Characterization of glycidyl methacrylate modified polyvinyl alcohol fiber and its effect on mechanical properties of thermoplastic starch
-
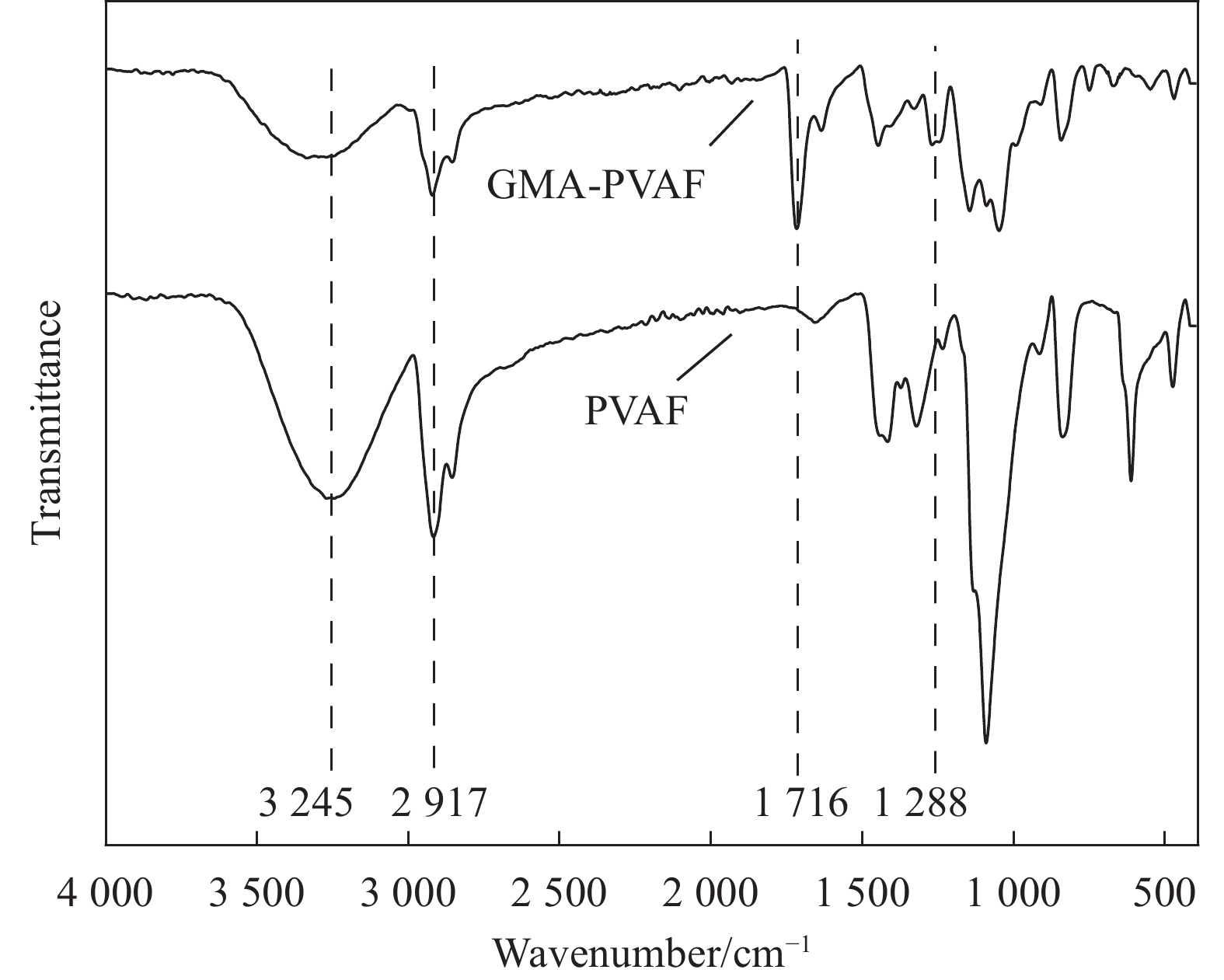
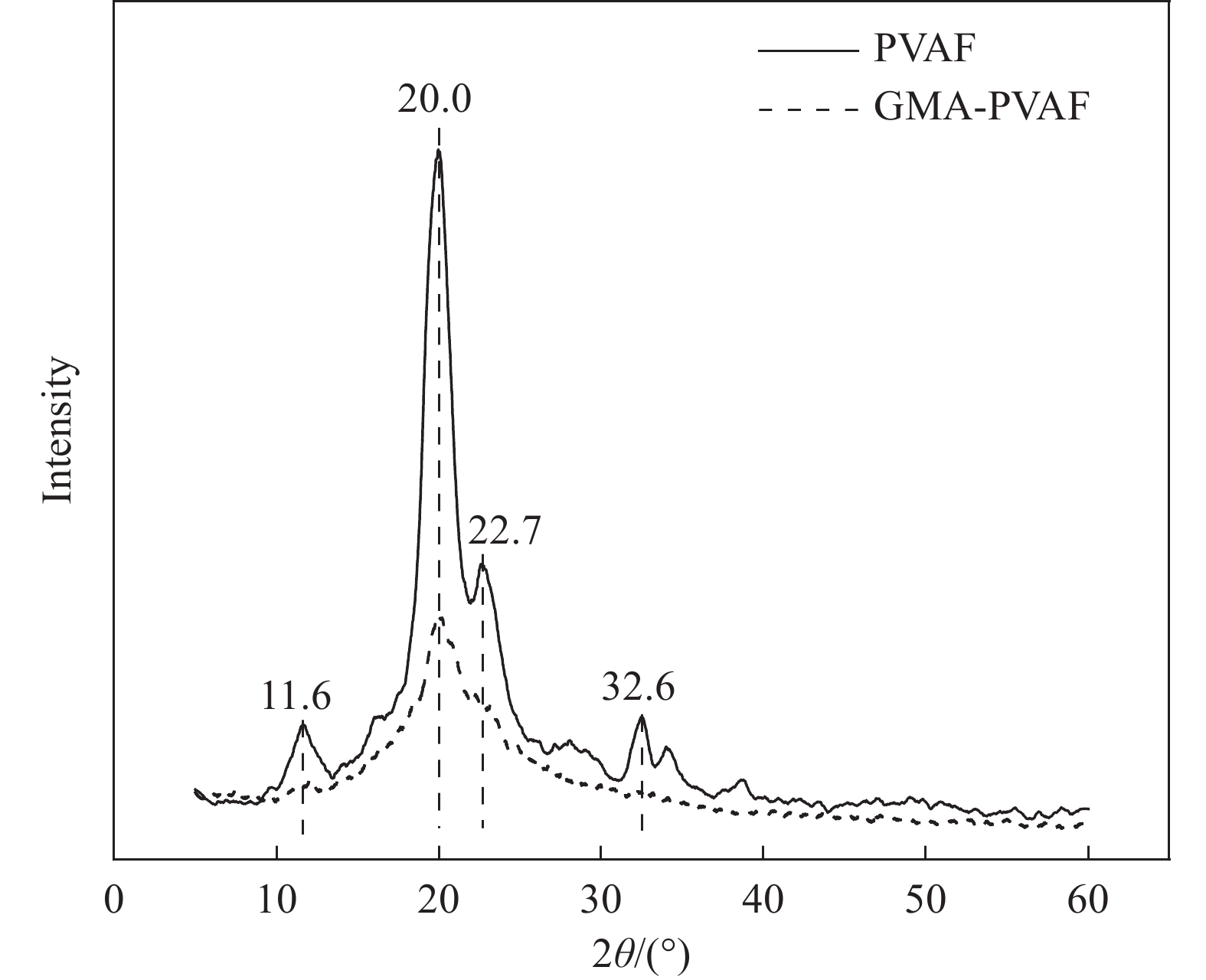
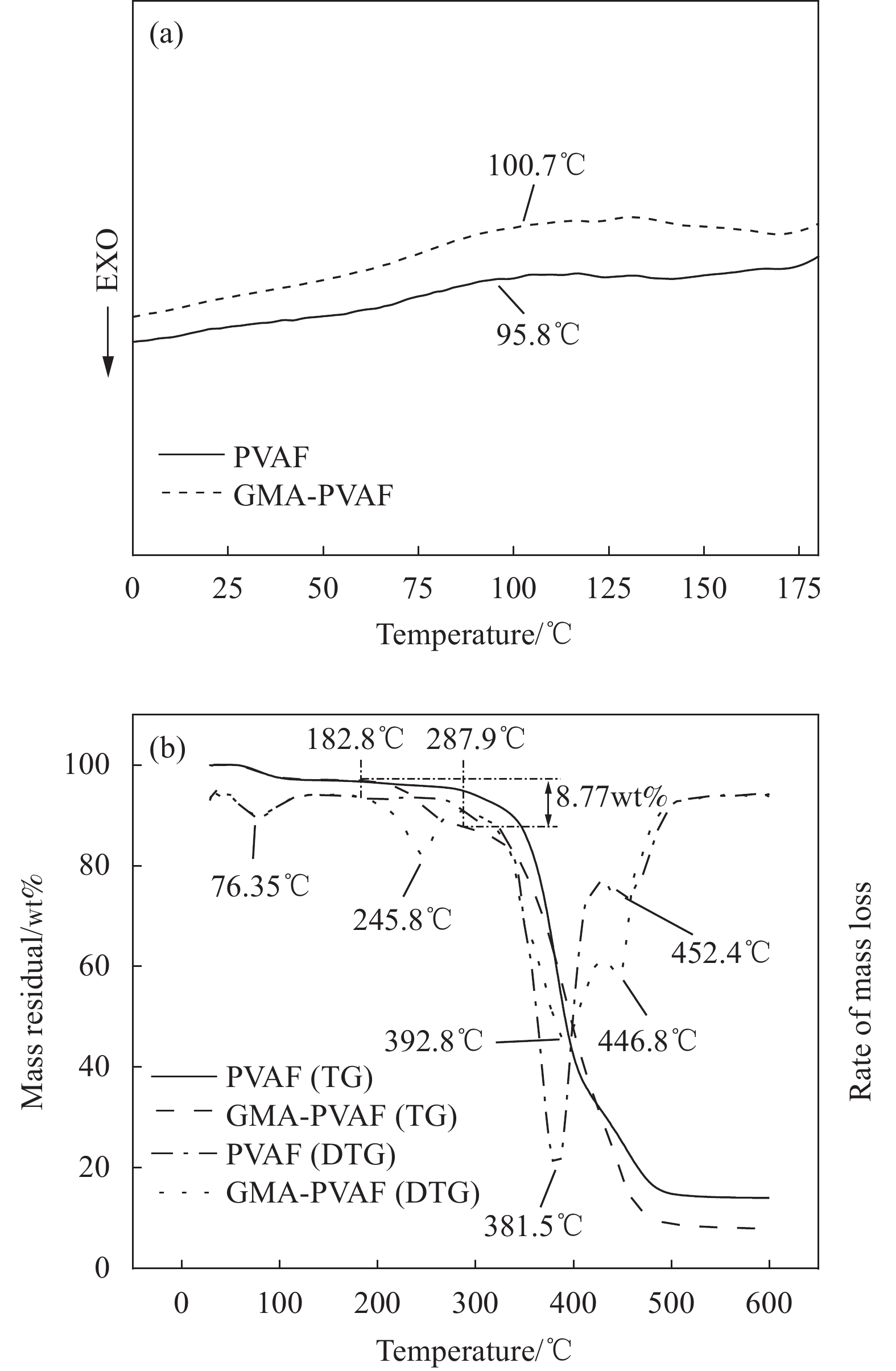
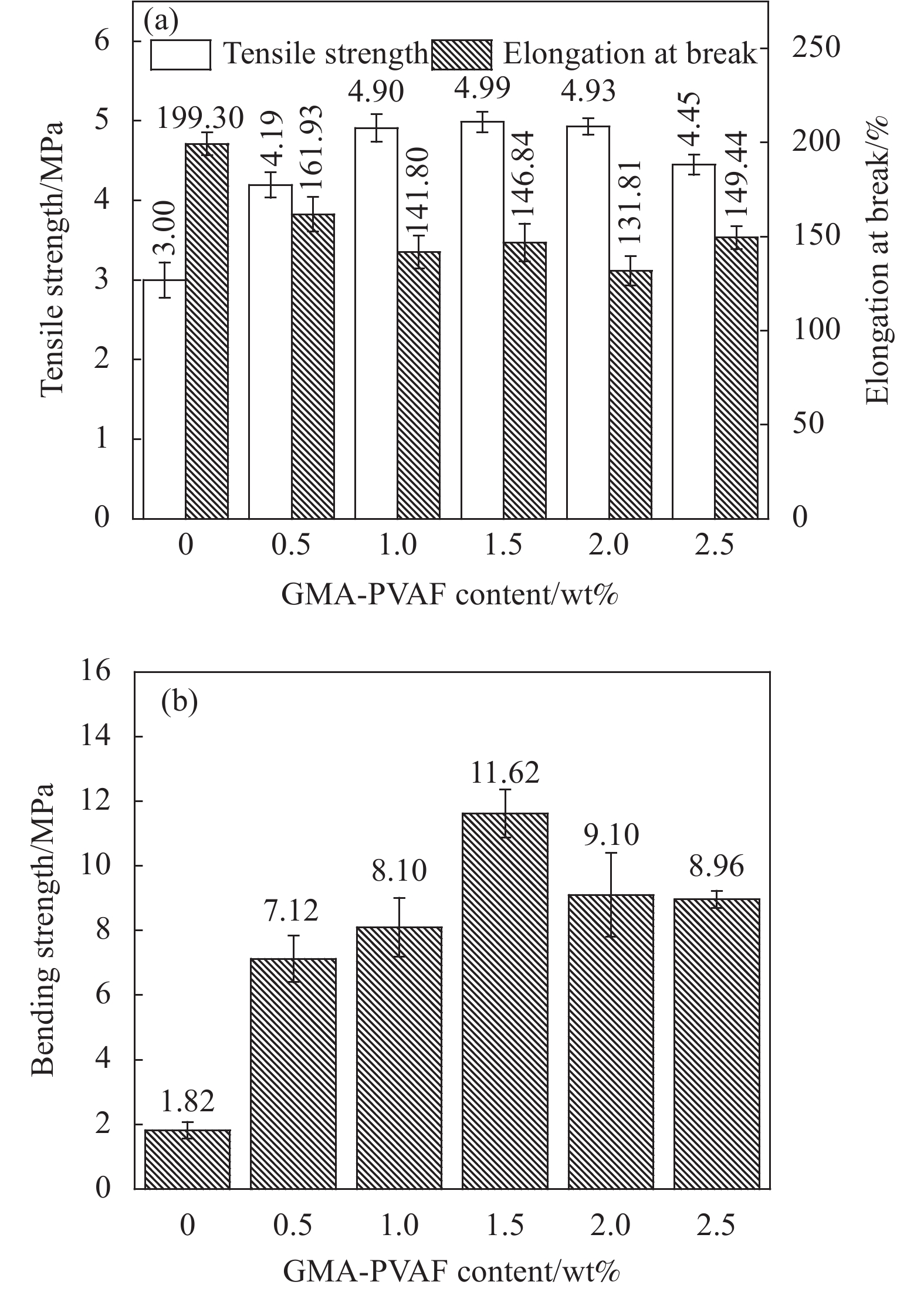
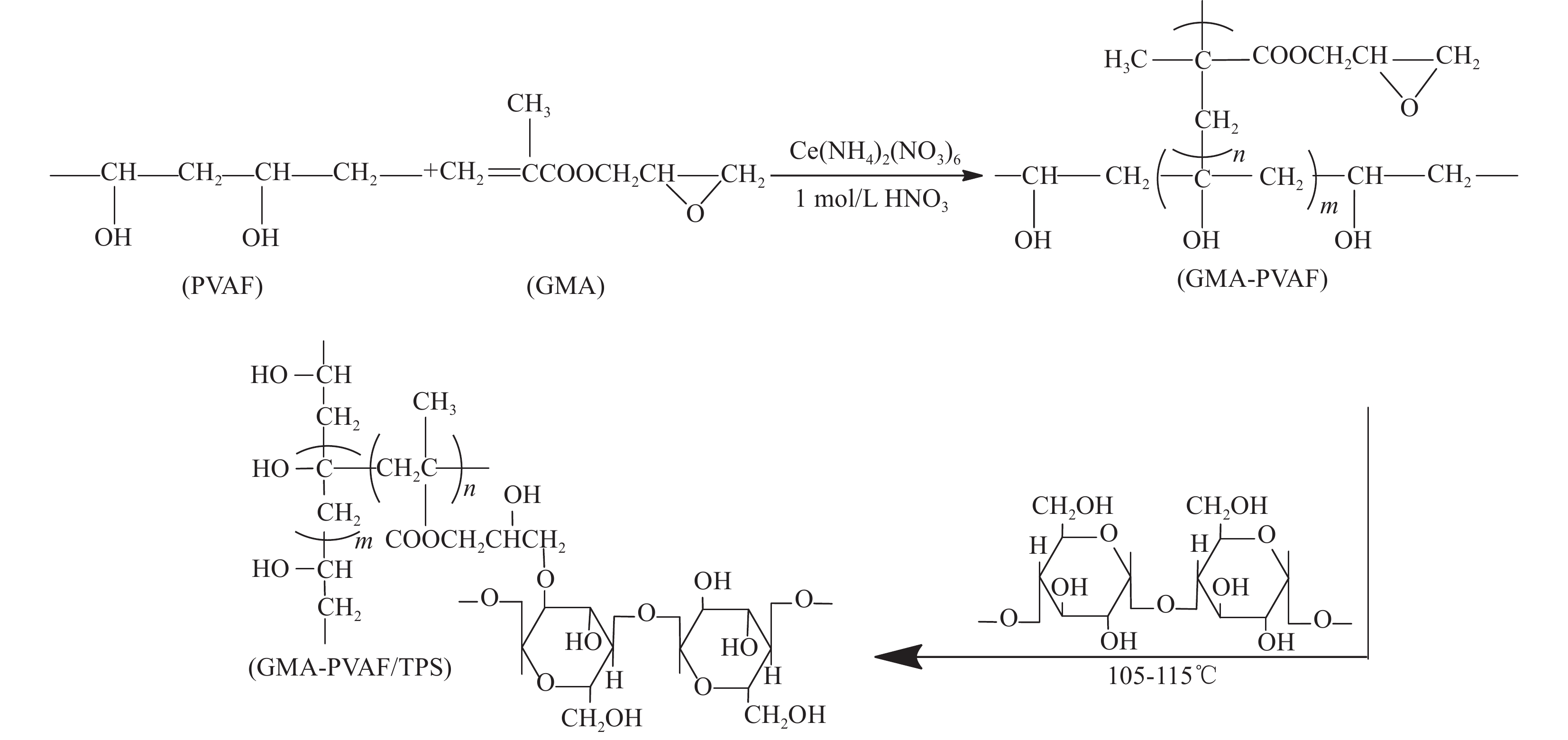
摘要: 以天然淀粉为原料制备的热塑性淀粉(TPS)具有可完全生物降解及与传统塑料类似的热塑加工性能,但力学性能和耐水性能较差限制了其发展。本文首先用含有环氧和乙烯基团的甲基丙烯酸缩水甘油酯(GMA)在可生物降解的聚乙烯醇纤维(PVAF)表面接枝改性,进一步经过双螺杆挤出加工过程,使淀粉大分子上的羟基和PVAF表面接枝GMA (GMA-PVAF)中的环氧基团发生化学反应,形成交联结构,从而提高热塑性淀粉塑料的力学性能。结果表明:GMA-PVAF出现了明显的包覆层,具有GMA中酯羰基和环氧基团的特征红外吸收峰,结晶度显著降低,玻璃化转变温度由95.8℃提高到100.7℃,热重分析计算表明包覆层质量分数约为8.77wt%;当GMA-PVAF的含量为1.5wt%时,复合材料GMA-PVAF/TPS的拉伸强度由纯TPS的3.00 MPa提高到4.99 MPa,断裂伸长率为146.84%,弯曲强度由1.82 MPa提高到11.62 MPa,力学性能显著提高。
-
关键词:
- 热塑性淀粉 /
- 聚乙烯醇纤维 /
- 甲基丙烯酸缩水甘油酯 /
- 力学性能 /
- 可生物降解
Abstract: Thermoplastic starch (TPS) prepared from natural starch has complete biodegradability and thermoplastic processability similar to traditional plastics, but its poor mechanical properties and water resistance limit its development. Biodegradable polyvinyl alcohol fiber (PVAF) was grafted onto its surface with glycyl methacrylate (GMA) containing epoxy and vinyl groups. In the process of twin-screw extrusion, the hydroxyl group on starch macromolecule reacted with the epoxy group of PVAF surface grafted with GMA (GMA-PVAF) to form a crosslinked structure, thus improving the mechanical properties of thermoplastic starch plastics. The results shows that GMA-PVAF shows obvious coating, which has the characteristic infrared absorption peaks of ester carbonyl group and epoxy group in GMA. The crystallinity decreases significantly, and the glass transition temperature (Tg) increases from 95.8℃ to 100.7℃. Thermogravimetric analysis shows that the mass fraction of coating is about 8.77wt%. When the content of GMA-PVAF is 1.5wt%, the tensile strength of GMA-PVAF/TPS composite increases from 3.00 MPa to 4.99 MPa, the elongation at break is 146.84%, the bending strength increases from 1.82 MPa to 11.62 MPa, and the mechanical properties are significantly improved. -
-
-
[1] 庄贵阳. 我国实现"双碳"目标面临的挑战及对策[J]. 人民论坛, 2021(18):50-53. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-3381.2021.18.012 ZHUANG Guiyang. Challenges and counter measures for China to achieve the goal of "double carbon"[J]. People's Tribune,2021(18):50-53(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1004-3381.2021.18.012
[2] 潘科, 徐海涛, 冯祥奕. "双碳"目标下我国新材料重点方向发展研究[J]. 信息通信技术与政策, 2022(3):74-81. PAN Ke, XU Haitao, FENG Xiangyi. Research on the development of key directions of new materials in China under the goal of "double carbon"[J]. Information and Communications Technology and Policy,2022(3):74-81(in Chinese).
[3] 扈蓉, 陈丽琼, 黄开胜, 等. 低碳生物基塑料研究进展[J]. 塑料科技, 2012, 40(2):94-98. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-3360.2012.02.017 HU Rong, CHEN Liqiong, HUANG Kaisheng, et al. Research progress of low carbon bio based plastics[J]. Plastics Science and Technology,2012,40(2):94-98(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-3360.2012.02.017
[4] 唐皞, 郭斌, 李本刚, 等. 热塑性淀粉的增强研究进展[J]. 塑料工业, 2013, 41(1):1-8, 28. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-5770.2013.01.001 TANG Hao, GUO Bin, LI Ben'gang, et al. Research progress on reinforcement of thermoplastic starch[J]. Plastic Industry,2013,41(1):1-8, 28(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-5770.2013.01.001
[5] 唐皞, 郭斌, 薛岚, 等. 增塑剂在热塑性淀粉中的应用研究进展[J]. 塑料工业, 2012, 40(7):1-4, 90. TANG Hao, GUO Bin, XUE Lan, et al. Research progress on the application of plasticizers in thermoplastic starch[J]. Plastic Industry,2012,40(7):1-4, 90(in Chinese).
[6] 查东东, 郭斌, 李本刚, 等. 热塑性淀粉耐水性的化学与物理作用机制[J]. 化学进展, 2019, 31(1):156-166. ZHA Dongdong, GUO Bin, LI Ben'gang, et al. Chemical and physical mechanism of water resistance of thermoplastic starch[J]. Chemical Progress,2019,31(1):156-166(in Chinese).
[7] 查东东, 周文, 银鹏, 等. 热塑性淀粉力学性能的提升途径及作用机理[J]. 化学进展, 2019, 31(7):1044-1055. DOI: 10.7536/PC181113 ZHA Dongdong, ZHOU Wen, YIN Peng, et al. Improving ways and mechanism of mechanical properties of thermoplastic starch[J]. Chemical Progress,2019,31(7):1044-1055(in Chinese). DOI: 10.7536/PC181113
[8] 周文, 张鑫, 马宏鹏, 等. 热塑性淀粉制备的化学与物理机制及方法[J]. 化学进展, 2021, 33(11):1972-1982. ZHOU Wen, ZHANG Xin, MA Hongpeng, et al. Chemical and physical mechanism and method of thermoplastic starch preparation[J]. Chemical Progress,2021,33(11):1972-1982(in Chinese).
[9] PAKRAVAN H R , JAMSHIDI M , LATIFI M. The effect of hydrophilic (polyvinyl alcohol) fiber content on the flexural behavior of engineered cementitious composites (ECC)[J]. Journal of the Textile Institute,2018,109(1):79-84.
[10] ZHAO Y, YANG X, ZHANG Q, et al. Crack resistance and mechanical properties of polyvinyl alcohol fiber-reinforced cement-stabilized macadam base[J]. Advances in Civil Engineering,2020,8(88):6564076.
[11] ZHU Y, LI H M, WU C X, et al. Preparation and characterisation of polyvinyl alcohol/nano-SiO2 composite fibre with high initial modulus[J]. Material Research Innovations,2015,18(S4):825-828.
[12] ALEXANDER R, DINKAR A, BISWAS S, et al. Comparative study of different carbon reinforcements at different length scales on the properties of polyvinyl alcohol composites[J]. Polymer Composites,2021,42(9):4239-4252. DOI: 10.1002/pc.26142
[13] ZHOU W, ZHA D, ZHANG X, et al. Ordered long polyvinyl alcohol fiber-reinforced thermoplastic starch composite having comparable mechanical properties with polyethylene and polypropylene[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2020,250(3):116913.
[14] YIN P, DONG X, ZHOU W, et al. A novel method to produce sustainable biocomposites based on thermoplastic corn-starch reinforced by polyvinyl alcohol fibers[J]. RSC Advances,2020,10(40):23632-23643. DOI: 10.1039/D0RA04523C
[15] JIANG L, LIU Z, HU K, et al. Preparation and properties of environment-friendly acrylic latex laminating adhesives applied in plastic/plastic composite films[J]. Journal of Adhesion Science and Technology,2019,33(1):2-17.
[16] DAFADER N C, RAHMAN N, MAJUMDAR S K, et al. Preparation and characterization of iminodiacetate group containing nonwoven polyethylene fabrics and its application in chromium adsorption[J]. Journal of Polymers and the Environment,2018,26(2):740-748. DOI: 10.1007/s10924-017-0991-8
[17] RANDALL J D, EYCKENS D J, SARLIN E, et al. Mixed surface chemistry on carbon fibers to promote adhesion in epoxy and PMMA polymers[J]. Industrial & Engineering Chemistry Research,2022,61(4):1615-1623.
[18] 柯勇, 沈一丁, 费贵强, 等. GMA改性水溶性PVA纤维的制备及其对纸张增强作用[J]. 精细化工, 2013, 30(11):1247-1251. DOI: 10.13550/j.jxhg.2013.11.011 KE Yong, SHEN Yiding, FEI Guiqiang, et al. Preparation of GMA modified water-soluble PVA fiber and its strengthening effect on paper[J]. Fine Chemicals,2013,30(11):1247-1251(in Chinese). DOI: 10.13550/j.jxhg.2013.11.011
[19] 柯勇, 沈一丁, 费贵强, 等. 甲基丙烯酸缩水甘油酯对水溶性聚乙烯醇纤维的表面改性及增强机理[J]. 高分子材料科学与工程, 2013, 29(12):103-106. KE Yong, SHEN Yiding, FEI Guiqiang, et al. Surface modification and reinforcing mechanism of water soluble polyvinyl alcohol fiber by glycidyl methacrylate[J]. Polymeric Materials Science and Engineering,2013,29(12):103-106(in Chinese).
[20] 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 塑料 拉伸性能的测定 第一部分: 总则: GB/T 1040.1—2018[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2018. Standardization Administration of the People's Republic of China. Plastics—Determination of tensile properties—Part 1: General principles: GB/T 1040.1—2018[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2018(in Chinese).
[21] 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 塑料 弯曲性能的测定: GB/T 9341—2008[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2008. Standardization Administration of the People's Republic of China. Plastics—Determination of flexural properties: GB/T 9341—2008[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2008(in Chinese).
[22] 柯勇. 悬浮接枝共聚改性聚乙烯醇纤维的制备及应用[D]. 陕西: 陕西科技大学, 2014. KE Yong. Preparation and application of polyvinyl alcohol fiber modified by suspension graft copolymerization[D]. Shaanxi: Shaanxi University of Science & Technology, 2014(in Chinese).
[23] QU L J, GUO X Q, TIAN M W, et al. Antimicrobial fibers based on chitosan and polyvinyl-alcohol[J]. Fibers & Polymers,2014,15(7):1357-1363.
[24] FAN L, DU Y, WANG X, et al. Preparation and characterization of alginate/poly(vinyl alcohol) blend fibers[J]. Jour-nal of Macromolecular Science Part A,2007,42(1):41-50.
[25] FADIL F, ADLI F A, AFFANDI N, et al. Dope-dyeing of polyvinyl alcohol (PVA) nanofibres with remazol yellow FG[J]. Polymers,2020,12(12):3043. DOI: 10.3390/polym12123043
-




 下载:
下载: