Effect of sulfate corrosion on the fracture properties of PVA fiber reinforced cement-based composite materials with steel slag powder
-
摘要: 为研究固体废料钢渣及硫酸盐溶液侵蚀作用下水泥基复合材料断裂特性,本文设计掺入不同质量分数的钢渣粉制备聚乙烯醇纤维增强水泥基复合材料(PVA/ECC),通过对硫酸盐侵蚀后的预制初始裂缝梁式试件进行三点弯曲性能试验,同时结合掺钢渣粉PVA/ECC在Na2SO4溶液(质量分数为5wt%)中的表观形态和微观结构特征,探究硫酸盐侵蚀对钢渣粉PVA/ECC断裂性能的影响。结果表明:在未受硫酸盐侵蚀钢渣粉掺量为20wt%时,试件起裂荷载、失稳荷载提升效果最优,较未掺钢渣粉试件分别提高约61%、110%;PVA/ECC断裂韧度随侵蚀时间先增大后减小,侵蚀60天到达峰值,120天后S80组劣化最明显,起裂韧度Kini和失稳韧度Kun分别减小了约23%、13%;适量钢渣粉的掺入能有效缓解PVA/ECC的侵蚀损伤,钢渣粉掺量不超过60wt%时在试验研究的龄期范围内材料未出现明显劣化。在此基础上通过Weibull分布模型预测试件耐久性寿命,其中钢渣粉掺量为20wt%的PVA/ECC使用寿命最长,可达到444次左右。Abstract: In order to study the fracture characteristics of cement-based composite materials under the solid waste steel slag and erosion of sulfate solution, the polyvinyl alcohol fiber reinforced cement-based composite materials (PVA/ECC) were prepared by adding different mass fractions of steel slag powder. Three-point bending performance test was conducted on prefabricated initial crack beam specimens after sulfate erosion. Combined with the apparent morphology and microstructure characteristics of steel slag powder PVA/ECC in Na2SO4 solution (mass fraction of 5wt%), the effect of sulfate corrosion on the fracture performance of steel slag powder PVA/ECC was investigated. The results show that when the content of steel slag powder without sulfate attack is 20wt%, the cracking load and instability load of the specimen are the best, with an increase of about 61% and 110% compared to the specimens without steel slag powder, respectively. The fracture toughness of PVA/ECC first increases and then decreases with erosion time, reaching its peak after 60 days of erosion. After 120 days, the S80 group shows the most obvious degradation, with the initiation toughness Kini and instability toughness Kun decreasing by about 23% and 13%, respectively. The addition of an appropriate amount of steel slag powder can effectively alleviate the erosion damage of PVA fiber reinforced cement-based composite materials. When the amount of steel slag powder does not exceed 60wt%, there is no significant deterioration of the material within the age range of the experimental study. On this basis, the durability life of the specimens was predicted using a Weibull distribution model, PVA/ECC with a 20wt% steel slag powder content having the longest service life, reaching around 444 cycles.
-
Keywords:
- PVA fiber /
- steel slag powder /
- sulfate erosion /
- dry and wet cycle /
- fracture toughness /
- durability performance
-
世界环境污染问题日趋严重,其中有机废水污染对人类健康和环境构成了极大的威胁[1-2]。光催化技术作为一种高效、安全的环境友好型净化技术,被广泛应用于降解环境中的有机污染物,具有广阔的应用前景[3-6]。
TiO2是众多光催化材料中最具有潜力的,因其无毒、稳定、廉价、可循环利用等优点而得到广泛的研究和商业应用[7-9],但是TiO2存在低表面积、禁带宽、电子空穴对复合率高、光吸收能力低等问题限制了它的光催化性能[10-11]。为此,研究者们提出了多种方法来提高TiO2的光催化性能,如贵金属掺杂[12]、非金属元素掺杂[13-14]、稀土或过渡金属掺杂、构建异质结等[15-16]。结果表明,经复合改性后的TiO2催化效率均有不同程度的提高[17]。但是,制备一种禁带宽度小、光吸收范围大、光生电子还原能力强的基于TiO2的光催化复合材料仍然是一个关键挑战[18]。在众多改性方法中,构建异质结是较有效的方法[19]。相比于成本较高的贵金属等催化材料,碳材料具有特殊的结构和形态,而在不同结构的碳材料中,空心碳球(HCS)为独特的中空结构[20],具有比表面积大、亲水性好、化学稳定性高、热稳定性高、密度低等特点[21]。
本文基于HCS与TiO2两者之间可以通过氢键和范德华力,形成HCS@TiO2范德华异质结,HCS作为导电基板的引入,提高了光生电子对从TiO2中的分离效率[22],高比表面积和良好的亲水性增大了TiO2与染料的接触面积[23]及对染料颗粒的吸附性能,使染料被高效地光催化降解,同时具有优异的重复使用性和广谱性,为光催化降解有机染料的复合材料的设计和制备提供了一条新的途径。通过简单的湿化学法制备了HCS@TiO2光催化复合材料,探索了在模拟太阳光下光催化降解活性红195 (RR195)的光催化性能。通过SEM、TEM、XRD、XPS、TG、N2吸附-脱附曲线、接触角测试对其进行形貌与结构的表征;通过紫外-可见吸收光谱(UV-Vis DRS)、Mott-Schottky测试分析其光学特性;通过UV-Vis DRS、电化学阻抗谱(EIS)测试、瞬态光电流响应图和循环降解试验分析其光催化降解性能,同时对HCS@TiO2光催化复合材料的光催化机制进行了探究,结合自由基捕获实验、电子顺磁共振波谱(ESR)表征的方法提出了HCS@TiO2光催化复合材料的光催化降解机制。
1. 实验材料及方法
1.1 原材料
活性红195,工业级,浙江龙盛化工研究有限公司;乙酰丙酮钛、吡咯、过硫酸铵、硝酸、氢氧化钠、硫酸、无水乙醇,分析纯,均购自国药集团化学试剂有限公司。
1.2 HCS@TiO2复合材料的合成
HCS的制备:采用乳液聚合法[24]合成了聚苯乙烯(PS)纳米球。PS母液(1 mg·mL−1,2 mL)作为模板,分散在去离子水(100 mL)中,搅拌10 min,然后,向溶液中加入吡咯单体(0.2 mL)的同时逐滴添加过硫酸铵(0.13 g,30 mL),反应4 h,将沉淀物过滤并用水和乙醇洗涤数次,所得产物记为PS@聚吡咯(PPy)。最后,将PS@PPy在5℃·min−1的加热速率下从20℃碳化至850℃,并在氩气(Ar)流下保持2 h,得到HCS。
HCS的酸化处理:将制备的HCS加入体积比为1∶3的H2SO4/HNO3混合物中,在60℃下搅拌24 h。然后过滤沉淀用水和乙醇洗涤数次,直至pH值达到7.0。接着在70℃下真空干燥酸化的HCS。
HCS@TiO2复合材料的制备:将HCS (5 mg)加入到无水乙醇(4 mL)和去离子水(1 mL)的混合物中。在超声波作用下持续振荡0.5 h至形成黑色悬浮液。然后,在HCS悬浮液中加入乙酰丙酮钛(50 mg),搅拌24 h,去除残留溶剂;所得产物记为HCS@二氧化钛前驱体(TOAC)。然后,将一定数量的HCS@TOAC (质量比1∶10)在空气气流下以350℃碳化1 h,然后在Ar气流下以5℃·min−1的加热速率加热至650℃,保温2 h。冷却至室温后,经后处理得到HCS@TiO2。采用不同煅烧温度(250℃、300℃、350℃、550℃、650℃)可制备不同煅烧温度下的HCS@TiO2复合材料。图1为HCS@TiO2复合材料的合成示意图。
1.3 样品表征
采用Gemini 300扫描电镜(德国蔡司)、Tecnai G2F20 200 kV场发射透射电子显微镜(美国FEI公司)分析光催化复合材料的整体形貌和结构。利用Philips X'pert PRO X射线衍射仪(荷兰帕纳科公司)分析了煅烧温度和煅烧气流对TiO2结晶度的影响。以MgKα为X射线源在Shimadzu ESCA-3400型 X 射线光电子能谱仪(宁波欧普仪器有限公司)上对样品进行XPS测量。采用ASAP 2020 比表面与孔隙度分析仪(麦克仪器),在77 K下以N2为吸附剂测得样品的N2吸附-脱附等温线,并利用BET方程计算其表面积。采用TGA400型热重分析仪(珀金埃尔默),在空气下,温度范围为30~650℃,对样品进行热重(TG)分析,加热速率为10℃·min−1。通过接触角测试分析样品的亲疏水性能。采用TU-1901 UV-Vis 分光光度计(普析)测试样品的漫反射光谱,以BaSO4为参比,扫描范围为200~600 nm。在上海辰华CHI660 E 电化学工作站上测量制备的复合材料的电化学阻抗谱、瞬态光电流响应图和Mott-Schottky曲线,测试条件:三电极系统(对电极:铂电极;参比电极:银/氯化银电极;工作电极:氧化铟锡(Indium tin oxide,ITO);底液:0.1 mol/L硫酸钠溶液;偏压:0 V;光源:氙灯(> 420 nm),光电流测试光照时间间隔为5 s (开灯5 s,关灯5 s),进行14个循环,EIS测试频率范围为0.1 Hz~100 kHz,Mott-Schottky曲线测试范围为−0.4~0.8 V,频率为500、1000、1500 Hz。采用EMX-8 spectrometer电子顺磁共振波谱仪(德国布鲁克公司)测试反应体系中自由基和光生电子空穴。测试方法:取适量光催化剂分散到含有四甲基哌啶(TEMPO)的甲醇溶液中,超声3 min使其均匀分散,然后打开氙灯,光照2 min后,放入仪器中进行检测e−。
1.4 光催化性能测试
以RR195为实验对象,测试制备的HCS@TiO2复合材料的光催化性能,同时分析各种样品对浓度为20 mg/L (100 mL)的RR195溶液的降解率,验证HCS和TiO2之间是否存在协同效应。另外,利用HCS@TiO2复合材料分别对RR195、活性黑5 (RB5)和碱性蓝9 (MB)进行光催化降解,验证复合材料的广谱性。在进行光催化降解RR195的实验之前,使用H2SO4/NaOH ±(0.5 mol/L)将染料废水的pH调整到3~11 (±0.1)。然后,将复合材料(10 mg)加入到100 mL的RR195溶液中。超声分散后,在黑暗中搅拌30 min达到吸附平衡。然后打开氙气灯(250 W,输出波长290~800 nm),开始光催化反应。光反应开始后,以给定的时间间隔,取约4 mL的悬浮液,离心(4000 r/ min,3 min)去除光催化剂,然后使用UV-Vis分光光度计进行测试,在543 nm处分析残留染料浓度,计算其降解率,如下式所示:
D=C0−CtC0×100% (1) 其中:D为降解率;C0为染料初始浓度;Ct为时间t的染料浓度。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 HCS@TiO2的形貌和结构分析
为了观察光催化复合材料的形貌,通过SEM、TEM对TiO2和HCS@TiO2进行表征,结果如图2所示。由图2(a)和图2(b)可以看出,HCS为规整光滑、尺寸均匀的中空球体,粒径约为200 nm。图2(c)可以看出TiO2 均匀地负载在HCS上,且HCS负载TiO2后仍保持球形结构,稳定性好。图2(d)可以看出该材料没有出现TiO2纳米颗粒聚集的现象。图2(e)的C、N (来自吡咯衍生物)、O、Ti元素的映射图说明TiO2纳米颗粒分布在HCS表面。图2(f)可以观察到无定形碳包围着TiO2晶格条纹,其晶格间距为0.352 nm,对应锐钛矿型TiO2的(101)晶面[25],图2(g)也证实了晶面间距为0.352 nm。
通过XRD分析煅烧温度和煅烧气流对TiO2结晶度的影响,结果如图3和图4所示。图3为Ar气流下650℃煅烧制备HCS@TiO2的XRD图谱,其中TiO2的衍射峰不尖锐,晶体结构不够规整。图4为不同煅烧温度下制备HCS@TiO2的XRD图谱,TiO2的衍射峰与锐钛矿型TiO2 (JCPDS No. 21-1272) 和金红石型TiO2 (JCPDS No. 21-1276)相匹配良好,表明在空气中650℃煅烧得到的TiO2是一种双晶结构[26-27]。HCS在空气气流下400℃左右碳化时,其骨架开始坍塌,HCS@TiO2需先在O2气流中煅烧,后在Ar气流下进行煅烧。将不同煅烧温度下的HCS@TiO2的XRD进行分析对比,可得HCS@TiO2 350℃(O2)-650℃(Ar)的锐钛矿型衍射峰最强,说明晶体结构最规整,在2θ=25.2°、37.8°、48.0°、53.8°、55.0°和62.6°处的特征衍射峰与锐钛矿相的(101)、(004)、(200)、(105)、(211)、(204)晶面对应,而锐钛矿型TiO2具有比金红石型TiO2更优异的光催化性能[28]。
此外,在不同热解温度(O2和Ar气流)下制备的HCS@TiO2在TiO2相同的2θ位置上出现衍射峰,表明HCS对TiO2晶体结构的影响可以忽略不计。
图5为TiO2、HCS及HCS@TiO2的XPS全谱图,可以看出HCS@TiO2在284.8 eV、459.4 eV和530.0 eV的位置存在C1s峰、Ti2p峰和O1s峰,表明HCS@TiO2中仅存在C、O和Ti元素,没有被污染。
图6为样品不同元素的高分辨XPS光谱。图6(a)和图6(b)分别为HCS和HCS@TiO2在C1s区域的高分辨XPS光谱,可以看出HCS的C1s XPS有3个特征峰,对应C=C、C—C和O—C=O键,分别位于284.4 eV、285.2 eV和288.3 eV处,而在HCS@TiO2中观察到两个处于283.3 eV(C—Ti)和286.1 eV(C=O)的新峰,说明HCS和TiO2之间有很强的相互作用,且前3个峰均呈轻微的负位移。由TiO2和HCS@TiO2的O1s高分辨XPS光谱(图6(c)、图6(d))可以看出,TiO2在529.5 eV和530.8 eV处显示的两个特征峰,属于Ti—O—Ti和Ti—OH键。与TiO2相比,HCS@TiO2的O1s XPS中的两个特征峰发生了负位移。在TiO2和HCS@TiO2的Ti2p高分辨XPS光谱(图6(e)、图6(f))中,TiO2的Ti2p3/2和Ti2p1/2[29]的结合能分别为458.2 eV和463.9 eV,而HCS@TiO2的Ti2p3/2和Ti2p1/2峰值信号与TiO2相比,向上移动了约0.5 eV,可能是TiO2和HCS之间形成C—Ti的原因。基于上述说明TiO2成功锚定在HCS上。
TiO2和HCS@TiO2的N2吸附-脱附等温线如图7所示,两种材料均为IV型等温线,表明两种材料中均存在大孔或介孔,TiO2等温线中存在H3型磁滞回环,而HCS@TiO2的滞回环类型变为H1型,这归功于HCS具有大量孔隙。根据BET方程计算得出,TiO2和HCS@TiO2的比表面积分别为19.6 m2/g和91.1 m2/g,表明HCS的加入,大大增加了HCS@TiO2的比表面积,减少了TiO2的团聚。
为了测试HCS@TiO2的定量组分和热稳定性,采用TGA对HCS@TiO2的热稳定性进行了研究,结果如图8所示。
可以看出,样品发生两次明显的质量损失。第一次质量损失是样品在100℃以下损失2.4wt%,主要归因于物理吸附和水的蒸发;第二次质量损失是样品在400℃以上损失17.2wt%,主要归因于燃烧HCS去除碳框架。最后,在600℃以上保持在80wt%不变。因此,确定HCS@TiO2中TiO2的质量分数为80wt%,具有优异的热稳定性。
通过接触角测试,分析HCS、酸化后的HCS、TiO2、HCS@TiO2的亲疏水性能,测试结果如图9所示,HCS、酸化后的HCS、TiO2、HCS@TiO2的接触角分别为135°、38°、85°和55°。HCS为疏水性材料,经过强酸酸化后,接触角明显减小了,说明酸化使HCS表面引入了大量极性基团,使其具有优异的亲水性和分散性。TiO2的接触角为85°,易发生团聚现象。与TiO2相比,HCS@TiO2的亲水性得到了明显提升,利于染料的吸附。
2.2 HCS@TiO2的光学特性
TiO2和HCS@TiO2的紫外-可见吸收光谱如图10(a)所示。可以看出,TiO2的吸收边带在390 nm左右,而HCS@TiO2的吸收边带发生了红移,在450 nm左右。
采用公式
(αhv)n=A(hv−Eg) (2) 其中:α为吸光度;h为普朗克常数;v为频率;指数n与半导体类型直接相关;A为比例常数;Eg为半导体的能隙,可以计算得到TiO2和HCS@TiO2的能量间隙图,利用切线法较精确地得到TiO2和HCS@TiO2复合材料的带隙能图,如图10(b)所示,TiO2的带隙能为3.13 eV,而HCS@TiO2的带隙能为2.83 eV,即HCS@TiO2的带隙能降低了,对光吸收范围更大了。
对TiO2和HCS@TiO2进行了Mott-Schottky测试,结果如图11所示。样品的曲线斜率均为正,这说明TiO2和HCS@TiO2均为n型半导体;且HCS@TiO2的斜率明显小于TiO2的斜率,表明HCS@TiO2的载流子浓度比TiO2的载流子浓度高。
2.3 HCS@TiO2复合材料的光催化降解染料性能
通过EIS研究TiO2和HCS@TiO2的电荷转移效率,结果如图12(a)所示。可以看出,HCS@TiO2的圆弧半径明显小于TiO2,说明其电荷转移电阻较低,促进电荷转移的同时抑制光生电子空穴对的复合,有利于光催化性能的提高[30]。图12(b)展示了HCS@TiO2和TiO2在可见光下反复开/关时的瞬态光电流,两种材料均展示出快速可逆的瞬态光电流响应,且随着光照时间的增强,光电流密度没有明显的衰减,同时,HCS@TiO2的光电流密度明显高于TiO2。表明HCS@TiO2的光生电子空穴对复合率更低,为光催化过程中提供稳定数量的光生电子[6]。
图13为HCS、TiO2 和HCS@TiO2这3种材料对RR195的降解曲线图,图14为HCS@TiO2光催化降解RR195、RB5和MB的曲线图。由图13可以看出,在暗箱吸附30 min 后,HCS的吸附达到平衡,之后一直保持不变;光照120 min后,TiO2降解率为62.93%,而HCS@TiO2降解率为95.36%,这是由于HCS和TiO2之间存在协同效应,提高了光生电子空穴对的分离效率,加速了污染物的降解。由图14可以看出,HCS@TiO2在光照120 min内对3种不同结构染料的降解率均高达95.00%,故HCS@TiO2具有广谱性。
图15为HCS@TiO2降解RR195的紫外-可见光吸收光谱图及降解过程中的染液颜色变化图。可以看出,反应初始,RR195在510 nm和543 nm处均出现了吸收峰,对应—N=N—。随着反应的进行,RR195的颜色由艳红逐渐变为无色,最大吸收峰逐渐降低,说明其发色基团被有效降解。另外,为了考察HCS@TiO2的可重复利用性,进行了5次降解RR195的循环实验,每个循环周期都要进行30 min的暗箱吸附和120 min的光降解,结果如图16所示。可以看出,该复合材料5次循环后,降解率为93.34%,依旧保持很高的光催化活性,这归因于其本身独特的3D球形结构,可以防止负载在HCS上的TiO2掉落。另外,降解后,HCS@TiO2的回收率可达91.30%。
2.4 HCS@TiO2的光催化降解机制
为了研究光催化降解中起主要作用的活性物质,采用苯醌(BQ)、乙二胺四乙酸钠(EDTA-2Na)和异丙醇(IPA)分别作为•O−2、h+和•OH的捕获试剂,结果如图17所示。
可以看出,在反应体系中加入捕获试剂后,光催化降解效率都会受到不同程度的抑制。其中加入BQ后,光催化效率下降最明显,降解率为49.83%,说明•O−2在光催化反应体系中起主要作用;而加入EDTA-2Na和IPA,降解率分别为83.50%和89.67%,说明h+和•OH在光催化反应体系中起次要作用,由此说明3种自由基的降解效率,•O−2最高,h+次之,•OH最低。可以推断,RR195可能在紫外照射下主要被•O2 −和h+分解。
为了进一步探究光催化机制,通过ESR研究了自由基产生和转移机制,结果如图18所示。由于四甲基哌啶(TEMPO)作为电子e−的自旋标记分子,能够被检测到信号强度为1∶1∶1的信号峰,信号峰越弱,表明该样品生成的光生电子越多。可以看出,0 min即不光照时,TiO2的信号强度低于HCS@TiO2的信号强度;辐照10 min后,TiO2和HCS@TiO2的信号强度均有所减弱,且HCS@TiO2信号强度明显低于TiO2的信号强度,这是由于HCS作为电子陷阱促进了电子的转移,提高了光生电子空穴对的分离效率,因而HCS@TiO2相比于TiO2可以生成更多的光生电子。
基于上述实验结果与分析,提出了HCS@TiO2复合材料光催化活性增强机制,如图19所示。由图可以看出:在光照下,e−从TiO2的价带(VB)跃迁到导带(CB)上,HCS功函高于TiO2,e−从TiO2的CB转移到HCS表面;TiO2上的h+会与H2O发生反应生成•OH;HCS表面的e−会与O2发生反应,使其生成•O−2,O−2还会与H+反应,生成过氧化氢自由基(H2O•),H2O•是H2O2的前躯体,后续反应生成H2O2,氧化反应和还原反应分别在TiO2和HCS上进行。此外,HCS的高比表面积可以使TiO2均匀负载,改善TiO2团聚现象,增加吸附点和活性位点,提高反应体系的降解速率。
3. 结 论
(1)利用简单的湿化学法可以制备空心碳球(HCS)@TiO2光催化复合材料,且TiO2均匀负载在HCS上,形成亲水性强、比表面积大、热稳定性优异的球形复合材料。
(2)光电化学性质分析表明,HCS@TiO2比TiO2禁带宽度更小,光响应范围更大,光生电子还原能力更强。
(3) HCS和TiO2之间的协同效应,提高了光生电子空穴对的分离效率,加速了污染物的降解。相同条件下,TiO2降解率仅为62.93%,而HCS@TiO2的降解率为95.36%,5次循环后降解率为93.34%,回收率为91.30%,且具有广谱性。
(4) 结合自由基捕获实验及电子顺磁共振光谱,提出了HCS@TiO2光催化复合材料的光催化降解机制,证实了•O−2在光催化反应体系中起主要作用。
-
表 1 水泥化学组成(wt%)
Table 1 Chemical composition of cement (wt%)
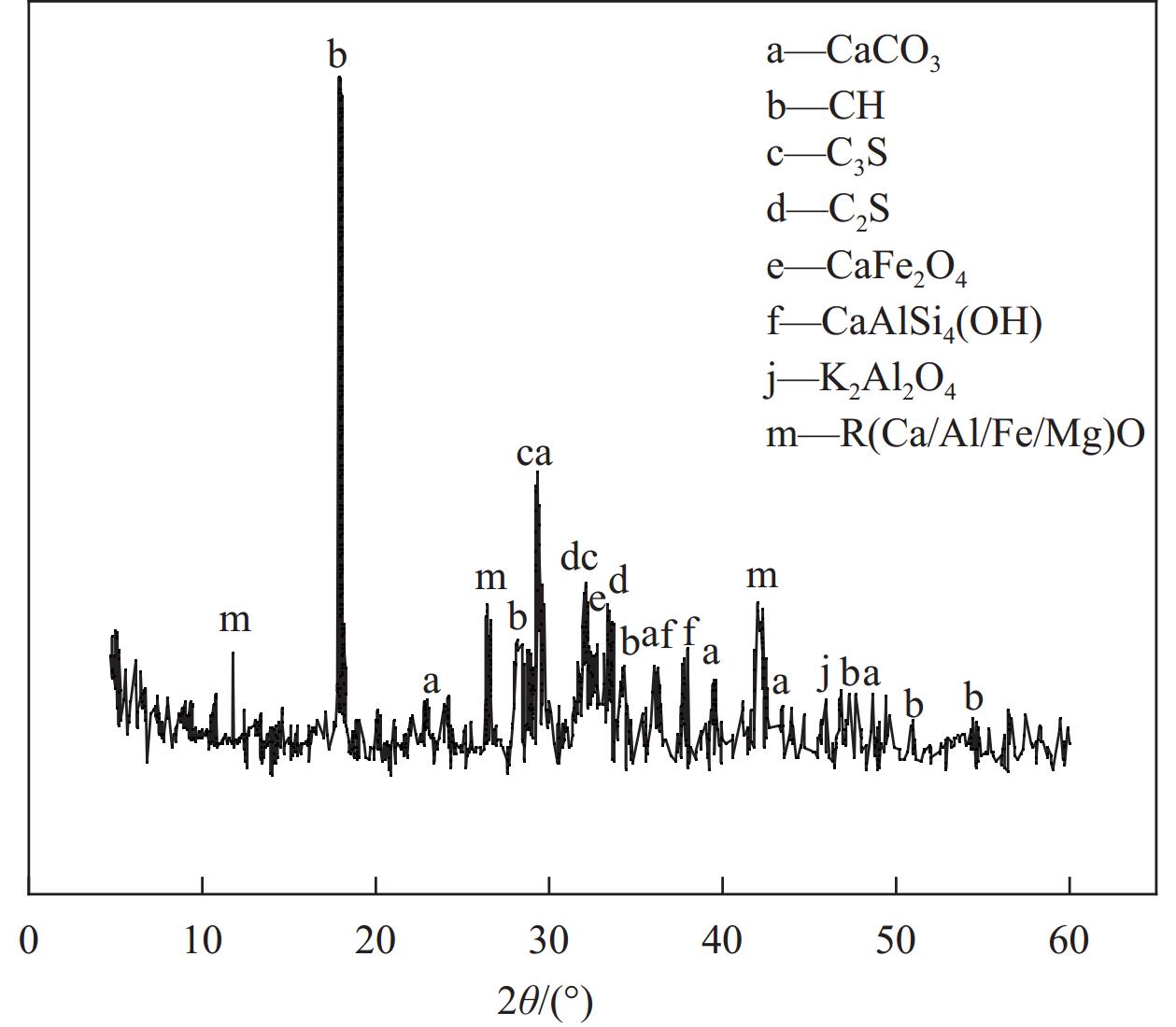
SiO2 CaO Fe2O3 Al2O3 K2O Na2O MgO P2O5 TiO2 SO3 17.63 65.39 4.11 5.35 0.70 0.20 1.43 0.16 0.33 3.51 表 2 钢渣粉的基本性能
Table 2 Basic properties of steel slag powder
Name Density/(g·cm−3) Specific surface area/(m2·kg−1) Activity index/% 7 d 28 d Steel slag powder 5.3 400 71.63 84.27 Specification ≥3.2 — ≥65 ≥80 表 3 钢渣粉X射线荧光光谱(XRF)检测结果(%)
Table 3 X-ray fluorescence spectrometer (XRF) testing results of steel slag powder (%)
CaO SiO2 Fe2O3 Al2O3 MgO Na2O SO3 P2O5 43.55 14.22 24.26 2.86 4.34 2.98 1.39 1.24 表 4 钢渣粉的粒度分布结果
Table 4 Particle size distribution results of steel slag powder
Particle size/μm Content/wt% 0-2 13.2 2-5 14.1 5-10 14.3 10-20 33.3 20-30 9.1 30-40 5.6 40-45 1.4 >45 9.1 表 5 聚乙烯醇(PVA)纤维物理性能指标
Table 5 Physical performance indicators of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) fibers
Length/mm Diameter/mm Aspect ratio Tensile strength/MPa Elongation rate/% Tensile modulus of elasticity/GPa Density/(g·cm−3) 12 40 300 1600 7 42 1.3 表 6 掺钢渣粉聚乙烯醇纤维增强水泥基复合材料(PVA/ECC)材料配合比
Table 6 Mix proportion of polyvinyl alcohol fiber engineered cementitious composites (PVA/ECC) material mixed with steel slag powder
Group Cement Silica fume Steel slag powder Water Sand Water reducing agent/% PVA dosage/% S0 0.98 0.02 0 0.25 0.2 1 2 S20 0.78 0.02 0.2 0.25 0.2 1 2 S40 0.58 0.02 0.4 0.25 0.2 1 2 S60 0.38 0.02 0.6 0.25 0.2 1 2 S80 0.18 0.02 0.8 0.25 0.2 1 2 Note: In the table, except for the volume ratio of PVA content, all others are mass ratios. 表 7 掺钢渣粉PVA/ECC材料试件
Table 7 PVA/ECC material specimens mixed with steel slag powder
Group Steel slag powder
dosage/wt%Number of wet
and dry cyclesL0 — 0 L2 — 2 L4 — 4 L6 — 6 L8 — 8 S0 0 — S20 20 — S40 40 — S60 60 — S80 80 — 表 8 Weibull分布两参数
Table 8 Two parameters of Weibull distribution
Number Shape parameter m Scaling parameter θ S0 3.614 127.966 S20 2.198 161.564 S40 2.525 131.077 S60 4.112 125.191 S80 3.910 108.872 -
[1] 杨波, 史林. 钢渣混凝土研究现状分析[J]. 中国新技术新产品, 2011(7): 11-12. YANG Bo, SHI Lin. Analysis of the current research status of steel slag concrete[J]. China New Technologies and Products, 2011(7): 11-12 (in Chinese).
[2] 於林锋, 徐兵, 王琼, 等. 钢渣混凝土性能的试验研究及应用前景分析[J]. 混凝土, 2014(1): 79-81. YU Linfeng, XU Bing, WANG Qiong, et al. Experimental study and application-benefit analysis of steel slag concrete[J]. Concrete, 2014(1): 79-81(in Chinese).
[3] 涂昆, 刘家祥, 邓侃. 钢渣粉和钢渣水泥的活性及水化机理研究[J] . 北京化工大学学报(自然科学版) , 2015, 42(1) : 62-68. TU Kun, LIU Jiaxiang, DENG Kan. Study of the hydration behaviour of steel slag and steel slag cement complex powders[J]. Journal of Beijing University of Chemical Technology (Natural Science Edition), 2015, 42(1): 62-68(in Chinese).
[4] 万江凯, 张朝晖, 刘佰龙, 等. 钢渣在混凝土中的应用[J]. 硅酸盐通报, 2016, 35(12): 4020-4024. WAN Jiangkai, ZHANG Chaohui, LIU Bailong, et al. Application of steel slag in concrete[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2016, 35 (12): 4020-4024(in Chinese).
[5] 陈苗苗, 冯春花, 李东旭. 钢渣作为混凝土掺合料的可行性研究[J]. 硅酸盐通报, 2011, 30(4): 751-754. CHEN Miaomiao, FENG Chunhua, LI Dongxu. Research on feasibility of using steel slag as mineral admixture in concrete[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society, 2011, 30(4): 751-754(in Chinese).
[6] 徐世烺, 李贺东. 超高韧性水泥基复合材料研究进展及其工程应用[J]. 土木工程学报, 2008, 41(6): 45-60. XU Shilang, LI Hedong. A review on the development of research and application of ultra high toughness cementitious composites[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2008, 41(6): 45-60(in Chinese).
[7] 刘俊, 牛荻涛, 宋华. 掺合料对混凝土抗硫酸盐侵蚀性能的影响[J]. 混凝土, 2014(3): 79-83. LIU Jun, NIU Ditao, SONG Hua. Influences brought by admixtures to the sulfate corrosion of concrete[J]. Concrete, 2014(3): 79-83(in Chinese).
[8] 高润东, 赵顺波, 李庆斌, 等. 干湿循环作用下混凝土硫酸盐侵蚀劣化机理试验研究[J]. 土木工程学报, 2010, 43(2): 48-54. DOI: 10.15951/j.tmgcxb.2010.02.018 GAO Rundong, ZHAO Shunbo, LI Qingbin, et al. Experimental study of the deterioration mechanism of concrete under sulfate attack in wet-dry cycles[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2010, 43(2): 48-54(in Chinese). DOI: 10.15951/j.tmgcxb.2010.02.018
[9] 徐世烺, 赵国藩. 混凝土结构裂缝扩展的双K断裂准则[J]. 土木工程学报, 1992(2): 32-38. DOI: 10.15951/j.tmgcxb.1992.02.005 XU Shilang, ZHAO Guofan. A double-K fracture criterion for the crack propagatiom in goncrete structures[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 1992(2): 32-38(in Chinese). DOI: 10.15951/j.tmgcxb.1992.02.005
[10] 钱维民, 苏骏, 赵家玉, 等. 超低温作用对超高韧性水泥基复合材料断裂性能的影响[J]. 建筑材料学报, 2022, 25(9): 901-909, 916. QIAN Weimin, SU Jun, ZHAO Jiayu, et al. Effect of ultra-low temperature on fracture behavior of ultra-high toughness cementitious composites[J]. Journal of Building Materials, 2022, 25(9): 901-909, 916(in Chinese).
[11] 甘磊, 沈振中, 徐力群, 等. 不同pH值硫酸盐侵蚀下水泥砂浆断裂韧度[J]. 应用基础与工程科学学报, 2023, 31(3): 690-702. GAN Lei, SHEN Zhenzhong, XU Liqun, et al. Fracture toughness of cement mortar under sulfate attack at different pH values[J]. Journal of Basic Science and Engineering, 2023, 31(3): 690-702(in Chinese).
[12] 肖建庄, 许金校, 罗素蓉, 等. 剑麻纤维对再生骨料混凝土断裂性能的影响[J]. 建筑材料学报, 2023, 26(6): 587-595. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9629.2023.06.003 XIAO Jianzhuang, XU Jinxiao, LUO Surong, et al. The effect of sisal fiber on the fracture performance of recycled aggregate concrete[J]. Journal of Building Materials, 2023, 26(6): 587-595(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1007-9629.2023.06.003
[13] LIU H Z, ZHANG Q, LI V, et al. Durability study on engineered cementitious composites (ECC) under sulfate and chloride environment[J]. Construction & Building Materials, 2017, 133: 171-181.
[14] WANG Y M, HU S W, HE Z. Mechanical and fracture properties of geopolymer concrete with basalt fiber using digital image correlation[J]. Theoretical and Applied Fracture Mechanics, 2021, 112: 102909. DOI: 10.1016/j.tafmec.2021.102909
[15] 冷发光, 马孝轩, 田冠飞. 混凝土抗硫酸盐侵蚀试验方法[J]. 东南大学学报(自然科学版), 2006, 36(S2): 45-48. LENG Faguang, MA Xiaoxuan, TIAN Guanfei. Investigation of test methods of concrete under sulfate corrosion[J]. Journal of Southeast University (Natural Science Edition), 2006, 36(S2): 45-48(in Chinese).
[16] 董宜森. 硫酸盐侵蚀环境下混凝土耐久性能试验研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2011. DONG Yisen. Experimental research on the durability of concrete exposed to sulfate environment[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang University, 2011(in Chinese).
[17] 中国工程建设协会. 纤维混凝土试验方法标准: CECS 13: 2009[S]. 北京: 计划出版社, 2010. China Engineering Construction Association. Standard for test methods for fiber reinforced concrete: CECS 13: 2009[S]. Beijing: Planning Press, 2010(in Chinese).
[18] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 混凝土结构试验方法标准: GB/T 50152—2012[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2012. Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People's Republic of China. Standard for test methods of concrete structures: GB/T 50152—2012[S]. Beijing: China Construction Industry Press, 2012(in Chinese).
[19] 韦选纯, 汤盛文, 何真, 等. 聚乙烯醇纤维增强钢渣粉-水泥复合材料基本力学性能及微观结构[J]. 复合材料学报, 2019, 36(8): 1918-1925. DOI: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20181108.008 WEI Xuanchun, TANG Shengwen, HE Zhen, et al. Mechanical and microstructural characteristics of polyvinyl alcohol fiber reinforced cementitious composites containing steel slag powder[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2019, 36(8): 1918-1925(in Chinese). DOI: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20181108.008
[20] 史占崇, 苏庆田, 邵长宇, 等. 粗骨料UHPC的基本力学性能及弯曲韧性评价方法[J]. 土木工程学报, 2020, 53(12): 86-97. SHI Zhanchong, SU Qingtian, SHAO Changyu, et al. Basic mechanical behavior and flexural toughness evaluation method of coarse aggregate UHPC[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal, 2020, 53(12): 86-97(in Chinese).
[21] 陈红莉. 干湿循环下混凝土受硫酸盐腐蚀断裂性能试验研究[D]. 郑州: 郑州大学, 2016. CHEN Hongli. Experimental research on anti-sulfate corrosion fracture properties of concrete under wet and dry cycles[D]. Zhengzhou: Zhengzhou University, 2016(in Chinese).
[22] GUINEA G V, PASTOR J Y, PLANAS J, et al. Stress intensity factor, compliance and CMOD for a general three-point-bend beam[J]. International Journal of Fracture, 1998, 89(2): 103-116. DOI: 10.1023/A:1007498132504
[23] 乔宏霞. 高性能混凝土抗硫酸盐侵蚀试验研究[D]. 兰州: 兰州理工大学, 2003. QIAO Hongxia. Experimental study on sulfate attack resistance of high-performance concrete[D]. Lanzhou: Lanzhou University of Technology, 2003(in Chinese).
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 李梦涵,魏娜,徐瑞琪,杨泽钰,崔洪芝. 三维碳纳米管/硅藻土基多孔陶瓷复合材料的制备及其光热水蒸发性能. 复合材料学报. 2023(08): 4577-4586 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 吴玉萍,王乾廷,孙炜,周忠华,谢宗丽,宋铭雨. 含椭圆叶片状SiO_2/聚乙烯醇渗透汽化复合膜的制备与性能. 复合材料学报. 2022(06): 2783-2791 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 赵士雄. 反渗透复合膜制备及其改性方法研究进展. 云南化工. 2022(06): 20-21+38 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)
-
-
为研究固体废料钢渣以及硫酸盐溶液侵蚀作用下PVA-ECC材料的断裂特性,本文设计了掺入不同质量分数的钢渣粉制备PVA纤维增强水泥基复合材料,通过对硫酸盐侵蚀后的预制初始裂缝梁式试件进行三点弯曲性能试验,同时结合掺钢渣粉PVA-ECC在Na2SO4溶液(质量分数为5%)中的表观形态和微观结构特征,探究硫酸盐侵蚀对钢渣粉PVA-ECC断裂性能的影响。
在未受硫酸盐侵蚀条件下钢渣粉掺量为20%时,试件起裂荷载、失稳荷载提升效果最佳,较未掺钢渣粉试件分别提高约61%、110%;PVA-ECC断裂韧度随侵蚀时间先增大后减小,侵蚀60d到达峰值,120d后S80组劣化最明显,起裂韧度Kini和失稳韧度Kun分别减小了约23%、13%;适量钢渣粉的掺入能有效缓解PVA-ECC材料的侵蚀损伤,钢渣粉掺量不超过60%时在试验研究的龄期范围内材料未出现明显劣化。在此基础上通过Weibull分布模型预测了PVA-ECC试件的耐久性寿命,其中钢渣粉掺量为20%的PVA-ECC使用寿命最长,可达到444次左右。

起裂荷载和失稳荷载的变化规律

不同钢渣粉掺量耐久性寿命预测曲线





 下载:
下载: