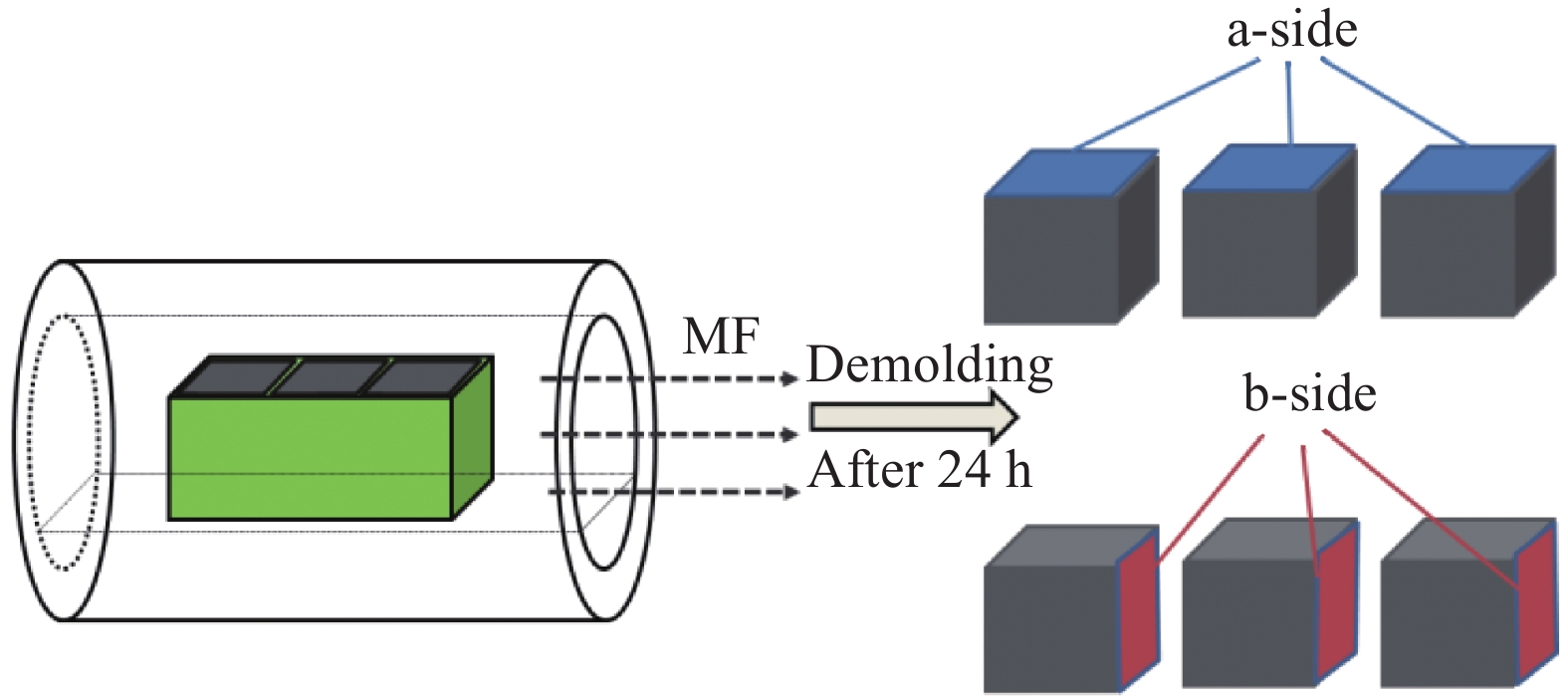
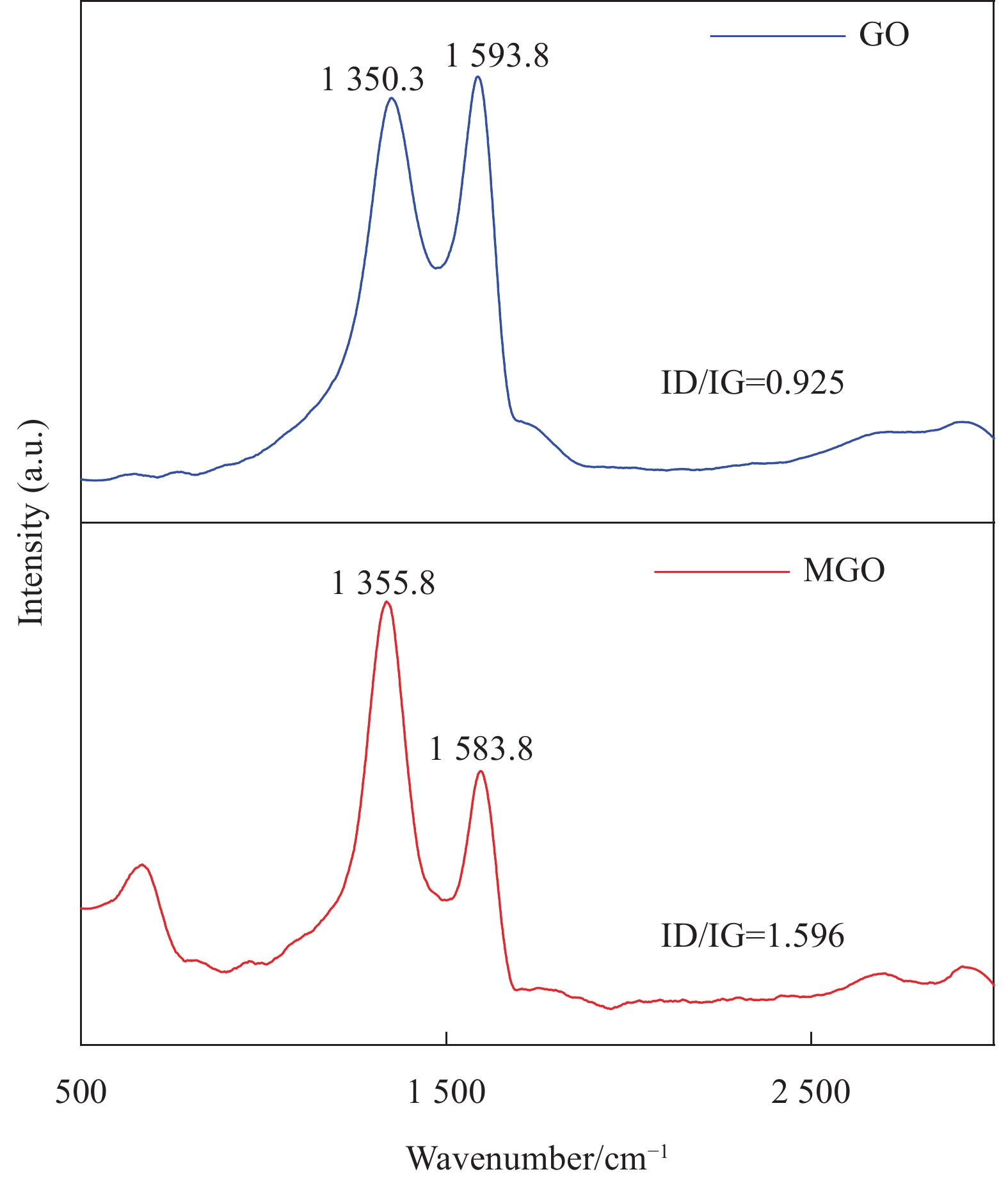
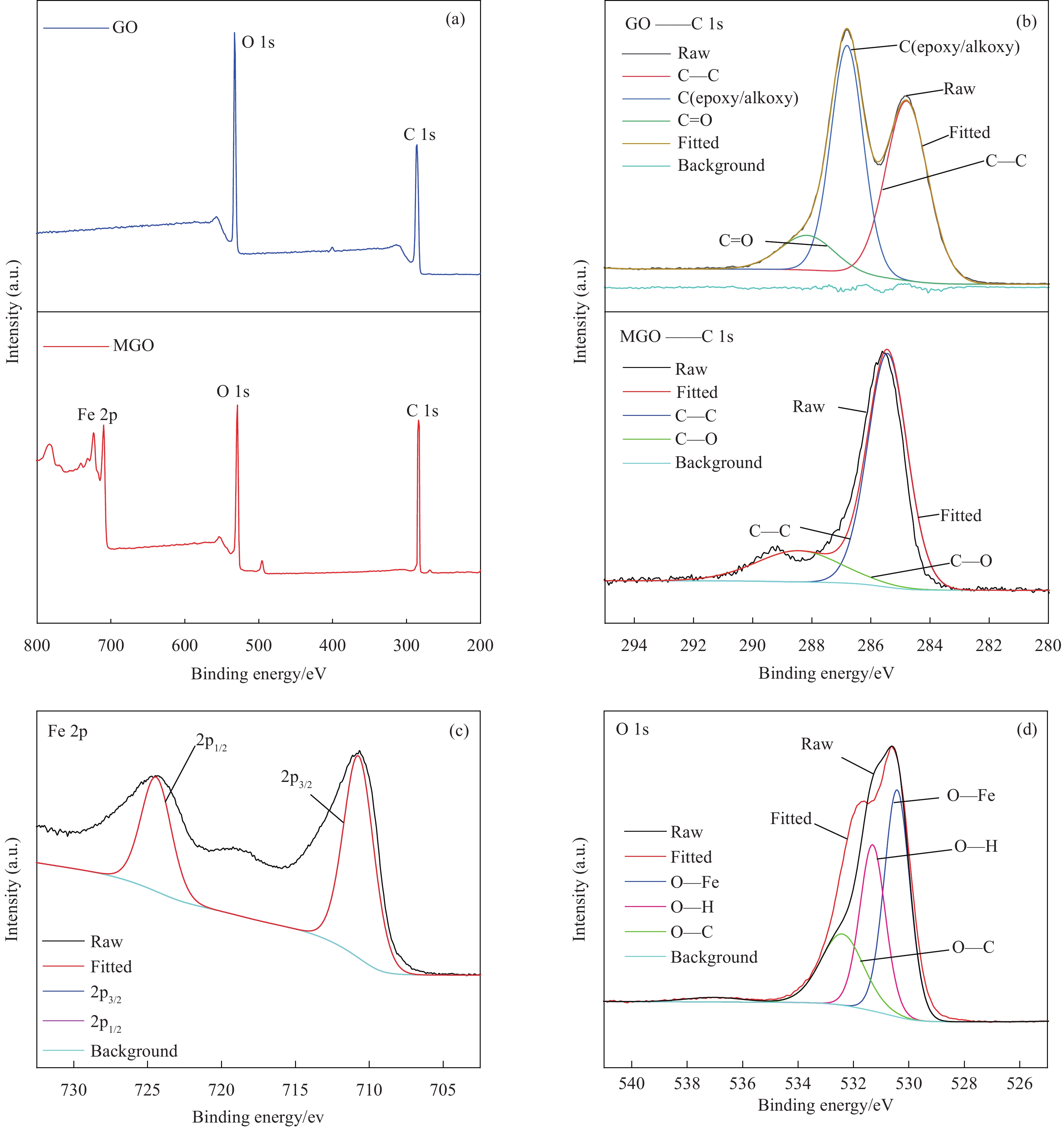
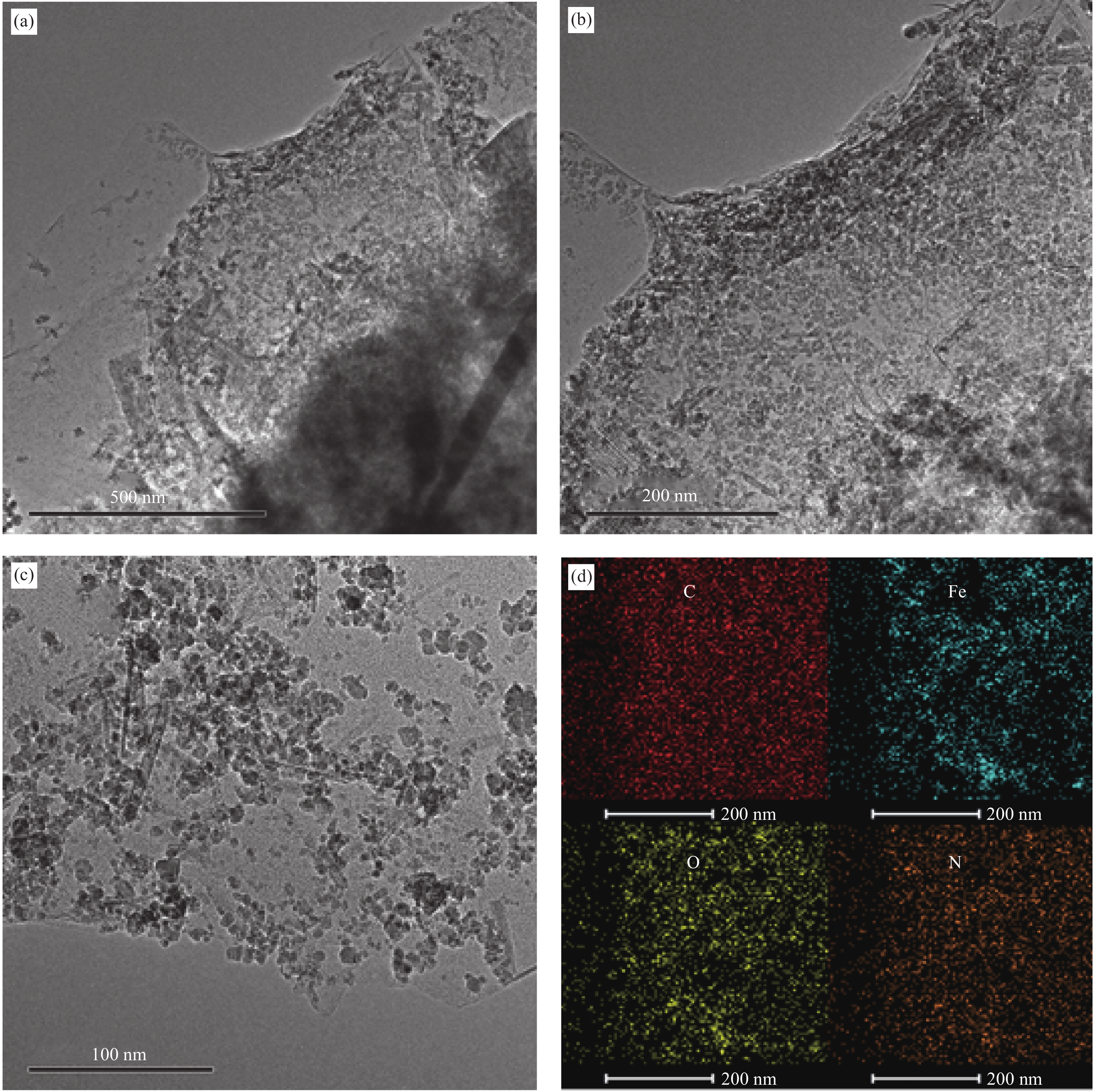
Study on the effect of magnetic field induction on the compressive strength of magnetic graphene-modified cement paste
-
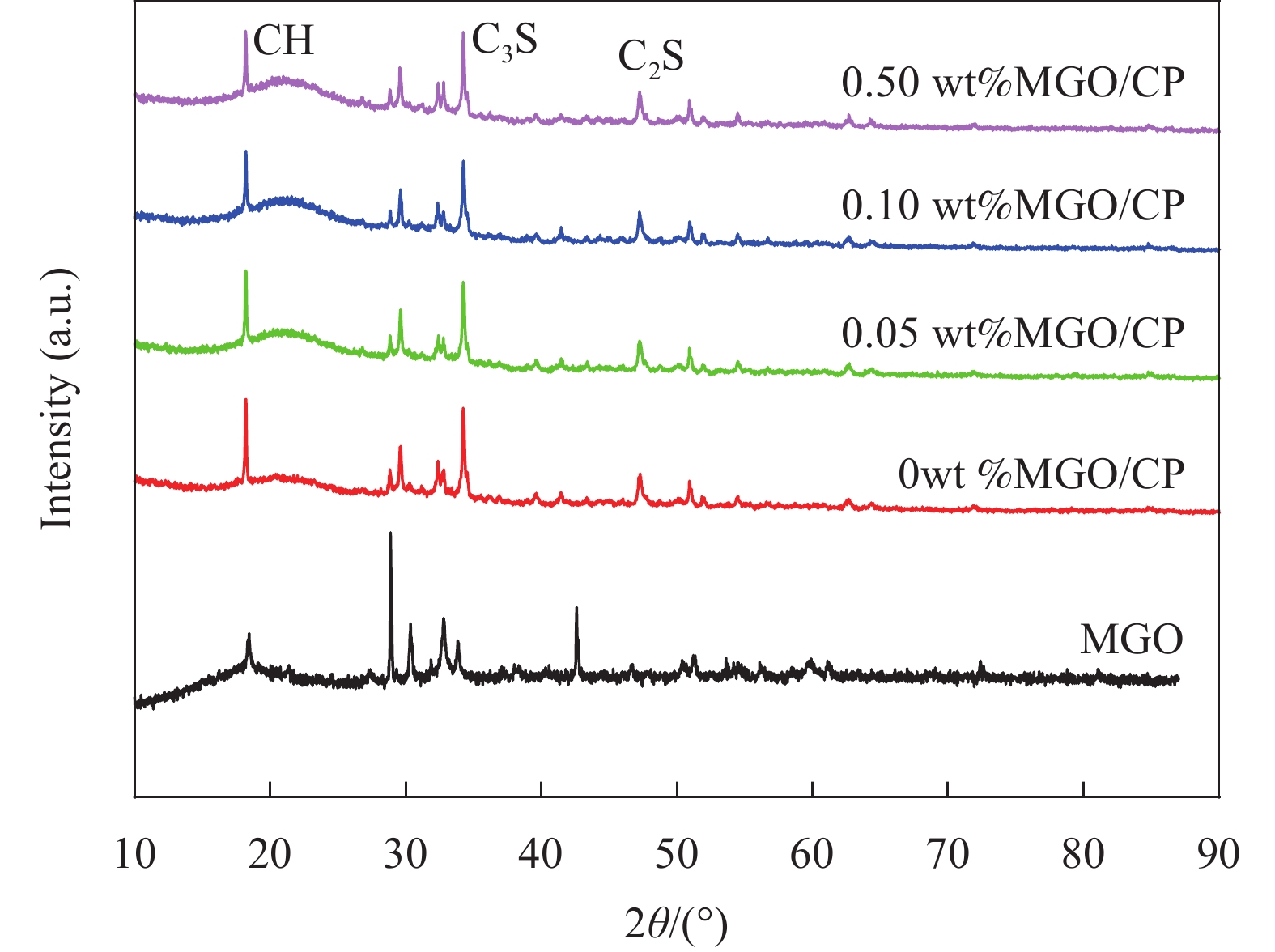
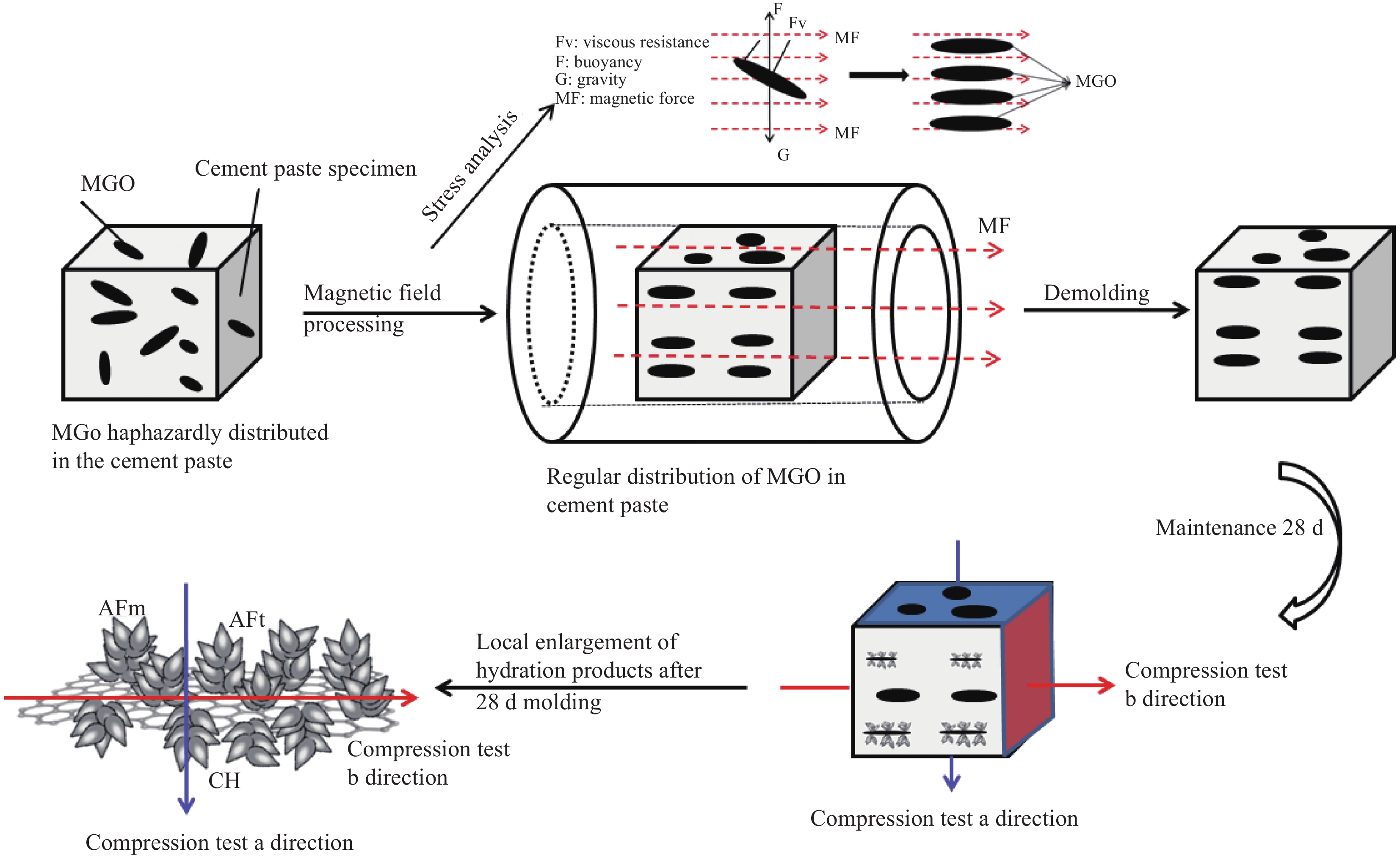
摘要: 二维石墨烯(G)纳米片对水泥基材料有显著的增强效果,但通常情况下G是杂乱无章地分布在水泥基材料中。为了更好地发挥G的强化作用,本研究通过一步共沉淀法将Fe3O4纳米颗粒附着热还原氧化石墨烯(RGO)纳米片上制备了磁性纳米复合材料 Fe3O4@ RGO(MGO),通过施加外磁场(MF)使不同掺量的MGO纳米片在水泥净浆(CP)中沿一定方向排列,分别通过测试垂直和平行于磁场方向上的硬化水泥净浆的抗压强度。研究结果表明经磁场诱导后掺入不同量MGO的水泥净浆平行于磁场方向的截面抗压强度均大于垂直于磁场方向的截面抗压强度;当MGO掺量为0.1%时,在平行于磁场方向的截面抗压强度比垂直于磁场方向的截面抗压强度高12.20%。说明MGO纳米片经磁场诱导后发生了定向排列,水泥水化产物更多的在平行于磁场方向上规整排列生长。本研究通过外部磁场诱导调控石墨烯纳米片定向排布,为特定用途下实现更高强度的水泥基材料提供了一种有效途径。Abstract: Two-dimensional graphene (G) nanosheets have a significant enhan cement effect on cement-based materials, but generally G is distributed haptically in cement-based materials. In order to better exert the strengthening effect of G, the magnetic nanocomposite Fe3O4@RGO (MGO) was prepared by one-step co-precipitation method by adhering Fe3O4 nanoparticles to thermal-reduced graphene oxide (RGO) nanosheets. By applying an external magnetic field (MF), the MGO nanosheets with different contents were arranged in a certain direction in the cement paste. The compressive strength of the hardened cement paste perpendicular and parallel to the magnetic field was tested respectively. The results show that the compressive strength of the cement paste mixed with different amounts of MGO in the direction parallel to the magnetic field is greater than that perpendicular to the magnetic field; when the content of MGO is 0.1%, the compressive strength of the section parallel to the magnetic field is 12.20% higher than that perpendicular to the magnetic field. The results indicated that the MGO nanosheets were oriented after induction by magnetic field, and the hydration products of cement grew in a regular arrangement parallel to the magnetic field. This study provides an effective way to achieve higher strength cement-based materials for specific applications by regulating the orientation of graphene nanosheets induced by an external magnetic field.
-
Keywords:
- Fe3O4 /
- graphene /
- magnetic fields /
- directional arrangement /
- mechanical property /
- cement paste
-
高性能热塑性复合材料具有能够快速成型、原材料可无限期存贮、制件可多次加热成型、废旧制件可回收利用等优点[1-3],符合经济型、环保性的发展要求,成为各个国家高端复合材料领域研究和发展的重点[4]。早在上个世纪80年代[5],国外科研院所、企业等在热塑性复合材料的应用方面投入了大量的研发力量[6],经过多年的发展,国外热塑性复合材料在军用、民用航空的应用已完成从飞机内饰、舱门、口盖、整流罩等非承力部件到飞机固定面前后缘、襟翼、副翼、方向舵等受载较小部位[7],再到机翼盒段、机身壁板、蒙皮等主承力结构的转变[8]。高性能热塑性复合材料的实际应用取得了显著的效果,有效弥补了热固性复合材料制造和使用过程中面临的诸多问题。
高性能热塑性复合材料中,碳纤维增强聚芳醚酮(CF/PAEK)复合材料,具有优异的韧性[9]、耐老化性能及耐疲劳性能[10],使CF/PAEK热塑性复合材料得以替代部分传统热固性复合材料,在航空、航天等领域取得成功应用,但是在使用的过程中仍然面临损伤、失效的风险。复合材料典型损伤模式包括层内损伤和层间损伤,层内损伤如基体开裂、纤维与基体脱粘和纤维断裂等,层间损伤如层间脱粘等[11],因此,复合材料的界面性能及层间性能得到了研究者们的关注。Lu等[12]研究了CCF300碳纤维与不同树脂基体间的界面剪切强度,结果显示聚醚醚酮(Polyetheretherketone,PEEK)与碳纤维间的界面强度约为44.87 MPa;一些研究者认为由于PEEK链惰性和碳纤维表面能较低,导致界面强度稍低,复合材料的界面强度仍然有提升的空间,Su等[13]采用碳纳米管优化了CF/PEEK复合材料的层间剪切性能,将复合材料的短梁剪切强度提高35.8%;Yan等[14]研制了水溶性胺化聚醚醚酮(PEEK-NH2)上浆剂将CF/PEEK复合材料的层间剪切强度提高了43.1%;除此之外,成型工艺也能够影响复合材料的界面及层间性能,Wu等[15]研究了孔隙率及树脂结晶度对CF/PEEK复合材料的层间剪切性能的影响,结果显示较低的孔隙率和较高的结晶度能够提高复合材料的层间剪切性能;史如静等[16]研究了成型工艺参数对CF/PEEK复合材料Ⅰ型断裂性能的影响,结果显示较高的成型温度、适当的成型压力及较快的降温速率能够提高复合材料的Ⅰ型断裂韧性。上述研究主要集中于研究工艺条件对复合材料性能的影响,而对树脂基体的特性对复合材料性能的影响研究较少,Chen等[17]研究了不同流动性能的PEEK树脂的流变行为,并根据结果优化了PEEK树脂基体对碳纤维的浸渍参数,并测试了优化浸渍参数后的复合材料的力学性能,但并未对比具有不同流动性能的PEEK基复合材料的力学性能。
本文中使用具有不同特性的PAEK树脂基体和国产T300级SCF35碳纤维制备了连续碳纤维增强PAEK热塑性复合材料,以微球脱粘性能、90°拉伸性能、短梁剪切性能、Ⅰ型断裂韧性、Ⅱ型断裂韧性为指标,研究了树脂基体的特性对复合材料的界面性能和层间性能的影响,为航空、航天领域所用轻质高强复合材料的设计和制造提供了选材参考。
1. 试验材料及方法
1.1 原材料
基体树脂为汤原县海瑞特工程塑料有限公司生产的聚芳醚酮(Polyaryletherketone,PAEK)树脂,其中流动性稍低的树脂基体牌号为PAEK-L,流动性稍高的树脂基体牌号为PAEK-H,树脂基体的性能如表1所示;碳纤维为中国石化上海石油化工股份有限公司生产的T300级碳纤维,牌号为SCF35,碳纤维性能如表2所示,表面形貌如图1所示;热塑性单向预浸料由黑龙江英创新材料有限公司生产,牌号分别为SCF35/PAEK-L及SCF35/PAEK-H,预浸料的纤维面密度约为147 g/m2,纤维体积分数约为52vol%,树脂质量分数约为40wt%。
表 1 聚芳醚酮(PAEK)树脂基体的性能Table 1. Properties of poly aryl ether ketone (PAEK) resin matrixProperty Tensile
strength/MPaTensile
modulus/GPaElongation/% Notched impact
strength/(kJ∙m–2)Apparent viscosity
(360℃)/(Pa·s)PAEK-L 96±0.5 4.0±0.2 109±7.2 5.7±0.2 1139 PAEK-H 95±0.5 3.9±0.2 101±4.4 5.7±0.2 399 Notes: PAEK-L—Low flow poly aryl ether ketone resin matrix; PAEK-H—High flow poly aryl ether ketone resin matrix. 表 2 国产T300级碳纤维(SCF35)的性能Table 2. Properties of domestic T300 grade carbon fiber (SCF35)Fibre Specification Tensile strength
/MPaTensile modulus
/GPaElongation
/%Bulk density
/(g∙cm−3)Linear density
/(g∙m−1)SCF35 12 K 4300 230 1.85 1.8 0.8 1.2 复合材料层压板制备
采用模压成型的方法制备复合材料层压板,首先将预浸料裁切成所需的长度规格,采用超声波焊机将预浸料铺贴为预成型体,然后将预制体放入高温脱模剂处理后的模具型腔,最后将模具放入平板硫化仪(LSVI-50 T,广州市普同实验分析仪器有限公司)进行模压成型,成型工艺如图2所示,图2(a)为薄板成型工艺,适用于铺层方式为[0°]14的90°拉伸试样;图2(b)为厚板成型工艺,适用于断裂韧性试样及铺层方式为[0°]42的短梁剪切试样。上述断裂韧性试样所用层压板的铺层方式为[0°]24,预制体中间层铺放厚度为0.03 mm的聚酰亚胺胶带作为预制缺陷,如图3所示。
1.3 测试与表征
SCF35碳纤维与聚芳醚酮(PAEK)树脂间界面强度的测试,采用微球脱粘实验测试纤维与树脂间的界面强度,所用设备为日本东荣株式会社生产的复合材料界面性能评价装置,设备型号为HM410。测试过程中首先将PAEK树脂330℃熔融成球,然后使树脂浸润单根纤维约10 s,待挂在纤维上的树脂由于表面张力形成微球后,再使用树脂熔体蘸取纤维表面上多余的树脂,将纤维上挂载的小球修理至长度为40~60 μm的小球,随后将纤维和树脂在330℃下保温10 min使树脂充分浸润纤维,最后将保温后的样品冷却至室温进行测试,测试原理如图4所示,界面剪切强度的计算公式如下所示:
τ=Fmaxπdl (1) 式中:τ为平均剪切强度;Fmax为小球剥脱时的力;d为纤维直径;l为纤维埋入树脂中的长度。
SCF35/PAEK复合材料的力学性能采用美国英斯特朗公司生产的万用材料试验机进行测试,设备型号为Instron 5982,90°拉伸性能采用测试标准ASTM D3039/D3039 M-14[18],测试样条尺寸为175 mm×25 mm×2 mm,测试加载速度为2 mm/min,90°拉伸强度计算公式如下所示:
σt=Pbd (2) 式中:σt为极限拉伸强度;P为破坏前最大载荷;b为试样宽度;d为试样厚度。
复合材料的短梁剪切性能测试采用标准ASTM D2344/D2344 M-16[19],试样长度∶跨距∶宽度∶厚度=6∶4∶2∶1,SCF35/PAEK-L的试样尺寸为36.6 mm×12.2 mm×6.1 mm,SCF35/PAEK-H的试样尺寸为35.4 mm×11.8 mm×5.9 mm,测试过程中加载头的半径为3.0 mm,支座的半径为1.5 mm,试样加载速度为1.0 mm/min,短梁剪切强度计算公式如下所示:
Fsbs=0.75Pmbd (3) 式中:
Fsbs 为短梁剪切强度;Pm 为试样破坏的最大载荷;b为试样宽度;d为试样厚度。Ⅰ型断裂韧性采用测试标准ASTM D5528/D5528 M-21[20],试样的尺寸为180 mm×25 mm,预制裂纹长度约为50 mm,测试过程中加载速度为2.0 mm/min,Ⅰ型断裂韧性的计算公式如下所示:
GIC=nPδ2ba (4) 式中:
GIC 为Ⅰ型断裂韧性;n为柔度标定系数,是lg(δi/Pi)与lg(ai)的最小二乘法拟合的直线斜率;i为测试过程中的取样点;P为裂纹扩展临界载荷;δ 为对应于P的加载点位移;a为裂纹长度。Ⅱ型断裂韧性采用测试标准ASTM D7905/D7905 M-19[21],采用预制试样的方法进行测试,试样的尺寸为140 mm×25 mm,预制裂纹长度约为40 mm,测试过程中加载速度为2.0 mm/min,Ⅱ型断裂韧性的计算公式如下所示:
GПC=3mP2Maxa2pc2B 式中:
GПC 为Ⅱ型断裂韧性;m为合规校准系数;PMax 为载荷的最大值;apc 为实际裂纹长度;B为试件宽度。除上述测试外,还采用日立Regulus 8230型场发射扫描电子显微镜及浩视RH 8800超景深显微镜对相关试样的微观形貌进行测试表征。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 SCF35/PAEK复合材料的界面性能
SCF35/PAEK复合材料的界面性能如表3所示,SCF35碳纤维与低流动性树脂PAEK-L的界面剪切强度约为64 MPa,接触角约为35.8°,90°拉伸强度约为55 MPa,90°拉伸模量约为8.6 GPa,短梁剪切强度约为86 MPa;SCF35碳纤维与高流动性树脂PAEK-H的界面剪切强度约为79 MPa,接触角约为34.4°,90°拉伸强度约为76 MPa,90°拉伸模量约为9.7 GPa,短梁剪切强度约为92 MPa。
表 3 SCF35/PAEK复合材料的界面性能Table 3. Interfacial properties of SCF35/PAEK compositesSystem Interfacial shear
strength/MPaContact angle/
(°)90° tensile
strength/MPa90° tensile
modulus/GPaShort beam shear
strength/MPaSCF35/PAEK-L 64±3.4 35.8±1.0 55±2.9 8.6±0.1 86±1.9 SCF35/PAEK-H 79±6.0 34.4±3.0 76±5.4 9.7±0.4 92±1.4 SCF35/PAEK复合材料界面剪切测试后,树脂剥脱后的表面形貌如图5所示,微球脱粘的截面形貌如图6所示,纤维与树脂间的接触角如图7所示。图5(a)中PAEK-L微球剥脱的前端呈现撕裂状,后端树脂呈现整体剥脱状;图5(b)中PAEK-H微球剥脱的前端和后端均呈现撕裂状。图6(a)中SCF35/PAEK-L复合材料界面处存在空隙,而图6(b)中SCF35/PAEK-H复合材料界面处树脂基体与纤维结合紧密。图7(a)中PAEK-L树脂在表面张力的作用下在纤维上形成独立的树脂微球,而图7(b)中PAEK-H树脂与纤维结合较紧密,出现树脂粘连、不能形成微球的现象,出现这种现象的原因是,在没有额外压力的作用下,树脂对带有沟槽的SCF35碳纤维浸润的驱动力主要来自于毛细管压力[22],流动性低的PAEK-L树脂具有较高的内摩擦阻力,毛细管压力不足以克服树脂的内摩擦阻力[23],树脂液滴与空气界面处的树脂分子不能克服自由能势垒[24],无法彻底的将纤维表面的沟槽浸润,从而与纤维表面沟槽形成Cassie接触状态[25],并且在表面张力的作用下,团聚成为独立的树脂微球;PAEK-H树脂基体具有较高的流动性能,即较低的内摩擦阻力,因此在毛细管压力的作用下,树脂液滴与空气界面处的树脂分子能够克服自由能势垒与纤维表面沟槽接触并发生黏附,形成Wenzel接触状态[26]。上述结果说明,造成SCF35/PAEK-L界面强度稍低于SCF35/PAEK-H的原因是PAEK-H树脂的流动性较好,能够与带有沟槽的SCF35碳纤维形成较好的结合能力。
![]() 图 5 SCF35/PAEK微球脱粘的表面形貌:(a) SCF35/PAEK-L:(1) 整体形貌、(2) 微球脱粘的示意图、(3) 微球脱粘的前端形貌、(4) 微球脱粘的后端形貌;(b) SCF35/PAEK-H:(1) 整体形貌、(2) 微球脱粘的示意图、(3) 微球脱粘的前端形貌、(4) 微球脱粘的后端形貌Figure 5. Surface morphologies of SCF35/PAEK microsphere debonding: (a) SCF35/PAEK-L: (1) Overall Shape, (2) Schematic diagram of microsphere debonding, (3) Shape of the front end of microsphere debonding, (4) Shape of the back end of microsphere debonding; (b) SCF35/PAEK-H: (1) Overall Shape, (2) Schematic diagram of microsphere debonding, (3) Shape of the front end of microsphere debonding, (4) Shape of the back end of microsphere debonding
图 5 SCF35/PAEK微球脱粘的表面形貌:(a) SCF35/PAEK-L:(1) 整体形貌、(2) 微球脱粘的示意图、(3) 微球脱粘的前端形貌、(4) 微球脱粘的后端形貌;(b) SCF35/PAEK-H:(1) 整体形貌、(2) 微球脱粘的示意图、(3) 微球脱粘的前端形貌、(4) 微球脱粘的后端形貌Figure 5. Surface morphologies of SCF35/PAEK microsphere debonding: (a) SCF35/PAEK-L: (1) Overall Shape, (2) Schematic diagram of microsphere debonding, (3) Shape of the front end of microsphere debonding, (4) Shape of the back end of microsphere debonding; (b) SCF35/PAEK-H: (1) Overall Shape, (2) Schematic diagram of microsphere debonding, (3) Shape of the front end of microsphere debonding, (4) Shape of the back end of microsphere debondingSCF35/PAEK复合材料的90°拉伸测试的破坏形貌如图8所示,可以看出,SCF35/PAEK-L复合材料的90°拉伸试样破坏后,在纤维表面存在不均匀分布的残留树脂;SCF35/PAEK-H复合材料的90°拉伸试样破坏后,纤维被树脂基体均匀包覆。造成复合材料界面呈现不同的破坏模式的原因是PAEK-H树脂基体相较于PAEK-L树脂基体具有较高的流动性,能够填充SCF35碳纤维表面的微小沟槽,形成较强的机械啮合作用,进而表现出较高的界面强度,破坏的过程中界面强度大于树脂的断裂强度时,裂纹在树脂基体中扩展,纤维表面粘连较多的树脂基体。
SCF35/PAEK热塑性复合材料短梁剪切测试的典型应力-应变结果如图9所示。相同的铺层条件下,SCF35/PAEK-H复合材料的短梁剪切强度略大于SCF35/PAEK-L,SCF35/PAEK-L试样达到最大载荷后,出现了载荷突降的现象,随着应变的增加,试样被迅速破坏,载荷快速下降;SCF35/PAEK-H试样的载荷达到最大值前缓慢增加,存在明显的屈服行为,试样的载荷在到达最大值后,试样通常出现一段载荷下降的过程,然后随着剪切形变量的增加,试样发生剪切破坏。
复合材料短梁剪切的截面形貌如图10所示,试样中压头下方的受载区域呈现锥形塑性变形,在剪切力的作用下塑性变形区域边缘萌生裂纹并发生裂纹扩展。短梁剪切试样压头处的表面形貌如图11所示,试样在压头施加的载荷的作用下呈现圆弧形的塑性变形,图11(a)中SCF35/PAEK-L复合材料表面较光滑,纤维随树脂的塑性变形发生弯曲,图11(b)中SCF35/PAEK-H复合材料表面存在纤维断裂痕迹,纤维随树脂的塑性变形发生弯曲与断裂。结合图9与图10、图11,分析造成短梁剪切强度出现差异的原因是,SCF35/PAEK-L复合材料的界面强度稍弱,试样在加载的过程中,复合材料中的纤维在稍低的载荷下发生滑移,导致试样的载荷降低,随着应变的增加,进而萌生裂纹并发生扩展;SCF35/PAEK-H复合材料的界面强度稍强,试样在加载的过程中,复合材料中的纤维较难发生滑移,而是随着试样应变的增加出现纤维弯曲、基体屈服等非线性硬化的效应[11],进而能够承受更高的载荷,当试样的应变达到极限时,试样在剪应力的作用下萌生裂纹并最终发生断裂。
2.2 SCF35/PAEK复合材料的层间性能
连续纤维增强树脂基复合材料中重要的破坏模式是层间破坏,SCF35/PAEK复合材料的层间性能如表4所示。其中SCF35/PAEK-L的Ⅰ型断裂韧性约为938 J/m2,Ⅱ型断裂韧性约为2232 J/m2;SCF35/PAEK-H的Ⅰ型断裂韧性约为638 J/m2,Ⅱ型断裂韧性约为1702 J/m2。
表 4 SCF35/PAEK复合材料的断裂韧性Table 4. Fracture toughness of SCF35/PAEK compositesSystem GIC/(J∙m−2) GIIC/(J∙m−2) SCF35/PAEK-L 938±38 2232±208 SCF35/PAEK-H 638±38 1702±46 Notes: GIC—Type I fracture toughness of SCF35/PAEK composites; GIIC—Type Ⅱ fracture toughness of SCF35/PAEK composites. 对比两种复合材料体系的典型加载曲线如图12所示,结果显示SCF35/PAEK-L复合材料的破坏载荷及其破坏曲线包络的面积均高于SCF35/PAEK-H复合材料,证明SCF35/PAEK-L复合材料的断裂韧性较高。两种复合材料体系的断裂形貌如图13所示,可以看出,SCF35/PAEK-L复合材料中树脂基体均呈现撕裂状,在Ⅱ型断裂韧性试样中树脂基体在剪切应力的作用下沿剪切力方向撕裂破坏;SCF35/PAEK-H复合材料中树脂基体同样呈现撕裂状,但不同的是,SCF35/PAEK-H复合材料中树脂基体撕裂的尺寸较小。研究认为复合材料层间断裂韧性是基体延展性和界面结合强度之间复杂相互作用的结果,而基体的塑性变形能力是影响复合材料韧性的主要因素[27],图14为表1中冲击试样及拉伸试样的破坏形貌。可以看出PAEK-L树脂试样的冲击断面形貌相对于PAEK-H树脂试样具有更大尺寸的断裂变形,PAEK-L树脂试样拉伸断面处存在因塑性变形而产生的齿状树脂残留,而PAEK-H树脂试样拉伸断面处存在片状树脂残留,对比两种树脂试样的断裂形貌及复合材料的断裂形貌可以发现,复合材料中PAEK-L树脂基体较大撕裂形貌将导致复合材料在破坏的过程中消耗更多的能量[28],这是造成SCF35/PAEK-L复合材料断裂韧性较高的原因。
![]() 图 13 SCF35/PAEK断裂形貌:(a) SCF35/PAEK-L Ⅰ型断裂形貌;(b) SCF35/PAEK-L Ⅱ型断裂形貌;(c) SCF35/PAEK-H Ⅰ型断裂形貌;(d) SCF35/PAEK-H Ⅱ型断裂形貌Figure 13. Fracture morphology of SCF35/PAEK: (a) Type I fracture morphology of SCF35/PAEK-L; (b) Type Ⅱ fracture morphology of SCF35/PAEK-L; (c) Type I fracture morphology of SCF35/PAEK-H; (d) Type Ⅱ fracture morphology of SCF35/PAEK-H
图 13 SCF35/PAEK断裂形貌:(a) SCF35/PAEK-L Ⅰ型断裂形貌;(b) SCF35/PAEK-L Ⅱ型断裂形貌;(c) SCF35/PAEK-H Ⅰ型断裂形貌;(d) SCF35/PAEK-H Ⅱ型断裂形貌Figure 13. Fracture morphology of SCF35/PAEK: (a) Type I fracture morphology of SCF35/PAEK-L; (b) Type Ⅱ fracture morphology of SCF35/PAEK-L; (c) Type I fracture morphology of SCF35/PAEK-H; (d) Type Ⅱ fracture morphology of SCF35/PAEK-H![]() 图 14 PAEK树脂试样断裂形貌:(a) PAEK-L冲击断面形貌;(b) PAEK-L拉伸断面形貌;(c) PAEK-H冲击断面形貌;(d) PAEK-H拉伸断面形貌Figure 14. Fracture morphology of PAEK resin specimens: (a) Impact section morphology of PAEK-L; (b) Tensile section morphology of PAEK-L; (c) Impact section morphology of PAEK-H; (d) Tensile section morphology of PAEK-H
图 14 PAEK树脂试样断裂形貌:(a) PAEK-L冲击断面形貌;(b) PAEK-L拉伸断面形貌;(c) PAEK-H冲击断面形貌;(d) PAEK-H拉伸断面形貌Figure 14. Fracture morphology of PAEK resin specimens: (a) Impact section morphology of PAEK-L; (b) Tensile section morphology of PAEK-L; (c) Impact section morphology of PAEK-H; (d) Tensile section morphology of PAEK-H3. 结 论
(1) 国产碳纤维增强聚芳醚酮(SCF35/PAEK)复合材料的界面性能受到树脂基体流动性的影响,流动性较高的PAEK-H树脂能够与纤维之间形成较好的界面结合及较高的界面强度。SCF35/PAEK-L的界面剪切强度约为64 MPa,接触角约为35.8°,90°拉伸强度约为55 MPa,90°拉伸模量约约为8.6 GPa,短梁剪切强度约为86 MPa;SCF35/PAEK-H的界面剪切强度约为79 MPa,接触角约为34.4°,90°拉伸强度约为76 MPa,90°拉伸模量约为9.7 GPa,短梁剪切强度约为92 MPa。
(2) SCF35/PAEK复合材料的层间性能受到树脂基体塑性变形能力的影响,基体塑性变形能力较强的PAEK-L相较于PAEK-H,其复合材料具有较高的断裂韧性。SCF35/PAEK-L的Ⅰ型断裂韧性约为938 J/m2,Ⅱ型断裂韧性约为2232 J/m2;SCF35/PAEK-H的Ⅰ型断裂韧性约为638 J/m2,Ⅱ型断裂韧性约为1702 J/m2。
-
表 1 水泥的化学成分
Table 1 Chemical composition of cement
Mineral Al2O3 SiO2 Fe2O3 CaO MgO SO3 NaO f-CaO Content / wt% 4.47 21.50 3.37 65.84 3.18 0.30 0.49 0.78 Note: f-CaO−Free calcium oxide. 表 2 不同MGO掺量的水泥净浆配合比
Table 2 Mix ratios of cement paste with different contents of MGO
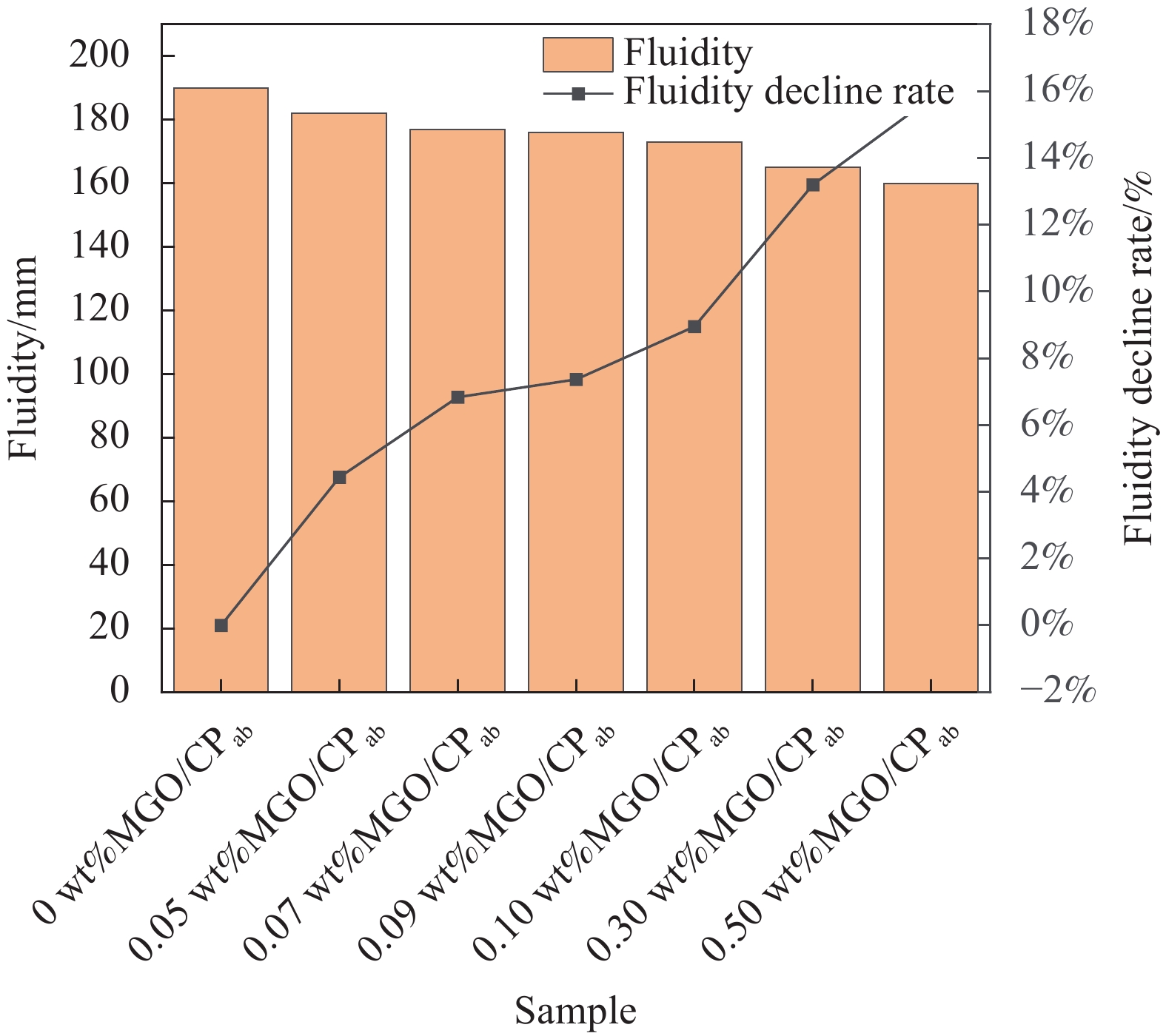
Sample① Cement/g PCE②/g water/g MGO③/wt% 0 wt%MGO/CP
0.05 wt%MGO/CPab
0.07 wt%MGO/CPab
0.09 wt%MGO/CPab
0.10 wt%MGO/CPab
0.30 wt%MGO/CPab
0.50 wt%MGO/CPab470
470
470
470
470
470
4700.5
0.5
0.5
0.5
0.5
0.5
0.5149.2
149.2
149.2
149.2
149.2
149.2
149.2/
0.05
0.07
0.09
0.10
0.30
0.50Notes:①X wt% MGO/CP denotes a cement paste specimen with a content of X% MGO;CP stands for cement paste; The subscript a indicates parallel to the direction of the magnetic field, and b indicates perpendicular to the direction of the magnetic field.②PCE is polycarboxylic acid water reducing agent;MGO is Fe3O4@ RGO.③Content of MGO is its mass ratio to Cement. 表 3 不同掺量的MGO对水泥净浆抗压强度的影响
Table 3 Effect of different MGO contents on compressive strength of cement paste
SampleCompressive strength(MPa)/growth rate(%)
Perpendicular to the magnetic fieldCompressive strength(MPa)/growth rate(%)
Parallel to the magnetic field7 d 28 d 7 d 28 d 0wt%MGO/CP
0.05wt%MGO/CP
0.07wt%MGO/CP
0.09wt%MGO/CP
0.10wt%MGO/CP
0.30wt%MGO/CP
0.50wt%MGO/CP39.1/0
40.0/2.30
42.1/7.67
45.3/15.86
46.8/19.69
44.1/12.79
42.4/8.4453.1/0
54.9/3.39
55.8/5.08
57.4/8.10
58.2/9.60
56.1/5.65
55.1/3.7739.1/0
41.1/5.12
44.5/13.81
48.2/23.27
50.7/29.67
45.0/15.09
42.2/7.9353.1/0
56.8/6.97
59.6/12.24
62.4/17.51
65.3/22.98
64.1/20.72
62.6/17.89 -
[1] 桂尊曜, 蒲云东, 张惠一, 等. 石墨烯量子点对水泥砂浆流动度、强度和耐盐腐蚀性的影响[J]. 复合材料学报, 2024, 41(04): 2043-2054. GUI Zunyao, PU Yundong, ZHANG Huiyi, et al. Effect of graphene quantum dots on fluidity, strength and salt corrosion resistance of cement mortar[J] . Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2024, 41(04): 20432054. (in Chinese).
[2] 程志海, 杨森, 袁小亚. 石墨烯及其衍生物掺配水泥基材料研究进展[J]. 复合材料学报, 2021, 38(2): 339-360. CHENG Zhi-Hai, YANG Sen, YUAN Xiao-Ya. Research progress of cement-based materials blended with graphene and its derivatives[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2021, 38(2): 339-360(in Chinese).
[3] KAKISAWA H, SUMITOMO T. The toughening mechanism of nacre and structural materials inspired by nacre[J/OL]. Science and Technology of Advanced Materials, 2011, 12(6): 064710. DOI: 10.1088/1468-6996/12/6/064710
[4] 吕生华, 马宇娟, 邱超超, 等. 氧化石墨烯对水泥石微观结构及性能的影响[J]. 混凝土, 2013, (8): 51-54. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3550.2013.08.014 LV Shenghua, MA Yujuan, QIU Chaochao, et al. Effects of graphene oxide on microstructure of hardened cement paste and its properties[J]. Concrete, 2013, (8): 51-54(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3550.2013.08.014
[5] 曹蔚琦, 魏致强, 刘川, 等. 氧化石墨烯/热还原氧化石墨烯改性砂浆的力学/电学性能研究[J]. 功能材料, 2024, 55(1): 1111-1116. CAO Weiqi, WEI Zhiqiang, LIU Chuan, et al. Study on mechanical/electrical properties of cement mortar modified by graphene oxide/thermal reduction graphene oxide[J]. Journal of Functional Materials, 2024, 55(1): 1111-1116(in Chinese).
[6] 罗素蓉, 姚佳敏, 周恩泉, 等. 氧化石墨烯改性纤维增强水泥基材料的拉伸性能[J]. 建筑材料学报, 2024, 27(5): 400-407. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9629.2024.05.003 LUO Surong, YAO Jiamin, ZhOU Enquan, et al. Tensile Properties of Fibers Reinforced[J]. Journal of Building Materials, 2024, 27(5): 400-407(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9629.2024.05.003
[7] 齐孟, 蒲云东, 杨森, 等. 氧化石墨烯对水泥基渗透结晶型防水材料抗渗性能的影响[J]. 复合材料学报, 2023, 40(03): 1598-1610. QI Meng, PU Yundong, YANG Sen, et al. Effect of graphene oxide on the impermeability of ce mentitious capillary crystalline waterproofing[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2023, 40(03): 15981610. (in Chinese).
[8] 袁小亚, 曾俊杰, 高军, 等. 氧化石墨烯与石墨烯复掺对水泥砂浆性能影响研究[J]. 重庆交通大学学报(自然科学版), 2019, 38(9): 45-50. YUAN Xiaoya, ZENG Junjie, GAO Jun, et al. Effect of Addition of Graphene Oxide and Graphene on Properties of Cement Mortar[J]. Journal Of Chongqing Jiaotong University (Natural Science), 2019, 38(9): 45-50(in Chinese).
[9] 吕生华, 张佳, 殷海荣, 等. 氧化石墨烯调控水化产物增强增韧水泥基复合材料的研究进展[J/OL]. 陕西科技大学学报, 2019, 37(3): 136-145. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5811.2019.03.022 LV S H, ZhANG J, YIN H R, et al. Research progress of graphene oxide reinforced and toughened cement-bas- sed composite[J/OL]. Journal of Shaanxi University of Science & Technology, 2019, 37(3): 136-145(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5811.2019.03.022
[10] 苟鸿翔, 朱洪波, 周海云, 等. 定向分布钢纤维对超高性能混凝土的增强作用[J]. 硅酸盐学报, 2020, 48(11): 17561764. GOU H. X. , ZhU H. B. , ZHOU H. Y. , et al. Reinforcement of Directionally Distributed Steel Fibers on Ultrahigh Performance Concrete[J]. Journal Of The Chinese Ceramic Society, 2020, 48(11): 17561764. (in Chinese).
[11] MU R, LI H, QING L, et al. Aligning steel fibers in cement mortar using electro-magnetic field[J/OL]. Construction and Building Materials, 2017, 131: 309-316. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2016.11.081
[12] GENG J, MEN Y, LIU C, et al. Preparation of rGO@Fe3O4 nanocomposite and its application to enhance the thermal conductivity of epoxy resin[J/OL]. RSC Advances, 2021, 11(27): 16592-16599. DOI: 10.1039/D1RA02254G
[13] ZHANG H, WU W, CAO J, et al. Magnetic induced wet-spinning of graphene oxide sheets grafted with ferroferric oxide and the ultra-strain and elasticity of sensing fiber[J/OL]. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2019, 170: 1-10. DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.04.018
[14] 邓富泉, 张丽, 杨松, 等. 氧化石墨烯有序排列对碳纤维增强环氧树脂复合材料低温性能影响[J]. 高分子材料科学与工程, 2017, 33(07): 38-44. DENG FQ, ZHANG L, YANG S, et al. Effects of Grahene Oxide Alligned in Matrix on Mechanical Properties of Carbon Fiber Reinforced Epoxy Composites at Cryogenic Temperature[J]. Polymer Materials Science And Engineering, 2017, 33(07): 3844. (in Chinese).
[15] LIU S, CHEN Y, LI X, et al. Development of bio-inspired cement-based material by magnetically aligning graphene oxide nanosheets in cement paste[J/OL]. Construction and Building Materials, 2023, 369: 130545. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2023.130545
[16] YAN Y, TIAN L, ZHAO W, et al. Dielectric and mechanical properties of cement pastes incorporated with magnetically aligned reduced graphene oxide[J/OL]. Developments in the Built Environment, 2024, 18: 100471. DOI: 10.1016/j.dibe.2024.100471
[17] 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 水泥胶砂强度检验方法(ISO法): GB/T 17671−2021[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2021 China National Standardization Management Committee. Strength test method of cement mortar (ISO method): GB/T 17671−2021[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2021(in Chinese).
[18] 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 水泥胶砂流动度测定方法: GB/T 2419−2005[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2005. Standardization Administration of the People's Republic of China. Method for determining the flowability of cement mortar: GB/T 2419-2005[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2005(in Chinese)
[19] LIU Y, LU M, WU K, et al. Anisotropic thermal conductivity and electromagnetic interference shielding of epoxy nanocomposites based on magnetic driving reduced graphene oxide@Fe3O4[J/OL]. Composites Science and Technology, 2019, 174: 1-10. DOI: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2019.02.005
[20] 姜晓琳, 李君, 刘臻, 等. 石墨烯炭材料的结构表征方法[J]. 洁净煤技术, 2023, 29(12): 75-82. JIANG Xiaolin, LI Jun, LIU Zhen, et al. Research on the characterization methods of graphene carbon materials[J]. Clean Coal Technology, 2023, 29(12): 7582. (in Chinese).
[21] STANKOVICH S, DIKIN D A, PINER R D, et al. Synthesis of graphene-based nanosheets via chemical reduction of exfoliated graphite oxide[J/OL]. Carbon, 2007, 45(7): 1558-1565. DOI: 10.1016/j.carbon.2007.02.034
[22] 袁小亚, 杨雅玲, 周超, 等. 氧化石墨烯改性水泥砂浆力学性能及微观机制研究[J]. 重庆交通大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 36(12): 36-42. YUAN Xiaoya, YANG Yaling, ZHOU Chao, et al. Mechanical Properties and Microcosmic Mechanism of Cement Mortar Modified by Graphene Oxide[J]. Journal Of Chongqing Jiaotong University (Natural Science), 2017, 36(12): 36-42(in Chinese).
[23] 桂尊曜, 蒲云东, 张惠一, 等. 水中可分散型石墨烯对水泥净浆导电、发热及热电性能的影响[J/OL]. 复合材料学报, 2023, 40(11): 63366350. GUI Zunyao, PU Yundong, ZHANG Huiyi, et al. Effects of dispersible graphene in water on the electrical conductivity, heat generation and thermoelectric properties of cement slurry[J/OL]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2023, 40(11): 63366350(in Chinese).
[24] PU Y. Synergistic effect of graphene oxide and hydroxylated graphene on the enhanced properties of cement composites[J/OL]. RSC Advances, 2022.
[25] NAIR S D, FERRON R D. Set-on-demand concrete[J/OL]. Cement and Concrete Research, 2014, 57: 13-27. DOI: 10.1016/j.cemconres.2013.12.001
[26] WU N, XU D, WANG Z, et al. Achieving superior electromagnetic wave absorbers through the novel metal-organic frameworks derived magnetic porous carbon nanorods[J/OL]. Carbon, 2019, 145: 433-444. DOI: 10.1016/j.carbon.2019.01.028
[27] 袁小亚, 张维福, 曹潘磊, 等. 复掺石墨烯/氧化石墨烯改性砂浆电学与融雪化冰性能研究[J]. 功能材料, 2021, 52(12): 12100-12110. YUAN Xiaoya, ZHANG Weifu, CAO Panlei, et al. Study on performace of wollastonite reinforced fly ash-basedgeopolymer. (in Chinese).
[28] 吕生华, 孙婷, 刘晶晶, 等. 氧化石墨烯纳米片层对水泥基复合材料的增韧效果及作用机制[J/OL]. 复合材料学报, 2014, 31(3): 644-652. LV S H, SUN T, LIU J J, et al. Toughening effect and mechanism of graphene oxide nanosheets on cement matrix composites[J/OL]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2014, 31(3): 644652. (in Chinese).
[29] 袁小亚, 蒲云东, 桂尊曜, 等. 羟基化石墨烯对粉煤灰-水泥基复合材料性能的影响[J]. 材料导报, 2024, 38(11): 148-155. YUAN Xiaoya, PU Yundong, GUI Zunyao, et al. Effect of Hydroxylated Graphene on Properties of Fly Ash-Cement Matrix Composites[J]. Materials Reports, 2024, 38(11): 148-155(in Chinese).
[30] 张惠一, 桂尊曜, 蒲云东, 等. 羟基化石墨烯对水泥基渗透结晶型防水材料力学性能的影响[J]. 硅酸盐通报, 2023, 42(5): 15691577+1588-1577+1588. ZHANG Hui-Yi, GUI Zun-Yao, PU Yun-Dong, et al. Effect of Hydroxylated Graphene on Mechanical Properties of Cement-Based Permeable Crystalline Waterproof Materials[J]. Bulletin Of The Chinese Ceramic Society, 2023, 42(5): 15691577+1588-1577+1588(in Chinese).
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 冯葆炜,王华清. 层合板和蜂窝夹心结构复合材料敲击特性研究. 新技术新工艺. 2024(02): 56-59 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 顾洋洋,张金栋,刘刚,刘衍腾,甘建,杨曙光. 聚芳醚酮(PAEK)树脂熔体黏度及冲击能量对其复合材料冲击损伤行为的影响. 复合材料学报. 2023(10): 5641-5653 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(3)
-
目的
本研究通过外部磁场诱导调控石墨烯纳米片在水泥基材料中的定向排列,以显著提升水泥基材料的力学性能。石墨烯(G)作为二维纳米材料,因其优异的机械性能和导电导热性能,在增强水泥基材料方面展现出巨大潜力。然而,传统方法下石墨烯在水泥基体中的随机分布限制了其强化效果的充分发挥。因此,本研究聚焦于开发一种磁性纳米复合材料FeO@RGO(MGO),并通过磁场诱导技术实现MGO纳米片在水泥净浆中的定向排列,以期达到优化水泥基材料力学性能的目的。
方法本研究采用一步共沉淀法,将FeO纳米颗粒成功附着在热还原氧化石墨烯(RGO)纳米片上,制备出具有磁性的纳米复合材料MGO。该方法利用FeO的磁性特性,使得MGO纳米片能够在外部磁场的作用下发生定向移动和排列。随后,将不同掺量的MGO纳米片加入水泥净浆中,并在制备过程中施加外磁场,使MGO纳米片沿磁场方向定向排列。为了评估磁场诱导对水泥基材料力学性能的影响,本研究分别测试了硬化水泥净浆在垂直和平行于磁场方向上的抗压强度。
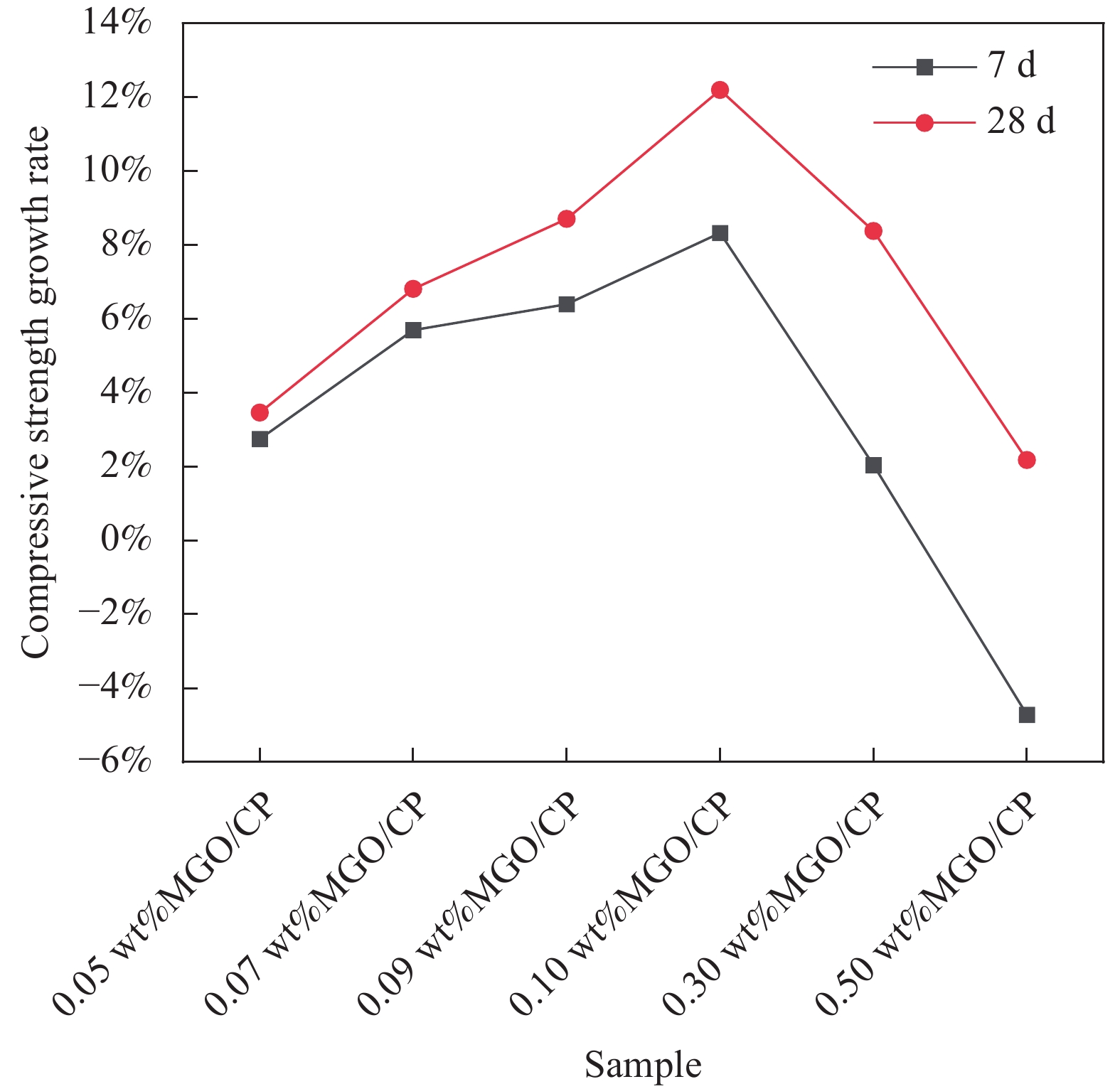
结果实验结果表明,当不同掺量的MGO掺加至水泥净浆中并进磁场处理后,水泥净浆不同截面的7d、28d抗压强度均高于空白组,且随着MGO掺量的增加,水泥净浆抗压强度表现出先增加后降低的趋势。当MGO的掺量为0.1 wt %时,试件平行于磁场方向的截面7d、28d抗压强度达到最高值,此时7d抗压强度从39.1 MPa增加至50.7 MPa,较普通水泥净浆提升了29.67 %;28d抗压强度从53.1 MPa提升至65.3 MPa,较普通水泥净浆提升了22.98 % 。当MGO的掺量分别为0.1wt %时,试件平行于磁场方向的截面7 d抗压强度较垂直于磁场方向的截面强度增长了8.33 %;28 d时平行于磁场方向的截面抗压强度较垂直于磁场方向的截面强度增长了12.20 %。这表明在水泥净浆中磁场诱导了MGO中石墨烯纳米片的定向排列,由于MGO具有模板作用调控水化产物的形貌,优化水泥水化产物的完整度和结晶度,从而使得水泥净浆在某一截面上的抗压强度得到了提高。但随着MGO掺量的增多,这种改善作用会慢慢减弱,这是由于MGO掺量较大时,有部分的MGO可能会发生团聚,从而造成试件的力学性能下降。具体而言,当MGO掺量为0.1%时,平行于磁场方向的截面抗压强度比垂直于磁场方向的截面抗压强度高出了12.20%。这一结果直接证明了MGO纳米片在磁场诱导下确实发生了定向排列,且这种排列方式促进了水泥水化产物的规整排列和生长,从而提高了水泥基材料的力学性能。
结论本研究通过外部磁场诱导技术,成功实现了石墨烯纳米片在水泥基材料中的定向排列,为制备高性能水泥基材料提供了一种创新且有效的途径。实验结果表明,磁场诱导下的MGO纳米片定向排列能够显著提升水泥基材料的抗压强度,特别是在平行于磁场方向上表现出更为优异的力学性能。这一发现不仅丰富了石墨烯增强水泥基材料的研究内容,也为未来高性能建筑材料的设计和开发提供了新的思路和方法。此外,本研究还揭示了磁场诱导对水泥水化过程及产物结构的影响机制,为深入理解水泥基材料的微观结构与宏观性能之间的关系提供了重要参考。
-
在建筑和工程领域,提升水泥基材料的力学性能是实现结构耐久性和稳定性的关键。传统方法中,石墨烯作为一种高性能的纳米填料,由于其在水泥基材料中的随机分散,未能充分发挥其增强潜力。
本研究针对这一工程技术难点,本研究通过一步共沉淀法成功制备了磁性纳米复合材料Fe3O4@RGO(MGO),并通过外部磁场诱导石墨烯纳米片在水泥净浆中的有序定向排列,显著提升了水泥基材料的力学性能,磁性MGO对水泥净浆的力学性能产生了显著影响。实验数据显示,当MGO掺量为0.1%时,平行于磁场方向的截面7天抗压强度提升了29.67%,28天抗压强度提升了22.98%;而垂直于磁场方向的截面抗压强度分别增长了8.33%和12.20%。研究揭示了MGO作为模板在水泥水化过程中促进水化产物规整排列生长的机制,并通过微观结构测试深入理解了MGO与水泥水化产物的相互作用,为开发具有更优性能的水泥基复合材料提供了科学依据和有效途径。

Growth rate of compressive strength of the same contents of MGO in the cross section parallel compared to perpendicular to the magnetic field direction

Schematic diagram of the functional role of MGO in cement paste




 下载:
下载: