Influence of coral waste on the strength and volume stability of cement mortar
-
摘要: 在混凝土中应用珊瑚废弃物是制备适用于远海岛礁建设所需建筑材料的有效策略,然而过量应用珊瑚废弃物会导致混凝土性能急剧降低。为保证砂浆性能的同时提升珊瑚废弃物的应用率,本文联合应用珊瑚砂(CS)和珊瑚粉(CP)分别取代部分骨料和粘结剂制备砂浆,研究了CS取代率对砂浆的力学性能、自收缩和干燥收缩的影响,并结合微观形貌和孔隙结构分析其影响机制。结果表明:相比于未掺加CS的砂浆,联合应用10wt%~40wt%CS和10wt%CP制备的砂浆具有更高的力学性能。当CS的取代率为30wt%时,砂浆的强度最高,并且其28天抗压强度较基准组提升29.5%。同时,随着CS含量的升高,砂浆的自收缩变形降低。当CS的含量为40wt%时,砂浆的28天自收缩变形与基准组相比降低33.74%。另外,掺加CS也有益于降低砂浆的干燥收缩,当CS的取代率为30wt%时砂浆的干燥收缩值达到最低。CS的多孔结构使其与水泥基体间紧密咬合,并且其内养护作用也促进了界面性能的提升。通过氮吸附测试的孔隙结果也表明掺加30wt%的CS使样品的孔隙率降低,但进一步增加CS的掺量不利于样品的孔隙结构发展。Abstract: Application of coral waste in concrete is an effective strategy to produce building materials suitable for offshore island construction, but excessive application of coral waste can lead to drastic degradation of concrete properties. In order to improve the replacement ratio of coral waste while ensuring the performance of mortar, this study combined coral sand (CS) and coral powder (CP) to replace part of the aggregate and binder to produce mortar, and the effect of CS substitution ratio on the mechanical properties, autogenous shrinkage and drying shrinkage of mortar was investigated, and its influencing mechanism was analyzed in combination with microstructure and pore structure. The results demonstrate that the mortar produced by combined application of 10wt%-40wt%CS and 10wt%CP has higher strength than the mortar without CS. When the replacement ratio of CS is 30wt%, the strength of the mortar is the highest, and its 28 days compressive strength is increased by 29.50% compared with the reference group. Meanwhile, with the increase of CS content, the autogenous shrinkage of mortar decreases. When the CS content is 40wt%, the 28 days autogenous shrinkage value of the mortar is decreased by 33.74%, compared with the reference group. In addition, the addition of CS is also beneficial to reduce the drying shrinkage of mortar, and the drying shrinkage of mortar reaches the lowest when the substitution ratio of CS is 30wt%. The porous structure of CS makes it tightly occluded with the cement matrix, and its internal curing effect also promotes the improvement of interface performance. The results of the specific surface area (BET) also show that adding 30wt%CS reduces the porosity of the sample, but further increasing the CS content is not conducive to the development of the pore structure of the sample.
-
Keywords:
- coral aggregate /
- mortar /
- strength /
- volume stability /
- microstructure
-
-
表 1 原材料的化学组成
Table 1 Chemical composition of raw materials
Material CaO/wt% SiO2/wt% Al2O3/wt% Fe2O3/wt% SO3/wt% MgO/wt% LOI/wt% Cement 48.16 26.41 6.24 5.02 4.53 2.27 3.69 CP 52.70 1.70 0.35 0.37 0.61 0.24 41.27 Note: LOI—Loss on ignition. 表 2 珊瑚废弃物基砂浆配合比
Table 2 Mix proportions of coral waste-based mortar
Sample Mix proportions/wt% Cement CP ISO CS Water 0%CS-10%CP/M 405 45 1350 0 135 10%CS-10%CP/M 1215 135 135 20%CS-10%CP/M 1080 270 135 30%CS-10%CP/M 945 405 135 40%CS-10%CP/M 810 540 135 Notes: ISO—International standard sand; CS—Coral sand; M—Mortar. -
[1] FU Q, BU M, SU L, et al. Dynamic triaxial compressive response and failure mechanism of basalt fibre-reinforced coral concrete[J]. International Journal of Impact Engi-neering,2021,156:103930. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijimpeng.2021.103930
[2] 朱德举, 李高升. 短切纤维及预应力对玄武岩织物增强水泥基复合材料拉伸力学性能的影响[J]. 复合材料学报, 2017, 34(11):2631-2641. ZHU Deju, LI Gaosheng. Effect of short fibers and prestress on the tensile mechanical properties of basalt textile reinforced cementitious matrix composite[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2017,34(11):2631-2641(in Chinese).
[3] 荀涛, 胡鹏, 梅弢, 等. 西沙群岛珊瑚砂运动特性试验研究[J]. 水道港口, 2009, 30(4):277-281. XUN Tao, HU Peng, MEI Tao, et al. Study on movement characteristics of coral sands in Xisha islands[J]. Journal of Waterway and Harbor,2009,30(4):277-281(in Chinese).
[4] SHI H, WU Q, YU Z, et al. Properties of eco-friendly coral sand powder—Calcium sulfoaluminate cement binary system[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2020,263:120181. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.120181
[5] 游伟国, 徐亦冬, 邹毅松, 等. 基于科学计量方法分析珊瑚骨料混凝土研究进展[J]. 功能材料, 2019, 50(5):5064-5071. YOU Weiguo, XU Yidong, ZOU Yisong, et al. A scientometric review of research focusing on coral aggregate concrete[J]. Journal of Functional Materials,2019,50(5):5064-5071(in Chinese).
[6] DA B, YU H, MA H, et al. Experimental investigation of whole stress-strain curves of coral concrete[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2016,122:81-89. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2016.06.064
[7] 糜人杰, 余红发, 麻海燕, 等. 全珊瑚骨料海水混凝土力学性能试验研究[J]. 海洋工程, 2016, 34(4):47-54. MI Renjie, YU Hongfa, MA Haiyan, et al. Study on the mechanical property of coral concrete[J]. The Ocean Engineering,2016,34(4):47-54(in Chinese).
[8] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 混凝土结构设计规范: GB/T 50010—2010[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2010. Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People's Republic of China. Code for design of architecture & concrete structures: GB/T 50010—2010[S]. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 2010(in Chinese).
[9] WANG X, YU R, SHUI Z, et al. Mix design and characteristics evaluation of an eco-friendly ultra-high performance concrete incorporating recycled coral based materials[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production,2017,165:70-80. DOI: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2017.07.096
[10] 韦灼彬, 李仲欣, 沈锦林. 珊瑚混凝土性能影响因素及早期力学性质研究[J]. 工业建筑, 2017, 47(3):130-136. WEI Zhuobin, LI Zhongxin, SHEN Jinlin. Research on the influencing factors of performance of coral concrete and its early mechanical property[J]. Industrial Construction,2017,47(3):130-136(in Chinese).
[11] QIN Y, YAO T, WANG R, et al. Particle breakage-based analysis of deformation law of calcareous sediments under high-pressure consolidation[J]. Rock and Soil Mechanics,2014,35(11):3123-3128.
[12] LIU K, YU R, SHUI Z, et al. Influence of external water introduced by coral sand on autogenous shrinkage and microstructure development of ultra-high strength concrete (UHSC)[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2020,252:119111. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.119111
[13] 王磊, 赵艳林, 吕海波. 珊瑚骨料混凝土的基础性能及研究应用前景[J]. 混凝土, 2012(2):99-100, 113. WANG Lei, ZHAO Yanlin, LYU Haibo. Prospect on the properties and application situation of coral aggregate concrete[J]. Concrete,2012(2):99-100, 113(in Chinese).
[14] 王磊, 范蕾. 珊瑚碎屑混凝土的强度特性及破坏形态分析[J]. 混凝土与水泥制品, 2015(1):1-4. WANG Lei, FAN Lei. Strength characteristic and failure pattern analysis on coral debris concrete[J]. China Concrete and Cement Products,2015(1):1-4(in Chinese).
[15] WATTANACHAI P. A study on chloride ion diffusivity of porous aggregate concretes and improvement method[J]. Advanced Materials Research,2009,65(1):30-44.
[16] KAKOOEI S, AKIL H M, DOLATI A, et al. The corrosion investigation of rebar embedded in the fibers reinforced concrete[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2012,35:564-570. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2012.04.051
[17] KAKOOEI S, AKIL H M, JAMSHIDI M, et al. The effects of polypropylene fibers on the properties of reinforced concrete structures[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2012,27(1):73-77. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2011.08.015
[18] CHENG S, SHUI Z, SUN T, et al. Effects of fly ash, blast furnace slag and metakaolin on mechanical properties and durability of coral sand concrete[J]. Applied Clay Science,2017,141:111-117. DOI: 10.1016/j.clay.2017.02.026
[19] 贾慧娜, 李亚丽, 张舜泉. 膨润土和石灰石粉对珊瑚混凝土力学与耐久性能的影响[J]. 混凝土与水泥制品, 2020(11):87-91. JIA Huina, LI Yali, ZHANG Shunquan. Experimental study on the mechanical properties and durability of coral concrete mixed with bentonite and limestone powder[J]. China Concrete and Cement Products,2020(11):87-91(in Chinese).
[20] ZELIC J, KRSTULOVIC R, TKALCEC E, et al. The properties of portland cement-limestone-silica fume mortars[J]. Cement and Concrete Research,2000,30(1):145-152. DOI: 10.1016/S0008-8846(99)00216-1
[21] HE Z, HAN X, SHI J, et al. Multi-scale characteristics of eco-friendly marine binder using coral waste[J]. Powder Technology,2022,403:117395. DOI: 10.1016/j.powtec.2022.117395
[22] QIN Q, MENG Q, LI W, et al. Surface chemical properties of coral powder and its effect on hydration and pore structure of cement slurry[J]. Thermochimica Acta,2022,717:179356. DOI: 10.1016/j.tca.2022.179356
[23] American Society for Testing Materials. Standard test method for autogenous strain of cement paste and mortar: ASTM C1698—2009[S]. West Conshohocken: American Society for Testing Materials, 2009.
[24] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 普通混凝土长期性能和耐久性能试验方法标准: GB/T 50082—2009[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2009. Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People's Republic of China. Standard for test methods of long-term performance and durability of ordinary concrete: GB/T 50082—2009[S]. Beijing: China Building Industry Press, 2009(in Chinese).
[25] WU W, WANG R, ZHU C, et al. The effect of fly ash and silica fume on mechanical properties and durability of coral aggregate concrete[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2018,185:69-78. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.06.097
[26] ARUMUGAM R A, RAMAMURTHY K. Study of compressive strength characteristics of coral aggregate concrete[J]. Magazine of Concrete Research,1996,48(176):141-148. DOI: 10.1680/macr.1996.48.176.141
[27] WU L, FARZADNIA N, SHI C, et al. Autogenous shrinkage of high performance concrete: A review[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2017,149:62-75. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.05.064
[28] FUJIWARA T. Effect of aggregate on drying shrinkage of concrete[J]. Journal of Advanced Concrete Technology,2008,6(1):31-44. DOI: 10.3151/jact.6.31
[29] LIU J, OU Z, MO J, et al. Effectiveness of saturated coral aggregate and shrinkage reducing admixture on the autogenous shrinkage of ultrahigh performance concrete[J]. Advances in Materials Science and Engineering, 2017, 2017: 2703264.
[30] DA B, YU H F, MA H Y, et al. Experimental research on whole stress-strain curves of coral aggregate seawater concrete under uniaxial compression[J]. Journal of Building Structures,2017,38(1):144-151.
[31] CHENG S, SHUI Z, SUN T, et al. Durability and microstructure of coral sand concrete incorporating supplementary cementitious materials[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2018,171:44-53. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2018.03.082
[32] 薛维培, 刘晓媛, 姚直书, 等. 不同损伤源对玄武岩纤维增强混凝土孔隙结构变化特征的影响[J]. 复合材料学报, 2020, 37(9):2285-2293. XUE Weipei, LIU Xiaoyuan, YAO Zhishu, et al. Effects of different damage sources on pore structure change characteristics of basalt fiber reinforced concrete[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2020,37(9):2285-2293(in Chinese).
-
目的
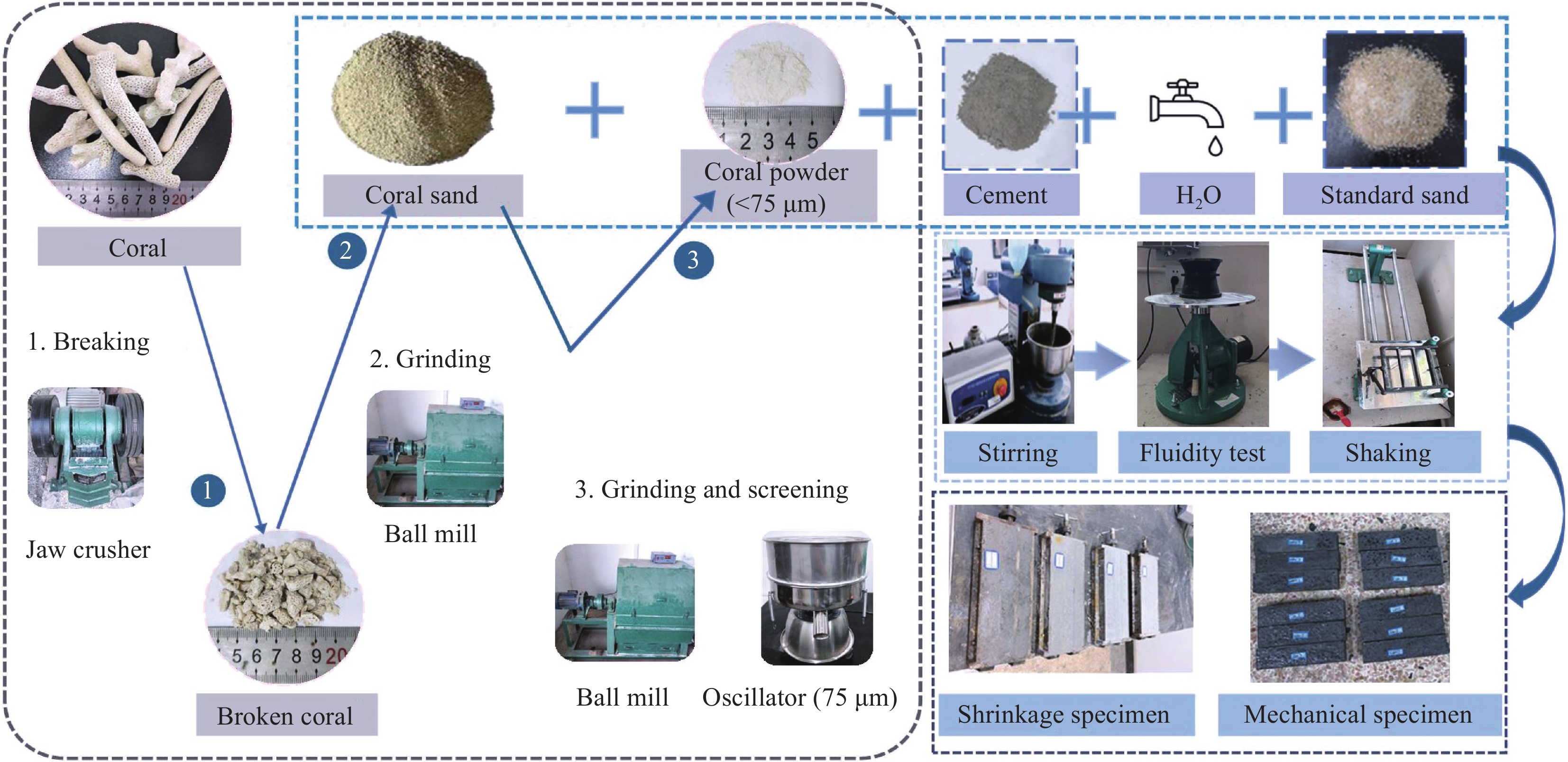
随着我国对远海的开发和建设的重视程度加强,海上基础设施的建设量不断增多。在基础设施建设中,混凝土扮演着不可或缺的角色。然而,水泥和骨料等混凝土的传统原材料在远海地区属于稀缺资源。从内陆地区向远海地区运输混凝土原材料将耗费大量的劳动力、财力和物力。因此,本着因地制宜的方针,利用珊瑚废弃物作为潜在的原材料制备绿色-低成本的混凝土是有必要的。为了实现珊瑚废弃物的高值化利用,本研究提出协同应用珊瑚砂(CS)与珊瑚粉(CP)的思路。在CS替代标准砂的基础上,掺入少量CP以制备高体积珊瑚废弃物基砂浆,并克服大取代率珊瑚废弃物对砂浆性能造成的不利影响。
方法本研究联合应用CS和CP分别取代部分骨料和粘结剂制备环境友好型砂浆,研究CS取代率对砂浆的力学性能、自收缩、干燥收缩和微结构的影响。重点考察CS、CP对于砂浆微观形貌、孔隙结构的影响。从砂浆的微观结构演变来解释其宏观性能的变化,从而为珊瑚废弃物在水泥基材料中的高值化利用提供参考依据。
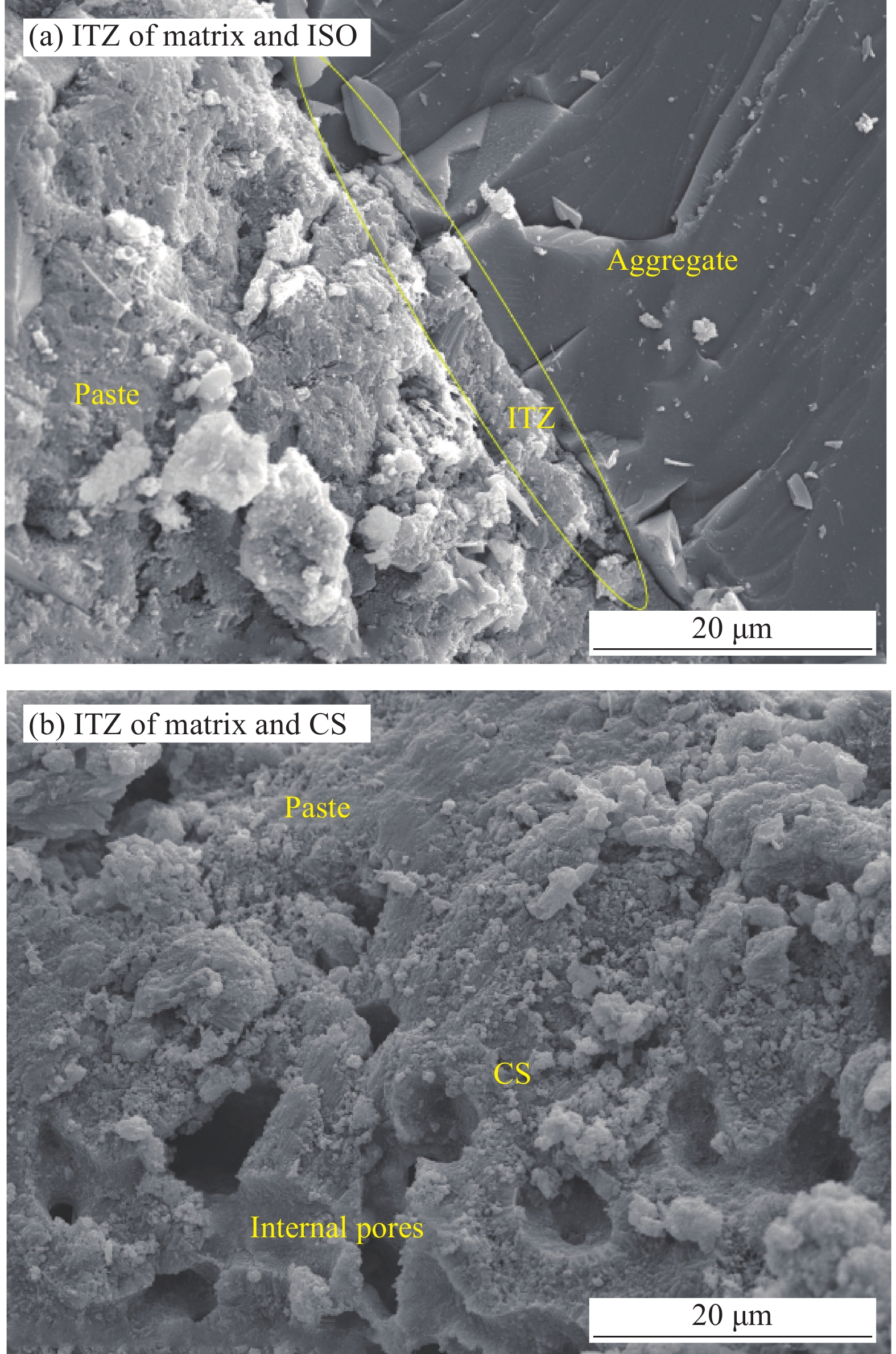
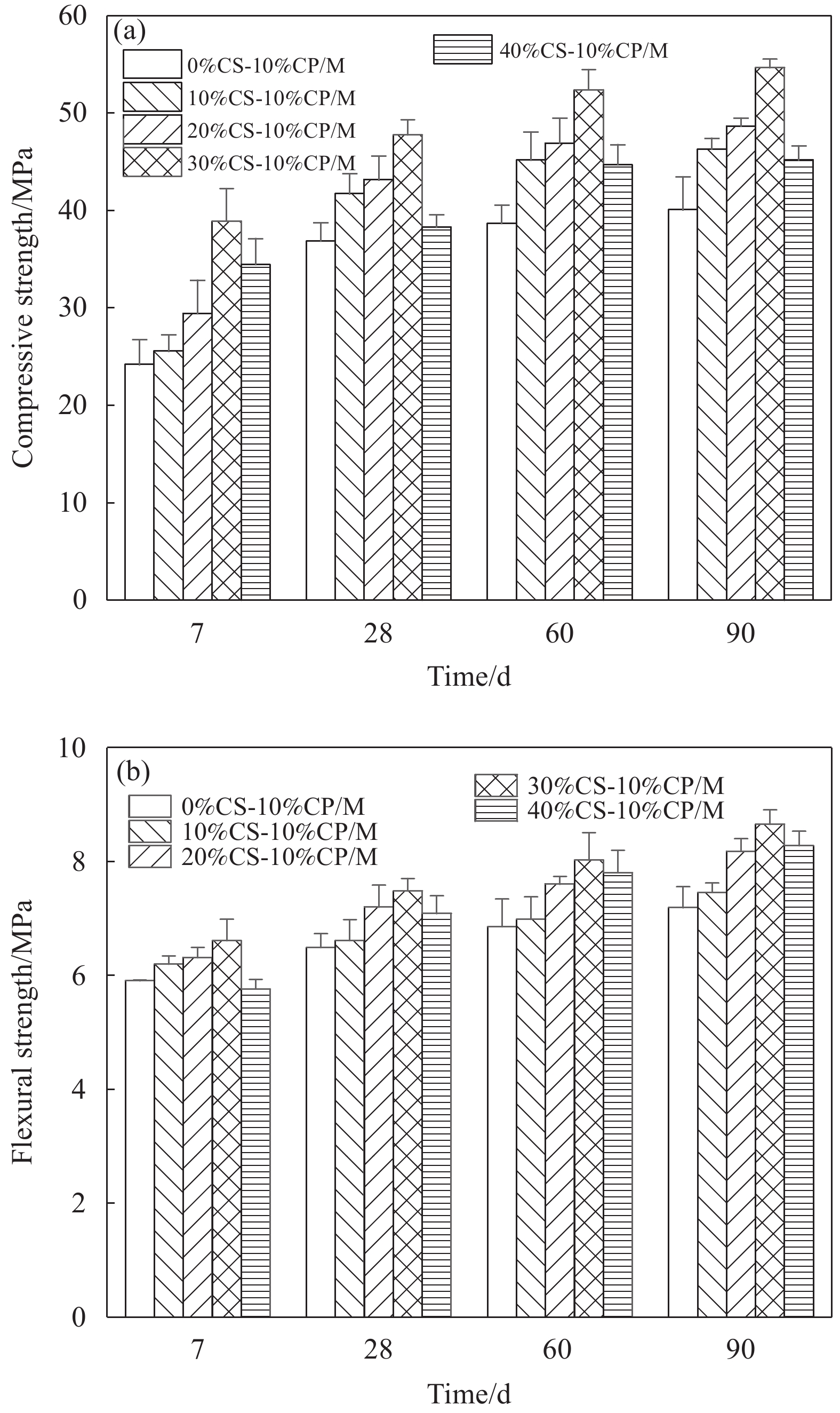
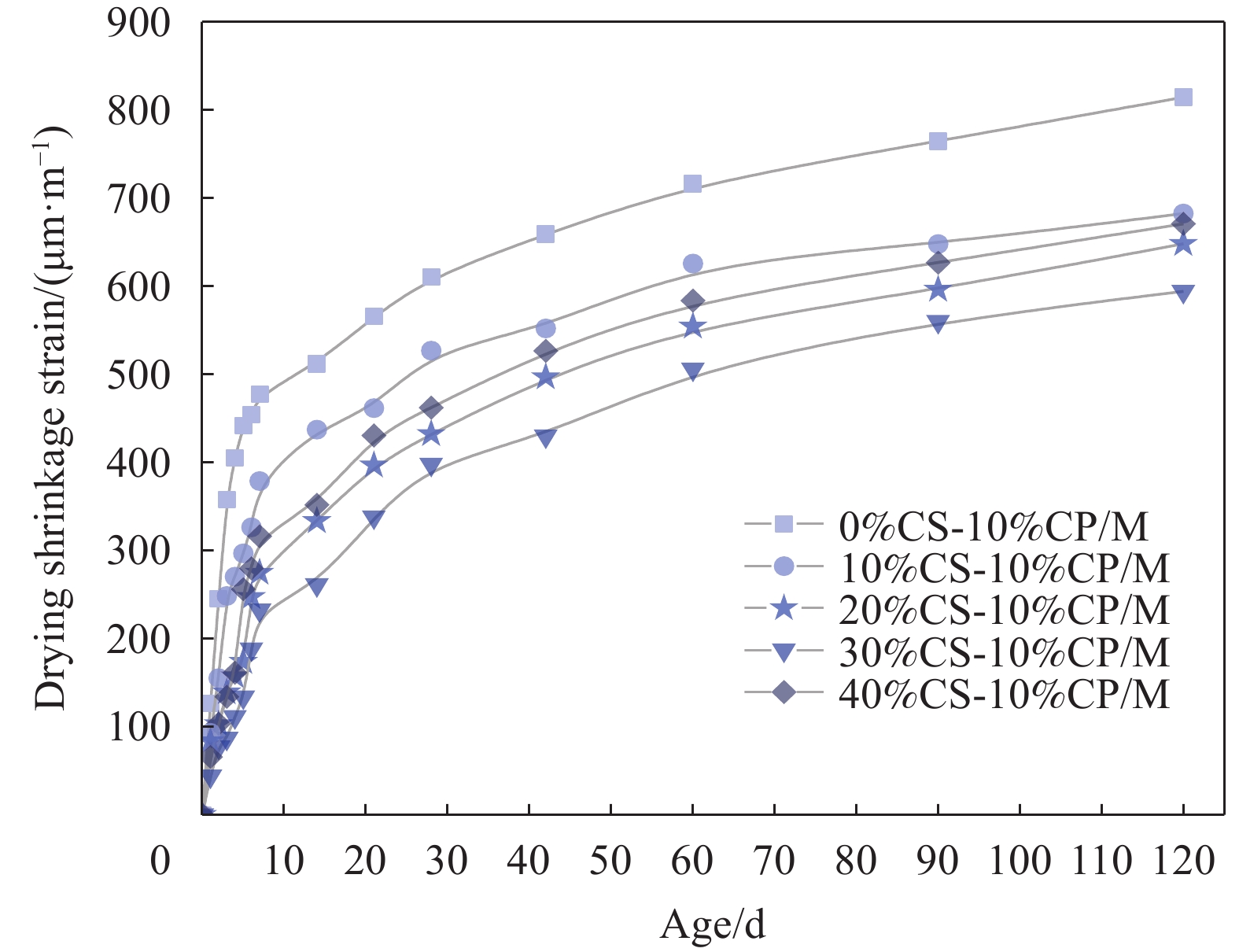
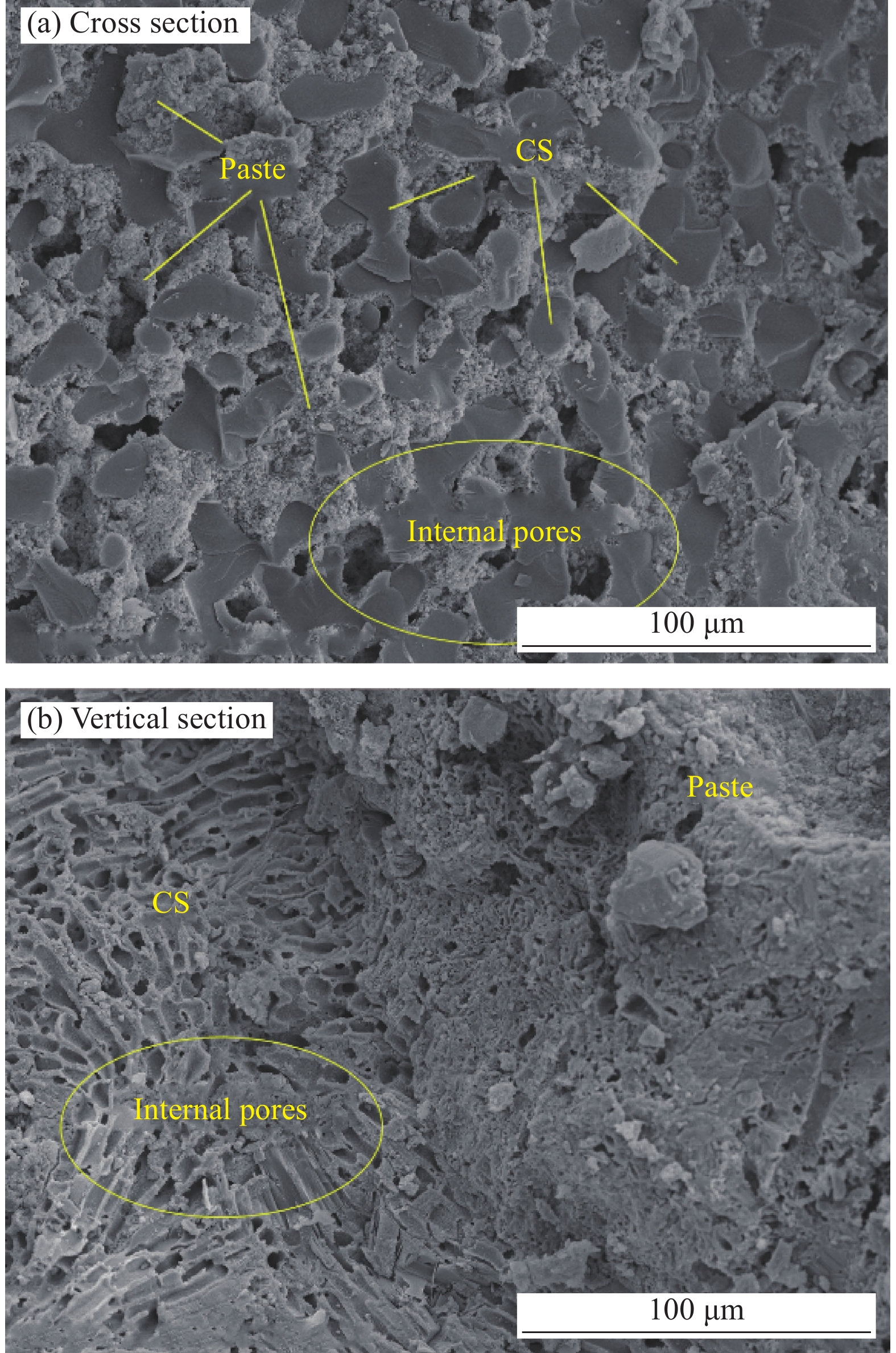
结果通过测试联合应用CS和CP的水泥砂浆力学性能、自收缩、干燥收缩、孔隙结构和微观形貌,得出以下测试结果。①联合应用CS与CP制备的珊瑚废弃物基砂浆相比于天然骨料制备的水泥砂浆具有更为优越的力学性能。当CS的取代率为30wt%时,砂浆的抗压强度最高,并且其28天抗压强度相比与基准组增加29.5%。随着CS掺量的进一步增加,掺入40wt%的砂浆的28天力学性能有所降低,但仍然略高于基准组,其较基准组增加4%。②珊瑚废弃物基砂浆的自收缩应变显著低于普通砂浆,这有助于降低水泥基材料的收缩开裂风险。随着CS取代水平的增加,砂浆的自收缩逐渐降低。当CS取代水平为40wt%时,其28天自收缩应变较基准组降低了33.74%。③珊瑚废弃物基砂浆的干燥收缩应变随CS掺量的增加呈先降低后增加的趋势。当CS掺量小于30wt%时,砂浆的干燥收缩应变随着CS掺量的增加而降低。但随着CS掺量进一步增加,掺入40%CS的砂浆的干燥收缩应变有所增加,但仍然低于基准组。④相比于标准砂,CS与硬化水泥基体具有更加紧密的结合,并且没有发现明显的界面过渡区。这主要是因为饱水CS具有良好的内部固化作用和机械啮合作用。⑤掺入30wt%CS能够明显优化珊瑚废弃物基砂浆的孔隙结构,其累计孔隙体积为0.018cm/g,较基准组降低了23.2%。但随着CS掺量进一步增加,掺入40wt%CS孔隙结构劣化,累计孔隙体积增加,为0.025 cm/g,较基准组增加19.1%。
结论联合应用CS和CP能够有效提高水泥砂浆的力学性能与体积稳定性,这对因地制宜的开发海工混凝土具有重要意义,有利于实现珊瑚废弃物的高值化利用。结果表明适量掺入CS与CP有利于水泥砂浆的28天力学性能发展,掺入30wt%CS与10wt%CP时,砂浆的抗压强度最高。随着CS掺量的进一步增加,掺入40wt%CS与10wt%CP的砂浆的28天力学性能有所降低,但仍然略高于基准组。因此,联合应用CS和CP取代标准砂与水泥所制备海工水泥砂浆与普通砂浆相比具有更好的性能,这为远海岛礁建设提供了潜在的建筑材料。
-
针对于远海岛礁建设,混凝土仍是主要的建筑材料之一。然而,远海建设却面临着自然资源缺乏和远洋运输费用高昂等问题。因此,本着因地制宜-就地取材的方针,利用珊瑚废弃物作为潜在的原材料制备混凝土是有必要的。以往研究表明单一增加珊瑚骨料(CS)或珊瑚粉(CP)不仅对珊瑚废弃物的利用率低,而且二者掺量有一定限值。因此,本研究提出联合应用CS和CP的思路来提升珊瑚废弃物的利用率并克服增加单一掺量而带来的不利影响。
本研究联合应用CS和CP分别取代部分骨料和粘结剂制备砂浆,研究CS取代率对砂浆的力学性能、自收缩、干燥收缩和微结构的影响。研究表明,与未掺加CS的砂浆相比,联合应用10wt%~40wt%的CS和10wt%的CP制备的砂浆具有更高的强度。同时,随着CS含量的增加,砂浆的自收缩变形降低。另外,掺加CS也有益于降低砂浆的干燥收缩,当CS的取代率为30wt%时砂浆的干燥收缩值达到最低。由于内养护作用和啮合作用,CS和水泥基体紧密结合,并且适量CS也细化了样品的孔隙结构。本研究通过联合应用CS和CP制备出了强度、自收缩和干燥收缩均优于普通砂浆的海工水泥砂浆,这为远海岛礁建设提供了潜在的建筑材料。
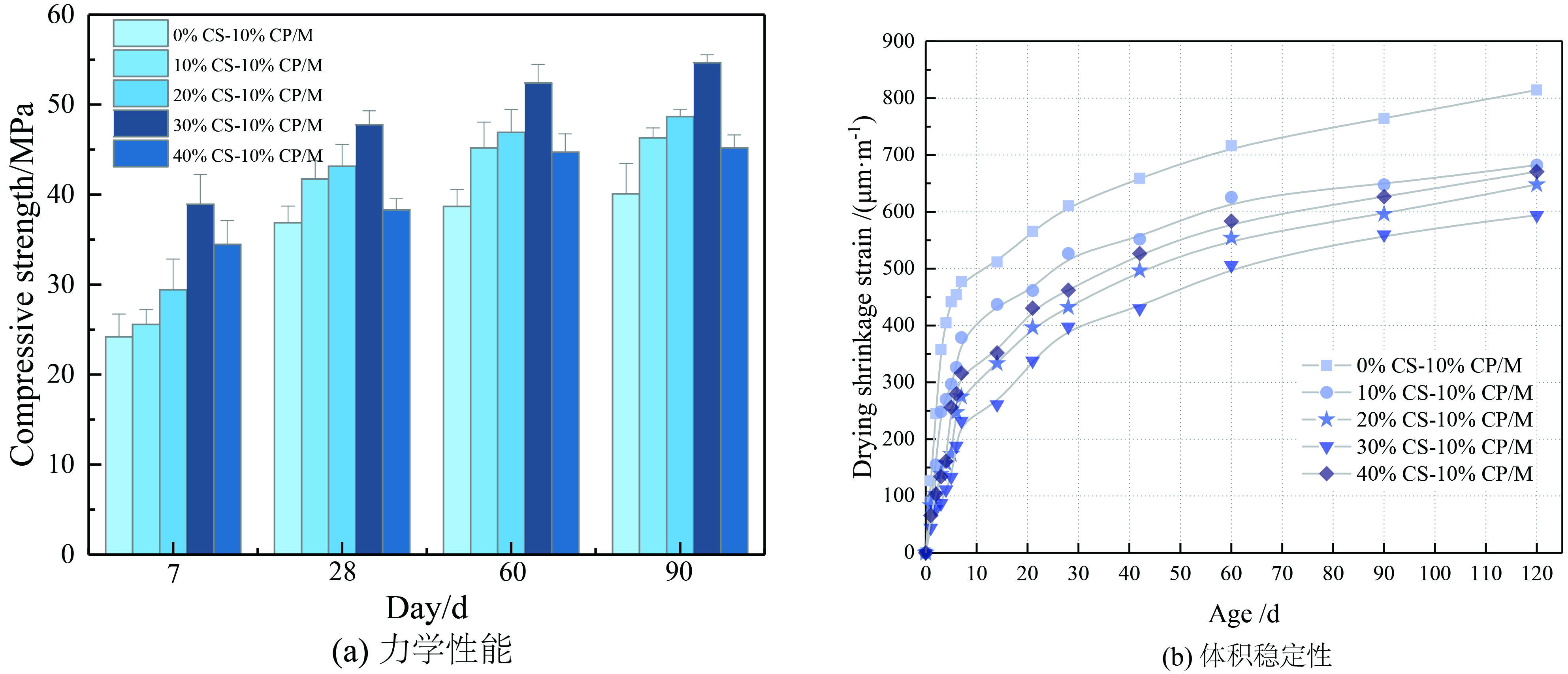
珊瑚废弃物对水泥砂浆强度和体积稳定性的影响结果





 下载:
下载: