Study on the interlayer bonding property of dry fiber tows used in automated fiber placement for aerospace composites
-
摘要: 为了保证干纤维预成型体的层间良好贴覆,分别对一种成熟应用于航空级主承力构件的干纤维自动铺放材料和一种研发级材料进行层间粘结性研究。采用热压工艺模拟自动铺丝过程,通过T型剥离和多种表征方法测试干纤维层间粘结力、表面性能和定型剂扩展,比较两种干纤维的层间粘结力,并研究其层间粘结机制。研究发现:成熟干纤维的层间粘结力在一定范围内远大于研发干纤维,二者均显著受到层压温度、层压时间及协同作用的影响,但最显著的影响因素不同;干纤维层间粘结机制与干纤维表面性能、定型剂性能及受热扩展过程有关,推测成熟干纤维的较高层间粘结力与定型剂的交联有关;此外,通过自动铺放工艺的验证,在一定层压时间范围内,采用热压工艺代替自动铺丝进行干纤维层间粘结性的评价具有良好可靠性;最后,干纤维表面涂覆热塑性增韧材料后,层间粘结力大幅下降。通过对材料和工艺的研究,本文为干纤维自动铺丝工艺的优化提供了数据及理论支持。Abstract: In order to guarantee the good adhesion between layers of dry fiber preform, the interlayer bonding properties of two kinds of automatic fiber placement dry fiber tows were investigated, one has been maturely used in aerospace primary force-taking structure and the other one is under development. Dry fiber laminate samples were prepared by hot pressing to simulate the automatic fiber placement. The interlayer bonding property, surface properties and binder extension of dry fibers were measured by the T-type peeling test and various characterization methods. The interlayer bonding strength of the two kinds of dry fibers was compared and the interlayer bonding mechanism was studied. The results show that the interlayer bonding strength of mature dry fibers is much greater than that of developing dry fibers in a certain temperature range. Both of them are significantly affected by lamination temperature, lamination time and the synergistic effect, but the most significant factors of the two materials are different. The interlayer bonding mechanism of dry fibers is related to surface properties of dry fibers, properties of binder and the binder extension at elevated temperature. It is speculated that the interlayer bonding force of mature dry fibers is related to the crosslinking of the binder. In addition, through the verification of the automatic laying process, the hot pressing process has good reliability in the evaluation of interlayer bonding between the dry fiber layers within a certain lamination time comparing to the automatic fiber placement. Finally, when the dry fiber surface is coated with the thermoplastic toughening material, the adhesion between layers decreases significantly. Through the study of materials and technology, this paper provides data and theoretical support for the optimization of automatic fiber placement process.
-
Keywords:
- automated fiber placement /
- dry fiber tow /
- preform /
- interlayer bonding /
- binder
-
自动铺丝技术是先进的复合材料零件预制体的制造技术,综合了自动纤维缠绕和自动纤维带铺放的特点,具有铺放精度高、可重复性好的优点,可实现复杂曲面型复合材料构件的铺层制造[1-4]。与液体成型技术进行结合,能够实现复杂曲面型复合材料构件的高性能、低成本、高精度的制造[5]。目前,自动铺丝技术与液体成型技术相结合,已成功应用在俄罗斯M21单通道客机机翼的制造,使得机翼生产周期降低至30 h,飞机总减重45%,制造成本大大降低[6-7]。而国内,由于自动铺丝技术和液体成型技术的前期研究基础薄弱,使得材料的工艺适应性研究严重缺乏,研究进展相对缓慢[3-4]。综合以上,本文对一种成熟应用于航空级主承力构件的干纤维自动铺丝材料和一种研发级自动铺丝材料的层间粘结性能进行研究,采用不同热压参数模拟铺丝过程,用T型剥离的方法对干纤维层间剥离力进行测试,用于表征干纤维层间粘结性,研究热压参数对干纤维层间粘结性的影响;并结合多种材料性能表征手段,通过对干纤维表面性能、定型剂热力学性能的分析,研究两种干纤维的层间粘结机制;最后,为了证明热压工艺模拟自动铺丝工艺的可靠性,对比了分别用这两种工艺制备的层压样条的层间粘结性,并探究了喷涂热塑性树脂后干纤维的层间粘结性变化。通过本文的研究,验证了一种简便的评价干纤维层间粘结性能测试方法的可靠性,通过层间粘结机制的研究,为干纤维材料的自动铺丝工艺优化提供了数据和理论支持,促进了干纤维自动铺放技术的发展。
因此,对纤维自动铺放技术和液体成型技术的材料工艺适应性的研究具有重要的意义。采用自动铺丝技术制备预成型体过程中,需要制备出结构紧实、型面准确、保型性好的干纤维预成型体用于液体成型制备复合材料零件[1-4]。干纤维自动铺丝材料,与预浸丝束不同,表面分布少量呈点阵分布定型剂以实现干纤维丝束的良好粘结和贴覆[8-9]。为了避免纤维束自身发生错动,影响预成型体精度,在铺丝过程中需要精确控制铺丝温度、铺丝压力等关键参数[10-12]。尽管了解到自动铺丝过程中干纤维的铺放与温度、压力[13-14]、定型剂的状态变化有关[15-16],然而对于干铺放过程中的层间粘结力的形成机制,尚未进行充分研究[17]。另外,干纤维的自动铺丝过程消耗功率大、对材料和自动铺丝设备的要求高,若能提出一种可替代自动铺丝工艺的测试方法对材料粘结性进行评估,可大大简化工艺研究过程,促进相关技术的发展。实际应用中,为了提高复合材料的冲击阻抗和损伤容限,往往需要对复合材料进行层间增韧[18-21],而在增强干纤维表面涂覆高性能热塑性树脂增韧剂是层间增韧的常用方法[22-24],目前增韧剂的施加,对干纤维层间粘结性能的影响尚不明确,需要进一步探究。
1. 实验材料及方法
1.1 原材料
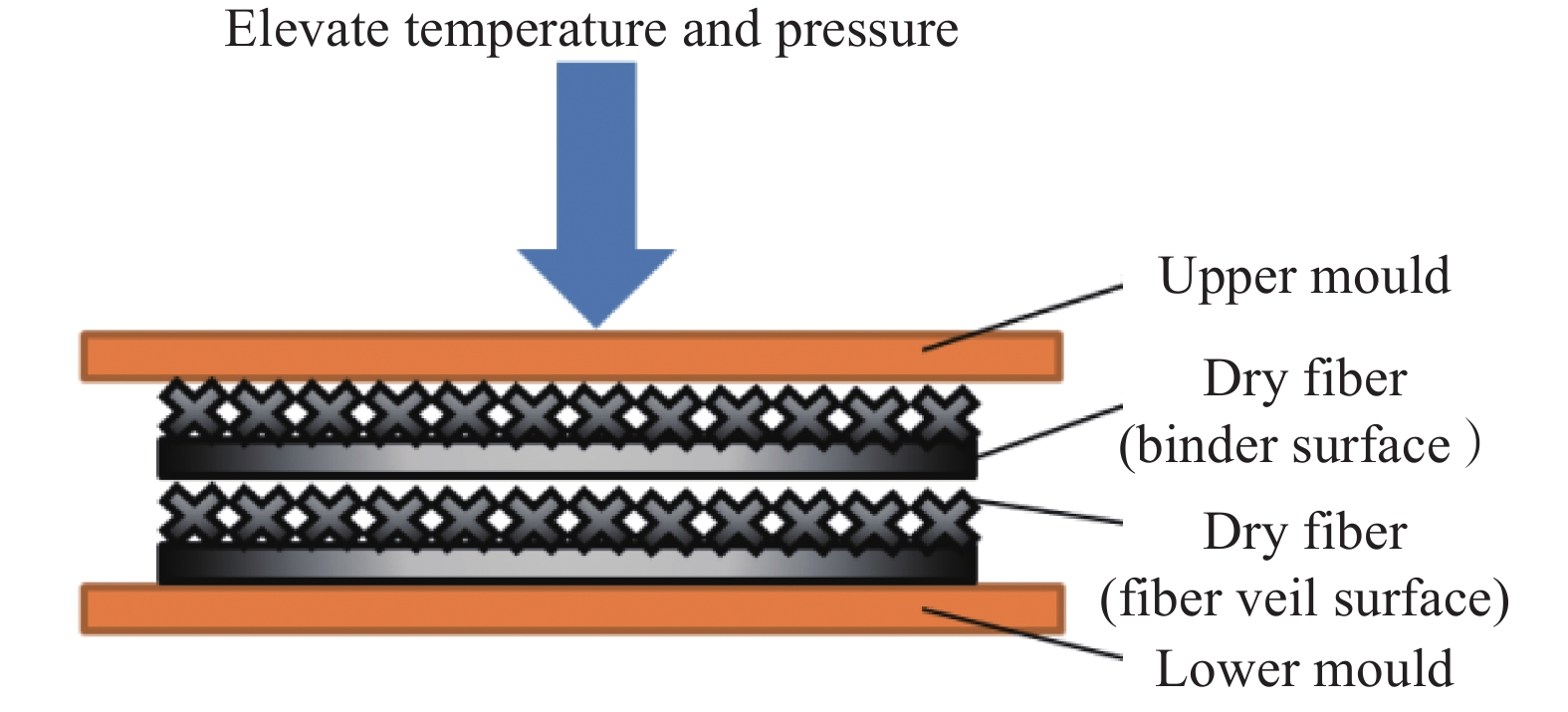
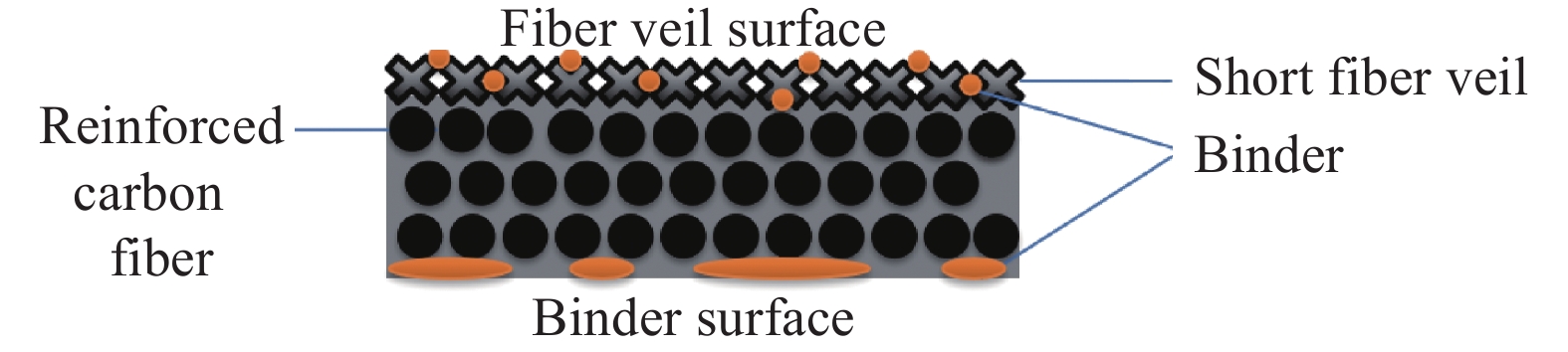
原材料为成熟应用于航空级主承力构件的干纤维自动铺丝材料(以下简称成熟干纤维)和一种研发级自动铺丝材料(以下简称研发干纤维)。两种材料均为碳纤维单向带,宽度6.35 mm,克重均为200 g/m2,两种单向带的一侧表面均覆盖着无规排列的短切纤维毡。两侧表面均有定型剂分布(图1)。在自动铺丝过程中,两层干纤维叠合在一起,下层干纤维的网纱与上层干丝的定型剂面贴合,在激光和压辊的作用下形成层间粘结力,制造出结构稳定性的预成型体。
1.2 干纤维层合样条的制备及测试方法
采用平板硫化机(XLB-D/S 0.5 MN热压机,上海德弘橡塑机械公司)将两根干纤维带重叠在一起后进行热压制备干纤维层合样条,并采用T型剥离的方法对干纤维层合样条的剥离力进行测试,用于表征干纤维的层间粘结性。平板硫化机的层压过程如图2所示,层压时上层干纤维带的定型剂面与下层干纤维的网纱面叠合,受压前模具在压机内加热30 min至受热均匀后开始压制,到达特定的压制时间后停止,工装冷却至室温后脱模,得到多个干纤维样条。
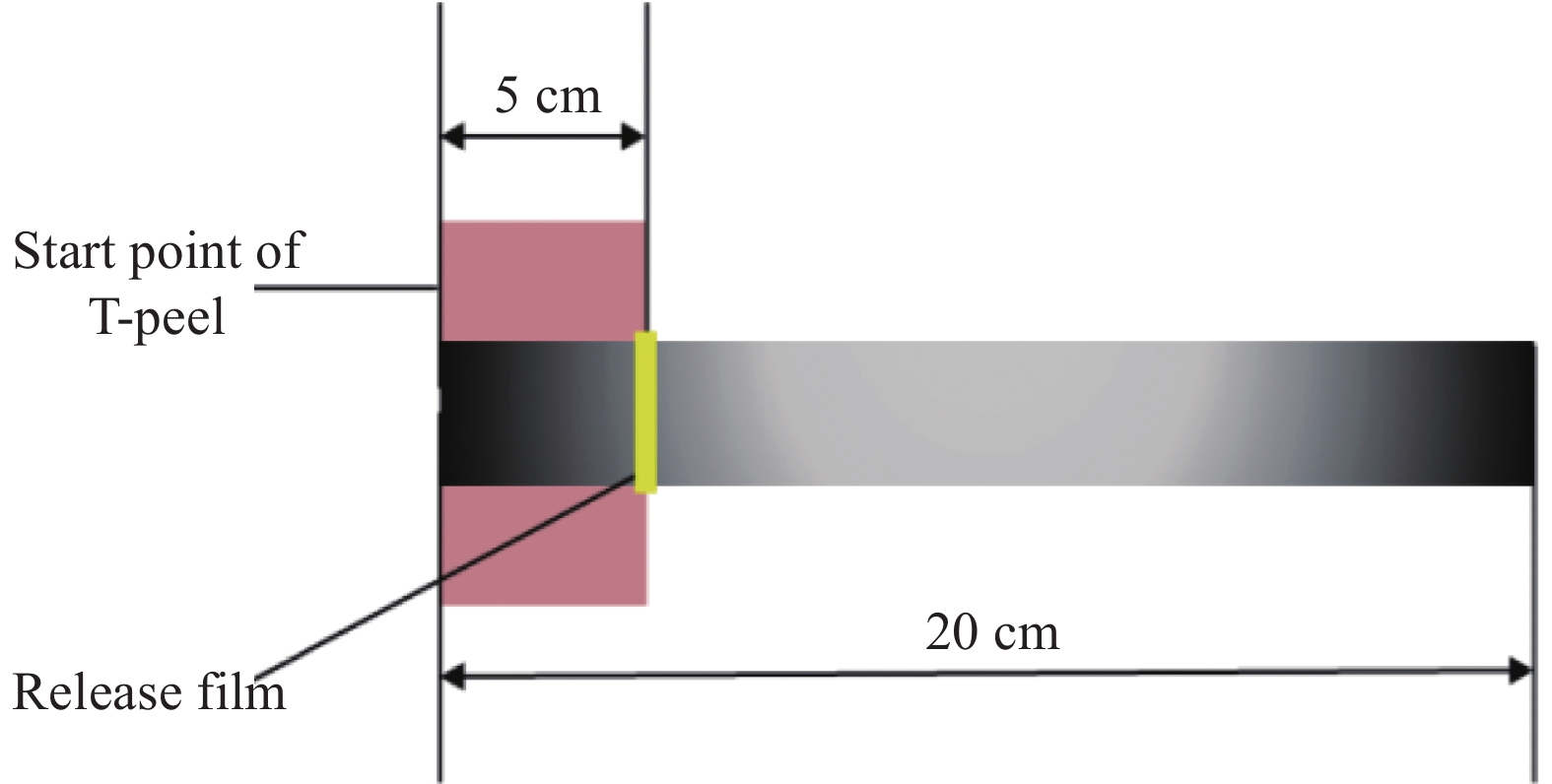
干纤维样条被压制好后进行T型剥离,此时干纤维样条长度20 cm,粘结部分长度15 cm,样条前段5 cm衬有隔离膜,作为T型剥离实验的夹持端(图3),宽度6.35 mm。T型剥离的测试方法参考国标GB/T 2791—1995[25],T型剥离试样长度为20 cm,宽度为2.5 cm,胶粘剂粘结部分长度15 cm,试样未胶接端分开并对称的夹在上下夹头中,上下夹头以(100±10) mm/min的速率分离。由于干纤维带实际形状较窄,在实际标准上进行了改进,样条宽度改为单根干纤维带的宽度,而样条长度、粘结长度保持不变。将样条置于E42.503万能试验机(美国MTS公司)进行拉伸(图4),上下夹头隔距6 cm,夹头的分离速度为100 mm/min,记录样条的拉伸-位移曲线。
采用差示扫描量热仪(DSC)取未热压的成熟干纤维进行测试,测试气氛为N2, 温度为40~240℃,上升速率为10℃/min。
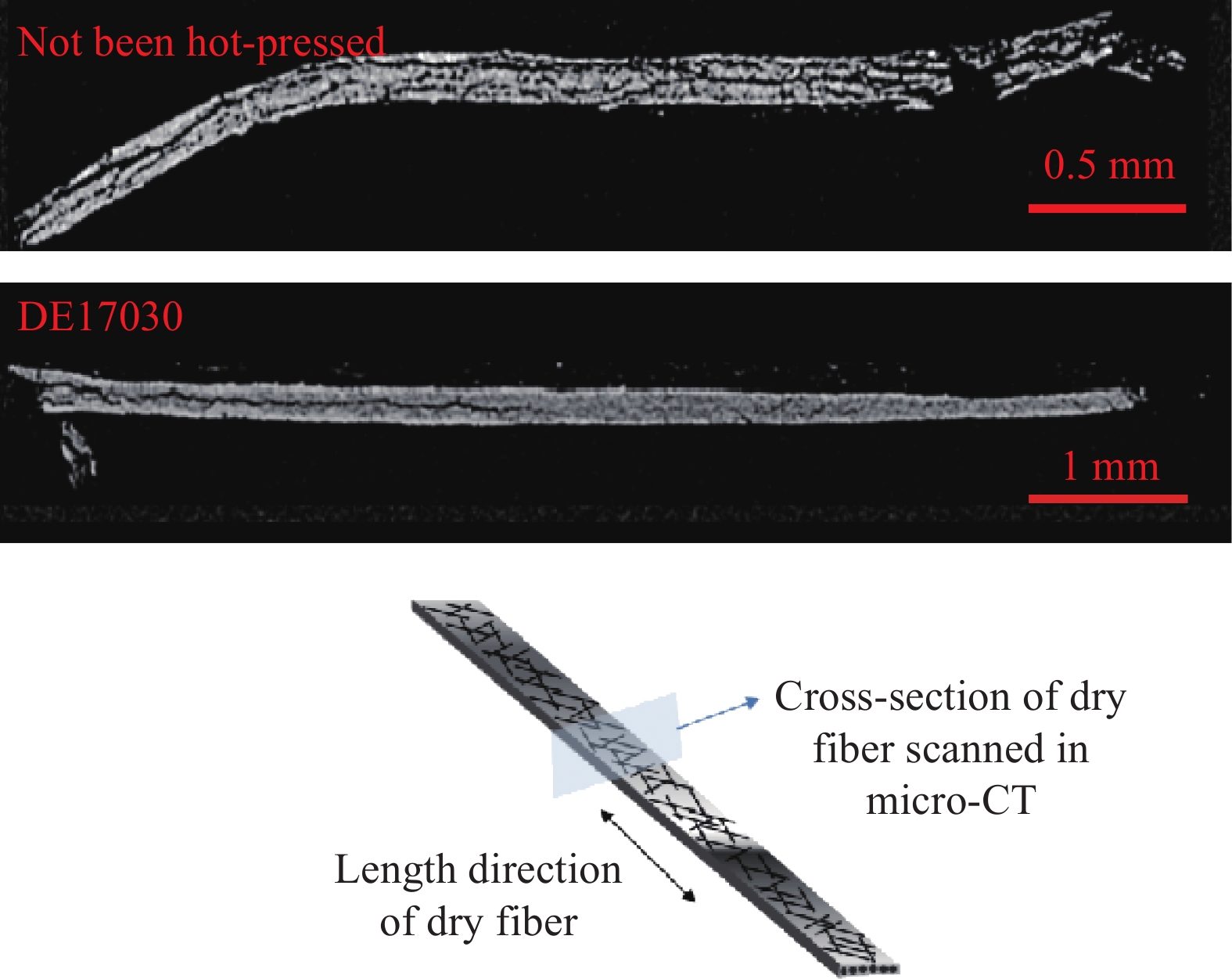
采用GE Nanotom180显微断层扫描仪(Micro CT,Gerneral Electric)分别对未热压和经过170℃热压的研发干纤维进行扫描[26],观察干纤维内部的纤维排列状态。
1.3 实验设计(DOE)
本实验旨在研究干纤维在自动铺丝过程中,成熟干纤维和研发干纤维的层间粘结性能受铺放温度和铺放速度的影响,假设热压工艺可模拟自动铺丝工艺,本实验中假定压机压力不变,样条单位面积所受压强1.1~1.4 MPa,与自动铺丝过程中压辊压强基本一致。实验选取热压温度和压力作用时间这两个因子为变量,每个变量设置三水平,实验因子及水平设置见表1。由于因子个数不多,并且需要考察因子间的相互作用,选用全因子设计方法,包含测试名称、材料和压制参数的实验计划见表2,每组处理包括4~5次重复实验。
表 1 实验设计因子及水平信息Table 1. Experiment design factor and levels informationFactor Level Value Compression temperature/oC 3 110, 140, 170 Compression time/s 3 10, 30, 60 表 2 层合样条名称、材料和制备参数Table 2. Name, materials and experiments parameters of test samplesSample
lablesCompression temperature/℃ Compression time/s Sample
materialMA11010 110 10 Mature MA14010 140 10 Mature MA17010 170 10 Mature MA11030 110 30 Mature MA14030 140 30 Mature MA17030 170 30 Mature MA11060 110 60 Mature MA14060 140 60 Mature MA17060 170 60 Mature DE11010 110 10 Developing DE14010 140 10 Developing DE17010 170 10 Developing DE11030 110 30 Developing DE14030 140 30 Developing DE17030 170 30 Developing DE11060 110 60 Developing DE14060 140 60 Developing DE17060 170 60 Developing 1.4 热压工艺与自动铺丝工艺的对比
为了检验热压工艺代替自动铺丝进行干纤维层间粘结性测试的可靠性,采用自动铺丝设备在相同温度、压力等参数下铺放成熟干纤维预成型体(图5)。比较自动铺丝层合样条的平均剥离力和标准偏差与热压工艺制备层合样条的区别。
1.5 涂覆热塑性材料后的干纤维层间粘结性变化
为了提高复合材料的层间韧性,在研发干纤维表面涂覆定型剂后,将热塑性增韧乳剂以雾状形态均匀喷淋在研发干纤维的定型剂面,之后迅速经过200℃的热风进行固化。取增韧后的研发干纤维进行热压样条制备,测试喷淋乳剂后对层间粘结性的影响并与未喷淋乳剂的干纤维层间粘结性进行对比。
1.6 平均剥离力测试方法
采用平板硫化机制备干纤维层合样条后进行T型剥离,根据剥离力和夹具竖直位移的关系计算干纤维的平均剥离力及其波动。为了保证剥离力的稳定,避开试样前段的剥离,截取夹具竖直位移50 mm处作为起点,夹具竖直位移250 mm处作为终点(若试样在夹具竖直位移250 mm内某位置处完全剥离,则已完全剥离时的夹具位移为终点),提取起点与终点间的剥离力-位移曲线,对每条曲线的剥离力求积分后除以位移,计算样条的平均剥离力,并统计同一处理内样条平均剥离力的标准偏差。比较不同压制参数不同材料样条的平均剥离力大小和波动程度。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 平均剥离力的大小与波动
2.1.1 成熟干纤维
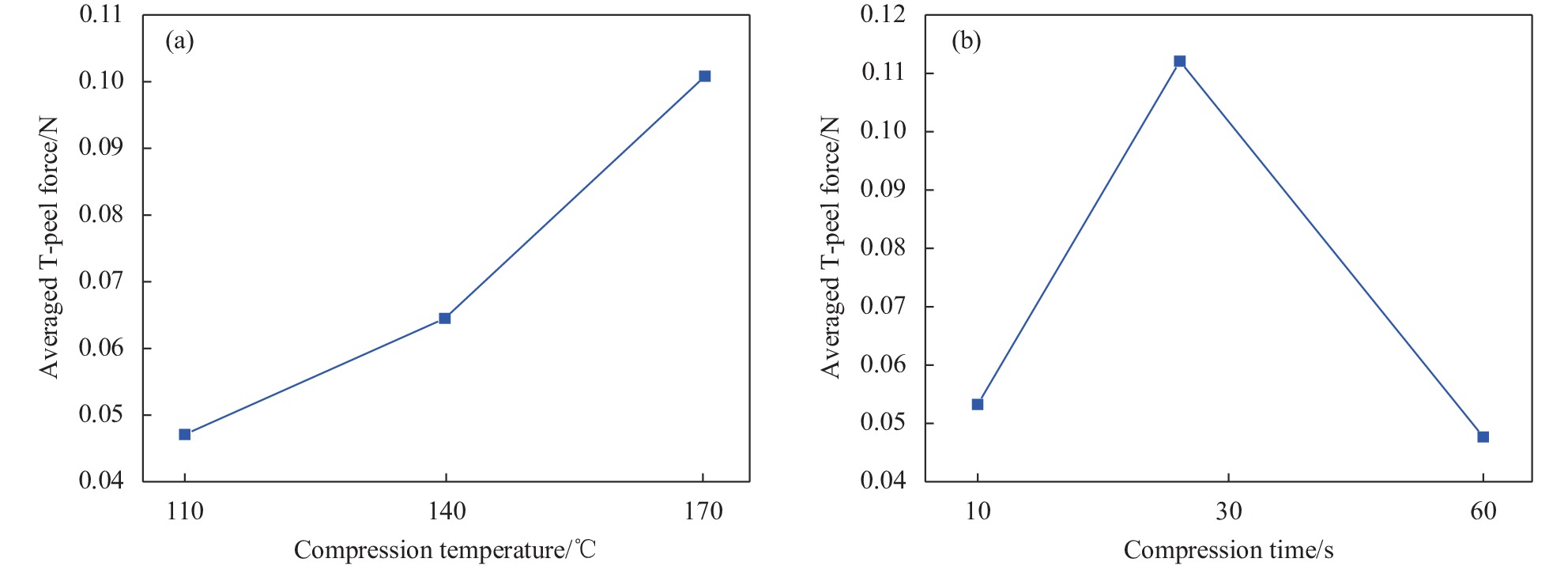
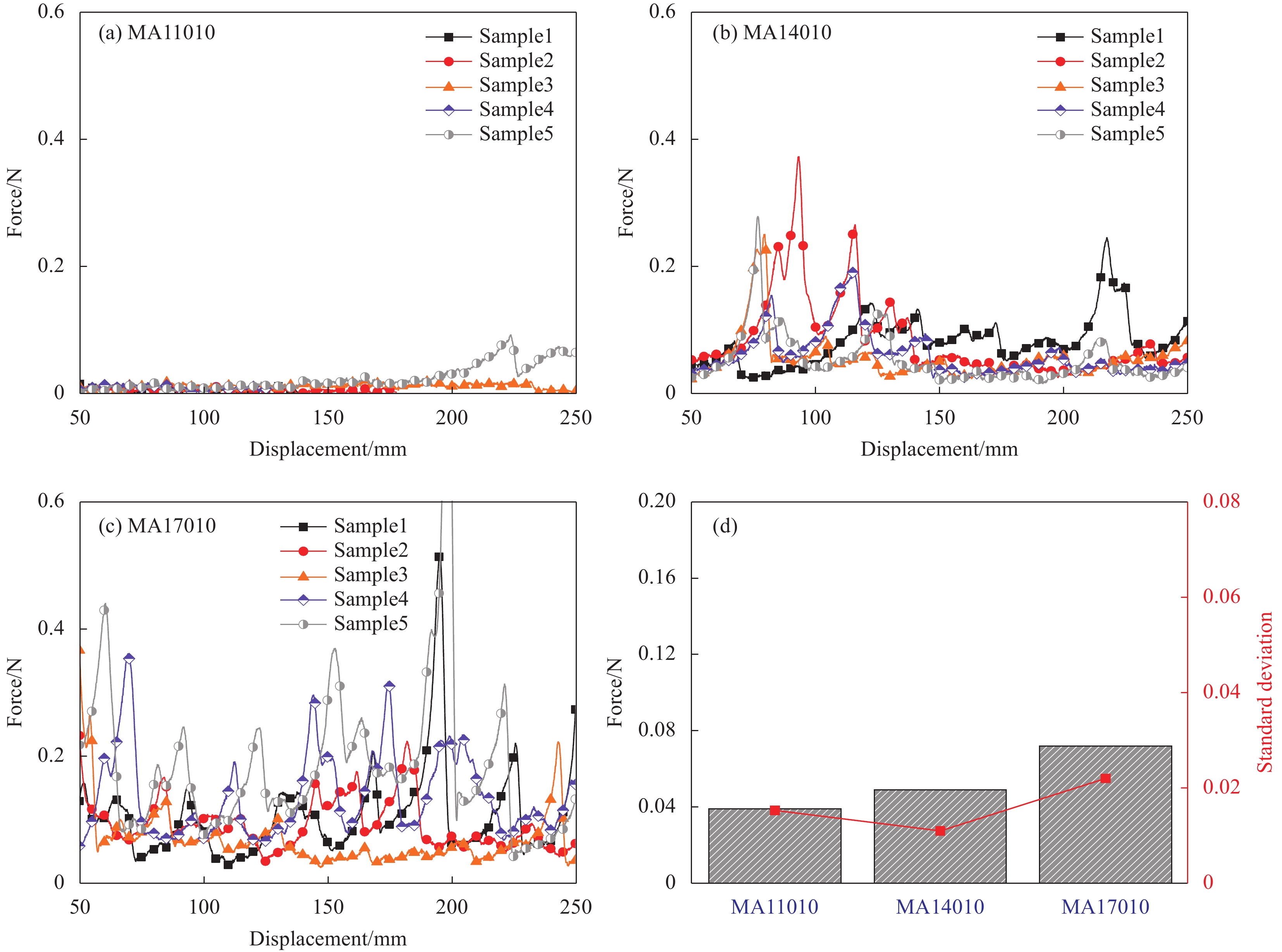
成熟干纤维的样条分别在110℃、140℃及170℃的温度下压制,压力作用时间分别为10 s、30 s和60 s。当压力作用时间为10 s时,成熟干纤维样条的T型剥离力-位移曲线如图6所示。可知,当层压温度为110℃时和170℃时,样条在夹头位移小于250 mm处就产生了完全分离;而在层压温度140℃时,样条在夹头位移到达250 mm后才开始分离。样条剥离过程中,干纤维剥离力的最大值可达0.4 N左右,压制温度170℃的样条具有最多的剥离力峰值,其次是140℃压制的样条。样条的平均剥离力和波动程度如图6(d)所示,压力作用时间10 s时,从110℃至170℃,样条平均剥离力逐渐增大,而140℃热压样条的平均剥离力的波动程度最小。
![]() 图 6 压力作用时间10 s时成熟干纤维层合样条的T型剥离力-位移曲线:(a) 层压温度110℃;(b) 层压温度140℃;(c) 层压温度170℃;(d) 层间粘结力与标准偏差Figure 6. Relationship curves between T-peel force and displacement for mature dry fiber tow samples with compression time of 10 s: (a) Compression temperature 110℃; (b) Compression temperature 140℃; (c) Compression temperature 170℃; (d) Average T-peel force and standard deviation
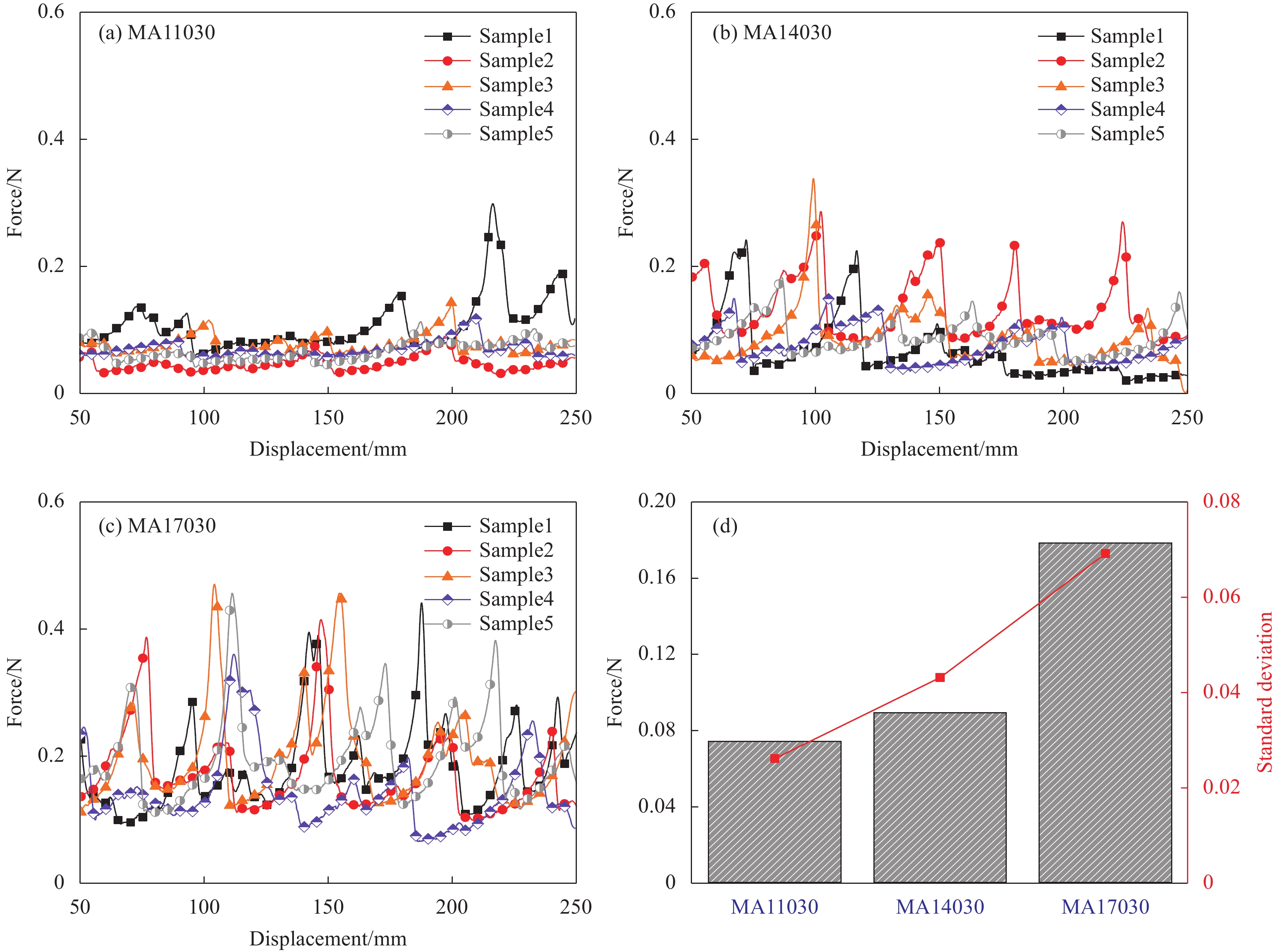
图 6 压力作用时间10 s时成熟干纤维层合样条的T型剥离力-位移曲线:(a) 层压温度110℃;(b) 层压温度140℃;(c) 层压温度170℃;(d) 层间粘结力与标准偏差Figure 6. Relationship curves between T-peel force and displacement for mature dry fiber tow samples with compression time of 10 s: (a) Compression temperature 110℃; (b) Compression temperature 140℃; (c) Compression temperature 170℃; (d) Average T-peel force and standard deviation当压力作用时间为30 s时,成熟干纤维样条的T型剥离力-位移曲线如图7所示。此时,压制温度在110~170℃范围内,所有样条均在夹头位移到达250 mm后才开始分离。样条剥离过程中,压制温度170℃的样条的剥离力最大可达0.5 N左右,且出现的频率较多,分布均匀;其次是压制温度140℃的样条;最后,110℃压制的样条,最大剥离力较小,且出现的频率最低。样条的平均剥离力和波动程度如图7(d)所示,从110℃至170℃,样条平均剥离力逐渐增大,压制温度170℃的干纤维样条平均剥离力甚至可达110℃、140℃热压样条平均剥离力的2倍,且平均剥离力的波动程度也随之变大。
![]() 图 7 压力作用时间30 s时成熟干纤维层合样条的T型剥离力-位移曲线:(a) 层压温度110℃;(b) 层压温度140℃;(c) 层压温度170℃;(d) 本测试中平均T型剥离力与标准偏差Figure 7. Relationship curves between T-peel force and displacement for mature dry fiber tow samples wtth compression time of 30 s: (a) Compression temperature 110℃; (b) Compression temperature 140℃; (c) Compression temperature 170℃; (d) Average T-peel force and standard deviation
图 7 压力作用时间30 s时成熟干纤维层合样条的T型剥离力-位移曲线:(a) 层压温度110℃;(b) 层压温度140℃;(c) 层压温度170℃;(d) 本测试中平均T型剥离力与标准偏差Figure 7. Relationship curves between T-peel force and displacement for mature dry fiber tow samples wtth compression time of 30 s: (a) Compression temperature 110℃; (b) Compression temperature 140℃; (c) Compression temperature 170℃; (d) Average T-peel force and standard deviation当压力作用时间为60 s时,成熟干纤维样条的T型剥离力-位移曲线见图8。层压温度为110℃和170℃时,样条在夹头位移接近200 mm处即产生了完全分离;而在层压温度140℃时,样条在夹头位移到达250 mm后才开始分离。样条剥离过程中,压制温度140℃的样条的出现了最大剥离力,可达0.5 N左右,且出现的频率较高;而压制温度110℃和170℃的样条的最大剥离力较小。样条的平均剥离力和波动程度如图8(d)所示,从110℃至170℃,样条平均剥离力先增大后减小,最大剥离力在140℃热压样条处获得,平均剥离力波动程度的趋势相同。
![]() 图 8 压力作用时间60 s时成熟干纤维层合样条的T型剥离力-位移曲线:(a) 层压温度110℃;(b) 层压温度140℃;(c) 层压温度170℃;(d) 本测试中平均T型剥离力与标准偏差Figure 8. Relationship curves between T-peel force and displacement for mature dry fiber tow samples with compression time of 60 s: (a) Compression temperature 110℃; (b) Compression temperature 140℃; (c) Compression temperature 170℃; (d) Average T-peel force and standard deviation
图 8 压力作用时间60 s时成熟干纤维层合样条的T型剥离力-位移曲线:(a) 层压温度110℃;(b) 层压温度140℃;(c) 层压温度170℃;(d) 本测试中平均T型剥离力与标准偏差Figure 8. Relationship curves between T-peel force and displacement for mature dry fiber tow samples with compression time of 60 s: (a) Compression temperature 110℃; (b) Compression temperature 140℃; (c) Compression temperature 170℃; (d) Average T-peel force and standard deviation2.1.2 研发干纤维
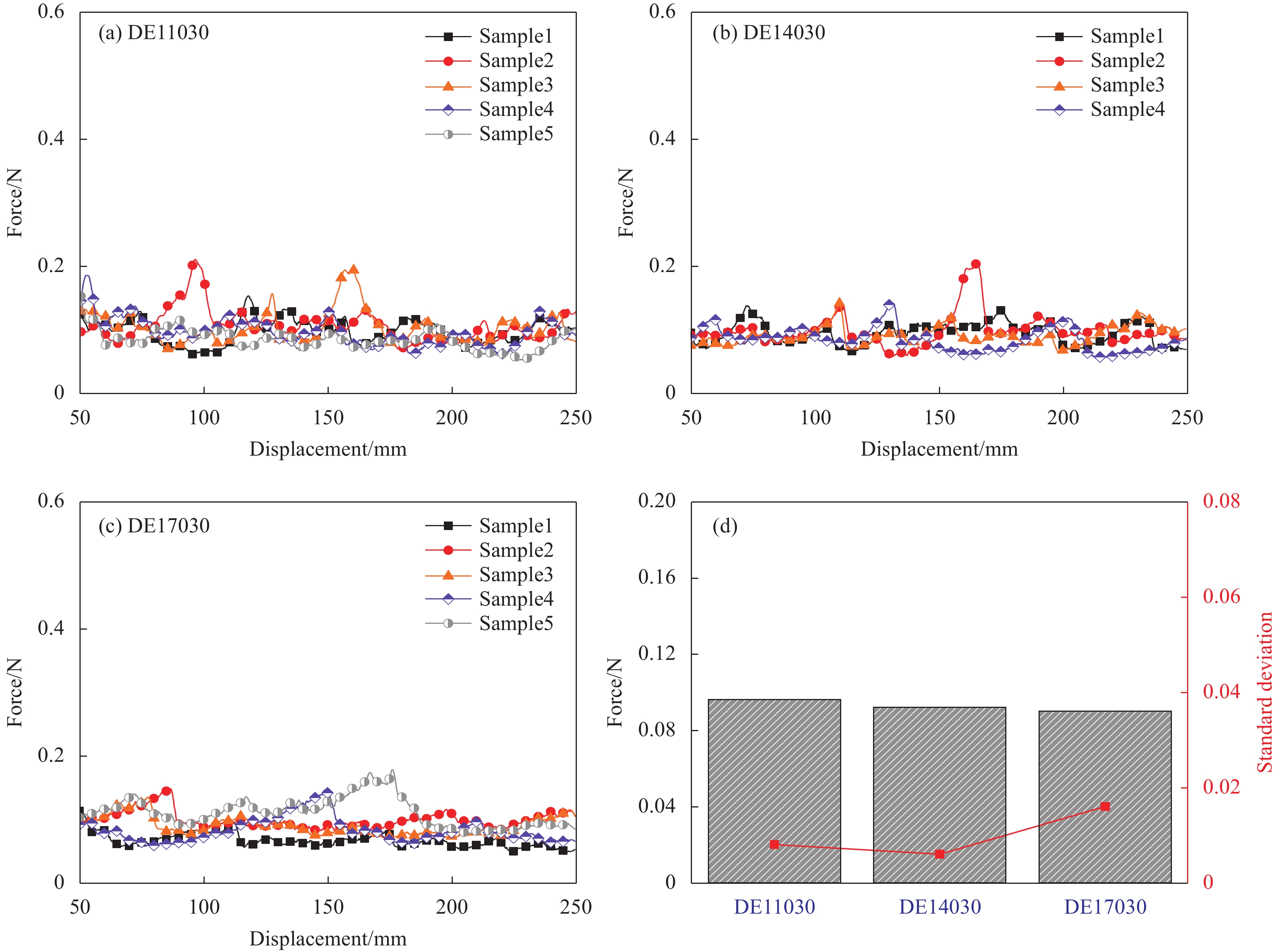
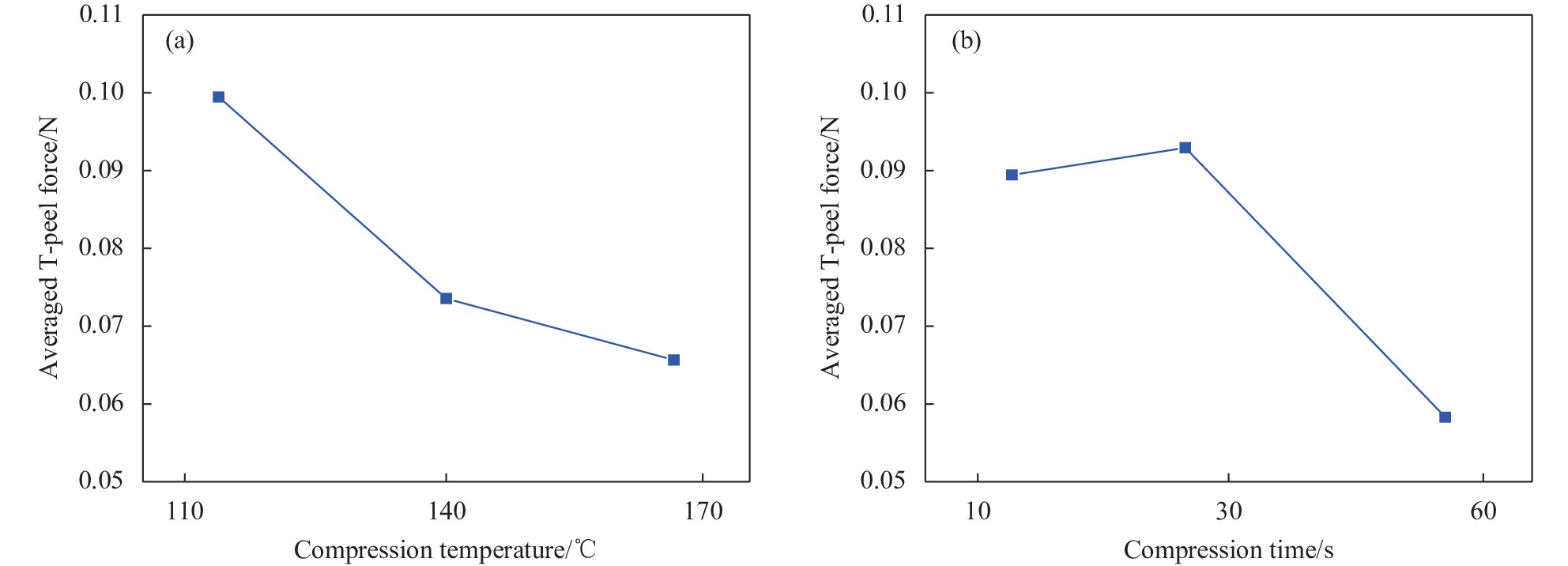
同样,研发干纤维的样条分别在110℃、140℃及170℃的温度下压制,压力作用时间分别为10 s、30 s和60 s。当压力作用时间为10 s时,研发干纤维样条的T型剥离力-位移曲线如图9所示。可知,所有样条均在夹头位移到达250 mm后才开始分离。样条剥离过程中,压制温度110℃的样条的剥离力峰较陡峭,最大剥离力较高约为0.35 N;而热制温度为140℃和170℃的样条的剥离力峰较平缓,最大剥离力也更低。样条的平均剥离力和波动程度如图9(d)所示,压力作用时间10 s时,从110℃至170℃,样条平均剥离力呈现先下降然后略回升的趋势,在110℃时样条平均剥离力最大,平均剥离力波动程度也呈相同趋势。
![]() 图 9 压力作用时间10 s时研发干纤维层合样条的T型剥离力-位移曲线:(a) 层压温度110℃;(b) 层压温度140℃;(c) 层压温度170℃;(d) 本测试中平均T型剥离力与标准偏差Figure 9. Relationship curves between T-peel force and displacement for developing dry fiber tow samples with compression time of 10 s: (a) Compression temperature 110℃; (b) Compression temperature 140℃; (c) Compression temperature 170℃; (d) Average T-peel force and standard deviation
图 9 压力作用时间10 s时研发干纤维层合样条的T型剥离力-位移曲线:(a) 层压温度110℃;(b) 层压温度140℃;(c) 层压温度170℃;(d) 本测试中平均T型剥离力与标准偏差Figure 9. Relationship curves between T-peel force and displacement for developing dry fiber tow samples with compression time of 10 s: (a) Compression temperature 110℃; (b) Compression temperature 140℃; (c) Compression temperature 170℃; (d) Average T-peel force and standard deviation当压力作用时间为30 s时,研发干纤维样条的T型剥离力-位移曲线如图10所示。所有样条均在夹头位移到达250 mm后才开始分离。从110℃至170℃,样条的剥离力峰逐渐变得更加平缓,但最大剥离力一直维持在0.2 N左右。样条的平均剥离力和波动程度如图10(d)所示,从110℃至170℃,样条平均剥离力保持不变,平均剥离力的波动程度在热压140℃时具有最小值。
![]() 图 10 压力作用时间30 s时研发干纤维层合样条的T型剥离力-位移曲线:(a) 层压温度110℃;(b) 层压温度140℃;(c) 层压温度170℃;(d) 本测试中平均T型剥离力与标准偏差Figure 10. Relationship curves between T-peel force and displacement for developing dry fiber tow samples with compression time of 30 s: (a) Compression temperature 110℃; (b) Compression temperature 140℃; (c) Compression temperature 170℃; (d) Average T-peel force and standard deviation
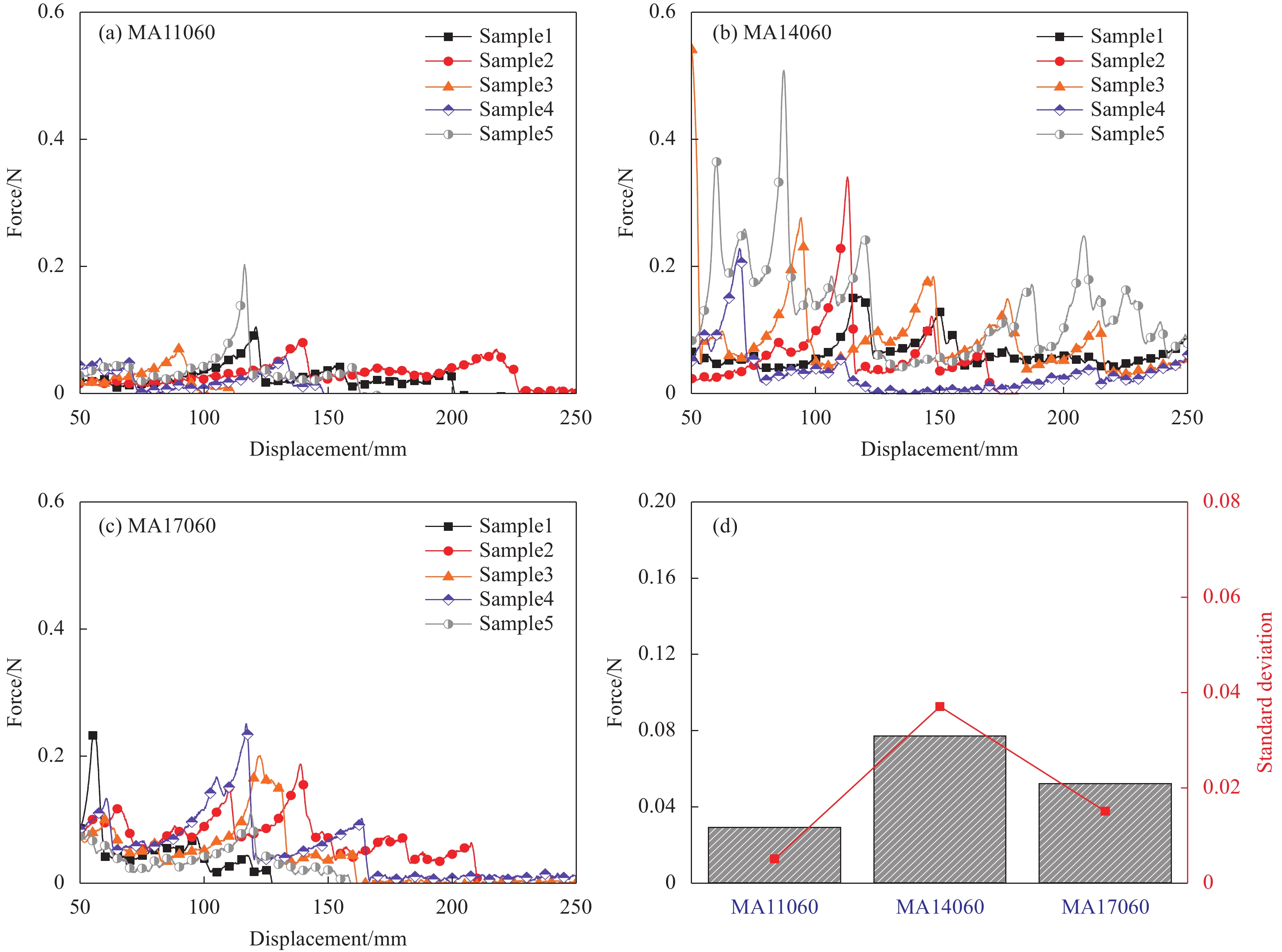
图 10 压力作用时间30 s时研发干纤维层合样条的T型剥离力-位移曲线:(a) 层压温度110℃;(b) 层压温度140℃;(c) 层压温度170℃;(d) 本测试中平均T型剥离力与标准偏差Figure 10. Relationship curves between T-peel force and displacement for developing dry fiber tow samples with compression time of 30 s: (a) Compression temperature 110℃; (b) Compression temperature 140℃; (c) Compression temperature 170℃; (d) Average T-peel force and standard deviation当压力作用时间为60 s时,研发干纤维样条的T型剥离力-位移曲线如图11所示。所有样条均在夹头位移到达250 mm后才开始分离。从110℃至170℃,样条的剥离力峰逐渐变得更加平缓,但最大剥离力在压制温度为170℃的样条处急剧下降。样条的平均剥离力和波动程度如图11(d)所示,压力作用时间为60 s时,从110℃至170℃,样条平均剥离力逐渐下降,压制温度170℃的样条平均剥离力仅为压制温度110℃样条平均剥离力的一半,然而平均剥离力的波动程度却随温度增大有所上升。
![]() 图 11 压力作用时间60 s时研发干纤维层合样条的T型剥离力-位移曲线:(a) 层压温度110℃;(b) 层压温度140℃;(c) 层压温度170℃;(d) 本测试中平均T型剥离力与标准偏差Figure 11. Relationship curves between T-peel force and displacement for developing dry fiber tow samples with compression time of 60 s: (a) Compression temperature 110℃; (b) Compression temperature 140℃; (c) Compression temperature 170℃; (d) Average T-peel force and standard deviation
图 11 压力作用时间60 s时研发干纤维层合样条的T型剥离力-位移曲线:(a) 层压温度110℃;(b) 层压温度140℃;(c) 层压温度170℃;(d) 本测试中平均T型剥离力与标准偏差Figure 11. Relationship curves between T-peel force and displacement for developing dry fiber tow samples with compression time of 60 s: (a) Compression temperature 110℃; (b) Compression temperature 140℃; (c) Compression temperature 170℃; (d) Average T-peel force and standard deviation总的来说,成熟干纤维样条的平均层间剥离力大于研发干纤维样条。但是两种材料的平均剥离力随层压温度和层压时间的变化却不同。因此下面对两种材料进行主效应及交互效应等影响参数的显著性分析,对研究两种材料的层间粘结机制具有重要意义。
2.1.3 实验结果分析
采用统计学方法对以上实验结果进行方差分析,设定显著性水平为0.05,判断热压温度、压力作用时间及二者的协同因素对两种干纤维的层间粘结性是否有显著性影响。
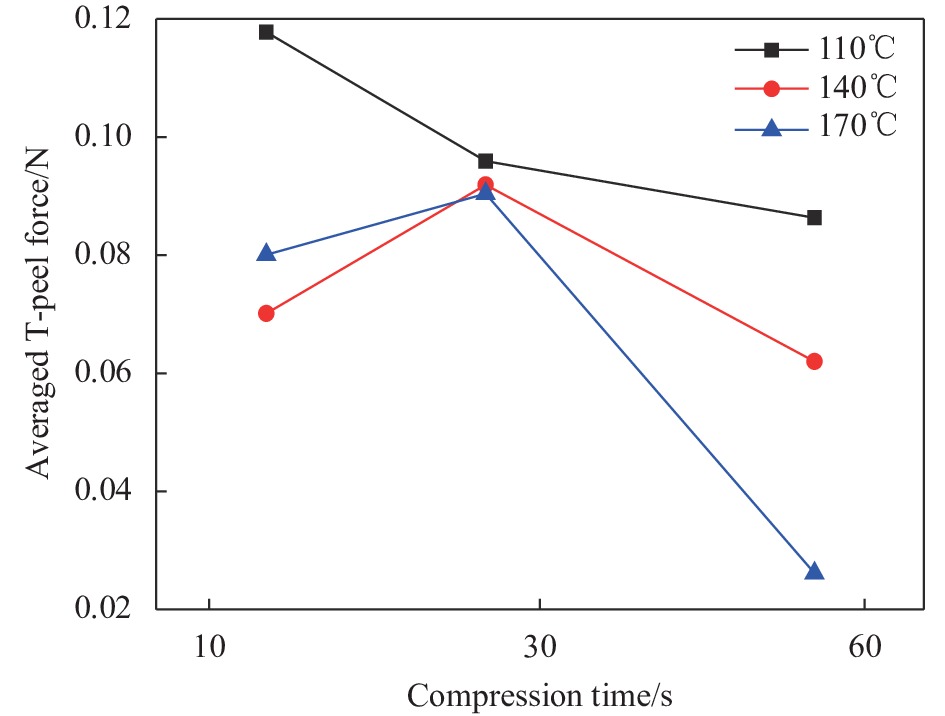
成熟干纤维平均剥离力的方差分析如表3所示。可知,热压温度、压力作用时间及二者的协同因素的P值均小于0.05,表示以上三项均对成熟干纤维的层间粘结性有显著影响。而根据以上三项对应F值的大小,说明最显著影响成熟干纤维层间粘结性能的因子为压力作用时间,其次是热压温度,最后为二者的协同作用。成熟干纤维平均剥离力的主效应图见图12,发现因子热压温度、压力作用时间的回归线较陡,甚至出现弯折,说明对平均剥离力的主效应影响确实显著。成熟干纤维平均剥离力的交互作用见图13,结果显示,压力作用时间在10~30 s区间,热压温度在110~140℃区间时,两条效应线平行,说明此时压力作用时间和热压温度之间的交互作用不显著。其他效应线皆不平行,证明其他阶段内压力作用时间和热压温度之间具有显著的交互作用。
表 3 成熟干纤维测试结果方差分析Table 3. Analysis of variance of test results of developing dry fiberSources Degree of freedom Adjusted sum of squares of deviation from mean Adjusted mean value F-value of
hypothesis-testingP-value of
hypothesis-testingTemperature 2 0.022 0.011 40.78 0.000 Time 2 0.030 0.015 56.32 0.000 Temperature×time 4 0.018 0.004 16.33 0.000 研发干纤维平均剥离力的方差分析如表4所示。可知热压温度、压力作用时间及二者的协同因素的P值均小于0.05,同样表示以上三项均对研发干纤维的层间粘结性有显著影响。通过比较对应F值的大小,发现与成熟干纤维不同,最显著影响研发干纤维层间粘结性能的因子为热压温度,其次是压力作用时间,最后为二者的协同作用。研发干纤维平均剥离力的主效应如图14所示,发现在压力作用时间为10~30 s时,回归线较平,此时主效应影响不显著。而热压温度在140~170℃时,对主效应影响也相对不显著。研发干纤维平均剥离力的交互作用如图15所示,结果显示尽管压力作用时间和热压温度之间具有显著的交互作用,但研发干纤维各因子效应线的走势与成熟干纤维几乎完全不同。
表 4 国产干纤维测试结果方差分析Table 4. Analysis of variance of test results of developing dry fiberSources Degree of freedom Adj SS Adj MS F-value P-value Temperature 2 0.0107 0.005 43.55 0.000 Time 2 0.010 0.005 38.73 0.000 Temperature×time 4 0.006 0.001 12.16 0.000 2.2 层间粘结机制的分析
通过以上对热压参数及协同效应对干纤维层间粘结性能的影响分析,发现成熟干纤维和研发干纤维具有较大区别,因此对两种材料层间结合机制进行分析非常必要。根据材料的产品说明,研发干纤维材料的定型剂主要成分为线性环氧聚合物,而成熟干纤维材料的定型剂为含有环氧基团的多成分混合物。根据两种干纤维所用碳纤维的产品说明,对应的上浆剂也含有环氧基团。上浆剂和定型剂均含有极性集团,因此碳纤维和定型剂之间存在相互作用。
2.2.1 成熟干纤维
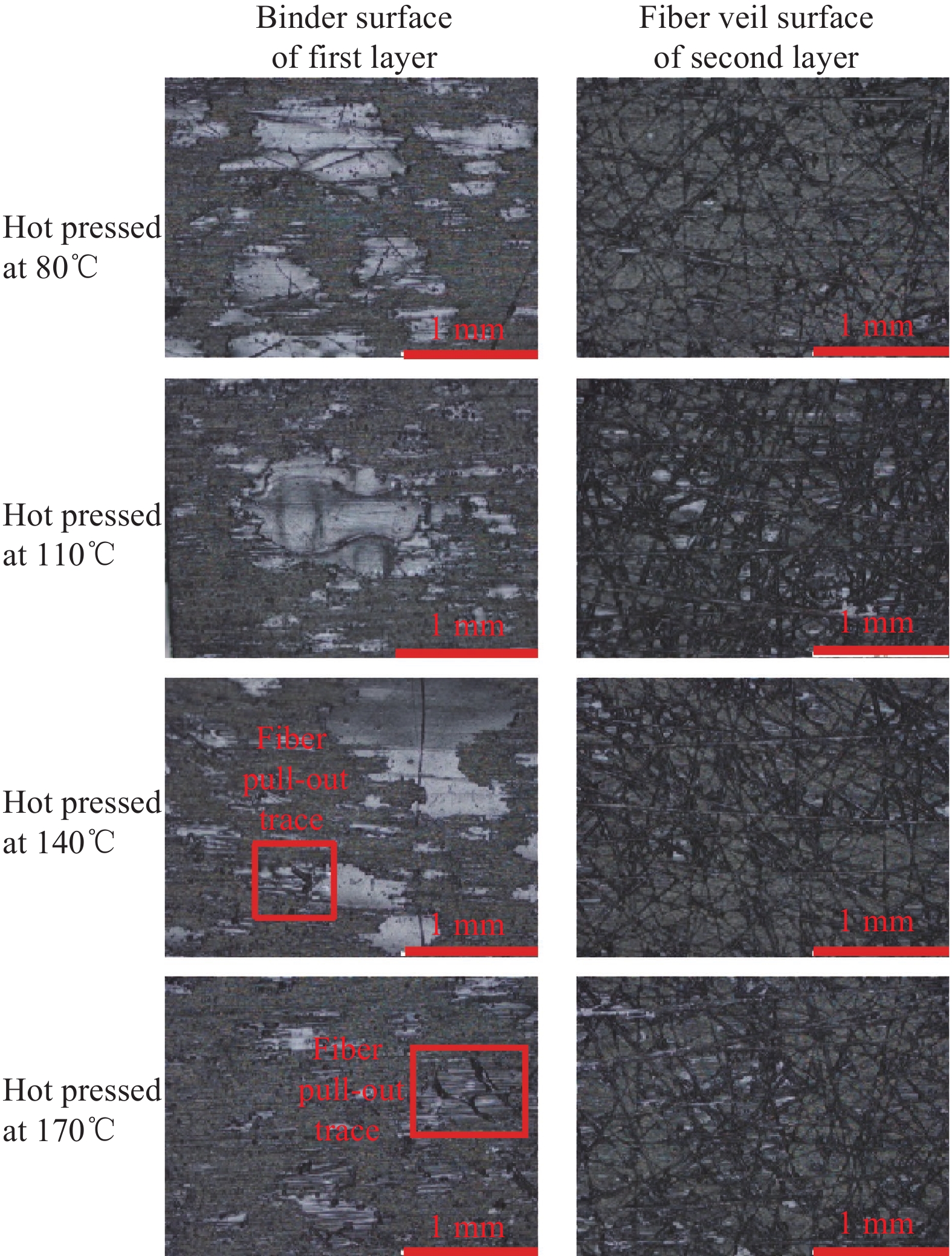
对成熟干纤维以不同温度热压后剥离的表面进行金相观测,分析不同温度下成熟干纤维层间的定型剂分布(见图16)。当热压温度≥110℃时,第一层定型剂面上的定型剂部分附着在第二层的网纱面上,说明定型剂开始发生了软化。热压温度≥140℃时,定型剂边缘存在明显收缩,且网纱纤维在剥离后留下抽拔痕迹,证明网纱纤维和定型剂具有很好的界面性能。热压温度到达170℃时,经剥离后第一层定型剂面上残存的定型剂明显变少,说明在140~170℃之间,定型剂受压后进行扩展,且扩展程度较其他温度区间都高,推断此时定型剂经历了一个黏度迅速下降的阶段。
取未热压的成熟干纤维,用热台显微镜观察干纤维两个表面上定型剂随温度的变化。温度上升速率10℃/min,到达指定温度后停留5 min(图17)。发现从80℃至170℃,网纱面上的定型剂随温度升高未发生明显变化,而定型剂面上的定型剂仅在边缘处略微变得平滑,无明显的扩展或收缩。说明尽管定型剂黏度随温度升高有所下降,但若不经过外界压力,定型剂仍然维持原有形状,并不向周边扩展。
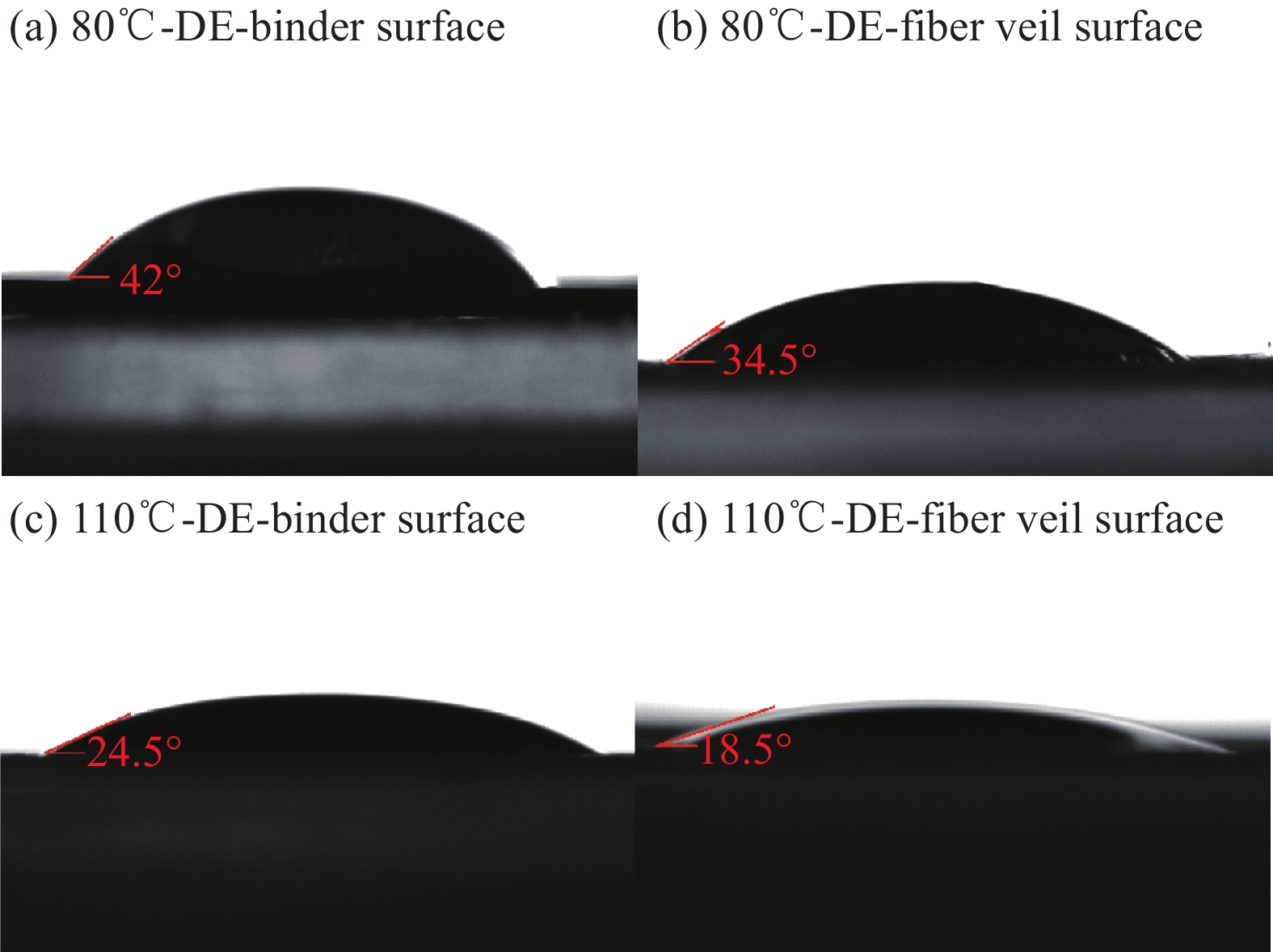
由于成熟干纤维具体的定型剂成分无法获得,也难以分离出来,因此采用一种常用的环氧基树脂代替原成熟干纤维上的定型剂进行网纱面和定型剂面接触角的测试。实验在80℃和110℃两种温度下进行(140℃和170℃时环氧树脂黏度过小导致渗入干纤维内部不能进行接触角测试),实验结果如图18所示,两个表面与环氧树脂的接触角均小于90°,证明干纤维带表面具有亲环氧树脂的特性;随着温度增大,干纤维带两个表面与树脂的接触角均逐渐减小,且网纱面接触角小于定型剂面接触角,证明随着温度增大,干纤维表面上的环氧基定型剂在此阶段产生扩展,且在网纱面上扩展更加容易。
![]() 图 18 环氧树脂与成熟干纤维带在不同温度下的接触角:(a) 成熟干纤维定型剂面在80℃时与环氧树脂的接触角;(b) 成熟干纤维网纱面在80℃时与环氧树脂的接触角;(c) 成熟干纤维定型剂在110℃时与环氧树脂的接触角;(d) 成熟干纤维网纱面在110℃时与环氧树脂的接触角Figure 18. Contact angle between epoxy resin and mature dry fiber tow at varied temperature: (a) Contact angle between epoxy resin and binder surface of mature dry fiber tow at 80℃; (b) Contact angle between epoxy resin and fiber veil surface of mature dry fiber tow at 80℃; (c) Contact angle between epoxy resin and binder surface of mature dry fiber tow at 110℃; (d) Contact angle between epoxy resin and fiber veil surface of mature dry fiber tow at 110℃
图 18 环氧树脂与成熟干纤维带在不同温度下的接触角:(a) 成熟干纤维定型剂面在80℃时与环氧树脂的接触角;(b) 成熟干纤维网纱面在80℃时与环氧树脂的接触角;(c) 成熟干纤维定型剂在110℃时与环氧树脂的接触角;(d) 成熟干纤维网纱面在110℃时与环氧树脂的接触角Figure 18. Contact angle between epoxy resin and mature dry fiber tow at varied temperature: (a) Contact angle between epoxy resin and binder surface of mature dry fiber tow at 80℃; (b) Contact angle between epoxy resin and fiber veil surface of mature dry fiber tow at 80℃; (c) Contact angle between epoxy resin and binder surface of mature dry fiber tow at 110℃; (d) Contact angle between epoxy resin and fiber veil surface of mature dry fiber tow at 110℃取未热压的成熟干纤维连续测试两次,其热流与温度曲线分别如图19所示。在第一次的热流曲线中,发现存在一个明显的放热峰,放热开始温度为73℃,放热结束温度不明显。而第二次热流曲线中没有放热峰出现。对比两次测试结果,推断成熟干纤维上的定型剂可能存在活化基团,加热后发生不可逆转的固化交联反应。
根据以上测试结果,总结成熟干纤维带中层间粘结的形成因素。首先,成熟干纤维的定型剂在110~170℃的温度区间内保有一定黏度,几乎不渗入增强纤维内部,保证定型剂存在于层间。其次,温度上升后,定型剂发生了软化,与网纱面接触的部分会产生更大程度的扩展,提高了层间粘结面积。最后,推测定型剂具有活化基团,成熟干纤维在温度≥110℃经过热压时,定型剂在层间发生固化交联反应,使层间粘结力进一步提升,这也解释了2.1.1节中的测试结果,成为干纤维层间剥离力随着温度的升高大幅度增长的原因。2.1.3节中显著性分析表明,压力作用时间在10~30 s内、热压温度在110~140℃内,压力作用时间和热压温度之间的交互作用不显著,这可能由于温度在110~140℃之间时,定型剂黏度变化较小,因此压力作用时间的提升对剥离力的提升影响更大。
2.2.2 研发干纤维
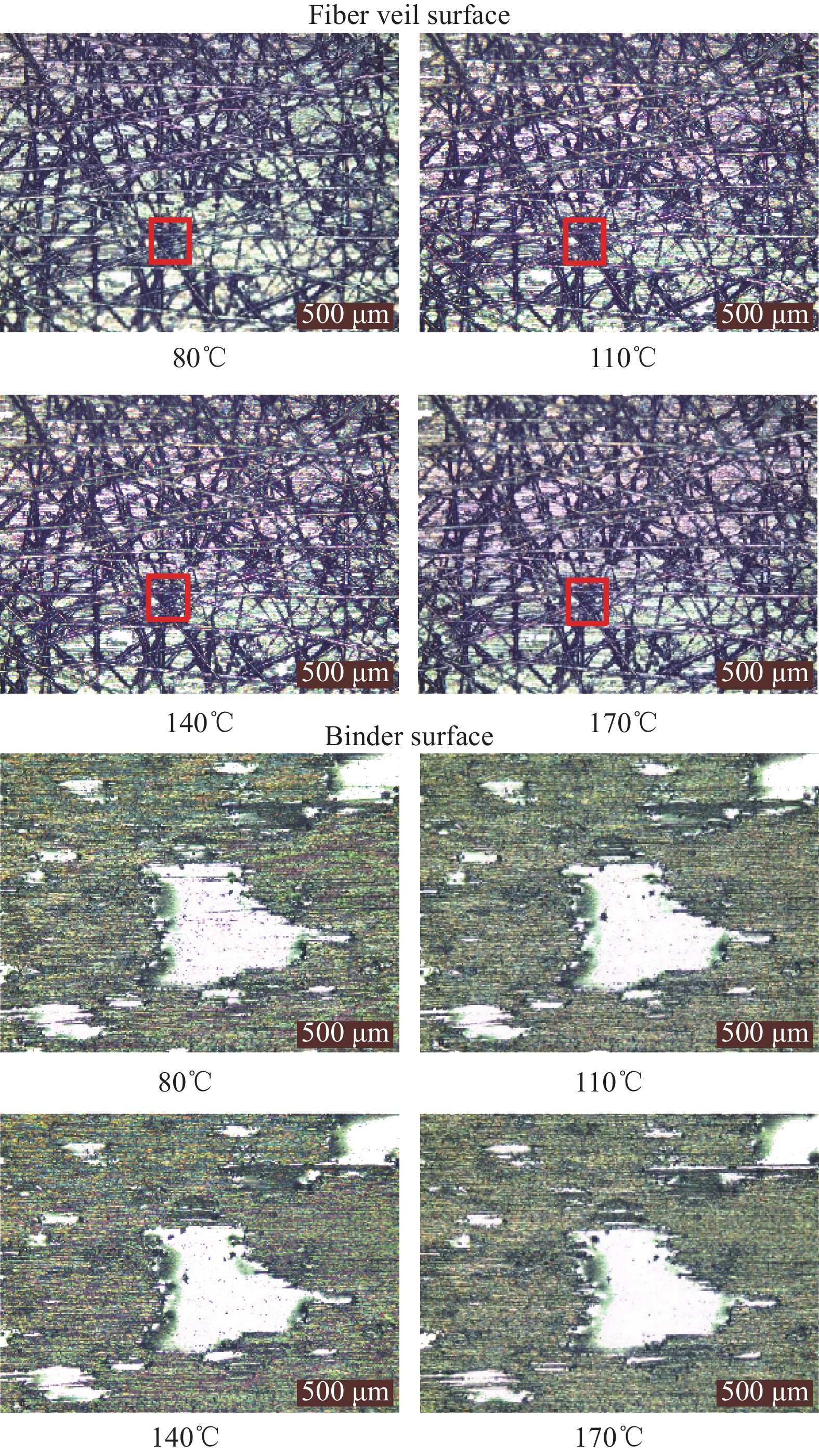
对研发干纤维的剥离表面进行金相观测,分析不同热压温度下干纤维剥离后的定型剂分布(图20)。可以看到,当热压温度为110℃时,定型剂受压后出现明显的扩展,但是随着温度的升高,定型剂边缘逐渐收缩,分布密度也逐渐变小,直至170℃,第一层定型剂面和第二层网纱面上的定型剂几乎消失。
取未热压的研发干纤维,置于热台加热,用显微镜观察干纤维两个表面上定型剂随温度的变化(图21),热台加热速率10℃/min, 每个温度区间停留5 min。从80℃至170℃,网纱面上的定型剂随温度升高逐渐消失,定型剂面上的定型剂面积也随温度升高逐渐缩小。
观察干纤维内部的纤维排列状态(图22)。对于未层压的研发干纤维,探测到其内部结构松散、层间孔隙较多,甚至贯穿整个长度方向,单向带形态弯曲。而经过170℃热压后,干纤维内部结构变得紧密,内部孔隙裂缝变小,形态更加平直。这种现象证明定型剂熔融后逐渐渗入增强纤维内部,减少了内部空隙,提高了干纤维的整体性。
采用接触角测试的方法对研发干纤维的界面性能进行表征。测试方法与参数和成熟干纤维的接触角测试相同,实验结果如图23所示,研发干纤维两个表面与环氧树脂的接触角均小于90°,证明干纤维带表面具有亲环氧树脂的特性;随着温度增大,干纤维带两个表面与树脂的接触角均逐渐减小,证明随着温度增大,干纤维表面上的环氧基定型剂在此阶段扩展;然而,与成熟干纤维不同,研发干纤维定型剂面的接触角仅略大于网纱面的接触角,证明研发干纤维的网纱起的导流作用较小,所以相对于在表面扩展,研发干纤维的定型剂更容易渗入纤维内部。此外,在两种温度下,研发干纤维表面的接触角小于成熟干纤维的接触角,说明研发干纤维表面上的网纱和助剂较成熟干纤维具有更强的亲环氧树脂特性,这一特性使研发干纤维的环氧基定型剂更容易渗入干纤维内部。
![]() 图 23 环氧树脂与研发干纤维带在不同温度下的接触角:(a)定型剂面在80℃时与环氧树脂的接触角;(b)网纱面在80℃时与环氧树脂的接触角;(c)定型剂在110℃时与环氧树脂的接触角;(d)网纱面在110℃时与环氧树脂的接触角Figure 23. Contact angle between epoxy resin and developing dry fiber tow at varied temperature: (a) Contact angle between epoxy resin and binder surface at 80℃; (b) Contact angle between epoxy resin and veil surface at 80℃; (c) Contact angle between epoxy resin and binder surface at 110℃; (d) Contact angle between epoxy resin and veil surface at 110℃
图 23 环氧树脂与研发干纤维带在不同温度下的接触角:(a)定型剂面在80℃时与环氧树脂的接触角;(b)网纱面在80℃时与环氧树脂的接触角;(c)定型剂在110℃时与环氧树脂的接触角;(d)网纱面在110℃时与环氧树脂的接触角Figure 23. Contact angle between epoxy resin and developing dry fiber tow at varied temperature: (a) Contact angle between epoxy resin and binder surface at 80℃; (b) Contact angle between epoxy resin and veil surface at 80℃; (c) Contact angle between epoxy resin and binder surface at 110℃; (d) Contact angle between epoxy resin and veil surface at 110℃干纤维进热流-温度曲线如图24所示。发现热流曲线中没有放热峰出现,推断研发干纤维上的定型剂不存在任何活化基团,无化学反应发生。
根据以上测试结果,总结研发干纤维带中层间粘结的形成因素,由于研发干纤维的定型剂不含活性反应基团,因此其层间粘结只能通过表面定型剂的熔融冷却而形成的内聚力获得,定型剂软化到某种黏度后,热压后可停留在纤维表面且具有良好扩展性,此时层间粘结力达到最大值。之后,温度升高后定型剂黏度大幅度减小浸润到干纤维内部,干纤维表面上的定型剂几乎消失,导致了层间粘结力的下降。这也验证了2.1.2节中研发干纤维最大平均剥离力在110℃,压力作用时间10 s时获得,而温度的升高及压力作用时间的增大,都会导致平均剥离力的降低这一现象。根据2.1.3节中的显著性分析,压力作用时间为10~30 s时,对主效应影响不显著,这说明此时定型剂依然大部分停留在干纤维表面形成层间粘结,随着压力作用时间的增长,定型剂逐渐进入了干纤维内部,层间粘结迅速减小。热压温度在140~170℃时,对主效应影响也相对不显著,说明此时定型剂黏度已经很小且进入了干纤维内部,因此温度改变对剥离力的影响较小。
2.3 与自动铺丝工艺的对比
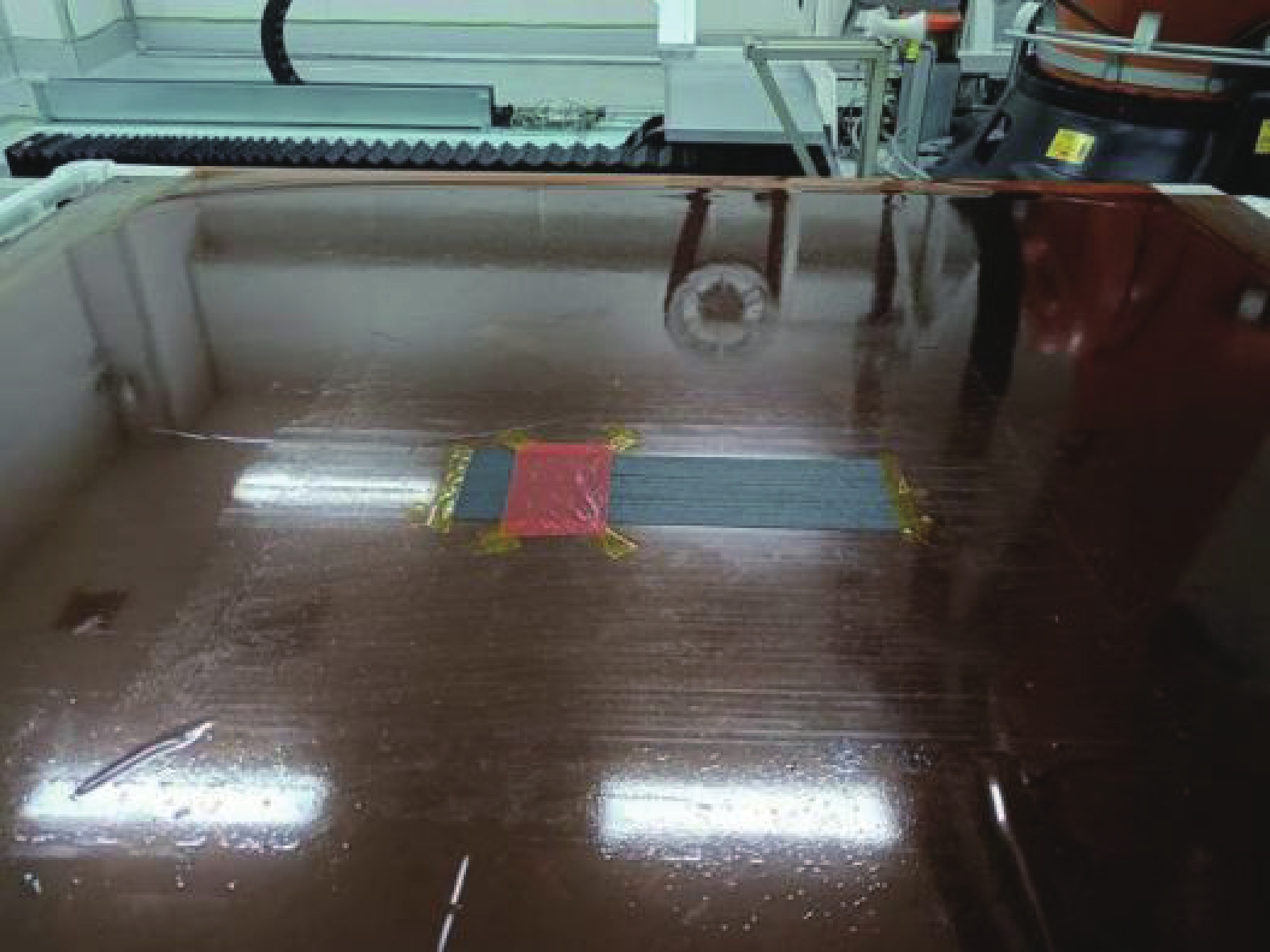
自动铺丝机(M.Torres公司)的铺丝头按照设定轨迹运动,使干纤维经铺丝头经过传送切割等操作,并在柔性压辊的作用下堆叠模具表面。铺丝过程中采用激光加热,并有红外温度显示仪实(M.Torres公司)时显示压辊与干纤维接触位置的温度。实际上,由于自动铺放过程无法准确设定温度,仅能设定激光功率,而激光所达到的温度取决于所需的铺贴速度、所用材料、加热面积等。本实验中设定铺丝头铺放速度为0.06 m/s,通过调试激光功率,使铺放时红外温度显示仪达到目标温度。自动铺丝实验的各项参数见表5。
表 5 自动铺丝(AFP)实验制备的层合样条名称及制备参数Table 5. Name and experiments parameters of test samples made by automated fiber placement (AFP)Sample lables Target temperature/℃ Setting power/W Actual temperature/℃ AFP110 110 260 107±15 AFP140 140 340 143±15 AFP170 170 420 176±15 铺放过程中,设定干纤维层与层间的错层距离为0,并在前段位置处放置隔离膜,避免形成层间粘结(图25)。铺放完毕后,预成型体与工装接触的首层弃之不用,将剩下两层干纤维叠合的预成型体沿长度方向裁开,制备T型剥离样条,并测试层间平均剥离力和波动程度。
由于研发干纤维尚未达铺丝水平,采用成熟干纤维进行铺丝实验。成熟干纤维样条的T型剥离力-位移曲线如图26所示。可知,铺丝温度为110℃左右时,部分样条一直维持着超低剥离力,且大部分样条在夹头未到达250 mm处即产生分离;当铺丝温度到达140℃左右后,样条在夹头位移到达250 mm后才开始分离,此时干纤维剥离力的最大值可达0.4 N左右;而铺丝温度为170℃时,样条具有最高的剥离力峰值,甚至超过了0.6 N,且剥离高峰分布的频率最高。样条的平均剥离力和波动程度如图26(d)所示,从110℃至170℃,样条平均剥离力逐渐增大,同时平均剥离力的波动程度也遵循这一趋势。
![]() 图 26 不同铺丝温度时,成熟干纤维层合样条的T型剥离力-位移曲线:(a) 铺丝温度110℃;(b) 铺丝温度140℃;(c) 铺丝温度170℃;(d) 本测试中平均T型剥离力与标准偏差Figure 26. Relationship curve between T-peel force and displacement for mature dry fiber tow samples when placed by automatic placement machine:(a) Placing temperature 110℃; (b) Placing temperature 140℃; (c) Placing temperature 170℃; (d) Average T-peel force and standard deviation
图 26 不同铺丝温度时,成熟干纤维层合样条的T型剥离力-位移曲线:(a) 铺丝温度110℃;(b) 铺丝温度140℃;(c) 铺丝温度170℃;(d) 本测试中平均T型剥离力与标准偏差Figure 26. Relationship curve between T-peel force and displacement for mature dry fiber tow samples when placed by automatic placement machine:(a) Placing temperature 110℃; (b) Placing temperature 140℃; (c) Placing temperature 170℃; (d) Average T-peel force and standard deviation将自动铺放干纤维样条的平均剥离力和热压干纤维样条的平均剥离力进行对比(图27)。发现当自动铺放干纤维样条铺放温度为110℃左右时,平均剥离力小于所有热压的干纤维样条平均剥离力,这是因为自动铺丝的温度由通过设定激光功率间接调试,偏差较大,而110℃时成熟干纤维的层间粘结性能较弱,介于有无之间,导致对比结果误差较大。事实上,当平均剥离力变大后,如温度介于140~170℃之间时,自动铺放干纤维样条的平均剥离力随温度变化的趋势与压力作用时间为30 s和10 s的热压干纤维样条的趋势类似。因此,可设定一个介于10~30 s的热压时间,能够较好地代替自动铺丝工艺制备层合样条用于评价干纤维层间粘结性。
2.4 涂覆热塑性材料后的研发干纤维层间粘结性
在研发级干纤维表面喷涂热塑性增韧乳剂后,对比其喷涂前和喷涂后的层间粘结性变化,计算涂覆乳剂的研发干纤维的平均层间粘结力,并与未涂覆乳剂的材料进行对比(图28)。其中,DE14030-1和DE17030-1分别为喷涂热塑乳剂后进行140℃和170℃热压并剥离的试验代号。发现涂覆乳剂的研发干纤维层间粘结力均有不同程度的下降。当热压温度140℃时,其平均剥离力下降18%。而热压温度为170℃时,喷涂乳剂的干纤维平均剥离力下降59%。因此在实际工艺中,为了保证增韧干纤维具有良好的层间粘结性能,需通过改性手段令增韧组分也具有良好的粘结性能。
3. 结 论
(1) 成熟干纤维的层间粘结力在一定范围内远大于研发干纤维,二者均显著受到层压温度、压力作用时间及协同作用的影响,但对成熟干纤维的最显著的影响为压力作用时间;而对研发干纤维的最显著的影响为温度。
(2) 成熟干纤维表面的定型剂保有一定黏度,在较大温度范围区间内几乎不渗入增强纤维内部,并且定型剂可能具有活化基团,定型时发生固化交联反应,进一步提高了层间粘结力,因此到达指定温度阶段后,为使交联反应充分发生,压力作用时间对成熟干纤维的层间粘结影响最显著。
(3) 而研发干纤维仅通过定型剂的熔融冷却后的内聚力形成层间粘结,其层间粘结力随着温度的增高而增大,达到最大后不再变化甚至略有下降,这与定型剂黏度降低后渗入纤维内部有关,由于温度与研发干纤维定型剂黏度直接相关,因此温度对研发干纤维的层间粘结影响最显著。
(4) 尽管自动铺丝工艺的温度离散型较大,若合理控制热压工艺的层压时间,热压可在一定程度上代替自动铺丝进行干纤维层间粘结性的评价。
(5) 研发级干纤维涂覆定型剂后继续在表面涂覆雾状热塑性增韧材料,层间粘结力进一步降低,下降范围可达18%~59%,为了保证增韧干纤维具有良好的层间粘结性能,增韧组分需进行改性使其具有足够的粘结性能。
致谢:感谢上海飞机制造有限公司复合材料中心同事孟嘉、章镇、陈晨对干纤维显微断层扫描测试和试样制造提供的帮助和给予的建议。
-
图 6 压力作用时间10 s时成熟干纤维层合样条的T型剥离力-位移曲线:(a) 层压温度110℃;(b) 层压温度140℃;(c) 层压温度170℃;(d) 层间粘结力与标准偏差
Figure 6. Relationship curves between T-peel force and displacement for mature dry fiber tow samples with compression time of 10 s: (a) Compression temperature 110℃; (b) Compression temperature 140℃; (c) Compression temperature 170℃; (d) Average T-peel force and standard deviation
图 7 压力作用时间30 s时成熟干纤维层合样条的T型剥离力-位移曲线:(a) 层压温度110℃;(b) 层压温度140℃;(c) 层压温度170℃;(d) 本测试中平均T型剥离力与标准偏差
Figure 7. Relationship curves between T-peel force and displacement for mature dry fiber tow samples wtth compression time of 30 s: (a) Compression temperature 110℃; (b) Compression temperature 140℃; (c) Compression temperature 170℃; (d) Average T-peel force and standard deviation
图 8 压力作用时间60 s时成熟干纤维层合样条的T型剥离力-位移曲线:(a) 层压温度110℃;(b) 层压温度140℃;(c) 层压温度170℃;(d) 本测试中平均T型剥离力与标准偏差
Figure 8. Relationship curves between T-peel force and displacement for mature dry fiber tow samples with compression time of 60 s: (a) Compression temperature 110℃; (b) Compression temperature 140℃; (c) Compression temperature 170℃; (d) Average T-peel force and standard deviation
图 9 压力作用时间10 s时研发干纤维层合样条的T型剥离力-位移曲线:(a) 层压温度110℃;(b) 层压温度140℃;(c) 层压温度170℃;(d) 本测试中平均T型剥离力与标准偏差
Figure 9. Relationship curves between T-peel force and displacement for developing dry fiber tow samples with compression time of 10 s: (a) Compression temperature 110℃; (b) Compression temperature 140℃; (c) Compression temperature 170℃; (d) Average T-peel force and standard deviation
图 10 压力作用时间30 s时研发干纤维层合样条的T型剥离力-位移曲线:(a) 层压温度110℃;(b) 层压温度140℃;(c) 层压温度170℃;(d) 本测试中平均T型剥离力与标准偏差
Figure 10. Relationship curves between T-peel force and displacement for developing dry fiber tow samples with compression time of 30 s: (a) Compression temperature 110℃; (b) Compression temperature 140℃; (c) Compression temperature 170℃; (d) Average T-peel force and standard deviation
图 11 压力作用时间60 s时研发干纤维层合样条的T型剥离力-位移曲线:(a) 层压温度110℃;(b) 层压温度140℃;(c) 层压温度170℃;(d) 本测试中平均T型剥离力与标准偏差
Figure 11. Relationship curves between T-peel force and displacement for developing dry fiber tow samples with compression time of 60 s: (a) Compression temperature 110℃; (b) Compression temperature 140℃; (c) Compression temperature 170℃; (d) Average T-peel force and standard deviation
图 18 环氧树脂与成熟干纤维带在不同温度下的接触角:(a) 成熟干纤维定型剂面在80℃时与环氧树脂的接触角;(b) 成熟干纤维网纱面在80℃时与环氧树脂的接触角;(c) 成熟干纤维定型剂在110℃时与环氧树脂的接触角;(d) 成熟干纤维网纱面在110℃时与环氧树脂的接触角
Figure 18. Contact angle between epoxy resin and mature dry fiber tow at varied temperature: (a) Contact angle between epoxy resin and binder surface of mature dry fiber tow at 80℃; (b) Contact angle between epoxy resin and fiber veil surface of mature dry fiber tow at 80℃; (c) Contact angle between epoxy resin and binder surface of mature dry fiber tow at 110℃; (d) Contact angle between epoxy resin and fiber veil surface of mature dry fiber tow at 110℃
图 23 环氧树脂与研发干纤维带在不同温度下的接触角:(a)定型剂面在80℃时与环氧树脂的接触角;(b)网纱面在80℃时与环氧树脂的接触角;(c)定型剂在110℃时与环氧树脂的接触角;(d)网纱面在110℃时与环氧树脂的接触角
Figure 23. Contact angle between epoxy resin and developing dry fiber tow at varied temperature: (a) Contact angle between epoxy resin and binder surface at 80℃; (b) Contact angle between epoxy resin and veil surface at 80℃; (c) Contact angle between epoxy resin and binder surface at 110℃; (d) Contact angle between epoxy resin and veil surface at 110℃
图 26 不同铺丝温度时,成熟干纤维层合样条的T型剥离力-位移曲线:(a) 铺丝温度110℃;(b) 铺丝温度140℃;(c) 铺丝温度170℃;(d) 本测试中平均T型剥离力与标准偏差
Figure 26. Relationship curve between T-peel force and displacement for mature dry fiber tow samples when placed by automatic placement machine:(a) Placing temperature 110℃; (b) Placing temperature 140℃; (c) Placing temperature 170℃; (d) Average T-peel force and standard deviation
表 1 实验设计因子及水平信息
Table 1 Experiment design factor and levels information
Factor Level Value Compression temperature/oC 3 110, 140, 170 Compression time/s 3 10, 30, 60 表 2 层合样条名称、材料和制备参数
Table 2 Name, materials and experiments parameters of test samples
Sample
lablesCompression temperature/℃ Compression time/s Sample
materialMA11010 110 10 Mature MA14010 140 10 Mature MA17010 170 10 Mature MA11030 110 30 Mature MA14030 140 30 Mature MA17030 170 30 Mature MA11060 110 60 Mature MA14060 140 60 Mature MA17060 170 60 Mature DE11010 110 10 Developing DE14010 140 10 Developing DE17010 170 10 Developing DE11030 110 30 Developing DE14030 140 30 Developing DE17030 170 30 Developing DE11060 110 60 Developing DE14060 140 60 Developing DE17060 170 60 Developing 表 3 成熟干纤维测试结果方差分析
Table 3 Analysis of variance of test results of developing dry fiber
Sources Degree of freedom Adjusted sum of squares of deviation from mean Adjusted mean value F-value of
hypothesis-testingP-value of
hypothesis-testingTemperature 2 0.022 0.011 40.78 0.000 Time 2 0.030 0.015 56.32 0.000 Temperature×time 4 0.018 0.004 16.33 0.000 表 4 国产干纤维测试结果方差分析
Table 4 Analysis of variance of test results of developing dry fiber
Sources Degree of freedom Adj SS Adj MS F-value P-value Temperature 2 0.0107 0.005 43.55 0.000 Time 2 0.010 0.005 38.73 0.000 Temperature×time 4 0.006 0.001 12.16 0.000 表 5 自动铺丝(AFP)实验制备的层合样条名称及制备参数
Table 5 Name and experiments parameters of test samples made by automated fiber placement (AFP)
Sample lables Target temperature/℃ Setting power/W Actual temperature/℃ AFP110 110 260 107±15 AFP140 140 340 143±15 AFP170 170 420 176±15 -
[1] SUN S, HAN Z, FU H, et al. Defect characteristics and online detection techniques during manufacturing of FRPs using automated fiber placement: A review[J]. Polymers,2020,12(6):1337-1359. DOI: 10.3390/polym12061337
[2] BUDELMANN D, SCHMIDT C, MEINERS D, et al. Prepreg tack: A review of mechanisms, measurement, and manufacturing implication[J]. Polymer Composites,2020,41(9):3440-3458. DOI: 10.1002/pc.25642
[3] 陈吉平, 李岩, 刘卫平, 等. 连续纤维增强热塑性树脂基复合材料自动铺放原位成型技术的航空发展现状[J]. 复合材料学报, 2019, 36(4):784-794. DOI: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20190102.001 CHEN Jiping, LI Yan, LIU Weiping, et al. Development of AFP in-situ consolidation technology on continuous fiber reinforced thermoplastic matrix composites in aviation[J]. Acta Materiae Composite Sinica,2019,36(4):784-794(in Chinese). DOI: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20190102.001
[4] 张洋, 钟翔屿, 包建文. 先进树脂基复合材料自动丝束铺放技术研究现状及发展方向[J]. 航空制造技术, 2013, 23: 131-136, 140(in Chinese). ZHANG Yang, ZHONG Xiangyu, BAO Jianwen. Research status and future trend of automated fiber placement technology for advanced polymer matrix composites[J]. Aeronautical Manufacturing Technology, 2013, 23: 131-136, 140(in Chinese).
[5] KADIYALA A K, PORTELA A, DEVLIN K, et al. Mechanical evaluation and failure analysis of composite laminates manufactured using automated dry fibre tape placement followed by liquid resin infusion[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2021,201:108512. DOI: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2020.108512
[6] GINGER G. Resin infused MS-21 wings and wing box[J]. High Performance Composites,2014,1:29.
[7] JUAN S. OAK aero composites choose innovative solutions to build the MS-21 composire wings[R]. Paris: JEC composite, 2012.
[8] WEI K, LIANG D, MEI M, et al. Preforming behaviors of carbon fiber fabrics with different contents of binder and under various process parameters[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering,2019,166:221-232. DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2018.11.143
[9] LIU Y N, YUAN C, LIU C, et al. Study on the resin infusion process based on automated fiber placement fabricated dry fiber preform[J]. Scientific Reports,2019,9(1):7440. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-43982-1
[10] VELDENZ L, DI M, ASTWOOD S, et al. Characteristics and processability of bindered dry fiber material for automated fiber placement[J]. ECCM17-17 th European Conference on Composite Materials, Munich, Germany,2016.
[11] CROSSLEY R J, SCHUBEL P J, WARRIOR N A. The experimental determination of prepreg tack and dynamic stiffness[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2012,43(3):423-434. DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2011.10.014
[12] DI FRANCESCO M, VELDENZ L, DELLANNO G, et al. Heater power control for multi-material, variable speed automated fibre placement[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2017,101:408-421. DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2017.06.015
[13] CROFT K, LESSARD L, PASINI D, et al. Experimental study of the effect of automated fiber placement induced defects on performance of composite laminates[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2011,42(5):484-491. DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2011.01.007
[14] VELDENZ L, DI FRANCESCO M, GIDDINGS P, et al. Material selection for automated dry fiber placement using the analytical hierarchy process[J]. Advanced Manufacturing: Polymer & Composites Science,2018,4(4):83-96.
[15] BELHAJ M, DELEGLISE M, COMAS-CARDONA S, et al. Dry fiber automated placement of carbon fibrous preforms[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering,2013,50:107-111. DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2013.01.014
[16] ROHATGI V, LEE L J. Moldability of tackified fiber preforms in liquid composite molding[J]. Journal of Composite Materials,1997,31(7):720-744. DOI: 10.1177/002199839703100705
[17] RAO S, UMER R, THOMAS J. Investigation of peel resistance during the fibre placement process[J]. Journal of Reinforced Plastics and Composites,2015,35(4):275-286.
[18] 钟翔屿, 张代军, 包建文, 等. 增韧剂含量对国产高强中模炭纤维环氧复合材料耐冲击性的影响[J]. 固体火箭技术, 2017, 40(3):372-379. ZHONG Xiangyu, ZHANG Daijun, BAO Jianwen, et al. Effect of toughening thermoplastic particles content on impact resistance of epoxy matrix composite reinforced by domestic intermediate modulus carbon fiber[J]. Journal of Solid Rocket Technology,2017,40(3):372-379(in Chinese).
[19] NASH N H, YOUNG T M, MCGRAIL P T, et al. Inclusion of a thermoplastic phase to improve impact and post-impact performances of carbon fibre reinforced thermosetting composites — A review[J]. Materials & Design,2015,85:582-597.
[20] WONG D W Y, LIN L, MCGRAIL P T, et al. Improved fracture toughness of carbon fibre/epoxy composite laminates using dissolvable thermoplastic fibres[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2010,6:759-767.
[21] SAZ-OROZCO B D, RAY D, KERVENNIC A, et al. Toughening of carbon fibre/polybenzoxazine composites by incorporating polyethersulfone into the interlaminar region[J]. Materials & Design,2016,93:297-303.
[22] 闫丽, 安学峰, 董慧民. RTM用ES-Fabric 增强织物的制备及其复合材料性能研究[J]. 化工新型材料, 2016, 44(4):94-96. YAN Li, AN Xuefeng, DONG Huimin, et al. Preparation of ES-fabric reinforced fabric for RTM process and study on the property of the composite[J]. New Chemical Materials,2016,44(4):94-96(in Chinese).
[23] ZHAO X, CHEN W, HAN X, et al. Enhancement of interlaminar fracture toughness in textile-reinforced epoxy composites with polyamide 6/graphene oxide interlaminar toughening tackifier[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2020,191:108094. DOI: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2020.108094
[24] QUAN D, BOLOGNA F, SCARSELLI G, et al. Mode-II fracture behaviour of aerospace-grade carbon fibre/epoxy composites interleaved with thermoplastic veils[J]. Composites Science and Technology,2020,191:108065. DOI: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2020.108065
[25] 国家技术监督局. 胶粘剂T剥离强度试验方法-挠性材料对挠性材料: GB/T 2791—1995[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 1995. The State Bureau of Quality and Technical Supervision. Adhesives, T peel strength test method for a flexible-to-flexible test specimen assembly: GB/T 2791—1995[S]. Beijing: China Standard Press, 1995(in Chinses).
[26] NGUYEN N Q, MEHDIKHANI M, STRAUMIT I, et al. Micro-CT measurement of fibre misalignment: Application to carbon/epoxy laminates manufactured in autoclave and by vacuum assisted resin transfer moulding[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2018,104:14-23. DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2017.10.018
-
期刊类型引用(4)
1. 彭公秋,白钰,钟翔屿,张连旺,包建文,曹正华. 干纤维自动铺放液体成型复合材料技术的研究进展. 复合材料科学与工程. 2024(03): 113-120 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 张润博,于柏峰,遇家运. 人工智能在纤维增强复合材料制造中的应用研究. 高科技纤维与应用. 2024(06): 37-47 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 聂玉强,付晨辰,彭运松. 干纤维自动铺放-液体成型技术进展研究. 材料开发与应用. 2023(04): 19-26 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 陈超,张帅,倪敏轩,郭长龙,刘秀,孙萌萌,王希,范启阳. 自动铺丝技术在民航复合材料的应用及发展. 纤维复合材料. 2022(04): 131-134 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)
-




 下载:
下载: