Progress in preparation and research of VO2-based composite structure films for smart windows
-
摘要:
二氧化钒(VO2)在68℃附近发生绝缘体-金属相转变,同时伴随着近红外光透射率突变,因此在智能节能窗领域具有巨大的应用潜力。近年来,关于 VO2的制备方法、相变机制及改善光学性能方面取得了显著进展。然而,在实际应用中,VO2仍面临一系列挑战,包括本征相变温度较高、可见光透过率(Tlum)较低、太阳能调节效率(∆Tsol)不佳、耐候性差及颜色舒适度较差(呈现棕黄色)。针对这些问题,国内外的研究者进行了大量研究,发现复合结构对改善VO2性能具有显著作用,对推进其实际应用具有重要意义。然而,目前关于VO2基复合结构的综述相对较少。本文概括了VO2基复合结构的制备方法及在智能窗领域的性能研究进展,并对VO2基复合结构薄膜未来发展前景进行了展望。
Abstract:Vanadium dioxide (VO2) exhibits an insulator-metal phase transition near 68℃, coupled with a sudden alteration in near-infrared light transmittance, rendering it highly promising for intelligent energy-saving windows. Despite extensive research in recent years on preparation methods, phase transition mechanisms, and enhancement of dimming capabilities for VO2, practical applications face numerous challenges. These include its high intrinsic phase transition temperature, low visible light transmittance (Tlum), inefficient regulation of solar energy (∆Tsol), poor weather resistance, and limited color comfort (brownish-yellow hue). Addressing these challenges, researchers worldwide have conducted extensive investigations, with composite structures emerging as a promising avenue for enhancing the overall performance of VO2 and advancing its practical applications. However, there remains a paucity of comprehensive reviews on VO2-based composite structures. This paper provides a synthesis and discussion of the preparation methods and performance research progress in the field of smart windows of VO2-based composite structures, while also exploring the future prospects of VO2-based composite structures.
-
Keywords:
- vanadium dioxide /
- thermochromism /
- smart windows /
- energy conservation /
- composite structure
-
随着能源的日益枯竭和环境污染问题日益严峻,迫切需求采取节能减排措施[1]。在能源总消耗中,约有1/3用于建筑领域,而其中一半的建筑能耗用于空调和供暖。门窗是室内外能量交换的主要途径。因此,通过窗口调节室内温度是降低建筑能耗的可行途径。
在20世纪80年代,Granqvist首次提出“智能窗”(Smart window)概念,指的是一种调光材料与玻璃等基材结合构成的节能窗户。这种窗户利用调光材料对各种物理刺激(如光、电、气、热等)的响应,导致其光学性质(透射率、反射率、吸收率等性能)发生变化,从而实现对室内环境温度的可控调节。根据变色机制的不同,智能窗可分为电致变色[2-5]、热致变色[6-7]、气致变色[8-9]和光致变色[10-12]等。其中,热致变色智能窗可根据环境温度的变化自动调整太阳光透过率,且无能源消耗,因此成为当前研究的焦点。
二氧化钒(VO2)是一种典型的热致变色材料[7, 13-14],其在图1中展示了在68℃(340 K)相变温度下发生的金属相-绝缘相的可逆相变(MIT)[15]。
为了全面描述VO2(M/R)的相变过程,通常会考虑晶体场理论的分子图,该理论由Goodenough[16]于1971年首次提出。如图1所示,VO2(R)的能带宽度约为2.5 eV,未填充的π和d//带部分重叠,费米能级(Ef)在π和d//带重叠时下降,表现出金属的特性。随着温度的降低,d//键分裂为d键和反键,π*键和d//键之间形成了0.7 eV的带隙,形成了绝缘相。
在低温下,它呈现单斜相结构的绝缘相,当温度升至68℃以上时,绝缘相转变为高温金属相,晶体结构从单斜转变为四方金红石结构。在此过程中,对近红外光的透射率从高变为低,而对可见光的透射率几乎没有明显变化。因此,VO2不仅能够调节室内温度,还能保持室内一定的明亮度,使其成为最理想的智能窗材料之一。
1. VO2智能窗性能评价指标
评估VO2智能窗性能有多个指标,包括相变温度(Tc)、可见光透射率(Tlum)、太阳调制能力(∆Tsol)和稳定性等。在这些指标中,热致变色性能(Tlum、∆Tsol)和稳定性是评估VO2智能窗性能的关键参数。本文总结了这些关键指标的计算方法,以便对VO2智能窗进行客观而全面的评估。
1.1 光学性能
VO2薄膜光学性能的计算基于其紫外-可见-近红外(UV-Vis-NIR)透射光谱[17]。Tlum(λ1–λ2)和∆Tsol(λ3–λ4)的计算公式如下:
Tlum, sol =∫φlum, sol(λ)T(λ)dλ∫φlum, sol(λ)dλ (1) ΔTsol =Tsol (25∘C)−Tsol (90∘C) (2) 其中:λ为波长,λ1–λ2为可见光的波长范围,λ3–λ4为紫外-可见-近红外光的波长范围;T(λ)为λ波长处的透过率值;φlum(λ)为人眼视觉敏感度,代入公式(1)所得为Tlum;φsol(λ)为距地平线37°、大气质量数为1.5时的太阳辐照光谱,代入公式(1)所得为Tsol。Tsol(25℃)为VO2绝缘相时Tsol;Tsol(90℃)为VO2金属相时Tsol。
1.2 稳定性
对于VO2环境稳定性的评估,采用高温、高湿的加速老化方法作为标准测试手段,以获取可靠而客观的结果。为建立测试数据与实际使用寿命之间的可靠关系,使用Hallberg-Peck加速模型进行模拟计算。
AF=exp[Eak(1Tuse −1Ttest )](RHtest RHuse )n (3) 其中:AF为加速因子;Ea为活化能(eV),VO2的活化能为0.7 eV;玻尔兹曼常数k为8.617×10−5 eV/K;n是湿度的加速速率常数,不同的类型对应不同的值,一般在2到3之间;Tuse和Ttest分别是工作温度(K)和加速度测试温度(K);RHuse和RHtest分别是工作湿度和加速测试湿度。
为满足智能窗实际应用的需求,研究者们在提高二氧化钒薄膜的可见光透射率(Tlum)、增大VO2薄膜的太阳调制能力(∆Tsol)、降低VO2薄膜的相变温度(Tc)及提高其稳定性等方面进行了大量研究。然而,关于VO2基复合结构薄膜的综述目前还相对较少。本文综述了VO2基复合结构薄膜的制备方法及性能提升策略的研究进展,并最后对智能窗用VO2基复合结构薄膜未来的发展方向进行了展望。
2. VO2纳米颗粒基复合结构
首先,制备VO2纳米颗粒是必要的,如图2(a)、图2(b)所示[18-19]。水热法是最常用的VO2纳米颗粒制备方法之一。该方法在高温高压环境下通过化学反应进行,可获得具有粒径分布窄、团聚程度低、晶格完整、较高纯度的粉体。水热法在制备过程中污染较小,能耗较低,是在相对较低温度下获得VO2纳米颗粒的有效途径。制备VO2纳米颗粒的水热法主要使用V2O5、NH4VO3和VOSO4等作为钒源,以及H2C2O4、H2O2和N2H4·H2O等作为还原剂,在高压环境下进行氧化还原反应。水热法的VO2纳米颗粒制备通常包括两步法和一步法。中国科学院合肥物质科学研究院李广海课题组的专利[20-21]采用类似的水热合成方式,首先制备VO2(B)或VO2(D)粉体,然后在高温下转变为VO2(M)粉体。Popuri等[18]以V2O5和柠檬酸为先驱体,采用一步水热法成功制备了VO2(B),180℃仅需2 h、220 ℃仅需1 h。并且制备出的VO2(B)在真空中550℃反应1 h即可得到VO2(M),如图2(a)所示。中国科学院上海硅酸盐研究所高彦峰教授课题组[22]首次采用V2O5、H2C2O4和少量的掺杂剂H2WO4为原料,一步水热制备了VO2(M)粉体。Alie等[23]以V2O5和H2C2O4为前驱体,通过调控前驱体的摩尔比、浓度、合成温度和时间等参数,直接采用水热法合成了具有热致变色特性的VO2(M)粉体。
2.1 VO2核壳结构
由于表面效应和离子间的范德华力等因素,纳米颗粒在溶液中容易发生团聚,难以实现单一纳米颗粒的分散。为了获得单分散的纳米颗粒,新兴的核壳结构应运而生。核壳结构以其改性性能而著称,通过外层的保护,能够显著提高VO2纳米颗粒的分散性和稳定性。
2.1.1 无机壳层结构
形成VO2核壳结构的方法涉及将不同材料与VO2结合,其中有一些稳定的透明氧化物材料,如TiO2[24]、SiO2[25]、SnO2[26]和ZnO[27],被用作保护外壳,从而强化VO2基复合结构薄膜的热致变色性能以满足实际应用需求。
VO2核壳结构的制备通常采用溶胶凝胶包覆法,即在溶液中首先形成溶胶或凝胶,然后用于包覆VO2纳米颗粒。Li等[28]采用错配应变异质外延法,以钛酸四丁酯(TBOT)为原料,在VO2表面包覆TiO2,成功制备了VO2@TiO2纳米颗粒,并对其热致变色性能进行了研究。此外,Li等[26]还报道了一种方法,水热法合成VO2纳米颗粒,溶胶-凝胶法制备TiO2前驱体涂层,并通过严格控制真空退火法制备TiO2外壳,从而制备出VO2@TiO2纳米棒。如图2(c)、图2(d)所示,首先在80℃条件下通过回流冷凝器进行2 h的溶胶-凝胶反应,使TBOT水解并沉淀到VO2纳米棒表面,然后进行过滤和收集。接着,将干燥后的粉末放入真空石英管中,在适当的温度和压力下进行退火,使外壳转化为TiO2晶体。
VO2的核壳结构还可以采用异相成核法,例如采用均匀沉淀法制备ZnS和CdS,在其生成过程中在VO2表面异相成核,形成包覆在VO2表面的结构。
Xie等[29]在研究中采用了有效介质理论和转移矩阵法,以探讨壳层材料的光学常数对光学性能的影响。结果表明,在壳层材料的折射率介于1.6和2.3之间(例如ZnO)时,可获得最大∆Tsol的最佳壳层厚度。Chen等[27]的研究考察了核壳结构对Tlum值、∆Tsol值和稳定性的影响。首先通过水热法合成了VO2纳米颗粒,然后在其表面包覆ZnO,VO2@ZnO纳米颗粒在热致变色性能中展现出卓越的性能。相对于VO2薄膜,Tlum提高了31.1%,∆Tsol提高了11%。在稳定性方面,经过
1000 h的高温高湿度条件测试后,∆Tsol仍然保持在77%水平,表现出超高的耐久性。Du等[30]利用VOOH纳米颗粒与正硅酸乙酯(TEOS)的水解反应,随后进行退火处理,成功制备了VO2(M)@SiO2纳米颗粒。研究结果显示,VOOH纳米颗粒在SiO2的包裹下水解并转化为VO2(P)@SiO2纳米颗粒。随后,通过在400~550℃进行退火处理,VO2(P)@SiO2纳米颗粒进一步转化为VO2(M)@SiO2纳米颗粒。SiO2的包覆有效地阻碍了VO2(M)纳米颗粒在退火过程中的生长和团聚。通过精确控制退火温度,调节了VO2(M)@SiO2复合薄膜的热致变色性能,在450℃的退火温度下,∆Tsol达到18.9%,Tlum达到38%,实现了最佳的热致变色性能。
2.1.2 有机壳层结构
对于VO2有机壳层结构的设计,Chen等[31]报道了一步法合成VO2@AA纳米颗粒的制备方法。该方法采用抗坏血酸(AA)作为供电子分子,通过将AA分子处理VO2纳米颗粒,实现AA分子在VO2纳米颗粒表面的吸附,并形成新的C—O—V键。AA修饰的机制是:VO2纳米颗粒与AA通过新的C—O—V键进行配位,从而赋予VO2抗酸和抗氧化性能。VO2@AA纳米颗粒具有强大的抗酸和抗氧化性能。在H2SO4溶液中浸泡4 h后,纯VO2薄膜完全被腐蚀,失去了∆Tsol,而VO2@AA膜几乎没有变化。此外,它们在高温、高湿环境中表现出较高的稳定性。
如图2(e)、图2(f)所示,Guo等[32]将聚多巴胺(PDA)包覆在VO2纳米颗粒上,成功将VO2的相变温度降低到室温,并且提高了∆Tsol。VO2@PDA薄膜不仅避免了掺杂引起的光学性能退化,而且由于PDA的包覆作用改善了色散效应,其光学性能优于VO2薄膜。在保持Tlum不变的情况下,∆Tsol从11.2%提高到14.5%。此外,由于稳定的PDA壳和VO2与PDA之间的界面作用,VO2@PDA纳米颗粒在酸性和含氧条件下表现出良好的稳定性。
表 1 VO2核壳结构复合薄膜的光学性能Table 1. Optical properties of VO2 core-shell composite thin filmsStructure Tlum/% ∆Tsol/% Tc/℃ Ref. VO2@SiO2 38.0 18.9 — Du et al[30] VO2@ZnO 51.0 19.1 — Chen et al[27] VO2@SiO2 50.6 14.7 25.2 Zhu et al[34] VO2@TiO2 59.3 6.2 — Li et al[28] VO2@PDA 56.3 14.5 33.8 Guo et al[32] VO2@PMMA — 17.5 57 Hu et al[35] VO2@Polymer — 20.34 — Zhao et al[36] VO2@MgF2@PDA — 25.0 — Zhao et al[33] Notes:Tlum—Luminous transmittance; ∆Tsol—Modulation of solar energy; Tc—Transition temperature; A@B—Core(A)@shell(B) structure; PMMA—Polymethyl methacrylate. 2.1.3 无机-有机壳层结构
如图2(g)、图2(h)所示,Zhao等[33]制备出了VO2@MgF2@PDA的无机-有机壳层结构薄膜。首先,将VO2(M)纳米颗粒分散在溶剂中,形成分散良好的悬浮液。然后将适量MgCl6·6H2O、NH4F溶解在溶剂中,以一定的速率在剧烈搅拌下注入悬浮液。将悬浮液离心,洗涤得到VO2@MgF2纳米颗粒。然后将VO2@MgF2分散于溶有PDA的NH2C(CH2OH)3溶液中,搅拌,离心,最终得到VO2@MgF2@PDA纳米颗粒。最终,在聚对苯二甲酸乙酯(PET)衬底上成膜。VO2@MgF2@PDA核壳结构的环境耐久性大大提高。不同VO2核壳结构复合薄膜的光合性能见表1[27-28, 30, 32-36]。
2.2 VO2纳米颗粒基质材料
直接将VO2纳米颗粒分散到基质中形成单层薄膜是一种常用成膜方法[37]。
为了对VO2纳米复合颗粒成膜进行理论模拟,Li等[38]基于有效介质理论构建了在均匀透明的基体中分布VO2纳米颗粒的光学模型。他们的模拟采用了低VO2负载质量百分比(1%)和高厚度(5 μm)的复合薄膜,结论证明,与VO2薄膜相比,VO2纳米颗粒分散于基质中的薄膜在Tlum和∆Tsol方面表现优异。Zhou等[39]解释,ΔTsol的提升与VO2纳米颗粒的表面等离子体共振(SPR)有关,该表面等离子体共振位于约
1200 nm处,显著扩大了低温和高温下的透射率差异。对于实验研究,Cao等[22]对VO2纳米颗粒进行了早期工作和系统研究,从高质量VO2纳米颗粒的制造方法到VO2纳米颗粒与有机基质复合。2008年,他们报道了通过一步水热法成功合成纯单晶VO2(M)。随后,通过引入Sb3+掺杂来控制颗粒尺寸(可调尺寸为8~30 nm)和形貌。进一步将获得的VO2纳米颗粒分散到聚氨酯(PU)基体中,获得了Tlum为55%和ΔTsol为7.5%的柔性VO2-PU复合薄膜,证明了有机复合薄膜与传统薄膜相比的性能优势。目前,多种透明有机物已被用作基质材料,包括聚氨酯(PU)、水性聚氨酯(WPU)、聚二甲基硅氧烷(PDMS)、聚乙二醇(PEG)、聚乙烯醇(PVA)、聚乙烯吡咯烷酮(PVP)、乙烯-醋酸乙烯共聚物(EVA)、聚氯乙烯(PVC)和聚乙烯(PE)等。
2.2.1 可变色基质材料
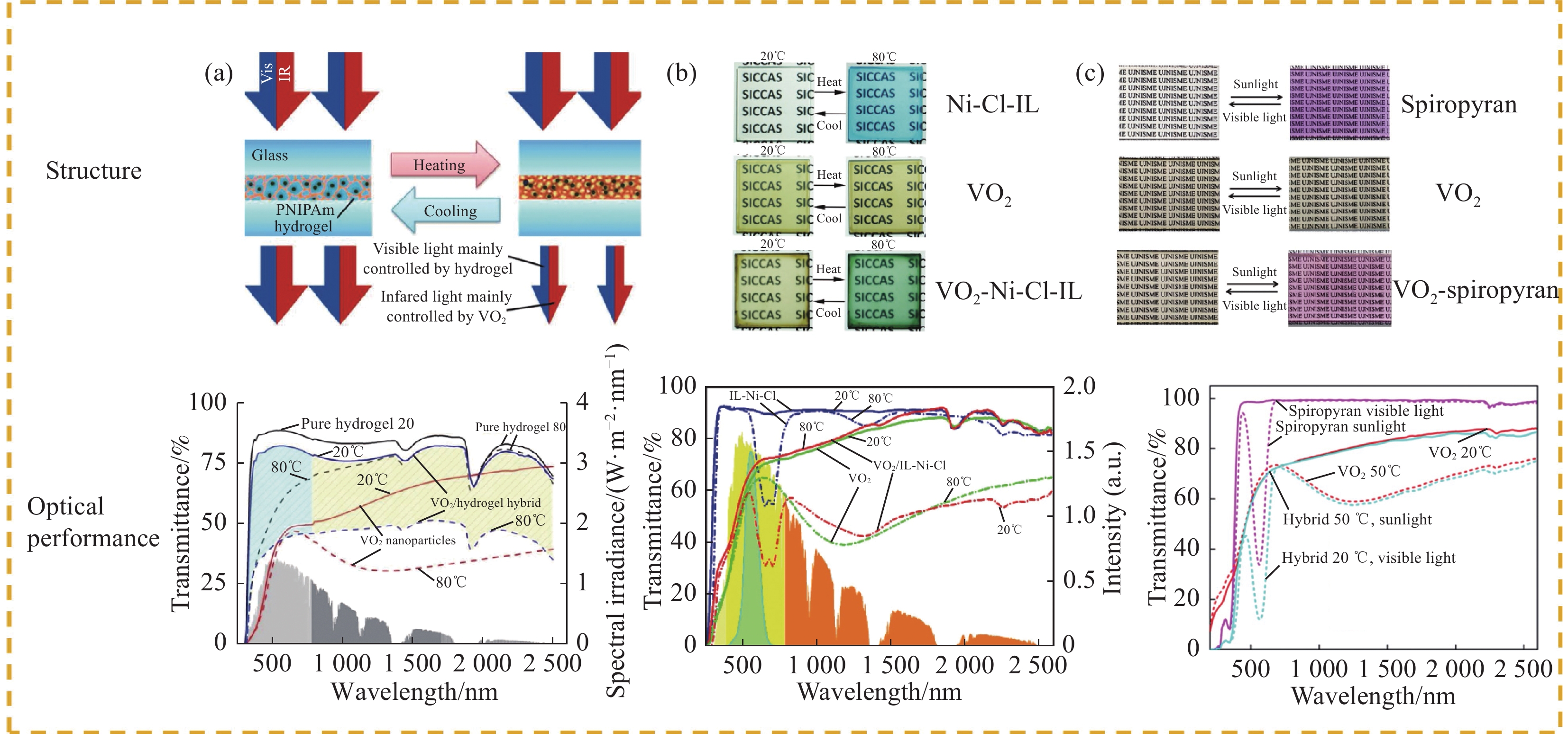
将VO2纳米颗粒分散到可变色基质中可以显著改善VO2基复合结构薄膜的太阳能调制能力(∆Tsol),并且赋予VO2基复合结构薄膜新的颜色。如图3(a)所示,通过将VO2与聚(N-异丙基丙烯酰胺)水凝胶混合,可以获得具有卓越太阳光调制性能和可见光透过率的结构[40]。该水凝胶在32℃经历亲水-疏水相变,表现出优异的光调制能力(∆Tsol = 29.7%)。因此,通过将VO2纳米颗粒与水凝胶混合,可以实现高达34.7%的∆Tsol和62.6%的Tlum。
如图3(b)所示,Zhu等[41]首次将Ni-Cl-离子液体(IL)引入VO2纳米颗粒的复合材料中。Ni-Cl-IL随着温度的上升,该材料的颜色从无色变为蓝色。VO2-Ni-Cl-IL复合薄膜表现出卓越的热致变色性能,∆Tsol达到26.45%,Tlum为66.44%。这种策略不仅显著提高了光学性能,而且随温度升高,颜色也呈现出明显的变化,从浅棕色变为深绿色。类似的研究报道了将VO2纳米颗粒与Ni-Br-IL[42]、Co-Br-三羟甲基丙烷(TMP)[43]和Ni-I-TMP[44]结合的工作。与传统的VO2薄膜相比,这一类复合薄膜在热致变色性能和颜色方面均取得了显著提升。
如图3(c)所示,Zhao等[45]研究了一种新型的VO2-螺吡喃复合薄膜。在可见光照射下,复合膜的颜色为淡黄色;当它暴露在阳光下时,颜色变成粉红色;当它受到紫外线照射时,随着紫外线能量的增加,逐渐变成深紫色。该复合薄膜可以调节紫外、可见光和近红外光,∆Tsol达到了23.58%,Tlum可以达到48.58%。
2.2.2 多孔基质材料
多孔结构中空气具有较低的折射率(n=1),能降低薄膜整体折射率,降低反射率[46]。因此,多孔结构的VO2薄膜相对于致密薄膜VO2往往具有更加优异的光学性能。模拟计算也证明了孔隙率的增加对VO2薄膜的光学性能有利[47]。
如图4(a)所示,Yao等[48]报道了一种利用界面工程方法合成SiO2@TiO2@VO2三层空心纳米球(TLHNs)的多功能复合结构薄膜。所制备的复合薄膜展现出卓越的热致变色性能(VO2(M)外层)、光催化自清洁能力(TiO2(A)中间层)和抗反射性能(SiO2空心纳米球内部)。
类似地,如图4(b)所示,Qu等[49]提出一种双层空心核壳结构(DSHNs)的VO2@SiO2复合结构薄膜。由于其独特的空心核和双壳结构,VO2@SiO2 DSHNs复合薄膜相较于连续致密的VO2涂层表现出卓越的光学性能,Tlum提升至61.8%,∆Tsol达到12.6%。
如图4(c)所示,Xu等[50]采用了一种双原位合成方法来制备多孔结构的VO2-Mg1.5VO4复合结构薄膜。基于多孔结构的抗反射和高度分散的VO2纳米颗粒引起的局域表面等离子体共振(LSPR),所得复合薄膜表现出卓越的光学性能:透光率(Tlum)高达70.0%,太阳能调制能力(∆Tsol)为12.2%。在100℃、50%湿度的条件下,经过744 h老化后,∆Tsol能保持87%,相当于20年的等效寿命。不同基质材料VO2基复合薄膜的光学性能见表2[40-41, 45, 48-49, 51-53]。
表 2 不同基质材料VO2基复合薄膜的光学性能Table 2. Optical properties of VO2-based composite films of different matrix materialsStructure Tlum/% ∆Tsol/% Ref. VO2-hydrogel 62.6 34.7 Zhou et al[40] VO2-Ni-Cl-IL 66.85 23.77 Zhu et al[41] VO2-{[(C2H5)2NH2]2NiBr4@SiO2} 52.9 25.7 Zhao et al[51] VO2-spiropyran 48.58 23.58 Zhao et al[45] VO2@SiO2 61.8 12.6 Qu et al[49] SiO2@TiO2@VO2 73.9 12.0 Yao et al[48] VO2-[1, 4-bis (benzoxazol-2-yl) naphthalene] 73.0 9.0 Qin et al[52] VO2-PDA 56.23 7.64 Wang et al[53] Notes: A-B is the mixture of A and B; Ni-Cl-IL is the ionic liquid-nickel-chlorine complexes. 3. 多层结构
3.1 缓冲层
在改善VO2薄膜的热致变色性能方面,一种有效的策略是在VO2薄膜和碱石灰玻璃衬底之间引入缓冲层。在碱石灰玻璃中,钠离子的存在会阻碍VO2薄膜的形成[54],且这些钠离子可以在室温下扩散[55]。通过引入缓冲层,可以作为钠离子的扩散屏障[56]。此外,缓冲层还能够改变VO2薄膜的表面形貌[57],降低发射率[58-60],从而提高其热致变色性能[61]。
磁控溅射法不仅具有成膜温度低、薄膜均匀性好等优点,还具有成膜速度快、易于大面积成膜的特点,是目前VO2薄膜最常用的制备方法之一。通常选择直流或射频磁控溅射来制备VO2薄膜[62-64]。
Koo等[65]选择了与VO2结构相似的氧化物作为缓冲层,包括ZnO、TiO2、SnO2和CeO2,并深入研究了它们对VO2不同相和热致变色性能的影响。研究结果显示,当ZnO、TiO2和SnO2充当缓冲层时,成功实现在370℃下形成VO2(M);而使用CeO2作为缓冲层时,得到了VO2(B)。采用ZnO、TiO2和SnO2缓冲层制备的VO2(M)薄膜表现出卓越的相变特性。其中,沉积在ZnO缓冲层上的VO2薄膜展示出最佳的相变性能,包括更大的转变幅度、更陡的转变陡度及更小的磁滞宽度。这表明缓冲层对VO2薄膜的生长过程具有关键作用。
Zhu等[62]采用直流磁控溅射法在ZnO缓冲层上成功制备了VO2薄膜,并深入研究了ZnO缓冲层厚度与薄膜结晶性和热致变色性能之间的关系。随着缓冲层厚度从0 nm增加至235 nm,Tlum从33.90%提升至40.51%,和∆Tsol从8.81%提升至13.11%。结果表明,随着ZnO缓冲层厚度的增加,薄膜的结晶性和热致变色性能显著提高。
Long等[66]在石英衬底和VO2薄膜之间引入一层V2O3作为缓冲层。他们观察到,当缓冲层厚度为60 nm时,VO2薄膜的∆Tsol增加了76%(从7.5%增至13.2%),而磁滞宽度减小了79%(从21.9℃减至4.7℃)。此外,V2O3缓冲层还显著提高了VO2薄膜的稳定性。
3.2 减反射层
构建高效的抗反射(AR)涂层是提升整体性能的另一重要途径。
对于VO2薄膜而言,其光学常数(折射率n和消光系数k)在可见光范围内相对较高,因而导致可见光的高反射。引入抗反射层可以显著降低可见光的反射[67-68],并提高太阳能调制能力[58, 69]。为了改善VO2薄膜的光学性能,早期采用了包含Cr2O3[70]、SiO2[71]、TiO2[72]、CeO2[73]和ZrO2[68]等透明氧化物的单层抗反射涂层。
Chen等[61]采用溶液工艺制备了SiO2和TiO2为抗反射(AR)层的双层薄膜。通过优化薄膜厚度和抗反射层设计,TiO2-VO2双层结构的Tlum提高至84.8%。通过调整抗反射峰的位置,可以实现高达15.1%的∆Tsol。在2003年,Jin等[69]沉积了TiO2-VO2-TiO2多层薄膜,相较于在玻璃衬底上的单层VO2薄膜,其Tlum显著增加了约86%(从30.9%增加到57.6%)。正如图5(b)所示,Wu等[74]通过光学模拟设计了抗反射TiO2-VO2薄膜,并通过磁控溅射法制备了不同厚度的薄膜,显著提高了薄膜的整体性能。与单层VO2薄膜相比,TiO2-VO2薄膜的Tlum值从29.03%显著提高到46.29%,∆Tsol值提高至16.03%。
2017年,Dou等[75]使用一步浸涂法制备了具有树枝状微结构的双面VO2(M)薄膜,该方法可以在保持较高∆Tsol的同时大大提高Tlum。VO2(M)薄膜的微观结构是由于PVP的分解和薄膜在低升温速率下退火时的收缩而形成的。Tlum值的提高是由于VO2(M)薄膜的双面微结构降低了反射率,增加了近红外透射率差异,导致∆Tsol增加。
2020年,Dou等[76]又使用一种简单通用的溶胶-凝胶法,制备了具有双面局域等离子共振吸收效应(LSPR)的VO2复合薄膜。双面薄膜的光学性能可以通过控制纳米颗粒的尺寸和形貌来优化。VO2双面薄膜具有优异的热致相变性能(Tlum为68.7%,∆Tsol为11.7%)并且这种光学性能在
1500 次循环后保持稳定,显示出显著的热循环稳定性。除了传统的抗反射(AR)层,Xu等[77]提出使用H2O作为一种可移除的抗反射涂层以增强光学性能,并通过采用新型VO2-H2O双层结构实现了高∆Tsol(18.2%)和Tlum(42.5%)。通过进一步优化,采用了VO2-HfO2-H2O多层结构,将太阳能调制能力提高到20.8%,优于以往报道的所有多层结构。
3.3 多功能层
除了提升热致变色性能以外,还可以引入抗氧化层、自清洁层和防雾层等,实现多功能的多层结构复合薄膜。Powell等[78]使用常压化学气相沉积技术在玻璃衬底上制备了多功能VO2-SiO2-TiO2多层复合薄膜。SiO2-TiO2双层保护层可以有效防止化学侵蚀,并改善涂层的力学性能,使薄膜更具附着力和坚固性。SiO2作为阻挡层,阻止了Ti4+离子扩散到VO2层,表面的TiO2层表现出优异的自清洁功能。
对于多功能多层结构的研究,Zheng等[79]通过中频反应磁控溅射在n型Si(100)晶面和玻璃上沉积了大规模(400 mm×400 mm)多功能TiO2(R)-VO2(M)-TiO2(A)多层膜。该膜具有三重功能:中间的VO2(M)层具有热致变色功能;顶部的TiO2(A)层具有光催化功能和亲水性;从而呈现防雾和自清洁效果;底部的金红石相TiO2层在VO2层单斜相的形成中发挥着关键作用,并起到了抗反射层的作用。此外,适当厚度的TiO2层还能够提高复合薄膜的Tlum和∆Tsol。
如图5(c)所示,Yao等[80]通过浸涂方法成功地沉积了4层涂层,从下到上依次为抗反射SiO2层(HSi)、热致变色VO2层(V)、保护性氟硅烷-SiO2层(FSi)和防雾交联聚乙烯醇和丙烯酸层(P)。该结构展现出卓越的太阳能调制能力(∆Tsol = 16.4%)、适度的可见光透过率(Tlum=54.0%)、卓越的防雾、自修复性能及稳定性。如图5(d)所示,Chang等[81]探究了不同界面对VO2薄膜劣化过程的影响规律,并提出了一种新型封装结构。该结构采用疏水性且性能稳定的HfO2封装于VO2的表面和截面,显著延长了VO2薄膜的使用寿命。通过调整HfO2膜层的结构和厚度,可以有效抑制VO2的劣化。在高温高湿条件下(温度60℃,相对湿度90%),经过100天的测试后仍能保持性能稳定,相当于在自然环境下能够使用16年之久。不同VO2多层结构复合薄膜的光学性能见表3[61, 69, 72, 74, 81-89]。
表 3 VO2多层结构复合薄膜的光学性能Table 3. Optical properties of VO2 multilayer composite filmsStructure Tlum/% ∆Tsol/% Ref. Double-layer ZnO-VO2 46.4 6.0 Gagaoudakis et al[82] VO2-TiO2 61.5 15.1 Chen et al[61] TiO2-VO2 50.49 20.11 Wu et al[74] TiO2-VO2 47.3 8.8 Ji et al[83] VO2-HfO2 55.8 15.9 Chang et al[81] VO2-C₈H20O₄Si 52.7 16.4 Liu et al[84] TiO2-VO2 49.0 7.0 Jin et al[72] Three-layer SiNx-VO2-SiNx 40.4 14.5 Long et al[85] Cr2O3-VO2-SiO2 50.0 16.1 Chang et al[86] TiO2-VO2-TiO2 57.6 2.9 Jin et al[69] Multi-layer VO2-fluorescent brightener-organic polymer 78.87 7.34 Gao et al[87] SiNx-NiCrOx-SiNx-VOx-SiNx-NiCrOx-SiNx 40.5 18.4 Zhan et al[88] TiO2-VO2-TiO2-VO2-TiO2 45 12.1 Mlyuka et al[89] HSi-VO2-FSi-P 54.0 16.4 Yao et al[80] Notes: A-B is the multi-layer structure of the lower layer (A) and the upper layer (B); HSi is the antireflective hollow SiO2 layer; FSi is the protective fluorosilane SiO2 layer; P is the antifogging cross-linked poly(vinyl alcohol) and poly(acrylic acid)layer. 4. 总结与展望
本综述回顾了智能窗用VO2基复合结构薄膜的主要制备方法,并深入分析了这些结构在改善VO2的热致变色性能、稳定性和颜色等方面最新研究进展。综合总结表明,增加壳层结构、改变纳米颗粒的分散基质,设计多层结构,可以实现高热致变色性能。通过将VO2纳米颗粒与无机或有机材料形成核壳结构,可获得卓越的热致变色性能和稳定性;改变VO2纳米颗粒的基质,无机VO2与有机热致变色材料巧妙结合展现了前所未有的热致变色性能;多孔基质薄膜,具备抗反射和高度分散性的VO2纳米颗粒,表现出卓越的光学性能;多层结构的设计不仅有助于改善光学性能,还能赋予自洁和防雾等附加功能。
为推动智能窗在日常生活中的实际应用,有必要进一步深入讨论该领域的科学技术问题。关于VO2基复合结构薄膜的未来研究方向,提出以下展望以供参考:
(1)光学性能和环境耐久性的研究是VO2基热致变色智能窗的主要研究方向。然而,为了满足VO2基热致变色智能窗能够实际应用的需求,需要考虑各项研究均能达到应用标准。复合结构在同时改善VO2光学性能和稳定性方面优势显著,但VO2复合结构仍单调,限制了其综合性能提升幅度。因此,需探究新的制备方法来丰富复合结构,进一步改善VO2的综合性能,促进其在智能窗等节能领域的实际应用;
(2)针对建筑节能窗,除了调节太阳辐射总量外,还需关注室内人体舒适度。VO2基热致变色智能窗可以调节
1350 ~2500 nm的太阳光谱,满足皮肤敏感的波段需求,包括阻隔有害的紫外波段和调节产生热效应的红外波段。可通过选择合适的复合材料与VO2基复合结构薄膜来调节不同波段的透射率,但对VO2复合结构薄膜的皮肤舒适性设计和相关评估标准尚需系统深入研究。 -
图 2 ((a), (b)) VO2纳米颗粒[18-19];((c), (d))无机壳层结构[24];((e), (f))有机壳层结构[32];((g), (h))无机-有机壳层结构[33]
DA—Dopamine; PDA—Polydopamine; PET—Polyethylene terephthalate; PVB—Polyvinyl butyral
Figure 2. ((a), (b)) Nanocomposite particle[18-19]; ((c), (d)) Inorganic shell structure[24]; ((e), (f)) Organic shell structure[32]; ((g), (h)) Inorganic-organic shell structure[33]
图 4 (a) SiO2@TiO2@VO2三层空心纳米球结构[48];(b) VO2@SiO2双层空心核壳结构[49];(c) VO2-Mg1.5VO4多孔结构[50]
VS1-VS4—VO2@SiO2 bivalve particles prepared by reaction of vanadium dioxide precursor solution at 60℃ for 1-4 h
Figure 4. (a) SiO2@TiO2@VO2 three-layer hollow nanospheres[48]; (b) VO2@SiO2 double layer hollow core-shell structure[49]; (c) VO2-Mg1.5VO4 porous structure[50]
图 5 (a) Cr2O3-VO2缓冲层结构[70];(b) VO2-TiO2减反射结构[74];(c) 空心SiO2-VO2-FSiO2-聚合物多功能结构[80];(d) VO2-HfO2多功能结构[81]
Figure 5. (a) Cr2O3-VO2 buffer layer structure[70]; (b) VO2-TiO2 antireflection structure[74]; (c) Hollow SiO2-VO2-FSiO2-polymer multi-function structure[80]; (d) VO2-HfO2 multi-function structure[81]
表 1 VO2核壳结构复合薄膜的光学性能
Table 1 Optical properties of VO2 core-shell composite thin films
Structure Tlum/% ∆Tsol/% Tc/℃ Ref. VO2@SiO2 38.0 18.9 — Du et al[30] VO2@ZnO 51.0 19.1 — Chen et al[27] VO2@SiO2 50.6 14.7 25.2 Zhu et al[34] VO2@TiO2 59.3 6.2 — Li et al[28] VO2@PDA 56.3 14.5 33.8 Guo et al[32] VO2@PMMA — 17.5 57 Hu et al[35] VO2@Polymer — 20.34 — Zhao et al[36] VO2@MgF2@PDA — 25.0 — Zhao et al[33] Notes:Tlum—Luminous transmittance; ∆Tsol—Modulation of solar energy; Tc—Transition temperature; A@B—Core(A)@shell(B) structure; PMMA—Polymethyl methacrylate. 表 2 不同基质材料VO2基复合薄膜的光学性能
Table 2 Optical properties of VO2-based composite films of different matrix materials
Structure Tlum/% ∆Tsol/% Ref. VO2-hydrogel 62.6 34.7 Zhou et al[40] VO2-Ni-Cl-IL 66.85 23.77 Zhu et al[41] VO2-{[(C2H5)2NH2]2NiBr4@SiO2} 52.9 25.7 Zhao et al[51] VO2-spiropyran 48.58 23.58 Zhao et al[45] VO2@SiO2 61.8 12.6 Qu et al[49] SiO2@TiO2@VO2 73.9 12.0 Yao et al[48] VO2-[1, 4-bis (benzoxazol-2-yl) naphthalene] 73.0 9.0 Qin et al[52] VO2-PDA 56.23 7.64 Wang et al[53] Notes: A-B is the mixture of A and B; Ni-Cl-IL is the ionic liquid-nickel-chlorine complexes. 表 3 VO2多层结构复合薄膜的光学性能
Table 3 Optical properties of VO2 multilayer composite films
Structure Tlum/% ∆Tsol/% Ref. Double-layer ZnO-VO2 46.4 6.0 Gagaoudakis et al[82] VO2-TiO2 61.5 15.1 Chen et al[61] TiO2-VO2 50.49 20.11 Wu et al[74] TiO2-VO2 47.3 8.8 Ji et al[83] VO2-HfO2 55.8 15.9 Chang et al[81] VO2-C₈H20O₄Si 52.7 16.4 Liu et al[84] TiO2-VO2 49.0 7.0 Jin et al[72] Three-layer SiNx-VO2-SiNx 40.4 14.5 Long et al[85] Cr2O3-VO2-SiO2 50.0 16.1 Chang et al[86] TiO2-VO2-TiO2 57.6 2.9 Jin et al[69] Multi-layer VO2-fluorescent brightener-organic polymer 78.87 7.34 Gao et al[87] SiNx-NiCrOx-SiNx-VOx-SiNx-NiCrOx-SiNx 40.5 18.4 Zhan et al[88] TiO2-VO2-TiO2-VO2-TiO2 45 12.1 Mlyuka et al[89] HSi-VO2-FSi-P 54.0 16.4 Yao et al[80] Notes: A-B is the multi-layer structure of the lower layer (A) and the upper layer (B); HSi is the antireflective hollow SiO2 layer; FSi is the protective fluorosilane SiO2 layer; P is the antifogging cross-linked poly(vinyl alcohol) and poly(acrylic acid)layer. -
[1] WARWICK M E A, BINIONS R. Advances in thermochromic vanadium dioxide films[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2014, 2(10): 3275-3292. DOI: 10.1039/C3TA14124A
[2] MANJAKKAL L, PEREIRA L, BARIMAH E K, et al. Multifunctional flexible and stretchable electrochromic energy storage devices[J]. Progress in Materials Science, 2024, 142: 101244.
[3] MA D, YANG T, FENG X, et al. Quadruple control electrochromic devices utilizing Ce4W9O33 electrodes for visible and near-infrared transmission intelligent modulation[J]. Advanced Science, 2024, 11(14): 2307223.
[4] WANG J, WANG Z, ZHANG M, et al. A semi-solid, polychromatic dual-band electrochromic smart window: Visualizing sunlight and solar heat transmission[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2024, 484: 149628.
[5] ZHANG Z, MO H, LI R, et al. The counterbalancing role of oxygen vacancy between the electrochromic properties and the trapping effect passivation for amorphous tungsten oxide films[J]. Small Science, 2024, 4(3): 2300219.
[6] ZHAO X, SUN J, GUO Z, et al. One-step hydrothermal synthesis of monoclinic vanadium dioxide nanoparticles with low phase transition temperature[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2022, 446: 137308. DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2022.137308
[7] ZHANG Z, ZHANG L, ZHOU Y, et al. Thermochromic energy efficient windows: Fundamentals, recent advances, and perspectives[J]. Chemical Reviews, 2023, 123(11): 7025-7080. DOI: 10.1021/acs.chemrev.2c00762
[8] LA M, ZHOU H, LI N, et al. Improved performance of Mg-Y alloy thin film switchable mirrors after coating with a superhydrophobic surface[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2017, 403: 23-28. DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.01.106
[9] WITTWER V, DATZ M, ELL J, et al. Gasochromic windows[J]. Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, 2004, 84(1-4): 305-314. DOI: 10.1016/j.solmat.2004.01.040
[10] LI N, LI Y, LI W, et al. One-step hydrothermal synthesis of TiO2@MoO3 core-shell nanomaterial: Microstructure, growth mechanism, and improved photochromic property[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2016, 120(6): 3341-3349. DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.5b10752
[11] LI N, LI Y, ZHOU Y, et al. Interfacial-charge-transfer-induced photochromism of MoO3@TiO2 crystalline-core amorphous-shell nanorods[J]. Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, 2017, 160: 116-125. DOI: 10.1016/j.solmat.2016.10.016
[12] WANG S, FAN W, LIU Z, et al. Advances on tungsten oxide based photochromic materials: Strategies to improve their photochromic properties[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2018, 6(2): 191-212. DOI: 10.1039/C7TC04189F
[13] GU J, WEI H, ZHAO T, et al. Unprecedented spatial manipulation and transformation of dynamic thermal radiation based on vanadium dioxide[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2024, 16: 10352-10360.
[14] WEI H, YAN X, GU J, et al. A universal approach to fabricating infrared-shielding smart coatings based on vanadium dioxide[J]. Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, 2022, 241: 111728. DOI: 10.1016/j.solmat.2022.111728
[15] WANG S, LIU M, KONG L, et al. Recent progress in VO2 smart coatings: Strategies to improve the thermochromic properties[J]. Progress in Materials Science, 2016, 81: 1-54. DOI: 10.1016/j.pmatsci.2016.03.001
[16] GOODENOUGH J B. The two components of the crystallographic transition in VO2[J]. Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 1971, 3(4): 490-500. DOI: 10.1016/0022-4596(71)90091-0
[17] CHANG T, CAO X, LONG Y, et al. How to properly evaluate and compare the thermochromic performance of VO2-based smart coatings[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2019, 7(42): 24164-24172. DOI: 10.1039/C9TA06681K
[18] POPURI S R, MICLAU M, ARTEMENKO A, et al. Rapid hydrothermal synthesis of VO2(B) and its conversion to thermochromic VO2(M1)[J]. Inorganic Chemistry, 2013, 52(9): 4780-4785.
[19] WANG C, XU H, WANG C, et al. Preparation of VO2(M) nanoparticles with exemplary optical performance from VO2(B) nanobelts by ball milling[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2021, 877: 159888.
[20] 钟莉, 李明, 李广海. D相二氧化钒纳米星粉体及其制备方法: 中国专利, CN104402050B [P]. 2016-02-10. ZHONG Li, LI Ming, LI Guanghai. D-phase vanadium dioxide nano-star powder and preparation method: Chinese patent, CN 104402050B[P]. 2016-02-10(in Chinese).
[21] 李登兵, 李明, 潘静, 等. 单分散的M相二氧化钒纳米颗粒的制备方法: 中国专利, CN104071843A [P]. 2014-10-01. LI Dengbing, LI Ming, PAN Jing, et al. Preparation method of monodisperse M phase vanadium dioxide nanoparticles: Chinese patent, CN104071843A[P]. 2014-10-01(in Chinese).
[22] CAO C, GAO Y, LUO H. Pure single-crystal rutile vanadium dioxide powders: Synthesis, mechanism and phase-transformation property[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C, 2008, 112(48): 18810-18814. DOI: 10.1021/jp8073688
[23] ALIE D, GEDVILAS L, WANG Z, et al. Direct synthesis of thermochromic VO2 through hydrothermal reaction[J]. Journal of Solid State Chemistry, 2014, 212: 237-241. DOI: 10.1016/j.jssc.2013.10.023
[24] LI Y, JI S, GAO Y, et al. Core-shell VO2@TiO2 nanorods that combine thermochromic and photocatalytic properties for application as energy-saving smart coatings[J]. Scientific Reports, 2013, 3(1): 1370. DOI: 10.1038/srep01370
[25] ZHOU Y, JI S, LI Y, et al. Microemulsion-based synthesis of V1− xW xO2@SiO2 core-shell structures for smart window applications[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry C, 2014, 2(19): 3812-3819. DOI: 10.1039/C3TC32282C
[26] LI W, JI S, QIAN K, et al. Preparation and characterization of VO2(M)-SnO2 thermochromic films for application as energy-saving smart coatings[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science, 2015, 456: 166-173. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcis.2015.06.013
[27] CHEN Y, ZENG X, ZHU J, et al. High performance and enhanced durability of thermochromic films using VO2@ZnO core-shell nanoparticles[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2017, 9(33): 27784-27791.
[28] LI Y, JI S, GAO Y, et al. Modification of mott phase transition characteristics in VO2@TiO2 core/shell nanostructures by misfit-strained heteroepitaxy[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2013, 5(14): 6603-6614.
[29] XIE Y M, ZHAO X P, MOFID S A, et al. Influence of shell materials on the optical performance of VO2 core-shell nanoparticle-based thermochromic films[J]. Materials Today Nano, 2021, 13: 100102. DOI: 10.1016/j.mtnano.2020.100102
[30] DU Z, LI M, ZOU F, et al. VO2@SiO2 nanoparticle-based films with localized surface plasmon resonance for smart windows[J]. ACS Applied Nano Materials, 2022, 5: 12972-12979. DOI: 10.1021/acsanm.2c02788
[31] CHEN Y, SHAO Z, YANG Y, et al. Electrons-donating derived dual-resistant crust of VO2 nano-particles via ascorbic acid treatment for highly stable smart windows applications[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019, 11(44): 41229-41237.
[32] GUO X, XU H, MA X, et al. Photothermal polydopamine coated VO2 nanoparticle thin film with enhanced optical property and stability[J]. Vacuum, 2022, 196: 110776. DOI: 10.1016/j.vacuum.2021.110776
[33] ZHAO S, TAO Y, CHEN Y, et al. Room-temperature synthesis of inorganic-organic hybrid coated VO2 nanoparticles for enhanced durability and flexible temperature-responsive near-infrared modulator application[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019, 11(10): 10254-10261.
[34] ZHU J, ZHOU Y, WANG B, et al. Vanadium dioxide nanoparticle-based thermochromic smart coating: High luminous transmittance, excellent solar regulation efficiency, and near room temperature phase transition[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2015, 7(50): 27796-27803.
[35] 呼啸, 李文婷, 付勍玮, 等. VO2@PMMA 微胶囊的原位制备及其热致变色涂层性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2023, 40(8): 4587-4600. HU Xiao, LI Wenting, FU Qingwei, et al. In situ preparation of VO2@PMMA microcapsule and thermochromic properties of its coating[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2023, 40(8): 4587-4600(in Chinese).
[36] ZHAO X, SUN J, MA J, et al. Combining reversible addition-fragmentation chain transfer polymerization and thiolene click reaction for application of core-shell structured VO2@polymer nanoparticles to smart window[J]. Sustainable Materials and Technologies, 2022, 32: e00420. DOI: 10.1016/j.susmat.2022.e00420
[37] LAAKSONEN K, LI S Y, PUISTO S R, et al. Nanoparticles of TiO2 and VO2 in dielectric media: Conditions for low optical scattering, and comparison between effective medium and four-flux theories[J]. Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, 2014, 130: 132-137. DOI: 10.1016/j.solmat.2014.06.036
[38] LI S Y, NIKLASSON G A, GRANQVIST C G. Nanothermochromics: Calculations for VO2 nanoparticles in dielectric hosts show much improved luminous transmittance and solar energy transmittance modulation[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2010, 108(6): 063525. DOI: 10.1063/1.3487980
[39] ZHOU Y, HUANG A, LI Y, et al. Surface plasmon resonance induced excellent solar control for VO2@SiO2 nanorods-based thermochromic foils[J]. Nanoscale, 2013, 5(19): 9208-9213. DOI: 10.1039/c3nr02221h
[40] ZHOU Y, CAI Y, HU X, et al. VO2/hydrogel hybrid nanothermochromic material with ultra-high solar modulation and luminous transmission[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2015, 3(3): 1121-1126. DOI: 10.1039/C4TA05035E
[41] ZHU J, HUANG A, MA H, et al. Composite film of vanadium dioxide nanoparticles and Ionic liquid-nickel-chlorine complexes with excellent visible thermochromic performance[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2016, 8(43): 29742-29748.
[42] CHEN Y, ZHU J, MA H, et al. VO2/nickel-bromine-ionic liquid composite film for thermochromic application[J]. Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, 2019, 196: 124-130. DOI: 10.1016/j.solmat.2019.03.047
[43] ZHU J, HUANG A, MA H, et al. Solar-thermochromism of a hybrid film of VO2 nanoparticles and Co II-Br-TMP complexes[J]. RSC Advances, 2016, 6(71): 67396-67399. DOI: 10.1039/C6RA14232J
[44] XU F, CAO X, ZHU J, et al. Broadband thermochromic VO2-based composite film with ultra-high solar modulation ability[J]. Materials Letters, 2018, 222: 62-65. DOI: 10.1016/j.matlet.2018.03.176
[45] ZHAO X, HU X, SUN J, et al. VO2-based composite films with exemplary thermochromic and photochromic performance[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2020, 128(18): 185107. DOI: 10.1063/5.0015382
[46] CAO X, WANG N, LAW J Y, et al. Nanoporous thermochromic VO2 (M) thin films: Controlled porosity, largely enhanced luminous transmittance and solar modulating ability[J]. Langmuir, 2014, 30(6): 1710-1715. DOI: 10.1021/la404666n
[47] LONG S, CAO X, HUANG R, et al. Self-template synthesis of nanoporous VO2-based films: Localized surface plasmon resonance and enhanced optical performance for solar glazing application[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019, 11(25): 22692-22702.
[48] YAO L, QU Z, PANG Z, et al. Three-layered hollow nanospheres based coatings with ultrahigh-performance of energy-saving, antireflection, and self-cleaning for smart windows[J]. Small, 2018, 14(34): 1801661. DOI: 10.1002/smll.201801661
[49] QU Z, YAO L, LI J, et al. Bifunctional template-induced VO2@SiO2 dual-shelled hollow nanosphere-based coatings for smart windows[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019, 11(17): 15960-15968.
[50] XU H, GUO X, WANG S, et al. Double in-situ synthesis of highly dispersed VO2-Mg1.5VO4 porous film with excellent optical performance and durability for advanced smart windows[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2023, 622: 156851. DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2023.156851
[51] ZHAO X, YAO W, SUN J, et al. Thermochromic composite film of VO2 nanoparticles and [(C2H5)2NH2]2NiBr4@SiO2 nanospheres for smart window applications[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 460: 141715. DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2023.141715
[52] 秦成远, 高迎, 王程, 等. 二氧化钒-1, 4-双 (苯并噁唑-2-基) 萘复合薄膜及其热致变色和发光性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2021, 38(10): 3412-3423. QIN Chengyuan, GAO Ying, WANG Cheng, et al. Vanadium dioxide-1, 4-bis (benzoxazol-2-yl) naphthalene composite films and their thermochromic and photoluminescent property[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2021, 38(10): 3412-3423(in Chinese).
[53] 王彬彬, 高阳, 杨帅军, 等. 二氧化钒-聚二乙炔热致变色复合薄膜及其调光性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2023, 40(6): 3417-3427. WANG Binbin, GAO Yang, YANG Shuaijun, et al. Vanadium dioxide-polydiacetylene thermochromic composite films and their solar regulation properties[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2023, 40(6): 3417-3427(in Chinese).
[54] GUZMAN G, MORINEAU R, LIVAGE J. Synthesis of vanadium dioxide thin films from vanadium alkoxides[J]. Materials Research Bulletin, 1994, 29(5): 509-515. DOI: 10.1016/0025-5408(94)90039-6
[55] FITZGERALD J V. Anelasticity of glass: II, internal friction and sodium ion diffusion in tank plate glass, a typical soda-lime-silica glass[J]. Journal of the American Ceramic Society, 1951, 34(11): 339-342. DOI: 10.1111/j.1151-2916.1951.tb13481.x
[56] KOO H, YOU H, KO K E, et al. Thermochromic properties of VO2 thin film on SiNx buffered glass substrate[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2013, 277: 237-241. DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2013.04.031
[57] NAGASHIMA K, YANAGIDA T, TANAKA H, et al. Interface effect on metal-insulator transition of strained vanadium dioxide ultrathin films[J]. Journal of Applied Physics, 2007, 101(2): 026103. DOI: 10.1063/1.2424321
[58] ZHANG Z, GAO Y, LUO H, et al. Solution-based fabrication of vanadium dioxide on F: SnO2 substrates with largely enhanced thermochromism and low-emissivity for energy-saving applications[J]. Energy & Environmental Science, 2011, 4(10): 4290-4297.
[59] KANG L, GAO Y, LUO H, et al. Thermochromic properties and low emissivity of ZnO: Al/VO2 double-layered films with a lowered phase transition temperature[J]. Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, 2011, 95(12): 3189-3194. DOI: 10.1016/j.solmat.2011.06.047
[60] KANG L, GAO Y, CHEN Z, et al. Pt/VO2 double-layered films combining thermochromic properties with low emissivity[J]. Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, 2010, 94(12): 2078-2084. DOI: 10.1016/j.solmat.2010.06.023
[61] CHEN Z, GAO Y, KANG L, et al. VO2-based double-layered films for smart windows: Optical design, all-solution preparation and improved properties[J]. Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, 2011, 95(9): 2677-2684. DOI: 10.1016/j.solmat.2011.05.041
[62] ZHU M, QI H, WANG B, et al. Thermochromism of vanadium dioxide films controlled by the thickness of ZnO buffer layer under low substrate temperature[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2018, 740: 844-851. DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.01.066
[63] GU J, WEI H, REN F, et al. VO2-based infrared radiation regulator with excellent dynamic thermal management performance[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2022, 14(2): 2683-2690.
[64] REN F, WEI H, GU J, et al. In situ preparation of VO2 films with controlled ionized flux density in hipims and their regulation of thermal radiance[J]. ACS Applied Electronic Materials, 2020, 2(7): 2203-2210. DOI: 10.1021/acsaelm.0c00383
[65] KOO H, XU L, KO K E, et al. Effect of oxide buffer layer on the thermochromic properties of VO2 thin films[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2013, 22(12): 3967-3973. DOI: 10.1007/s11665-013-0696-7
[66] LONG S, CAO X, SUN G, et al. Effects of V2O3 buffer layers on sputtered VO2 smart windows: Improved thermochromic properties, tunable width of hysteresis loops and enhanced durability[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2018, 441: 764-772. DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.02.083
[67] XU G, JIN P, TAZAWA M, et al. Optimization of antireflection coating for VO2-based energy efficient window[J]. Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, 2004, 83(1): 29-37. DOI: 10.1016/j.solmat.2004.02.014
[68] KOO H, SHIN D, BAE S H, et al. The effect of CeO2 antireflection layer on the optical properties of thermochromic VO2 film for smart window system[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance, 2014, 23: 402-407. DOI: 10.1007/s11665-013-0740-7
[69] JIN P, XU G, TAZAWA M, et al. Design, formation and characterization of a novel multifunctional window with VO2 and TiO2 coatings[J]. Applied Physics A: Materials Science & Processing, 2003, 77: 455-459.
[70] CHANG T, CAO X, LI N, et al. Facile and low-temperature fabrication of thermochromic Cr2O3/VO2 smart coatings: Enhanced solar modulation ability, high luminous transmittance and UV-shielding function[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2017, 9(31): 26029-26037.
[71] LEE M H, CHO J S. Better thermochromic glazing of windows with anti-reflection coating[J]. Thin Solid Films, 2000, 365(1): 5-6. DOI: 10.1016/S0040-6090(99)01112-8
[72] JIN P, XU G, TAZAWA M, et al. A VO2-based multifunctional window with highly improved luminous transmittance: Surfaces, interfaces, and films[J]. Japanese Journal of Applied Physics, 2002, 41(3): L278-L280.
[73] SAITZEK S, GUINNETON F, SAUQUES L, et al. Thermochromic CeO2-VO2 bilayers: Role of ceria coating in optical switching properties[J]. Optical Materials, 2007, 30(3): 407-415. DOI: 10.1016/j.optmat.2006.11.067
[74] WU W, WANG C, CHEN C, et al. Design of antireflection and enhanced thermochromic properties of TiO2/VO2 thin films[J]. Advanced Materials Interfaces, 2023, 10(15): 2202506. DOI: 10.1002/admi.202202506
[75] DOU S, WANG Y, ZHANG X, et al. Facile preparation of double-sided VO2 (M) films with micro-structure and enhanced thermochromic performances[J]. Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, 2017, 160: 164-173. DOI: 10.1016/j.solmat.2016.10.025
[76] DOU S, ZHAO J, ZHANG W, et al. A universal approach to achieve high luminous transmittance and solar modulating ability simultaneously for vanadium dioxide smart coatings via double-sided localized surface plasmon resonances[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2020, 12(6): 7302-7309.
[77] XU F, CAO X, SHAO Z, et al. Highly enhanced thermochromic performance of VO2 film using "movable" antireflective coatings[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2019, 11(5): 4712-4718.
[78] POWELL M J, QUESADA-CABRERA R, TAYLOR A, et al. Intelligent multifunctional VO2/SiO2/TiO2 coatings for self-cleaning, energy-saving window panels[J]. Chemistry of Materials, 2016, 28(5): 1369-1376. DOI: 10.1021/acs.chemmater.5b04419
[79] ZHENG J, BAO S, JIN P. TiO2(R)/VO2(M)/TiO2(A) multilayer film as smart window: Combination of energy-saving, antifogging and self-cleaning functions[J]. Nano Energy, 2015, 11: 136-145. DOI: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2014.09.023
[80] YAO L, QU Z, SUN R, et al. Long-lived multilayer coatings for smart windows: Integration of energy-saving, antifogging, and self-healing functions[J]. ACS Applied Energy Materials, 2019, 2(10): 7467-7473. DOI: 10.1021/acsaem.9b01382
[81] CHANG T, CAO X, LI N, et al. Mitigating deterioration of vanadium dioxide thermochromic films by interfacial encapsulation[J]. Matter, 2019, 1(3): 734-744. DOI: 10.1016/j.matt.2019.04.004
[82] GAGAOUDAKIS E, APERATHITIS E, MICHAIL G, et al. Low-temperature RF sputtered VO2 thin films as thermochromic coatings for smart glazing systems[J]. Solar Energy, 2018, 165: 115-121. DOI: 10.1016/j.solener.2018.03.010
[83] JI Y, MATTSSON A, NIKLASSON G A, et al. Synergistic TiO2/VO2 window coating with thermochromism, enhanced luminous transmittance, and photocatalytic activity[J]. Joule, 2019, 3(10): 2457-2471. DOI: 10.1016/j.joule.2019.06.024
[84] LIU C, WANG S, ZHOU Y, et al. Index-tunable anti-reflection coatings: Maximizing solar modulation ability for vanadium dioxide-based smart thermochromic glazing[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2018, 731: 1197-1207. DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2017.10.045
[85] LONG S, CAO X, LI N, et al. Application-oriented VO2 thermochromic coatings with composite structures: Optimized optical performance and robust fatigue properties[J]. Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, 2019, 190: 138-148.
[86] CHANG T, CAO X, DEDON L R, et al. Optical design and stability study for ultrahigh-performance and long-lived vanadium dioxide-based thermochromic coatings[J]. Nano Energy, 2018, 44: 256-264. DOI: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2017.11.061
[87] 高迎, 秦成远, 聂永, 等. 二氧化钒-荧光增白剂-有机聚合物三层多功能复合薄膜[J]. 复合材料学报, 2022, 39(8): 3828-3844. GAO Ying, QIN Chengyuan, NIE Yong, et al. Three-layer multifunctional vanadium dioxide-fluorescent brightener-organic polymer composite films[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2022, 39(8): 3828-3844(in Chinese).
[88] ZHAN Y, LU Y, XIAO X, et al. Tuning thermochromic performance of VO x-based multilayer films by controlling annealing pressure[J]. Ceramics International, 2020, 46(2): 2079-2085. DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2019.09.188
[89] MLYUKA N R, NIKLASSON G A, GRANQVIST C G. Thermochromic multilayer films of VO2 and TiO2 with enhanced transmittance[J]. Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, 2009, 93(9): 1685-1687. DOI: 10.1016/j.solmat.2009.03.021
-
目的
近年来,关于VO的制备方法、相变机制以及改善热致变色性能的研究取得了显著进展。然而,在实际应用中,VO仍面临一系列挑战,包括较高的本征相变温度()、较低的可见光透过率()、不尽人意的太阳能调制能力()、较差的耐候性以及不美观的棕黄色外观。针对这些问题,国内外研究者开展了大量研究,发现复合结构能够显著改善VO的性能。然而,目前关于VO基复合结构薄膜的综述相对较少。因此,迫切需要对这一领域的最新研究进展进行全面综述。
方法本文综述了VO基复合结构薄膜的制备方法及性能提升策略的研究进展,并最后对智能窗用VO基复合结构薄膜未来的发展方向进行了展望。①本文阐述了VO基智能窗的性能评价指标;②总结了VO纳米颗粒基复合结构的制备方法及其性能提升策略,包括核壳结构和基质材料,核壳结构涵盖无机、有机及无机-有机外壳材料,基质材料则包括变色基质及具有不同微纳结构的基质;③总结了多层结构的制备方法及其性能提升策略,包括缓冲层、减反射层和多功能层;④展望了智能窗用VO基复合结构薄膜的发展前景。
结果通过调节壳层结构、改变VO纳米颗粒的分散基质以及设计多层结构等方式,可以制备具有优异热致变色性能的VO基复合薄膜。①通过将VO纳米颗粒与无机或有机材料形成核壳结构,复合薄膜可获得卓越的热致变色性能和稳定性;②选择有机热致变色材料作为基质的复合薄膜展现了丰富的颜色,而以多孔材料作为基质的复合薄膜则具备减反射效果和高度分散性的VO纳米颗粒,表现出优异的光学性能;③多层结构的设计不仅有助于改善复合薄膜的光学性能,还能赋予其自清洁和防雾等附加功能。
结论随着能源日益枯竭和环境污染问题的日益严峻,迫切需求采取节能减排措施。热致变色智能窗可根据环境温度的变化自动调整太阳光透过率,无能源消耗,因此成为当前研究的焦点。VO基热致变色智能窗的主要研究方向是光学性能和环境耐久性。然而,为了满足实际应用的需求,需要确保各项指标达到应用标准。复合结构在同时改善VO光学性能和稳定性方面优势显著,但现有的VO复合结构较为简单,限制了其综合性能的提升。因此,有必要探索新的制备方法以丰富复合结构,进一步改善VO的综合性能,促进其在智能窗等节能领域的实际应用。
-
近年来,关于VO2 制备方法、相变机制以及改善热致变色性能的研究取得了显著进展。然而,在实际应用中,VO2仍面临一系列挑战,包括本征相变温度较高、可见光透过率(Tlum)较低、太阳能调节效率(∆Tsol)不够高、耐候性不佳,以及呈现棕黄色的颜色舒适度较差。针对这些问题,国内外的研究者进行了大量研究,发现复合结构可以显著改善VO2的性能,因此迫切需要对这一领域的最新研究进展进行综述。围绕“智能窗用二氧化钒基复合结构薄膜的制备及研究进展”这一主题,本文涵盖四部分内容:(1)阐述了二氧化钒基智能窗的性能评价指标;(2)总结了二氧化钒纳米颗粒基复合结构的制备方法及其性能提升策略,其中包括核壳结构和二氧化钒纳米颗粒基质材料;(3)总结了多层结构的制备方法及其性能提升策略,其中包括缓冲层,减反射层和多功能层;(4)对智能窗用二氧化钒基复合结构薄膜的发展前景进行了展望。





 下载:
下载: