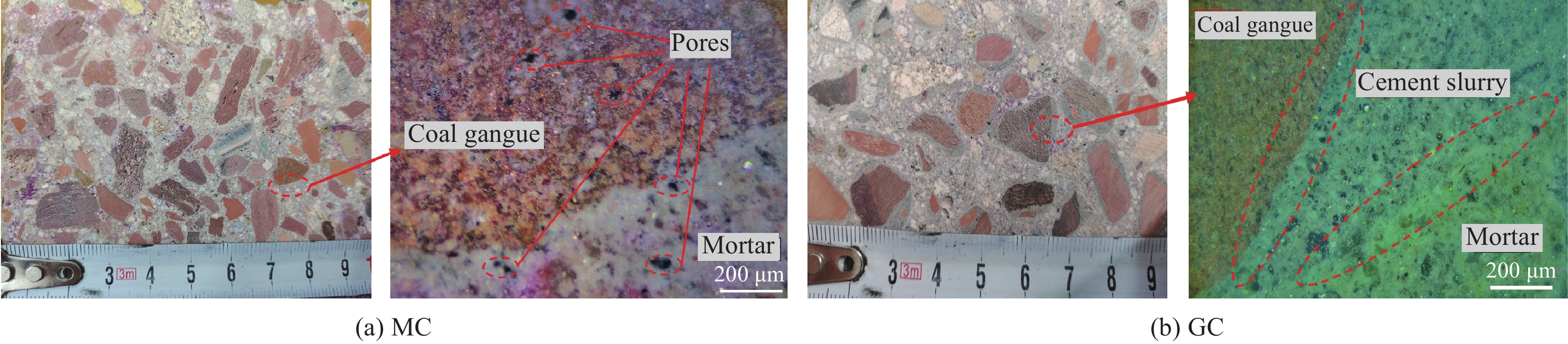
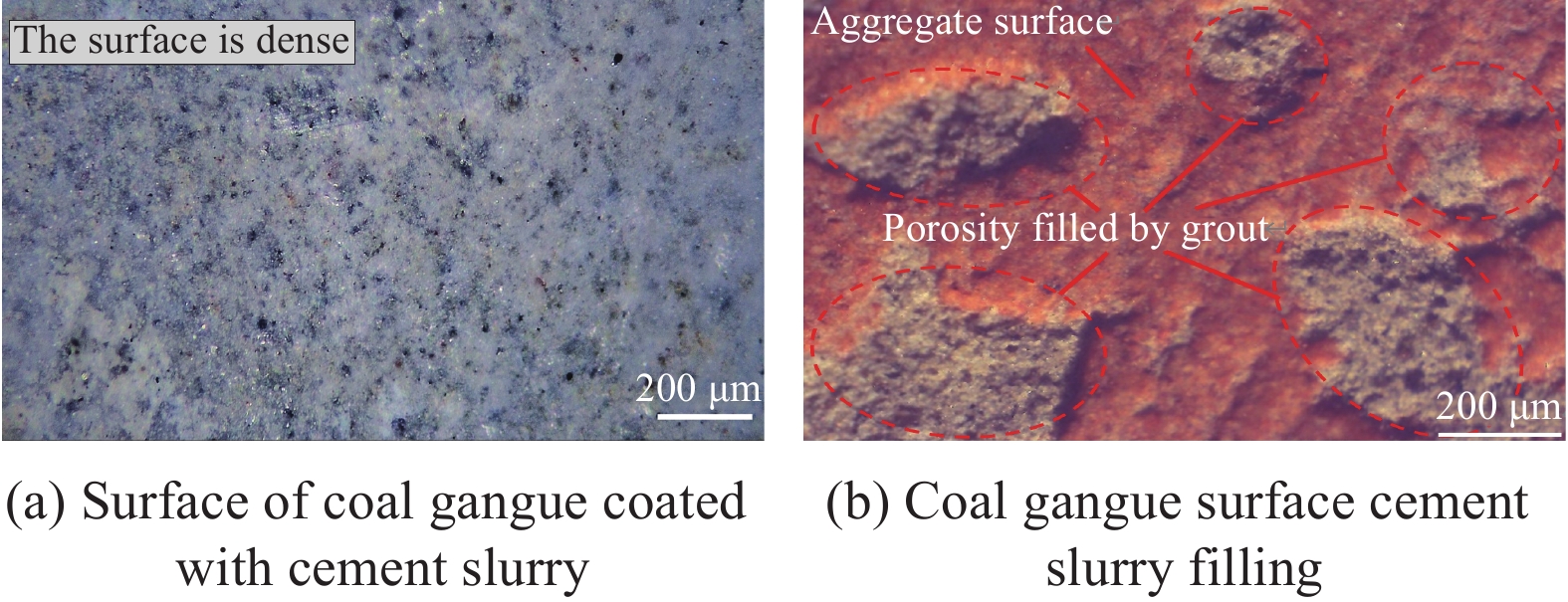
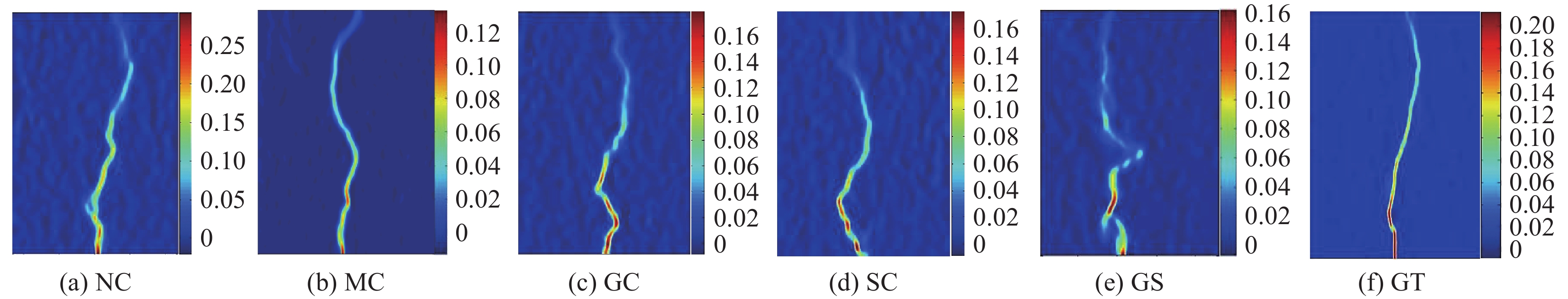
结果强化后煤矸石骨料的吸水率、表观密度、压碎指标等较普通煤矸石骨料都有所提升,说明强化方法对煤矸石的基本物理力学性质有增强效果。试件破坏时,碎石混凝土呈现出砂浆剥离碎石粗骨料、碎石表面完整的现象;煤矸石混凝土呈现出骨料发生破碎的现象,这是由于煤矸石在开采、破碎的过程中出现的原始裂缝所致,而强化组试件中这一现象有明显改善。对包裹水泥浆的煤矸石骨料进行打磨处理,去除表面浆体,对骨料进行亚微观扫描,可以发现水泥浆填充了骨料的原始孔隙与裂缝。
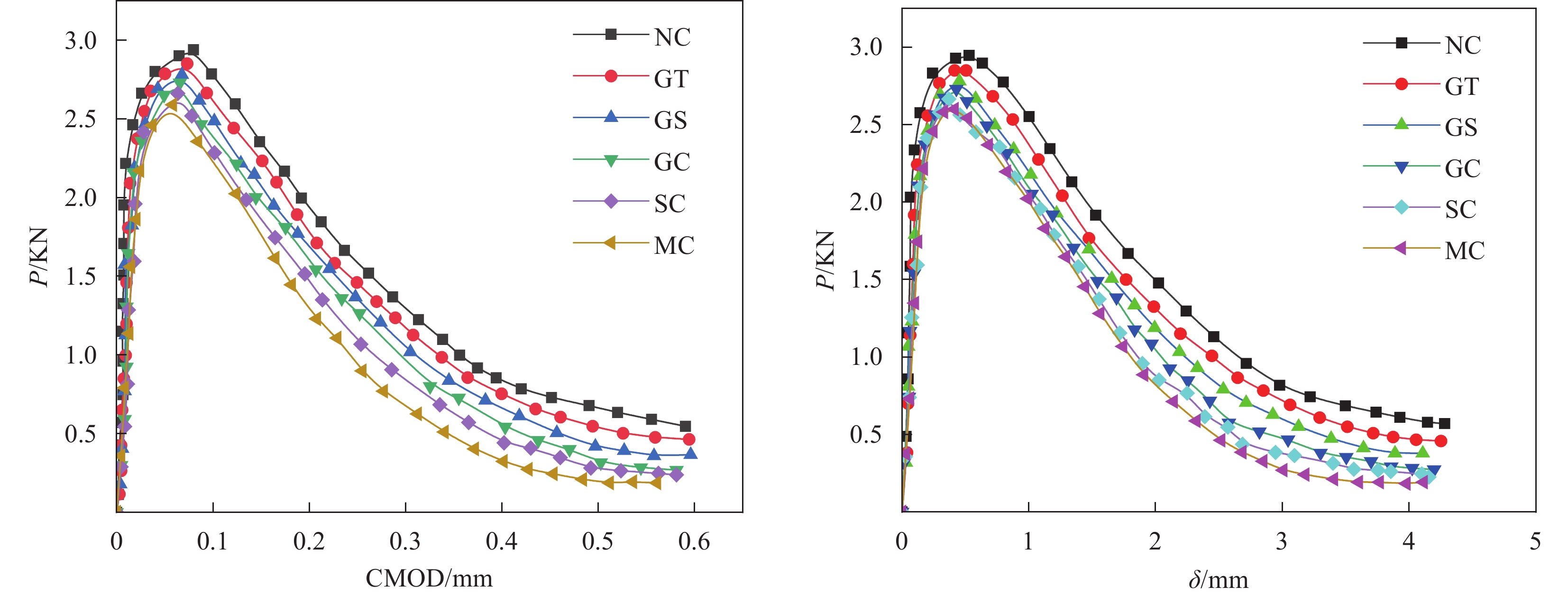
结论(1)水泥浆包裹、水玻璃浸泡、水泥浆-水玻璃协同强化和水泥浆-碳化协同强化对煤矸石混凝土的裂缝起裂和扩展均起到了一定的延缓作用,增强了混凝土的韧性。其中水泥浆-碳化协同强化组的起裂韧度及失稳韧度提高最大,分别提高了25.0%、36.21%,对混凝土断裂性能的改善更明显。(2)数字图像相关法(DIC)与位移引伸计所测得的曲线的吻合度较高,其误差大部分在5%以下,说明DIC法在煤矸石混凝土的断裂试验中有较高的准确性。(3)四种强化方式均提高了煤矸石混凝土的断裂能以及破坏时的极限应变,增强了煤矸石混凝土发生断裂时的耗能能力,改善了断裂性能。其中水泥浆-碳化协同强化的效果最为显著,断裂能提高了17.94%。
-
煤矸石资源化利用符合我国绿色发展理念,但煤矸石骨料强度低、吸水率大等原因导致煤矸石混凝土的实际工程应用受到限制。为了研究不同骨料强化方法对煤矸石混凝土的损伤和断裂特性的影响,本文通过水泥浆包裹法(GC)、水玻璃浸泡法(SC)、水泥浆-碳化协同强化法(GT)和水泥浆-水玻璃协同强化法(GS)四种强化处理方法对煤矸石骨料进行强化处理。以碎石混凝土(NC)和无强化的煤矸石混凝土(MC)作为对照组,结合数字图像相关(DIC)技术,对强化后的煤矸石混凝土断裂性能进行了试验研究。结果表明:四种强化方式均可以延缓裂缝的产生与发展,提高煤矸石混凝土的抗断裂能力,其中协同强化效果最为明显,GS、GT组与MC组相比,试件的起裂韧度与失稳韧度分别提高了9.09%、13.64%和25.0%、36.21%;断裂能分别提高了12.63%、17.94%。GT组断裂性能提高幅度最大,与NC组相当。这为煤矸石混凝土的实际工程应用提供了理论依据。
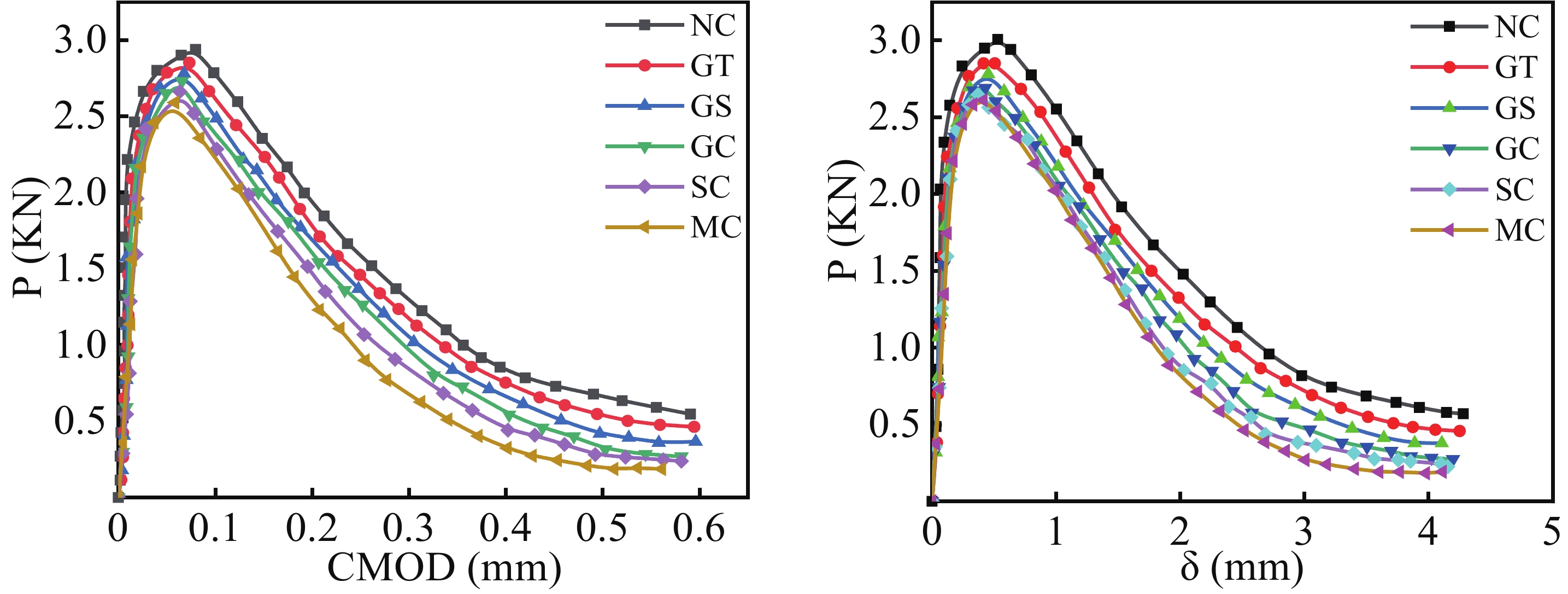
碎石混凝土及强化前后煤矸石混凝土P-CMOD、P-δ曲线
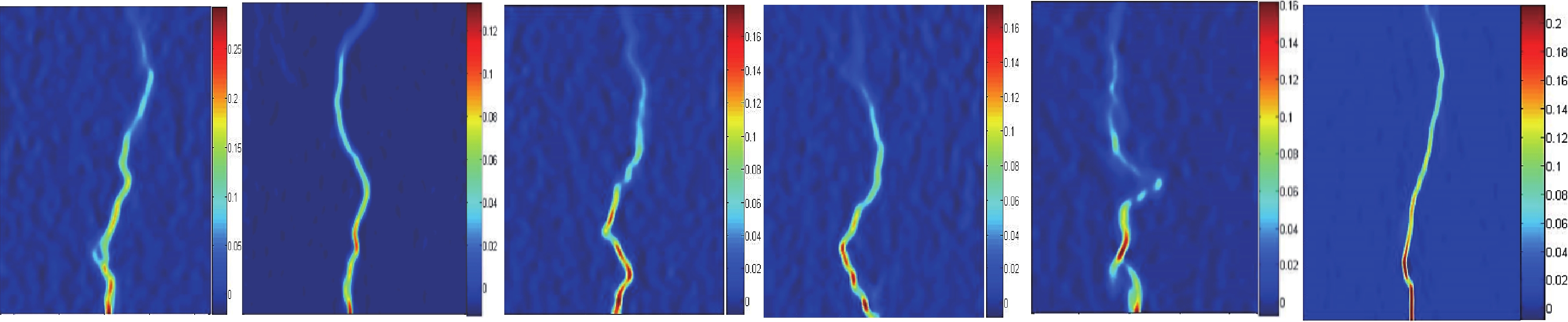
混凝土的应变变化




 下载:
下载: