Preparation and properties of lignin-based flame retardant-modified polyurethane insulation materials
-
摘要:
建筑保温材料的阻燃抑烟性能事关消防安全。本文基于聚磷酸铵(APP),针对其界面相容性和抑烟性能差的问题,利用碱木素(AL)、双(4-异氰酸酯基苯基)甲烷(MDI),制备了核壳结构的膨胀型阻燃剂APP@AL (APP∶MDI∶AL质量比为9∶2∶1),并应用于硬质聚氨酯(RPU)泡沫保温材料的阻燃处理(添加量25wt%)。通过SEM-EDS、XPS、FTIR等方法分析APP@AL的结构及组成,采用锥形量热仪(CONE)、热重(TG)等仪器分析了阻燃抑烟性能。结果表明,APP@AL与RPU泡沫基体具有良好的界面相容性。与添加APP的RPU泡沫复合材料相比,APP@AL改性RPU泡沫复合材料的抗压强度显著提高(达31.8%),导热系数降低(7.0%);此外,CONE测试表明,平均放热速率和总放热量分别降低27.2%和24.4%,同时抑烟性能显著增强(总产烟量减少 47.6%,总CO产量降低 57.0%)。TG分析表明,APP@AL阻燃剂的热稳定性明显高于APP,且更有助于构建稳定的残炭层。综上,木质素基膨胀型阻燃剂对RPU泡沫保温材料具备优异的阻燃抑烟作用。
Abstract:The fire retardant and smoke suppression performance of thermal insulation materials are crucial factors in ensuring building fire safety. In this study, based on ammonium polyphosphate (APP), a intumescent flame-retardant APP@AL (Mass ratio APP∶MDI∶AL=9∶2∶1) with core-shell structure was prepared by utilizing alkali lignin (AL) and bis(4-isocyanatophenyl) methane (MDI) for its poor interfacial compatibility and smoke suppression performance, and applied to the flame-retardant treatment of rigid polyurethane (RPU) thermal insulation materials (25wt% addition). The structure and composition of APP@AL were analyzed by SEM-EDS, XPS and FTIR, and the flame retardant and smoke suppression properties were analyzed by CONE and TG instruments. The results show that APP@AL has excellent interfacial compatibility with the RPU matrix. The compressive strength of the APP@AL-modified RPU foam is significantly increased (up to 31.8%) compared with the APP-added RPU foam and the thermal conductivity is reduced (7.0%). CONE test show that mean heat release rate and total heat release are reduced by 27.2% and 24.4%, respectively, while smoke suppression is notably enhanced (47.6% reduction in total smoke production and 57.0% reduction in total CO production). TG analysis show that the thermal stability of APP@AL flame retardant is obviously higher than that of APP, and it is more beneficial to build a stable residual char layer. In conclusion, lignin-based intumescent flame retardant has excellent flame retardant and smoke suppression effect on RPU foam insulation materials.
-
硬质聚氨酯(RPU)泡沫具有高强重比、导热系数低、耐湿耐腐等优点,国内外广泛用作建筑围护结构的芯层保温材料[1-2]。但是,RPU泡沫易燃且燃烧会产生浓烟,释放大量 CO 、HCN 等有毒气体,导致其应用受到局限[3-4]。开发具有出色阻燃和抑烟能力RPU泡沫十分迫切。研究发现,膨胀型阻燃剂(IFR)对聚合物有较好的阻燃效果[5-6]。最典型的IFR配方由酸源(如:铵盐和磷酸盐)、炭源(包括多元醇等含羟基化合物)和气源(如:三聚氰胺)组成。燃烧过程中,膨胀型阻燃剂在受热时能够迅速膨胀,炭源在酸源的催化作用下炭化,形成致密的保护层,有效隔离氧气,从而降低燃烧速度,气源使炭层膨胀,从而在基体表面形成稳定牢固的炭层,隔绝空气从而有效保护基体材料[7-8]。
聚磷酸铵(APP)富含氮和磷元素,能够同时提供酸源和气源,同时不含卤素,被广泛用作聚合物的阻燃体系[9-10]。但是,APP在抑烟方面表现不佳。此外,当用作 IFR 时APP 通常需要添加成炭剂才能达到最佳阻燃效果,弱化了与材料基体的界面相容性[11]。Tan 等[12]通过在 APP 和各种脂肪族多胺(如:二乙烯三胺、哌嗪等)之间进行阳离子交换反应,设计出一种“三源一体”膨胀阻燃剂(DETA-APP)。在环氧树脂中添加 15wt% 的 DETA-APP,可显著提升阻燃性能和抑烟效果,但是并没有改善环氧树脂与APP之间的界面相容性。Wan等[13]利用微胶囊来改善APP与材料之间的界面相容性,制备出一种多层核壳阻燃剂(APP@SiO2@UiO-66-NH2(Zr)),并将其应用于热塑性聚氨酯(TPU)。TPU/APP@SiO2@UiO-66-NH2(Zr)复合材料的总放热量(THR)、总产烟量(TSP)和 CO产生速率(COP)分别降低87.7%、52.4% 和 76.8%,并且力学性能得到改善。然而,大多数方法都无法同时提高聚合物的阻燃性和力学性能,或者由于工艺复杂、成本高昂而难以实际应用。
制浆造纸工业每年产生大量“黑液”,其中富含木质素,尚未得到规模化利用[14-15]。Lu等[16]在 RPU 泡沫中使用磺化木质素代替季戊四醇作为成炭剂。结果表明,木质素作为成炭剂时,泡沫复合材料的极限氧指数(LOI)和残炭率得到改善,质量损失减少 18%,热稳定性得到提高。此外,木质素结构中含有丰富的活性基团,如醇羟基和酚羟基,是胺化和接枝共聚等化学改性的关键反应位点,从而为进一步的化学改性提供可能[17-18]。研究表明,通过在木质素上接枝 N/P 元素化合物,可制备木质素基阻燃剂。与原始木质素相比,N 或 P修饰的木质素基阻燃剂在聚合物中表现出更高的阻燃效率[19-20]。然而,将木质素与阻燃剂混合或与 N / P 化合物接枝在提高聚合物阻燃性的同时,会削弱其力学性能。
本研究利用碱木素(AL)作为成炭剂,与双(4-异氰酸酯基苯基)甲烷(MDI)和APP制备了核壳结构膨胀型阻燃剂APP@AL,并应用于RPU泡沫的阻燃处理,重点研究了APP@AL的结构组成以及阻燃性能和机制。
1. 实验材料与方法
1.1 原材料
聚醚多元醇(LY-4110)、多亚甲基多苯基异氰酸酯(PAPI)购自烟台万华化学集团股份有限公司;催化剂二丁基锡二月桂酸(LC)、表面活性剂硅油(AK-8805)、聚磷酸铵(APP)、双(4-异氰酸酯基苯基)甲烷(MDI)购自麦克林生物有限公司;氢氟烃发泡剂(HFC-365mfc)购自上海锐一环保科技有限公司;碱木质素(AL)、乙酸乙酯购自国药集团化学试剂有限公司。
1.2 实验方法
1.2.1 制备APP@AL
APP@AL配方如表1所示,在配备有冷凝管和机械搅拌器的500 mL三颈烧瓶中,将45 g APP粉末均匀分散在250 mL乙酸乙酯中,取一定量的MDI加入烧瓶中,在50℃氮气氛围中搅拌1 h。然后将一定量的AL加到悬浮液中。完成后,将溶液加热至60℃,并在此温度下保持5 h。过滤悬浮液以除去残留的乙酸乙酯,然后将粗产物用乙酸乙酯洗涤3次,放入烘箱在80℃干燥24 h,过0.18 mm筛网,得到最终产物。分别命名为APP@AL1(APP∶MDI∶AL质量比为9∶1∶2)、APP@AL2 (APP∶MDI∶AL质量比为6∶1∶1)、APP@AL3 (APP∶MDI∶AL质量比为9∶2∶1)和APP@AL4 (APP∶MDI∶AL质量比为12∶3∶1)。
表 1 聚磷酸铵(APP)改性配方Table 1. Formula of ammonium polyphosphate (APP) modificationFormulation APP@AL1 APP@AL2 APP@AL3 APP@AL4 APP/g 45 45 45 45 MDI/g 5 7.5 10 11.25 AL/g 10 7.5 5 3.75 Notes: MDI—4, 4'-methylenebiphenyl isocyanate; AL—Alkali lignin. 1.2.2 制备RPU泡沫
不同RPU泡沫复合材料的配方显示在表2中,并且制备路线如下。RPU泡沫的制备涉及两个步骤。首先,通过使用顶置式搅拌器以约
1500 r/min的速度将LY-4110、阻燃剂、催化剂、表面活性剂和发泡剂搅拌5 min来制备均匀的共混物(A部分)。随后,使用相同的顶置式搅拌器,将PAPI(B部分)与A部分以约3000 r/min的速度搅拌10 s,迅速将搅拌后的混合溶液倒入开放的模具中使泡沫自由上升,并将泡沫置于80℃烘箱中固化24 h。此外,通过相同的方法制备其他各组试样泡沫,分别命名为Pure RPU、25APP/RPU、25APP@AL1/RPU、25APP@AL2/RPU、25APP@AL3/RPU和25APP@AL4/RPU,其中25表示阻燃剂的添加量为LY-4110和PAPI总质量的25wt%。表 2 硬质聚氨酯(RPU)泡沫复合材料配方Table 2. Preparation formula of rigid polyurethane (RPU) foam compositesFormulation Pure RPU 25APP/RPU 25APP@AL1/RPU 25APP@AL2/RPU 25APP@AL3/RPU 25APP@AL4/RPU APP/g 0 50 0 0 0 0 APP@AL1/g 0 0 50 0 0 0 APP@AL2/g 0 0 0 50 0 0 APP@AL3/g 0 0 0 0 50 0 APP@AL4/g 0 0 0 0 0 50 LY-4110/g 100 100 100 100 100 100 AK-8805/g 2 2 2 2 2 2 LC/g 1.5 1.5 1.5 1.5 1.5 1.5 HFC-365mfc/g 33 33 33 33 33 33 PAPI/g 100 100 100 100 100 100 Notes: LY-4110—Polyetherpolyol; AK-8805—Silicone surfactant; LC—Dibutyltin dilaurate; HFC-365mfc—Foaming agent; PAPI—Poly-methylene polyphenyl isocyanate; 25APP/RPU, 25APP@AL1/RPU, 25APP@AL2/RPU, 25APP@AL3/RPU, 25APP@AL4/RPU, the 25 indicates that the amount of flame retardant added is 25wt% of the total mass of LY-4110 and PAPI. 1.3 性能测试与表征
1.3.1 阻燃剂成分及结构
采用Regulus 8100场发射扫描电子显微镜(JSM-760OF,Japan Electronics Co., Ltd.)在3 kV加速电压下观察APP@AL和APP阻燃剂的表面形貌。表面元素浓度采用能谱仪(EDS Ultima Max 170,Oxford Instruments Co., Ltd.,Oxford,UK)进行表征。在10 kV的加速电压下,选定区域的元素以不同的颜色显示。通过元素分析仪(Elementar-UNICUBE,Germany)测量APP@AL和APP中的碳和氮含量,通过电感耦合等离子体原子发射光谱法(US-Perkin Elmer-Avio 200 (OES))测量APP@AL和APP的磷含量。APP和APP@AL的表面元素组成通过X射线光电子能谱(AXIS UltraDLD,Shimazu Co., Ltd.,UK)测试。傅里叶红外光谱(FTIR)分析在红外光谱仪(VTMR20-010-T,Bruker Corporation,Karlsruhe,Germany)上进行。经 KBr 压片法,分辨率为设置为 1 cm−1,扫描次数设置为 40 次,扫描范围设置为
4000 ~400 cm−1。1.3.2 物理性能
通过扫描电子显微镜(SEM Phenom ProX,Netherlands)以10 kV的加速电压观察RPU泡沫的泡孔结构,所有样品都真空镀金。通过万能试验机(Instron 5966,USA)以5 mm/min的十字头速度在室温下对50 mm×50 mm× 50 mm(长×宽×厚)立方体样品进行压缩强度试验,每个样品的结果是5个样本的平均值,抗压强度计算如下:
σm=Fmax (1) 其中: \sigma_{\mathrm{m}} 为抗压强度(MPa);Fmax为相对形变小于10%的最大载荷(N);A0为试样的初始横截面积(mm2)。
泡沫的导热系数用热流计(HC-074-200,美国)进行测试。按照 ASTM C518—10[21]标准,将样品切割成长方体(100 mm×100 mm×25 mm)。试样置于两个等温板上,等温板的温度分别保持在 10℃(上板)和 35℃(下板)。
1.3.3 燃烧性能
极限氧指数(LOI)参考ASTM D2863—19 [22]通过氧指数仪(HC-2C,江宁分析仪器厂)测量,样品尺寸为100 mm×100 mm×10 mm,测试 15个样品,获取平均值。锥形量热仪测试根据ISO 5660-1[23]标准在锥形量热计(CONE FTT i-Cone 0402,Fire Testing Technology Limited Co., Ltd.,London,UK)上以35 kW/m2的热通量进行,样品尺寸为100 mm×100 mm×25 mm,测试时间为600 s。
1.3.4 热稳定性
热重测试(TG)在 TG209 热分析系统(Netzsch STA 409,Karlsruhe,Germany)上进行,样品质量 8~12 mg,N2气氛下,气体流速 20 mL/min,升温速率 10℃/min,测试温度范围40~800℃。
1.3.5 阻燃机制
样品残炭的表面形态观察使用与第 1.3.2 节所述相同的扫描电镜设备。采用拉曼光谱技术(DXR532,Thermo,USA)与 532 nm氩离子激光器(Torus532,Bonphot,China)相结合,分析 CONE 测试后残留炭层的石墨化程度。
2. 结果分析
2.1 APP@AL成分及结构分析
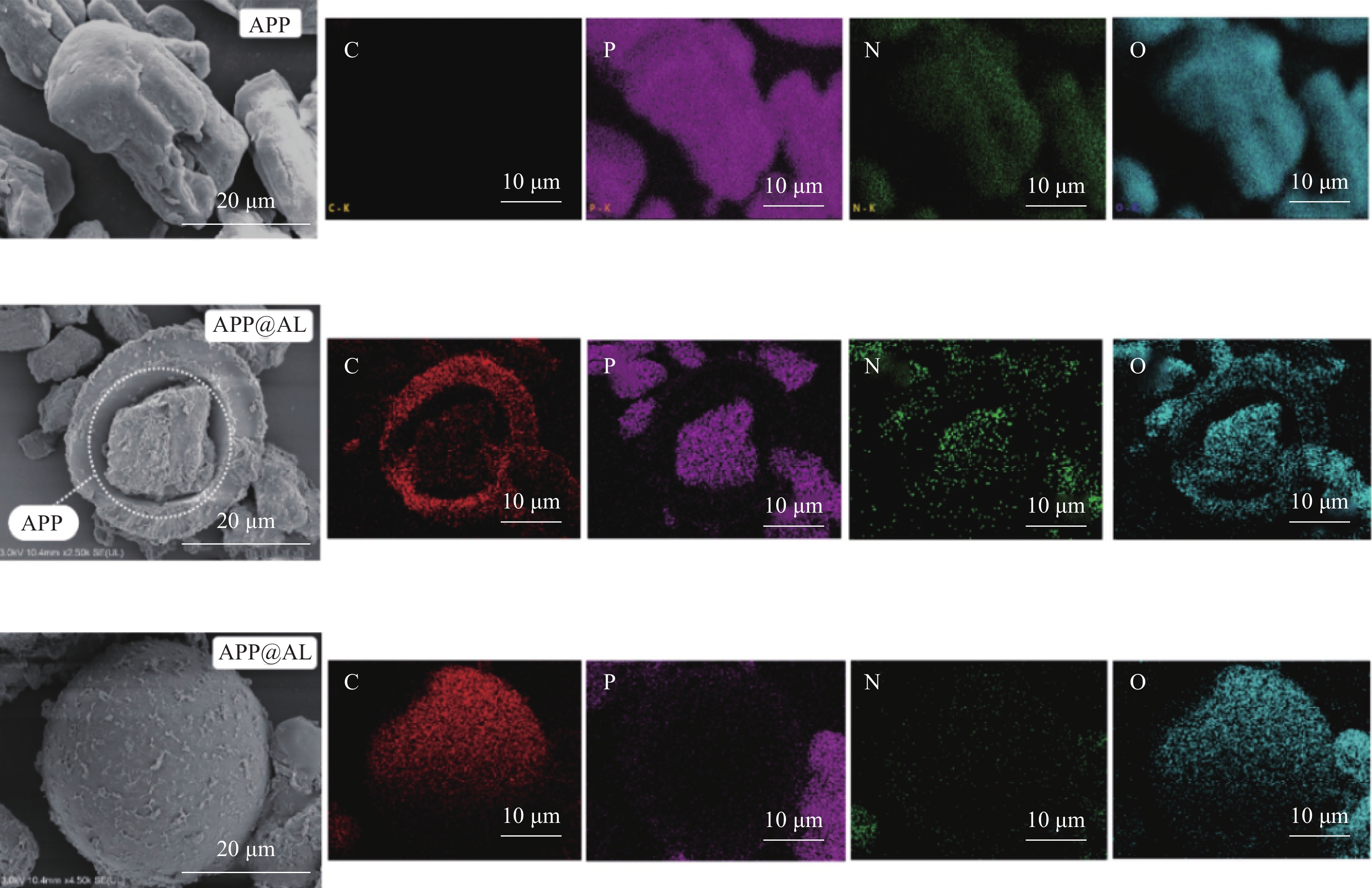
利用SEM观察APP和APP@AL的表面形貌,如图1所示,未改性的APP颗粒表面光滑,与APP相比,改性后的APP@AL明显被外壳包裹形成核壳结构。结合EDS测试分析核壳表面的元素分布,可以看出,APP中含有丰富的N、P元素,不含C元素, 而APP@AL外壳中含有丰富的C元素,芯层中含有N、P元素。由于木质素中有丰富的碳含量并且其中含有的羟基与MDI能发生酯化反应生成聚氨酯,推断该外壳为聚氨酯。同时,利用元素分析仪和电感耦合等离子体发射光谱分析改性前后APP的元素含量变化,如表3所示。改性后的APP都含有C元素,其中APP@AL3中C、P、N元素的含量分别为11.6wt%、22.1wt%和12.8wt%,APP中C、P、N的含量分别为0wt%、26.0wt%和14.4wt%。该结果表明,APP@AL中高含量C的存在表明有机外壳生成,从而导致APP@AL中P、N的含量下降。
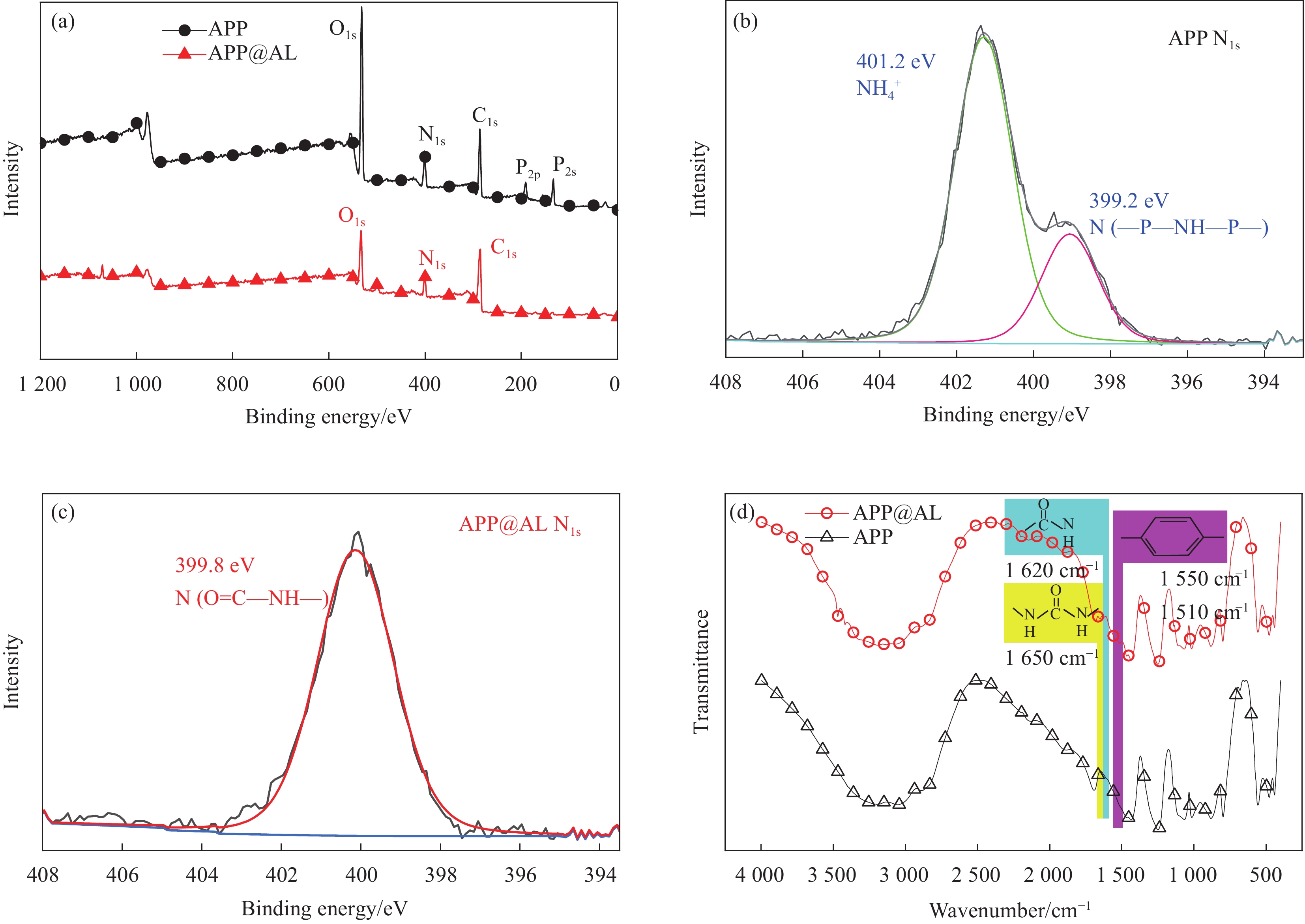
表 3 APP和APP@AL中C、P和N元素含量Table 3. Elemental C, P and N contents in APP and APP@ALSamples C/wt% P/wt% N/wt% APP 0 26.0 14.4 APP@AL1 13.8 19.5 11.9 APP@AL2 12.9 20.6 12.2 APP@AL3 11.6 22.1 12.8 APP@AL4 11.1 21.5 13.2 进一步通过XPS表征APP和APP@AL的表面元素含量,如图2(a)所示。位于133、190和399 eV处的峰归因于APP的P2s、P2p和N1s。对于APP@AL,能谱中不能观察到P2s和P2p峰,该结果表明APP已被聚氨酯有机壳完全包覆。此外,还研究了APP和APP@AL的N1s XPS图谱。如图2(b)和图2(c)所示,APP中N1s的对应的峰可以被分解为两个特征峰。在401.2 eV处的结合能对应于NH4+,并且在399.2 eV处的峰归因于—P—NH—P—基团中的N。在APP上构建有机聚氨酯壳层后,NH4+和—P—NH—P—中N的结合能峰消失,在399.8 eV处出现新的结合能峰,这归因于O=C—NH—基团中N的结合能,该结果表明改性后在APP颗粒的表面产生了聚氨酯结构[11]。最后对APP和APP@AL进行FTIR测试,如图2(d)所示,在APP@AL的FTIR图谱中,
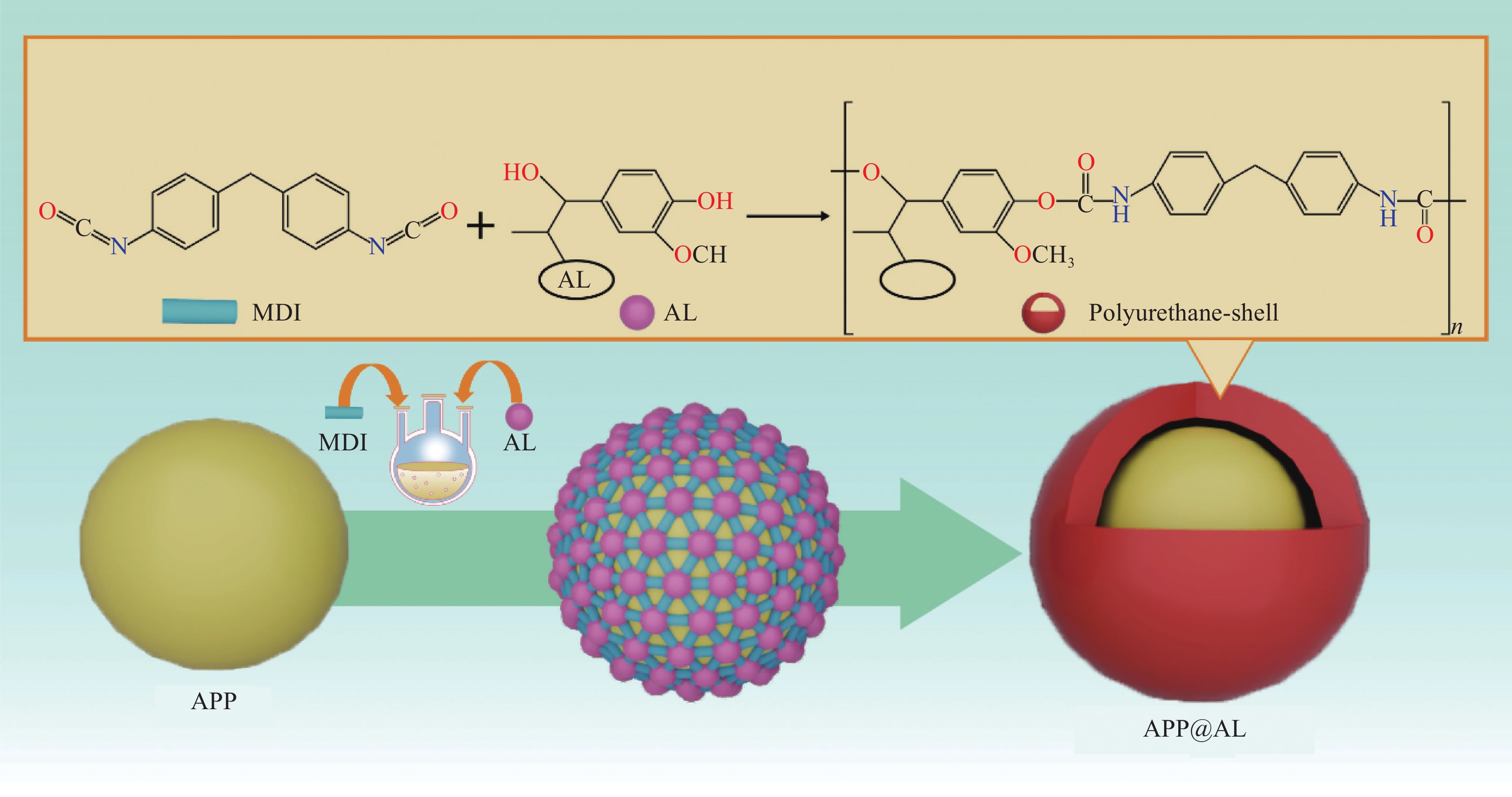
1550 和1510 cm−1的吸收峰来自于MDI的苯环振动,在1620 cm−1出现一个新的吸收峰,对应于MDI中的—N—(CO)—N—的振动,1650 cm−1的吸收峰来自于聚氨酯中的C=O,证明该外壳即为聚氨酯。根据以上分析结果,提出了APP@AL中聚氨酯核壳结构的形成机制(图3)。在APP溶液中加入MDI后,部分MDI通过—NCO与NH4+的相互作用锚定在APP表面。由于MDI的空间位阻效应和相对较短的反应时间,未反应的—NCO基团分散在APP上,这构成了聚氨酯的附着位点。当加入AL时,它们会与APP表面附着的MDI发生反应,使聚氨酯沿着附着位点生长,从而包裹住整个APP形成核壳结构,最终形成APP@AL。
2.2 APP@AL的物理性能
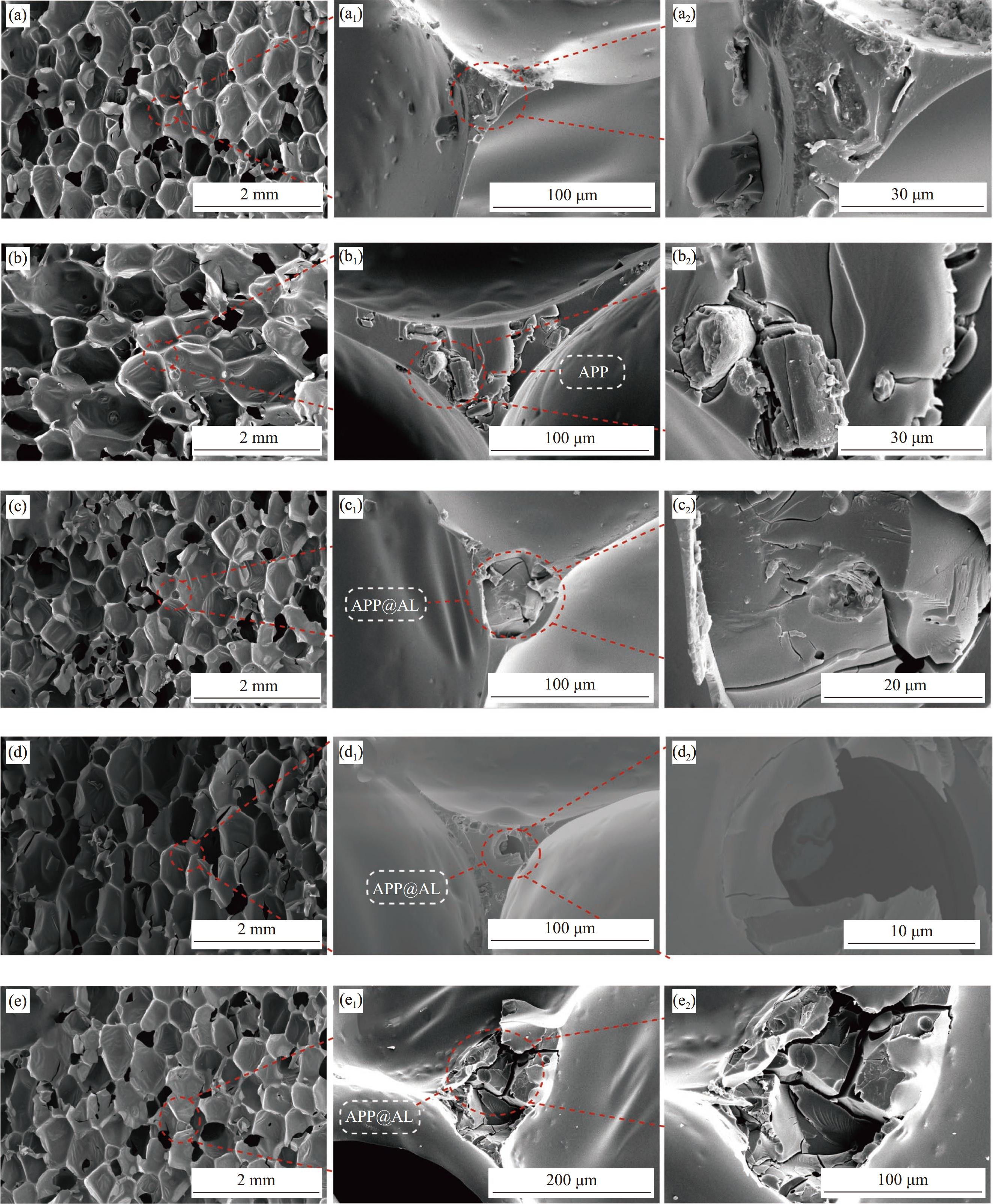
RPU泡沫物理性能主要取决于表观密度和微观结构。与纯RPU相比,添加25wt% APP后,泡沫的表观密度有所降低;而添加APP@AL后,泡沫的表观密度增大,其中25APP@AL3/RPU表观密度达到52.0 kg/m3 (表4)。进一步通过SEM观察样品表面的微观结构,并且应用ImageJ对SEM图像进行统计分析,以确定RPU泡沫泡孔产生的形态及孔径大小。垂直切割的纯RPU、25APP/RPU、25APP@AL1/RPU、25APP@AL2/RPU和25APP@AL3/RPU试样截面如图4所示。纯RPU样品中,泡孔主要由紧密封闭的细胞组成,泡孔大小分布均匀,平均孔径为533 μm。25APP/RPU的孔径大小分布广泛,并发现一些泡孔壁没有完全连接。图4(b)~4(b2)证实位于泡孔壁内的APP较少,且只是附着在泡孔壁内,不能与之融合。这是由于APP和RPU泡沫基体相容性差,不适合在泡孔壁内。且在泡孔壁外聚集的APP颗粒会干扰泡孔的形成,会撕裂或破坏泡孔壁。因此,APP的加入会导致泡孔直径增大。当添加APP@AL时,泡孔直径明显减小,其中25APP@AL3/RPU的平均孔径最小为444 μm,泡孔大小分布最均匀。这归功于APP@AL的聚氨酯外壳与RPU泡沫基体物质相似,能很好地与泡孔壁结合,作为成核剂使发泡过程更加稳定,形成更多闭孔结构。
表 4 RPU泡沫复合材料的孔径尺寸、表观密度、导热系数和压缩强度Table 4. Cell diameter, apparent density, thermal conductivity and compression strength of RPU foam compositesSample Cell diameter/μm Apparent density/(kg·m−3) Thermal conductivity/(mW·m−1·K−1) Compressive strength/kPa Pure RPU 533±80* 50.5±1.2 23.2±0.1 194±20 25APP/RPU 601±90 49.4±1.5 24.2±0.2 173±25 25APP@AL1/RPU 455±60 51.8±1.1 22.7±0.1 214±18 25APP@AL2/RPU 458±55 51.7±1.0 22.7±0.2 215±14 25APP@AL3/RPU 444±65 52.0±0.9 22.5±0.2 228±20 25APP@AL4/RPU 449±70 51.9±1.0 22.6±0.2 221±21 Note: *—Average and standard deviations. 从表4中可以得到每种RPU泡沫复合材料的导热系数。与纯RPU 相比,APP的加入会造成泡沫的表观密度降低以及泡孔尺寸增大,导致导热系数增大。添加 APP@AL后,泡沫的孔径尺寸减小、孔径大小分布更加均匀使导热系数有所降低,其中25APP@AL3/RPU 的导热系数比 25APP/RPU 降低了 7.0%,这归因于聚氨酯外壳与基体之间的高度的相容性,从而使25APP@AL3/RPU 具有更高的表观密度和更小的泡孔尺寸,该特性保证了RPU泡沫优异的保温性能。从表4可知,当APP添加量为 25wt% 时,泡沫的抗压强度为 173 kPa,与纯RPU 相比,抗压强度降低10.8%。符合以往的研究结果:添加型阻燃剂的高负载量会导致聚合物力学性能降低[24]。相反,添加APP@AL后,泡沫的压缩强度却都有所增强,25APP@AL3/RPU比纯RPU 提高17.5%。这归功于 APP@AL表层有聚氨酯外壳与泡沫基体有良好的相容性,混合搅拌过程中阻燃剂颗粒分布均匀,有利于发泡进行。如图4(e)~4(e2)图像显示,APP@AL可以和基体界面很好的相容,并牢固地与泡孔壁结合提高泡沫的压缩强度。
2.3 APP@AL的燃烧性能
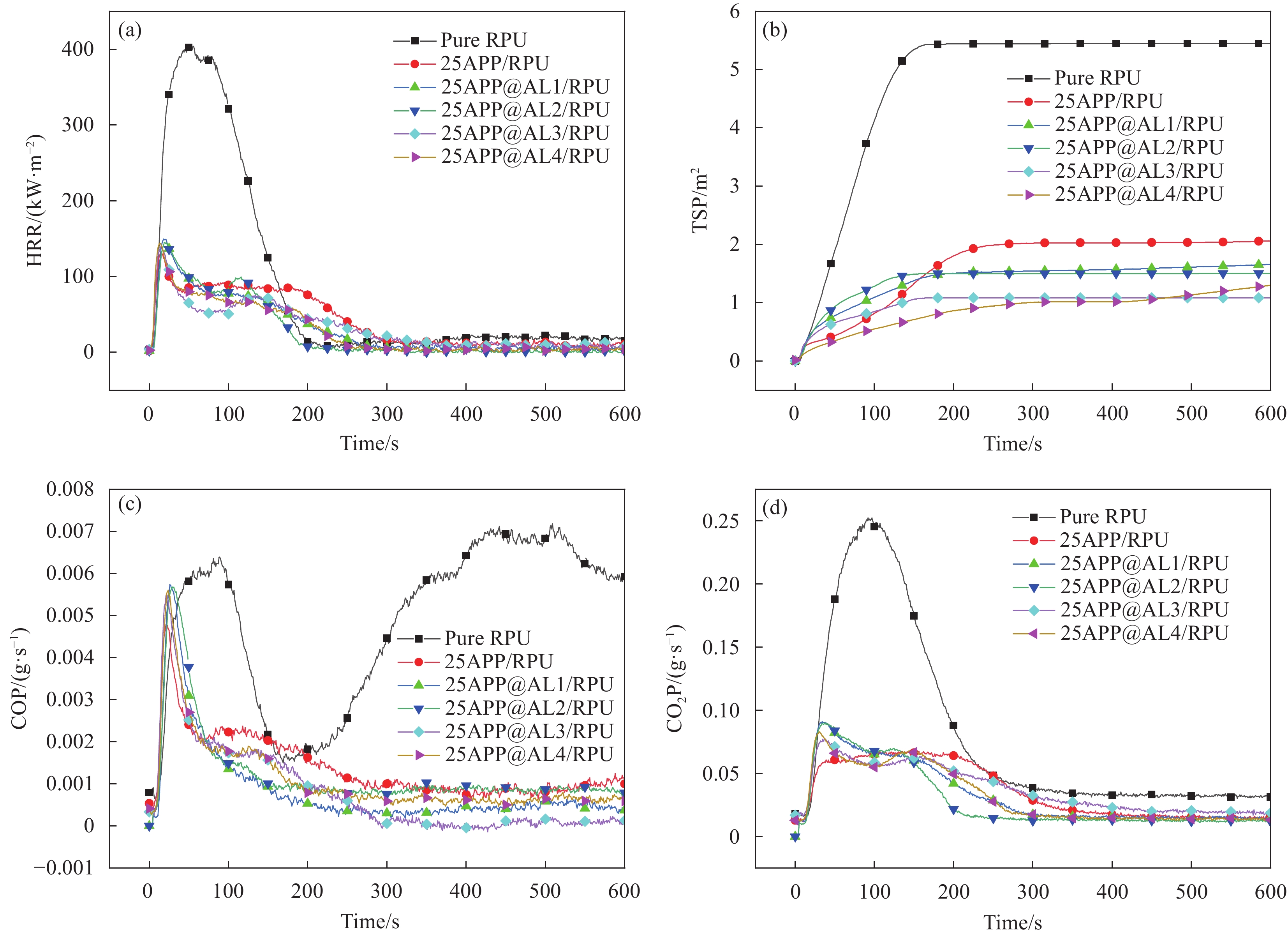
LOI值是表征材料阻燃性能的常见指标,通常LOI值高于25%的材料在燃烧过程中倾向于自发熄灭,被认为是难以点燃的材料[25]。纯RPU泡沫是一种易燃聚合物,LOI值仅为18.5%;当加入阻燃剂后,LOI明显提升(最高可达27.0%,表5)。锥形量热仪(CONE)测试意义在于模拟评估材料在真实火灾场景下的燃烧行为。从图5和表5可见,由于RPU泡沫本身的多孔结构,氧气与材料的接触面积较大,导致点燃时间(TTI)均较短,燃烧较快[26]。峰值放热速率(PHRR)、平均放热速率(MHRR)是表征火灾强度的重要参数,PHRR、MHRR值越低,火灾危险性越小。纯RPU泡沫着火后燃烧迅速,短时间PHRR达到403.8 kw/m2,MHRR为253.1 kw/m2,说明纯RPU泡沫易燃烧,火灾危险性大。无论是APP还是APP@AL的加入,都能极大降低RPU泡沫的PHRR、MHRR值。25APP@AL3/RPU的MHRR仅为50.0 kW/m2 比25APP/RPU下降27.2%,PHRR为140.5 kW/m2略高于25APP/RPU。这可能是由于APP@AL3中P相对含量减少,升温初期含磷自由基抑制燃烧活性分子的能力不如纯APP,抑制热释放的能力减弱,放热峰值有所增大。当温度继续升高时,APP@AL3中的C、N和P元素开始产生协同效应,其中AL具有丰富的C含量,可以作为成炭剂与芯层APP产生协同阻燃作用,能够形成更加致密的炭层阻隔空气与基体的接触,从而达到更好的阻燃效果。此外,25APP@AL3/RPU的THR比25APP/RPU下降24.4%。阻燃效果还可以通过炭残余率来评价。纯RPU在CONE测试后残留物仅为7.4%,表明其燃烧成炭性能差。APP@AL的引入,为成炭性能差的RPU泡沫提供充足的炭源,形成致密的炭层保护基体,使RPU泡沫的燃烧残炭率显著提升(最高可达29.2%,表5)。
一般情况下,火灾发生时的死亡主要是由烟雾造成的,因此烟释放速率(SPR)、烟总释放量(TSP)、CO产生速率(COP)、CO2产生速率(CO2P)和CO产生量(COY)是评价RPU泡沫火灾安全性的重要参数[27]。研究发现APP用于聚合物阻燃时抑烟性能较差,这是限制APP应用的主要因素之一,然而APP经杂化改性后的APP@AL抑烟性能却有大幅度提升。如表5所示,25APP/RPU的SPR、TSP和COY分别为
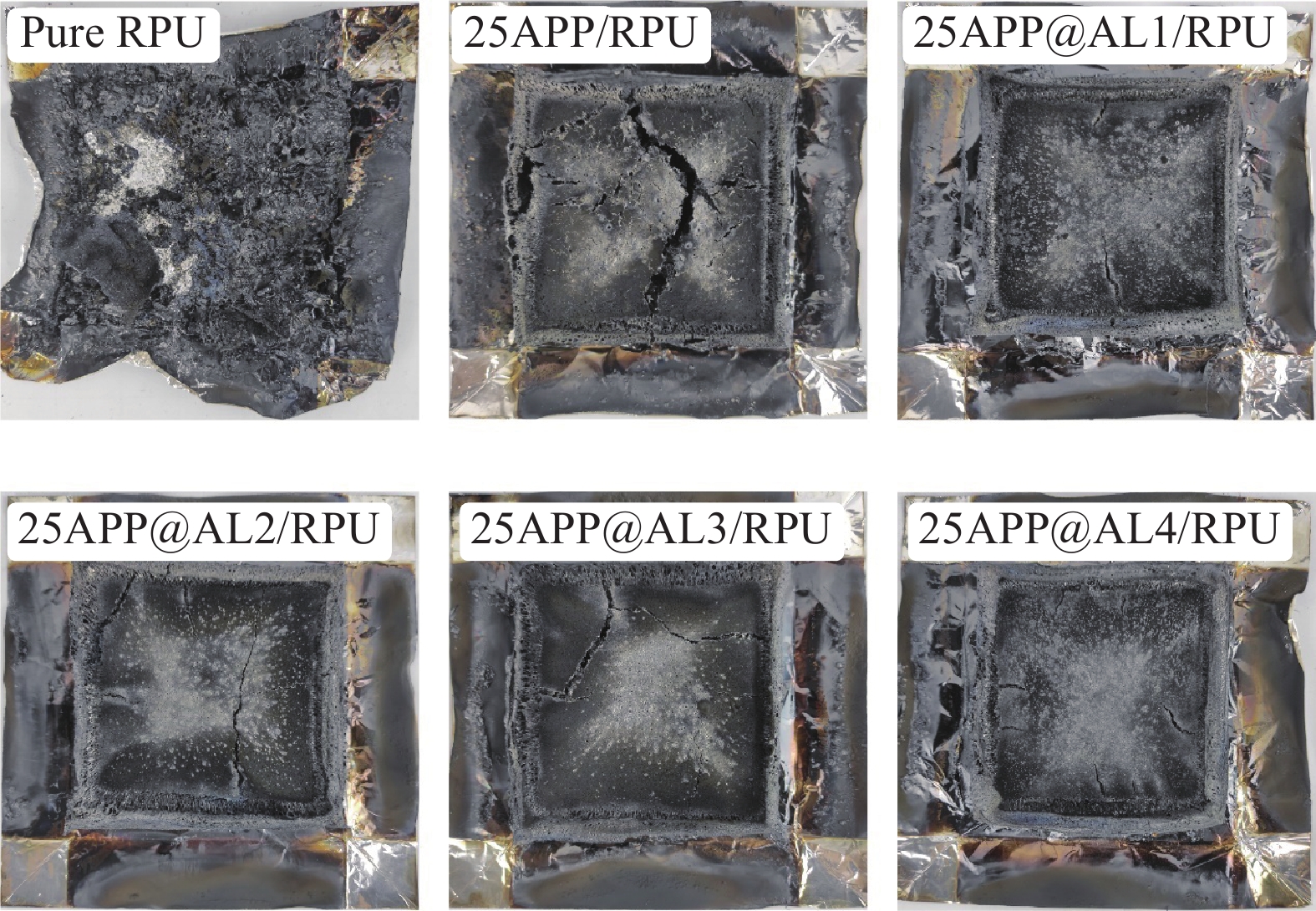
0.0034 m2·s−1、2.1 m2和54.2 kg·kg−1。当添加25wt% APP@AL3时,SPR、TSP和COY分别为0.0023 m2·s−1、1.1 m2和23.3 kg·kg−1,与25APP/RPU相比分别降低32.4%、47.6%和57.0%。结果表明,APP@AL3与APP相比有优异的抑烟效果,能够在火灾发生时,减少有烟气的释放,降低对人体的损害。表 5 RPU泡沫复合材料燃烧性能测试结果Table 5. Test results of fire performance of flame-retardant RPU foam compositesSample HRR/(kW·m−2) LOI/% TTI/s THR/(MJ·m−2) SPR/(m2·s−1) TSP/m2 COY/(kg·kg−1) Residue/% PHRR MHRR Pure RPU 403.8 253.1 18.5 6 56.0 0.0094 5.5 279.2 7.4 25APP/RPU 132.6 68.7 26.2 3 25.0 0.0034 2.1 54.2 25.4 25APP@AL1/RPU 149.2 58.6 26.8 5 19.1 0.0027 1.7 27.1 29.2 25APP@AL2/RPU 145.0 56.5 26.9 5 19.0 0.0026 1.5 26.5 28.5 25APP@AL3/RPU 140.5 50.0 27.0 5 18.9 0.0023 1.1 23.3 28.7 25APP@AL4/RPU 150.1 61.6 26.7 5 19.3 0.0025 1.3 25.8 28.0 Notes: PHRR—Peak heat release rate; MHRR—Mean heat release rate; LOI—Limiting oxygen index; TTI—Time to ignition; THR—Total heat release; SPR—Smoke production rate; TSP—Total smoke production; COY—CO yield; Residue—Charcoal residue rate. 图6为CONE测试后RPU泡沫的残留情况。纯RPU残炭不连续,分散且有孔洞,燃烧时为热和氧气穿透内部提供了大量通道。添加阻燃剂后,尽管残炭也出现了一定程度的开裂和一些孔洞, 但是仍然能保持一定的形状,25APP/RPU炭层的裂缝和孔洞明显多于其他试样。虽然纯APP的P和N含量最高,能够提供足够的酸源和气源,但是APP自身无炭源,泡沫基体也无法提供足够的炭源,导致其炭层薄而易裂。APP@AL中含有丰富的炭源,能够弥补APP中没有炭源的缺陷,增强基体的成炭性,使得燃烧后的残炭致密紧实,形成屏障有效隔绝空气保护未燃烧的泡沫基体。
2.4 APP@AL的热稳定性
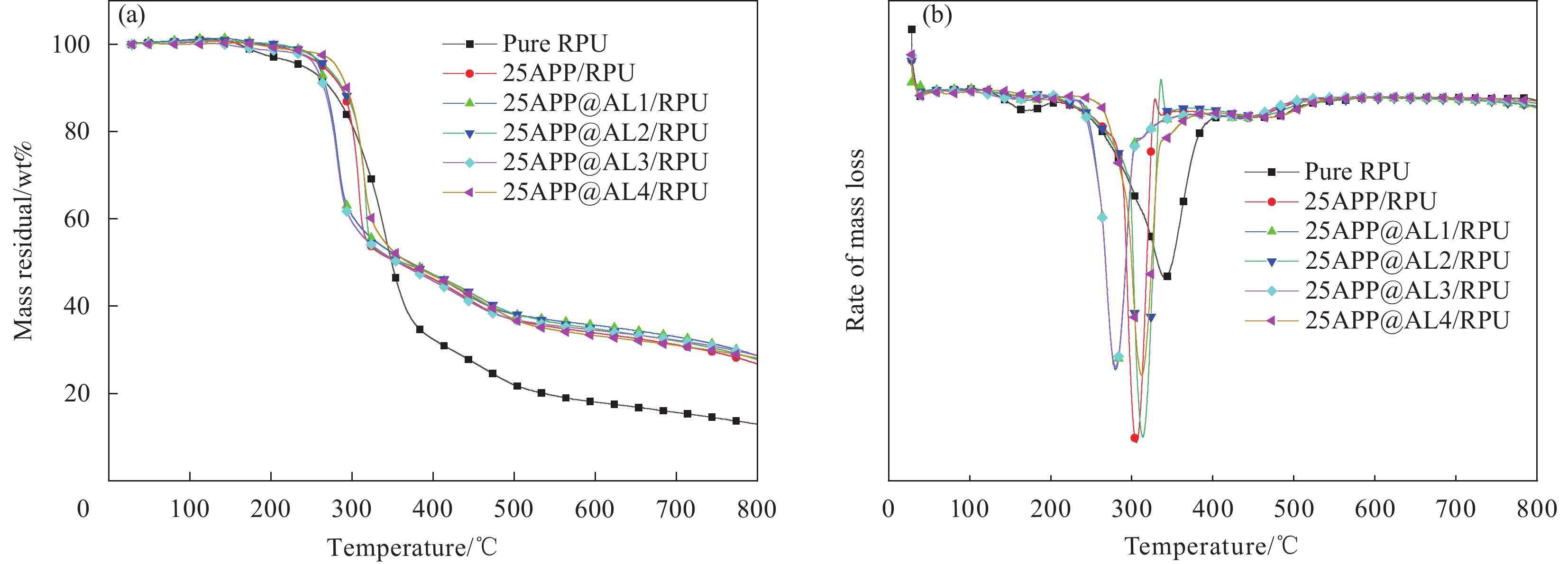
图7 显示了不同 RPU泡沫复合材料在 N2气氛下的降解行为,详细数据见表6。可以明显看出,纯 RPU 的热降解过程分为两个阶段,而所有阻燃处理的RPU泡沫均呈现三阶段热解特征。第一阶段为聚氨酯主链降解,形成多元醇和异氰酸酯前驱体,异氰酸酯二聚体形成碳二亚胺并产生挥发性分子,如碳氧化物、醇、胺和醛等挥发性分子;第二阶段是软链段多元醇的降解;第三阶段形成残炭[28]。25APP/RPU 的降解温度低于纯 RPU,这是由于 APP 对泡沫的催化降解作用。添加 APP@AL 后,泡沫的降解温度升高,这可能是由于APP@AL中聚氨酯外壳的存在,在降解过程中需要吸收热量。25APP@AL3/RPU 的 W800 (800℃时的残炭量)为 28.8wt%高于25APP/RPU的26.8wt%,泡沫的质量损失率降低,热稳定性和成炭能力得到提升。
表 6 在相应温度下RPU泡沫复合材料不同热解阶段和800℃的残炭Table 6. Corresponding temperatures of RPU foam composites at different pyrolysis stages and the char residue at 800℃Sample T10%/℃ T50%/℃ W800/wt% Pure RPU 272 348 13.0 25APP/RPU 263 333 26.8 25APP@AL1/RPU 287 361 28.7 25APP@AL2/RPU 281 358 28.1 25APP@AL3/RPU 274 352 28.8 25APP@AL4/RPU 276 355 28.4 Notes: T10% and T50% represent the temperature where 10wt% and 50wt% of weight lost; W800 represents the mass residual at 800℃. 2.5 APP@AL的阻燃机制
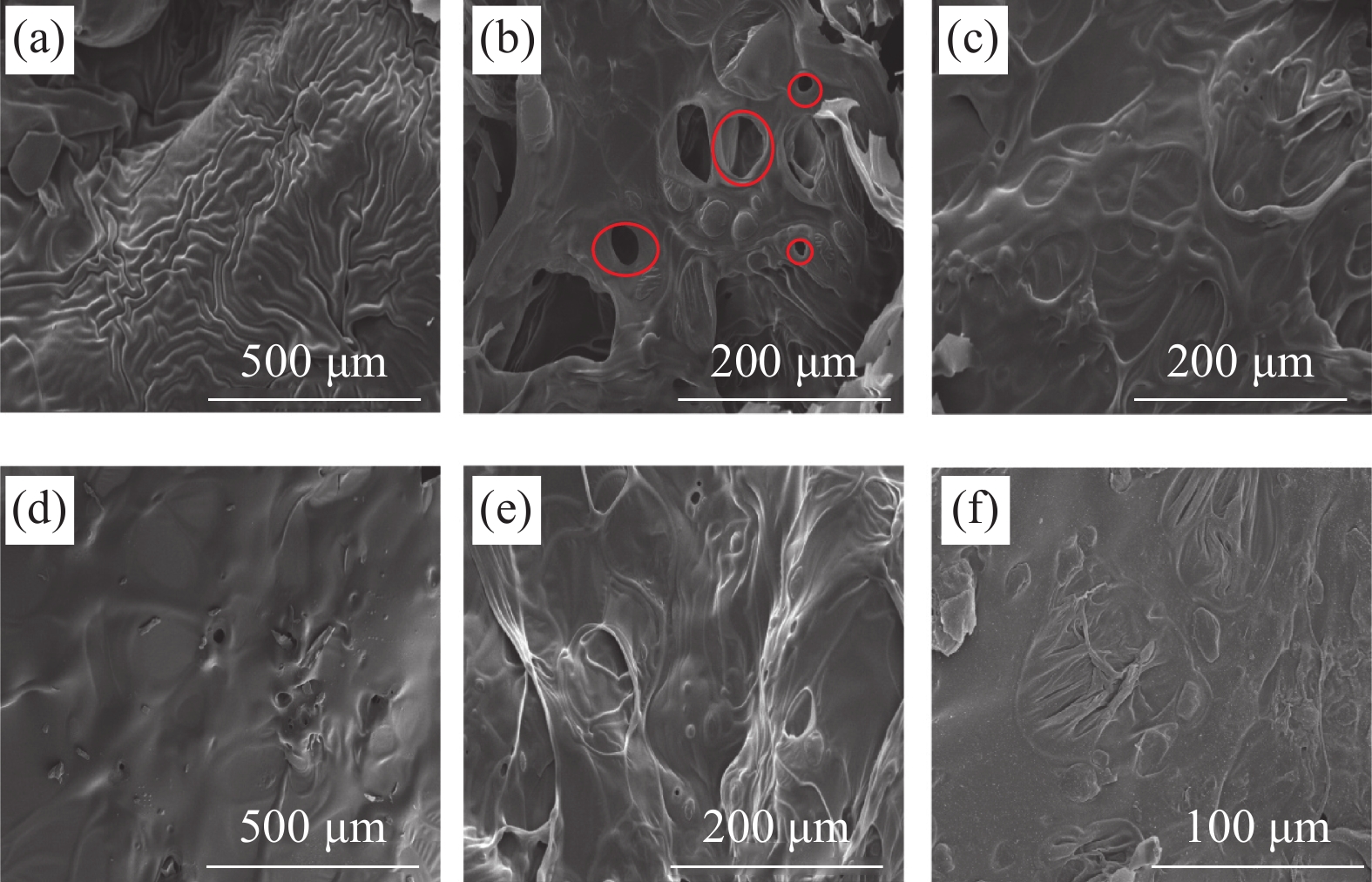
CONE和TG测试结果表明,RPU泡沫中添加APP@AL3能够更好地抑制热量和烟气,降低火灾危险。为了进一步分析 APP@AL对成炭和阻燃机制的影响。采用SEM观察CONE 试验后各试样残炭的微观结构,如图8所示。纯RPU 的残炭出现明显收缩(图8(a)),泡沫原本结构无法保持。在添加阻燃剂后,残炭显示出膨胀和连续性,并且可以看到清晰的泡孔结构。有趣的是,泡孔表面覆盖了一层薄膜状结构。结合APP的阻燃机制分析,当泡沫基体中的 APP 受到高温时,APP 的酸源在高温下与含碳物质酯化后形成熔融体。该熔融体被 APP 不断释放出的不燃气体吹散,在基体表面扩散形成膜状结构,隔绝空气与基体接触,从而达到保护未燃烧基体的效果。从图8(b)中可以看出,25APP/RPU出现较多的孔洞且膜的覆盖面积和厚度较小;加入 APP@AL 后,泡沫的熔体覆盖率更大,膜的完整性更好,几乎没有孔洞,如图8(c)~8(f)所示。APP@AL阻燃效果提升得益于聚氨酯外壳能够发挥炭源的作用,芯层中的 APP 可以作为酸源和气源发挥作用,两者产生协同阻燃效果,增强RPU泡沫防火安全性。
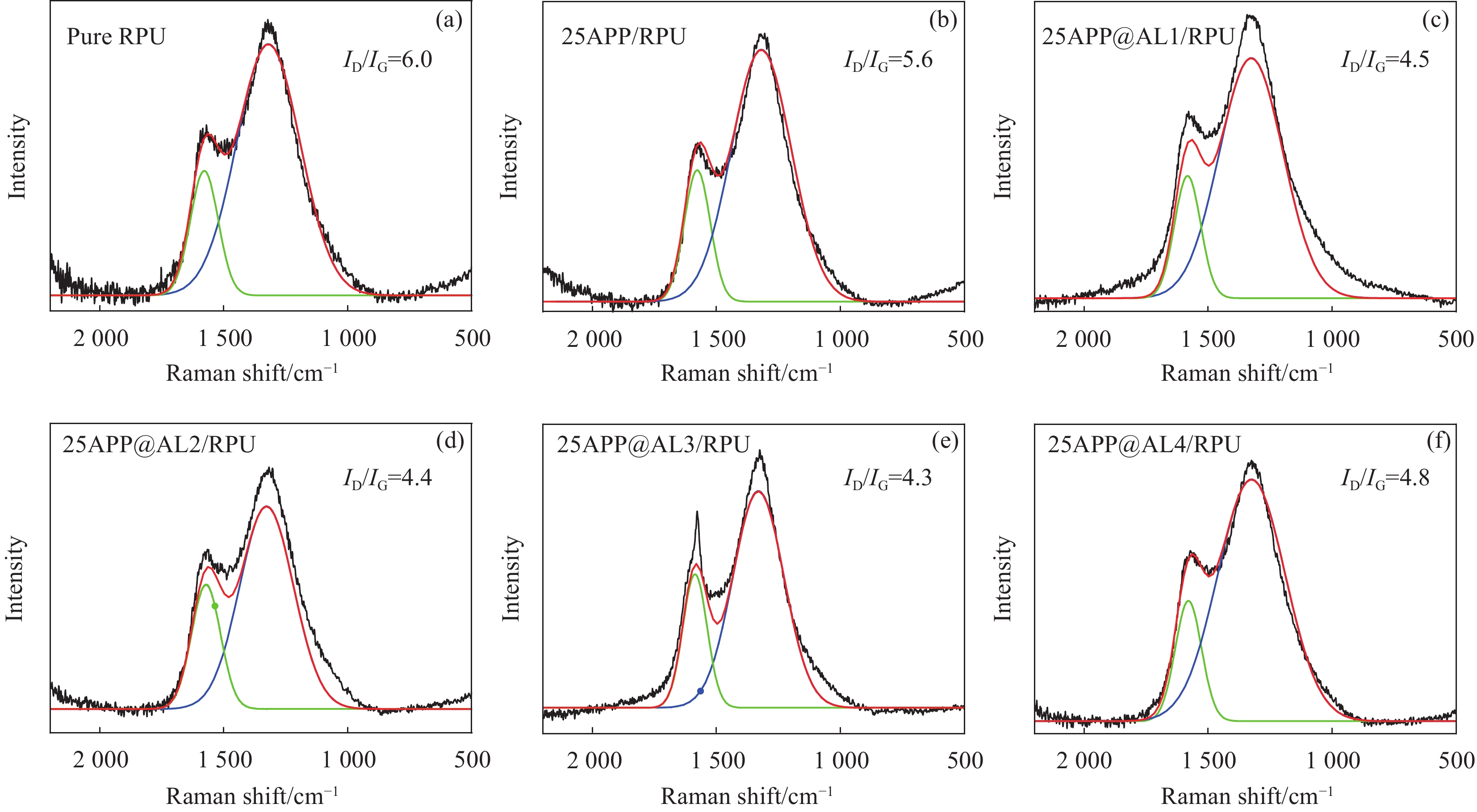
采用拉曼光谱进一步研究APP@AL复合材料的阻燃机制(图9),可见,纯RPU泡沫和阻燃处理的RPU材料在
1379 cm−1和1579 cm−1处呈现两个特征峰,分别对应于D带和G带。通常,D带与G带的面积比(ID/IG)是指炭残渣的石墨化程度,ID/IG值越低,则表示残炭层具有致密结构。根据图9,ID/IG值遵循25APP@AL3/RPU(4.3)< 25APP@AL2/RPU(4.4)<25APP@AL1/RPU(4.5)<25APP@AL4/RPU(4.8)<25APP/RPU(5.6)<Pure RPU(6.0)的顺序, 25APP@AL3/RPU的ID/IG值最低,表明25APP@AL3/RPU的残炭显示出最小的微晶尺寸和最佳的残炭结构。因此,可能是其致密连续的炭层结构,导致25APP@AL3/RPU具有良好的防火安全性。结合APP、APP@AL3和AL的TG结果分析(图10),AL的高残炭率(达47.7wt%)证明其可以在IFR中起到成炭剂的作用。在N2气氛下,相较于APP,APP@AL3残炭量从19.3wt%增加到23.6wt%,说明APP@AL的聚氨酯外壳作为成炭剂与芯层的APP之间存在协同作用,这可以促进炭物质与磷酸化交联结构在高温下形成以提升热稳定性。图11进一步示意描述了APP@AL的阻燃机制。C和P元素在固相阻燃中发挥作用,在APP@AL的初始分解过程中会产生酸性物质如磷酸、聚磷酸和焦磷酸等,这些酸性物质催化RPU泡沫产生脱水反应形成含碳物质,同时聚氨酯外壳可以为基体提供更多的炭源,促进形成更多含碳物质[29-30]。随着温度的升高,RPU泡沫主链的降解并分解成各类化合物,这些化合物与含碳物质反应,生成稠密的残炭熔融体覆盖在未燃烧的基体上,防止氧气的渗透,从而抑制RPU泡沫的燃烧。此外,APP@AL分解过程中产生的各种含磷自由基(如:PO•、PO2•)可以捕捉泡沫燃烧释放氢自由基(如:H•、HO•)。N元素则在气相阻燃中发挥作用, APP@AL分解会释放不可燃气体(如:N2、NH3),稀释可燃气体浓度,进一步提高RPU泡沫的防火安全性。APP@AL的固相阻燃机制与气相阻燃机制的组合显著减少了RPU泡沫燃烧期间烟气和热的释放。综上所述,APP@AL的聚氨酯外壳可以作为炭源,APP芯层可以作为酸源和气源,产生协同阻燃效果形成更加致密稳定的炭层,使RPU泡沫具有良好的阻燃和抑烟性能。
3. 结 论
(1)基于聚磷酸铵(APP),利用碱木素(AL)和双(4-异氰酸酯基苯基)甲烷(MDI)成功制备了核壳结构的膨胀型阻燃剂APP@AL (APP∶MDI∶AL为9∶2∶1)。相较于APP,APP@AL的残炭率由19.3wt%增加到23.6wt%,质量损失率降低,热稳定性提高。
(2) APP@AL提高了RPU复合材料的力学和保温性能。 APP@AL与RPU基体之间表现出良好的界面相容性,与添加25wt%APP的RPU泡沫复合材料相比,添加25wt%APP@AL的RPU泡沫复合材料的抗压强度提高31.8%,导热系数降低7.0%。
(3) APP@AL提高了RPU复合材料的阻燃性能。与添加25wt%APP的RPU泡沫复合材料相比,添加25wt%APP@AL的RPU泡沫复合材料的平均放热速率和总放热量分别降低了 27.2% 和 24.4%;同时,总产烟量和CO产生量分别显著降低了 47.6% 和 57.0%。
(4)核壳结构的APP@AL,聚氨酯外壳可以作为炭源,芯层的APP可以作为酸源和气源,它们之间相互作用产生协同效应,使APP@AL具有良好的阻燃和抑烟性能。
-
表 1 聚磷酸铵(APP)改性配方
Table 1 Formula of ammonium polyphosphate (APP) modification
Formulation APP@AL1 APP@AL2 APP@AL3 APP@AL4 APP/g 45 45 45 45 MDI/g 5 7.5 10 11.25 AL/g 10 7.5 5 3.75 Notes: MDI—4, 4'-methylenebiphenyl isocyanate; AL—Alkali lignin. 表 2 硬质聚氨酯(RPU)泡沫复合材料配方
Table 2 Preparation formula of rigid polyurethane (RPU) foam composites
Formulation Pure RPU 25APP/RPU 25APP@AL1/RPU 25APP@AL2/RPU 25APP@AL3/RPU 25APP@AL4/RPU APP/g 0 50 0 0 0 0 APP@AL1/g 0 0 50 0 0 0 APP@AL2/g 0 0 0 50 0 0 APP@AL3/g 0 0 0 0 50 0 APP@AL4/g 0 0 0 0 0 50 LY-4110/g 100 100 100 100 100 100 AK-8805/g 2 2 2 2 2 2 LC/g 1.5 1.5 1.5 1.5 1.5 1.5 HFC-365mfc/g 33 33 33 33 33 33 PAPI/g 100 100 100 100 100 100 Notes: LY-4110—Polyetherpolyol; AK-8805—Silicone surfactant; LC—Dibutyltin dilaurate; HFC-365mfc—Foaming agent; PAPI—Poly-methylene polyphenyl isocyanate; 25APP/RPU, 25APP@AL1/RPU, 25APP@AL2/RPU, 25APP@AL3/RPU, 25APP@AL4/RPU, the 25 indicates that the amount of flame retardant added is 25wt% of the total mass of LY-4110 and PAPI. 表 3 APP和APP@AL中C、P和N元素含量
Table 3 Elemental C, P and N contents in APP and APP@AL
Samples C/wt% P/wt% N/wt% APP 0 26.0 14.4 APP@AL1 13.8 19.5 11.9 APP@AL2 12.9 20.6 12.2 APP@AL3 11.6 22.1 12.8 APP@AL4 11.1 21.5 13.2 表 4 RPU泡沫复合材料的孔径尺寸、表观密度、导热系数和压缩强度
Table 4 Cell diameter, apparent density, thermal conductivity and compression strength of RPU foam composites
Sample Cell diameter/μm Apparent density/(kg·m−3) Thermal conductivity/(mW·m−1·K−1) Compressive strength/kPa Pure RPU 533±80* 50.5±1.2 23.2±0.1 194±20 25APP/RPU 601±90 49.4±1.5 24.2±0.2 173±25 25APP@AL1/RPU 455±60 51.8±1.1 22.7±0.1 214±18 25APP@AL2/RPU 458±55 51.7±1.0 22.7±0.2 215±14 25APP@AL3/RPU 444±65 52.0±0.9 22.5±0.2 228±20 25APP@AL4/RPU 449±70 51.9±1.0 22.6±0.2 221±21 Note: *—Average and standard deviations. 表 5 RPU泡沫复合材料燃烧性能测试结果
Table 5 Test results of fire performance of flame-retardant RPU foam composites
Sample HRR/(kW·m−2) LOI/% TTI/s THR/(MJ·m−2) SPR/(m2·s−1) TSP/m2 COY/(kg·kg−1) Residue/% PHRR MHRR Pure RPU 403.8 253.1 18.5 6 56.0 0.0094 5.5 279.2 7.4 25APP/RPU 132.6 68.7 26.2 3 25.0 0.0034 2.1 54.2 25.4 25APP@AL1/RPU 149.2 58.6 26.8 5 19.1 0.0027 1.7 27.1 29.2 25APP@AL2/RPU 145.0 56.5 26.9 5 19.0 0.0026 1.5 26.5 28.5 25APP@AL3/RPU 140.5 50.0 27.0 5 18.9 0.0023 1.1 23.3 28.7 25APP@AL4/RPU 150.1 61.6 26.7 5 19.3 0.0025 1.3 25.8 28.0 Notes: PHRR—Peak heat release rate; MHRR—Mean heat release rate; LOI—Limiting oxygen index; TTI—Time to ignition; THR—Total heat release; SPR—Smoke production rate; TSP—Total smoke production; COY—CO yield; Residue—Charcoal residue rate. 表 6 在相应温度下RPU泡沫复合材料不同热解阶段和800℃的残炭
Table 6 Corresponding temperatures of RPU foam composites at different pyrolysis stages and the char residue at 800℃
Sample T10%/℃ T50%/℃ W800/wt% Pure RPU 272 348 13.0 25APP/RPU 263 333 26.8 25APP@AL1/RPU 287 361 28.7 25APP@AL2/RPU 281 358 28.1 25APP@AL3/RPU 274 352 28.8 25APP@AL4/RPU 276 355 28.4 Notes: T10% and T50% represent the temperature where 10wt% and 50wt% of weight lost; W800 represents the mass residual at 800℃. -
[1] 孙俊杰, 杨素洁, 黄新杰, 等. 阻燃硬质聚氨酯泡沫的进展[J]. 塑料, 2023, 52(5): 109-117. SUN Junjie, YANG Sujie, HUANG Xinjie, et al. Advances in flame retardants rigid polyurethane foam[J]. Plastics, 2023, 52(5): 109-117(in Chinese).
[2] 张冰, 杨素洁, 杨亚东, 等. 三聚氰胺植酸/硬质聚氨酯泡沫复合材料的制备及其热解动力学特性[J]. 复合材料学报, 2021, 38(8): 2505-2516. ZHANG Bing, YANG Sujie, YANG Yadong, et al. Preparation and pyrolysis kinetics of melaminephytates/rigid polyurethane foam composites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2021, 38(8): 2505-2516(in Chinese).
[3] 王希, 董全霄, 谷晓昱, 等. 反应型阻燃聚氨酯研究进展[J]. 聚氨酯工业, 2020, 35(3): 1-4. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-1902.2020.03.001 WANG Xi, DONG Quanxiao, GU Xiaoyu, et al. Research progress on reactive flame retardant polyurethane[J]. Polyurethane Industry, 2020, 35(3): 1-4(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-1902.2020.03.001
[4] 杨亚东, 姜浩浩, 张冰, 等. 基于微胶囊化聚磷酸铵和微胶囊化膨胀石墨的阻燃硬质聚氨酯泡沫复合材料的制备及性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2021, 38(5): 1387-1397. YANG Yadong, JIANG Haohao, ZHANG Bing, et al. Preparation and properties of flame retardant rigid polyurethane foam composites based on microencapsulated ammonium polyphosphate and microencapsulated expanded graphite[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2021, 38(5): 1387-1397(in Chinese).
[5] ZHU M, MA Z, LIU L, et al. Recent advances in fire-retardant rigid polyurethane foam[J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology, 2022, 112: 315-328.
[6] TIAN F, MAO W, XU X. Effect of a layered combination of APP and TBC on the mechanics and flame retardancy of poplar strandboards[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2023, 401: 132881. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2023.132881
[7] YUAN Y, YU B, SHI Y, et al. Highly efficient catalysts for reducing toxic gases generation change with temperature of rigid polyurethane foam nanocomposites: A comparative investigation[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing, 2018, 112: 142-154. DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2018.05.028
[8] CHEN Y, LI L, QI X, et al. The pyrolysis behaviors of phosphorus-containing organosilicon compound modified APP with different polyether segments and their flame retardant mechanism in polyurethane foam[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2019, 173: 106784. DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2019.04.045
[9] 靳昕怡, 魏丽菲, 窦娟, 等. 无卤阻燃剂在聚合物阻燃中的应用研究进展[J]. 高科技纤维与应用, 2022, 47(6): 67-73. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9815.2022.06.011 JIN Xinyi, WEI Lifei, DOU Juan, et al. Research on the application of halogen-free flame retardants in polymer flame retardants[J]. Hi-Tech Fiber and Application, 2022, 47(6): 67-73(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9815.2022.06.011
[10] TAO J, YANG F, WU T, et al. Thermal insulation, flame retardancy, smoke suppression, and reinforcement of rigid polyurethane foam enabled by incorporating a P/Cu-hybrid silica aerogel[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 461: 142061. DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2023.142061
[11] ZHAO X, CHEN L, LI D F, et al. Biomimetic construction peanut-leaf structure on ammonium polyphosphate surface: Improving its compatibility with poly(lactic acid) and flame-retardant efficiency simultaneously[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2021, 412: 128737. DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2021.128737
[12] TAN Y, SHAO Z B, CHEN X F, et al. Novel multifunctional organic inorganic hybrid curing agent with high flame-retardant efficiency for epoxy resin[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces, 2015, 7(32): 17919-17928.
[13] WAN M, SHI C, QIAN X, et al. Design of novel double-layer coated ammonium polyphosphate and its application in flame retardant thermoplastic polyurethanes[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal, 2023, 459: 141448. DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2023.141448
[14] GAO C, ZHOU L, YAO S, et al. Phosphorylated kraft lignin with improved thermal stability[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules, 2020, 162: 1642-1652. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2020.08.088
[15] 宋艳, 林肯, 周宇彤, 等. 含硅-氮木质素协同聚磷酸铵阻燃聚乳酸[J]. 复合材料学报, 2024, 41(7): 3544-3556. SONG Yan, LIN Ken, ZHOU Yutong, et al. Synergistic flame retardant effect of lignin containing silicon-nitrogen with ammonium polyphosphate on polylactic acid[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2024, 41(7): 3544-3556(in Chinese).
[16] LU W, YE J, ZHU L, et al. Intumescent flame retardant mechanism of lignosulfonate as a char forming agent in rigid polyurethane foam[J]. Polymers, 2021, 13(10): 1585. DOI: 10.3390/polym13101585
[17] ARAUJO T R, BRESOLIN D, DE OLIVEIRA D, et al. Conventional lignin functionalization for polyurethane applications and a future vision in the use of enzymes as an alternative method[J]. European Polymer Journal, 2023, 188: 111934. DOI: 10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2023.111934
[18] 尚欣宇, 毕晓柯, 谭海彦, 等. 木质素和焦磷酸哌嗪复合膨胀型阻燃剂对环氧树脂材料阻燃性能的影响[J]. 东北林业大学学报, 2023, 51(6): 140-145, 149. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5382.2023.06.022 SHANG Xinyu, BI Xiaoke, TAN Haiyan, et al. Effect of lignin compounded with pyrophosphorie acid piperazine intumescent flame retardant on flame retardant properties of epoxy resin[J]. Journal of Northeast Forestry University, 2023, 51(6): 140-145, 149(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-5382.2023.06.022
[19] ZHANG S, LI S N, WU Q, et al. Phosphorus containing group and lignin toward intrinsically flame retardant cellulose nanofibril-based film with enhanced mechanical properties[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2021, 212: 108699. DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2021.108699
[20] WEI Y, ZHU S, QIAN Q, et al. Hexachlorocyclotriphosphazene functionalized lignin as a sustainable and effective flame retardant for epoxy resins[J]. Industrial Crops and Products, 2022, 187: 115543. DOI: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2022.115543
[21] American Society for Testing Material International. Standard test method for measuring the thermal conductivity: ASTM C518—10[S]. West Conshohocken: ASTM International, 2019.
[22] American Society for Testing Material International. Standard test method for measuring the minimum oxygen concentration to support candle-like combustion of plastics (oxygen index): ASTM D2863—19[S]. West Conshohocken: ASTM International, 2019.
[23] ISO. Reaction-to-fire tests-heat release, smoke production and mass loss rate—Part 1: Heat release rate (cone calorimeter method) and smoke production rate (dynamic measurement): ISO 5660-1: 2015[S]. Geneva: ISO, 2015.
[24] XU W, WANG G, ZHENG X. Research on highly flame-retardant rigid PU foams by combination of nanostructured additives and phosphorus flame retardants[J]. Polymer Degradation and Stability, 2015, 111: 142-150. DOI: 10.1016/j.polymdegradstab.2014.11.008
[25] 毛威, 田飞宇, 朱春锋, 等. 聚磷酸铵分层阻燃处理对杨木大片刨花板性能的影响[J]. 林业工程学报, 2023, 8(3): 71-78. MAO Wei, TIAN Feiyu, ZHU Chunfeng, et al. Effect of flame retarding treatment with ammonium polyphosphite on properties of poplar[J]. Journal of Forestry Engineering, 2023, 8(3): 71-78(in Chinese).
[26] GONG Q, QIN L, WANG N. Combining hyperbranched polyol containing three flame retardant elements, P, N and Si, with expanded graphite to improve the flame retardancy of bio-based rigid polyurethane foam[J]. European Polymer Journal, 2023, 196: 112307. DOI: 10.1016/j.eurpolymj.2023.112307
[27] ZHANG C, ZHANG C, JIANG Z, et al. Design and preparation of flame-retardant cellulose fabric with low strength loss using polycarboxylic acid as crosslinker[J]. Industrial Crops and Products, 2022, 180: 114738. DOI: 10.1016/j.indcrop.2022.114738
[28] XU W, WANG G, XU J, et al. Modification of diatomite with melamine coated zeolitic imidazolate framework-8 as an effective flame retardant to enhance flame retardancy and smoke suppression of rigid polyurethane foam[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials, 2019, 379: 120819. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.120819
[29] LIM K S, BEE S T, SIN L T, et al. A review of application of ammonium polyphosphate as intumescent flame retardant in thermoplastic composites[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering, 2016, 84: 155-174. DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2015.08.066
[30] 黄皓琪, 邓军平, 康乐, 等. 膨胀型阻燃剂的制备和阻燃机理研究进展[J]. 塑料科技, 2023, 51(8): 124-128. HUANG Haoqi, DENG Junping, KANG Le, et al. Research progress of preparation and flame retardant mechanism of intumescent flame retardant[J]. Plastics Science and Technology, 2023, 51(8): 124-128(in Chinese).
-
期刊类型引用(1)
1. 王振廷,赵国华,尹吉勇. 可膨胀石墨在组合聚醚中的沉降问题及阻燃性能. 黑龙江科技大学学报. 2025(01): 65-69 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)
-
目的:聚磷酸铵(APP)作为一种环保无卤素阻燃剂,富含氮和磷元素,能够同时提供酸源和气源,被广泛用作聚合物的阻燃体系。但是,APP在抑烟方面表现不佳。此外,当用作膨胀型阻燃剂时APP 通常需要添加成炭剂才能达到最佳阻燃效果,弱化了与材料基体的界面相容性。因此,本文通过碱木质素(AL)与双(4-异氰酸酯基苯基)甲烷(MDI)微胶囊化改性APP,用于RPU泡沫阻燃,以期在不牺牲力学性能的同时提高阻燃和抑烟性能。方法:(1)制备木质素基核壳结构阻燃剂。在配备有冷凝管和机械搅拌器的500 ml三颈烧瓶中,将45 g APP粉末均匀分散在250 ml乙酸乙酯中,取10 g MDI加入烧瓶中,在50℃氮气氛围中搅拌1 h。然后将5 g AL加到悬浮液中。完成后,将溶液加热至60℃,并在此温度下保持5 h。过滤悬浮液以除去残留的乙酸乙酯,然后将粗产物用乙酸乙酯洗涤三次,放入烘箱在80℃干燥24 h,过80目筛,得到最终产物APP@AL。(2)制备RPU泡沫复合材料。首先,通过使用顶置式搅拌器以约1500 rpm的速度将聚醚多元醇、阻燃剂、催化剂、表面活性剂和发泡剂搅拌5 min来制备均匀的共混物(A部分)。随后,使用相同的顶置式搅拌器,将多亚甲基多苯基异氰酸酯(B部分)与A部分以约3000 rpm的速度搅拌10 s,迅速将搅拌后的混合溶液倒入开放的模具中使泡沫自由上升,并将泡沫置于80℃烘箱中固化24 h。(3)使用SEM-EDS、元素分析仪、FT-IR和XPS分析APP@AL的成分及结构;通过力学性能、极限氧指数、锥形量热仪和拉曼光谱测试,探究APP@AL的阻燃性能及其机制。结果:(1)相较于APP,APP@AL的残炭率由19.3%增加到23.6%,质量损失率降低,热稳定性提高。(2)APP@AL提高了RPU复合材料的力学和保温性能。与添加25wt%APP的RPU泡沫复合材料相比,添加25wt%APP@AL的RPU泡沫复合材料的抗压强度提高31.8%,导热系数降低7.0%。(3)APP@AL提高了RPU复合材料的阻燃性能。与添加25wt%APP的RPU泡沫复合材料相比,添加25wt%APP@AL的RPU泡沫复合材料的平均放热速率和总放热量分别降低了 27.2% 和 24.4%;同时,总产烟量和CO产生量分别显著降低了 47.6% 和 57.0%。结论:(1)APP@AL表层的聚氨酯外壳与泡沫基体有良好的相容性,有利于提升发泡质量,并在发泡过程中牢固地与泡孔壁结合提高泡沫的压缩强度。(2)APP@AL中丰富的炭源使得RPU泡沫的残炭结构致密紧实,在燃烧时阻碍热量的交换和烟气的释放,大幅度提升了RPU泡沫的阻燃和抑烟性能。(3)核壳结构的APP@AL,聚氨酯外壳可以为成炭性能差的RPU泡沫提供炭源,芯层的APP可以作为酸源和气源,它们之间相互作用产生协同效应,使APP@AL具有良好的阻燃和抑烟性能。




 下载:
下载: