Influence of inorganic mineral fluorocarbon composite coating on salt freezing resistance of concrete
-
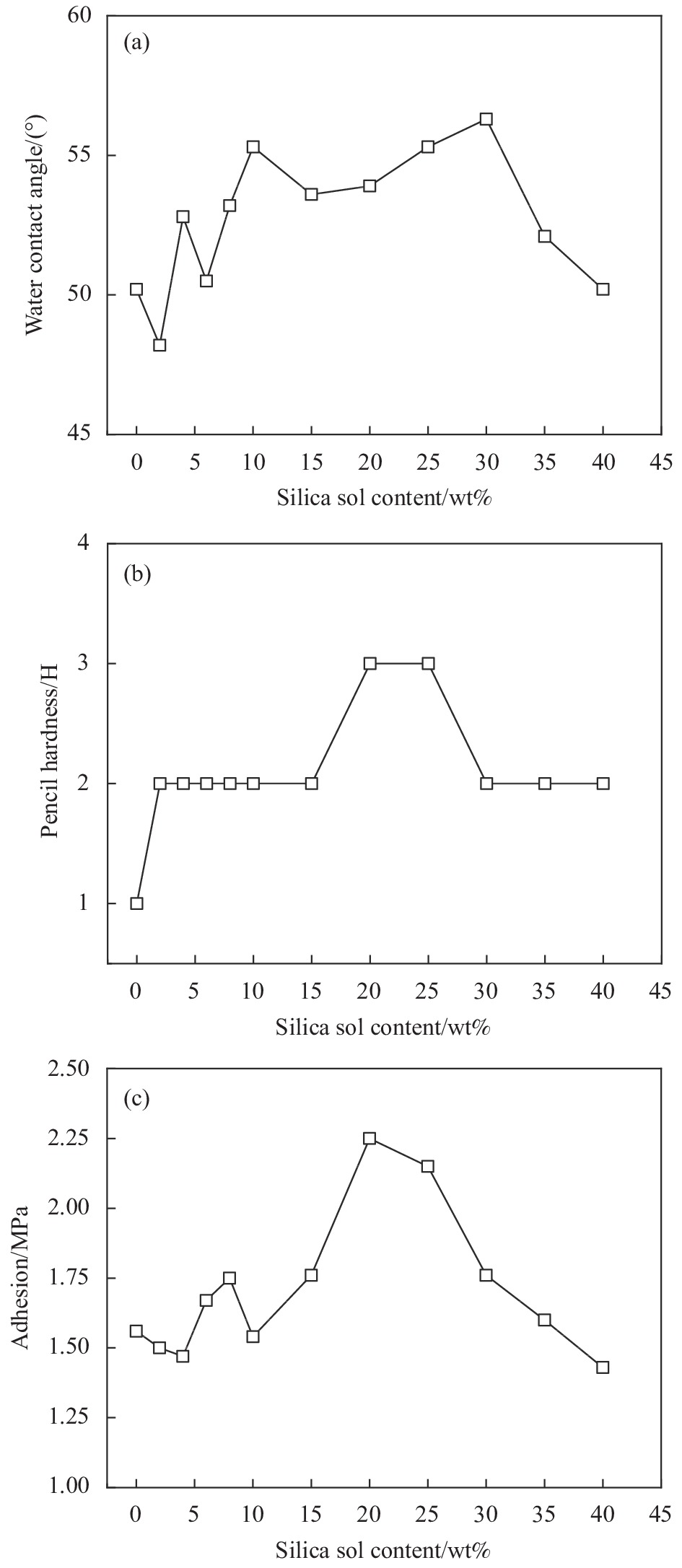
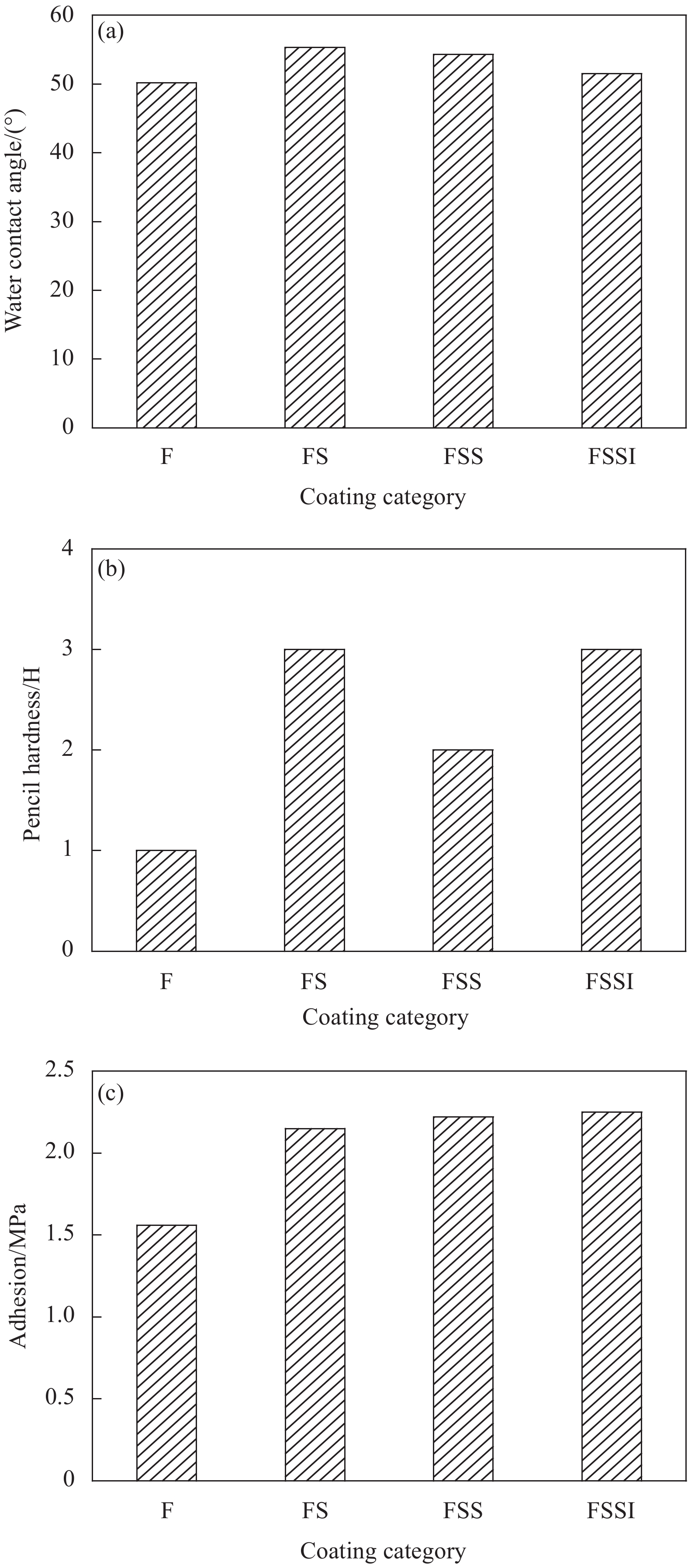
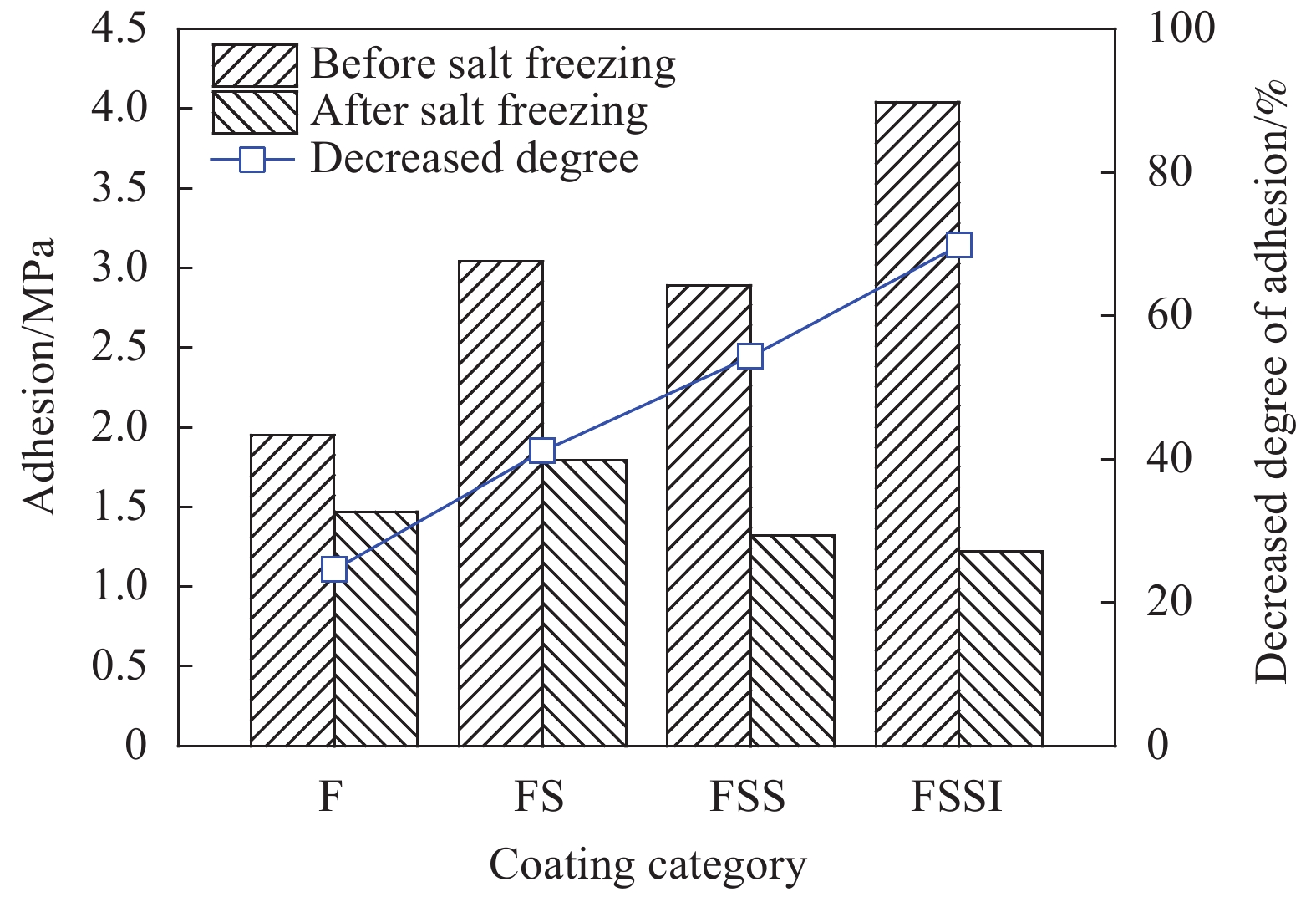
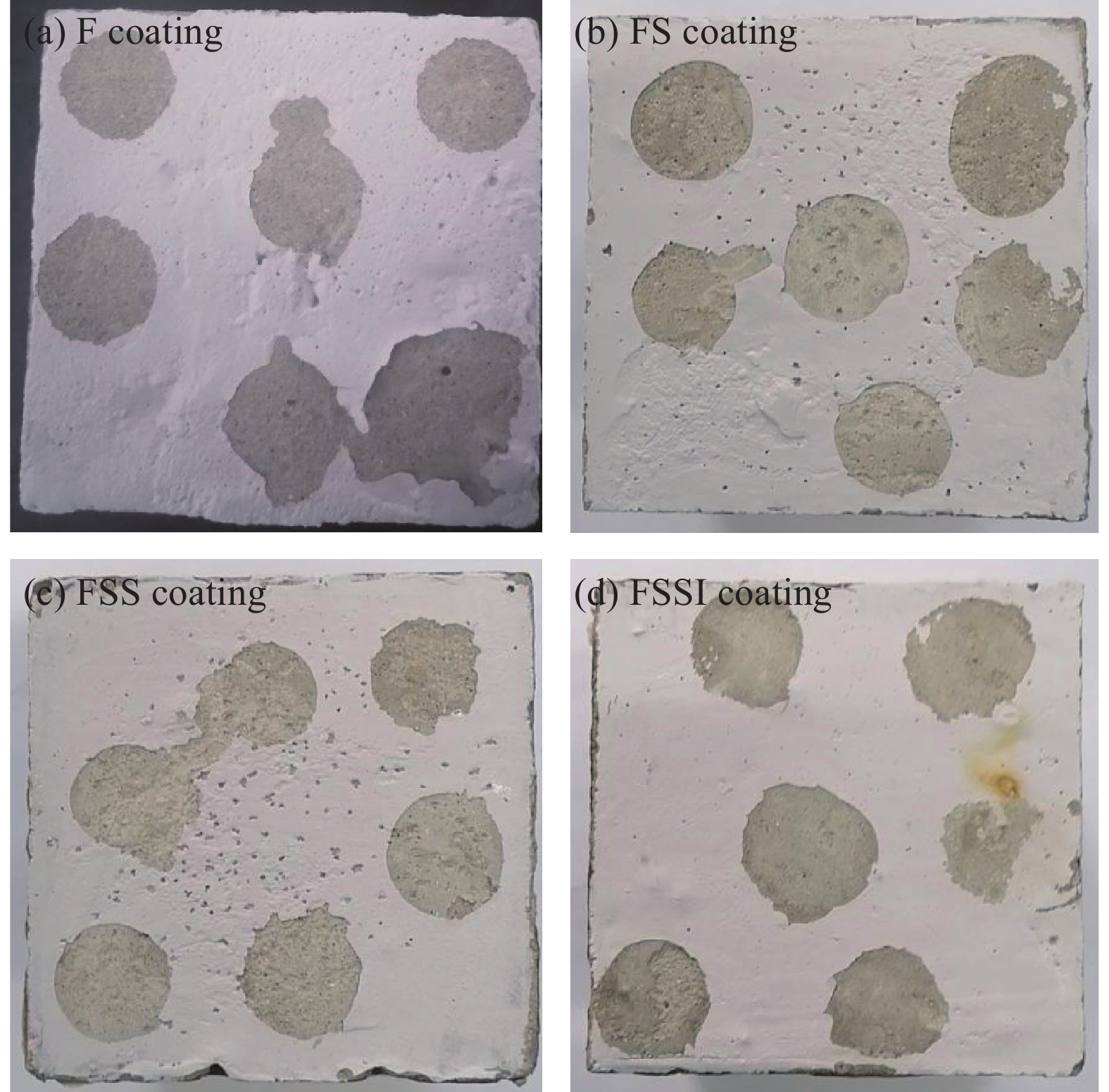
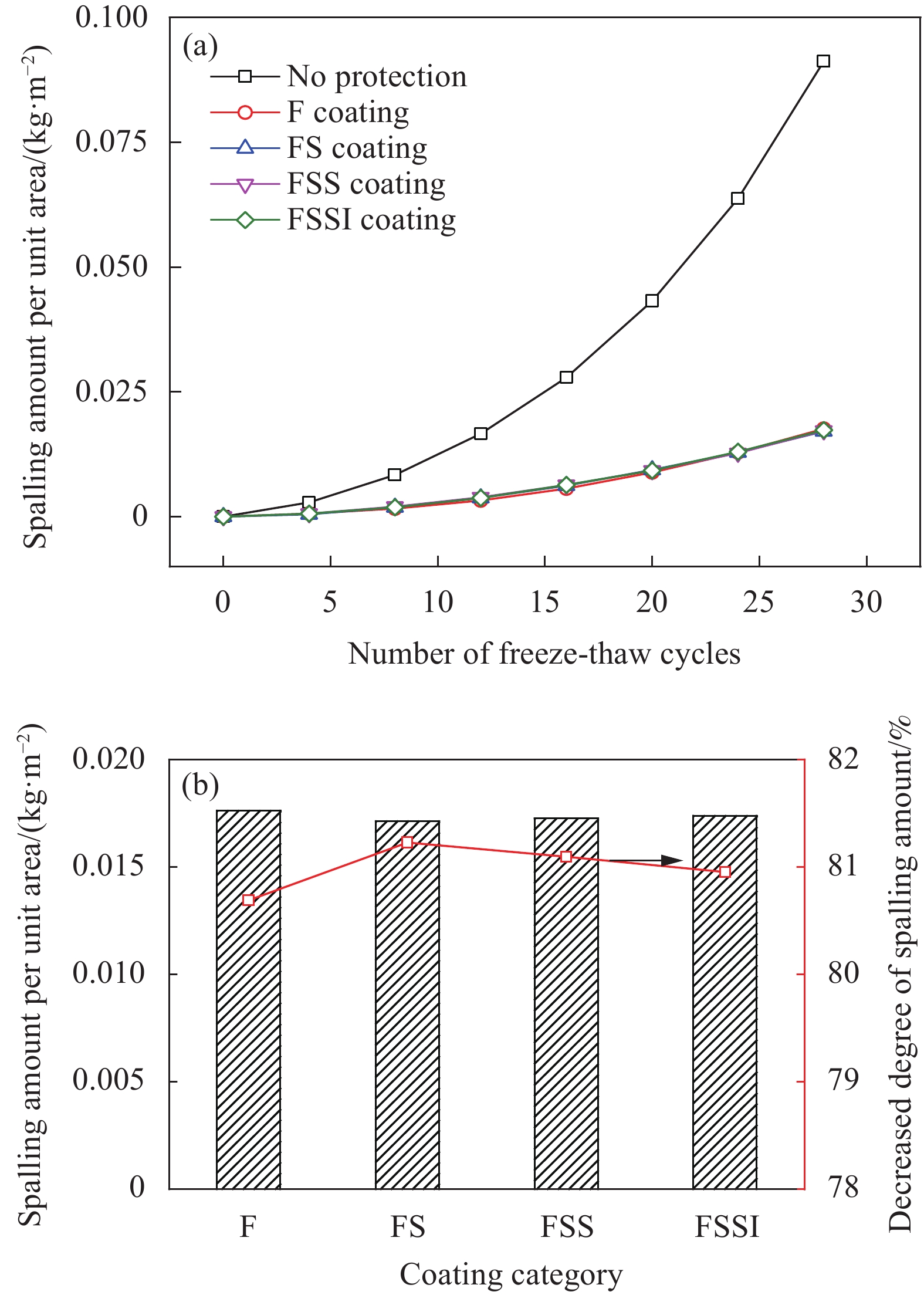
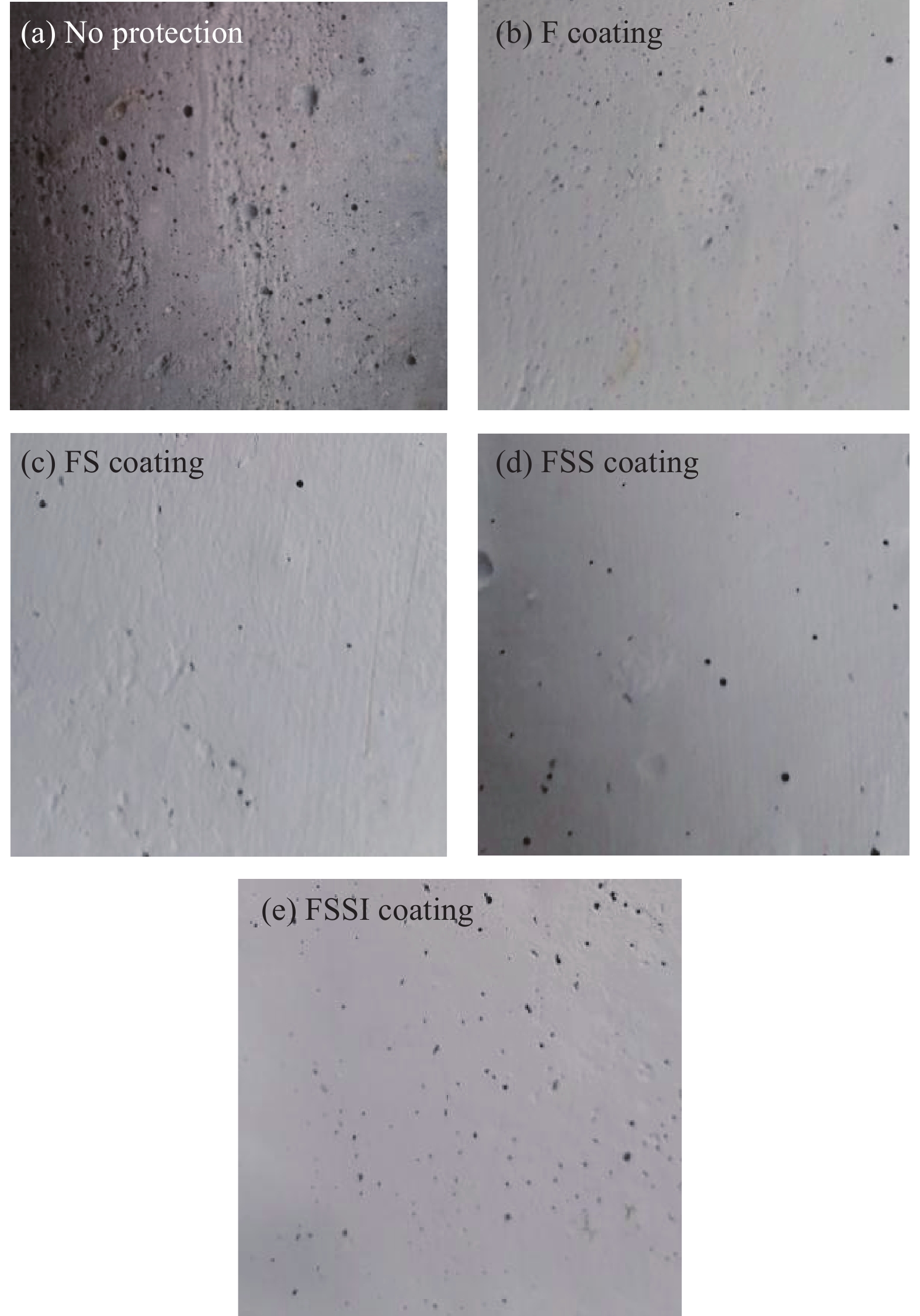
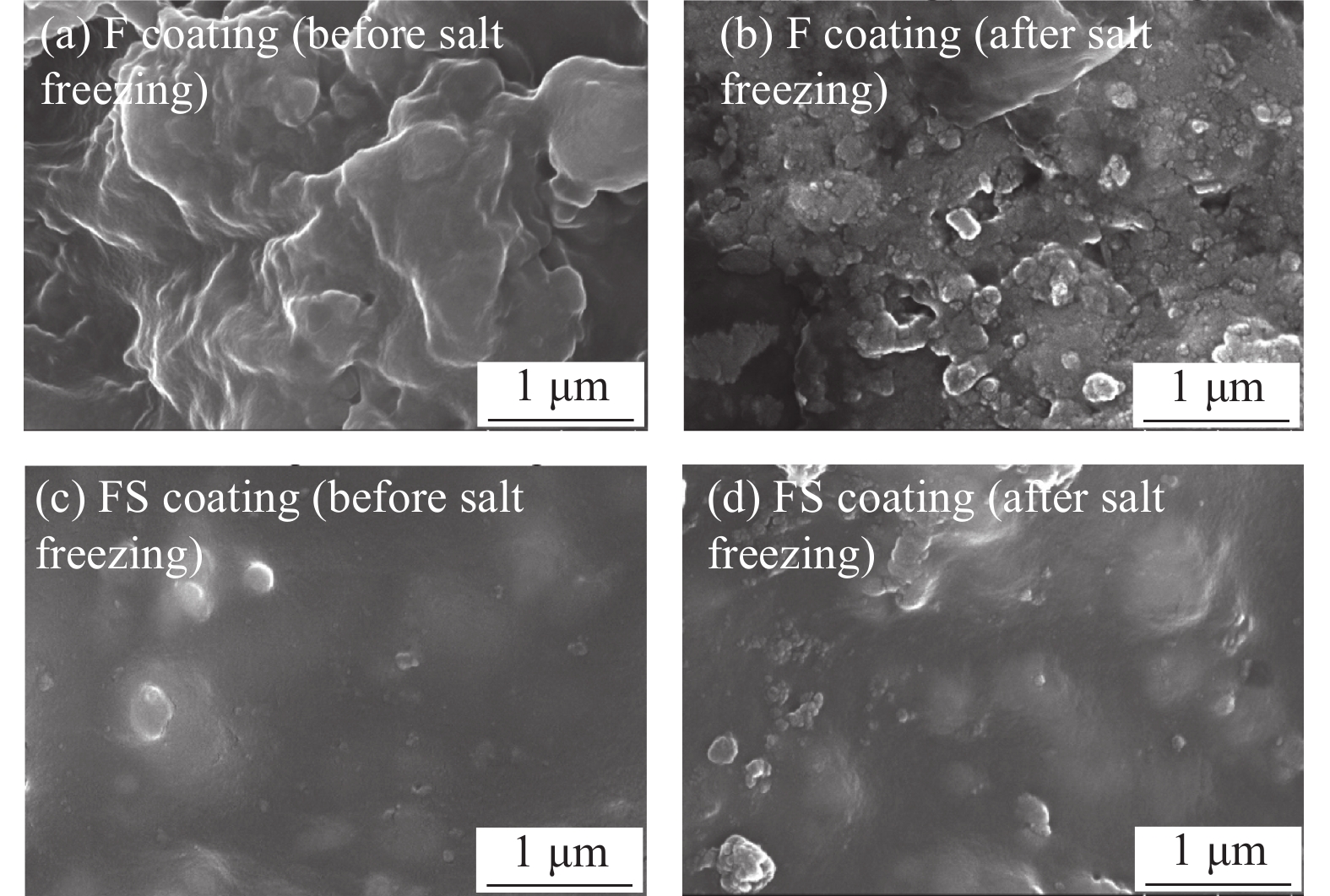
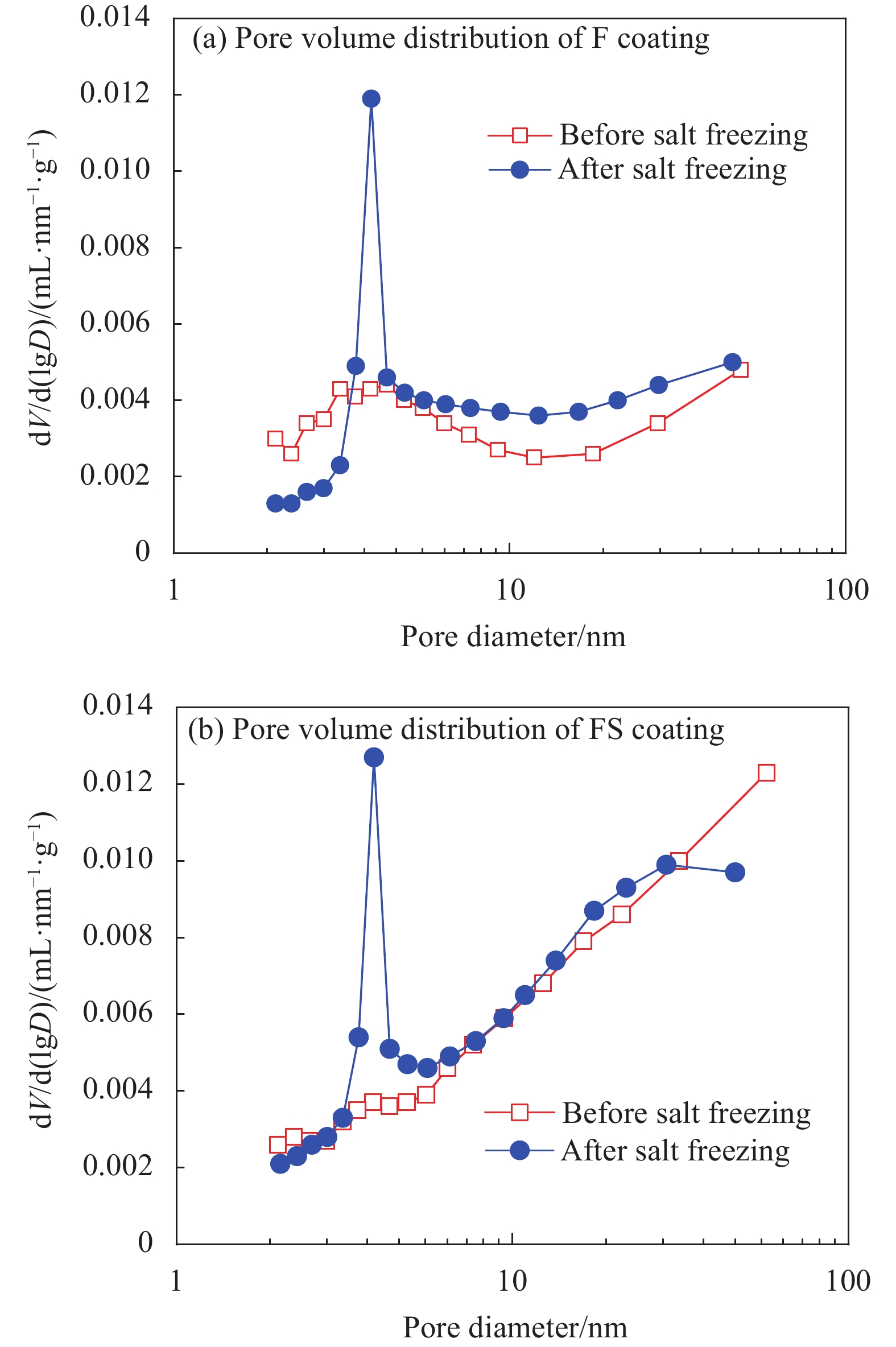
摘要: 通过表面疏水性能试验、力学性能试验、界面粘结性能试验和混凝土盐冻试验,研究了无机矿物对水性氟碳涂料性能的影响,研究了盐冻环境下无机矿物氟碳复合涂料附着力变化,分析了其对混凝土单位面积剥落量的影响,结合微观形貌变化和孔结构变化,分析了混凝土抗盐冻性能提升机制。结果表明:单掺硅溶胶时,氟碳复合涂料水接触角较氟碳涂料增大了10.2%,其铅笔硬度高达3 H;三掺硅溶胶、海泡石粉和铁尾矿粉时,氟碳复合涂料铅笔硬度高达3 H,其附着力增大了44.2%;复掺硅溶胶和海泡石粉时,氟碳复合涂料性能介于两者之间。盐冻环境下单掺硅溶胶氟碳复合涂料残余附着力最大。无机矿物氟碳复合涂料能显著改善混凝土抗剥蚀性能,但改善效果较氟碳涂料不显著。盐冻环境下水性氟碳涂料产生部分微孔,孔结构粗化,而单掺硅溶胶氟碳复合涂料微观结构仍较致密,其最可几孔径略有增大,涂料仅略有损伤。单掺硅溶胶氟碳复合涂料防护下混凝土微观结构更致密,其单位面积剥落量较未防护时降低幅度高达81.2%。为寒冷地区盐冻环境下混凝土防护涂料的设计提供了试验和理论依据。Abstract: The influences of inorganic mineral on the properties of waterborne fluorocarbon coating were studied, and the variation in adhesion of fluorocarbon composite coatings under the salt freezing environment was studied, and the influence of fluorocarbon composite coatings on the amount of spalling per unit area of concrete was analyzed, by surface hydrophobic property test, mechanical property test, interface bonding property test and salt freezing test of concrete. The improvement mechanism of salt freezing resistance of concrete was analyzed, combining the changes of microscopic appearance and pore structure. The results show that the water contact angle of the fluorocarbon composite coating with single doped silica sol increases by 10.2%, compared with fluorocarbon coating, and the pencil hardness is up to 3 H. The pencil hardness of the fluorocarbon composite coating with triple adding of silica sol, sepiolite powder and iron tailing powder is up to 3 H, and the adhesion increases by 44.2%. The properties of the fluorocarbon composite coating with double adding of silica sol and sepiolite powder lie between both coatings. The residual adhesion of the fluorocarbon composite coating with single doped silica sol is the largest. Inorganic mineral fluorocarbon composite coatings can significantly improve the exfoliation resistance of concrete, but the improvement effect is not significant compared with fluorocarbon coating. Some micropores are generated in the waterborne fluorocarbon coating under the salt freezing environment, and the pore structure is coarsened. However, the microstructure of the fluorocarbon composite coating with single doped silica sol is still denser, and the most probable pore diameter increases slightly, and the coating is only slightly damaged. The microstructure of concrete under the protection of the fluorocarbon composite coating with single doped silica sol is denser, and the spalling amount per unit area decreases by 81.2%, compared with that without protection. Research results provide experimental and theoretical bases for the design of concrete protective coating under the salt freezing environment in cold areas.
-
Keywords:
- salt freezing /
- fluorocarbon coating /
- inorganic mineral /
- concrete /
- amount of spalling /
- mechanism
-
复合材料以其比重小、比强度和比模量高等特点,在航空航天领域被广泛应用[1],常见于飞机机翼、尾翼和机身的加筋壁板结构。在压缩、剪切等面内载荷作用下,加筋板结构最常见的失效模式就是失稳(或称屈曲)[2]。
求解加筋板的屈曲问题常采用数值方法,大多通过ABAQUS、ANSYS等商业有限元软件对加筋板屈曲和后屈曲问题进行分析[3-7]。邵青等[8]讨论了侧边边界条件对轴压复合材料加筋板屈曲和后屈曲性能的影响。孙中雷等[9]指出在截面积相等的前提下,帽形加筋板比T型、工字型加筋板的屈曲载荷更高。相对于数值方法,工程简化分析方法求解速度更快,可通过设计手册/指南查取相应计算公式、设计曲线和修正系数,从而对加筋板的屈曲载荷进行快速估算[10-12],但计算精度不高,很大程度上依赖设计经验。Mo等[13]和葛东云等[14]在工程简化分析方法中考虑了蒙皮厚度、加筋板曲率和筋条间距的影响,给出了轴压复合材料帽形加筋曲板的初始屈曲修正公式。于振波[15]采用刚度等效的方法对理想边界条件下的复合材料平板压缩屈曲计算方法进行了修正。杨俊清等[16]考虑了帽形筋条底脚对蒙皮的支撑作用,研究了多种边界条件下按不同的厚度折算方式时工程简化分析方法对复合材料帽形加筋壁板轴压屈曲分析的适用性。汪厚冰等[17]采用几种工程分析方法对轴压复合材料帽形加筋板进行了屈曲载荷计算,通过与试验结果对比研究,得到一种简单有效的复合材料帽形加筋板轴压屈曲载荷计算方法。陈金睿等[18]考虑了筋条下缘条对蒙皮板元宽度的影响,利用加筋板横截面特性提出了一种里兹能量法的改进计算方法。
综上所述,目前对于复合材料帽形加筋板初始屈曲的工程修正分析主要围绕蒙皮板元宽度、刚度修正及边界支持条件修正等方面开展研究。本文首先对典型复合材料帽形加筋板进行了轴压稳定性试验,然后基于加筋板的弯曲刚度比提出了一种复合材料帽形加筋板蒙皮局部屈曲工程修正计算方法。该方法通过选择合适的蒙皮板元宽度及考虑帽形筋条下缘条的蒙皮板元刚度等效处理方法,采用加筋板的弯曲刚度比对等效蒙皮板元的工程简支解和固支解进行线性修正。随后采用有限元方法及本文修正方法对两类带筋条下缘条的帽形加筋板进行了对比分析,采用有限元方法、工程简化分析方法、能量法及本文修正方法对公开文献中的带横框帽形加筋板试验数据进行了对比分析,验证了本文方法的合理性和有效性,其结果满足工程精度要求,为复合材料帽形加筋板的结构设计与分析提供了一种新的快速分析思路。
1. 复合材料帽形加筋板轴压稳定性试验
1.1 试件概述
试件为带两根横框的五筋条复合材料帽形加筋板结构,加筋板采用X850碳纤维增韧树脂预浸料,筋条与蒙皮共胶接。横框为2024-T42铝合金结构,由L形型材和槽形型材连接而成且在帽形筋条交叉处打孔以保证帽形筋条连续。筋条铺层[45/0/0/−45/90]s,蒙皮铺层[45/−45/−45/90/45/0]s,定义铺层0°方向为筋条轴向,单层厚度0.185 mm。试件材料属性见表1。试件共两件,两端做灌胶处理,如图1所示。其中1#试件加筋板长度1005 mm (单侧灌胶端长度50 mm),宽度955 mm,两横框间距为626 mm,筋条间距为210 mm;2#试件加筋板尺寸长度890 mm (单侧灌胶端长度60 mm),宽度1155 mm,两横框间距为554 mm,筋条间距为260 mm。筋条截面尺寸参数见图2。
表 1 单层材料参数Table 1. Lamina material parametersMaterial E11/GPa E22/GPa G12/GPa ν12 X850 162.0 9.1 4.6 0.331 Notes:E11—Elastic modulus in fiber direction; E22—Elastic modulus transverse fiber direction; ν12—Poisson’s ratio; G12—Shear modulus. 1.2 试验概述
轴向压缩试验在2000 kN油压四柱拉压试验机(LY2000,长春新实验机有限责任公司)上进行。试验机加载构件与压缩夹具上部相连。试样放置在夹具中间,调整夹具前后位置,以调整试验机加载中心。为确保试验件承受沿筋条方向的纯压载荷,并保证失稳前对中度,将试验件垂直放置在试验机支持平台上,横框的左右两侧通过螺栓连接到搭接板上,搭接板可随试验件压缩在滑轨中上下移动,以模拟横框的面外扭转约束,支持与加载方式如图3所示。调正压心后,由试验机的上平台施加轴向压缩载荷,载荷合力作用点(试验机加载中心)与加筋板截面压心一致。
加筋板应变片位置如图4所示,图中L表示两横框间距,L1和L2分别表示灌胶端边缘到横框底边的距离。应变片按图4中位置从上到下、从左到右依次编号,编号共7位编码:第一位为试件编号,“1”为1#试件,“2”为2#试件;第二位表示零件类型,“1”为蒙皮,“2”为筋条,“3”为横框;第三位表示行数,从上到下蒙皮共5行、筋条共5行、横框共2行,分别计数;第四位表示列数,从左到右内侧蒙皮(有筋条一侧)共4列、外侧蒙皮(无筋条一侧)共9列、筋条共5列、横框共4列,分开计数;第五位表示应变片位于加筋板外侧或内侧,“1”为外侧,“2”为内侧;第六位表示应变片在筋条上的位置,如图4(c)所示;第七位为应变片方向,“1”、“2”、“3”分别为0°、45°、90°方向,其中0°方向为筋条轴线方向。编码方法如表2所示。
表 2 应变片编码方法Table 2. Coding method of strain gaugeCoding location Coding meaning Coding method First number Specimen number 1—Specimen 1#; 2—Specimen 2# Second number Part type 1—Skin; 2—Stiffener Third number Row number of strain gauge 5 rows on skin, 5 rows on stiffeners, 2 rows on 2 frames, counting from up to down respectively Fourth number Column number of strain gauge 4 columns on inner skin, 9 columns on outer skin, 5 columns on 5 stiffeners, 4 columns on frame, counting from left to right respectively Fifth number Strain gauge on inner skin or outer skin 1—Outer skin; 2—Inner skin Sixth number Strain gauge location on stiffener 1—Crown; 2—Left web; 3—Right web; 4—Left bottom flange; 5—Right bottom flange Seventh number Strain gauge direction 1—0° direction; 2—45° direction; 3—90° direction 1#试件加载到315 kN蒙皮开始屈曲(图5(a)),2#试件加载到185 kN蒙皮开始屈曲(图5(b)),此时蒙皮载荷应变曲线的斜率出现反号,筋条的载荷应变曲线斜率发生变化。
1.3 有限元模型验证
采用ABAQUS软件对上述试验进行线性特征值屈曲分析。单元类型采用四节点常规壳减缩积分(S4R)单元,网格尺寸经收敛性分析[18]取为10 mm×10 mm。为模拟两端灌胶区,边界条件一端固支,另一端只释放轴压方向的自由度,并施加单位压缩载荷。试验件网格划分及一阶屈曲模态见图6 (以1#试件为例)。计算得到1#试件屈曲载荷286.9 kN,2#试件屈曲载荷164.6 kN,与试验值误差分别为−8.9%和−11.0% (误差正值表示计算值大于试验值,误差负值表示计算值小于试验值,下同),表明该有限元建模方法较准确,结果可信。
2. 基于弯曲刚度比的复合材料帽形加筋板蒙皮局部屈曲工程修正算法
2.1 复合材料帽形加筋板蒙皮局部屈曲工程简化分析方法概述
由于复合材料加筋板筋条间蒙皮局部屈曲是最常见的屈曲模式,因此仅讨论该屈曲模式下的加筋板屈曲载荷计算。在工程简化分析方法中,复合材料帽形加筋板筋条间蒙皮局部屈曲分析可简化为侧边简支或固支的各向异性平板屈曲分析,其中板宽为b,一般取相邻帽腰之间的距离或者下缘条自由边缘之间的距离;板长为a,取加筋板两个横框之间的距离。加载边边界条件视加持情况取为简支或者固支。以加载边简支为例[12],四边简支正交各向异性矩形层压平板的屈曲载荷计算公式为
Nx=π2D22b2[D11D22(ba)2m2+2(D12+2D66D22)+(ab)21m2] (1) 式中:Nx为单位长度的轴压屈曲载荷;m为沿板方向的屈曲半波数;D11、D12、D22和D66为蒙皮弯曲刚度系数,下同。计算时取m为1,2,3···,计算相应的一组Nx,其中最小的Nx即为板的屈曲载荷Nxcr。
两加载边简支、两侧边固支的正交各向异性矩形层压平板屈曲载荷计算公式为
Nxcr=π2√D11D22b2[K−2.40(1−D12+2D66√D11D22)] (2) 式中,K为压缩屈曲系数,按正交各向异性矩形平板的轴压K-λ曲线(图7)查取,其中
λ=(a/b)4√D22/D11 。加载边固支的计算公式详见文献[12],此处不再赘述。2.2 基于弯曲刚度比的复合材料帽形加筋板蒙皮局部屈曲修正方法
由于筋条对于蒙皮的实际支持不能简单地简化为简支或者固支,这种支持的强弱可以通过加筋板筋条与蒙皮的面内刚度、扭转刚度、弯曲刚度的比值反映[18]。由于筋条的面内刚度、扭转刚度、弯曲刚度具有一定相关性,为简化计算量,仅采用弯曲刚度比对工程简化分析进行修正。该方法计算步骤如下:
(1) 根据工程简化分析方法,将加筋板的屈曲计算简化为加载边简支或者固支的蒙皮板元的屈曲计算。其中板宽为b,取相邻帽腰之间的距离;板长为a,取加筋板两个横框之间的距离。
(2) 采用工程简化分析方法的平板屈曲公式分别计算蒙皮板元侧边简支的屈曲载荷
NSSxcr 和侧边固支的屈曲载荷NCCxcr 。考虑筋条下缘条对蒙皮刚度的加强作用,根据刚度叠加原则,等效后的蒙皮板元的弯曲刚度为b {\boldsymbol{D}} + 2{b_{{\text{bf}}}} {\boldsymbol{D}}_{\text{f}}^{} ,经简化后采用下式对蒙皮板元的弯曲刚度系数进行等效处理:{\boldsymbol{D}}_{\text{R}}^{} = {\boldsymbol{D}}_{}^{} + {\boldsymbol{D}}_{\text{f}}^{}\frac{{2{b_{{\text{bf}}}}}}{b} (3) 式中:
{{\boldsymbol{D}}_{\text{R}}} 为蒙皮板元的修正弯曲刚度系数矩阵;{\boldsymbol{D}} 为未修正的蒙皮板元弯曲刚度系数矩阵;{\boldsymbol{D}}{}_{\text{f}} 为筋条下缘条的弯曲刚度系数矩阵;bbf为筋条下缘条宽度;b为蒙皮板元宽度。(3) 基于加筋板的弯曲刚度比对侧边简支解和侧边固支解进行修正,修正公式如下:
{N_{{\text{cr}}}} = N_{x{\text{cr}}}^{{\text{SS}}} + (N_{x{\text{cr}}}^{{\text{CC}}} - N_{x{\text{cr}}}^{{\text{SS}}})\frac{{(D - 3)}}{3} (4) 式中,D为加筋板的弯曲刚度比,即加筋板n根筋条的弯曲刚度之和与蒙皮的弯曲刚度的比值。加筋板截面的中性轴位置及筋条/蒙皮的弯曲刚度采用文献[2]中方法计算。将上述得到的Ncr除以蒙皮板元厚度即得到加筋板的局部屈曲应力。该方法适用于带筋条下缘条的复合材料帽形加筋板的筋间蒙皮初始屈曲分析。
对第一节的两个帽形加筋板试验件分别采用工程简化分析方法和修正方法进行计算。横框支持简化为简支,蒙皮板元宽度选为相邻帽腰之间的距离,分别为151 mm和201 mm。采用侧边简支公式(1)计算得到屈曲载荷分别为249 kN和154 kN。采用侧边固支公式(2)计算时,λ分别为4.4和2.9,K值分别取为7.0和7.2,计算得到屈曲载荷分别为383 kN和244 kN。采用修正方法计算时首先采用式(3)将下缘条刚度与蒙皮板元刚度进行等效处理,然后采用式(1)计算得到侧边简支载荷分别为285 kN和173 kN,采用式(2)计算得到侧边固支载荷分别为447 kN和275 kN,然后计算得到加筋板弯曲刚度比分别为3.501和3.456,最后采用修正式(4)计算得到修正后的屈曲载荷,分别为312 kN和189 kN,与试验值误差分别为1.0%和2.2%,均在3%以内。详细结果见表3。可以看出,传统的工程简化分析方法计算的屈曲载荷误差较大,而采用修正方法,其计算精度明显提高。
表 3 复合材料帽形加筋板轴压稳定性试验值与计算值对比Table 3. Comparison of calculated and experimental values of local buckling load of hat-stiffened composite panelNo. D Experimental
buckling load /kNEngineering simplified
method/kNUpdating
method/kNError/% Simply
supportedBuilt-in Simply
supportedBuilt-in Updating
method1# 3.501 315 249 383 312 −21.0 21.6 −1.0 2# 3.456 185 154 244 189 −16.8 31.9 2.2 Note: D—Flexural stiffness ratio. 3. 算例分析
以不带横框的三筋条复合材料帽形加筋板为研究对象,分别采用有限元方法、工程简化分析方法和本文修正方法进行对比分析,验证修正方法的合理性和有效性。随后引用文献试验数据,以带横框的三筋条复合材料帽形加筋板为研究对象,综合比较工程简化分析方法、能量法及本文修正方法,形成适用于帽形加筋板初步分析的工程估算方法。
3.1 不带横框的三筋条帽形加筋板屈曲分析
研究对象为两类含筋条下缘条的帽形筋条加筋板,如图8所示。两类加筋板的几何尺寸和材料属性如表4和表5所示。表4中a为加筋板长度,B为加筋板宽度,bc为筋条帽顶宽度,bw为筋条帽腰宽度,bf为筋条下缘条宽度,θ为帽腰与蒙皮夹角,bss为相邻筋条间蒙皮宽度,如图9所示。对于每一类加筋板,其几何尺寸不变,分别给定3种不同的加筋板铺层,共6种帽形加筋板,铺层顺序见表6。
有限元分析采用ABAQUS有限元软件进行线性特征值分析,模型采用四节点常规壳减缩积分(S4R)单元,并对网格尺寸进行收敛性分析[18];加筋板两侧边自由,两加载边采用参考点耦合约束,一参考点施加单位压缩载荷,另一参考点建立简支边界条件。
表 4 三筋条帽形加筋板有限元模型几何参数Table 4. Geometric parameters of finite element models of hat-stiffened panels with three stiffenersType a
/mmB
/mmbc
/mmbw
/mmbf
/mmθ/(°) bss
/mm1 300 278 10.4 10.7 16.5 82.9 70 2 590 532 25 33 25 60 103 Notes: a—Length of stiffened panel; B—Width of stiffened panel; bc—Width of stiffener’s crown; bw—Width of stiffener’s web; bf—Width of stiffener’s bottom flange; θ—Angle between stiffener’s web and skin; bss—Width of skin adjacent stiffener. 表 5 三筋条帽形加筋板单层材料参数Table 5. Lamina material parameters of hat-stiffened panels with three stiffenersType E11/GPa E22/GPa G12/ GPa {\nu _{12}} 1 98 10.8 5.2 0.31 2 154 8.5 4.5 0.35 图10为两类加筋板的一阶屈曲模态图。表7为分别采用有限元方法、工程简化分析方法和修正方法计算的6种加筋板的屈曲载荷。表中误差正值表示计算值大于有限元值,误差负值表示计算值小于有限元值。结果分析如下:
(1) 6种加筋板屈曲模式均为筋条间蒙皮局部屈曲,筋条无明显扭转、弯曲变形,符合本文研究前提;
(2) 采用工程简化分析方法,侧边简支解误差绝对值的算术平均值为48.7%,表明简支解比有限元值明显偏小。工程经验表明按简支和按固支计算的屈曲载荷相差可达一倍以上,对于帽形筋条工程上一般简化为固支[12]。因此按简支计算误差较大;
表 6 三筋条帽形加筋板有限元模型铺层顺序及铺层厚度Table 6. Stacking sequence and thickness of finite element models of hat-stiffened panels with three stiffenersNo. Skin Crown Web Flange Stacking
sequenceTotal
thickness/
mmStacking
sequenceTotal
thickness/
mmStacking
sequenceTotal
thickness/
mmStacking
sequenceTotal
thickness/
mm1.1 [45/0/0/−45/90]s 1 [09/−45/452/−452]s 2.8 [−45/452/−452]s 1 [03/−45/452/
−45/−45]s1.5 1.2 [45/0/−45/90/
45/−45/0]s1.4 [09/−45/452/−452]s 2.8 [−45/452/−452]s 1 [03/−45/452/
−45/−45]s1.5 1.3 [0/90]3s 1.2 [45/0/90/0/−45/
0/45/90]s1.5 [45/0/90/0/−45/
0/45/90]s1.5 [45/0/90/0/−45/
0/45/90]s1.5 2.1 [45/−45/−45/
90/45/0]s1.2 [45/0/0/−45/90]s 0.9 [45/0/0/−45/90]s 0.9 [45/0/0/−45/90]s 0.9 2.2 [45/−45/902/
45/0/90/0]s1.5 [0/45/0/0/−45/45]s 1.2 [0/45/0/0/−45/45]s 1.2 [0/45/0/0/−45/45]s 1.2 2.3 [45/−45/902/45/
0/90/0]s1.5 [45/0/0/−45/90]s 0.9 [45/0/0/−45/90]s 0.9 [45/0/0/−45/90]s 0.9 表 7 两类帽形加筋板轴压稳定性有限元值与计算值对比Table 7. Comparison of calculated and FEM values of local buckling load of two kinds of hat-stiffened composite panelsNo. D FEM
buckling
load/kNEngineering simplified method/kN Updating method /kN Error/% Simply supported Built-in Simply
supportedBuilt-in Updating method 1.1
1.2
1.3
2.1
2.2
2.32.750
4.713
4.842
4.014
4.019
3.81513.0
38.5
23.9
26.4
52.7
43.27.7
15.9
9.4
16.0
28.5
23.113.1
29.0
19.1
24.7
46.5
37.714.2
38.1
26.0
27.9
54.6
41.2−40.8
−58.7
−60.7
−39.4
−45.9
−46.50.8
−24.7
−20.1
−6.4
−11.8
−12.79.2
−1.0
8.8
5.7
3.6
−4.6(3) 采用工程简化分析方法,侧边固支解误差绝对值的算术平均值为12.8%,相较于侧边简支解误差有所减小,表明将帽形筋条简化为固支有一定合理性,但是由于筋条间蒙皮间距较小,筋条下缘条对于蒙皮屈曲的加强作用较明显,而工程简化分析方法没有考虑筋条下缘条的加强作用,因此计算结果仍有一定误差;
(4) 采用修正方法之后的屈曲载荷误差绝对值的算术平均值为5.5%,满足工程精度要求,相较于工程简化分析方法计算精度有所提高,表明修正方法合理有效。
3.2 带横框的三筋条帽形加筋板屈曲分析
采用试验方法、工程简化分析方法、能量法和本文修正方法对三筋条带横框的复合材料帽形加筋板进行轴压屈曲分析,加筋板外形见图11,详细尺寸参数、铺层信息、单层材料参数及稳定性试验结果详见文献[16]。
采用工程简化分析方法进行屈曲分析时,将加筋板简化为长度为500 mm、宽度为195 mm (帽腰之间的距离)的平板,采用式(1)计算得到侧边简支屈曲载荷143.3 kN。侧边固支屈曲载荷258 kN[16]。
采用修正方法计算得到弯曲刚度比3.641,分别采用式(1)和式(2)计算侧边简支和侧边固支屈曲载荷。计算固支载荷时λ=2.2,K值为7.2。计算得到简支载荷205.3 kN,固支载荷348.0 kN。采用式(4)计算得到修正后的屈曲载荷为235.8 kN。
采用能量法[18]进行屈曲分析时,将加筋板简化为长度为500 mm、宽度为195 mm的平板,帽形筋条的自由截面扭转刚度为7.48×108 N·mm2,代入到能量法计算模型中得到屈曲载荷为238.2 kN,计算结果见表8。表中误差正值表示计算值大于试验值,误差负值表示计算值小于试验值。结果分析如下:
(1) 对于带横框的帽形加筋板,工程简化分析方法、能量法和本文修正方法均将横框简化为简支。除工程简化分析方法简支解误差较大之外,工程简化分析方法固支解、能量法和本文修正方法计算精度满足工程要求,表明对帽形筋条简化为固支的一般工程假设是合理的,也表明对横框支持的简化是合理的;
(2) 从计算精度角度看,修正方法计算误差3.8%,能量法计算误差2.8%,两者计算精度相当,比工程简化分析方法精度稍高。其原因在于工程简化分析方法将帽形筋条简化为固支,对于某些带下缘条的帽形加筋板计算误差较大,能量法则简化为弹性支持,修正方法则基于弯曲刚度比对简支解和固支解综合修正,是对工程简化分析方法的修正和改善;
(3) 从时间成本上看,3种方法相比有限元方法均为快速计算方法,可编写计算程序,用时较短。
综上所述,工程简化分析方法算法简单,依赖设计员工程经验,适用于方案阶段结构参数打样;修正方法和能量法简化方式更合理,适用范围更广,适合于初步设计阶段结构参数化分析和稳定性校核,可相互对照使用。
表 8 带横框的三筋条帽形加筋板局部屈曲载荷计算值与试验值对比Table 8. Comparison of calculated and experimental values of local buckling load of hat-stiffened panels with three stiffeners and two framesD Experimental
buckling
load/kNEngineering simplified method/kN Energy method/kN Updating method/kN Error/% Simply supported Built-in Simply supported Built-in Energy method Updating method 3.641 245.0 143.3 258 238.2 235.8 −41.5 5.3 −2.8 −3.8 4. 结 论
(1) 对典型复合材料帽形加筋板进行了轴压稳定性试验,提出了一种基于加筋板弯曲刚度比的复合材料帽形加筋板蒙皮局部屈曲工程修正计算方法,所预测的屈曲载荷与稳定性试验值误差在3%以内。
(2) 对于带筋条下缘条的三筋条复合材料帽形加筋板,工程简化分析方法侧边简支解误差绝对值的算术平均值为48.7%,侧边固支解误差绝对值的算术平均值为12.8%,表明将帽形筋条简化为固支有一定合理性,但是由于没有考虑筋条下缘条对蒙皮的加强作用,因此计算结果仍有一定误差。修正方法误差绝对值的算术平均值为5.5%,验证了修正方法的合理性和有效性,对带筋条下缘条的复合材料帽形加筋板筋间初始屈曲载荷估算有一定的参考意义。
(3) 对于典型的带横框三筋条帽形加筋板,修正方法计算误差3.8%,与能量法计算精度相当,比工程简化分析方法精度稍高。工程简化分析方法算法简单,依赖设计员工程经验,适用于方案阶段结构参数打样;修正方法适用于初步设计阶段结构参数化分析和稳定性评估,可与能量法相互对照使用。
-
表 1 铁尾矿粉的化学组成
Table 1 Chemical composition of iron tailing powder
wt% SiO2 Al2O3 CaO MgO Fe2O3 Na2O K2O TiO2 51.70 18.00 9.36 5.86 5.29 3.69 2.67 1.39 表 2 无机矿物氟碳复合涂料配方
Table 2 Inorganic mineral fluorocarbon composite coating formulas
Serial number Fluorocarbon coating Silica sol Nano-SiO2 content/wt% F00 1 0 0 F02 1 0.02 1 F04 1 0.04 2 F06 1 0.06 3 F08 1 0.08 4 F10 1 0.10 5 F15 1 0.15 7.4 F20 1 0.20 9.8 F25 1 0.25 12.3 F30 1 0.30 14.7 F35 1 0.35 17.2 F40 1 0.40 19.6 Notes: The formula refers to the mass ratios of various materials; Nano-SiO2 content refers to the mass fraction of nano-SiO2 accounting for fluorocarbon resin in the coating. 表 3 水泥和煤粉灰的化学组成
Table 3 Chemical composition of cement and fly ash
wt% Category CaO SiO2 Al2O3 MgO Fe2O3 K2O Na2O SO3 Cement 59.80 21.35 6.80 2.93 2.55 1.02 0.18 3.66 Fly ash 4.94 48.28 35.60 1.03 3.66 0.88 0.21 0.86 表 4 混凝土配合比
Table 4 Concrete mix ratio
kg·m−3 Cement Fly ash Coarse aggregate Fine aggregate Water reducer Water 290 80 1 081 752 8.1 170 表 5 不同无机矿物掺加方式的氟碳复合涂料配方
Table 5 Formulas of fluorocarbon composite coatings with different inorganic mineral adding ways
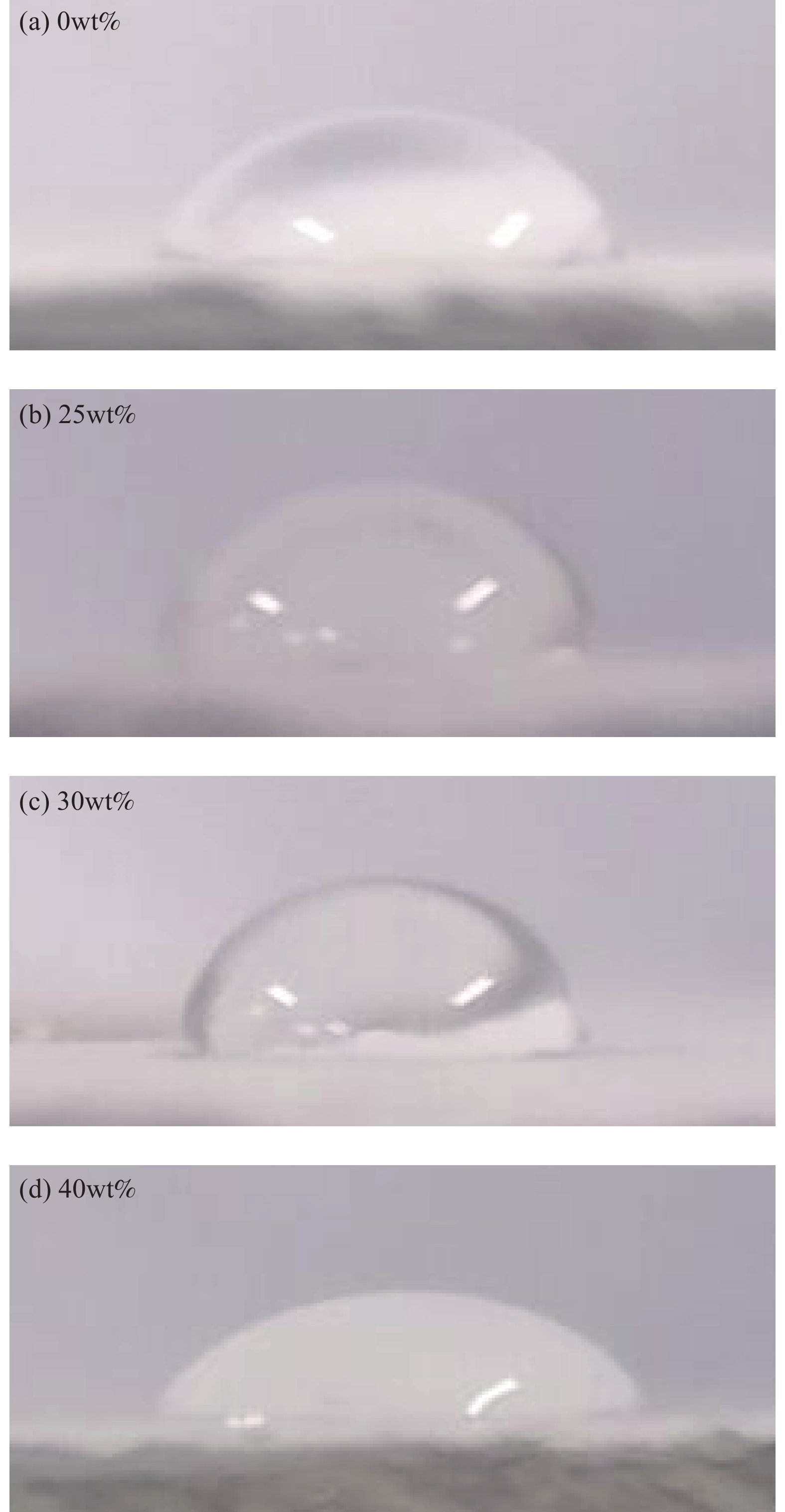
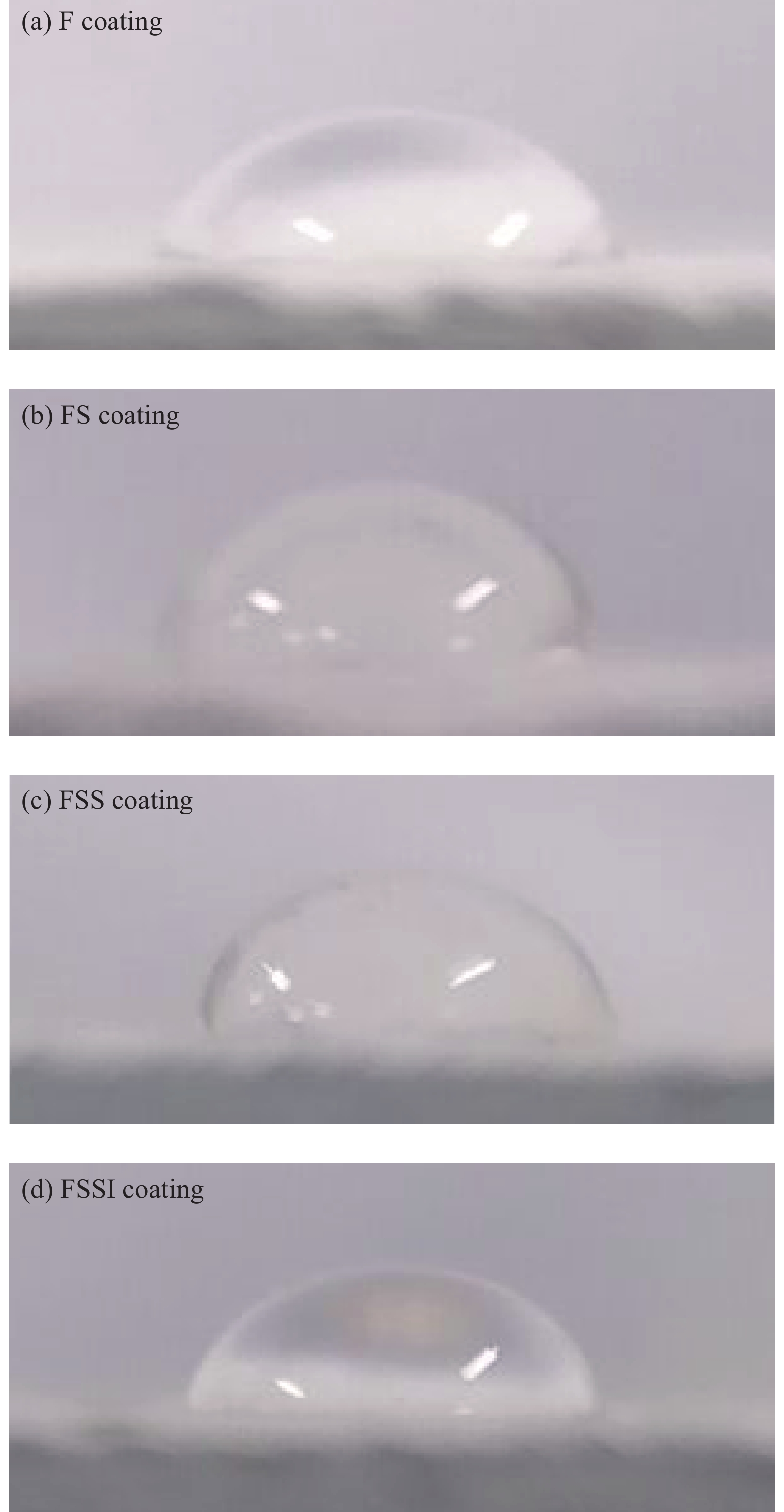
Serial number Fluorocarbon coating Silica sol Sepiolite powder Iron tailing powder F 1 — — — FS 1 0.250 — — FSS 1 0.125 0.1250 — FSSI 1 0.125 0.0625 0.0625 -
[1] 李中华, 巴恒静. 除冰盐环境下混凝土有机硅涂层防护性能研究[J]. 中国矿业大学学报, 2009, 38(1):41-45. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1964.2009.01.009 LI Zhonghua, BA Hengjing. A study of the protection of concrete from freeze-deicing salt by an organo-silicone coating[J]. Journal of China University of Mining and Technology,2009,38(1):41-45(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1000-1964.2009.01.009
[2] 郑焱. 水性氟碳涂料对混凝土防护作用的研究[D]. 北京: 北京工业大学, 2012. ZHENG Yan. Study on the protective function of water-borne fluorocarbon coating for concrete[D]. Beijing: Beijing University of Technology, 2012(in Chinese).
[3] PAN X Y, SHI Z G, SHI C J, et al. A review on concrete surface treatment Part Ⅰ: Types and mechanisms[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2017,132:578-590. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2016.12.025
[4] 房亚楠, 秦立光, 赵文杰, 等. 氟碳涂料在防腐领域的研发现状和发展趋势[J]. 中国腐蚀与防护学报, 2016, 36(2):97-106. FANG Yanan, QIN Liguang, ZHAO Wenjie, et al. Research progress and development trend on corrosion resistant fluorocarbon paint[J]. Journal of Chinese Society for Corrosion and Protection,2016,36(2):97-106(in Chinese).
[5] SHCHUKIN D, MÖHWALD H. A coat of many functions[J]. Science,2013,341:1458-1459. DOI: 10.1126/science.1242895
[6] 郑焱, 毛倩瑾, 王亚丽, 等. 水性氟碳涂料对混凝土防护作用的研究[J]. 化学工业与工程, 2012, 29(4):21-25. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9533.2012.04.005 ZHENG Yan, MAO Qianjin, WANG Yali, et al. Concrete protective function of fluorine carbon resin coating water[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering,2012,29(4):21-25(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-9533.2012.04.005
[7] 吕太勇, 刘波, 罗源军, 等. 水溶性氟碳涂料的研究进展[J]. 化工新型材料, 2016, 44(9):45-46. LYU Taiyong, LIU Bo, LUO Yuanjun, et al. Concrete protective function of fluorine carbon resin coating water[J]. New Chemical Materials,2016,44(9):45-46(in Chinese).
[8] 房亚楠, 刘栓, 赵文杰, 等. 石墨烯/氟碳涂层的制备及其耐蚀性能[J]. 表面技术, 2016, 45(11):67-75. DOI: 10.16490/j.cnki.issn.1001-3660.2016.11.010 FANG Yanan, LIU Shuan, ZHAO Wenjie, et al. Preparation and corrosion resistance of graphene/fluorocarbon coating[J]. Surface Technology,2016,45(11):67-75(in Chinese). DOI: 10.16490/j.cnki.issn.1001-3660.2016.11.010
[9] 田惠文, 李伟华, 宗成中, 等. 海洋环境钢筋混凝土腐蚀机理和防腐涂料研究进展[J]. 涂料工业, 2008, 38(8):62-67. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4312.2008.08.019 TIAN Huiwen, LI Weihua, ZONG Chengzhong, et al. Corrosion mechanism and research progress of anti-corrosion coatings for reinforced concrete used in marine environment[J]. Paint and Coatings Industry,2008,38(8):62-67(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4312.2008.08.019
[10] 詹耀. 海上风电钢结构防腐及氟碳涂料应用[J]. 涂料技术与文摘, 2012, 33(10):22-25. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2418.2012.10.006 ZHAN Yao. Anticorrosion technology for steel structure of offshore wind power system and application of fluorocarbon coatings[J]. Coating Technology and Abstracts,2012,33(10):22-25(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2418.2012.10.006
[11] MONCAYO-RIASCOS I, HOYOS B A. Fluorocarbon versus hydrocarbon organosilicon surfactants for wettability alteration: A molecular dynamics approach[J]. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry,2020,88:224-232. DOI: 10.1016/j.jiec.2020.04.017
[12] LUO S, PENG X X, ZHANG Y F, et al. Oil-repellent and antifog coatings based on poly(vinyl alcohol)/hydrolyzed poly(styrene-co-maleic anhydride)/fluorocarbon surfactant[J]. Progress in Organic Coatings,2020,141:105560. DOI: 10.1016/j.porgcoat.2020.105560
[13] UZOMA P C, LIU F C, HAN E H. Multi-stimuli-triggered and self-repairable fluorocarbon organic coatings with urea-formaldehyde microcapsules filled with fluorosilane[J]. Journal of Materials Science and Technology,2020,45:70-83. DOI: 10.1016/j.jmst.2019.11.022
[14] ZHU Z Y, ZHOU F, ZHAN S. Enhanced antifouling property of fluorocarbon resin coating (PEVE) by the modification of g-C3N4/Ag2WO4 composite step-scheme photocatalyst[J]. Applied Surface Science,2020,506:144934. DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.144934
[15] ZHENG H P, LIU L, MENG F D, et al. Multifunctional superhydrophobic coatings fabricated from basalt scales on a fluorocarbon coating base[J]. Journal of Materials Science and Technology,2021,84:86-96. DOI: 10.1016/j.jmst.2020.12.022
[16] GAO Q, WU X M, SHI F Y. Novel superhydrophobic NIR reflective coatings based on montmorillonite/SiO2 compo-sites for energy-saving building[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2022,326:126998. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2022.126998
[17] SU N, ZHOU F. Study of BiOI/BiOIO3 composite photocatalyst for improved sterilization performance of fluorocarbon resin coating (PEVE)[J]. Chemical Physics Letters,2021,766:138329. DOI: 10.1016/j.cplett.2021.138329
[18] ZHANG Q, LI L, CAO L X, et al. Coalescence separation of oil-water emulsion on amphiphobic fluorocarbon polymer and silica nanoparticles coated fiber-bed coalescer[J]. Chinese Journal of Chemical Engineering,2021,36:29-37. DOI: 10.1016/j.cjche.2020.07.034
[19] 胡涛. 水工混凝土表面氟碳纳米复合涂层的制备及防护耐久性研究[D]. 武汉: 长江科学院, 2017. HU Tao. Preparation and durability of fluorocarbon nanocomposite coating on hydraulic concrete surface[D]. Wuhan: Changjiang River Scientific Research Institute, 2017(in Chinese).
[20] 杨景花. 纳米二氧化钛改性氟碳涂料及涂装工艺的研究[D]. 长沙: 湖南大学, 2006. YANG Jinghua. Research on nano-TiO2 modified fluorocarbon coating and painting process[D]. Changsha: Hunan University, 2006(in Chinese).
[21] 高敬民, 聂小燕, 方冉, 等. 纳米SiO2改性核壳型氟碳乳液的合成及性能研究[J]. 涂料工业, 2003, 33(11):1-5. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4312.2003.11.001 GAO Jingmin, NIE Xiaoyan, FANG Ran, et al. Research on synthesis and properties of core-shell fluorocarbon emulsion modified by nano-SiO2[J]. Paint and Coatings Industry,2003,33(11):1-5(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0253-4312.2003.11.001
[22] 陈亮, 宋仁国, 郭燕清, 等. 改性纳米SiO2/三氟型FEVE复合氟碳涂料的制备及其性能[J]. 材料保护, 2014, 47(12):18-21. CHEN Liang, SONG Renguo, GUO Yanqing, et al. Preparation and properties of modified nano-SiO2/trifluoro FEVE composite fluorocarbon coating[J]. Materials Protection,2014,47(12):18-21(in Chinese).
[23] 周志文. 硅溶胶改性环氧树脂复合乳液的制备及性能研究[D]. 南昌: 南昌航空大学, 2013. ZHOU Zhiwen. Preparation and properties of silica sol modified epoxy resin emulsion[D]. Nanchang: Nanchang Hangkong University, 2013(in Chinese).
[24] 姜洪义, 栾聪梅. 改性海泡石粉体的孔结构与调湿性能[J]. 武汉理工大学学报, 2010, 32(5):9-11. DOI: 10.3963/j.issn.1671-4431.2010.05.003 JIANG Hongyi, LUAN Congmei. Pore structures and humidity controlling capabilities of activated sepiolite powder[J]. Journal of Wuhan University of Technology,2010,32(5):9-11(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3963/j.issn.1671-4431.2010.05.003
[25] 孙凯利, 王彩辉, 孙国文, 等. 海泡石对砂浆抗氯离子和碳化侵蚀性能的影响[J]. 硅酸盐通报, 2019, 38(10):3111-3120. SUN Kaili, WANG Caihui, SUN Guowen, et al. Effect of sepiolite on resistance to chloride ion and carbonization erosion of Mortar[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society,2019,38(10):3111-3120(in Chinese).
[26] 丁德宝, 汤庆国, 王菲, 等. 偶联改性对海泡石粉体表面官能团结构及性能的影响[J]. 科学技术与工程, 2017, 17(20):17-22. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2017.20.004 DING Debao, TANG Qingguo, WANG Fei, et al. Effect of coupling modification on the surface functional group and properties of sepiolite powder[J]. Science Technology and Engineering,2017,17(20):17-22(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1671-1815.2017.20.004
[27] 杨迎春, 毛宇光. 不同细度铁尾矿粉对水泥基材料性能的影响[J]. 西安建筑科技大学学报: 自然科学版, 2020, 52(2):241-247. YANG Yingchun, MAO Yuguang. Influence of iron tailing of different on properties of cement-based material[J]. Journal of Xi'an University of Architecture and Technology (Natural Science Edition),2020,52(2):241-247(in Chinese).
[28] 张伟, 刘梁友, 李莉丽, 等. 铁尾矿粉-粉煤灰-矿渣粉复合掺合料对混凝土性能的影响[J]. 硅酸盐通报, 2016, 35(11):3826-3831. ZHANG Wei, LIU Liangyou, LI Lili, et al. Influence of iron tailings slag-fly ash-slag powder composite admixture on the properties of concrete[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society,2016,35(11):3826-3831(in Chinese).
[29] 侯云芬, 刘锦涛, 赵思儒, 等. 铁尾矿粉对水泥砂浆性能的影响及机理分析[J]. 应用基础与工程科学学报, 2019, 27(5):1149-1157. HOU Yunfen, LIU Jintao, ZHAO Siru, et al. Effect mecha-nism of iron tailing powder on cement mortar properties[J]. Journal of Basic Science and Engineering,2019,27(5):1149-1157(in Chinese).
[30] 余茂林, 孙皓, 解亚, 等. 改性硅溶胶-苯丙乳液复合涂层的制备及性能[J]. 表面技术, 2021, 50(11):147-154. YU Maolin, SUN Hao, XIE Ya, et al. Preparation and properties of modified silica sol styrene acrylic emulsion compo-site coating[J]. Surface Technology,2021,50(11):147-154(in Chinese).
[31] 中华人民共和国国家质量监督检验检疫总局, 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 色漆和清漆 拉开法附着力试验: GB/T 5210—2006[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2006. General Administration of Quality Supervision, Inspection and Quarantine of the People's Republic of China, Standardization Administration of the People's Republic of China. Paints and varnishes—Pull-off test for adhesion: GB/T 5210—2006[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 2006(in Chinese).
[32] 国家技术监督局. 涂膜硬度铅笔测定法: GB/T 6739—1996[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 1996. The State Bureau of Quality and Technical Supervision. Determination of film hardness by pencil test: GB/T 6739—1996[S]. Beijing: Standards Press of China, 1996(in Chinese).
[33] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 普通混凝土长期性能和耐久性能试验方法标准: GB/T 50082—2009[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2009. Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People's Republic of China. Standard for test methods of long-term performance and durability of ordinary concrete: GB/T 50082—2009[S]. Beijing: China Building Industry Press, 2009(in Chinese).
[34] 郭寅川, 申爱琴, 郑盼飞, 等. 高寒地区桥面板水泥混凝土抗盐冻性能研究[J]. 公路交通科技, 2019, 36(3):73-79. GUO Yinchuan, SHEN Aiqin, ZHENG Panfei, et al. Study on salt-freeze resistance of bridge deck concrete in alpine region[J]. Journal of Highway and Transportation Research,2019,36(3):73-79(in Chinese).
[35] 金大铖. 新型含氟硅烷偶联剂的合成及其疏水涂层的构建[D]. 杭州: 浙江大学, 2019. JIN Dacheng. Synthesis of novel fluoride-containing silane coupling agents and their application in hydrophobic coating construction[D]. Hanzhou: Zhejiang University, 2019(in Chinese).
[36] 潘帅锋, 冯杰. PET膜用氟碳溶胶涂层性能研究[J]. 涂料技术与文摘, 2014, 35(1):16-18. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2418.2014.01.004 PAN Shuaifeng, FENG Jie. Research on property of fluorocarbon dispersion based layer for PET film[J]. Coating Technology and Abstracts,2014,35(1):16-18(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2418.2014.01.004
[37] 中华人民共和国工业和信息化部. 水性氟树脂涂料: HG/T 4104—2019[S]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2019. Ministry of Industry and Information Technology of the People's Republic of China. Water-based fluorocarbon resin coatings: HG/T 4104—2019[S]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2019(in Chinese).
[38] 王过之. 纳米防腐涂料原理与实践[J]. 四川兵工学报, 2003, 24(3):10-12. WANG Guozhi. Principle and practice of nanometer anticorrosive coatings[J]. Journal of Sichuan Ordnance,2003,24(3):10-12(in Chinese).
[39] WANG W S, GUO Y L, OTAIGBE J. The synthesis, characterization and biocompatibility of poly(ester urethane)/polyhedral oligomeric silesquioxane nanocomposites[J]. Polymer,2009,50(24):5749-5757. DOI: 10.1016/j.polymer.2009.05.037
[40] 张鸿儒, 季韬, 刘福江, 等. 不同养护制度下掺铁尾矿粉超高性能混凝土力学性能[J]. 福州大学学报:自然科学版, 2020, 48(1):90-97. ZHANG Hongru, JI Tao, LIU Fujiang, et al. Mechanical properties of UHPC prepared with iron tail mineral powder cured under different conditions[J]. Journal of Fuzhou University (Natural Science Edition),2020,48(1):90-97(in Chinese).
[41] KANG H J, SONG M S, KIM Y S. The effects of sepiolite on the properties of portland cement mortar[J]. Journal of the Korean Ceramic Society,2008,45(8):443-452. DOI: 10.4191/KCERS.2008.45.8.443
[42] KAVAS T, SABAH E, ÇELIK M S. Structural properties of sepiolite-reinforced cement composite[J]. Cement and Concrete Research,2004,34(11):2135-2139. DOI: 10.1016/j.cemconres.2004.03.015
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 陈向明,李新祥,柴亚南,陈普会,孙侠生. 复合材料壁板后屈曲设计与分析技术研究进展. 复合材料学报. 2024(09): 4673-4700 .  本站查看
本站查看
2. 吴菁,章向明,朱子旭,胡明勇,王安稳. 复合材料船体帽型加筋板面内刚度. 海军工程大学学报. 2023(04): 1-6+28 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(1)
-




 下载:
下载: