Preparation and degradation dyestuffs performance of HCS@TiO2 photocatalytic composites
-
摘要: 为了获得性能更加优异的光催化材料,本文通过简单的湿化学法制备了空心碳球(HCS)@TiO2光催化复合材料,并对其进行了表征。形貌与结构的表征结果显示,TiO2纳米颗粒均匀地锚定在HCS表面,形成亲水性强、比表面积大、热稳定性优异的球形复合材料,HCS@TiO2复合材料中TiO2的质量分数为80wt%;光电化学性质分析表明HCS@TiO2复合材料禁带宽度更小,光响应范围更大,光生电子还原能力更强。在模拟太阳光下,以活性红195 (RR195)为实验对象,测试制备的HCS@TiO2复合材料的光催化降解染料的性能和循环稳定性。结果表明:HCS@TiO2光生电子空穴对的分离效率更高,光催化活性优异,在120 min内染料降解率为95.36%,5次循环后仍高达93.34%,稳定性高,且易于回收。同时结合自由基捕获实验及电子顺磁共振光谱,对HCS@TiO2光催化复合材料的光催化机制进行了探究,证实了•O−2在光催化反应体系中起主要作用。Abstract: In order to obtain more efficient photocatalytic materials, hollow carbon sphere (HCS)@TiO2 photocatalytic composites was prepared by a facile wet-chemical method and characterized. The results of structural and morphology characterization showed that TiO2 nanoparticles were anchored uniformly on the surface of HCS, forming a spherical composites with high hydrophilia and specific surface area and excellent thermostability, the mass percentage of TiO2 anchored on HCS@TiO2 composites was 80wt%. The analysis of photoelectric chemical properties showed that HCS@TiO2 composites had smaller bandgap width, wider light response range, and stronger photogenic electron reduction ability. Using Reactive Red 195 (RR195) as the experimental object, the photocatalytic degradation dyes performance and cyclic stability of HCS@TiO2 composites were tested under simulated sunlight. The results show that the separation efficiency of photogenic electron hole pairs in the HCS@TiO2 is higher, and the photocatalytic activity is excellent. The degradation rate is 95.36% within 120 min, and it still reaches 93.34% after 5 cycles, with high stability and easy recovery. At the same time, the photocatalytic mechanism of HCS@TiO2 photocatalytic composites was proposed by combining free radical capture experiment and electron paramagnetic resonance spectroscopy. It was confirmed that •O−2 plays a major role in the photocatalytic reaction system.
-
Keywords:
- wet chemical method /
- titanium dioxide /
- hollow carbon spheres /
- photocatalytic /
- composites /
- degradation /
- Reactive Red 195
-
世界环境污染问题日趋严重,其中有机废水污染对人类健康和环境构成了极大的威胁[1-2]。光催化技术作为一种高效、安全的环境友好型净化技术,被广泛应用于降解环境中的有机污染物,具有广阔的应用前景[3-6]。
TiO2是众多光催化材料中最具有潜力的,因其无毒、稳定、廉价、可循环利用等优点而得到广泛的研究和商业应用[7-9],但是TiO2存在低表面积、禁带宽、电子空穴对复合率高、光吸收能力低等问题限制了它的光催化性能[10-11]。为此,研究者们提出了多种方法来提高TiO2的光催化性能,如贵金属掺杂[12]、非金属元素掺杂[13-14]、稀土或过渡金属掺杂、构建异质结等[15-16]。结果表明,经复合改性后的TiO2催化效率均有不同程度的提高[17]。但是,制备一种禁带宽度小、光吸收范围大、光生电子还原能力强的基于TiO2的光催化复合材料仍然是一个关键挑战[18]。在众多改性方法中,构建异质结是较有效的方法[19]。相比于成本较高的贵金属等催化材料,碳材料具有特殊的结构和形态,而在不同结构的碳材料中,空心碳球(HCS)为独特的中空结构[20],具有比表面积大、亲水性好、化学稳定性高、热稳定性高、密度低等特点[21]。
本文基于HCS与TiO2两者之间可以通过氢键和范德华力,形成HCS@TiO2范德华异质结,HCS作为导电基板的引入,提高了光生电子对从TiO2中的分离效率[22],高比表面积和良好的亲水性增大了TiO2与染料的接触面积[23]及对染料颗粒的吸附性能,使染料被高效地光催化降解,同时具有优异的重复使用性和广谱性,为光催化降解有机染料的复合材料的设计和制备提供了一条新的途径。通过简单的湿化学法制备了HCS@TiO2光催化复合材料,探索了在模拟太阳光下光催化降解活性红195 (RR195)的光催化性能。通过SEM、TEM、XRD、XPS、TG、N2吸附-脱附曲线、接触角测试对其进行形貌与结构的表征;通过紫外-可见吸收光谱(UV-Vis DRS)、Mott-Schottky测试分析其光学特性;通过UV-Vis DRS、电化学阻抗谱(EIS)测试、瞬态光电流响应图和循环降解试验分析其光催化降解性能,同时对HCS@TiO2光催化复合材料的光催化机制进行了探究,结合自由基捕获实验、电子顺磁共振波谱(ESR)表征的方法提出了HCS@TiO2光催化复合材料的光催化降解机制。
1. 实验材料及方法
1.1 原材料
活性红195,工业级,浙江龙盛化工研究有限公司;乙酰丙酮钛、吡咯、过硫酸铵、硝酸、氢氧化钠、硫酸、无水乙醇,分析纯,均购自国药集团化学试剂有限公司。
1.2 HCS@TiO2复合材料的合成
HCS的制备:采用乳液聚合法[24]合成了聚苯乙烯(PS)纳米球。PS母液(1 mg·mL−1,2 mL)作为模板,分散在去离子水(100 mL)中,搅拌10 min,然后,向溶液中加入吡咯单体(0.2 mL)的同时逐滴添加过硫酸铵(0.13 g,30 mL),反应4 h,将沉淀物过滤并用水和乙醇洗涤数次,所得产物记为PS@聚吡咯(PPy)。最后,将PS@PPy在5℃·min−1的加热速率下从20℃碳化至850℃,并在氩气(Ar)流下保持2 h,得到HCS。
HCS的酸化处理:将制备的HCS加入体积比为1∶3的H2SO4/HNO3混合物中,在60℃下搅拌24 h。然后过滤沉淀用水和乙醇洗涤数次,直至pH值达到7.0。接着在70℃下真空干燥酸化的HCS。
HCS@TiO2复合材料的制备:将HCS (5 mg)加入到无水乙醇(4 mL)和去离子水(1 mL)的混合物中。在超声波作用下持续振荡0.5 h至形成黑色悬浮液。然后,在HCS悬浮液中加入乙酰丙酮钛(50 mg),搅拌24 h,去除残留溶剂;所得产物记为HCS@二氧化钛前驱体(TOAC)。然后,将一定数量的HCS@TOAC (质量比1∶10)在空气气流下以350℃碳化1 h,然后在Ar气流下以5℃·min−1的加热速率加热至650℃,保温2 h。冷却至室温后,经后处理得到HCS@TiO2。采用不同煅烧温度(250℃、300℃、350℃、550℃、650℃)可制备不同煅烧温度下的HCS@TiO2复合材料。图1为HCS@TiO2复合材料的合成示意图。
1.3 样品表征
采用Gemini 300扫描电镜(德国蔡司)、Tecnai G2F20 200 kV场发射透射电子显微镜(美国FEI公司)分析光催化复合材料的整体形貌和结构。利用Philips X'pert PRO X射线衍射仪(荷兰帕纳科公司)分析了煅烧温度和煅烧气流对TiO2结晶度的影响。以MgKα为X射线源在Shimadzu ESCA-3400型 X 射线光电子能谱仪(宁波欧普仪器有限公司)上对样品进行XPS测量。采用ASAP 2020 比表面与孔隙度分析仪(麦克仪器),在77 K下以N2为吸附剂测得样品的N2吸附-脱附等温线,并利用BET方程计算其表面积。采用TGA400型热重分析仪(珀金埃尔默),在空气下,温度范围为30~650℃,对样品进行热重(TG)分析,加热速率为10℃·min−1。通过接触角测试分析样品的亲疏水性能。采用TU-1901 UV-Vis 分光光度计(普析)测试样品的漫反射光谱,以BaSO4为参比,扫描范围为200~600 nm。在上海辰华CHI660 E 电化学工作站上测量制备的复合材料的电化学阻抗谱、瞬态光电流响应图和Mott-Schottky曲线,测试条件:三电极系统(对电极:铂电极;参比电极:银/氯化银电极;工作电极:氧化铟锡(Indium tin oxide,ITO);底液:0.1 mol/L硫酸钠溶液;偏压:0 V;光源:氙灯(> 420 nm),光电流测试光照时间间隔为5 s (开灯5 s,关灯5 s),进行14个循环,EIS测试频率范围为0.1 Hz~100 kHz,Mott-Schottky曲线测试范围为−0.4~0.8 V,频率为500、1000、1500 Hz。采用EMX-8 spectrometer电子顺磁共振波谱仪(德国布鲁克公司)测试反应体系中自由基和光生电子空穴。测试方法:取适量光催化剂分散到含有四甲基哌啶(TEMPO)的甲醇溶液中,超声3 min使其均匀分散,然后打开氙灯,光照2 min后,放入仪器中进行检测e−。
1.4 光催化性能测试
以RR195为实验对象,测试制备的HCS@TiO2复合材料的光催化性能,同时分析各种样品对浓度为20 mg/L (100 mL)的RR195溶液的降解率,验证HCS和TiO2之间是否存在协同效应。另外,利用HCS@TiO2复合材料分别对RR195、活性黑5 (RB5)和碱性蓝9 (MB)进行光催化降解,验证复合材料的广谱性。在进行光催化降解RR195的实验之前,使用H2SO4/NaOH ±(0.5 mol/L)将染料废水的pH调整到3~11 (±0.1)。然后,将复合材料(10 mg)加入到100 mL的RR195溶液中。超声分散后,在黑暗中搅拌30 min达到吸附平衡。然后打开氙气灯(250 W,输出波长290~800 nm),开始光催化反应。光反应开始后,以给定的时间间隔,取约4 mL的悬浮液,离心(4000 r/ min,3 min)去除光催化剂,然后使用UV-Vis分光光度计进行测试,在543 nm处分析残留染料浓度,计算其降解率,如下式所示:
D=C0−CtC0×100% (1) 其中:D为降解率;C0为染料初始浓度;Ct为时间t的染料浓度。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 HCS@TiO2的形貌和结构分析
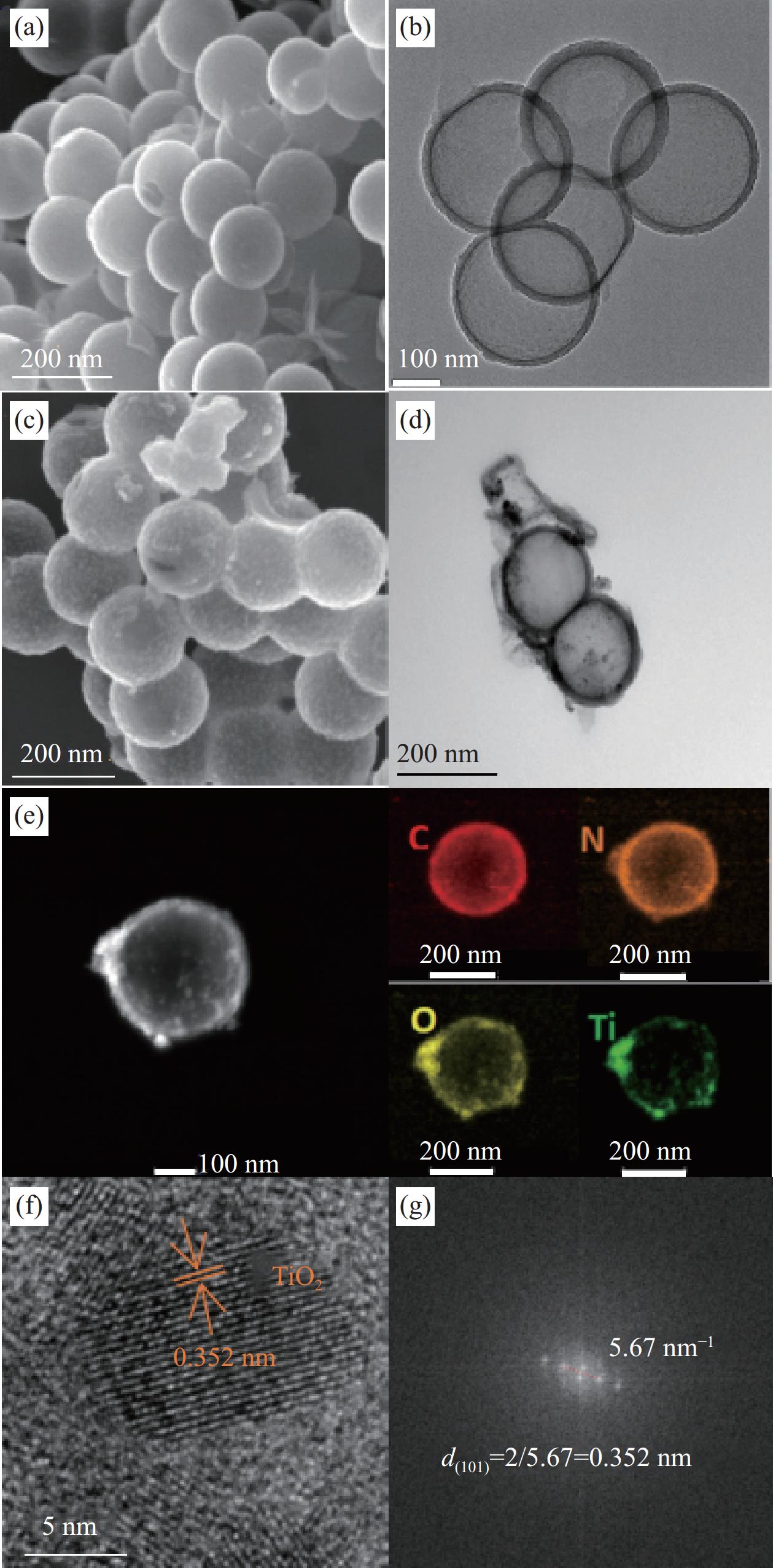
为了观察光催化复合材料的形貌,通过SEM、TEM对TiO2和HCS@TiO2进行表征,结果如图2所示。由图2(a)和图2(b)可以看出,HCS为规整光滑、尺寸均匀的中空球体,粒径约为200 nm。图2(c)可以看出TiO2 均匀地负载在HCS上,且HCS负载TiO2后仍保持球形结构,稳定性好。图2(d)可以看出该材料没有出现TiO2纳米颗粒聚集的现象。图2(e)的C、N (来自吡咯衍生物)、O、Ti元素的映射图说明TiO2纳米颗粒分布在HCS表面。图2(f)可以观察到无定形碳包围着TiO2晶格条纹,其晶格间距为0.352 nm,对应锐钛矿型TiO2的(101)晶面[25],图2(g)也证实了晶面间距为0.352 nm。
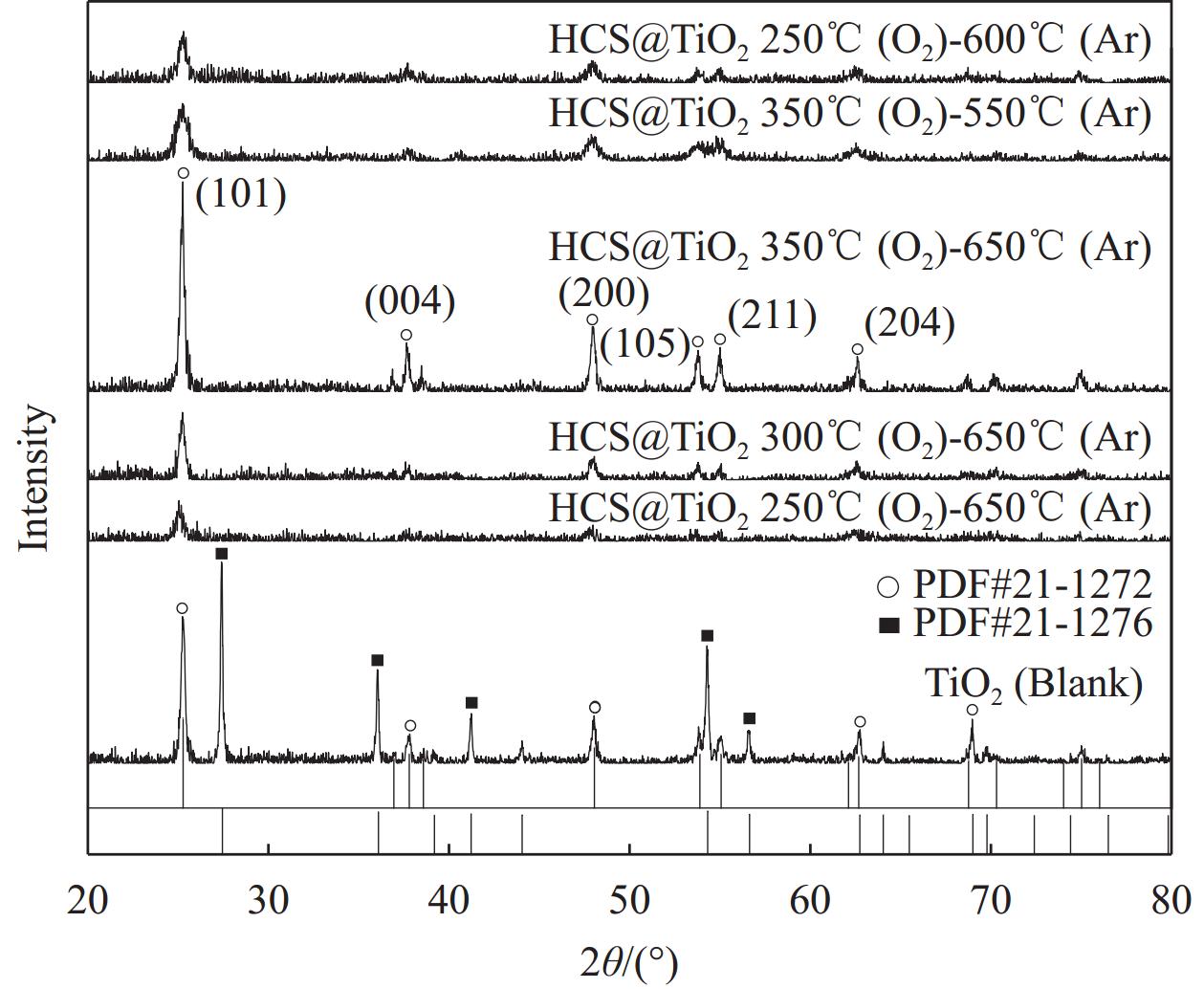
通过XRD分析煅烧温度和煅烧气流对TiO2结晶度的影响,结果如图3和图4所示。图3为Ar气流下650℃煅烧制备HCS@TiO2的XRD图谱,其中TiO2的衍射峰不尖锐,晶体结构不够规整。图4为不同煅烧温度下制备HCS@TiO2的XRD图谱,TiO2的衍射峰与锐钛矿型TiO2 (JCPDS No. 21-1272) 和金红石型TiO2 (JCPDS No. 21-1276)相匹配良好,表明在空气中650℃煅烧得到的TiO2是一种双晶结构[26-27]。HCS在空气气流下400℃左右碳化时,其骨架开始坍塌,HCS@TiO2需先在O2气流中煅烧,后在Ar气流下进行煅烧。将不同煅烧温度下的HCS@TiO2的XRD进行分析对比,可得HCS@TiO2 350℃(O2)-650℃(Ar)的锐钛矿型衍射峰最强,说明晶体结构最规整,在2θ=25.2°、37.8°、48.0°、53.8°、55.0°和62.6°处的特征衍射峰与锐钛矿相的(101)、(004)、(200)、(105)、(211)、(204)晶面对应,而锐钛矿型TiO2具有比金红石型TiO2更优异的光催化性能[28]。
此外,在不同热解温度(O2和Ar气流)下制备的HCS@TiO2在TiO2相同的2θ位置上出现衍射峰,表明HCS对TiO2晶体结构的影响可以忽略不计。
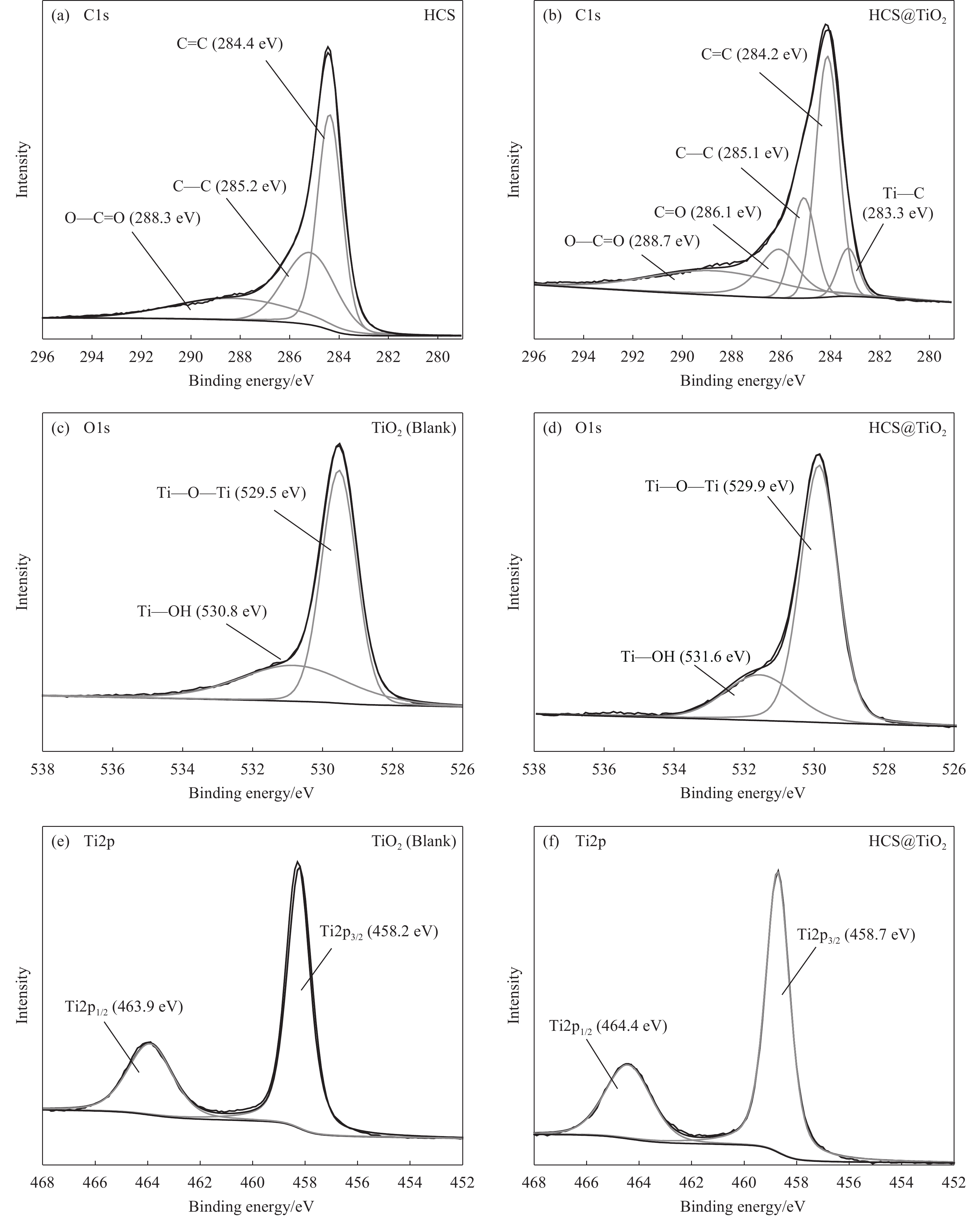
图5为TiO2、HCS及HCS@TiO2的XPS全谱图,可以看出HCS@TiO2在284.8 eV、459.4 eV和530.0 eV的位置存在C1s峰、Ti2p峰和O1s峰,表明HCS@TiO2中仅存在C、O和Ti元素,没有被污染。
图6为样品不同元素的高分辨XPS光谱。图6(a)和图6(b)分别为HCS和HCS@TiO2在C1s区域的高分辨XPS光谱,可以看出HCS的C1s XPS有3个特征峰,对应C=C、C—C和O—C=O键,分别位于284.4 eV、285.2 eV和288.3 eV处,而在HCS@TiO2中观察到两个处于283.3 eV(C—Ti)和286.1 eV(C=O)的新峰,说明HCS和TiO2之间有很强的相互作用,且前3个峰均呈轻微的负位移。由TiO2和HCS@TiO2的O1s高分辨XPS光谱(图6(c)、图6(d))可以看出,TiO2在529.5 eV和530.8 eV处显示的两个特征峰,属于Ti—O—Ti和Ti—OH键。与TiO2相比,HCS@TiO2的O1s XPS中的两个特征峰发生了负位移。在TiO2和HCS@TiO2的Ti2p高分辨XPS光谱(图6(e)、图6(f))中,TiO2的Ti2p3/2和Ti2p1/2[29]的结合能分别为458.2 eV和463.9 eV,而HCS@TiO2的Ti2p3/2和Ti2p1/2峰值信号与TiO2相比,向上移动了约0.5 eV,可能是TiO2和HCS之间形成C—Ti的原因。基于上述说明TiO2成功锚定在HCS上。
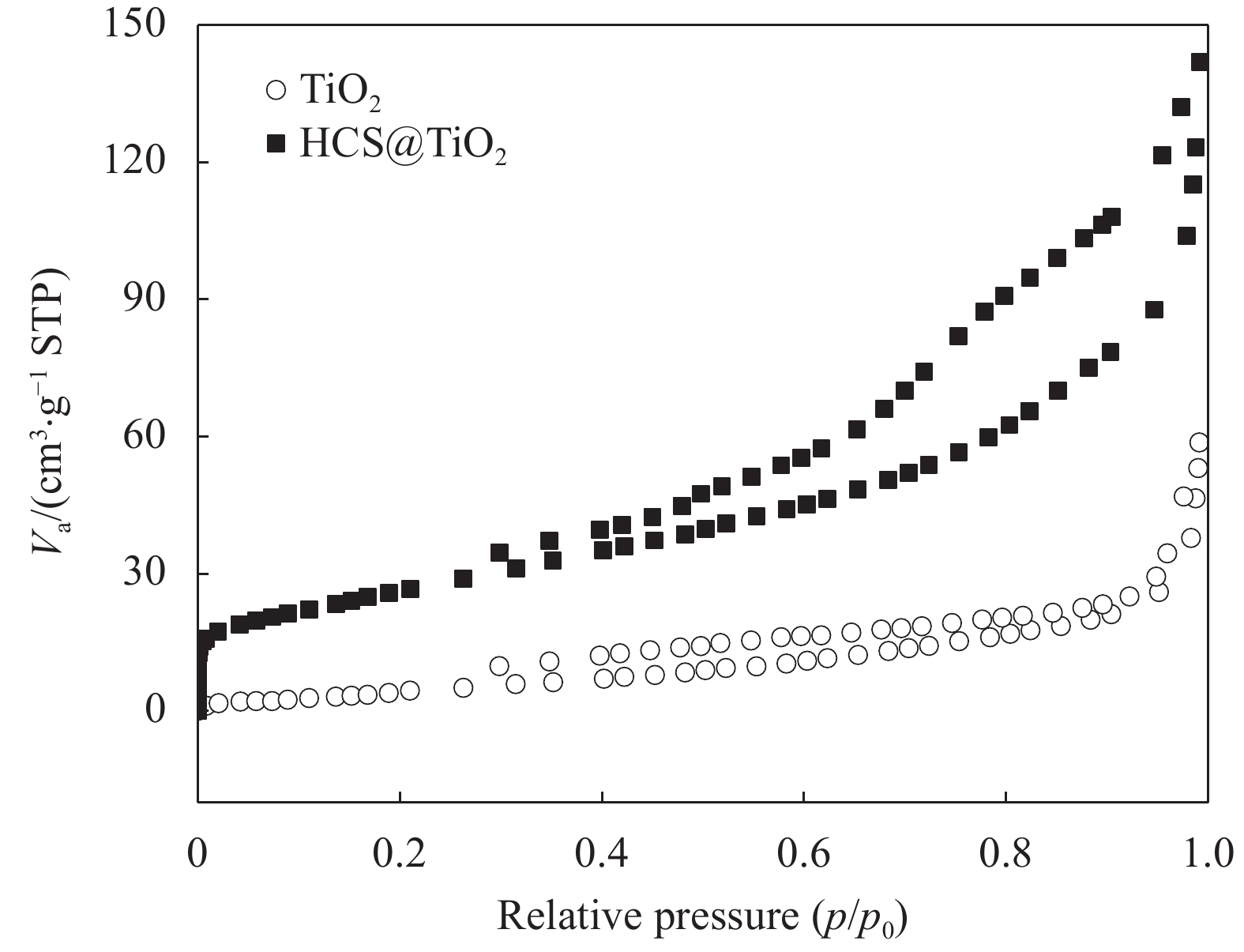
TiO2和HCS@TiO2的N2吸附-脱附等温线如图7所示,两种材料均为IV型等温线,表明两种材料中均存在大孔或介孔,TiO2等温线中存在H3型磁滞回环,而HCS@TiO2的滞回环类型变为H1型,这归功于HCS具有大量孔隙。根据BET方程计算得出,TiO2和HCS@TiO2的比表面积分别为19.6 m2/g和91.1 m2/g,表明HCS的加入,大大增加了HCS@TiO2的比表面积,减少了TiO2的团聚。
为了测试HCS@TiO2的定量组分和热稳定性,采用TGA对HCS@TiO2的热稳定性进行了研究,结果如图8所示。
可以看出,样品发生两次明显的质量损失。第一次质量损失是样品在100℃以下损失2.4wt%,主要归因于物理吸附和水的蒸发;第二次质量损失是样品在400℃以上损失17.2wt%,主要归因于燃烧HCS去除碳框架。最后,在600℃以上保持在80wt%不变。因此,确定HCS@TiO2中TiO2的质量分数为80wt%,具有优异的热稳定性。
通过接触角测试,分析HCS、酸化后的HCS、TiO2、HCS@TiO2的亲疏水性能,测试结果如图9所示,HCS、酸化后的HCS、TiO2、HCS@TiO2的接触角分别为135°、38°、85°和55°。HCS为疏水性材料,经过强酸酸化后,接触角明显减小了,说明酸化使HCS表面引入了大量极性基团,使其具有优异的亲水性和分散性。TiO2的接触角为85°,易发生团聚现象。与TiO2相比,HCS@TiO2的亲水性得到了明显提升,利于染料的吸附。
2.2 HCS@TiO2的光学特性
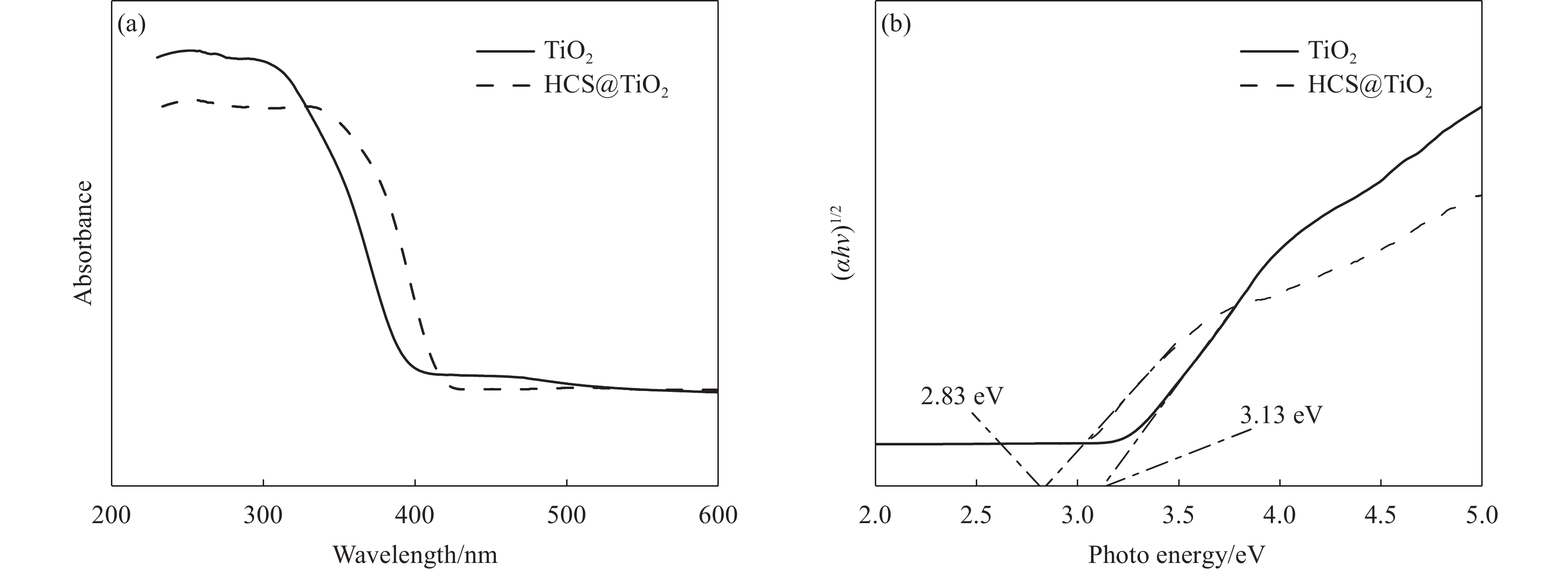
TiO2和HCS@TiO2的紫外-可见吸收光谱如图10(a)所示。可以看出,TiO2的吸收边带在390 nm左右,而HCS@TiO2的吸收边带发生了红移,在450 nm左右。
采用公式
(αhv)n=A(hv−Eg) (2) 其中:α为吸光度;h为普朗克常数;v为频率;指数n与半导体类型直接相关;A为比例常数;Eg为半导体的能隙,可以计算得到TiO2和HCS@TiO2的能量间隙图,利用切线法较精确地得到TiO2和HCS@TiO2复合材料的带隙能图,如图10(b)所示,TiO2的带隙能为3.13 eV,而HCS@TiO2的带隙能为2.83 eV,即HCS@TiO2的带隙能降低了,对光吸收范围更大了。
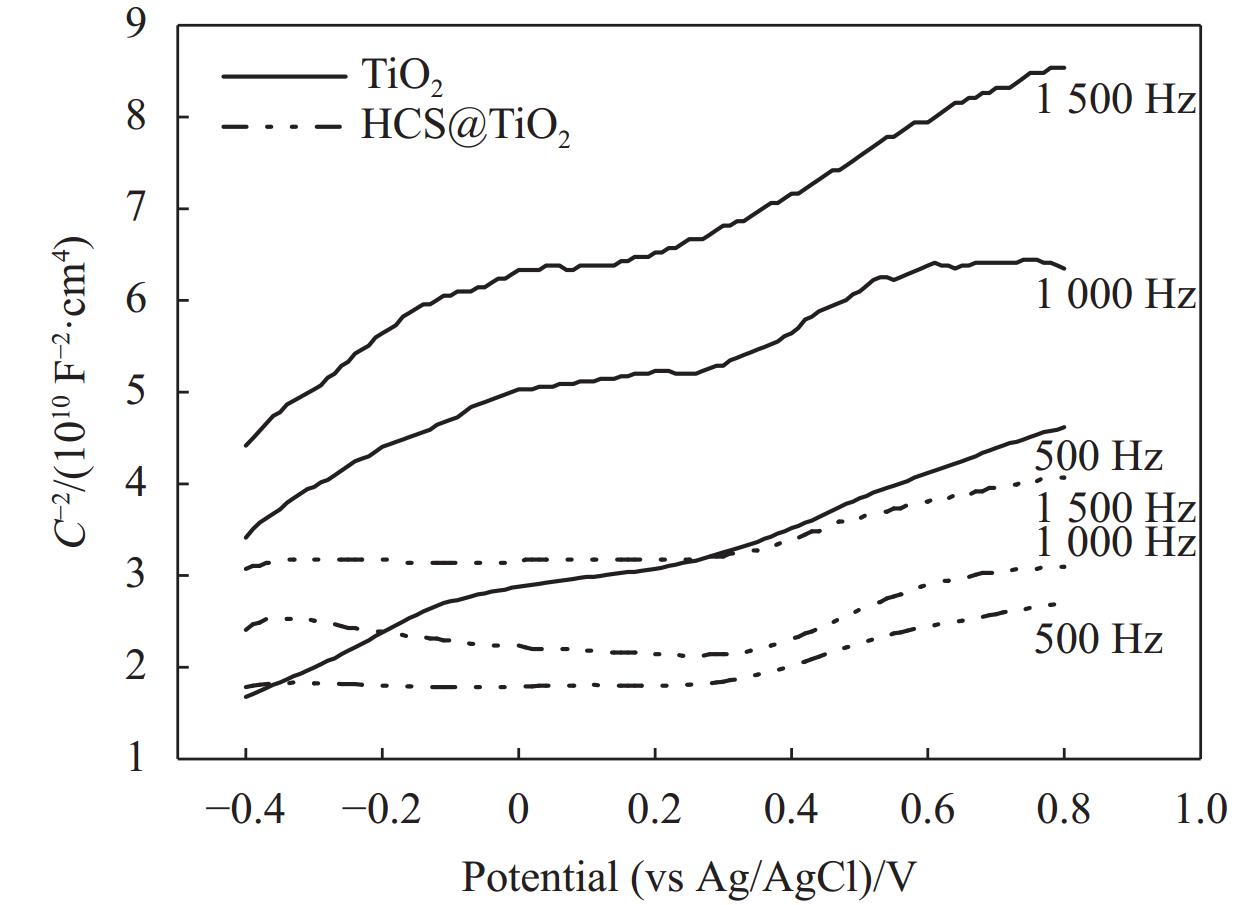
对TiO2和HCS@TiO2进行了Mott-Schottky测试,结果如图11所示。样品的曲线斜率均为正,这说明TiO2和HCS@TiO2均为n型半导体;且HCS@TiO2的斜率明显小于TiO2的斜率,表明HCS@TiO2的载流子浓度比TiO2的载流子浓度高。
2.3 HCS@TiO2复合材料的光催化降解染料性能
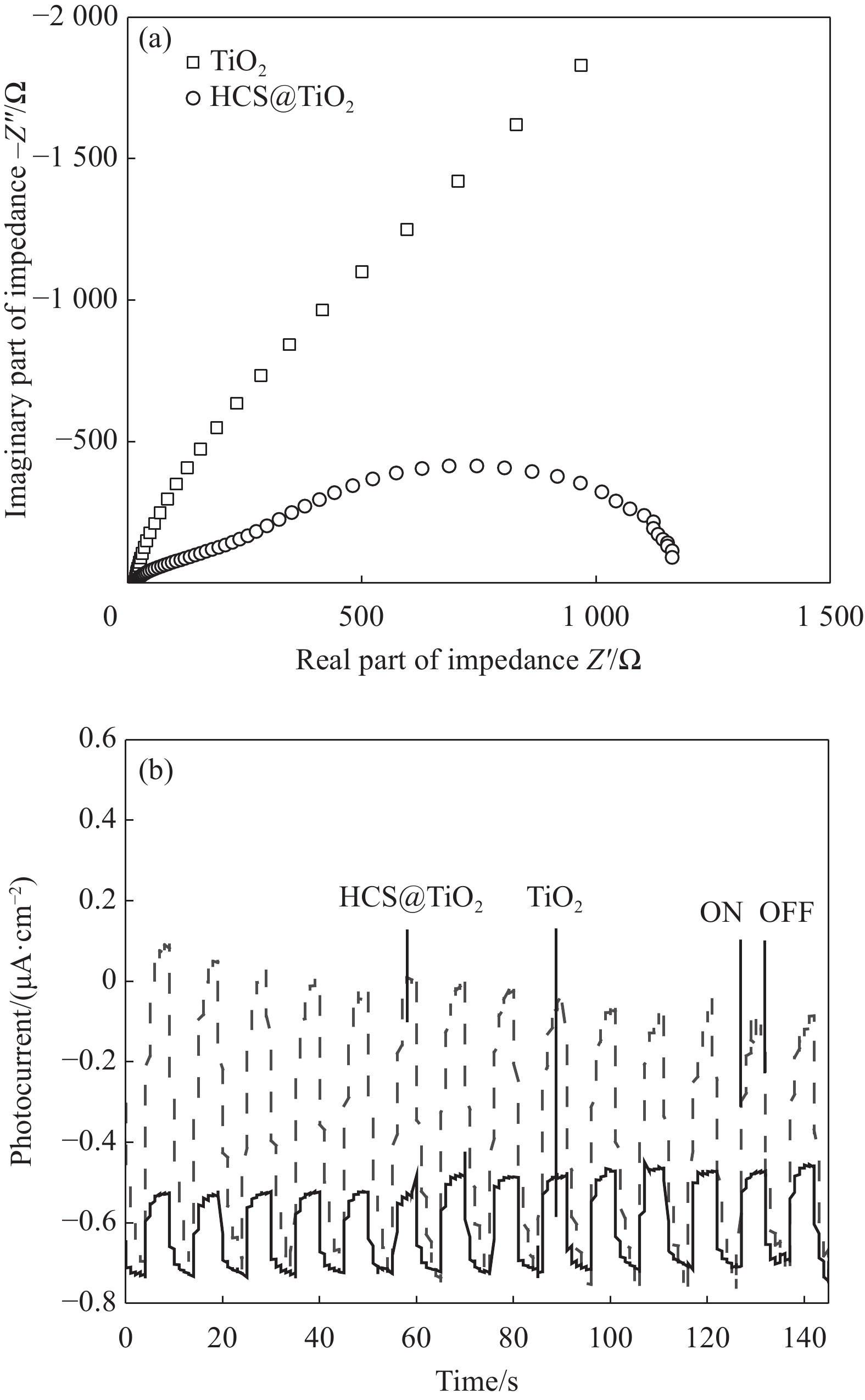
通过EIS研究TiO2和HCS@TiO2的电荷转移效率,结果如图12(a)所示。可以看出,HCS@TiO2的圆弧半径明显小于TiO2,说明其电荷转移电阻较低,促进电荷转移的同时抑制光生电子空穴对的复合,有利于光催化性能的提高[30]。图12(b)展示了HCS@TiO2和TiO2在可见光下反复开/关时的瞬态光电流,两种材料均展示出快速可逆的瞬态光电流响应,且随着光照时间的增强,光电流密度没有明显的衰减,同时,HCS@TiO2的光电流密度明显高于TiO2。表明HCS@TiO2的光生电子空穴对复合率更低,为光催化过程中提供稳定数量的光生电子[6]。
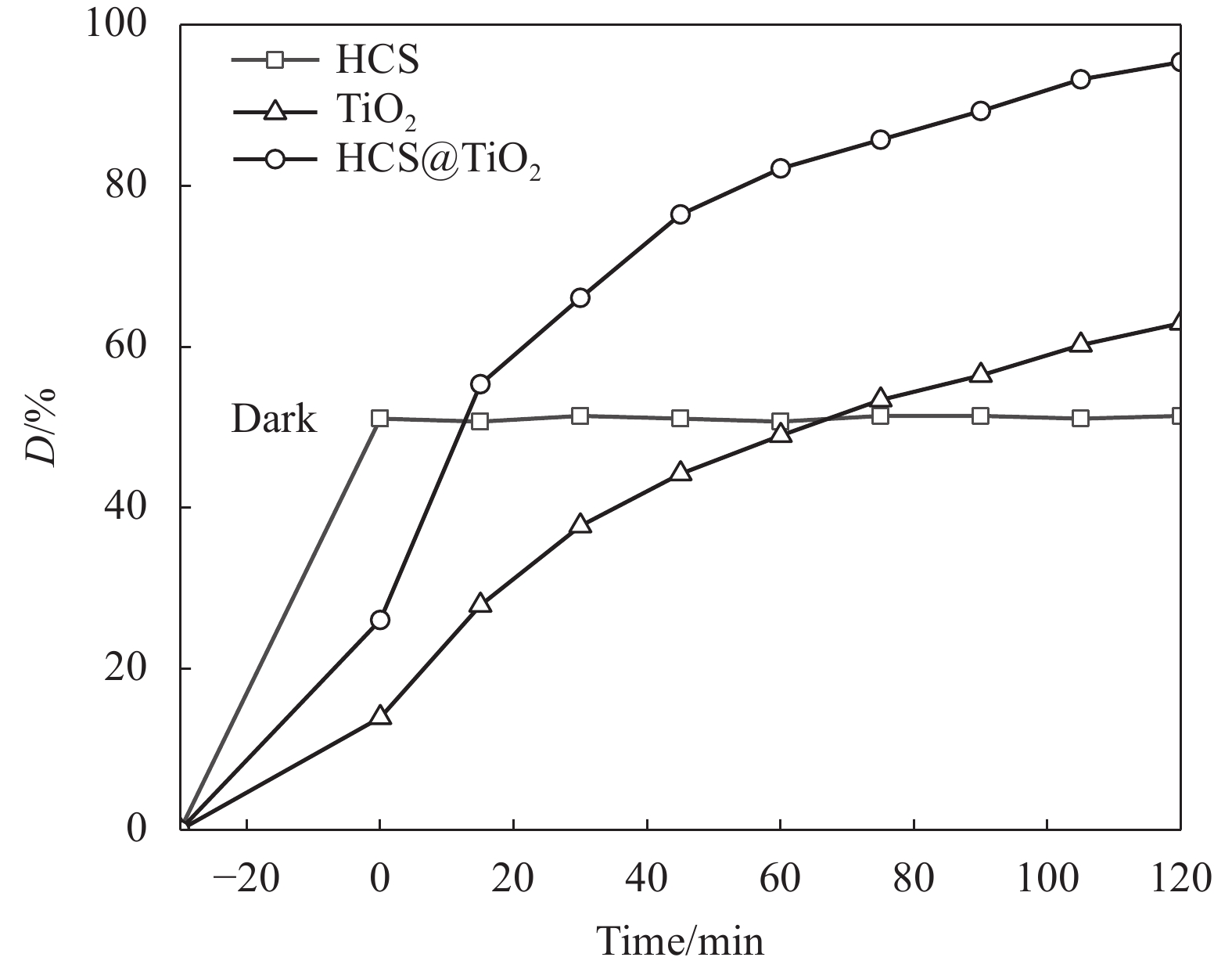
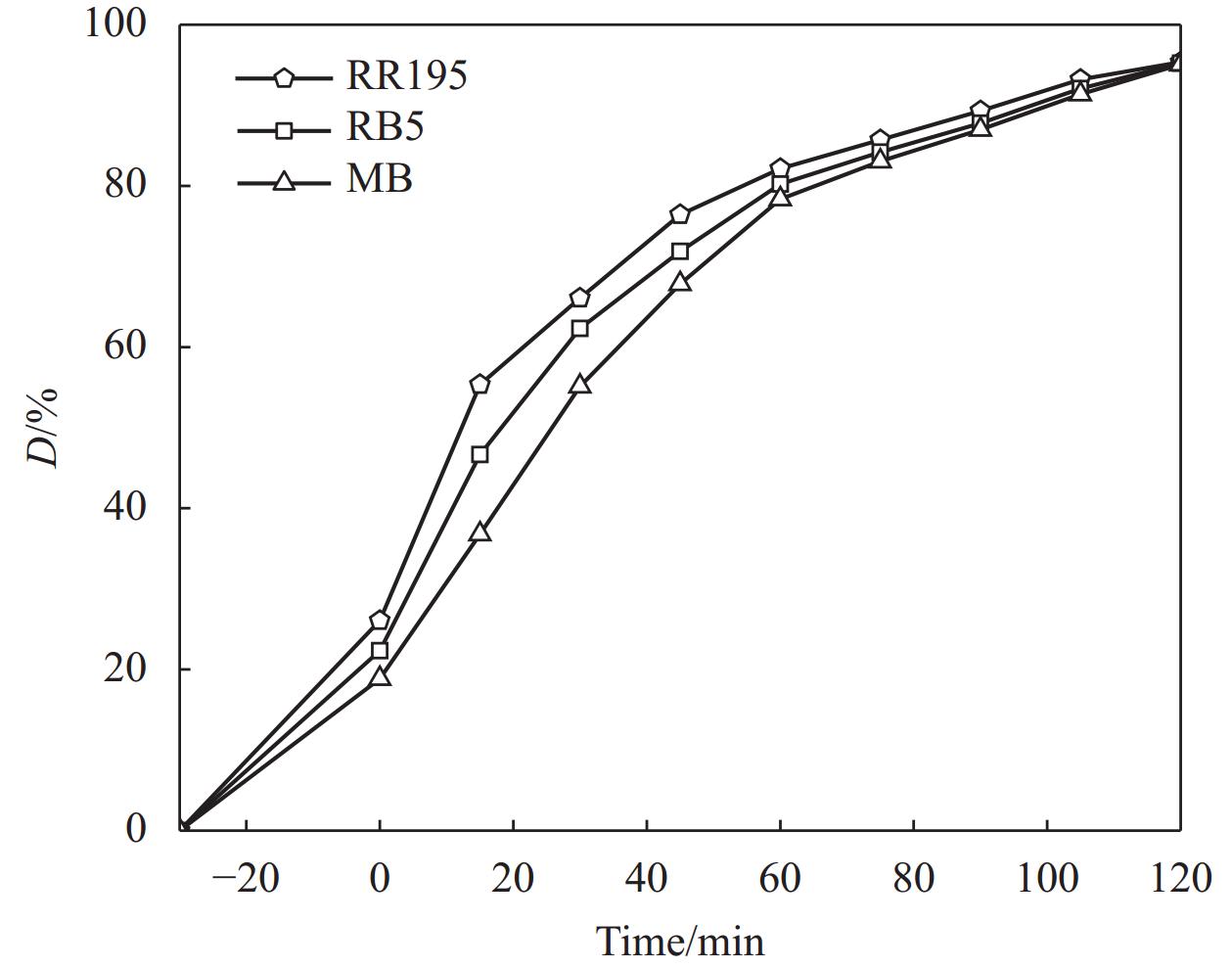
图13为HCS、TiO2 和HCS@TiO2这3种材料对RR195的降解曲线图,图14为HCS@TiO2光催化降解RR195、RB5和MB的曲线图。由图13可以看出,在暗箱吸附30 min 后,HCS的吸附达到平衡,之后一直保持不变;光照120 min后,TiO2降解率为62.93%,而HCS@TiO2降解率为95.36%,这是由于HCS和TiO2之间存在协同效应,提高了光生电子空穴对的分离效率,加速了污染物的降解。由图14可以看出,HCS@TiO2在光照120 min内对3种不同结构染料的降解率均高达95.00%,故HCS@TiO2具有广谱性。
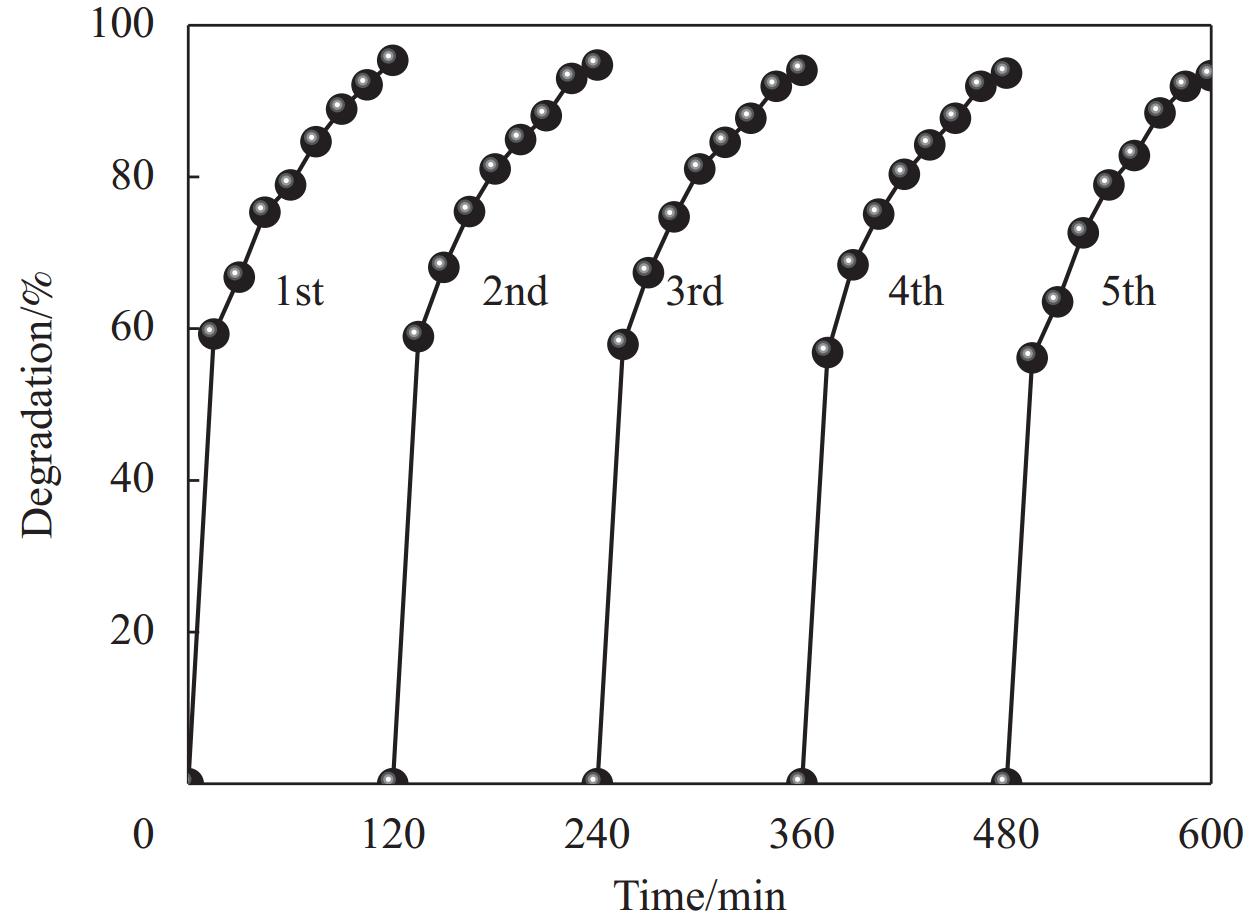
图15为HCS@TiO2降解RR195的紫外-可见光吸收光谱图及降解过程中的染液颜色变化图。可以看出,反应初始,RR195在510 nm和543 nm处均出现了吸收峰,对应—N=N—。随着反应的进行,RR195的颜色由艳红逐渐变为无色,最大吸收峰逐渐降低,说明其发色基团被有效降解。另外,为了考察HCS@TiO2的可重复利用性,进行了5次降解RR195的循环实验,每个循环周期都要进行30 min的暗箱吸附和120 min的光降解,结果如图16所示。可以看出,该复合材料5次循环后,降解率为93.34%,依旧保持很高的光催化活性,这归因于其本身独特的3D球形结构,可以防止负载在HCS上的TiO2掉落。另外,降解后,HCS@TiO2的回收率可达91.30%。
2.4 HCS@TiO2的光催化降解机制
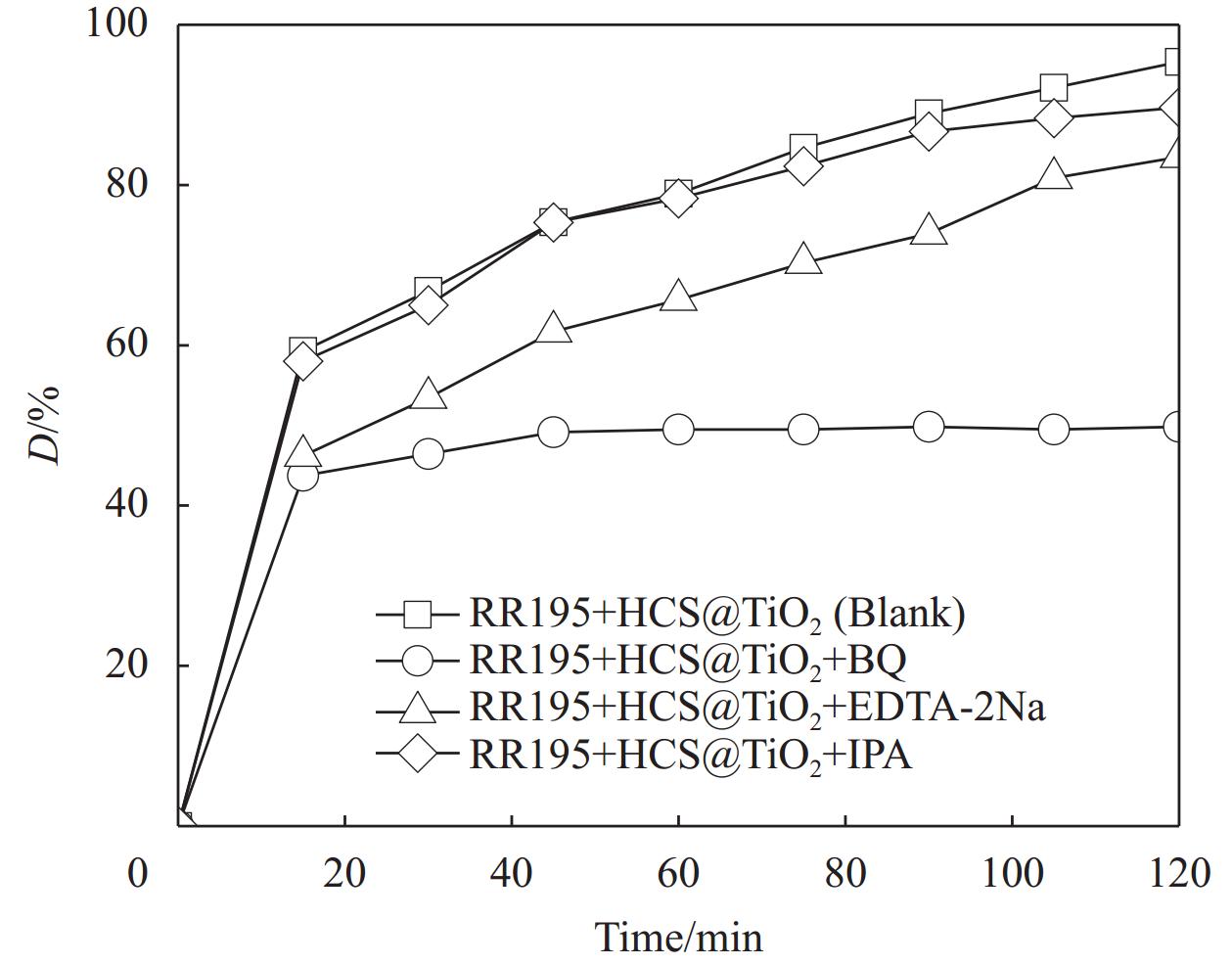
为了研究光催化降解中起主要作用的活性物质,采用苯醌(BQ)、乙二胺四乙酸钠(EDTA-2Na)和异丙醇(IPA)分别作为•O−2、h+和•OH的捕获试剂,结果如图17所示。
可以看出,在反应体系中加入捕获试剂后,光催化降解效率都会受到不同程度的抑制。其中加入BQ后,光催化效率下降最明显,降解率为49.83%,说明•O−2在光催化反应体系中起主要作用;而加入EDTA-2Na和IPA,降解率分别为83.50%和89.67%,说明h+和•OH在光催化反应体系中起次要作用,由此说明3种自由基的降解效率,•O−2最高,h+次之,•OH最低。可以推断,RR195可能在紫外照射下主要被•O2 −和h+分解。
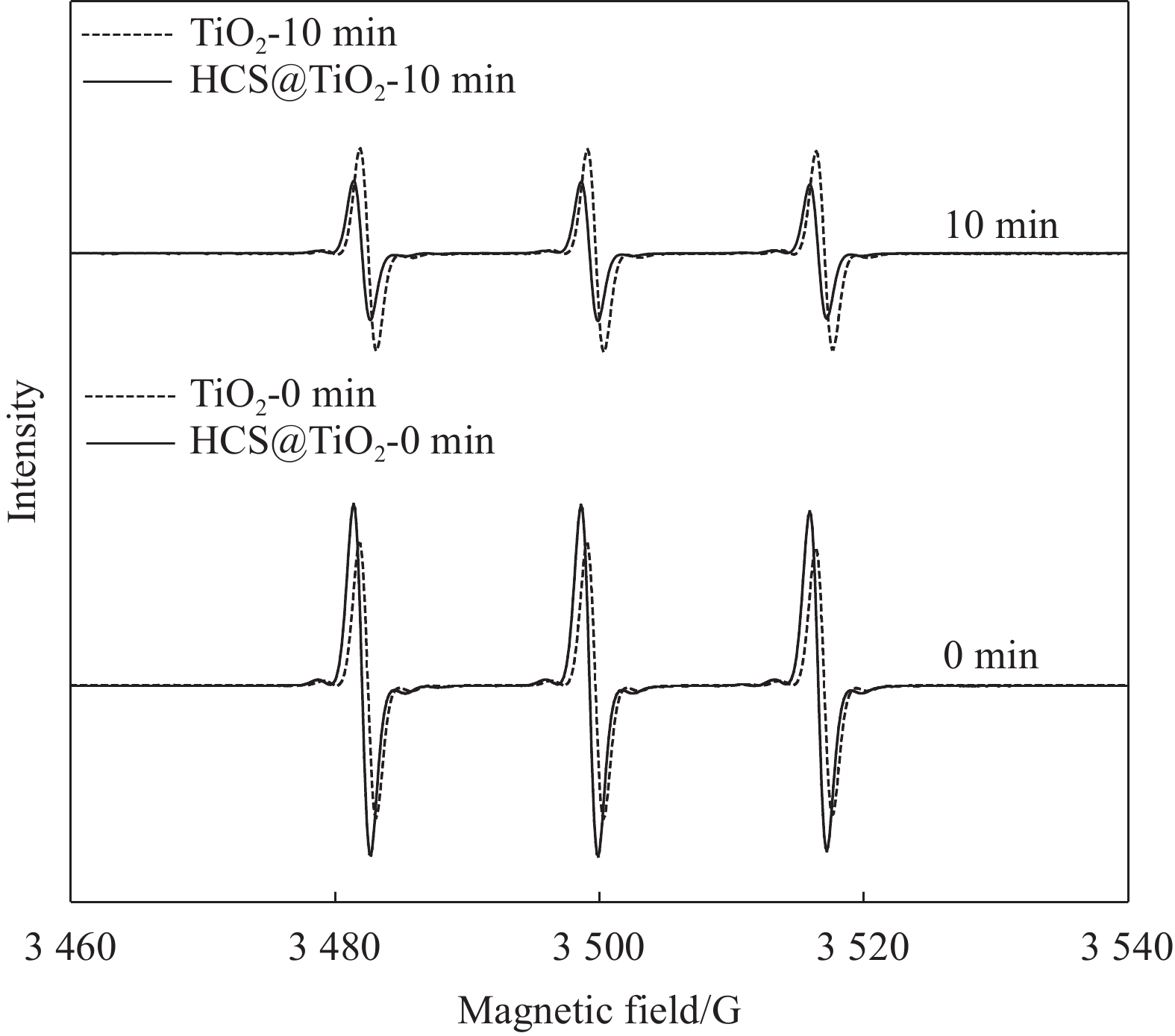
为了进一步探究光催化机制,通过ESR研究了自由基产生和转移机制,结果如图18所示。由于四甲基哌啶(TEMPO)作为电子e−的自旋标记分子,能够被检测到信号强度为1∶1∶1的信号峰,信号峰越弱,表明该样品生成的光生电子越多。可以看出,0 min即不光照时,TiO2的信号强度低于HCS@TiO2的信号强度;辐照10 min后,TiO2和HCS@TiO2的信号强度均有所减弱,且HCS@TiO2信号强度明显低于TiO2的信号强度,这是由于HCS作为电子陷阱促进了电子的转移,提高了光生电子空穴对的分离效率,因而HCS@TiO2相比于TiO2可以生成更多的光生电子。
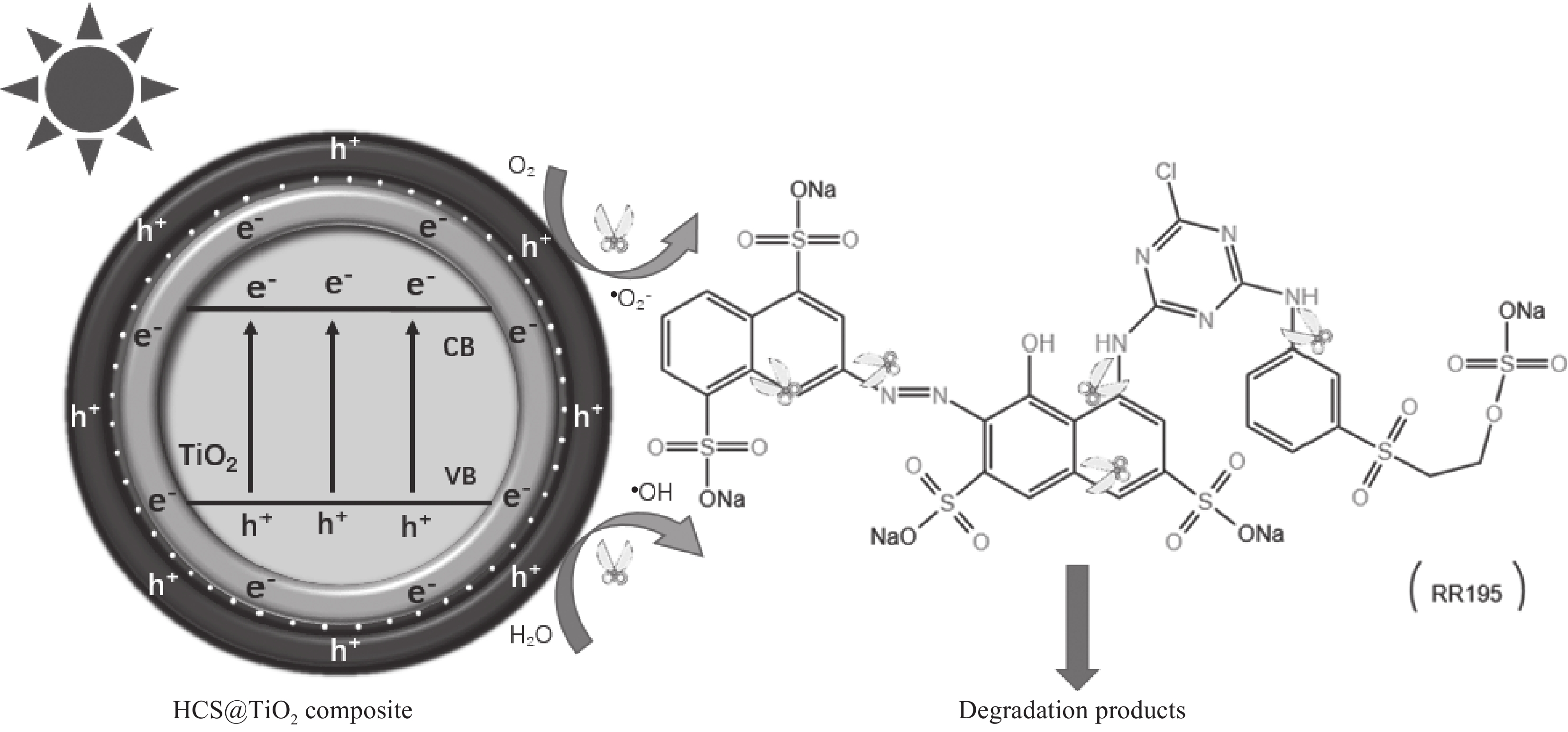
基于上述实验结果与分析,提出了HCS@TiO2复合材料光催化活性增强机制,如图19所示。由图可以看出:在光照下,e−从TiO2的价带(VB)跃迁到导带(CB)上,HCS功函高于TiO2,e−从TiO2的CB转移到HCS表面;TiO2上的h+会与H2O发生反应生成•OH;HCS表面的e−会与O2发生反应,使其生成•O−2,O−2还会与H+反应,生成过氧化氢自由基(H2O•),H2O•是H2O2的前躯体,后续反应生成H2O2,氧化反应和还原反应分别在TiO2和HCS上进行。此外,HCS的高比表面积可以使TiO2均匀负载,改善TiO2团聚现象,增加吸附点和活性位点,提高反应体系的降解速率。
3. 结 论
(1)利用简单的湿化学法可以制备空心碳球(HCS)@TiO2光催化复合材料,且TiO2均匀负载在HCS上,形成亲水性强、比表面积大、热稳定性优异的球形复合材料。
(2)光电化学性质分析表明,HCS@TiO2比TiO2禁带宽度更小,光响应范围更大,光生电子还原能力更强。
(3) HCS和TiO2之间的协同效应,提高了光生电子空穴对的分离效率,加速了污染物的降解。相同条件下,TiO2降解率仅为62.93%,而HCS@TiO2的降解率为95.36%,5次循环后降解率为93.34%,回收率为91.30%,且具有广谱性。
(4) 结合自由基捕获实验及电子顺磁共振光谱,提出了HCS@TiO2光催化复合材料的光催化降解机制,证实了•O−2在光催化反应体系中起主要作用。
-
-
[1] 高超民, 于海瀚, 赵悦含, 等. ZnO@SnO2异质结复合纳米管的可控构筑及其光催化性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2022, 39(12): 5856-5867. GAO Chaomin, YU Haihan, ZHAO Yuehan, et al. Controllable construction of ZnO@SnO2 heterojunction composite nanotubes and their photocatalytic properties[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2022, 39(12): 5856-5867(in Chinese).
[2] 蹇建, 杨德兴, 邝丹妮, 等. BiOBr@CdS/聚氨酯-蚕丝蛋白纳米复合膜的制备及其可见光催化性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2022, 39(8): 4037-4048. DOI: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20211012.002 JIAN Jian, YANG Dexing, KUANG Danni, et al. Synthesis and visible light photocatalystic of BiOBr@CdS/polyurethane-silk fibroin nanocomposite films[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2022, 39(8): 4037-4048(in Chinese). DOI: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20211012.002
[3] 傅炀杰, 张可欣, 毛惠秀, 等. AgI/NH2-UiO-66(Zr)异质结制备及其可见光催化性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2022, 39(7): 3369-3375. FU Yangjie, ZHANG Kexin, MAO Huixiu, et al. Preparation and photocatalytic performance of AgI/NH2-UiO-66(Zr) heterojunction[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2022, 39(7): 3369-3375(in Chinese).
[4] 李瑞瑞, 牛炳康, 柴猛, 等. CuxO/TiO2纳米颗粒的制备及其光催化性能研究[J]. 中北大学学报(自然科学版), 2023, 44(4): 403-415. LI Ruirui, NIU Bingkang, CHAI Meng, et al. The preparation of CuxO/TiO2 nanoparticles and its photocatalytic activity[J]. Journal of North University of China (Natural Science Edition), 2023, 44(4): 403-415 (in Chinese).
[5] 卫思颖, 马建中, 范倩倩. 量子点/TiO2复合光催化材料的研究进展[J]. 复合材料学报, 2021, 38(3): 712-721. WEI Siying, MA Jianzhong, FAN Qianqian. Research advances on quantum dots/TiO2 composite photocatalytic materials[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2021, 38(3): 712-721(in Chinese).
[6] 吴健博, 石亮, 郑小强, 等. g-C3N4/BiOCl复合光催化剂作为2D/2D异质结用于光催化降解染料性能研究[J]. 复合材料学报, 2023, 40(1): 323-333. WU Jianbo, SHI Liang, ZHENG Xiaoqiang, et al. g-C3N4/BiOCl composite photocatalyst used as 2D/2D heterojunction for photocatalytic degradation of dyes[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2023, 40(1): 323-333(in Chinese).
[7] 曾雄丰, 王梦幻, 王建省, 等. TiO2/石墨烯夹层结构复合材料的制备及光催化性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2022, 39(2): 656-663. ZENG Xiongfeng, WANG Menghuan, WANG Jiansheng, et al. Preparation and photocatalytic properties TiO2/graphene nanocomposites with sandwich structure[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2022, 39(2): 656-663(in Chinese).
[8] 谷麟, 俞海祥, 王宇, 等. TiO2/底泥复合材料的制备及其可见光催化性能评价[J]. 复合材料学报, 2019, 36(11): 2665-2673. GU Lin, YU Haixiang, WANG Yu, et al. Preparation of TiO2/river sediment composite and its visible light photocatalytic performance[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2019, 36(11): 2665-2673(in Chinese).
[9] 董晓珠, 曾雄丰, 王建省, 等. β-FeOOH/TiO2复合薄膜的制备及其光催化性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2022, 39(3): 1173-1179. DONG Xiaozhu, ZENG Xiongfeng, WANG Jiansheng, et al. Preparation of β-FeOOH/TiO2 composite film and its photocatalytic performance[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2022, 39(3): 1173-1179(in Chinese).
[10] 李跃军, 曹铁平, 孙大伟, 等. Bi@Bi4Ti3O12/TiO2等离子体复合纤维的制备及增强可见光催化性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2020, 37(3): 609-617. LI Yuejun, CAO Tieping, SUN Dawei, et al. Preparation and highly enhanced visible-light photocatalytic performances of Bi@Bi4Ti3O12/TiO2 plasmonic composite fibers[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2020, 37(3): 609-617(in Chinese).
[11] 樊婷玥, 任煜, 赵紫瑶, 等. Ag6Si2O7-TiO2/PP复合光催化材料的制备及其抗菌性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2022, 39(8): 3915-3921. FAN Tingyue, REN Yu, ZHAO Ziyao, et al. Preparation and antibacterial properties of Ag6Si2O7-TiO2/PP composite photocatalytic material[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2022, 39(8): 3915-3921(in Chinese).
[12] 胡金娟, 马春雨, 王佳琳, 等. Ag-Ag2O/TiO2-g-C3N4纳米复合材料的制备及可见光催化性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2020, 37(6): 1401-1410. DOI: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20191217.001 HU Jinjuan, MA Chunyu, WANG Jialin, et al. Preparation and photocatalytic properties of Ag-Ag2O/TiO2-g-C3N4 nanocomposites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2020, 37(6): 1401-1410(in Chinese). DOI: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20191217.001
[13] 郑小强, 佟占鑫, 吴健博, 等. Bi2O3-TiO2复合氧化物光催化环己烷选择氧化[J]. 复合材料学报, 2022, 39(7): 3262-3270. ZHENG Xiaoqiang, TONG Zhanxin, WU Jianbo, et al. Photocatalytic selective oxidation of cyclohexane with Bi2O3-TiO2 composite oxide[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2022, 39(7): 3262-3270(in Chinese).
[14] 李燕, 孙宝, 王爱国, 等. TiO2-g-C3N4复合材料的制备及其在水泥石表面的应用[J]. 复合材料学报, 2020, 37(8): 1981-1988. LI Yan, SUN Bao, WANG Aiguo, et al. Preparation of TiO2-g-C3N4 composites and its application in cement stone surface[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2020, 37(8): 1981-1988(in Chinese).
[15] 谢若兰, 何欢, 杨世利, 等. TiO2-g-C3N4-Bi2O3复合异质结构催化材料在水处理中的应用[J]. 复合材料学报, 2021, 38(9): 3036-3044. XIE Ruolan, HE Huan, YANG Shili, et al. Application of TiO2-g-C3N4-Bi2O3 composite heterogeneous catalytic materials in water treatment[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2021, 38(9): 3036-3044(in Chinese).
[16] 刘袁, 房国丽, 严祥辉, 等. 基底表面缺陷对TiO2/Bi2WO6复合材料微观结构和光催化性能的影响[J]. 复合材料学报, 2023, 40(5): 2783-2793. LIU Yuan, FANG Guoli, YAN Xianghui, et al. Effect of substrate surface defect on the microstructure and photocatalytic activities of TiO2/Bi2WO6 composites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2023, 40(5): 2783-2793(in Chinese).
[17] 廖燕敏, 黄俊健, 杨小霞, 等. 晶面异质结纳米二氧化钛/二维石墨相氮化碳复合材料的光催化性能研究[J]. 化学研究与应用, 2021, 33(5): 927-934. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1656.2021.05.020 LIAO Yanmin, HUANG Junjian, YANG Xiaoxia, et al. Study on photocatalytic performance of crystal surface heterojunction nanometer titanium dioxide/two-dimensional graphite phase carbon nitride composites[J]. Chemical Research and Application, 2021, 33(5): 927-934(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-1656.2021.05.020
[18] 周小桔, 钱俊, 胡正龙, 等. PbTi0.85Ni0.15O3/TiO2纳米棒阵列复合材料的压电光催化性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2024, 41(3): 1371-1382. ZHOU Xiaoju, QIAN Jun, HU Zhenglong, et al. Piezo-photocatalytic property of PbTi0.85Ni0.15O3/TiO2 nanorod array composite materials[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2024, 41(3): 1371-1382(in Chinese).
[19] 郭佳允, 傅炀杰, 张柯杰, 等. g-C3N4/POPs异质结制备及其可见光催化性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2023, 40(2): 904-910. GUO Jiayun, FU Yangjie, ZHANG Kejie, et al. Preparation and visible light catalytic performance of g-C3N4/POPs heterojunction[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2023, 40(2): 904-910(in Chinese).
[20] 杨光, 陈松, 丁会敏, 等. 空心纳微米碳球的制备研究进展[J]. 化学工程师, 2019, 33(9): 65-67. DOI: 10.16247/j.cnki.23-1171/tq.20190965 YANG Guang, CHEN Song, DING Huimin, et al. Effect of modified semi-coke structure on its adsorption performance[J]. Chemical Engineer, 2019, 33(9): 65-67(in Chinese). DOI: 10.16247/j.cnki.23-1171/tq.20190965
[21] 张兴淼, 张威, 李伟. 碳基空心结构纳米材料的制备与应用[J]. 黑龙江大学工程学报, 2021, 12(3): 42-56. DOI: 10.13524/j.2095-008x.2021.03.036 ZHANG Xingmiao, ZHANG Wei, LI Wei. Synthesis and aoolication of carbon-based hollow nanomaterials[J]. Journal of Engineering of Heilongjiang University, 2021, 12(3): 42-56(in Chinese). DOI: 10.13524/j.2095-008x.2021.03.036
[22] 李会敏, 王晓冬, 李玥, 等. 柔性Ag@TiO2/碳纳米纤维膜的制备及光催化性能[J]. 电镀与涂饰, 2021, 40(5): 393-399. LI Huimin, WANG Xiaodong, LI Yue, et al. Preparation and photocatalytic activity of flexible Ag@TiO2/carbon nanofiber membrane[J]. Electroplating & Finishing, 2021, 40(5): 393-399(in Chinese).
[23] 常薇, 雷超, 罗杰, 等. 二氧化钛/石墨烯气凝胶的制备及光催化性能[J]. 西安工程大学学报, 2022, 36(6): 54-59. DOI: 10.13338/j.issn.1674-649x.2022.06.008 CHANG Wei, LEI Chao, LUO Jie, et al. Preparation and photocatalytic activity of titanium dioxide/graphene aerogel[J]. Journal of Xi'an Polytechnic University, 2022, 36(6): 54-59(in Chinese). DOI: 10.13338/j.issn.1674-649x.2022.06.008
[24] SONG S Z, QIN T, LI Q, et al. Single Co atoms implanted into N-doped hollow carbon nanoshells with non-planar Co-N4-1-O2 sites for efficient oxygen electrochemistry[J]. Inorganic Chemistry, 2021, 60(10): 7498-7509.
[25] ZHOU S H, LIU S K, SU K, et al. Facile synthesis of Ti3+ self-doped and sulfur-doped TiO2 nanotube arrays with enhanced visible-light photoelectrochemical performance[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds, 2019, 804: 10-17.
[26] FANG J, GAO X H, SUN J, et al. An efficient TiO2/rGO hybrids with enhanced photocatalytic degradation toward Reactive Red 195[J]. Environmental Engineering Science, 2021, 38(6): 555-564.
[27] GGHICOV A, TSUCHIYA H, MACAK J M, et al. Annealing effects on the photoresponse of TiO2 nanotubes[J]. Physica Status Solidi, 2006, 203(4): R28-R30.
[28] 周毛毛, 蒋阳, 谢于辉, 等. 纳米二氧化钛的制备、改性及其在聚合物基复合材料中的应用研究进展[J]. 复合材料学报, 2022, 39(5): 2089-2105. DOI: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20211106.002 ZHOU Maomao, JIANG Yang, XIE Yuhui, et al. Preparation and modification of nano-TiO2 and its application in polymer matrix composites research progress[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2022, 39(5): 2089-2105(in Chinese). DOI: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20211106.002
[29] CRUZ M, GOMEZ C, DURAN-VALLE C J, et al. Bare TiO2 and graphene oxide TiO2 photocatalysts on the degradation of selected pesticides and influence of the water matrix[J]. Applied Surface Science, 2017, 416: 1013-1021.
[30] 郭佳允. 新型多孔有机聚合物复合材料的制备及其环境光催化性能研究[D]. 杭州: 浙江工商大学, 2022. GUO Jiayun. Preparation and environmental photocatalytic properties of novel porous organic polymer composites[D]. Hangzhou: Zhejiang Gongshang University, 2022(in Chinese).
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 李梦涵,魏娜,徐瑞琪,杨泽钰,崔洪芝. 三维碳纳米管/硅藻土基多孔陶瓷复合材料的制备及其光热水蒸发性能. 复合材料学报. 2023(08): 4577-4586 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 吴玉萍,王乾廷,孙炜,周忠华,谢宗丽,宋铭雨. 含椭圆叶片状SiO_2/聚乙烯醇渗透汽化复合膜的制备与性能. 复合材料学报. 2022(06): 2783-2791 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 赵士雄. 反渗透复合膜制备及其改性方法研究进展. 云南化工. 2022(06): 20-21+38 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)
-
目的
光催化技术作为一种高效、安全的环境友好型净化技术,被广泛应用于降解环境中的有机污染物,为了获得性能更加优异的光催化材料用来降解有机染料,以减小有机废水污染对人类健康和环境构成的极大威胁,本文基于空心碳球(HCS)与TiO两者之间可以通过氢键和范德华力形成HCS@TiO范德华异质结,制备了HCS@TiO光催化复合材料,研究其光催化降解有机染料的性能,并探究其降解机理。
方法利用简单的湿化学法制备HCS@TiO光催化复合材料。首先,合成HCS,作为TiO颗粒的基底;第二,对合成的HCS进行酸化处理,提高其表面亲和力;第三,随着溶剂的蒸发,TOAC粘附在HCS的表面,产生HCS@TOAC的前驱体。用特定的加热程序(先O气流后Ar气流)对HCS@TOAC进行热解,形成HCS@TiO复合材料。通过SEM、TEM、XRD、XPS、TG、N吸附-脱附曲线、接触角测试等对其进行形貌与结构的表征;通过紫外-可见吸收光谱(UV-Vis DRS)、Mott-Schottky分析其光学特性;通过UV-Vis DRS、电化学阻抗谱(EIS)测试、瞬态光电流响应图和循环降解试验分析其光催化降解性能,结合自由基捕获实验、电子顺磁共振波谱(ESR)表征对HCS@TiO光催化复合材料的光催化机制进行探究。
结果形貌与结构表征结果显示TiO 均匀地负载在HCS上,没有出现TiO纳米颗粒聚集的现象,且HCS负载TiO后仍保持球形结构;不同煅烧温度下的HCS@TiO的XRD分析对比,可得HCS@TiO 350℃(O2)-650℃(Ar)的锐钛矿型衍射峰最强,在2θ=25.2°、37.8°、48.0°、53.8°、55.0°和62.6°处的特征衍射峰与锐钛矿相的(101)、(004)、(200)、(105)、(211)、(204)晶面对应,锐钛矿型TiO具有比金红石型TiO更优异的光催化性能;N吸附-脱附等温线和接触角的测试证实了 HCS的加入,大大增加了HCS@TiO的比表面积,减少了TiO的团聚,与TiO相比,HCS@TiO的亲水性得到了明显提升,利于染料的吸附。光电化学性质分析可知TiO的带隙能为3.13 eV,而HCS@TiO的带隙能为2.83 eV,且HCS@TiO的载流子浓度比TiO的载流子浓度高;进一步通过电化学阻抗EIS和瞬态光电流响应发现HCS@TiO电荷转移电阻较 TiO的低,光电流密度高于TiO,表明HCS@TiO的光生电子空穴对复合率更低,有利于光催化性能的提高。光催化降解染料性能测试可以看出,光照120 min后,TiO降解率为62.93%,而HCS@TiO降解率为95.36%,五次降解循环使用后仍具有93.34%的降解率,且HCS@TiO在光照120 min内对三种不同结构染料的降解率均高达95.00%。采用苯醌(BQ)、乙二胺四乙酸钠(EDTA-2Na)和异丙醇(IPA)分别作为·O、h和·OH的捕获试剂进行自由基捕获实验,发现在反应体系中加入BQ后,光催化效率下降最明显,降解率为49.83%,说明·O在光催化反应体系中起主要作用,加入EDTA-2Na和IPA,降解率分别为83.50%和89.67%,说明h和·OH在光催化反应体系中起次要作用,由此说明三种自由基的降解效率,·O2-最高,h次之,·OH最低,可以推断,RR195可能在紫外照射下主要被·O和h分解。通过 ESR谱图进一步探究其光催化机制,发现HCS作为电子陷阱促进了电子的转移,提高了光生电子空穴对的分离效率,增强了HCS@TiO复合材料的光催化活性,因而其降解有机染料的能力更高。
结论利用简单的湿化学法可以制备HCS@TiO光催化复合材料,且TiO均匀负载在HCS上,形成亲水性强、比表面积大、热稳定性优异的球形复合材料。该复合材料禁带宽度更小,光响应范围更大,光生电子还原能力更强,相同条件下,TiO降解率仅为62.93%,而HCS@TiO的降解率为95.36%,5次循环后降解率为93.34%,回收率为91.30%,且具有广谱性。结合自由基捕获实验以及电子顺磁共振光谱,提出了HCS@TiO光催化复合材料的光催化降解机制,证实了·O在光催化反应体系中起主要作用。
-
TiO2是众多光催化材料中最具有潜力的,因其无毒、稳定、廉价、可循环利用等优点而得到广泛的研究和商业应用,但是TiO2存在低表面积、禁带宽、电子空穴对复合率高、光吸收能力低等问题限制了它的光催化性能。
本文基于三维空心碳球(HCS)具有优异的导电性、无毒、高稳定性、高比表面积和亲水性等特点,通过简单的湿化学法制备了异质结构的HCS@TiO2光催化复合材料,探索了在模拟太阳光下光催化降解RR195的光催化性能。通过SEM、TEM、XRD、XPS、TGA、N2吸附-脱附、接触角测试对HCS@TiO2光催化复合材料进行形貌与结构的表征;通过紫外-可见吸收光谱(UV-Vis DRS)、Mott-Schottky测试分析其光学特性;通过UV-Vis DRS、电化学阻抗谱(EIS)测试、瞬态光电流响应图和循环降解试验分析其光催化降解性能,同时结合自由基捕获实验、电子顺磁共振光谱表征的方法,对HCS@TiO2光催化复合材料的光催化机制进行了探究,证实了·O2-在光催化反应体系中起主要作用。
如图,在光照下,e-从TiO2的VB跃迁到CB上,HCS功函高于TiO2,e-从TiO2的CB转移到HCS表面;TiO2上的h+会与H2O发生反应生成·OH;HCS表面的e-会与O2发生反应,使其生成·O2-,O2- 还会与H+反应,生成过氧化氢自由基(H2O·),H2O·是H2O2的前躯体,后续反应生成H2O2,氧化反应和还原反应分别在TiO2和HCS上进行。此外,HCS的高比表面积,可以使TiO2均匀负载,改善了TiO2团聚现象,增加了吸附点和活性位点,提高了反应体系的降解速率。
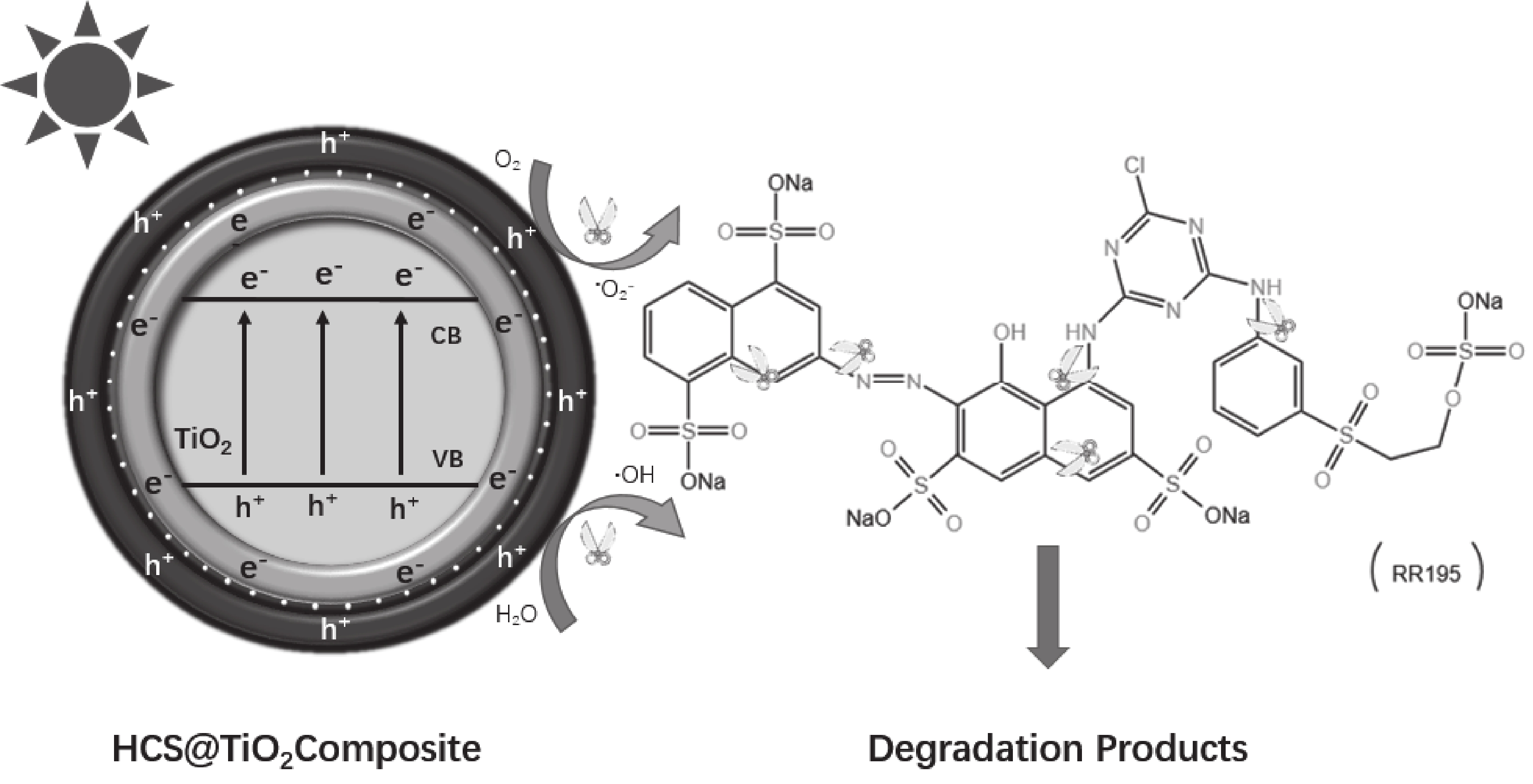
图1





 下载:
下载: