Improved interface performance of all inorganic carbon based CsPbI2Br perovskite solar cells using CuxO
-
摘要: 基于CsPbI2Br的全无机碳基钙钛矿太阳能电池由于碳电极与钙钛矿层间接触性能较差和能带不匹配等问题,导致其光电转化效率较低。本文采用简单的葡萄糖还原法结合煅烧技术制备了两种不同形貌和结构的规则八面体构型CuxO,将之作为无机空穴传输材料,制备了结构为导电玻璃(FTO)/SnO2/CsPbI2Br/CuxO/C的碳基钙钛矿太阳能电池,研究了CuO和Cu2O的形貌、结构对光电性能的影响机制。结果显示:CuO和Cu2O皆具有良好的化学稳定性和p型载流子传输特性,可有效增强CsPbI2Br钙钛矿层与碳电极层之间的界面接触,改善载流子传输性能,减少电荷复合,延长光电子寿命。基于Cu2O和CuO的CsPbI2Br基碳基钙钛矿太阳能电池(C-PSC)器件的光电转换效率最高分别为11.62%和13.22%,分别比空白对照器件的光电转化效率提高了19.5%和36.0%。此外,通过添加Cu2O和CuO,器件在空气中的长期稳定性也得到明显改善,该工作为提高碳基CsPbI2Br钙钛矿太阳能电池的光电性能提供了一种简单有效的方法。
-
关键词:
- 无机钙钛矿太阳能电池 /
- CuxO /
- CsPbI2Br /
- 转化效率 /
- 无机空穴传输材料
Abstract: All inorganic carbon-based CsPbI2Br perovskite solar cells (C-PSCs) have lower photoelectric conversion efficiency due to poor contact performance and mismatch of energy band between carbon electrode and perovskite laye. In this paper, two kinds of regular octahedral CuxO with different morphologies and structures were prepared by a simple glucose reduction method combined with calcination technology. As inorganic hole transport materials, C-PSCs with the structure of conductive glass (FTO)/SnO2/CsPbI2Br/CuO/C were prepared and the influence of morphologies and structures on the photoelectric performance was studied. The results show that CuxO has good chemical stability and p-type carrier transport characteristics, which can effectively enhance the interface contact between CsPbI2Br and carbon electrode, improve the carrier transport performance, reduce charge recombination, and extend the photoelectron life. The highest photoelectric conversion efficiency of CsPbI2Br based C-PSCs devices based on Cu2O and CuO is 11.62% and 13.22%, respectively, which is 19.5% and 36.0% higher than that of blank devices. In addition, by adding Cu2O and CuO, the long-term stability of the device in the air is also significantly improved. This work has a certain significance for improving the performance of CsPbI2Br based C-PSCs. -
齿轮和轴类零件常被用于高速、振动、摩擦磨损等恶劣工况,易产生断裂和磨损等失效[1-2]。此类零件多采用20 CrMnTi低碳钢材料,为提高零件使用寿命,使用电沉积方法在零件表面制备镀层增强零件性能已成为常用方法。Ni-P合金镀层具有良好的耐磨、耐腐蚀性能,还具有较高的硬度,因此被广泛应用于化工、汽车和机械等行业[3-5]。随着行业的进步与发展,Ni-P镀层已难以满足复杂特殊的使用环境,向镀液中添加纳米颗粒针对性的提升镀层性能已成为研究的热门方向[6]。目前一元纳米颗粒复合电沉积技术已比较成熟,如添加Al2O3、WC、SiC等硬质颗粒提升复合镀层的硬度及耐磨损性能[7-10],添加具有自润滑特性的BN(h)、MoS2、PTFE等降低复合镀层的摩擦系数[11-13],添加部分纳米颗粒还可以提高复合镀层的耐腐蚀性能和抗高温氧化性能[14-18]。
近年来部分学者已经对二元纳米颗粒复合镀层进行研究,徐义库[19]等通过脉冲电沉积法制备Ni-Mo-SiC-TiN复合镀层,两种纳米颗粒均匀的分散在Ni-Mo基体中显著提升了镀层的耐磨和耐腐蚀性;张银[20]等使用电沉积法制备不同浓度配比的 Ni-Co-P-BN(h)-Al2O3复合镀层,结果表明二元纳米颗粒掺杂配比会对纳米复合镀层表面产生巨大影响,且二元纳米颗粒复合镀层的耐磨性优于一元纳米颗粒复合涂层;王浩鑫[21]采用单脉冲电沉积制备Ni-TiC-GO复合镀层,该镀层具有优秀的减摩擦和耐磨性能。目前,研究对于二元纳米复合电沉积技术尤其是电沉积Ni-P-WC-BN(h)二元纳米复合镀层的表面结构和减磨耐磨性能的研究未见报道。
因此本文采用超声-脉冲电沉积法制备不同浓度BN(h)纳米颗粒的Ni-P-WC-BN(h)二元纳米颗粒复合镀层,与Ni-P、Ni-P-WC复合镀层对比,探究BN(h)质量浓度对复合镀层组织结构和减磨耐磨性能的影响
1. 实 验
1.1 基材预处理
采用20 CrMnTi钢为基体,其尺寸为40 mm×16 mm×12 mm。表面使用320#、800#、
1200 #、2000#金相砂纸打磨→抛光→去离子水超声清洗→电净除油→去离子水超声清洗并吹干→强活化→去离子水超声清洗并吹干→弱活化→去离子水超声清洗并吹干待用。1.2 实验条件
试验采用单因素实验法,首先通过预实验确定电沉积工艺参数、基础镀液成分(表1所示)和WC颗粒的最优浓度(30 g/L,纯度99.9%,平均粒度为50 nm)。实验装置如图1所示,工艺参数:电流密度3 A/dm2,脉冲频率2 kHz,占空比0.8,镀液温度50℃,电镀时间60 min,超声功率210 W,搅拌速率150 r/min,;阳极为纯Ni板。
表 1 电沉积Ni-P镀液配方Table 1. Formulation of electrodeposition Ni-P plating solutionElement Concentration/(g·L−1) NiSO4·6H2O 230 NiCl2·6H2O 30 H3PO3 5 NaH2PO2·H2O 8 NaC6H8O7·H2O 80 H3BO3 30 C₁₂H₂₅NaSO₄ 0.1 SC(NH₂)₂ 0.02 C₇H₅NO₃S 1 以上述内容为基础向镀液中分别添加15 g/L、20 g/L、25 g/L、30 g/L的BN(h)纳米颗粒(纯度99.9%,平均粒度为200 nm)。探究BN(h)添加量对Ni-P-WC-BN(h)复合镀层表面形貌、组织成分、显微硬度及耐磨性能的影响。
1.3 测试方法
试样制备完成后,使用线切割将样品切割为10 mm×10 mm×6 mm的测试试样进行下一步测试。使用Quanta FEG250扫描电子显微镜、能谱仪X Flash Detector 5030 BRUKER)对试样表面的镀层形貌和元素分布进行观察。采用Rigaku SmartLab SE型X射线衍射仪对复合镀层的物相结构进行分析。采用斯特尔显微硬度仪(Struers)对镀层的显微硬度进行测试,实验载荷
1000 g,加载时间10 s,在不同位置测量五次取平均值。采用CFT-I型综合材料表面性能测试仪(兰州中科凯华科技)对复合镀层的摩擦系数进行测试,磨件为Si3N4对磨球(直径4 mm,表面粗糙度Ra=0.06 μm,硬度为1400 -1700 HV1),加载载荷100 g,往复次数200次/min,往复行程4 mm,时长30 min。采用日本Keyence VK-X1000激光显微镜拍摄磨痕处形貌及磨痕截面轮廓并计算镀层磨损体积损失。2. 结果与讨论
2.1 复合镀层的微观形貌及元素分布
图2展示了不同镀液配方复合镀层的表面微观形貌,(a)图Ni-P镀层表面呈胞状结构,胞状结构的直径较大且分布不均匀。在镀液中加入WC纳米颗粒后,(b)图Ni-P-WC复合镀层表面和(a) Ni-P镀层相比粗糙,这是由于部分WC团聚被Ni-P镀层包裹在镀层内部,镀层表面产生了单元凸起,改变了阳极和阴极的间距,凸起部分受到电场力较大优先生长因此形成不平整的胞状物结构[22]。(c1)到(c4)图为在镀液中进一步添加15 g~30 g/L的BN(h)纳米颗粒的Ni-P-WC-BN(h)复合镀层表面的微观形貌,与Ni-P-WC复合镀层相比,随着BN(h)含量的增加,镀层表面平整度略有提高,究其原因,一方面两颗粒协同作用在一定程度上减小了团聚[20],另一方面还可能与BN(h)颗粒具有自润滑特性,层与层之间靠爱德华力连接易产生滑动有关[23]。但BN(h)浓度超过某一极值,镀液中纳米颗粒浓度过高从而使纳米颗粒团聚,阴极附近导电性下降从而使沉积效率降低。
![]() 图 2 复合镀层表面SEM图像 (a) Ni-P,(b)Ni-P-WC,(c1)Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(15 g/L),(c2) Ni-P-WC-BN(h) (20 g/L),(c3) Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(25 g/L),(c4) Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(30 g/L)Figure 2. SEM image of composite plated surface (a)Ni-P,(b)Ni-P-WC,(c1)Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(15 g/L),(c2) Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(20 g/L),(c3) Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(25 g/L),(c4) Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(30 g/L)
图 2 复合镀层表面SEM图像 (a) Ni-P,(b)Ni-P-WC,(c1)Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(15 g/L),(c2) Ni-P-WC-BN(h) (20 g/L),(c3) Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(25 g/L),(c4) Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(30 g/L)Figure 2. SEM image of composite plated surface (a)Ni-P,(b)Ni-P-WC,(c1)Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(15 g/L),(c2) Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(20 g/L),(c3) Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(25 g/L),(c4) Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(30 g/L)图3为不同镀液配方复合镀层的截面形貌及元素分布。WC纳米颗粒的加入后镀层厚度有所增加,但镀层内部存在裂痕等缺陷;加入BN(h)纳米颗粒后,镀层平整性略有提高且镀层内部缺陷减少,镀层厚度先增加后减小,在BN(h)浓度为25 g/L时最厚达80.0 μm。随着BN(h)浓度进一步增加,镀液中纳米颗粒浓度过高导致阴极导电性下降从而降低沉积效率,镀层厚度减小。
![]() 图 3 复合镀层截面SEM图像及截面元素分布 (a)Ni-P,(b)Ni-P-WC,(c1)Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(15 g/L),(c2) Ni-P-WC-BN(h) (20 g/L),(c3) Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(25 g/L),(c4) Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(30 g/L)Figure 3. SEM image of composite plating cross-section and section element distribution (a)Ni-P,(b)Ni-P-WC,(c1)Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(15 g/L),(c2) Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(20 g/L),(c3) Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(25 g/L),(c4) Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(30 g/L)
图 3 复合镀层截面SEM图像及截面元素分布 (a)Ni-P,(b)Ni-P-WC,(c1)Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(15 g/L),(c2) Ni-P-WC-BN(h) (20 g/L),(c3) Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(25 g/L),(c4) Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(30 g/L)Figure 3. SEM image of composite plating cross-section and section element distribution (a)Ni-P,(b)Ni-P-WC,(c1)Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(15 g/L),(c2) Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(20 g/L),(c3) Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(25 g/L),(c4) Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(30 g/L)由图中元素分布可以看出,WC和BN(h)纳米镶嵌在镀层中,镀层和基体的界面交界处存在约50 μm的中间区,该区域元素相互渗透,有助于改善镀层和基体的结合。
图4为不同镀镀液配方复合镀层表面元素分布,从元素分布图中可以看出Ni、P、W、B均匀分散在镀层中,并无明显团聚现象,这说明在该工艺参数下WC纳米颗粒和BN(h)纳米颗粒在镀层中分散效果较好。
![]() 图 4 复合镀层表面元素分布 (a)Ni-P,(b)Ni-P-WC,(c1)Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(15 g/L),(c2) Ni-P-WC-BN(h) (20 g/L),(c3) Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(25 g/L),(c4) Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(30 g/L)Figure 4. Composite plating surface element distribution (a)Ni-P,(b)Ni-P-WC,(c1)Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(15 g/L),(c2) Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(20 g/L),(c3) Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(25 g/L),(c4) Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(30 g/L)
图 4 复合镀层表面元素分布 (a)Ni-P,(b)Ni-P-WC,(c1)Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(15 g/L),(c2) Ni-P-WC-BN(h) (20 g/L),(c3) Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(25 g/L),(c4) Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(30 g/L)Figure 4. Composite plating surface element distribution (a)Ni-P,(b)Ni-P-WC,(c1)Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(15 g/L),(c2) Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(20 g/L),(c3) Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(25 g/L),(c4) Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(30 g/L)2.2 复合镀层的EDS能谱及相结构
图5为二元纳米颗粒掺杂下Ni-P-WC-BN(h)复合镀层的EDS能谱图,从图中可以看出,所制备的二元纳米复合镀层表面均含有Ni、P、W、C、B等元素,各元素含量随着BN(h)浓度的变化而变化。随着BN(h)添加量从15 g/L增加到30 g/L,B元素质量分数呈先波动增大后减小趋势,在BN(h)浓度为25 g/L时B元素的质量分数达到最大值0.85%;镀层表面W元素质量分数先减小后增大,与B元素呈相反趋势;镀层中P元素质量分数逐渐减小。这说明通过超声-脉冲电沉积法制备了Ni-P-WC-BN(h)二元纳米复合镀层。Ni元素的质量分数随着BN(h)浓度的提升而增大,这是因为镀液中加入WC和BN(h)两种纳米颗粒后,不同纳米颗粒相互作用,减小团聚,镀层表面吸附的颗粒数目增加,为Ni原子提供更好的成核条件[23],从而增大Ni元素的沉积量。
图6所示为不同复合镀层的XRD图谱,镀层在2θ为44.507°、51.846°、76.370°的位置上出现了的Ni峰,分别对应(111)、(200)、(220)晶面,与Ni-P-WC复合镀层相比,随着BN(h)浓度的增加,Ni-P-WC-BN(h)复合镀层的三个晶面方向出现了明显的结晶取向,且生长晶面以(111)面为主,这是由于Ni的结晶取向同时受到生长速度、方向的影响外还受到晶体竞争模式的影响[24];Ni-P-WC复合镀层的衍射图谱中,2θ为31.474°、35.626°、48.266°的位置出现了WC的特征峰,这说明WC颗粒成功沉积在复合镀层中;在Ni-P-WC-BN(h)复合镀层的衍射图谱中并没有表现出明显的BN(h)峰,但是可以检测到BN(h),结合图5中B元素的质量分数可知这可能是BN(h)颗粒沉积量较少所致。
表2为不同配方镀层中Ni(111)元素的晶粒尺寸数据,其中FWHM为半幅宽,D为镀层中垂直于晶面的晶粒尺寸。随着BN(h)浓度的提升,Ni(111)的晶粒尺寸先减小后增大,最小晶粒尺寸为8.9 nm,这是因为BN(h)对晶粒有一定的细化作用[25],合适浓度的BN(h)可以减小晶粒尺寸,但是BN(h)浓度过高会使晶粒尺寸增大。
表 2 不同复合镀层中Ni(111)元素的晶粒尺寸Table 2. Grain size of Ni(111) elements in different composite coatingsType of plating 2θ/(°) FWHM Diameter/nm Ni-P 44.480 0.941 9.2 Ni-P-WC 44.670 0.848 10.2 Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(15 g/L) 44.480 0.894 9.7 Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(20 g/L) 44.340 0.908 9.5 Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(25 g/L) 44.660 0.968 8.9 Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(30 g/L) 44.710 0.677 12.8 2.3 复合镀层的硬度
不同复合镀层的显微硬度测试结果如图7所示,从图中可知,Ni-P镀层硬度在700 HV1左右,添加WC纳米颗粒后镀层的显微硬度为
1141 HV1,这是因为WC在镀层中弥散分布,对镀层起到弥散强化作用[26],根据晶界强化原理,晶粒越细小镀层的显微硬度越高,WC纳米颗粒自身硬度较高且可以使镀层晶粒细化从而提高硬度。加入BN(h)后,随着BN(h)浓度从15 g/L到30 g/L的过程中,Ni-P-WC-BN(h)复合镀层硬度呈先增大后减小的变化趋势,在BN(h)浓度为25 g/L时Ni-P-WC-BN(h)复合镀层的硬度达到最大值115 6HV1,硬度最大值与Ni-P-WC复合镀层相当。分析认为, 纳米粒子在沉积过程中分为弱吸附和强吸附[27],随着镀液中纳米颗粒浓度增加,更多的颗粒发生强吸附作用,从而使镀层中纳米颗粒的含量增加从而使镀层硬度提升,但当其添加量过大时镀层易产生析氢现象[28],使镀层厚度下降,因此硬度下降。2.4 复合镀层的减磨耐磨性能
不同配方复合镀层的摩擦系数如图8所示,各复合镀层的摩擦系数均存在明显的摩擦系数急剧上升后趋于平稳的“磨合”阶段[29]。分析认为随着磨损试验的进行镀层表面的磨屑不断在磨痕处堆积,最终在压应力的作用下产生塑性变形使摩擦阻力增大,从而导致摩擦系数增大。
相同条件下,未添加纳米颗粒的Ni-P镀层的摩擦系数较大。摩擦系数和复合镀层中的硬质颗粒的尺寸、均匀性和数量有关[30],添加WC纳米颗粒后,纳米WC嵌入镀层,使晶粒细化并致密镀层组织,且WC自身硬度较高,因此可以减小摩擦时的接触面积从而降低摩擦系数。在Ni-P-WC镀层基础上添加BN(h)颗粒,随着BN(h)浓度增加,Ni-P-WC-BN(h)复合镀层摩擦系数呈先减小后增大的变化趋势。
摩擦磨损实验结束后,各镀层的磨损体积如表3所示,由数据可以看出Ni-P镀层磨损体积最大;加入WC纳米颗粒后镀层的磨损体积显著减小;加入BN(h)纳米颗粒后,随着浓度的提升,复合镀层的磨损量先减小后增大,Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(25 g/L)复合镀层的磨损体积最小,与Ni-P-WC复合镀层相当,显著优于其他镀层。将磨损体积与图5硬度测试结果对比,可以得出镀层磨损量和镀层硬度呈负相关。
表 3 镀层磨损体积Table 3. Plating wear volumeType of plating Wear volume /μm3 Ni-P 459553 Ni-P-WC 51945 Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(15 g/L) 256137 Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(20 g/L) 135765 Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(25 g/L) 53587 Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(30 g/L) 102966 各镀层磨痕形貌、轮廓线如图9所示,不同区域元素分布如表4所示。由磨痕形貌与图3镀层厚度对比及磨痕元素分布可知,磨损区域均不含Fe元素,摩擦磨损试验过程中镀层并未磨穿。Ni-P镀层磨痕与其他镀层磨痕相比较为明显,且磨痕处呈明显的黏着现象和犁沟状形貌,取磨痕中部长度为310 μm的截面轮廓线可知磨损过程中Ni-P复合镀层的磨损量较大,Ni-P涂层的硬度较低,易产生剥落现象,磨痕处含有少量Si元素,这说明Si3N4对磨球在摩擦磨损试验中摩擦热的作用下转移到镀层表面产生黏着磨损现象。镀层中加入WC纳米颗粒后,Ni-P-WC复合镀层磨痕表面无明显的犁沟形貌,这是因为WC颗粒在镀层中起到弥散强化作用,大幅度提升了复合镀层的硬度,减小了摩擦的接触面积,在磨损过程中,镀层先产生塑形形变,当形变量过大时部分WC颗粒脱落,形成镀层、WC粉末、摩擦副之间的三体磨损[31],此过程中摩擦热大幅增加导致氧化磨损,涂层的氧含量大幅提高。
![]() 图 9 复合镀层磨痕SEM(左)、磨痕形貌(中)、磨痕轮廓线(右):(a)Ni-P (b)Ni-P-WC (c)Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(15 g/L) (d)Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(20 g/L) (e)Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(25 g/L) (f)Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(30 g/L)Figure 9. SEM of composite plating wear marks (left), wear mark morphology (center), and wear mark contour lines (right): (a) Ni-P (b) Ni-P-WC (c) Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(15 g/L) (d) Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(20 g/L) (e) Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(25 g/L) (f) Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(30 g/L)表 4 磨痕元素分布Table 4. Distribution of abrasion elements
图 9 复合镀层磨痕SEM(左)、磨痕形貌(中)、磨痕轮廓线(右):(a)Ni-P (b)Ni-P-WC (c)Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(15 g/L) (d)Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(20 g/L) (e)Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(25 g/L) (f)Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(30 g/L)Figure 9. SEM of composite plating wear marks (left), wear mark morphology (center), and wear mark contour lines (right): (a) Ni-P (b) Ni-P-WC (c) Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(15 g/L) (d) Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(20 g/L) (e) Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(25 g/L) (f) Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(30 g/L)表 4 磨痕元素分布Table 4. Distribution of abrasion elementsArea Atomic fraction of an element at% Ni O P Si W B Au 1 75.01 14.08 5.15 2.71 — — 2.34 2 90.1 — 6.4 — — — 3.49 3 23.16 70.39 1.49 — 2.87 — 1.28 4 84.64 2.48 3.43 — 6.14 — 3.31 5 56.59 31.00 3.36 1.35 5.41 0.35 1.93 6 63.12 4.00 3.58 — 3.13 23.59 2.60 7 37.49 53.33 2.07 1.16 3.40 0.76 1.79 8 37.68 52.95 2.56 1.06 4.05 0.2 1.50 9 66.25 9.97 4.38 0.01 4.05 14.04 1.29 10 72.42 15.68 3.59 0.15 5.63 0.13 2.42 11 58.76 7.96 3.03 0.11 4.56 20.69 4.88 12 46.65 27.96 1.23 4.89 4.47 8.99 5.82 BN(h)纳米颗粒加入后磨痕形貌如图9(c)-(f)所示,BN(h)添加量为15 g/L时,对比图8中摩擦系数曲线及磨痕处轮廓线可以发现Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(15 g/L)复合镀层发生了较为严重的剥落现象,剥落的镀层在磨痕处随摩擦副一起在镀层表面摩擦,从而导致摩擦系数短时内上升,随着摩擦实验的进行,剥落的镀层被压应力压碎,摩擦系数也逐渐减小到该涂层的正常水平;BN(h)添加量为20 g/L时,镀层的剥落现象大幅减少,磨痕处的Si元素含量增加,镀层存在黏着磨损现象,此时摩擦系数略小于Ni-P-WC复合镀层,但是由于BN(h)沉积量较少,因此减磨能力有限;BN(h)添加量为25 g/L时,镀层基本无剥落现象,磨痕较为平整,这是因为BN(h)微粒在镀层中和WC共沉积,呈弥散分布,由于BN(h)为六方结构,层与层之间靠范德华力连接,在摩擦中易产生滑动,一方面滑动的BN(h)可以在镀层和对磨球间形成固体润滑膜减小摩擦,另一方面BN(h)可以在摩擦过程中填补磨痕处的缺陷,使磨痕更加平整,此时摩擦形式为磨料磨损,伴随极微的黏着磨损;BN(h)添加量为30 g/L时,磨痕呈现较为明显的犁沟状并伴随着严重的黏着现象,此时纳米浓度颗粒浓度过高,电沉积效率下降,镀层硬度和厚度减小,镀层中Si元素含量大幅提高,镀层主要磨损形式为黏着磨损。
3. 结 论
(1)不同纳米颗粒的质量浓度对纳米复合镀层表面的微观形貌和物相结构有重要影响,Ni-P镀层表面呈现明显的胞状结构;加入WC纳米颗粒后,Ni-P-WC复合镀层表面呈不平整“菜花”状形貌;加入BN(h)纳米颗粒后,Ni-P-WC-BN(h)复合镀层微观形貌无明显变化,镀层平均晶粒尺寸先减小后增大,合适浓度的BN(h)对晶粒有一定的细化作用。
(2)试验范围内,纳米颗粒的添加可以有效的提升复合镀层的显微硬度和厚度。Ni-P-WC和Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(25 g/L)复合镀层硬度最大,平均硬度达到
1150 HV1,纳米颗粒浓度过低或者过高均会降低镀层的显微硬度。(3)试验范围内,Ni-P镀层在摩擦磨损实验中存在较为严重的黏着和剥落现象且磨损量较大;加入WC纳米颗粒后,镀层无黏着现象,磨损形式为磨料磨损和氧化磨损,此时摩擦系数较小且磨损量较低;进一步加入BN(h)纳米颗粒后,随着BN(h)浓度的提升,镀层的摩擦系数和磨损量先减小后增大,在BN(h)质量浓度为25 g/L时镀层的摩擦系数最低,在保证镀态高硬度的同时,摩擦系数较Ni-P-WC复合镀层降低22.6%,这说明二元纳米颗粒掺杂发挥了协同生长的优势,具有更好的减磨耐磨性能。
-
图 5 (a)莫特-肖特基图(电容(C−2)-电压)曲线;(b) 开路电压衰减(OCVD)曲线;(c)正反扫光电流密度-电压 (J-V)曲线;(d)暗态下的光电流密度-电压 (J-V)曲线;(e) 电化学阻抗谱(EIS)曲线和电路模拟图;(f)基于FTO/C和FTO/CuxO/C结构的导电率
Voc—Open circuit voltage; Rs—Series resistance; Rrec—Charge recombination resistance; C—Capacitance; FTO—Conducting glass
Figure 5. (a) Mott-Schottky plot (Capacitance (C−2)-voltage); (b) Open circuit voltage decay (OCVD) curves; (c) Forward and reverse photocurrent density voltage (J-V) measurement; (d) Photocurrent density-voltage (J-V) curves under dark condition; (e) Electrochemical impedance spectroscopy (EIS) curves and circuit simulation diagram; (f) Conductivity based on FTO/C and FTO/CuxO/C structure
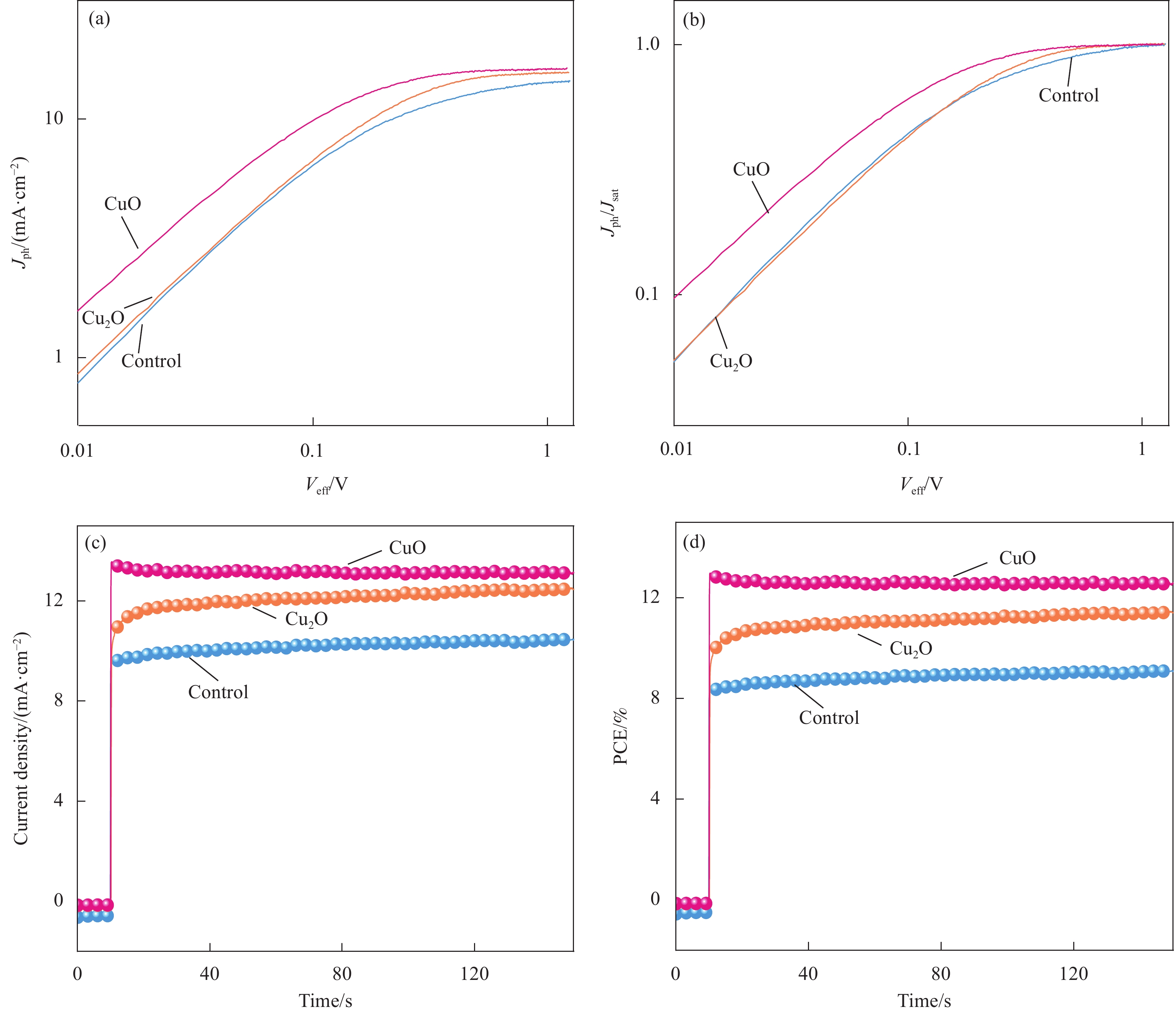
图 6 (a)光电流密度(Jph)曲线;(b) CsPbI2Br PSC的Jph/Jsat曲线;(c)器件的稳态电流密度输出; (d)稳态 PCE 输出曲线
Figure 6. (a) Photocurrent density Jph curves; (b) Jph/Jsat plots of CsPbI2Br PSC; (c) Current density of steady-state output; (d) Steady-state PCE output
Veff—Voltage effective value; Jph—Photocurrent density; Jsat—Dark saturation current density
表 1 CsPbI2Br钙钛矿太阳能电池(PSCs)的光电性能参数
Table 1 Photovoltaic parameters of CsPbI2Br perovskite solar cells (PSCs)
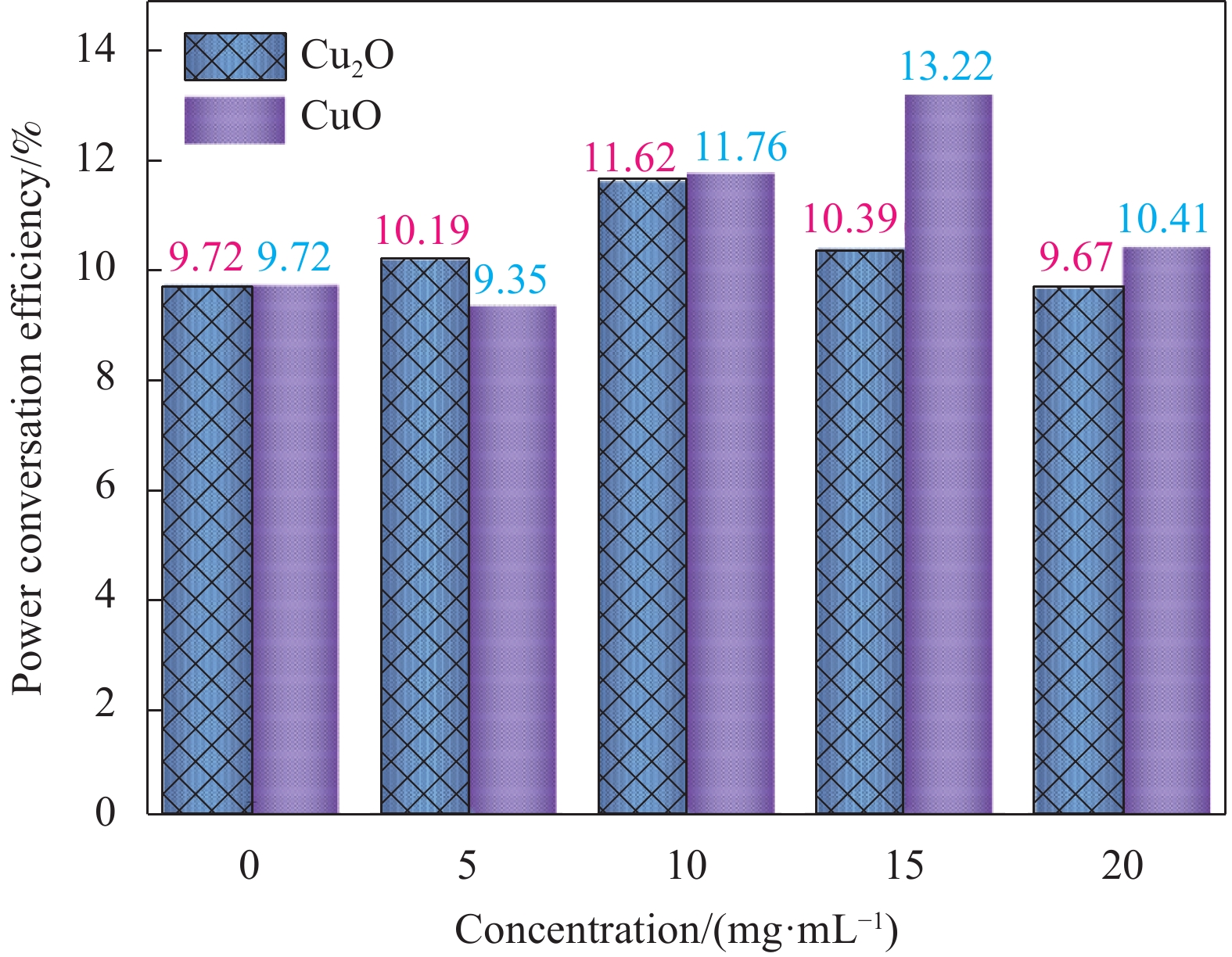
Voc/V Jsc/(mA·cm−2) FF PCE/% HI Control RS 1.21 13.60 0.59 9.72 0.34 FS 1.18 12.68 0.50 7.50 Cu2O RS 1.22 14.95 0.64 11.62 0.16 FS 1.16 14.90 0.57 9.80 CuO RS 1.21 15.55 0.70 13.22 0.15 FS 1.19 15.41 0.61 11.21 Notes: RS—Reverse scan; FS—Forward scan; Voc—Open-circuit voltage; Jsc—Short-circuit current density; FF—Fill factor; PCE—Power conversation efficiency; HI—Hysteresis index. -
[1] SUTTON R J, EPERON G E, MIRANDA L, et al. Bandgap-tunable cesium lead halide perovskites with high thermal stability for efficient solar cells bandgap-tunable cesium lead halide perovskites with high thermal stability for efficient solar cells[J]. Advanced Energy Materials,2016,6(8):1502458. DOI: 10.1002/aenm.201502458
[2] CHEN G, LI P, XUE T, et al. Design of low landgap CsPb1-xSnxI2Br perovskite solar cells with excellent phase stability[J]. Small,2021,17(30):2101380. DOI: 10.1002/smll.202101380
[3] WANG Y, QUINTANA X, KIM J, et al. Phase segregation in inorganic mixed-halide perovskites: From phenomena to mechanisms[J]. Photonics Research,2020,8(11):402411.
[4] NOH J H, IM S H, HEO J H, et al. Chemical management for colorful, efficient, and stable inorganic-organic hybrid nanostructured solar cells[J]. Nano Letters,2013,13(4):1764-1769. DOI: 10.1021/nl400349b
[5] ZHOU Y, ZHANG X, LU X, et al. Promoting the hole extraction with Co3O4 nanomaterials for efficient carbon-based CsPbI2Br perovskite solar cells[J]. Solar RRL,2019,3(4):1800315. DOI: 10.1002/solr.201800315
[6] BAI D, ZHANG J, JIN Z, et al. Interstitial Mn2+-driven high-aspect-ratio grain growth for low-trap-density microcrystalline films for record efficiency CsPbI2Br solar cells[J]. ACS Energy Letters, 2018, 3(4): 970-978.
[7] ZHAO Y, XU H, WANG Y, et al. 10.34%-efficient integrated CsPbBr3/bulk-heterojunction solar cells[J]. Journal of Power Sources,2019,440:227151. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2019.227151
[8] STOUMPOS C C, KANATZIDIS M G, The renaissance of halide perovskites and their evolution as emerging semiconductors[J]. Accounts of Chemical Research, 2015, 48(10): 2791-2802.
[9] CHUNG I, SONG J, IM J, et al. CsSnI3: Semiconductor or metal? High electrical conductivity and strong near-infrared photoluminescence from a single material. High hole mobility and phase-transitions[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society,2012,134(20):8579-8587. DOI: 10.1021/ja301539s
[10] DASTIDAR S, EGGER D A, TAN L A, et al. High chloride doping levels stabilize the perovskite phase of cesium lead iodide[J]. Nano Letters,2016,16(6):3563-3570. DOI: 10.1021/acs.nanolett.6b00635
[11] KUAN C, SHEN H, LIN C. Low photoactive phase temperature all-inorganic[J]. RSC Advances,2021,11:3264-3271.
[12] DU Y, TIAN Q, CHANG X J, et al. Ionic liquid treatment for highest-efficiency ambient printed stable all-inorganic CsPbI3 perovskite solar cells[J]. Advanced Materials,2022,34(10):2106705.
[13] ZENG Q, ZHANG X, FENG X, et al. Polymer-passivated inorganic cesium lead mixed-halide perovskites for stable and efficient solar cells with high open-circuit voltage over 1.3 V[J]. Advanced Materials,2018,30(9):1705393. DOI: 10.1002/adma.201705393
[14] FU S, ZHANG W, LI X, et al. Dual-protection strategy for high-efficiency and stable CsPbI2Br inorganic perovskite solar cells[J]. ACS Energy Letters,2020,5(2):676-684. DOI: 10.1021/acsenergylett.9b02716
[15] YANG S, ZHAO H, HAN Y, et al. Europium and acetate co-doping strategy for developing stable and efficient CsPbI2Br perovskite solar cells[J]. Small,2019,15(46):1904387. DOI: 10.1002/smll.201904387
[16] QIU J, YANG S. Material and interface engineering for high-performance perovskite solar cells: A personal journey and perspective[J]. The Chemical Record, 2020, 20(3): 209-229.
[17] SALIBA M, CORREA-BAENA J P, WOLFF C M, et al. How to make over 20% efficient perovskite solar cells in regular (n-i-p) and inverted (p-i-n) architectures[J]. Chemistry of Materials,2018,30(13):4193-4201.
[18] PATTANASATTAYAVONG P, NDJAWA G O N, ZHAO K, et al. Electric field-induced hole transport in copper(I) thiocyanate (CuSCN) thin-films processed from solution at room temperature[J]. Chemical Communications,2013,49(39):4154-4156. DOI: 10.1039/C2CC37065D
[19] BYRANVAND M M, KIM T, SONG S, et al. p-type CuI islands on TiO2 electron transport layer for a highly efficient planar-perovskite solar cell with negligible hysteresis[J]. Advanced Energy Materials,2018,8(5):1702235. DOI: 10.1002/aenm.201702235
[20] KIM J H, LIANG P W, WILLIAMS S T, et al. High-performance and environmentally stable planar heterojunction perovskite solar cells based on a solution-processed copper-doped nickel oxide hole-transporting layer[J]. Advanced Materials,2015,27(4):695-701. DOI: 10.1002/adma.201404189
[21] ZUO C, DING L. Solution-processed Cu2O and CuO as hole transport materials for efficient perovskite solar cells[J]. Small,2015,11(41):5528-5532. DOI: 10.1002/smll.201501330
[22] LI Q, WANG F, SUN L, et al. Design and synthesis of Cu@CuS yolk-shell structures with enhanced photocatalytic activity[J]. Nano-Micro Letters,2017,9(3):35. DOI: 10.1007/s40820-017-0135-7
[23] UMA B, ANANTHARAJU K S, RENUKA L, et al. Controlled synthesis of (CuO-Cu2O)Cu/ZnO multi oxide nanocomposites by facile combustion route: A potential photocatalytic, antimicrobial and anticancer activity[J]. Ceramics International,2021,47(10):14829-14844. DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2020.09.223
-
期刊类型引用(12)
1. 贾宝惠,任鹏,宋挺,崔开心,肖海建. 湿热环境下端径比对复合材料螺栓连接结构静力拉伸失效的影响. 材料导报. 2024(05): 246-252 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 张宇,郭盼盼,熊婕,黄峰,王波. 循环湿热环境对树脂基复合材料弯曲性能的影响. 科学咨询(科技·管理). 2024(02): 135-138 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 牛存洋,寿文凯,顾海萍,孔德良. 以价值观为导向的生态学课程思政教学设计——以种群生活史对策为例. 科学咨询(教育科研). 2024(03): 134-137 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 刘鸿森,黄凯,黄金钊,韩晓剑,逯浩,骆杨,张莉,果立成. 考虑温度效应的复合材料紧固结构面外拉脱性能和失效机制. 复合材料学报. 2024(09): 4778-4790 .  本站查看
本站查看
5. 王慧敏,任亮,范微微,陈阳,孙丽. 基于锥体结构复合材料制品布带缠绕成型关键工艺参数优化. 宇航材料工艺. 2024(05): 87-92 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 樊俊铃,马国庆,焦婷,陈曾美,韩啸. 温度和湿度对碳纤维增强复合材料老化影响研究综述. 航空科学技术. 2023(09): 1-13 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 刘宋婧,冯宇,张腾,毕亚萍,张铁军. 航空复合材料加筋板湿热环境下吸湿性能. 航空动力学报. 2023(09): 2231-2240 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 王静,程健,肖存勇,贾松,任荣,熊需海. 先进聚合物基复合材料超声焊接研究进展. 高分子材料科学与工程. 2023(09): 166-173 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 蒋平,吕太勇,吴丽华,José Pérez-Rigueiro,胡梦蕾,徐丽萍,黄诗怡,王安萍,郭聪. 形变导致的蜘蛛大壶状腺丝力学行为的记忆与变异. 材料导报. 2023(23): 237-245 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 吴志猛. 聚四氟乙烯芳纶1313纤维树脂基复合材料的摩擦学性能研究. 化学工程与装备. 2022(09): 40-41+44 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 王志平,陈灏,路鹏程. 电-湿耦合作用下碳纤维增强树脂基复合材料损伤机制. 中国塑料. 2022(10): 39-45 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 史超帆,陈叔平,王洋,金树峰,于洋,何远新,杨帅,熊珍艳,史庆智. 纤维方向对环氧树脂/玻纤复合材料导热性能影响. 工程塑料应用. 2022(11): 108-116 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(9)
-
目的
基于CsPbIBr的全无机碳基钙钛矿太阳能电池由于碳电极与钙钛矿层间接触性能较差和能带不匹配等问题,导致其光电转化效率较低。本文采用简单的葡萄糖还原法结合煅烧技术制备了两种不同形貌和结构的规则八面体构型CuO,将之作为无机空穴传输材料,制备结构为FTO/SnO/CsPbIBr/CuO/C的碳基钙钛矿太阳能电池。
方法CuO八面体纳米颗粒可在低温下使用简单的葡萄糖还原法合成,将CuO八面体在空气气氛中于500℃煅烧1 h得到表面凹凸不平的CuO八面体颗粒。在制备CsPbIBr无机钙钛矿电池的过程中分别将八面体纳米粒子CuO和CuO嵌入可化学加工的 CsPbIBr 层中,来增强钙钛矿和电子传输层之间的界面接触,从而改善载流子传输。利用SEM 图像和XRD谱图可以分析煅烧前后CuO 样品的相态。为了分析CuO和CuO 样品的更细微结构及价态,在100-800 cm范围内进行了拉曼表征和XPS分析,对CsPbIBr薄膜进行的XRD和XPS分析可以研究添加CuO/CuO对CsPbIBr 薄膜性能的影响。关于电化学性能表征,进行了Mott-Schottky分析与测试、电化学阻抗谱()、稳态光电流输出和等测试。同时为了评估 PSC 的长期稳定性,在空气环境下监测了未封装器件的 PCE变化。
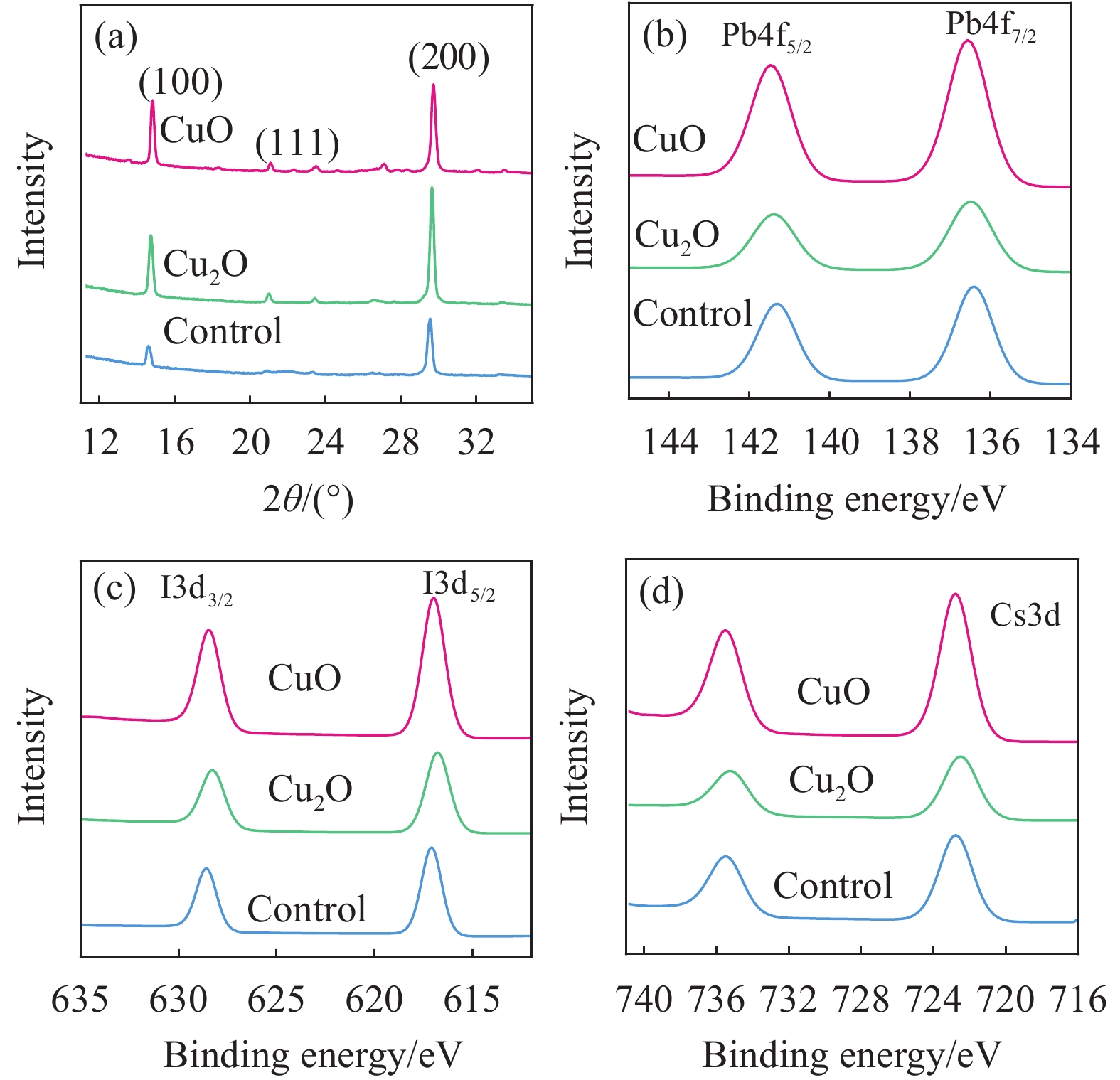
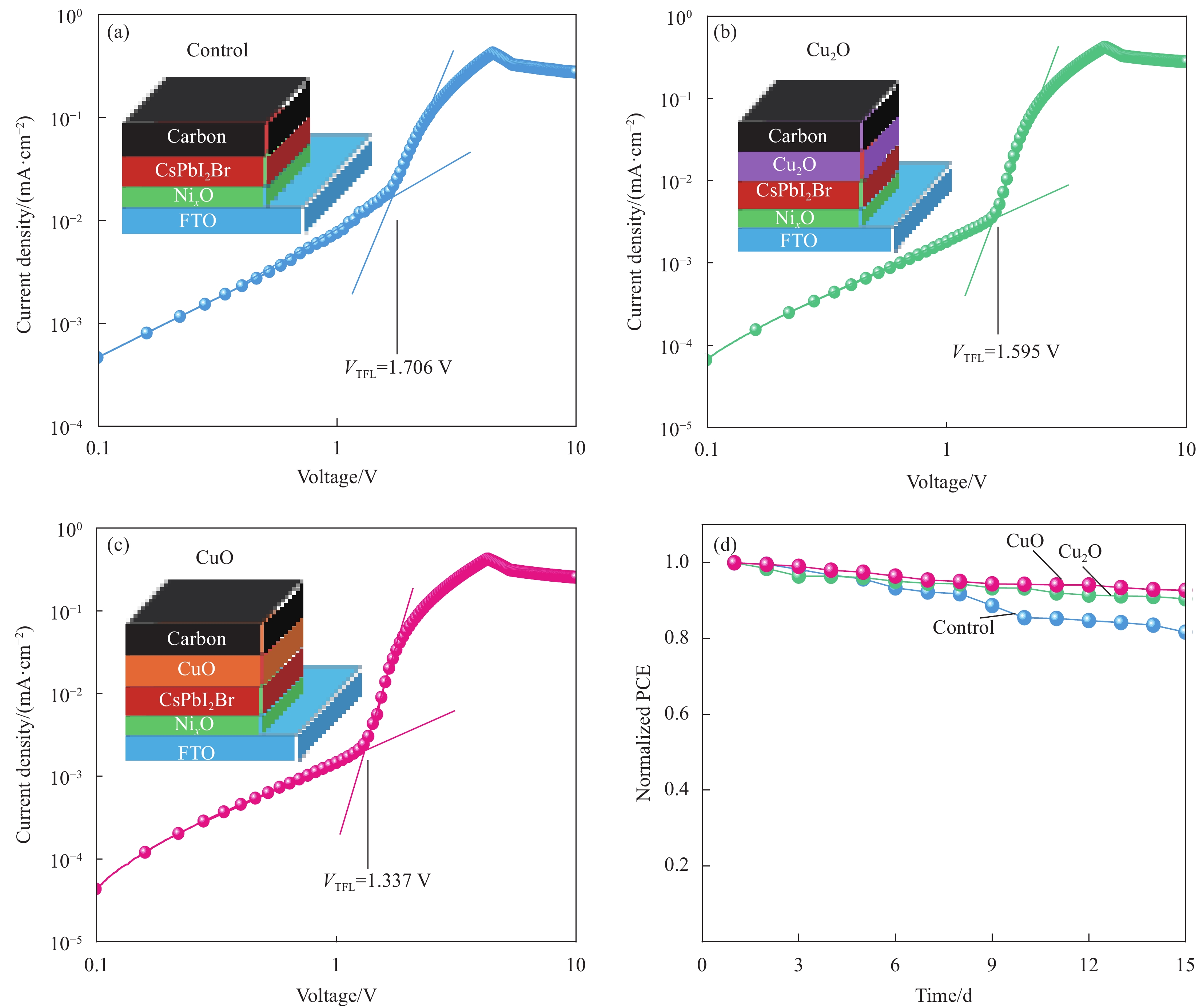
结果通过SEM 图像观察到CuO在煅烧后出现了褶皱和凸起,说明了产生了相的转变,XRD谱图的峰位置、峰宽度以及峰强度可以说明产生新的相结构为CuO。拉曼表征的特征峰进一步验证了研究结果,同时基于XPS分析也揭示了两种不同形貌CuO和CuO样品的表面化学组成和与形成的元素Cu的二价氧化态,从图中特征光谱对比可以看出,CuO相比于CuO具有更丰富的氧空位,有助于提升其载流子传输性能,从而提高器件的光电性能。在CsPbIBr薄膜的XRD和XPS图谱中,没有观测到CuO或CuO的特征峰,表明CuO和CuO的加入对CsPbIBr表面的化学成分没有影响。对CuO和CuO改性的C-PSC进行的Mott-Schottky分析,表明基于CuO和CuO改进的器件相对于空白器件提供了更大的更大的值意味着光生电荷载流子的分离、传输和提取需要更大的驱动力,从而导致更低的电荷复合。OCVD曲线与未经修饰的器件相比,表现了CuO和CuO基器件在暗态条件下衰减速率减慢,印证了电子/空穴复合过程减慢,载流子寿命更长。通过测试可以看出电池的、和 FF有着明显的改善,基于CuO和CuO的CsPbIBr基C-PSC器件的光电转换效率最高为分别为11.62%和13.22%,分别比空白对照器件的光电转化效率提高了19.5%和36.0%。对钙钛矿太阳能电池迟滞指数()进行的计算可以看出具有CuO和CuO改性的钙钛矿太阳能电池有着更低的迟滞指数,表明了添加 CuO 界面层可以有效降低迟滞现象。通过电化学阻抗谱()的测试,CuO和CuO的界面修饰减小了器件的,却明显增加了更小的意味着更大的空穴迁移率,即更大的而越高,意味着较低复合速率,表明了更好的载流子传输性能。光密度曲线显示基于CuO-CsPbIBr的器件具有更高的,这意味着更高的载流子分离效率。计算出的电子阱态密度分别低于对照组,这表明CuO可以有效地抑制Pb的氧化,从而降低器件的缺陷密度,而缺陷密度的降低更有利于提高钙钛矿太阳能电池的性能。同时PSC 的长期稳定性曲线,表明CuO和CuO的加入在改善器件长期稳定性方面也具有较好的效果。
结论CuO和CuO皆具有良好的化学稳定性和p型载流子传输特性,可有效增强CsPbIBr钙钛矿层与碳电极层之间的界面接触,改善载流子传输性能,减少电荷复合,降低了电池的迟滞效应,延长光电子寿命。同时CuO和CuO的加入也可以对钙钛矿起到保护的作用,从而增加其环境稳定性。
-
CsPbI2Br基的全无机钙钛矿太阳能电池由于碳电极与钙钛矿的接触性较差和能带不匹配等原因,导致其光电转换效率不高。无机空穴传输材料成本低、迁移率高、稳定性好,可有效提升界面性能,非常适合于全无机CsPbI2Br钙钛矿太阳能电池的优化改性。
本文采用简单的葡萄糖还原法结合煅烧技术制备了两种不同形貌和结构的规则八面体构型CuO和Cu2O,将之作为无机空穴传输材料,制备了结构为FTO/SnO2/CsPbI2Br/CuxO/C的碳基钙钛矿太阳能电池,研究了铜氧化物的形貌、结构对光电性能的影响机制。结果显示铜氧化物具有宽带隙、良好的化学稳定性和p型载流子输运性质等良好的性能,以之作为无机空穴传输材料,可有效增强CsPbI2Br钙钛矿层与碳电极层之间的界面接触,改善载流子传输性能,减少电荷复合,延长光电子寿命。基于Cu2O和CuO的CsPbI2Br基C-PSC器件的最终光电转化效率分别为11.62%和13.22%,分别比对照空白器件的光电转化效率提高了19.5%和36.0%。该工作利用简单的方法和材料,为提高全无机碳基CsPbI2Br钙钛矿太阳能电池的光电转化效率和稳定性提供了积极的策略。
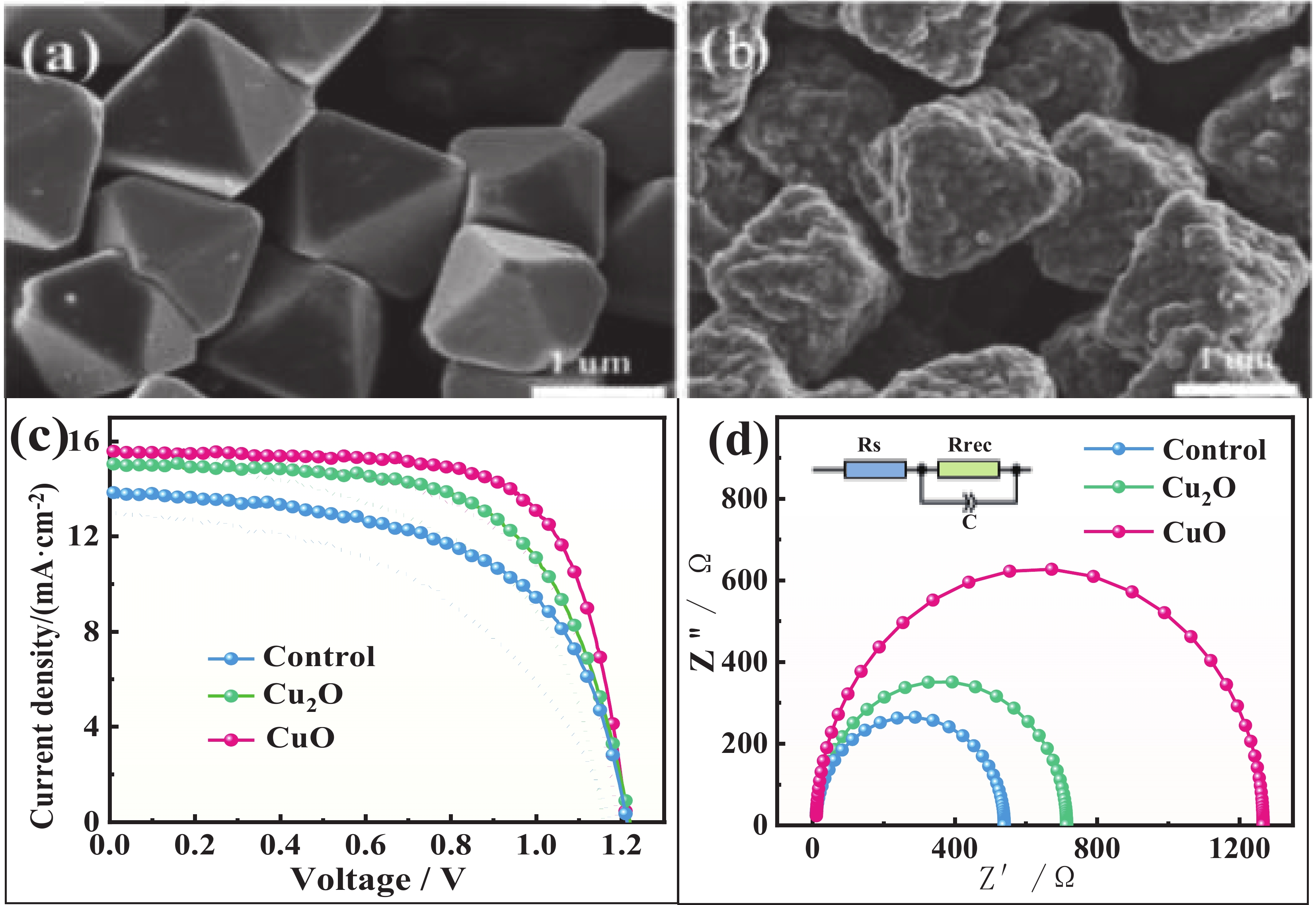
合成的 Cu2O(a)和 CuO(b)氧化物的 SEM 图;相应碳基 CsPbI2Br 钙钛矿太阳能电池的 J-V 曲线(c)和 EIS 测试图(d)




 下载:
下载: