Photodeposition Pt composite graphitic carbon nitride realizes efficient photocatalytic hydrogen production
-
摘要: 贵金属作为助催化剂,可以提高石墨相氮化碳(g-C3N4)光催化产氢的性能,引起了人们的广泛关注。但是,由于贵金属的不可再生性和高价格,“更少的贵金属,更好的性能”始终是目标。为了实现这一目标,通过光沉积还原法成功制备了一系列不同铂负载量氮化碳复合材料(Pt/CN),并用于光催化产H2。结果表明:不同Pt负载量的Pt/CN复合材料都表现出优异的光催化产氢性能。并发现当Pt的负载量为0.5wt%时, Pt/CN复合材料具有最优异的光催化产氢活性,产氢量为409.2 μmol/g,是纯CN (17.8 μmol/g)的23倍,同时证实了Pt和CN二者之间形成了肖特基势垒,使导带的电子快速迁移到Pt上,降低了CN的电子-空穴复合速率。并且Pt作为光催化分解水的活性位点,促进水中的绝大部分氢质子快速吸附到Pt位点,得到电子被还原为H2,实现了高效光催化产氢。Abstract: Noble-metal, as co-catalysts, can improve the photocatalytic hydrogen production performance of graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4). It has been paid extensive attention, however, due to the non-renewability and high expense of noble-metal, "less noble-metal, better performance" is always the goal. To achieve this goal, composite CN with different Pt loadings (Pt/CN) was successfully prepared by photoreduction deposition and used for photocatalytic hydrogen production. The results show that Pt/CN with different Pt loadings can improved photocatalytic hydrogen production performance than CN. It is found that Pt/CN loaded with 0.5wt%Pt have the best photocatalytic hydrogen production activity, with a hydrogen production rate of 409.2 μmol/g, which is 23 times higher than that of CN (17.8 μmol/g). At the same time, it is confirmed that a Schottky barrier is formed between Pt and CN, which makes the electrons of the conduction band migrate rapidly to Pt, which reduces the electron-hole recombination rate of CN. Moreover, Pt is used as the active site of photocatalytic water splitting, which promotes the rapid adsorption of most of the hydrogen protons in the water to the Pt site, and the electrons are reduced to hydrogen, realizing efficient photocatalytic hydrogen production.
-
Keywords:
- graphitic carbon nitride /
- photocatalytic hydrogen production /
- Pt /
- photodeposition /
- compound rad
-
-
图 6 (a)不同Pt负载量下Pt/CN的光解水产H2曲线;(b) 0.5wt%Pt/CN的循环光催化测试;反应前后0.5wt%Pt/CN的XRD图谱(c)和FTIR图谱(d)
Figure 6. (a) Photolyzed aquatic H2 curves of Pt/CN under different Pt doping amounts; (b) Cycling photocatalytic test of 0.5wt%Pt/CN; XRD patterns (c) and FTIR spectra (d) of 0.5wt%Pt/CN before and after reaction
-
[1] KARTHIKEYAN C, ARUNACHALAM P, RAMACHANDRAN K, et al. Recent advances in semiconductor metal oxides with enhanced methods for solar photocatalytic applications[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2020,828:154281. DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.154281
[2] ZHANG S, WANG K, LI F, et al. Structure-mechanism relationship for enhancing photocatalytic H2 production[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy,2022,47(88):37517-37530. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2021.10.139
[3] XIONG S, TANG R, GONG D, et al. Environmentally-friendly carbon nanomaterials for photocatalytic hydrogen production[J]. Chinese Journal of Catalysis,2022,43(7):1719-1748. DOI: 10.1016/S1872-2067(21)63994-3
[4] MUN S J, PARK S J. Graphitic carbon nitride materials for photocatalytic hydrogen production via water splitting: A short review[J]. Catalysts,2019,9(10):805. DOI: 10.3390/catal9100805
[5] ZHOU Y Z, ZHANG L X, QIN L X, et al. A mixed phase lanthanum vanadate in situ induced by graphene oxide/graphite carbon nitride for efficient photocatalytic hydrogen generation[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy,2021,46(54):27495-27505. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2021.05.213
[6] XUE F, CHEN C, FU W L, et al. Interfacial and dimensional effects of Pd co-catalyst for efficient photocatalytic hydrogen generation[J]. The Journal of Physical Chemistry C,2018,122(44):25165-25173. DOI: 10.1021/acs.jpcc.8b06943
[7] LI K, LIN Y Z, WANG K, et al. Rational design of cocatalyst system for improving the photocatalytic hydrogen evolution activity of graphite carbon nitride[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental,2020,268:118402. DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2019.118402
[8] WU Q K, JEONG T, KIM S H, et al. Synthesis of large area graphitic carbon nitride nanosheet by chemical vapor deposition[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2022,900:163310. DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.163310
[9] DING L, QI F, LI Y F, et al. In-situ formation of nanosized 1T-phase MoS2 in B-doped carbon nitride for high efficient visible-light-driven H2 production[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science,2022,614:92-101. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcis.2022.01.100
[10] JIANG W S, ZHAO Y J, ZONG X P, et al. Photocatalyst for high-performance H2 production: Ga-doped polymeric carbon nitride[J]. Angewandte Chemie International Edition,2021,60(11):6124-6129. DOI: 10.1002/anie.202015779
[11] LIU Y, GAO M Y, YANG W W, et al. Facile synthesis of monodisperse Pt nanoparticles on graphitic carbon Nitride for high-performance photocatalytic H2 evolution[J]. ChemistrySelect,2022,7(9):e202103882.
[12] PENG Y, LU B Z, CHEN L M, et al. Hydrogen evolution reaction catalyzed by ruthenium ion-complexed graphitic carbon nitride nanosheets[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A,2017,5(34):18261-18269. DOI: 10.1039/C7TA03826G
[13] WU J E, ZHANG Y Y, ZHANG B, et al. Zn-doped CoS2 nanoarrays for an efficient oxygen evolution reaction: Understanding the doping effect for a precatalyst[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2022,14(12):14235-14242.
[14] HUANG L, LIU X, WU H C, et al. Surface state modulation for size-controllable photodeposition of noble metal nanoparticles on semiconductors[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A,2020,8(40):21094-21102. DOI: 10.1039/C9TA14181B
[15] BAI L, LI Y J, ZHAO J, et al. Highly efficient utilization of precious metals for hydrogen evolution reaction with photo-assisted electro-deposited urchin-like Te nano- structure as a template[J]. ChemCatChem,2019,11(9):2283-2287. DOI: 10.1002/cctc.201900125
[16] WU H C, LIU Y D, CHEN G L, et al. Surface-confined photodeposition of noble metal nanoclusters on TiO2 in a fluidized bed for the catalytic oxidation of formaldehyde[J]. ACS Applied Nano Materials,2022,5(9):13100-13111. DOI: 10.1021/acsanm.2c02886
[17] KARÁCSONVI É, BAIA L, DONBI A, et al. The photocatalytic activity of TiO2/WO3/noble metal (Au or Pt) nanoarchitecture obtained by selective photodeposition[J]. Catalysis Today,2013,208:19-27. DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2012.09.038
[18] LIU Y D, NASERI A, LI T, et al. Shape-controlled photochemical synthesis of noble metal nanocrystals based on reduced graphene oxide[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2022,14(14):16527-16537.
[19] ONG W J, TAN L L, CHAI S P, et al. Heterojunction engineering of graphitic carbon nitride (g-C3N4) via Pt loading with improved daylight-induced photocatalytic reduction of carbon dioxide to methane[J]. Dalton Transactions,2015,44(3):1249-1257. DOI: 10.1039/C4DT02940B
[20] LIU Z, HUO P, LU Z, et al. Fabrication of magnetically recoverable photocatalysts using g-C3N4 for effective separation of charge carriers through like-Z-scheme mechanism with Fe3O4 mediator[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2018,331:615-625. DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2017.08.131
[21] 孟培媛, 郭明媛, 乔勋. WS2/g-C3N4异质结光催化分解水制氢性能及机制[J]. 复合材料学报, 2021, 38(2):591-600. MENG Peiyuan, GUO Mingyuan, QIAO Xun. H2 production performance of photocatalyst and mechanism of WS2/g-C3N4 heterojunction[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2021,38(2):591-600(in Chinese).
[22] 孙术博, 于海瀚, 李强, 等. NaNbO3@g-C3N4复合材料的可控构筑及其压电光催化性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2023, 40(3):1534-1540. SUN Shubo, YU Haihan, LI Qiang, et al. Controlled construction of NaNbO3@g-C3N4 composites and their piezo-photocatalytic properties[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2023,40(3):1534-1540(in Chinese).
-
-
石墨相氮化碳(CN)由于其带隙合适(2.7 eV)、化学稳定性高、无毒性和持久性等优点,在可见光光催化水分解和有机污染物降解方面得到了广泛的关注。但纯CN表现出很高的光诱导电子与空穴的复合率、催化剂表面活性位点少等缺陷。贵金属作为助催化剂,可以提高石墨相氮化碳光催化产氢的性能。其优异的性能引起了人们的关注。但是,由于贵金属的不可再生性和高价格,“更少的贵金属,更好的性能”始终是目标。
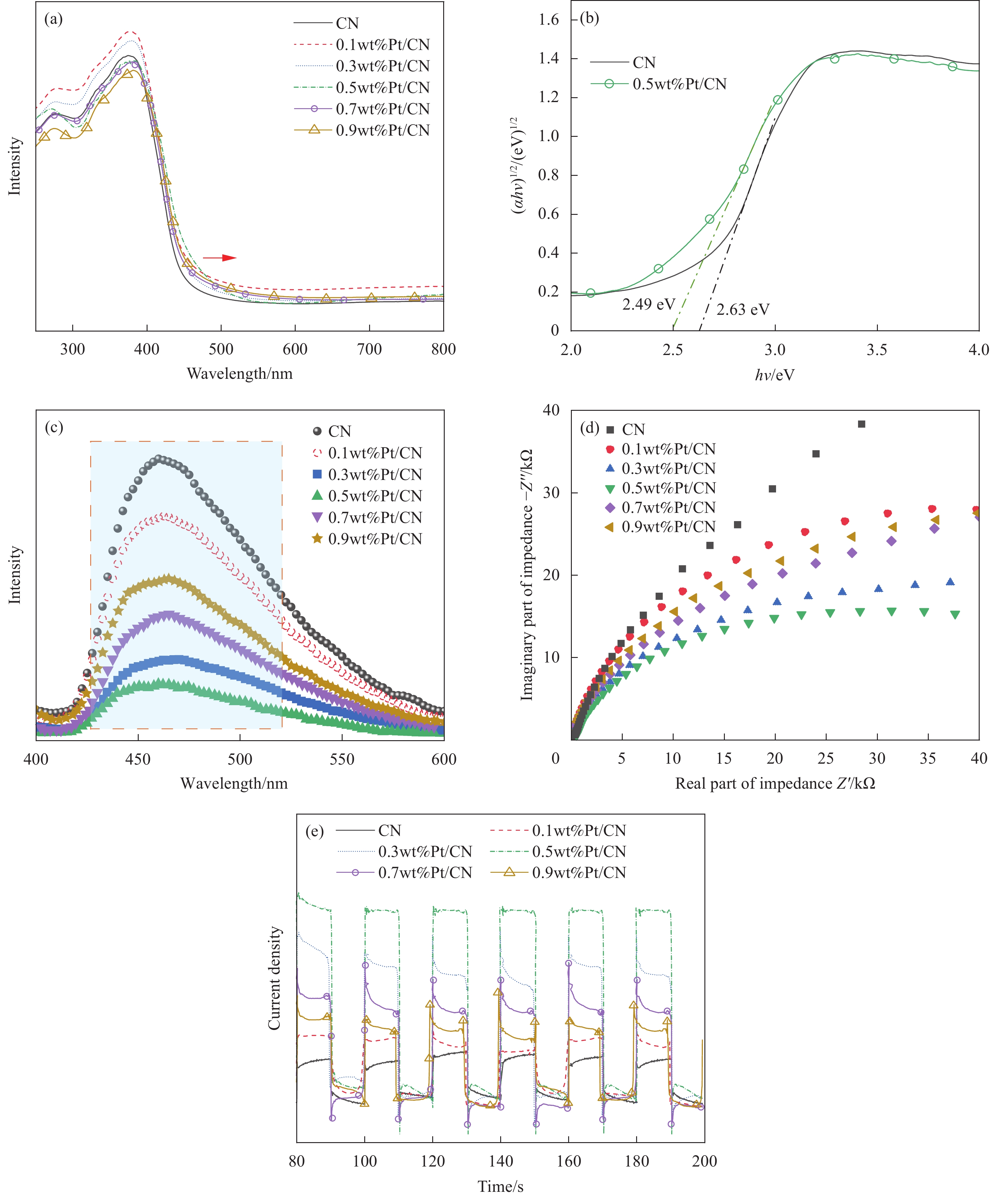
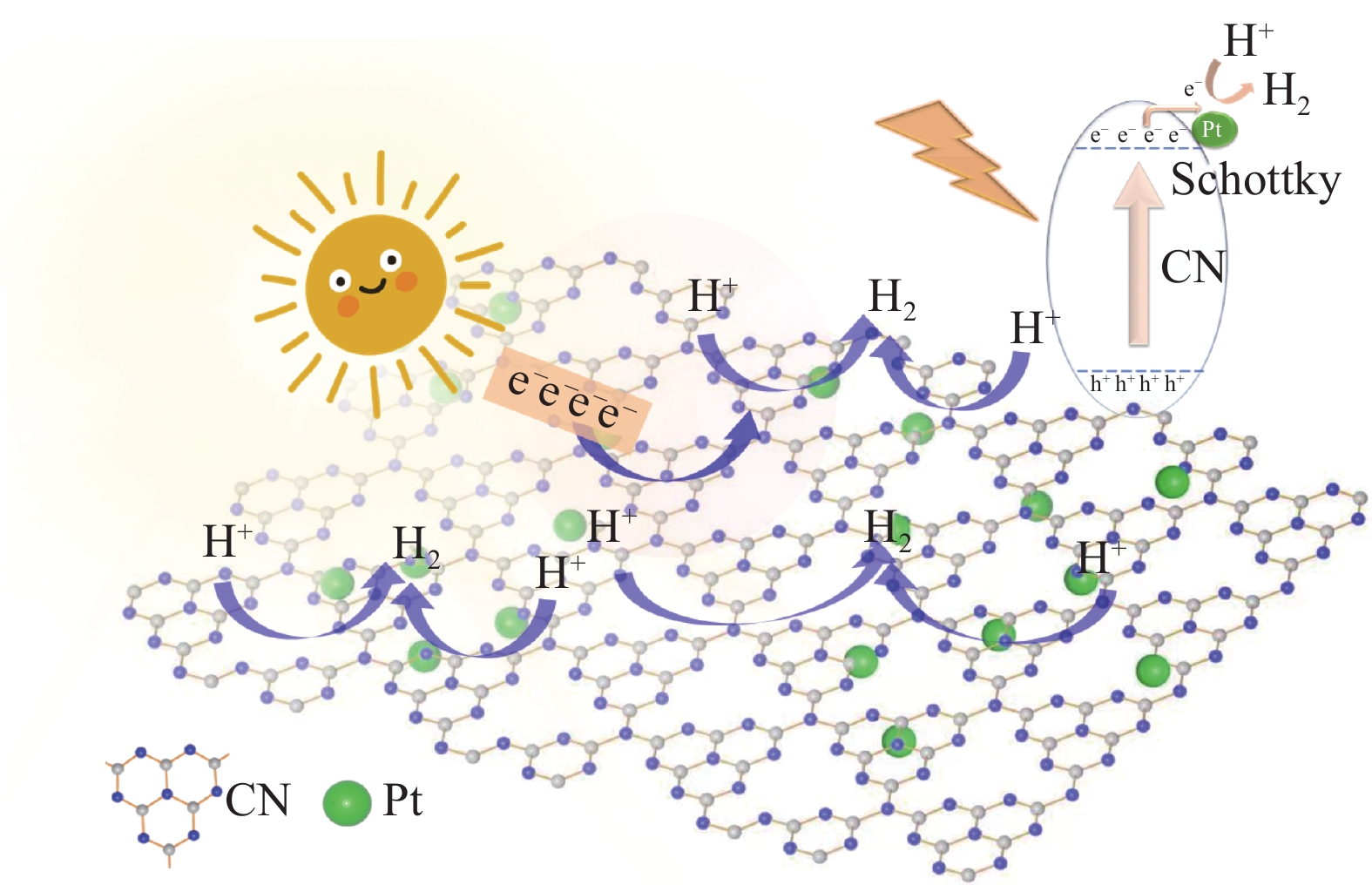
本工作通过光还原方式制备Pt负载氮化碳,研究了一系列负载量下Pt/CN材料的光催化水分解析氢性能。从光响应能力和载流子寿命方面分析了0.5wt % Pt/CN材料活性提升的内在原因,并提出Pt的原位负载导致了肖特基势垒的形成。这是光催化领域相关研究人员感兴趣的课题。并发现当Pt的负载量为0.5wt %时, Pt/CN具有最优异的光催化产氢活性,产氢量为409.2 μmol/g,是纯CN(17.8 μmol/g)的23倍。是现有文献中性能较好的样品之一。

不同负载量下Pt/CN的光解水产H2曲线 (a)、0.5wt % Pt/CN循环性能图 (b)、Pt/CN复合光催化产氢过程 (c)





 下载:
下载: