Strength and pore characteristics of highland barley straw ash-magnesium oxychloride cement composite under salt freezing coupling damage
-
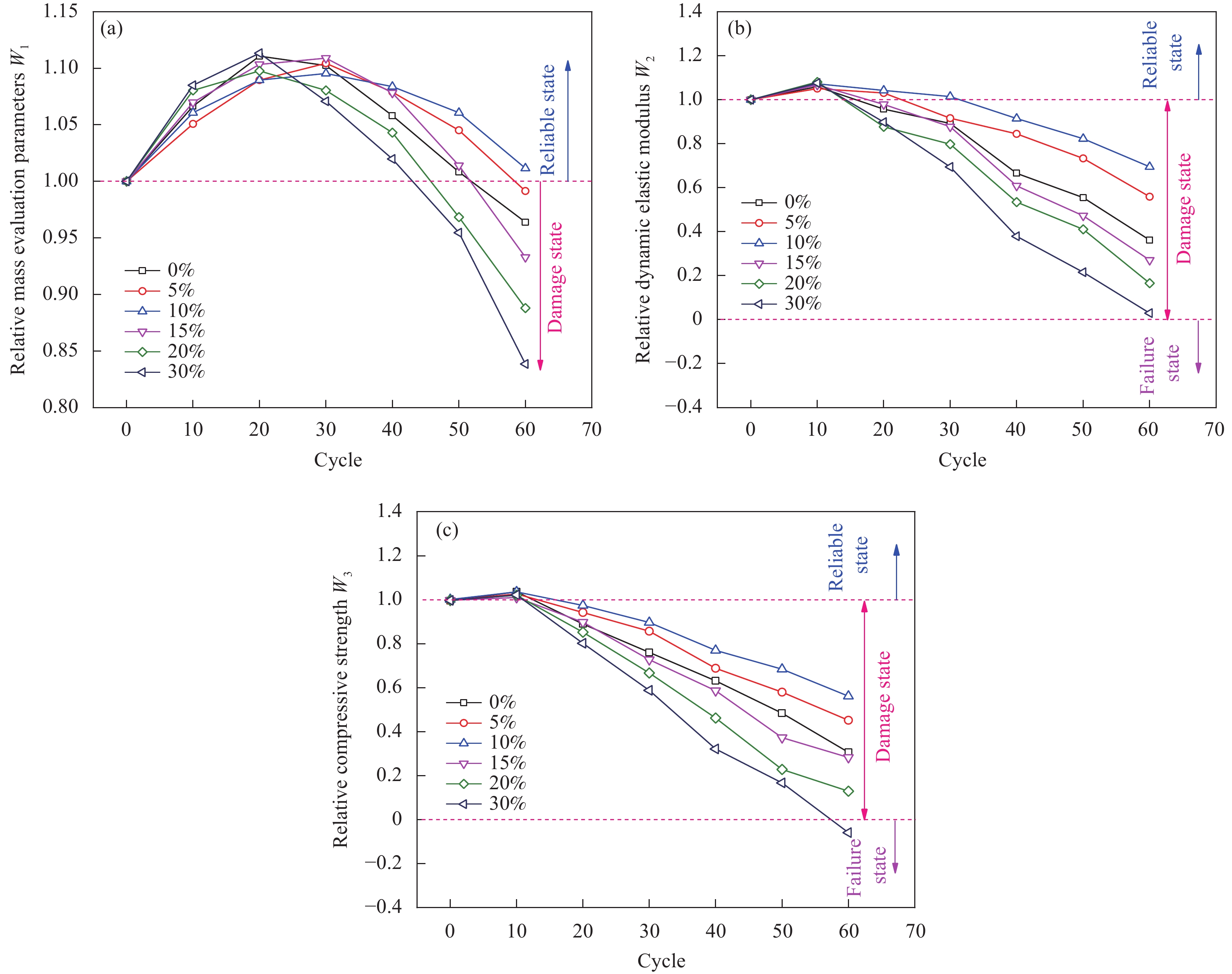
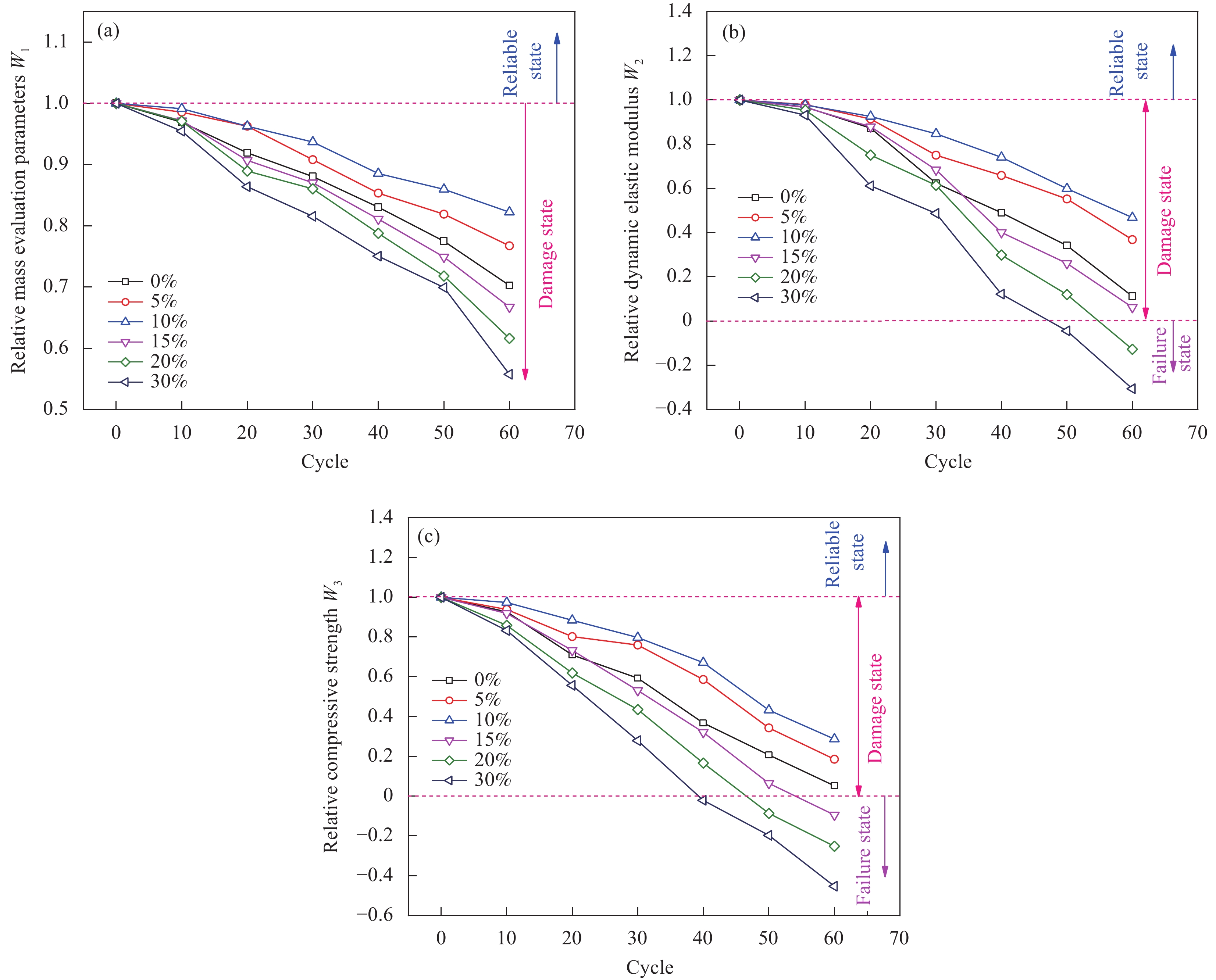
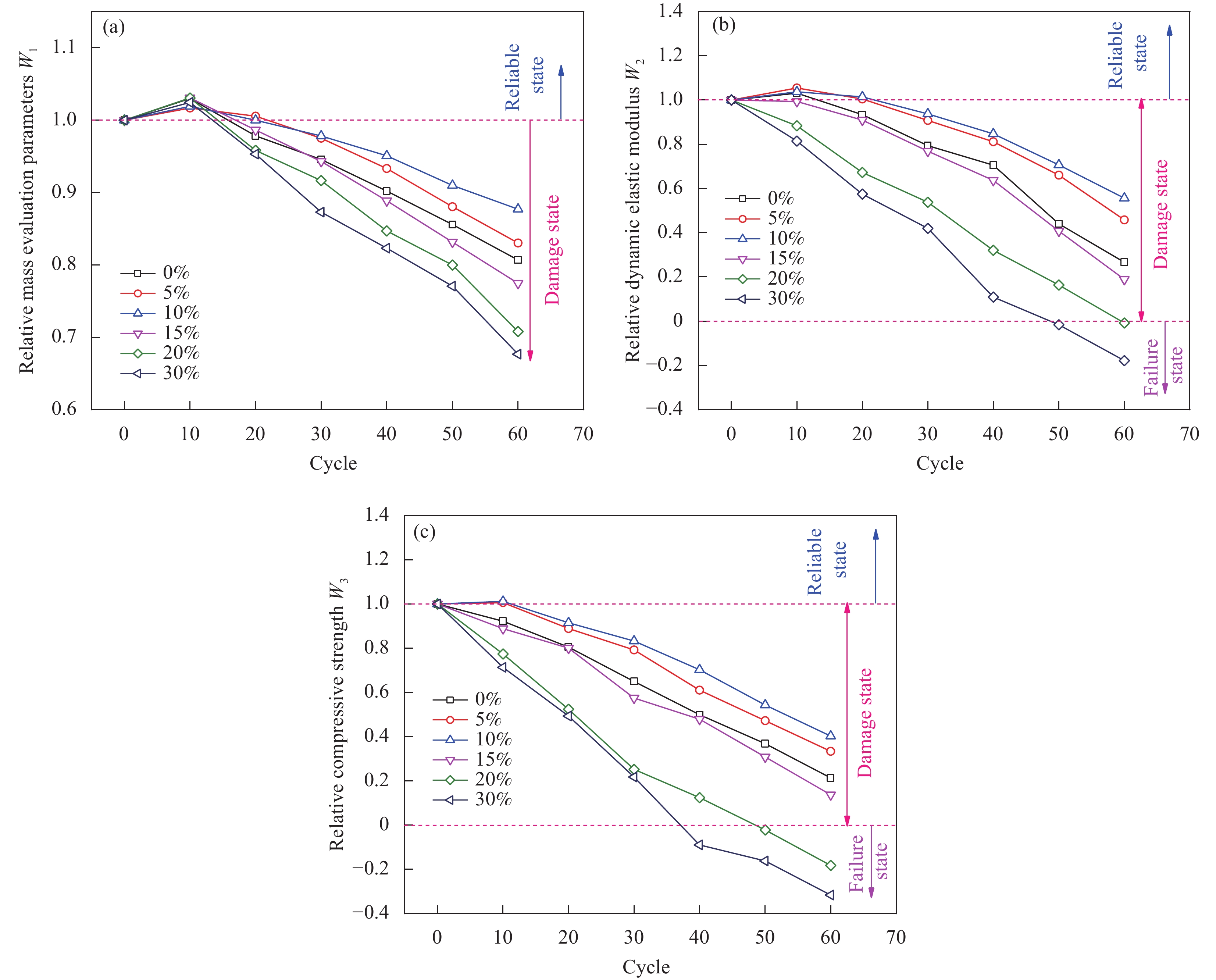
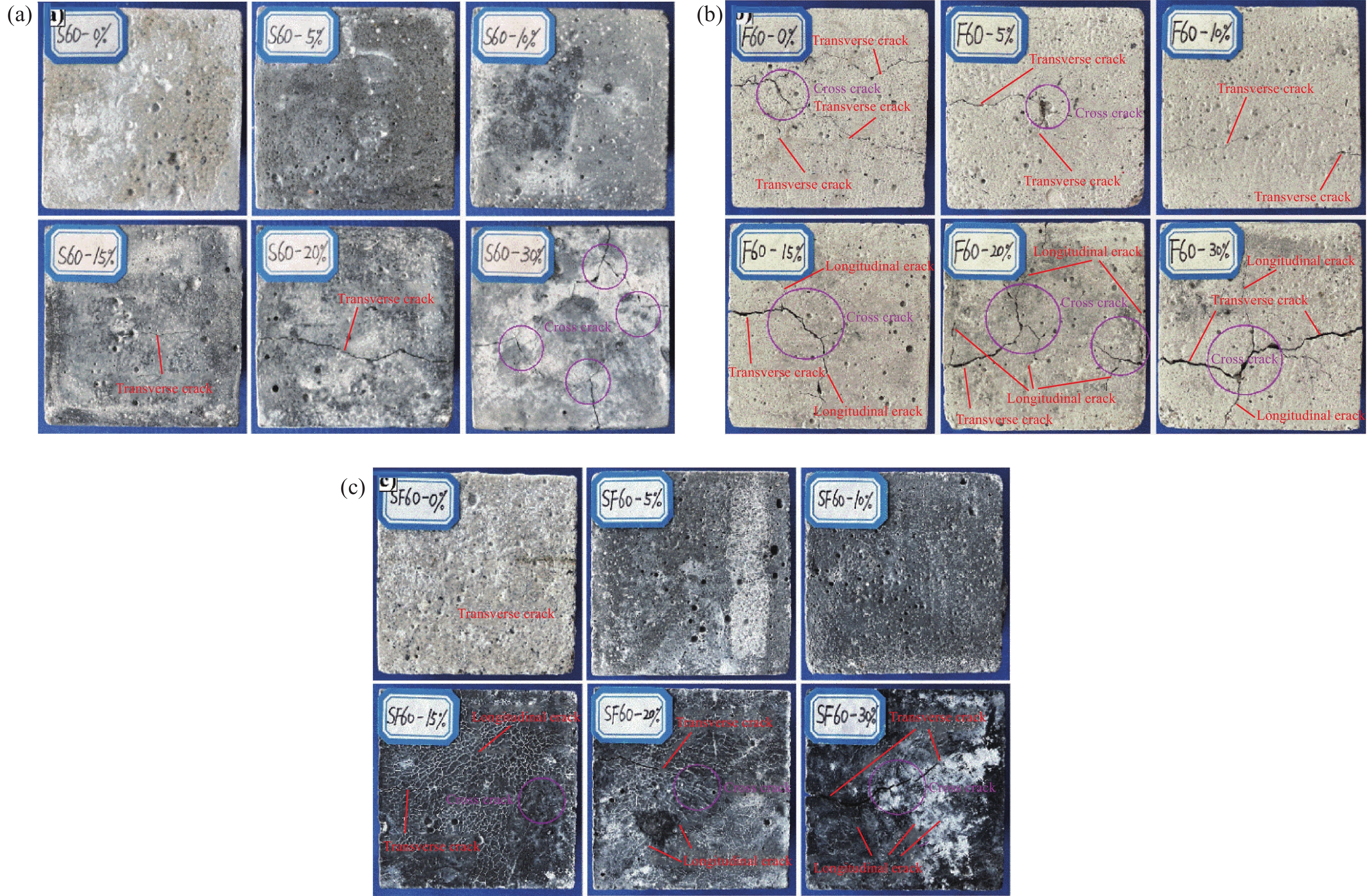
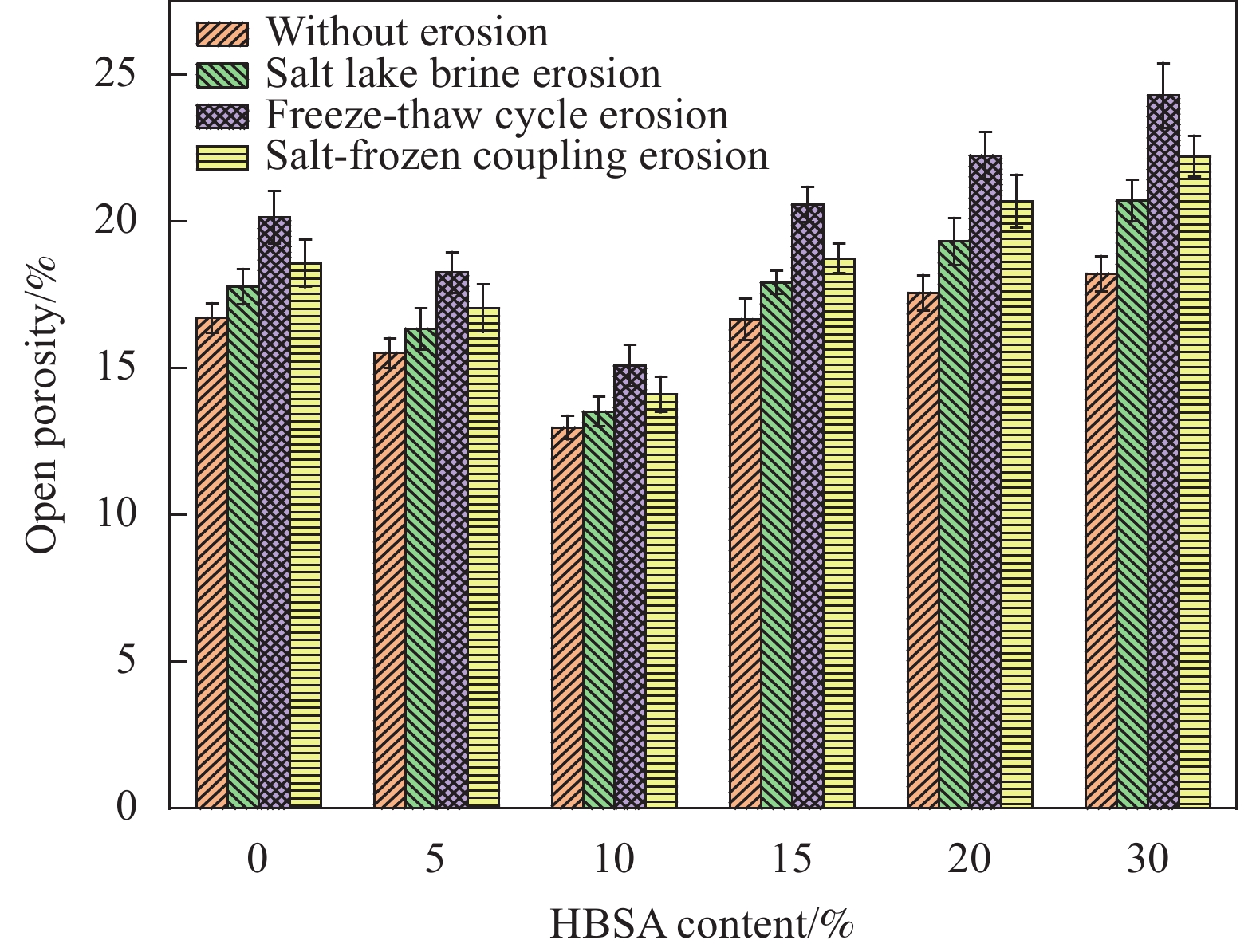
摘要: 为探究掺入青稞秸秆灰(HBSA)对氯氧镁水泥(MOC)的耐久性能与孔隙结构的影响,采用HBSA来改善MOC的耐久性能,制备青稞秸秆灰-氯氧镁水泥复合材料。对不同HBSA掺量的氯氧镁水泥砂浆(MOCM)分别在盐湖卤水侵蚀、冻融循环侵蚀及盐冻耦合侵蚀条件下的耐久性能进行研究,采用相对质量评价参数、相对动弹性模量评价参数及相对抗压强度评价参数3种耐久性评价指标来反映MOCM的耐久性能劣化规律,并确定HBSA的最佳掺量。通过表观形貌分析及孔隙结构测试,揭示不同侵蚀环境下MOCM的耐久性损伤劣化程度及孔隙结构特征。结果表明:冻融循环侵蚀对MOCM造成的耐久性损伤程度比盐卤侵蚀及盐冻耦合侵蚀更严重,MOCM试件表面产生了更多的宏观裂缝。HBSA掺入能够显著改善MOCM的耐久性能。当HBSA掺量为10wt%时,MOCM在盐湖卤水侵蚀、冻融循环侵蚀及盐冻耦合侵蚀条件下的耐久性能分别比未掺HBSA时提高了21.24%、23.48%和18.91%。掺入10wt%HBSA的MOCM的开口孔隙率减小,比表面积增大,最可几孔径和平均孔径减小,细化了MOCM的孔隙结构,提高了耐久性能。
-
关键词:
- 氯氧镁水泥(MOC) /
- 青稞秸秆灰(HBSA) /
- 耐久性能 /
- 表观形貌 /
- 开口孔隙率 /
- 孔隙特征
Abstract: In order to explore the effect of highland barley straw ash (HBSA) on the durability and pore structure of magnesium oxychloride cement (MOC), HBSA was used to improve the durability of MOC, and highland barley straw ash–magnesium oxychloride cement composites were prepared. The durability of magnesium oxychloride cement mortar (MOCM) with different HBSA contents were studied under the conditions of salt lake brine erosion, freeze-thaw cycle erosion and salt–frozen coupling erosion. Three durability evaluation indexes: Relative mass evaluation parameters, relative dynamic elastic modulus evaluation parameters and relative compressive strength evaluation parameters were used to reflect the durability deterioration law of MOCM, and determine the optimal content of HBSA. Through the analysis of apparent morphology and pore structure test, the durability damage degree and pore structure characteristics of MOCM under different erosion conditions were revealed. The results show that the durability damage of MOCM caused by freeze-thaw cycle erosion is more serious than salt brine erosion and salt-frozen coupling erosion, and more macro cracks are produced on the surface of MOCM specimens. The addition of HBSA can significantly improve the durability of MOCM. When the content of HBSA is 10wt%, the durability of MOCM under salt lake brine erosion, freeze-thaw cycle erosion and salt–frozen coupling erosion is 21.24%, 23.48% and 18.91% higher than that without HBSA, respectively. The opening porosity of MOCM added with 10wt%HBSA decreases, the specific surface area increases, and the most probable pore diameter and average pore diameter decrease, which refines the pore structure of MOCM and improves the durability. -
-
表 1 HBSA的化学成分
Table 1 Chemical compositions of HBSA
wt% SiO2 CaO SO3 MgO Al2O3 Fe2O3 K2O Na2O P2O5 Others 61.75 10.63 1.75 2.04 5.92 3.83 5.31 2.60 5.72 0.44 表 2 HBSA-氯氧镁水泥砂浆(MOCM)的配合比
Table 2 Mix ratios of HBSA-magnesium oxychloride cement mortar (MOCM)
(kg/m3) MgO MgCl2 Sand Superplasticizer Water repellent Water HBSA 583.4 221.7 937.5 16.0 6.9 203.4 0 211.7 29.2 220.0 58.3 228.4 87.5 236.7 116.7 253.2 175.0 表 3 HBSA-MOCM试件的编号
Table 3 Specimen number of HBSA-MOCM
Specimen number Cycle HBSA/wt% Specimen number Cycle HBSA/wt% 0%HBSA-MOCM(N0) 0 0 10%HBSA-MOCM(N0) 0 10 0%HBSA-MOCM(S60) 60 0 10%HBSA-MOCM(S60) 60 10 0%HBSA-MOCM(F60) 60 0 10%HBSA-MOCM(F60) 60 10 0%HBSA-MOCM(SF60) 60 0 10%HBSA-MOCM(SF60) 60 10 Notes: N stands for the specimen without erosion; S represents the specimen eroded by salt lake brine; F represents the specimen eroded by freeze-thaw cycle; SF represents the specimen eroded by salt-frozen coupling. 表 4 盐湖卤水的主要离子浓度 (g/L)
Table 4 Concentration of main ions in salt lake brine (g/L)
K++Na+ Ca2+ Mg2+ Cl− SO42− HCO3− TDS pH 83.25 52.78 52.71 128.22 137.60 0.12 457.68 7.60 Note: TDS—Total soluble solid content in salt lake brine. 表 5 HBSA-MOCM的比表面积计算结果
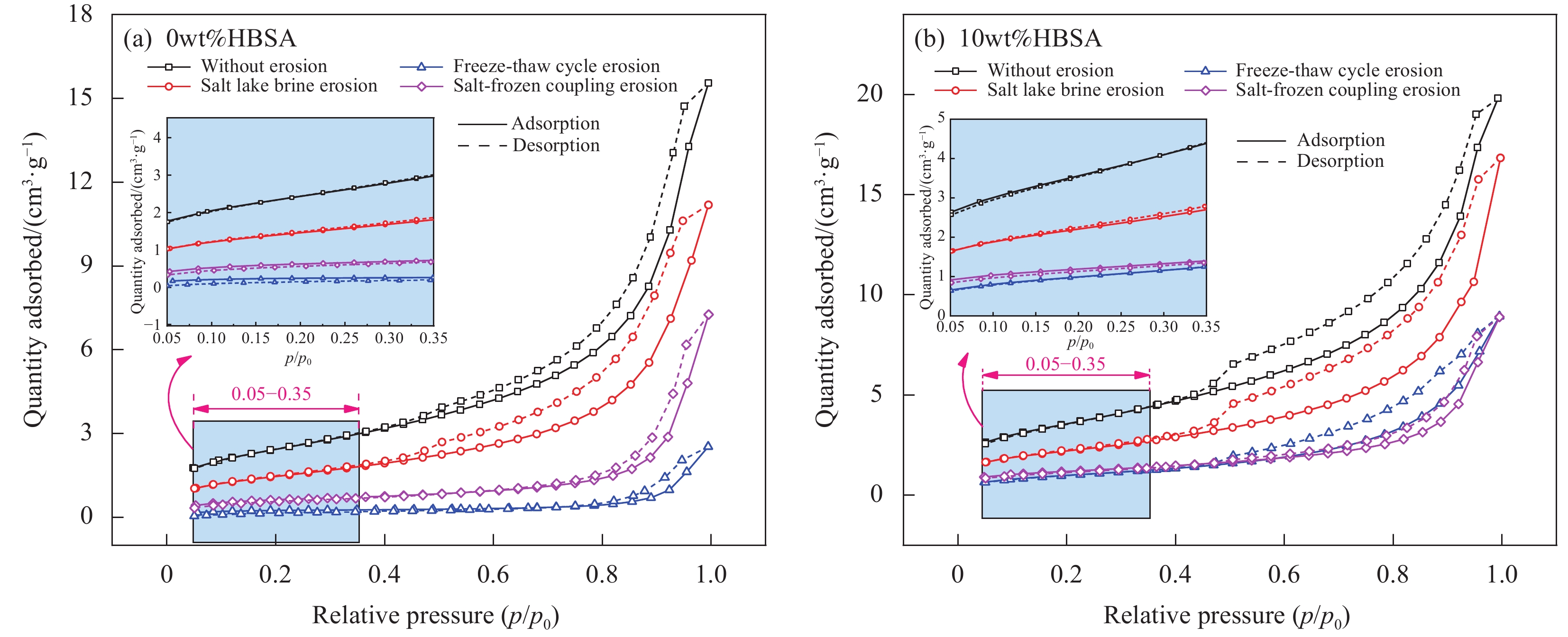
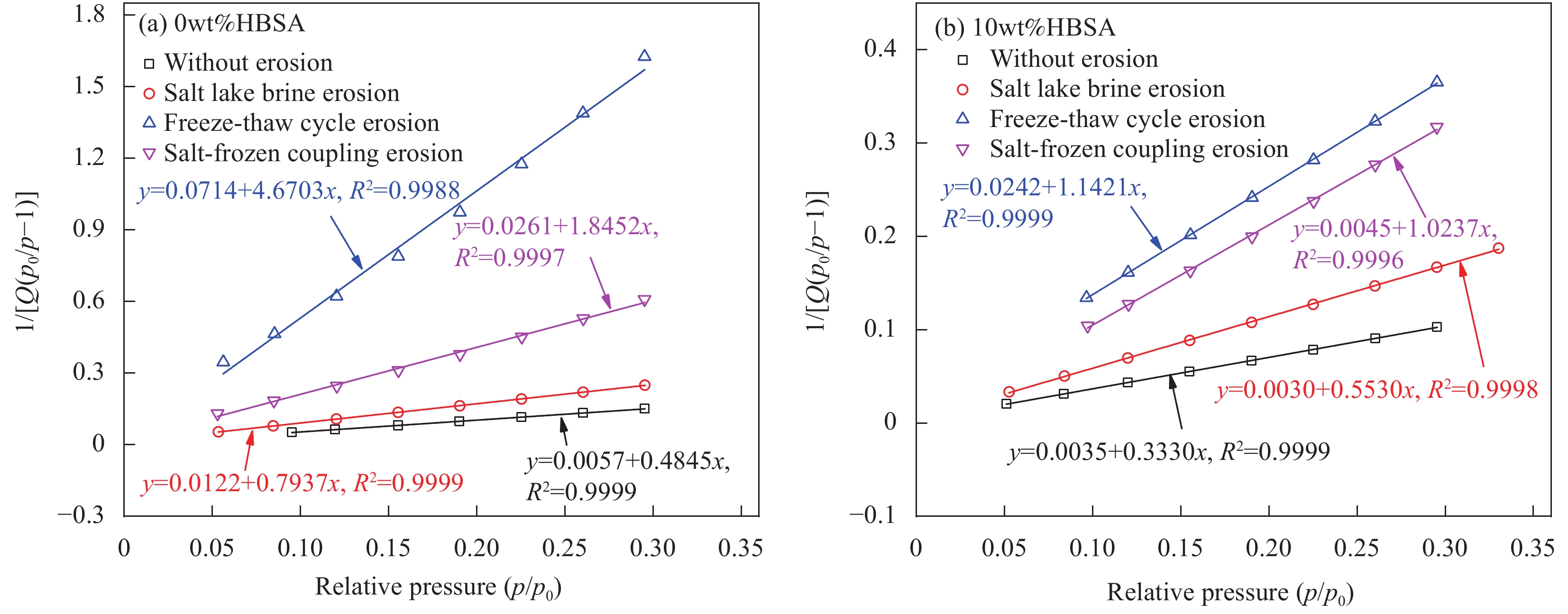
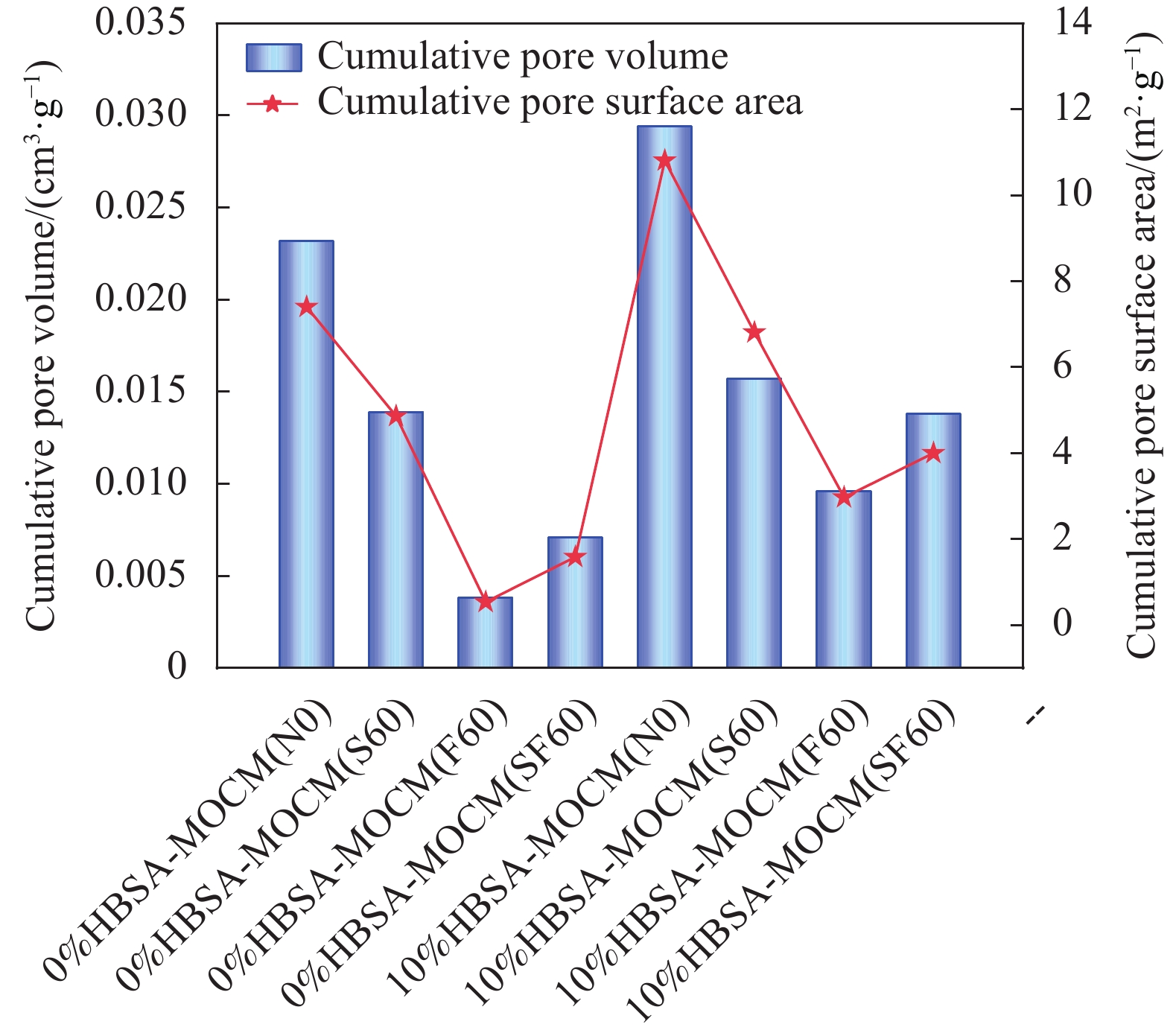
Table 5 Calculation results of specific surface area of HBSA-MOCM
Specimen number Vm/(cm3·g−1) C SSA/(m2·g−1) Specimen number Vm/(cm3·g−1) C SSA/(m2·g−1) 0%HBSA-MOCM(N0) 2.04 86.60 8.88 10%HBSA-MOCM(N0) 2.97 95.34 12.93 0%HBSA-MOCM(S60) 1.24 66.19 5.40 10%HBSA-MOCM(S60) 1.80 159.03 7.41 0%HBSA-MOCM(F60) 0.21 66.44 0.92 10%HBSA-MOCM(F60) 0.86 48.25 3.73 0%HBSA-MOCM(SF60) 0.53 71.57 2.33 10%HBSA-MOCM(SF60) 0.97 227.62 4.23 Notes: Vm—Amount of gas required to complete monolayer adsorption on the surface; C—Constant; SSA—Specific surface area. 表 6 HBSA-MOCM试件的各类孔径测试结果
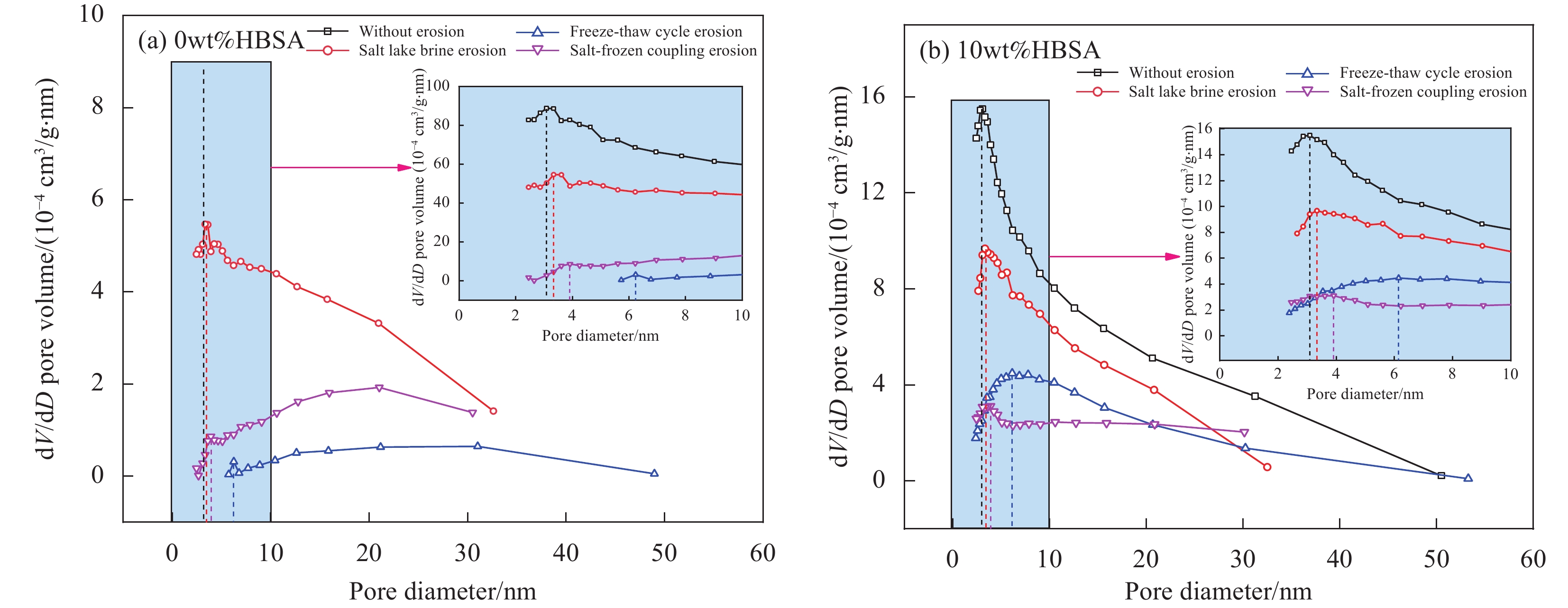
Table 6 Test results of various pore diameters of HBSA-MOCM specimens
nm Specimen number da db dm dw Specimen number da db dm dw 0%HBSA-MOCM(N0) 3.13 16.21 12.54 0.724 10%HBSA-MOCM(N0) 3.06 15.57 10.86 0.722 0%HBSA-MOCM(S60) 3.52 17.78 15.55 0.730 10%HBSA-MOCM(S60) 3.33 16.66 11.23 0.725 0%HBSA-MOCM(F60) 6.31 27.57 21.92 0.749 10%HBSA-MOCM(F60) 6.12 22.69 13.72 0.737 0%HBSA-MOCM(SF60) 3.96 21.95 17.94 0.738 10%HBSA-MOCM(SF60) 3.88 20.79 12.95 0.732 Notes: da—Most probable pore diameter (≤10 nm); db—Most probable pore diameter (>10 nm); dm—Average pore diameter; dw—Average pore width. -
[1] WU D Y, YU L W, GUO L, et al. Effect of highland barley on rheological properties, textural properties and starch digestibility of chinese steamed bread[J]. Foods,2022,11(8):1091-1109. DOI: 10.3390/foods11081091
[2] 白婷, 靳玉龙, 朱明霞, 等. 西藏地区不同青稞品种秸秆饲用品质分析[J]. 饲料工业, 2019, 40(12):59-64. DOI: 10.13302/j.cnki.fi.2019.12.011 BAI Ting, JIN Yulong, ZHU Mingxia, et al. Analysis of feeding quality of highland barley cultivars in Tibet[J]. Feed Industry,2019,40(12):59-64(in Chinese). DOI: 10.13302/j.cnki.fi.2019.12.011
[3] 李海朝, 徐贵钰, 汪航. 青稞秸秆化学成分及纤维形态研究[J]. 生物质化学工程, 2010, 44(2):40-42. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5854.2010.02.010 LI Haichao, XU Guiyu, WANG Hang. Research on chemical composition and fiber morphology of barley straw[J]. Biomass Chemical Engineering,2010,44(2):40-42(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-5854.2010.02.010
[4] OBADI M, QI Y J, XU B. Highland barley starch (Qingke): Structures, properties, modifications, and applications[J]. International Journal of Biological Macromolecules,2021,185:725-738. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijbiomac.2021.06.204
[5] ZHANG T W, WANG Q, LI J R, et al. Study on the origin traceability of Tibet highland barley (Hordeum vulgare L) based on its nutrients and mineral elements[J]. Food Chemistry,2021,346:128928.
[6] TOOPER B, CARTZ L. Structure and formation of magnesium oxychloride sorel cements[J]. Nature,1966,211:64-66. DOI: 10.1038/211064a0
[7] LI K, WANG Y S, YAO N N, et al. Recent progress of magnesium oxychloride cement: Manufacture, curing, structure and performance[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2020,255:119381. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.119381
[8] LI R Q, LIU C L, JIAO P C, et al. The present situation, existing problems, and countermeasures for exploitation and utilization of low-grade potash minerals in Qarhan Salt Lake, Qinghai Province, China[J]. Carbonates Evaporites,2020,35(10):128-145.
[9] 肖学英, 郑卫新, 黄青, 等. 抗腐性氯氧镁水泥混凝土在高寒、高盐渍地区的研究及应用[J]. 盐湖研究, 2018, 26(3):7-13. XIAO Xueying, ZHENG Weixin, HUANG Qing, et al. Study and application of anti-corrosion magnesium oxychloride cement concrete in high cold and high salinity areas[J]. Journal of Salt Lake Research,2018,26(3):7-13(in Chinese).
[10] SCRIVENER K L, JOHN V M, GARTNER E M. Eco-efficient cements: Potential economically viable solutions for a low-CO2 cement-based materials industry[J]. Cement and Concrete Research,2018,114:2-26.
[11] 王健, 肖俊华, 左迎峰, 等. 秸秆/氯氧镁水泥无机轻质复合材料制备与性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2018, 35(11):3162-3171. WANG Jian, XIAO Junhua, ZUO Yingfeng, et al. Preparation and properties of straw/magnesium oxychloride cement inorganic light mass composites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinaca,2018,35(11):3162-3171(in Chinese).
[12] AVANISH S, RAKESH K, PANKAJ G. Factors influencing strength of magnesium oxychloride cement[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2021,303:124571.
[13] GUO Y Y, ZHANG Y X, SOE K. Effect of sodium monofluorophosphate and phosphates on mechanical properties and water resistance of magnesium oxychloride cement[J]. Cement and Concrete Composites,2022,129:104472.
[14] 李学梅, 王继辉, 翁睿, 等. EVA乳胶液对纤维增强氯氧镁水泥界面性能的影响[J]. 复合材料学报, 2003(4):67-71. LI Xuemei, WANG Jihui, WENG Rui, et al. Effect of EVA emulsoid on the interfacial strength of the glass fiber reinforced magnesium oxychloride cement composites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinaca,2003(4):67-71(in Chinese).
[15] HUANG Q, ZHENG W X, XIAO X Y, et al. A study on the salt attack performance of magnesium oxychloride cement in different salt environments[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2022,320:126224.
[16] YAN Z B, YANG P W, HUANG J X, et al. Promoting effect and mechanism of several inorganic salts on hydration reaction of magnesium oxychloride cement at low tempera-ture[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2022,317:126171.
[17] ZHONG D Q, WANG S G, GAO Y, et al. Experimental study on freeze-thaw resistance of modified magnesium oxychloride cement foam concrete[J]. Journal of Physics: Conference Series,2021,1885:032009.
[18] HUANG Q, WEN J, LI Y, et al. The effect of silica fume on the durability of magnnesium oxychloride cement[J]. Ceramics-Silikáty,2019,63(3):338-346.
[19] ZHONG D Q, WANG S G, GAO Y, et al. Influence of rubber powder modification methods on the mechanical and durability properties of rubberized magnesium oxychloride cement[J]. Crystals,2021,11:1323-1336.
[20] MA C, CHEN G G, GAO L, et al. Effects and mechanisms of waste gypsum influencing the mechanical properties and durability of magnesium oxychloride cement[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production,2022,339:130679.
[21] CAO F, QIAO H X, LI Y K, et al. Effect of highland barley straw ash admixture on properties and microstructure of concrete[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2022,315:125802.
[22] 曹锋, 谭镇, 乔宏霞, 等. 青稞秸秆灰掺入氯氧镁水泥中的活性与作用机理[J]. 功能材料, 2021, 52(12):12196-12202, 12209. CAO Feng, TAN Zhen, QIAO Hongxia, et al. Activity and mechanism of highland barley straw ash added into magnesium oxychloride cement[J]. Journal of Functional Materials,2021,52(12):12196-12202, 12209(in Chinese).
[23] WANG J J, LIU E G. Upcycling waste seashells with cement: Rheology and early-age properties of portland cement paste[J]. Resources, Conservation & Recycling,2020,155(C):104680.
[24] XIE J H, HUANG L, GUO Y C, et al. Experimental study on the compressive and flexural behaviour of recycled aggre-gate concrete modified with silica fume and fibres[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2018,178:612-623.
[25] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 建筑砂浆基本性能试验方法标准: JGJ/T 70—2009[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2009. Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People's Republic of China. Standard for test method of basic properties of construction mortar: JGJ/T 70—2009[S]. Beijing: China Building Industry Press, 2009(in Chinese).
[26] 乔宏霞, 麻红卫, 王金磊, 等. 干燥和浸水环境下基于无损检测方法的镁水泥砼最佳配合比研究[J]. 硅酸盐通报, 2017, 36(4):1258-1265. QIAO Hongxia, MA Hongwei, WANG Jinlei, et al. Optimum mix ratio of magnesium cement concrete based on nondestructive testing method under different environment[J]. Bulletin of the Chinese Ceramic Society,2017,36(4):1258-1265(in Chinese).
[27] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 混凝土物理力学性能试验方法标准: GB/T 50081[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2019. Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People's Republic of China. Standard for test method of concrete physical and mechanical properties: GB/T 50081[S]. Beijing: China Building Industry Press, 2019(in Chinese).
[28] MANTELLATO S, PALACIONS M, FLATT R J. Reliable specific surface area measurements on anhydrous cements[J]. Cement and Concrete Research,2015,67:286-291.
[29] 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 压汞法和气体吸附法测定固体材料孔径分布和孔隙度 第2部分: 气体吸附法分析介孔和大孔: GB/T 21650.2[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2008. Standardization Administration of China. Pore size distribution and porosity of solid materials by mercury porosimetry and gas adsorption-Part 2: Analysis of mesopores and macropores by gas adsorption: GB/T 21650.2[S]. Beijing: China Building Industry Press, 2008(in Chinese).
[30] PANG Y, WANG S, YAO X Y, et al. Evaluation of gas adsorption in nanoporous shale by simplified local density model integrated with pore structure and pore size distribution[J]. Langmuir,2022,38:3641-3655.
[31] 陈金妹, 谈萍, 王建永. 气体吸附法表征多孔材料的比表面积及孔结构[J]. 粉末冶金工业, 2011, 21(2):45-49. CHEN Jinmei, TAN Ping, WANG Jianyong. Characterization of pore structure and specific surface area based on gas adsorption applied for porous materials[J]. Powder Metallurgy Industry,2011,21(2):45-49(in Chinese).
[32] WANG J, LIU M, WANG Y, et al. Synergistic effects of nano-silica and fly ash on properties of cement-based compo-sites[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2020,262:120737.
[33] BERNARD E, LOTHENBACH B, CHLIQUE C, et al. Characterization of magnesium silicate hydrate (M-S-H)[J]. Cement and Concrete Research,2019,116:309-330.
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 柯俊,李志虎,秦玉林. 金属主簧-复合材料副簧复合刚度计算模型. 汽车实用技术. 2021(05): 39-43 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 曾婷,王咏莉,尹忠旺,苏婷慧,师志峰,饶猛. 端面凸轮下压机构支承轴承冲击失效分析及优化(英文). 机床与液压. 2017(24): 37-42 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(5)
-





 下载:
下载: