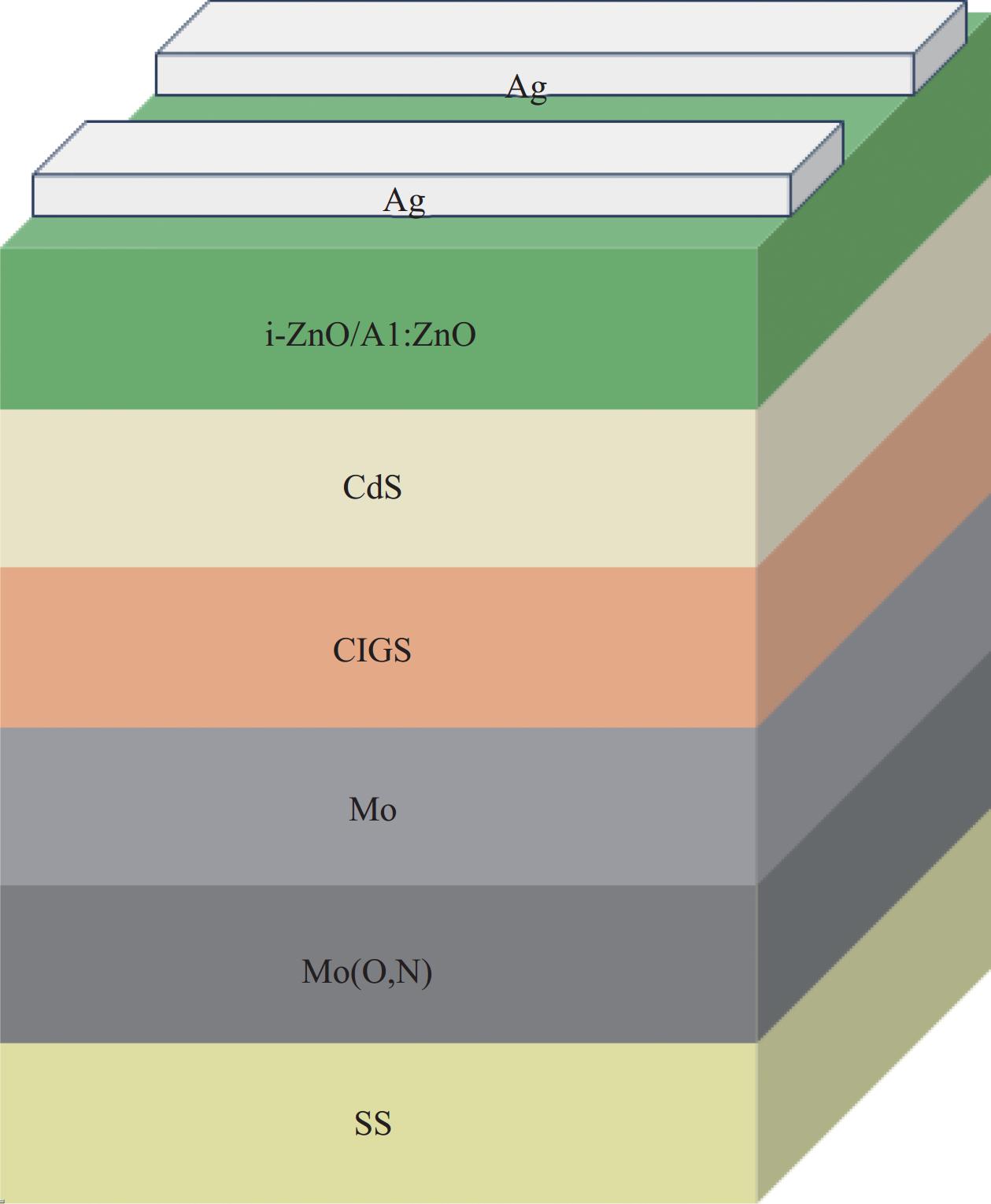
Barrier performance of Mo(N,O) thin films in CIGS solar cells based on stainless steel substrates
-
摘要: 不锈钢衬底铜铟镓硒(CIGS)太阳电池因其优异的光电转换效率和可弯曲特性而被广泛应用。但在制备CIGS薄膜过程中,衬底中的Fe元素会向CIGS薄膜扩散,导致电池性能下降。因此,需要在不锈钢衬底与Mo薄膜之间插入阻挡层来抑制Fe元素的扩散。采用反应磁控溅射方法制备了不同O2流量条件下的Mo(N,O)薄膜,通过XRD、SEM及XPS研究了O2流量对Mo(N,O)薄膜的晶体结构、微观形貌及元素组分的影响,二次离子质谱(SIMS)测试表明插入Mo(N,O)薄膜后,CIGS薄膜中Fe元素的相对强度由无阻挡层时的30 counts降至2 counts。通过优化选用O2流量0.25 mL/min制备Mo(N,O)阻挡层,并制备了CIGS太阳电池,电流密度-电压(J-V)特性测试表明插入Mo(N,O)阻挡层后,电池效率由11.07%提高到14.34%。Abstract: Copper indium gallium selenium (CIGS) solar cells on stainless steel substrate are widely used in the photovoltaics community due to their excellent photoelectric conversion efficiency and flexibility. However, the Fe element will diffuse into the CIGS thin film from the stainless-steel substrate during the process of the preparation of the CIGS thin films, which resulting deteriorated the performance of the devices. Therefore, it is necessary to insert a barrier layer between the stainless steel substrate and the Mo thin film to inhibit the diffusion of the Fe element. Mo(N,O) thin films were produced using reactive magnetron sputtering with varying O2 flow rates. The influence of the O2 flow rate on the crystal structure, microscopic morphology, and elemental composition of the Mo(N,O) thin films was analyzed using an XRD, SEM, and XPS. Base on secondary ion mass spectroscopy (SIMS) testing results, the addition of Mo(N,O) thin film to the fabrication process of CIGS solar cells results in a reduction of Fe element's relative intensity in the CIGS thin film from 30 counts to 2 counts. Moreover, current density-voltage (I-V) characteristic test demonstrated an increase in the photovoltaic conversion efficiency for the flexible CIGS solar cell on a stainless steel substrate, from 11.07% to 14.34%, upon the addition of the Mo(N,O) thin film.
-
Keywords:
- solar cells /
- barrier layer /
- Fe /
- Mo(N,O) thin film /
- O2 /
- CIGS /
- SIMS
-
骨组织缺损,即骨组织的结构遭到破坏,易由遗传、肿瘤、感染和外伤等因素引起,是临床上常见的骨科疾病[1]。小于临界尺寸骨缺损会自发愈合,创口达到6 cm以上的骨缺损通常需要植入人工骨修复材料以恢复损伤处的组织结构[2]。
聚氨基酸 [Poly (amino acid), PAA] 是一类以肽键连接,多种氨基酸为共聚单元的天然高分子聚合物。聚氨基酸与磷灰石类复合材料作为骨组织修复支架被广泛研究,其具有良好的生物相容性、力学性能和易塑形等优点[3-5]。本课题组前期研究表明,PAA与掺杂硒(Selenium, Se)的羟基磷灰石(Hydroxyapatite, HA)复合材料(PAA/Se-HA)具有良好的热稳定性和力学性能,Se-HA掺杂含量在30 wt%时,复合材料在体内外均具有良好的生物相容性和优异的促成骨作用,但其与骨组织的键合牢固性还有待提高[6]。
表面改性技术是一种通过物理或化学的方法改变材料表面的化学成分或组织结构以提高材料性能的一类技术[7]。聚多巴胺(polydopamine, PDA)是一种受蚌类生物启发而模拟形成的大分子,具有良好的生物相容性和可降解性能,可通过共价键或非共价键与多种材料表面形成一层紧密粘附的媒介[8]。多巴胺(dopamine, DA)氧化自聚合后可形成PDA,从而应用于多种材料表面的改性[9]。将材料浸入含有DA的碱性溶液中避光反应即可在材料表面得到PDA层[10]。聚多巴胺作为表面桥连剂可聚集钙离子而诱导物体表面活性HA的矿化和沉积[11]。
HA是骨的主要无机物成分,人工合成HA具有良好的细胞相容性,可促进成骨细胞的黏附和增殖,已被广泛研究并应用于骨缺损的修复[12]。HA中掺杂微量元素提高其促成骨性能是优化性能的重要手段之一[13]。Se是机体必需的微量元素,机体内Se水平与骨骼健康密切相关[14]。研究表明,Se-HA可促进人脂肪来源的间充质干细胞的黏附、增殖和矿化,提高细胞的成骨分化能力[15]。硒改性的磷酸钙骨水泥可促进去卵巢大鼠骨的形成[16]。而且,Se-HA除具有较好的促成骨特性外,还具备抗癌活性[17]。
本文利用PDA的粘性制备了一种表面修饰Se-HA的PAA/Se-HA复合材料(Se-HA@PDA@PAA/Se-HA),以期提高PAA/Se-HA复合材料的促成骨性能及优化其与自身骨组织的牢固键合,为临床修复大面积骨缺损提供理论依据(实验流程如图1所示)。
1. 实验材料及方法
1.1 原材料
四水硝酸钙和聚乙二醇6000 (国药集团化学试剂有限公司);三水磷酸铵、甲基丙烯酸甲酯和钙黄绿素(上海麦克林生化科技股份有限公司);亚硒酸钠和戊巴比妥钠(Sigma);4-氨基丁酸、6-氨基己酸、L-羟脯氨酸、丙氨酸(上海士锋科技有限公司);氨水(天津市天力化学试剂有限公司);磷酸(西陇化工股份有限公司);无水乙醇(天津市致远化学试剂有限公司);CCK-8试剂盒、BCA试剂盒、RIPA裂解液、蛋白抑制剂(武汉博士德生物工程有限公司);碱性磷酸酶(ALP)检测试剂盒(上海碧云天生物技术有限公司);瑞氏吉姆萨染液(比克曼生物科技有限公司);地塞米松(北京博奥拓达有限公司);β-甘油磷酸钠和抗坏血酸(北京索莱宝科技有限公司);二甲酚橙、甲苯胺蓝、碱性品红、青霉素钠和盐酸四环素(上海阿拉丁生化科技股份有限公司)。
1.2 材料的制备
1.2.1 Se-HA的制备
依据文献所述的方法合成Se-HA粉末[18]。具体方法如下:按照Ca/(P + Se)(摩尔比)为1.67配制Ca(NO3)2(0.5 M)、(NH4)3PO4(0.25 M)和Na2SeO3(0.1 M)溶液备用。将聚乙二醇加入Ca(NO3)2溶液中,磁力搅拌30 min后,用氨水调节pH至11。将(NH4)3PO4溶液和Na2SeO3溶液混合,并用氨水调节混合溶液pH至10,备用。在60℃下,将混合溶液缓慢加入Ca(NO3)2溶液中,持续搅拌3 h使其反应完全。反应完全后,室温静置陈化24 h。样品用去离子水和无水乙醇分别洗涤3次,60℃下干燥过夜。将干燥后的样品放入马弗炉中以5℃/min升温速率升温至700~
1200 ℃煅烧,保温3 h,取出研磨、过筛,得到Se-HA粉末。1.2.2 PAA/Se-HA复合材料的制备
PAA/Se-HA复合材料采用原位熔融聚合法合成[19]。称取117.9 g 6-氨基己酸、1.78 g丙氨酸、2.62 g L-羟脯氨酸、4.12 g 4-氨基丁酸加入到三颈烧瓶中,向三颈烧瓶加入1 mL磷酸溶液和45 mL去离子水。将三颈烧瓶置于油浴锅中,调节温度至200℃,不断搅拌,使水完全蒸发。完全蒸发后,停止搅拌并将温度上升至210℃。待三颈烧瓶中的反应物处于熔融状态时,将温度升至220℃,并搅拌1.5 h。然后,向三颈烧瓶中加入30 wt%的Se-HA粉末,继续搅拌2 h,冷却至室温。为防止样品在聚合过程中发生氧化,反应始终采用氮气保护,样品最终标记为PAA/Se-HA。同样方法制备纯PAA聚合物。
1.2.3 Se-HA@PDA@PAA/Se-HA复合材料的制备
Se-HA@PDA@PAA/Se-HA复合材料依据文献所述制备[20]。以10 M Tris-HCl溶液为溶剂配制2 mg/mL的多巴胺Tris溶液。将PAA/Se-HA复合材料浸入多巴胺溶液中,避光磁力搅拌24 h,然后用去离子水反复冲洗除去未聚合的多巴胺。样品60℃真空干燥8 h,备用。将2 g Se-HA粉末溶于10 mL 磷酸盐缓冲盐(PBS,0.001 M,pH=6.8)中,配制质量浓度为20 wt%的Se-HA溶液。将多巴胺改性后的PDA@PAA/Se-HA复合材料置于Se-HA溶液中,低速搅拌24 h。然后,用37℃真空干燥箱充分干燥聚多巴胺辅助Se-HA修饰的PAA/Se-HA复合材料,得到样品Se-HA@PDA@PAA/Se-HA。
1.2.4 复合材料的表征
采用X-射线衍射(XRD,日本理学 Ultima IV)分析材料晶型结构,扫描范围为10 ~ 80°,扫描速度为10 °/min;采用傅里叶红外光谱(FT-IR,日本岛津IRTracer 100)分析材料的官能团组成,测试范围为400 ~
4000 cm−1;采用同步热分析(TG-DSC, 瑞士-Mettler Toledo)在氮气氛围,加热速率为10℃/min条件下表征样品的热稳定性;采用扫描电子显微镜(SEM,美国FEI Quanta 250 FEG)对材料表面形貌进行表征;采用Reger30-50型万能力学试验机以5 mm/min的速度测试样品的力学性能,弯曲强度测试样品尺寸为4×10×50 mm3,抗压强度测试尺寸为10×10×15 mm3。1.2.5 蛋白吸附实验
机体活细胞难以与植入体内的生物材料直接接触发生作用,但其易黏附在生物材料表面吸附的细胞外基质蛋白上。细胞通过蛋白质层的介导而附着、黏附进而铺展到生物材料表面,因此材料体外蛋白吸附行为至关重要[21]。本实验以人体血液中含量最丰富的白蛋白为模型,探究样品的蛋白吸附能力。将样品置于离心管中,加入1 mg/mL的牛血清白蛋白(BSA)溶液,在37℃摇床下吸附24 h。吸取上清液,采用BCA试剂盒在波长为562 nm处测试上清液中蛋白含量,评估样品吸附蛋白后溶液中残余蛋白的剂量。
1.2.6 材料浸提液的制备
将复合材料放入烘箱中60℃干燥12 h,环氧乙烷灭菌。根据GB/T 16886.12[22],称取适量样品于无菌离心管中,将样品以200 mg/mL的标准加入含有1% 青霉素-链霉素溶液的MEM完全培养基中,置于细胞培养箱(37℃,5% CO2)浸提24 ± 2 h。将上清液通过0.22 μm滤膜后得到无菌浸提液。然后将无菌浸提液稀释至1 mg/mL,按照溶液体积加入10%(v/v)胎牛血清(FBS),4℃冷藏备用。通过;采用电感耦合等离子体质谱法(ICP-MS, 美国Agilent 7800)表征样品浸提液中Se离子的浓度。
1.2.7 复合材料的细胞相容性检测
小鼠骨髓间充质干细胞(Bone marrow mesenchymal stem cells,BMSCs,武汉普诺赛生命科技有限公司)在MEM完全培养基(含1%青霉素-链霉素,10% FBS)中复苏和传代,在细胞培养箱(5%CO2,37℃)中培养,取生长至对数期细胞用于实验。
(1) CCK-8检测细胞增殖
使用CCK-8法检测BMSCs在复合材料浸提液中的增殖能力,评估复合材料的生物相容性。将生长至对数期的BMSCs消化离心得到细胞悬液,以2×103个/孔接种至96孔板。细胞贴壁后,用含有样品浸提液的完全培养基代替旧培养基,并孵育1、2和3天。每个孵育期结束时,在避光条件下,将10 μL CCK-8溶液添加到96孔板中,培养箱中孵育2 h后,利用连续波长酶标仪(Molecular Devices,SPECTRA MAX 190)读取450 nm波长下的吸光度(OD值)。完全培养基为空白对照,完全培养基培养的细胞组作为对照组。
(2)瑞氏吉姆萨染色观察细胞形态
将上述96孔板中的培养基倒掉,用PBS清洗2次后,多聚甲醛固定20 min。固定结束后,用PBS洗去残留的多聚甲醛。然后用瑞氏吉姆萨染液染色10 min。随后,用蒸馏水洗去多余的染料,采用倒置显微镜(日本尼康,Ti2-N-ND-1)观察并拍照。
1.2.8 复合材料的ALP活性检测
成骨诱导培养液(Induce)是含有抗坏血酸(100 nM)、β-甘油磷酸钠(10 mM)和地塞米松(10 nM)的MEM完全培养基。
将生长至对数期的BMSCs消化离心得到细胞悬液,以8×103个/孔接种至12孔板。24 h后,用含有成骨诱导液和样品浸提液的培养基代替旧培养基,每2 d更换一次。7 d后,用PBS漂洗细胞,用含有蛋白抑制剂的RIPA裂解液裂解细胞。收集裂解细胞充分震荡,离心,取上清液。通过Bradford蛋白测定法(BCA)测定蛋白浓度。根据ALP检测试剂盒说明书,将蛋白、检测缓冲液和显色底物混合到96孔板,37℃孵育10 min,利用连续波长酶标仪读取405 nm波长下OD值,将其与蛋白浓度做归一化处理,即ALP活性。
1.2.9 复合材料的体内成骨性能
选择体重约3 kg的雄性新西兰大白兔进行体内实验。实验样品采用环氧乙烷灭菌(如图2(a)所示)。本实验得到成都达硕实验动物有限公司实验动物伦理委员会的批准(编号:DOSSYLL20221025001)。
在兔两侧股骨髁建立骨缺损模型。将戊巴比妥钠按照30 mg/kg的剂量从耳缘静脉注射进行麻醉。麻醉后,对股骨髁部位进行去毛和消毒处理,行股骨髁外侧纵行切口,暴露出股骨髁。在股骨髁松质骨区域钻取φ 6 mm×7 mm的骨洞(如图2(b)所示),将灭菌后的材料放入骨洞(如图2(c)所示),逐层缝合。术后分笼喂养,自由饮食。术后3天内按照40 mg/kg的剂量肌肉注射青霉素钠,预防伤口感染。术后2周、4周和6周分别静脉注射钙黄绿素、二甲酚橙和盐酸四环素(具体注射参数如表1所示)。
术后第8周处死上述实验动物,切取样品及周围组织。将样本放入甲醛溶液中浸泡1周进行固定。然后依次放入70%、75%、80%、85%、90%、95%、100%和100%的梯度乙醇溶液中进行脱水处理。脱水处理结束后,进行切片,一部分切片用1%甲苯胺蓝和0.3%碱性品红分别染色后,封片,用倒置显微镜观察组织形态。另外一部分未染色的切片用荧光倒置显微镜观察荧光标记物沉积情况。
表 1 荧光剂的注射参数Table 1. Injection parameters of the fluorescent agentCalcein Xylenol orange Tetracycline hydrochloride Solvent 2% NaHCO3 1% NaHCO3 Normal saline Concentration 5 mg/mL 50 mg/mL 10 mg/mL pH 6-8 6-8 6-8 Dosage 2 mL/kg 2 mL/kg 2 mL/kg Injection time 2 nd week 4 th week 6 th week Color Green Red Yellow Notes: 2 nd-Second; 4 th-Forth; 6 th-Sixth. 2. 结果与讨论
2.1 复合材料的结构和结晶性能表征
图3(a)为Se-HA、PAA、PAA/Se-HA和Se-HA@PDA@PAA/Se-HA复合材料的FT-IR图谱。由图可知,在PAA中,
1536 cm−1和3294 cm−1处为N-H弯曲振动吸收峰,1632 cm−1处为羰基(C=O)拉伸振动吸收峰,2861 cm−1和2933 cm−1处为C—H键的伸缩振动峰。这些特征吸收峰表明合成的PAA具有酰胺结构。在Se-HA中,1083 cm−1和1019 cm−1处为磷酸基不对称的伸缩振动,600 cm−1处为O-P-O不对称弯曲振动吸收峰,1648 cm−1处为O-H弯曲振动峰,767 cm−1处为O-Se-O特征吸收峰。在PAA/Se-HA和Se-HA@PDA@PAA/Se-HA复合材料中,上述特征吸收峰的强度略有变化,但并未出现新的吸收峰,这表明复合材料中并未形成其他物质。由XRD和FT-IR结果可得出Se-HA@PDA@PAA/Se-HA复合材料具有PAA和Se-HA的化学属性,其由PAA和Se-HA共同组成的。图3(b)为Se-HA、PAA、PAA/Se-HA和Se-HA@PDA@PAA/Se-HA复合材料的XRD图谱。2θ = 20°和2θ = 24°是PAA的特征衍射峰。Se-HA在(002)、(210)、(211)、(300)、(310)、(202)等处对应PDF 09-0423标准光谱[23,24]。在PAA/Se-HA和Se-HA@PDA@PAA/Se-HA中均存在PAA和Se-HA的特征衍射峰,未出现新的峰,说明这两种复合材料均由PAA和Se-HA组成,未形成新的物质。
2.2 复合材料的热稳定性
图4是PAA、PAA/Se-HA和Se-HA@PDA@PAA/Se-HA复合材料的TG(a)和DSC(b)曲线。由图4(a)可知,Se-HA@PDA@PAA/Se-HA复合材料的最大分解温度和最终剩余质量分别约为461℃和35.55%。Se-HA在PAA中的添加明显提高了复合材料的最大分解温度和最终剩余质量,表面Se-HA修饰的复合材料相比未修饰的复合材料最大分解温度和最终剩余
质量变化较小。Se-HA在PAA中的掺杂可能会限制PAA聚合物链的运动,阻碍其从固态到气态的转化,因此增加Se-HA在PAA中的掺杂能够提高材料的最大分解温度[25]。由图4(b)可知,Se-HA@PDA@PAA/Se-HA复合材料的熔融温度约为210℃,相比PAA/Se-HA复合材料有所增大, PAA的熔融温度约为207℃。Se-HA在PAA中的均匀掺杂提高了复合材料的熔融温度,推测可能是Se-HA的掺杂起到异相成核作用[26]。
2.3 复合材料的微观形貌
图5为Se-HA、PAA、PAA/Se-HA和Se-HA@PDA@PAA/Se-HA复合材料的SEM图像。由图可知,合成的Se-HA颗粒为大小均匀的纳米结构(约100 nm)。图5(b)显示PAA的表面几乎是光滑的,没有颗粒物质沉积。图5(c)显示PAA/Se-HA30复合材料表面粗糙,有颗粒物质沉积,无明显团聚,表明Se-HA可均匀分散在PAA基体中。图5(d)显示,Se-HA@PDA@PAA/Se-HA复合材料表面粗糙,Se-HA可较为均匀的分散在PAA/Se-HA复合材料表面,这可能有利于细胞的黏附[27]。
表2是PAA,PAA/Se-HA和Se-HA@PDA@PAA/Se-HA复合材料的力学性能。由表可知, Se-HA在PAA中的均匀掺杂明显提高了PAA/Se-HA复合材料的抗压强度和屈服强度,但弯曲强度有所下降;推测可能是聚合物中无机相的掺杂使材料刚性和脆性均增大,弯曲时材料中的亚微裂纹影响了弯曲强度,但压缩有利于裂纹的闭合,从而使复合材料的承重力增大。表面Se-HA修饰的PAA/Se-HA复合材料相比无表面修饰的复合材料力学性能均有所降低,推测可能是样品浸入多巴胺溶液表面改性过程中,溶液渗入样品亚微裂纹中使样品聚合物链有部分断裂。人体皮质骨抗压强度为50-140 MPa,弯曲强度为80-100 MPa[28],这表明本文所述的Se-HA@PDA@PAA/Se-HA复合材料具有良好的生物力学性能,能够满足骨修复的力学需求。
表 2 PAA,PAA/Se-HA 和 Se-HA@PDA@PAA/Se-HA 复合材料的力学性能Table 2. Mechanical properties of PAA,PAA/Se-HA and Se-HA@PDA@PAA/Se-HA compositesSamples Bending strength/MPa Compressive strength/MPa Yield strength/MPa PAA 89.64±0.25 92.34±0.88 83.74±0.92 PAA/Se-HA 85.34±0.69 104.25±0.79 98.67±0.98 Se-HA@PDA@PAA/Se-HA 80.28±0.44 103.81±0.25 96.36±0.83 2.4 复合材料的力学性能
2.5 复合材料表面生物活性表征
图6为PAA、PAA/Se-HA和Se-HA@PDA@PAA/Se-HA复合材料吸附蛋白后溶液中残余蛋白含量。结果显示,PAA/Se-HA和Se-HA@PDA@PAA/Se-HA复合材料组未被吸附的蛋白量明显少于PAA组,Se-HA@PDA@PAA/Se-HA复合材料组未被吸附的蛋白量少于PAA/Se-HA复合材料组,表明Se-HA@PDA@PAA/Se-HA复合材料组比PAA/Se-HA复合材料组吸附蛋白量更大,证明多巴胺辅助Se-HA修饰的PAA/Se-HA复合材料具有更好的表面生物活性,有利于细胞黏附。
2.6 复合材料的细胞相容性
通过CCK-8法检测PAA、PAA/Se-HA和Se-HA@PDA@PAA/Se-HA复合材料浸提液与BMSCs共培养1、2和3天的OD值,结果如图7所示。图8为样品浸提液与BMSCs共培养 1、2和3天后的瑞氏吉姆萨染色显微镜观察结果。由图7可知,随着培养时间的增加,每组样品OD值均有所增加。细胞培养三天后,PAA/Se-HA组和Se-HA@PDA@PAA/Se-HA组OD值明显高于对照组,说明这两组细胞增殖明显。结果表明,Se-HA在PAA中的掺杂对BMSCs增殖具有促进作用,表面吸附Se-HA后,Se-HA@PDA@PAA/Se-HA组的促BMSCs增殖作用最为明显。由图8可知,BMSCs骨架呈蓝紫色,细胞形态正常,呈扁平纺锤形。随着时间的增长,细胞呈旋涡式生长。图7和图8结果共同表明,Se-HA在PAA中的掺杂和在PAA/Se-HA复合材料表面的修饰对BMSCs无毒性,可促进细胞的增殖。
表3为ICP-MS检测的PAA/Se-HA和Se-HA@PDA@PAA/Se-HA复合材料浸提液中Se元素含量。高浓度的Se会对细胞产生毒性作用,通过测试复合材料浸提液中Se元素的浓度可评估该材料是否因Se的掺杂影响BMSCs的活力。表3显示,PAA/Se-HA组释放的Se元素浓度为184.04 μg/L,Se-HA@PDA@PAA/Se-HA组释放的Se元素浓度为564.55 μg/L。结合图7细胞增殖结果共同表明,本实验中Se-HA在PAA/Se-HA内部的掺杂和表面的覆盖均对细胞无毒,且能促进细胞增殖。
表 3 PAA/Se-HA和Se-HA@PDA@PAA/Se-HA复合材料浸提液中Se元素含量Table 3. The Se concentration from extract of PAA/Se-HA and Se-HA@PDA@PAA/Se-HA compositeSamples The theoretical doping of Se/% The actual release of Se/(μg·L−1) PAA/Se-HA 0.9 184.04 Se-HA@PDA@PAA/Se-HA —— 564.55 2.7 ALP活性
ALP是评价成骨细胞早期成骨分化的标志物[29],可用于评价材料诱导成骨细胞成骨分化的能力。图9是BMSCs在含有成骨诱导液和样品浸提液的培养基中培养7天的ALP活性。由图可知,ALP活性按大小排序为Se-HA@PDA@PAA/Se-HA组> PAA/Se-HA组>PAA组>Induce>Control,即PAA/Se-HA复合材料ALP活性高于PAA,表面覆盖Se-HA的复合材料相比未覆盖Se-HA的复合材料的ALP活性更高,表明PAA/Se-HA复合材料相比PAA具有更好的诱导细胞成骨分化的能力,表面Se-HA的覆盖使PAA/Se-HA复合材料促细胞成骨分化能力更佳,证实其具有优异的诱导细胞成骨分化性能。该结果与表面生物活性表征中蛋白吸附实验结果一致,Se-HA@PDA@PAA/Se-HA复合材料吸附蛋白能力最佳,具有较好的表面活性,该结果表明其表面有利于细胞的黏附;其浸提液与BMSCs共培养表现出较高的ALP活性,表明该复合材料能够较好的诱导成骨细胞成骨分化。
2.8 复合材料体内成骨性能
图10是PAA、PAA/Se-HA和Se-HA@PDA@PAA/Se-HA复合材料植入股骨髁缺损8周后的碱性品红和甲苯胺蓝染色结果。由图可知,所有样品植入骨缺损后均可与新形成的骨组织直接连接,无软组织包裹,骨细胞形态正常。但是,PAA和PAA/Se-HA复合材料植入骨缺损后经过脱水处理的样品与新骨有分离现象,说明植入物与新骨的键合紧密性差。Se-HA@PDA@PAA/Se-HA复合材料植入骨缺损后经过脱水处理的样品与新骨仍然紧密结合,说明植入物与新骨具有较好的键合,不易松动。结果表明,PAA、PAA/Se-HA和Se-HA@PDA@PAA/Se-HA复合材料均能够引导骨再生,Se-HA@PDA@PAA/Se-HA复
![]() 图 10 (a/d) PAA、(b/e) PAA/Se-HA和(c/f) Se-HA@PDA@PAA/Se-HA复合材料植入股骨髁缺损8周后的(a/b/c)碱性品红和(d/e/f)甲苯胺蓝染色结果(标尺:100 μm)Figure 10. The histological observation of (a/b/c) basic fuchsin and (d/e/f) toluidine blue staining after implantation of (a/d) PAA, (b/e) PAA/Se-HA and (c/f) Se-HA@PDA@PAA/Se-HA composite into the femoral condyle for 8 weeks (scale:100 μm)
图 10 (a/d) PAA、(b/e) PAA/Se-HA和(c/f) Se-HA@PDA@PAA/Se-HA复合材料植入股骨髁缺损8周后的(a/b/c)碱性品红和(d/e/f)甲苯胺蓝染色结果(标尺:100 μm)Figure 10. The histological observation of (a/b/c) basic fuchsin and (d/e/f) toluidine blue staining after implantation of (a/d) PAA, (b/e) PAA/Se-HA and (c/f) Se-HA@PDA@PAA/Se-HA composite into the femoral condyle for 8 weeks (scale:100 μm)合材料植入机体后与新骨的键合更加紧密,说明其与骨细胞的黏附更好,该结果与蛋白吸附实验结果一致,说明Se-HA@PDA@PAA/Se-HA复合材料能够更好的与细胞黏附。
荧光标记法是一种追踪骨矿化沉积的常用方法,可用于新骨的生长方向和形成定位的研究,选择不同时间点注射不同荧光标志物可追踪新骨形成情况[30]。图11是PAA、PAA/Se-HA和Se-HA@PDA@PAA/Se-HA复合材料植入股骨髁缺损部位8周后的荧光标记结果。由图可知,绿色荧光 (2 W)、红色荧光(4 W)和黄色荧光(6 W)均有显示,说明样品植入后2 W有新骨的形成。黄色荧光的密度最大,且其与样品直接接触,说明样品引导大量的新骨形成发生于6 W左右。
3. 结 论
人工骨修复材料是骨组织缺损修复的替代材料,理想的人工骨修复材料应具有良好的生物相容性和体内促成骨作用。聚多巴胺(PDA)是由多巴胺单体自聚合形成的大分子聚合物,具有良好的粘附性。本文将Se-HA通过PDA辅助粘附于含30% Se-HA的PAA/Se-HA复合材料(Se-HA@PDA@PAA/Se-HA)表面,提高PAA/Se-HA复合材料的促成骨性能。主要结论如下:
(1) FT-IR和XRD结果表明,Se-HA@PDA@PAA/Se-HA复合材料具有PAA和Se-HA的化学属性,其由PAA和Se-HA共同组成。SEM结果表明,Se-HA可均匀的分散在PAA/Se-HA复合材料内部和表面。
(2)热稳定性和力学性能结果表明,Se-HA@PDA@PAA/Se-HA复合材料的熔融温度约为210℃,最大分解温度为约为461℃,分解后最终剩余质量为35.55%。Se-HA@PDA@PAA/Se-HA复合材料的弯曲强度约80 MPa,抗压强度约104 MPa,屈服强度约96 MPa。
(3)蛋白吸附实验结果表明,Se-HA@PDA@PAA/Se-HA复合材料相比PAA/Se-HA复合材料蛋白吸附量更大,证明多巴胺辅助Se-HA修饰的PAA/Se-HA复合材料具有较好的表面生物活性,该结果表明其表面有利于细胞黏附。
(4) PAA/Se-HA复合材料浸提液释放的Se元素浓度为184.04 μg/L,Se-HA@PDA@PAA/Se-HA复合材料浸提液释放的Se元素浓度为564.55 μg/L。PAA/Se-HA复合材料浸提液能够促进BMSCs的增殖,Se-HA@PDA@PAA/Se-HA复合材料促BMSCs增殖作用更佳,两组复合材料浸提液中BMSCs形态正常,呈扁平纺锤形;随着时间的增长,细胞呈旋涡式生长。该结果共同表明,Se-HA在PAA中的掺杂和在PAA/Se-HA复合材料表面的覆盖对BMSCs无毒性,可明显促进细胞的增殖。
(5)碱性磷酸酶(ALP)活性实验结果表明,PAA/Se-HA复合材料ALP活性高于PAA,Se-HA@PDA@PAA/Se-HA复合材料相比PAA/Se-HA复合材料的ALP活性更高,表明PAA/Se-HA复合材料相比PAA具有更好的诱导细胞成骨分化的能力,表面Se-HA的修饰使PAA/Se-HA复合材料促细胞成骨分化能力更佳,证实其具有优异的诱导细胞成骨分化性能。
(6)动物实验结果表明,Se-HA@PDA@PAA/Se-HA复合材料植入机体后与新骨的键合牢固,与骨细胞的黏附好,该结果与蛋白吸附实验结果一致,说明Se-HA@PDA@PAA/Se-HA复合材料能够更好的与细胞黏附。样品植入骨缺损后2 w有新骨的形成,大量的新骨形成发生于6 w左右。该结果共同表明,复合材料能够引导新骨的生成。
综上所述,将Se-HA通过PDA辅助粘附于PAA/Se-HA复合材料表面可显著提高PAA/Se-HA复合材料的促成骨性能,且能增加其与骨组织的牢固键合,有望成为骨缺损修复替代生物材料。
-
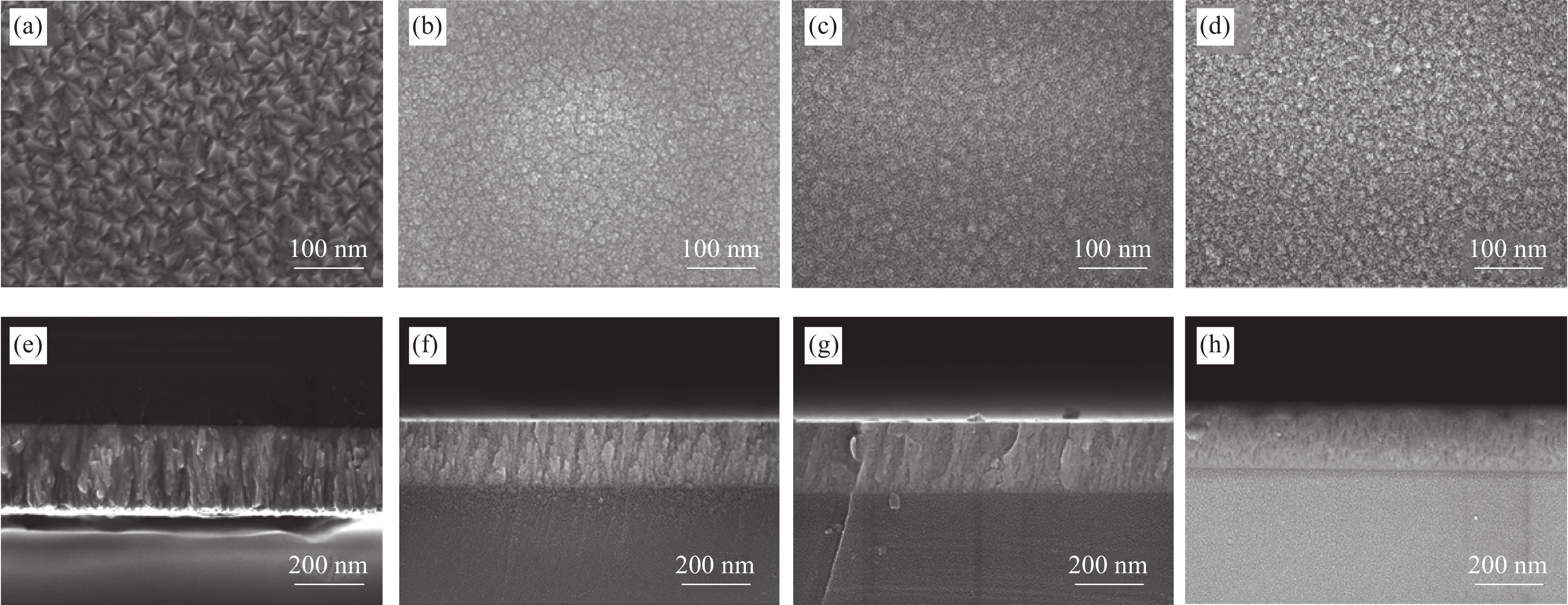
图 2 不同O2流量条件下Mo(N,O)薄膜的SEM图像:表面形貌:(a) 0 mL/min;(b) 0.15 mL/min;(c) 0.20 mL/min;(d) 0.25 mL/min;截面形貌:(e) 0 mL/min;(f) 0.15 mL/min;(g) 0.20 mL/min;(h) 0.25 mL/min
Figure 2. SEM images of Mo(N,O) thin films at different O2 flow rates: Surface: (a) 0 mL/min; (b) 0.15 mL/min; (c) 0.20 mL/min; (d) 0.25 mL/min; Section: (e) 0 mL/min; (f) 0.15 mL/min; (g) 0.20 mL/min; (h) 0.25 mL/min
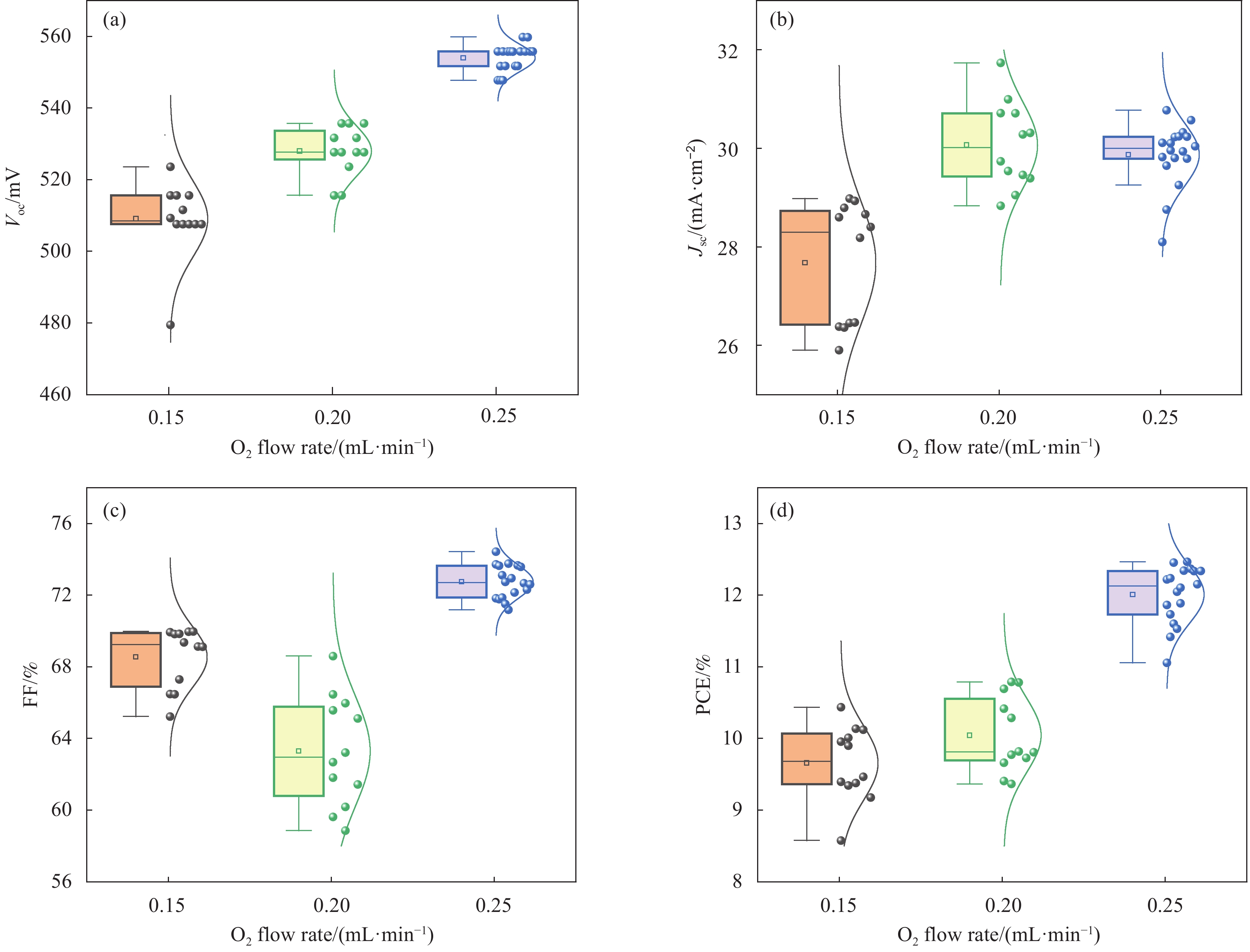
图 5 不同O2流量下制备的Mo(N,O)薄膜的CIGS太阳电池特性参数:(a)开路电压Voc;(b)短路电流密度Jsc;(c)填充因子(FF);(d)光电转换效率(PCE)
Figure 5. Parameters of CIGS thin-film solar cells with Mo(N,O) thin films deposited at different O2 flow rates: (a) Open circuit voltage Voc; (b) Short circuit current density Jsc; (c) Fill factor (FF); (d) Photoelectric conversion efficiency (PCE)
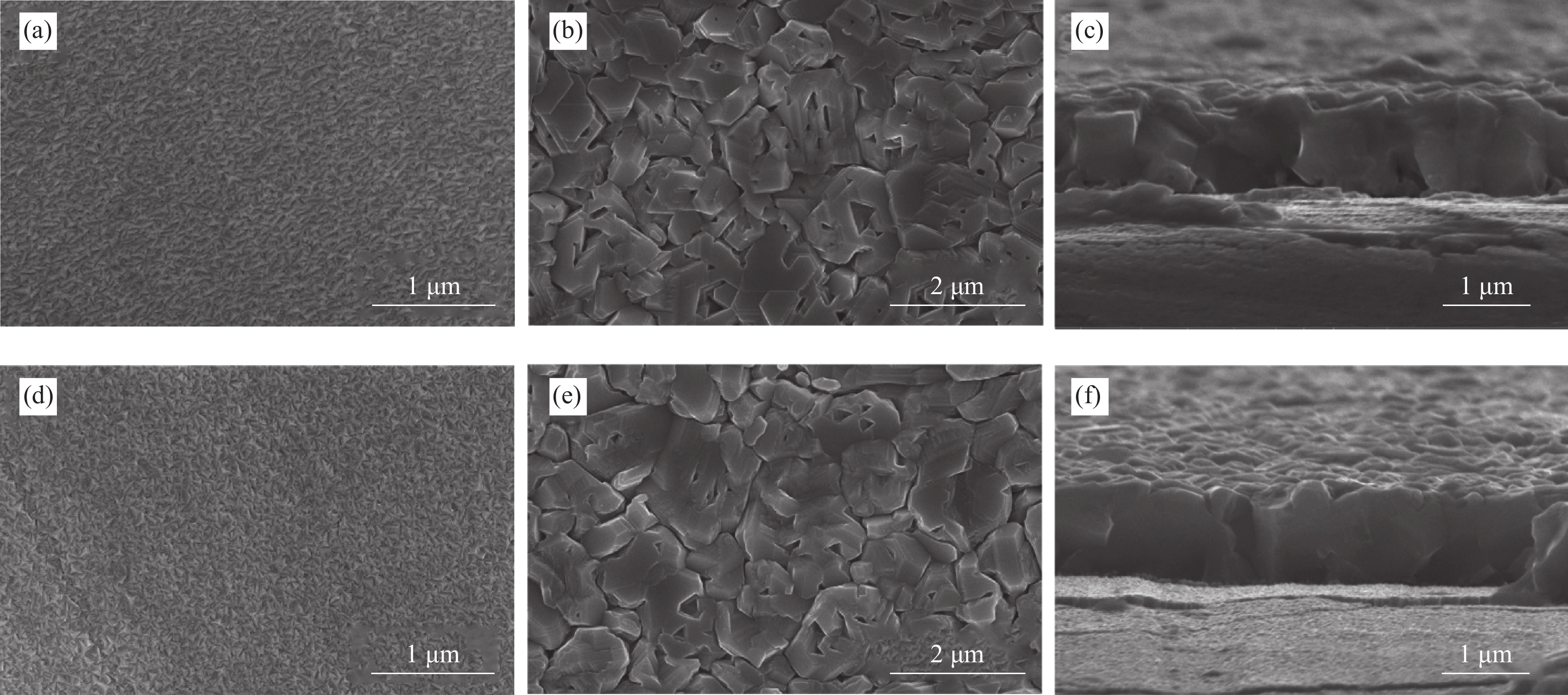
图 7 有无阻挡层所制备的Mo薄膜和CIGS薄膜的SEM图像:(a) SS/Mo表面形貌;(b) SS/Mo/CIGS表面形貌;(c) SS/Mo/CIGS截面形貌;(d) SS/Mo(N,O)/Mo表面形貌;(e) SS/Mo(N,O)Mo/CIGS表面形貌;(f ) SS/Mo(N,O)Mo/CIGS截面形貌
Figure 7. SEM images of Mo thin film and CIGS thin film prepared with and without barrier layer: (a) SS/Mo surface image; (b) SS/Mo/CIGS surface image; (c) SS/Mo/CIGS section image; (d) SS/Mo(N,O)/Mo surface image; (e) SS/Mo(N,O)Mo/CIGS surface image; (f) SS/Mo(N,O)Mo/CIGS section image
表 1 Mo(N,O)薄膜制备工艺参数
Table 1 Process parameters of Mo(N,O) thin film
Ar:N2:O2/
(mL·min−1)Sputtering
pressure/PaSputtering
power/WSubstrate
temperature/
℃Thickness/
nm30:20:0 1 150 100 300 30:20:0.15
30:20:0.20
30:20:0.251
1
1150
150
150100
100
100300
300
300表 2 不同O2流量下制备Mo(N,O)薄膜的CIGS太阳电池特性参数
Table 2 Parameters of CIGS solar cells with Mo(N,O) thin films deposited at different O2 flow rates
O2 flow rate/
(mL·min−1)Voc/mV Jsc/(mA·cm-2) FF/% PCE/% 0.15 509.1±10.6 27.7±1.2 68.6±1.7 9.7±0.5 0.20
0.25528.0±6.9
554.0±3.730.1±0.9
29.9±0.663.3±3.1
72.8±0.910.1±0.5
12.1±0.4表 3 有无阻挡层CIGS太阳电池特性参数
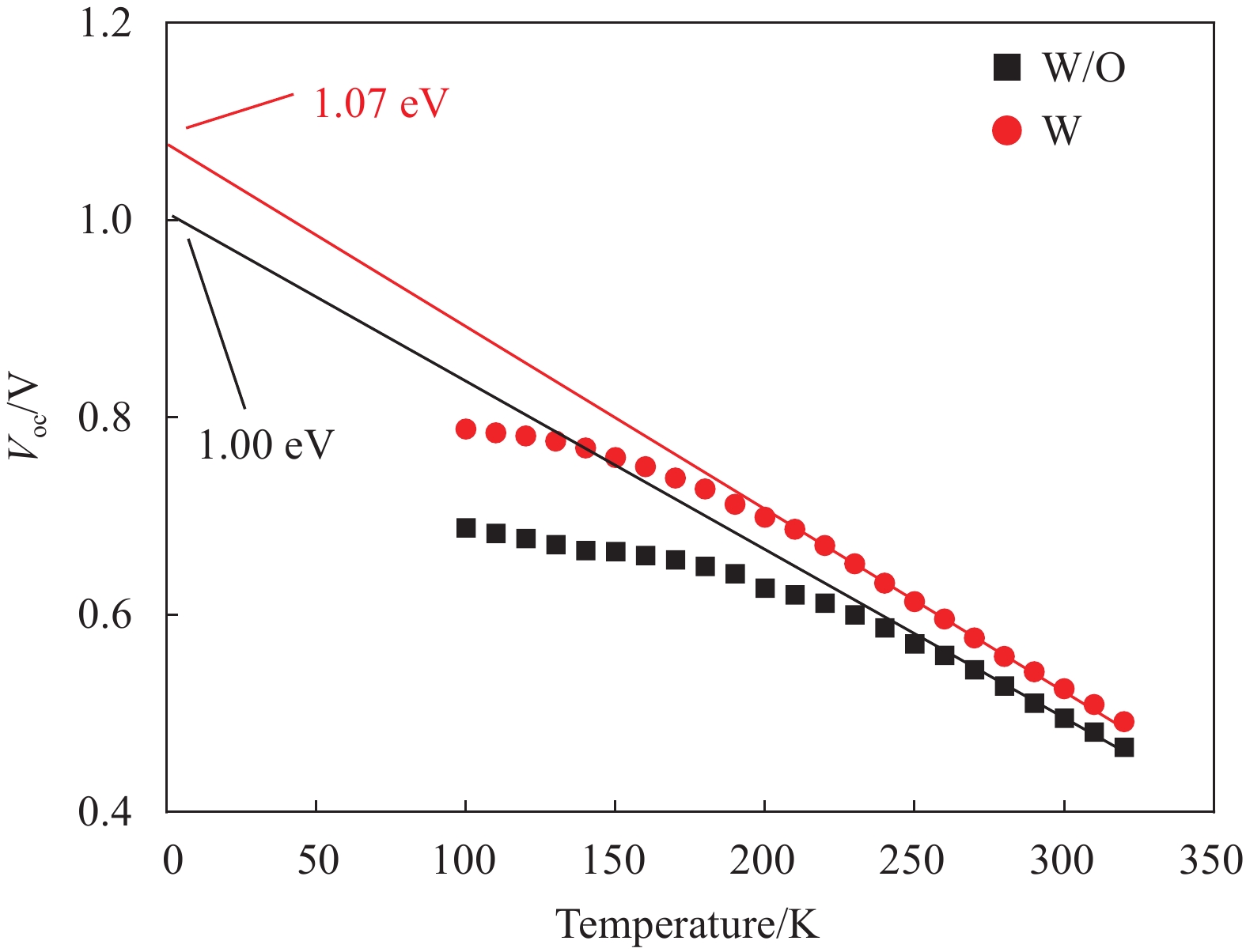
Table 3 Characteristic parameters of CIGS solar cells with or without barrier layer
R/(Ω·cm2) G/(mS·cm−2) A J0/(mA·cm−2) W/O
W1.70
1.273.07
1.291.74
1.512.16×10−4
7.59×10−5Notes: R—Series resistance; G—Reciprocal of the shunt resistance; A—Diode ideality factor; J0—Reverse saturation current. -
[1] BARMAN B, KALITA P. Influence of back surface field layer on enhancing the efficiency of CIGS solar cell[J]. Solar Energy, 2021, 216: 329-337. DOI: 10.1016/j.solener.2021.01.032
[2] FEURER T, REINHARD P, AVANCINI E, et al. Progress in thin film CIGS photovoltaics—Research and development, manufacturing, and applications[J]. Progress in Photovoltaics: Research and Applications, 2017, 25(7): 645-667. DOI: 10.1002/pip.2811
[3] HU D, MA B, LI X, et al. Innovative and sustainable separation and recovery of valuable metals in spent CIGS materials[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production, 2022, 350: 131426.
[4] NAKAMURA M, YAMAGUCHI K, KIMOTO Y, et al. Cd-free Cu(In,Ga)(Se,S)2 thin-film solar cell with record efficiency of 23.35%[J]. IEEE Journal of Photovoltaics, 2019, 9(6): 1863-1867. DOI: 10.1109/JPHOTOV.2019.2937218
[5] 赵彦民, 李威, 闫礼, 等. 卷对卷技术制备大面积柔性CIGS薄膜太阳电池吸收层[J]. 人工晶体学报, 2011, 40(2): 379-382. ZHAO Yanmin, LI Wei, YAN Li, et al. Deposition for scale-up absorption layer of CIGS thin-film solar cell on flexible substrate using roll-to-roll technology[J]. Journal of Synthetic Crystals, 2011, 40(2): 379-382(in Chinese).
[6] CHIRILA A, BUECHELER S, PLANEZZI F, et al. Highly efficient Cu(In,Ga)Se2 solar cells grown on flexible polymer films[J]. Nature Materials, 2011, 10(11): 857-861. DOI: 10.1038/nmat3122
[7] PIANEZZI F, CHIRILA A, BLOSCH P, et al. Electronic properties of Cu(In,Ga)Se2 solar cells on stainless steel foils without diffusion barrier[J]. Progress in Photovoltaics: Research and Applications, 2012, 20(3): 253-259. DOI: 10.1002/pip.1247
[8] OTTE K, MAKHOVA L, BRAUN A, et al. Flexible Cu(In,Ga)Se2 thin-film solar cells for space application[J]. Thin Solid Films, 2006, 511: 613-622.
[9] BREMAUD D, RUDMANN D, KAELIN M, et al. Flexible Cu(In,Ga)Se2 on Al foils and the effects of Al during chemical bath deposition[J]. Thin Solid Films, 2007, 515(15): 5857-5861. DOI: 10.1016/j.tsf.2006.12.152
[10] JACKSON P, GRABITA P, STROHM A, et al. Contamination of Cu(In,Ga)Se2 by metallic substrates[C]//Proceedings of the 19th European Photovoltaic Solar Energy Conference and Exhibition. Munich: WIP Renewable Energies, 2004: 1936-1938.
[11] HERZ K, EICKE A, KESSLER F, et al. Diffusion barriers for CIGS solar cells on metallic substrates[J]. Thin Solid Films, 2003, 431-432: 392-397.
[12] WUERZ R, EICKE A, FRANKENFELD M, et al. CIGS thin-film solar cells on steel substrates[J]. Thin Solid Films, 2009, 571(7): 2415-2418.
[13] SHI C Y, SUN Y, HE Q, et al. Cu(In,Ga)Se2 solar cells on stainless-steel substrates covered with ZnO diffusion barriers[J]. Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, 2009, 93(5): 654-656. DOI: 10.1016/j.solmat.2008.12.004
[14] PARK H, KIM S C, BAE H C, et al. ALD-grown Al2O3 as a diffusion barrier for stainless steel substrates for flexible Cu(In,Ga)Se2 solar cells[J]. Molecular Crystals and Liquid Crystals, 2011, 551(1): 147-153. DOI: 10.1080/15421406.2011.600634
[15] KIM K B, KIM M, BAEK J, et al. Influence of Cr thin films on the properties of flexible CIGS solar cells on steel substrates[J]. Electronic Materials Letters, 2014, 10: 247-251. DOI: 10.1007/s13391-013-3158-3
[16] HERZ K, KESSLER F, WACHTER R, et al. Dielectric barriers for flexible CIGS solar modules[J]. Thin Solid Films, 2002, 403: 384-389.
[17] 陈海波, 周继承, 李幼真. Ta基纳米薄膜扩散阻挡特性的比较研究[J]. 功能材料, 2007, 4(38): 655-658. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9731.2007.04.043 CHEN Haibo, ZHOU Jicheng, LI Youzhen. Comparison of diffusion barrier properties of nanoscale Ta-based thin- films[J]. Journal of Functional Materials, 2007, 4(38): 655-658(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1001-9731.2007.04.043
[18] 韩胜男, 常宣, 陈静伟, 等. MoNx薄膜制备及其在柔性不锈钢CIGS太阳电池中的应用[J]. 太阳能学报, 2023, 44(7): 122-128. HAN Shengnan, CHANG Xuan, CHEN Jingwei, et al. Fabrication of MoNx thin films and its applications in flexible stainless steel CIGS solar cells[J]. Acta Energiae Solaris Sinica, 2023, 44(7): 122-128(in Chinese).
[19] XU C K, ZHANG H W, PARRY J, et al. A single source three-stage evaporation approach to CIGS absorber layer for thin film solar cells[J]. Solar Energy Materials and Solar Cells, 2013, 117: 357-362. DOI: 10.1016/j.solmat.2013.06.006
[20] ULICNA S, ARNOU P, ABBAS A, et al. Deposition and application of a Mo-N back contact diffusion barrier yielding a 12.0% efficiency solution-processed CIGS solar cell using an amine-thiol solvent system[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A, 2019, 7(12): 7042-7052. DOI: 10.1039/C8TA12089G
[21] KIM G T, PARK T K, CHUNG H, et al. Growth and characterization of chloronitroaniline crystals for optical parametric oscillators: I. XPS study of Mo-based compounds[J]. Applied Surface Science, 1999, 152(1-2): 35-43. DOI: 10.1016/S0169-4332(99)00293-7
[22] LI B Y, ZHANG Y, WANG H, et al. Preferred orientation of Cu(In,Ga)Se2 thin film deposited on stainless steel substrate[J]. Progress in Photovoltaics: Research and Applications, 2013, 21(5): 838-848. DOI: 10.1002/pip.2164
[23] 陈永翀, 黎振华, 其鲁, 等. 固体中的扩散应力研究[J]. 金属学报, 2006, 42(3): 225-233. CHEN Yongchong, LI Zhenhua, QI Lu, et al. Diffusion-induced stresses in solids[J]. Acta Metallurgica Sinica, 2006, 42(3): 225-233(in Chinese).
[24] OKADA K. Activation energy of mullitization from various starting materials[J]. Journal of the European Ceramic Society, 2008, 28(2): 377-382.
[25] WANG C, ZHUANG D M, ZHAO M, et al. The effects of preheating temperature on CuInGaSe2/CdS interface and the device performance[J]. Solar Energy, 2019, 194: 11-17. DOI: 10.1016/j.solener.2019.10.054
[26] WEI Y W, ZHUANG D M, ZHAO M, et al. Pre-deposition of CdS layer to improve the diode quality of CZTSSe solar cells[J]. Materials Letters, 2018, 229: 372-374. DOI: 10.1016/j.matlet.2018.07.066
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 雷东,刘锟,杨富康,裴坤坤,胡国新,高寒阳. 石墨烯/聚氨酯复合材料的制备及其力学性能分析. 功能材料. 2022(01): 1181-1184+1189 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 彭旭涛,熊巍,侯世维,刘濮源,何文俊,李贤娟,李晓燕. 后处理对连续玻璃纤维增强聚氨酯复合材料的影响. 塑料工业. 2022(07): 97-105 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(3)
-
目的
不锈钢衬底铜铟镓硒太阳电池因其优异的光电转换效率和可弯曲特性而被广泛应用。但在制备铜铟镓硒(CIGS)薄膜过程中,衬底中的Fe元素会向CIGS薄膜扩散,形成Fe、Fe深能级缺陷,降低电池的开路电压、短路电流导致电池性能下降。因此,需要在不锈钢衬底与Mo薄膜之间插入阻挡层来抑制Fe元素的扩散。按照阻挡能力排名,单晶、纳米晶和非晶材料居前;其次是填充结构和巨大晶粒材料;多晶材料阻挡能力相对较弱。本文采用反应磁控溅射方法制备非晶Mo(N,O)薄膜作为不锈钢衬底CIGS太阳电池的阻挡层。
方法采用反应磁控溅射制备Mo(N,O)薄膜,通过扫描电子显微镜(SEM)和X射线衍射仪(XRD)研究了O流量对Mo(N,O)薄膜特性的影响,同时通过SEM、XRD和二次离子质谱(SIMS)研究了阻挡层对Mo、CIGS薄膜特性影响,并制备了结构为SS/Mo(N,O)/Mo/CIGS/CdS/i-ZnO/Al:ZnO/Ag的CIGS太阳电池,通过I-V和EQE分析阻挡层对电池器件的影响。
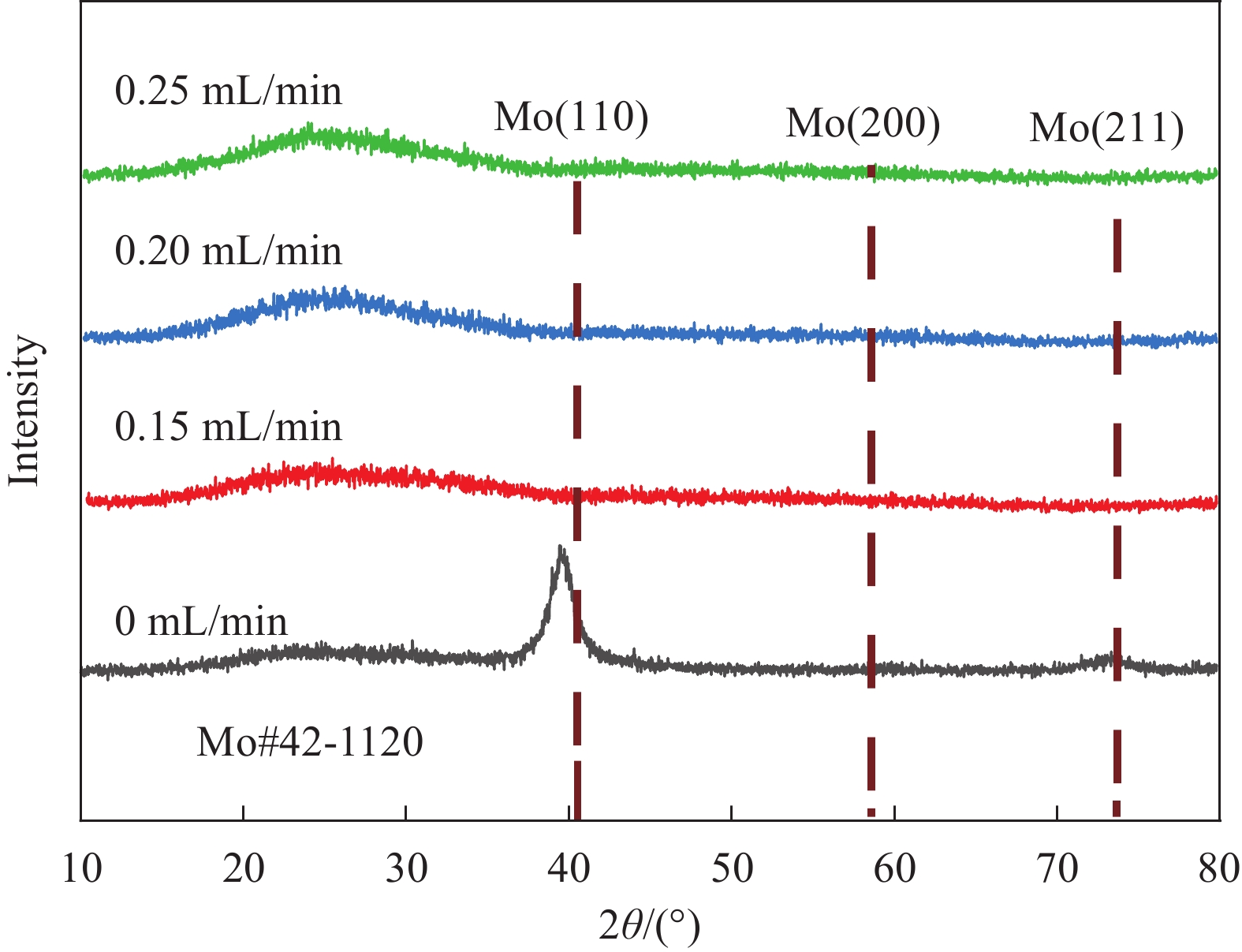
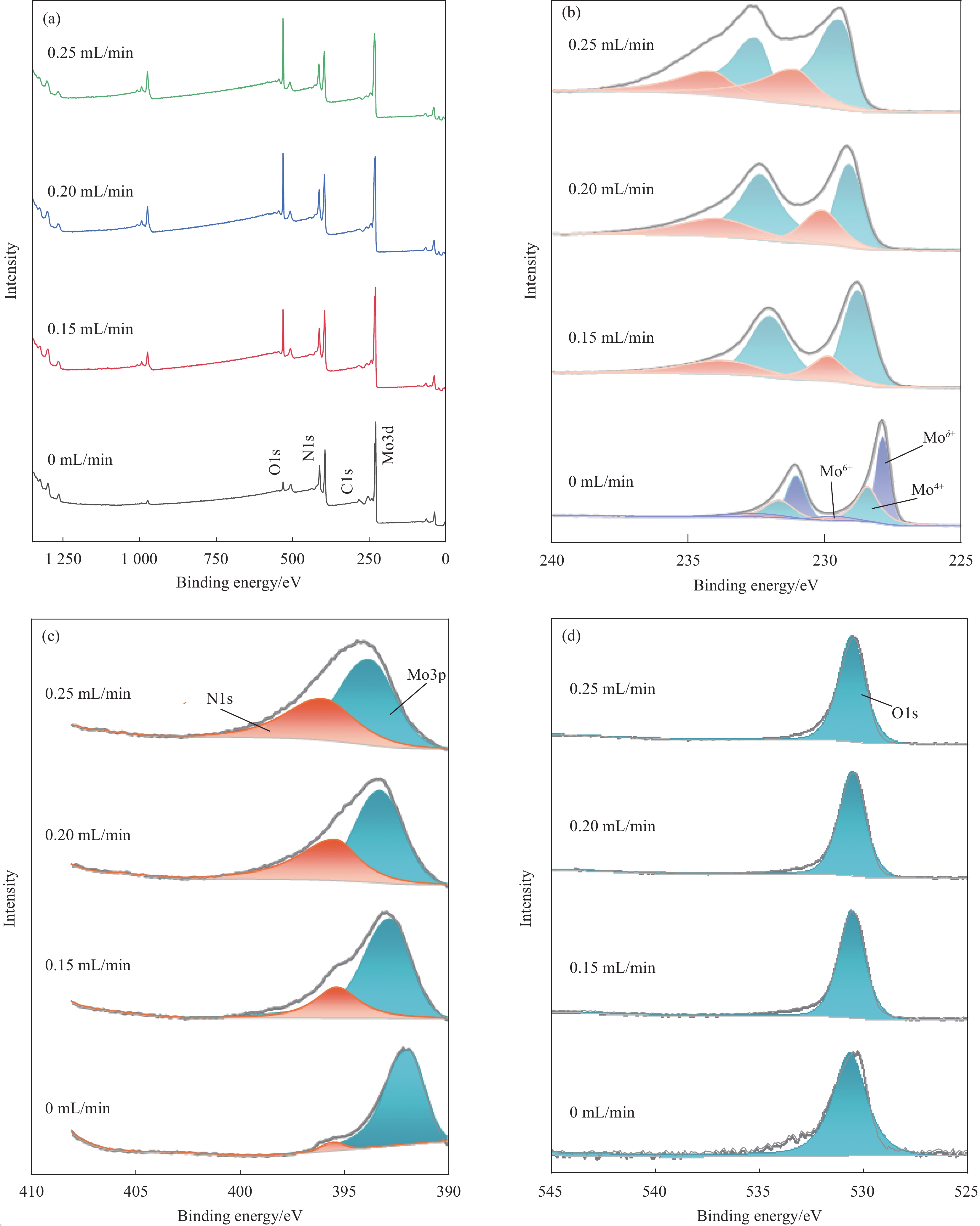
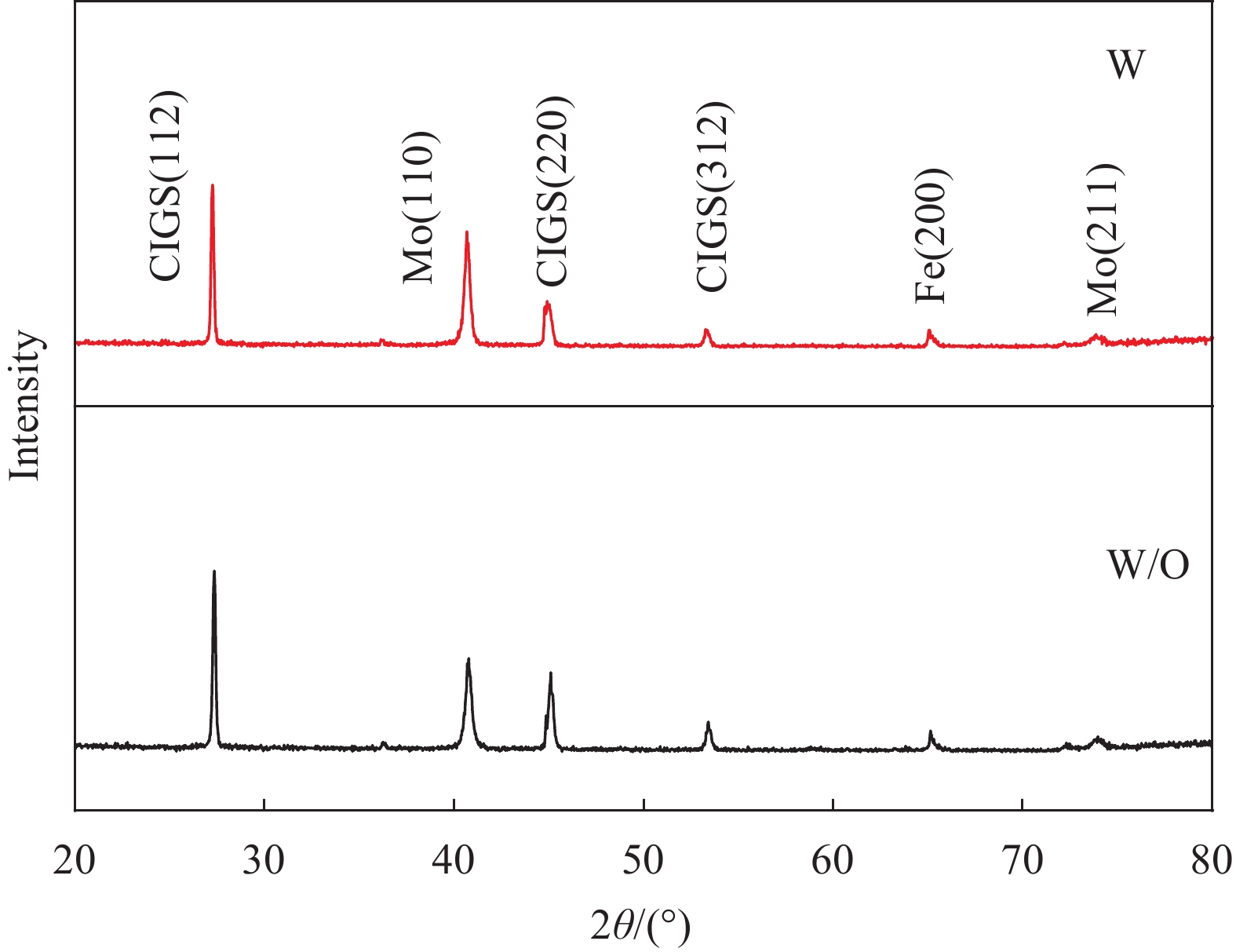
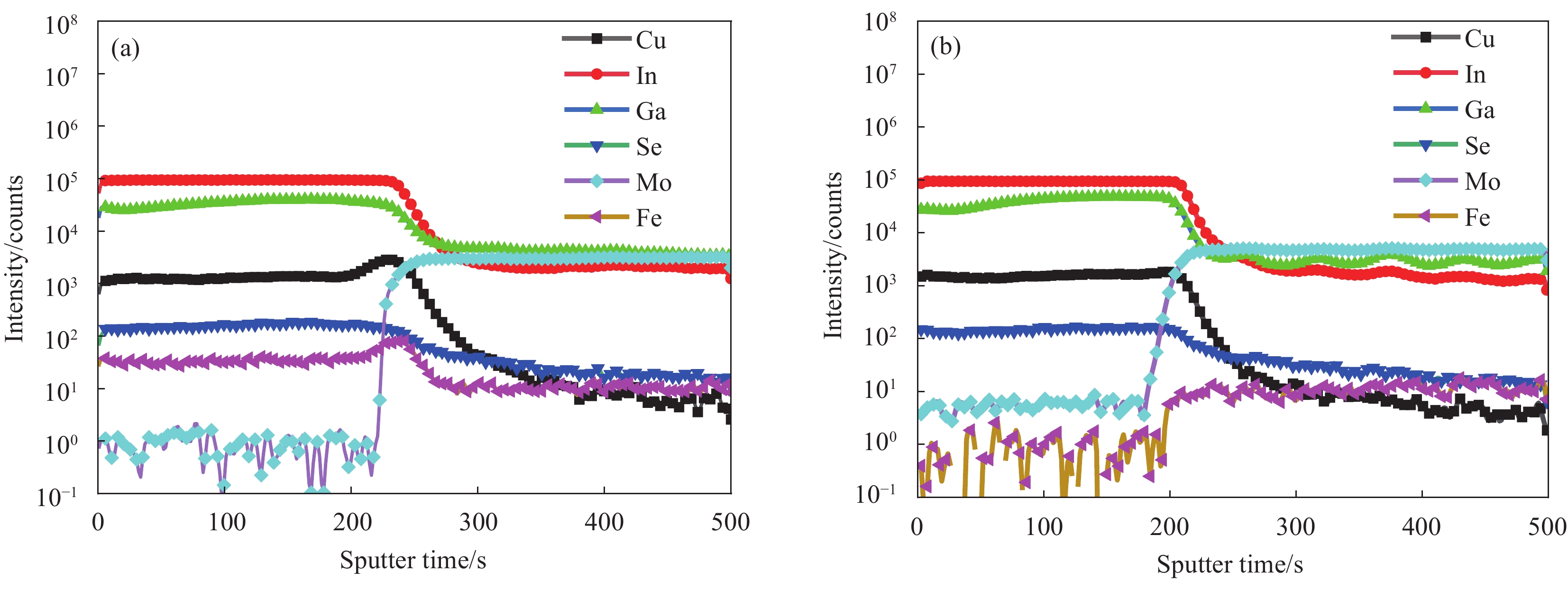
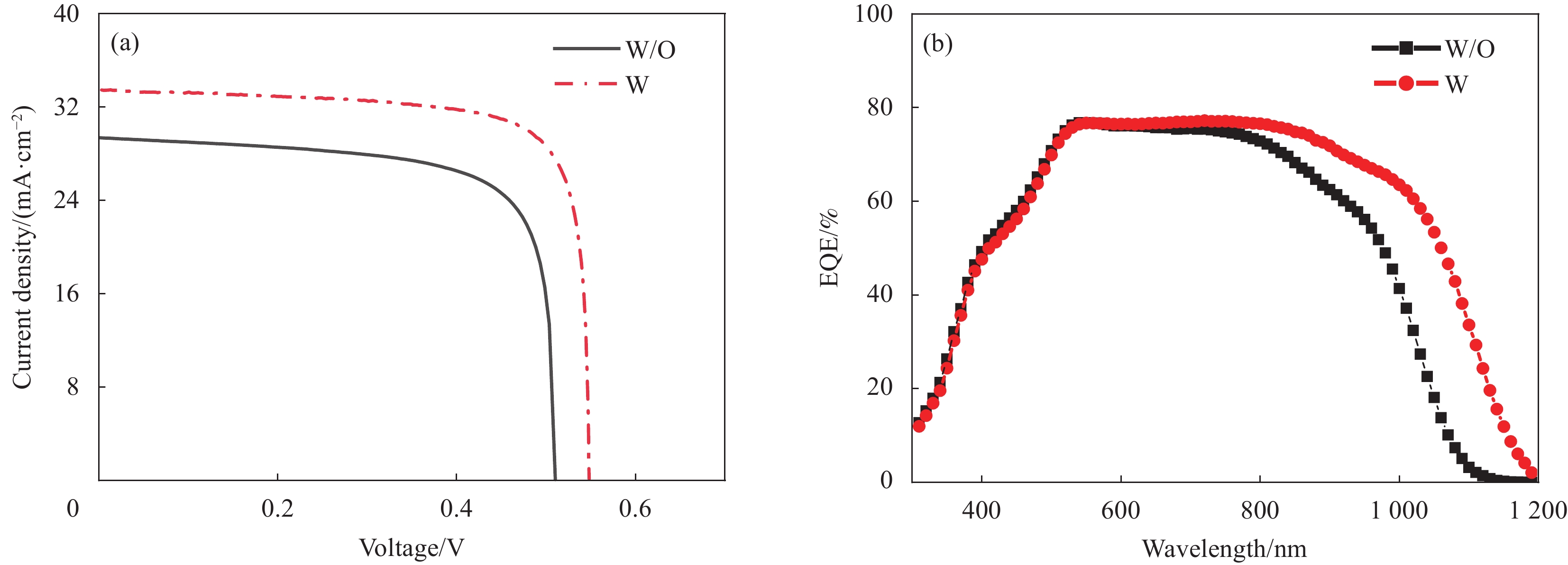
结果1.根据Mo(N,O)薄膜的表征结果可以看出:未通O时,薄膜表面呈现形状为金字塔结构的晶粒,通入0.15 mL/min O后,薄膜表面形貌发生改变,原来的金字塔结构的晶粒消失,转变为团簇的菜花状的晶粒,随着O流量的增加,薄膜的晶粒尺寸变小,晶界越来越不明显;XRD结果表明未通入O时,薄膜在39°左右出现明显的衍射峰,通入0.15 mL/min O后,薄膜的衍射峰消失,随着O流量的增加,没有衍射峰的出现;说明通入O后改变了薄膜的生长方式且形成非晶Mo(N,O)薄膜。2.把不同O流量条件下制备的Mo(N,O)薄膜作为阻挡层并完成太阳电池的制备,O流量为0.25 mL/min时,对应的太阳电池光电转换效率最佳。3. 选用0.25 mL/min O条件下制备的Mo(N,O)薄膜为阻挡层,通过XRD、SEM和SIMS测试观察阻挡层对Mo薄膜以及CIGS薄膜特性影响,结果表明有无阻挡层对Mo薄膜和CIGS薄膜的微观结构影响不大,Mo薄膜均呈现(110)择优生长,表面形貌呈现为三角形状的晶粒;CIGS薄膜均呈现(112)择优生长和连续且致密的大晶粒,但插入Mo(N,O)阻挡层使CIGS(220)/(112)的比值明显下降;SIMS结果表明插入Mo(N,O)阻挡层后,CIGS薄膜中Fe元素的相对信号强度由30 counts降至2 counts。4.通过优化工艺,并前掺NaF作为碱金属源,制备有无Mo(N,O)阻挡层的CIGS电池器件,I-V测试结果表明插入Mo(N,O)阻挡层后,器件的V由508 mV提高到了548 mV,J从29.5 mA·cm提高到33.1 mA·cm,FF从74%提高到78%,最终光电转换效率从11.07%提高到14.34%。EQE测试结果表明插入Mo(N,O)阻挡层明显提高了波长在800 nm至1100 nm的光谱响应。
结论本文通过反应磁控溅射制备了不同O流量的Mo(N,O)薄膜并应用于CIGS太阳电池,发现通入O使晶粒形状为金字塔结构的多晶MoN薄膜转变为团簇菜花状的非晶Mo(N,O)薄膜,O流量为0.25 mL/min时,电池器件性能最佳;Mo(N,O)薄膜不会影响Mo薄膜及CIGS薄膜的晶体结构和微观形貌,但可以有效阻挡衬底中Fe元素的扩散,使CIGS薄膜中Fe元素的相对信号强度由30 counts降至2 counts;引入Mo(N,O)阻挡层后,CIGS太阳电池光电转换效率由11.07%提高到14.34%。





 下载:
下载: