Effect of substrate surface defect on the microstructure and photocatalytic activities of TiO2/Bi2WO6 composites
-
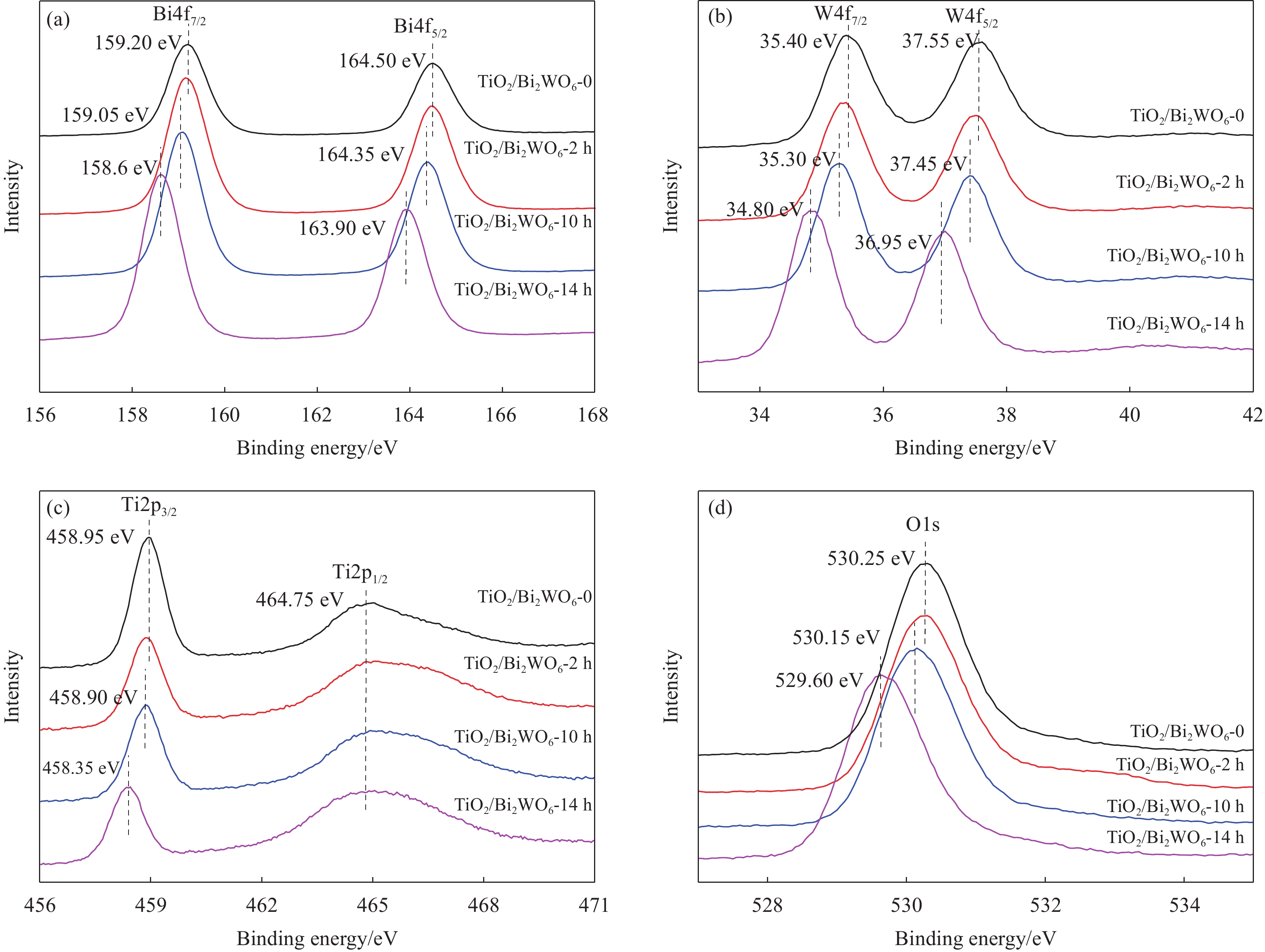
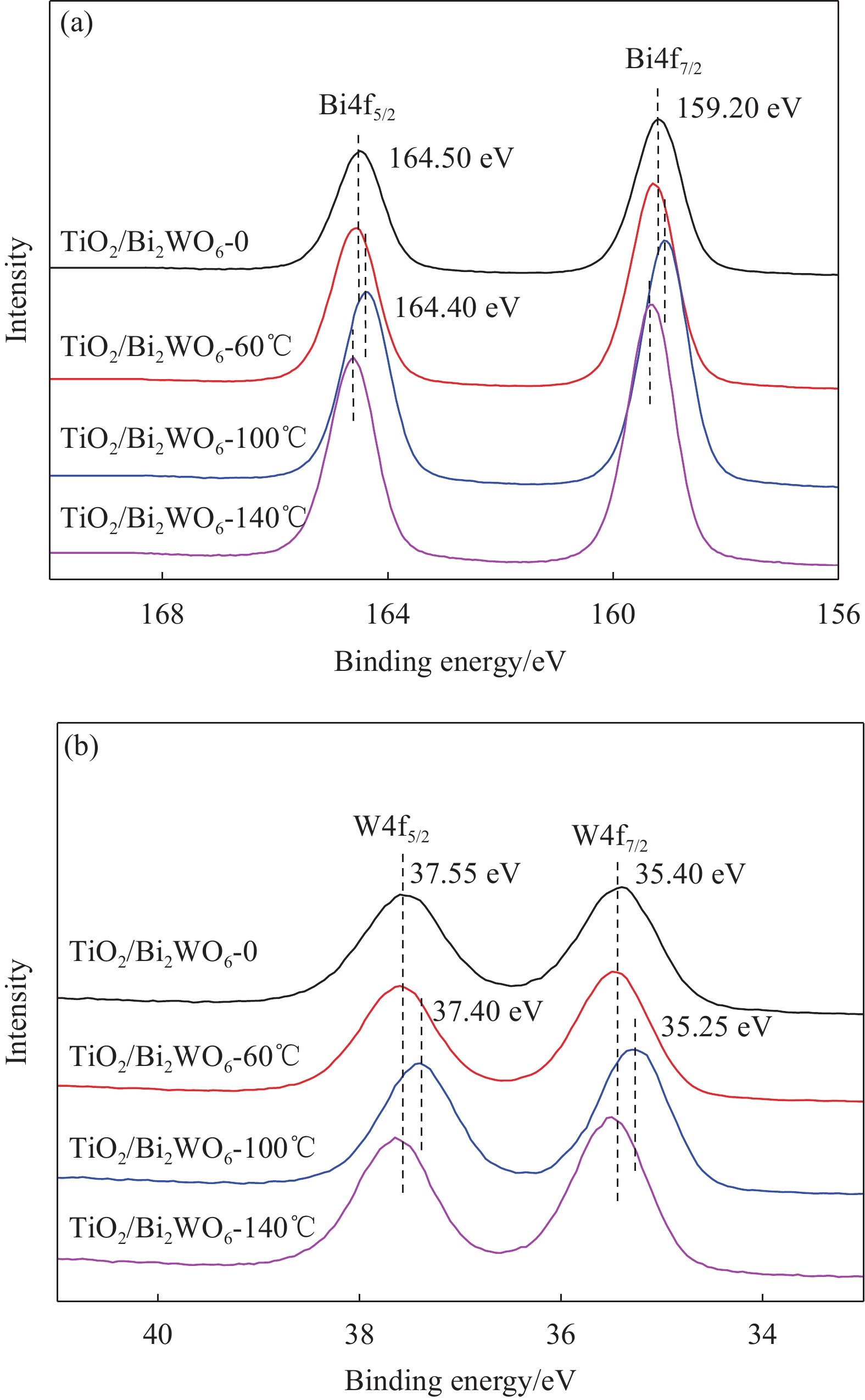
摘要: TiO2/Bi2WO6异质结复合材料是可见光响应光催化活性最高的物质之一,其界面结构和微观形貌是影响光催化性能的重要因素。但是,如何可控“裁剪”TiO2/Bi2WO6异质结复合材料的界面结构与微观形貌仍面临巨大的挑战。本文采用缺陷诱导可控合成TiO2/Bi2WO6异质结复合材料,研究了TiO2基底表面缺陷尺寸、分布密度等对TiO2/Bi2WO6复合材料微观结构和光催化性能的影响。结果表明:热腐蚀合成温度、腐蚀时间是影响TiO2纳米带基底表面缺陷尺寸和分布的关键因素。TiO2纳米带基底表面的缺陷尺寸为26 nm,缺陷分布密度为12个/μm2,有利于合成界面结合良好的TiO2/Bi2WO6异质结复合材料。所得TiO2/Bi2WO6异质结复合材料在可见光辐照12 min后使罗丹明B(RhB)完全降解,辐照20 min后使亚甲基蓝(MB)完全降解,辐照70 min后对苯酚的降解率达43.8%。
-
关键词:
- TiO2/Bi2WO6复合材料 /
- 缺陷诱导异质生长 /
- 异质结构 /
- 缺陷分布 /
- 光催化活性
Abstract: TiO2/Bi2WO6 heterojunction composite is one of the most promising visible-light derived photocatalysts. Its photocatalytic performance mainly depends on the interface structure and micro-morphology. However, it is a great challenge to control and tailor the micro-morphology and interface structure of TiO2/Bi2WO6 heterojunction. Herein, TiO2/Bi2WO6 heterojunction was synthesized by defect induced hetero-growth method. The influences of the defect size and distribution density, located on TiO2 nanobelts substrate, on the microstructure and photocatalytic activity of the TiO2/Bi2WO6 composites was further investigated. The results indicate that the corroding temperature and retention time are the key to modify the defect size and distribution density on the substrates. The defect size and distribution density are 26 nm and 12 per μm2 respectively, which facilitate to construct TiO2/Bi2WO6 heterojunction composites with well interface structure. With the as-prepared TiO2/Bi2WO6 heterojunction as photocatalyst under visible light, rhodamine B (RhB) and methylene blue (MB) can be completely photodegraded after irradiation for 12 min and 20 min respectively, and the degradation percentage of phenol also is reached 43.8% after 70 min of irradiation. -
-
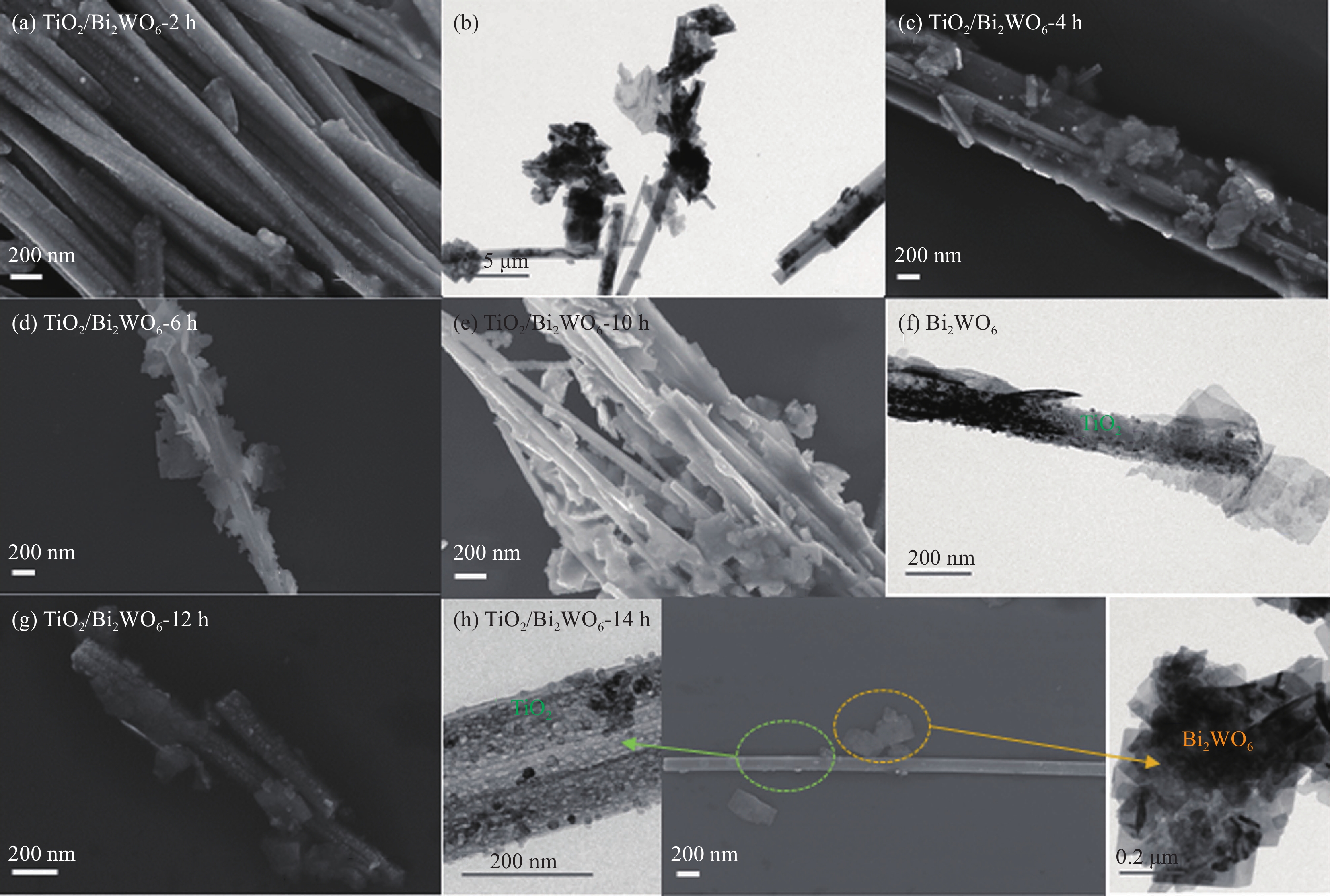
图 4 ((a), (b)) TiO2/Bi2WO6-2 h的SEM和TEM图像;TiO2/Bi2WO6-4 h (c)、TiO2/Bi2WO6-6 h (d)的SEM图像;((e), (f)) TiO2/Bi2WO6-10 h的SEM和TEM图像;(g) TiO2/Bi2WO6-12 h的SEM图像;(h) TiO2/Bi2WO6-14 h的SEM和TEM图像
Figure 4. ((a), (b)) SEM and TEM images of TiO2/Bi2WO6-2 h; SEM images of TiO2/Bi2WO6-4 h (c) and TiO2/Bi2WO6-6 h (d); ((e), (f)) SEM and TEM images of TiO2/Bi2WO6-10 h; (g) SEM image of TiO2/Bi2WO6-12 h; (h) SEM and TEM images of TiO2/Bi2WO6-14 h
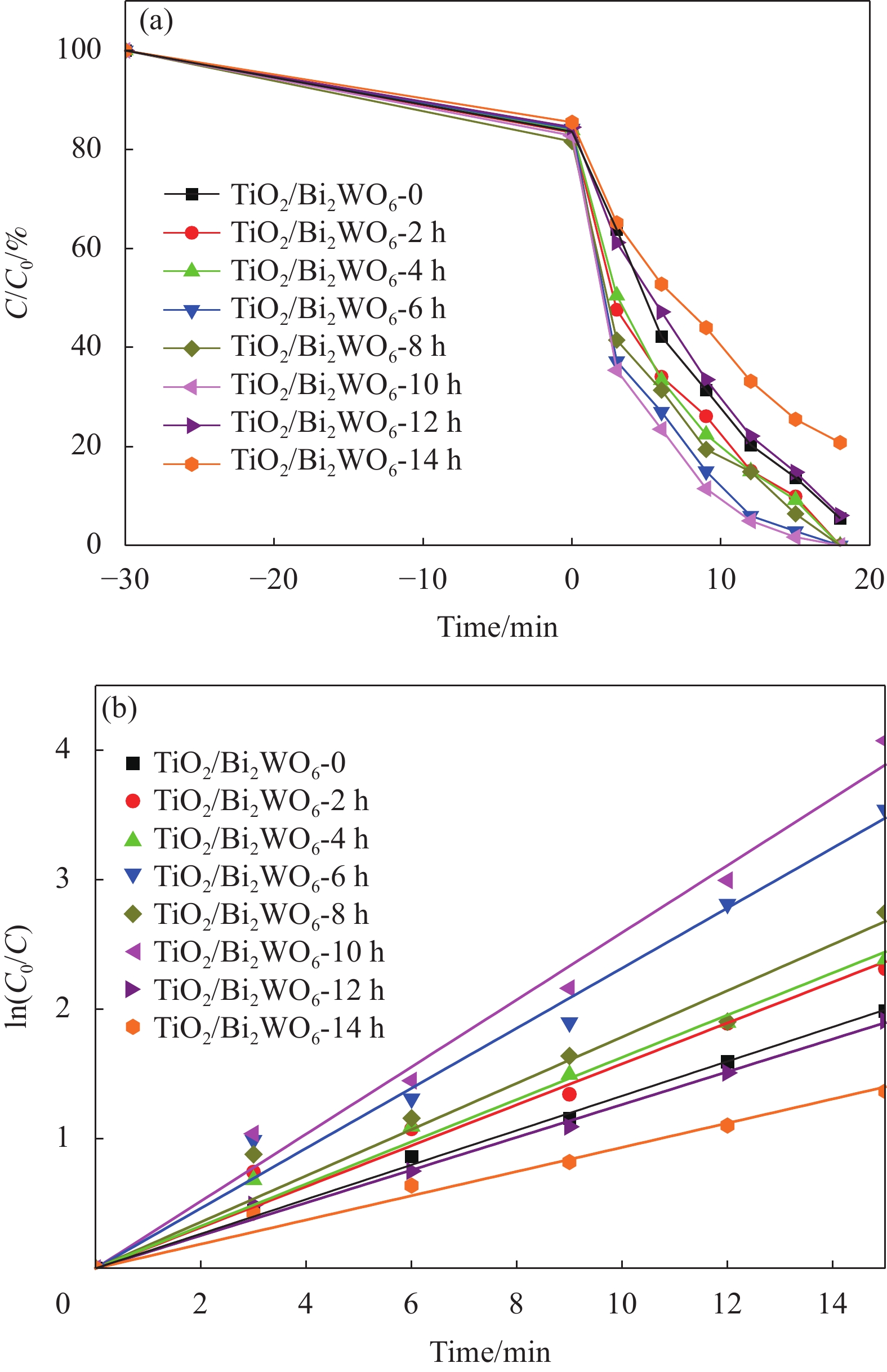
图 5 可见光下不同TiO2/Bi2WO6复合材料对罗丹明B(RhB)的光催化活性:(a) RhB浓度随辐照时间的演化图谱;(b) RhB光降解速率的一阶动力学拟合曲线
C0—Initial concentration of RhB solution; C—Instantaneous concentration of RhB solution for different irradiation times;
Figure 5. Photocatalytic activities of the different TiO2/Bi2WO6 composites for the degradation of rhodamine B (RhB) under visible light irradiation: (a) Evolution of RhB concentration over irradiation time; (b) Corresponding first-order kinetic linear fitting curves for photo-degradation of RhB
(1–C/C0)×100%—Photo-degradation percentage of RhB
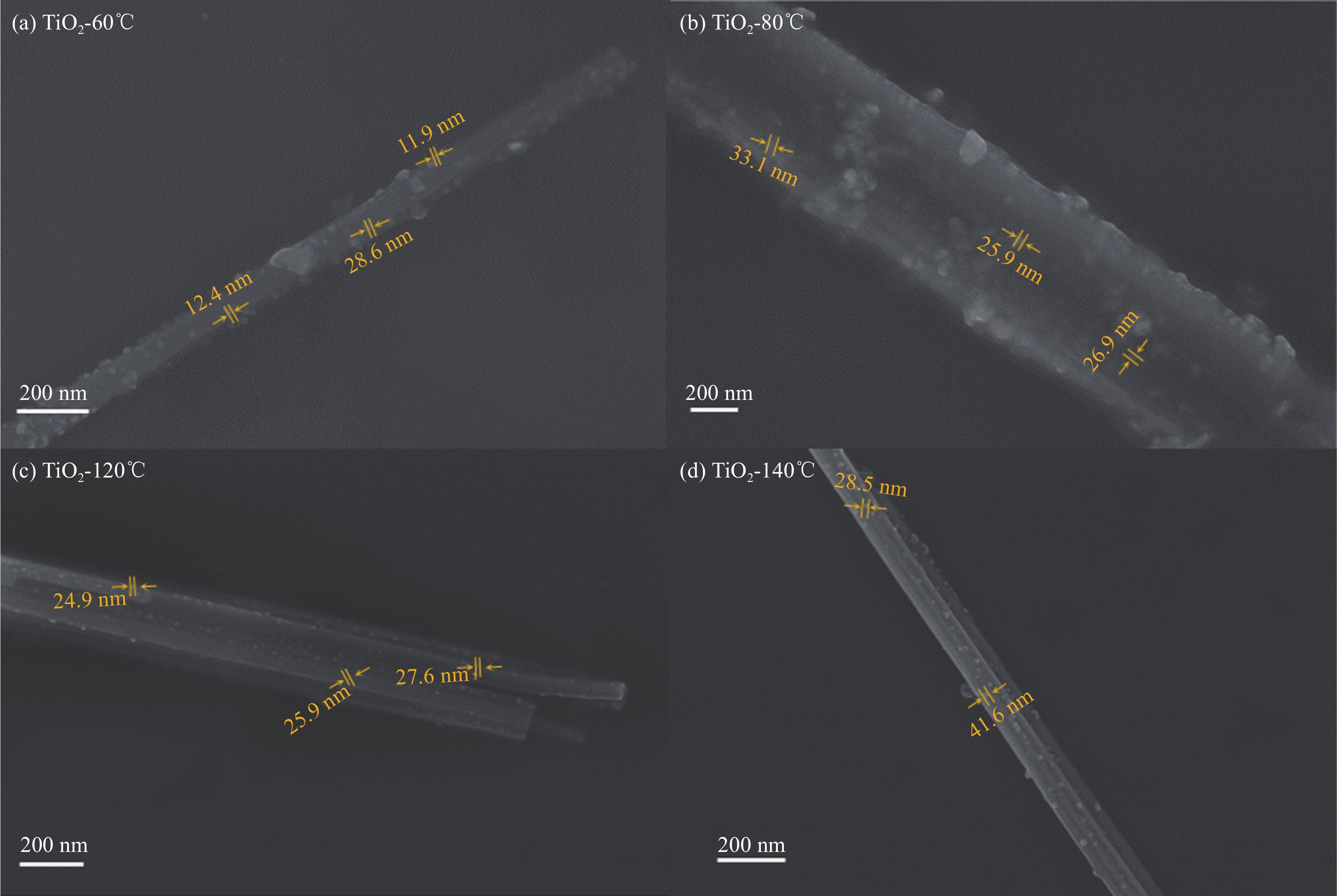
表 1 不同热腐蚀合成温度和时间TiO2纳米带基底的比表面积
Table 1 Specific surface area of the TiO2 nanobelts substrates synthesized for different corroding time and temperature
Sample Tcor/℃ Time/h Special surface area/(m2·g−1) Resulted composites TiO2-0 — — 13.95 TiO2/Bi2WO6-0 TiO2-2 h 100 2 14.68 TiO2/Bi2WO6-2 h TiO2-4 h 100 4 15.78 TiO2/Bi2WO6-4 h TiO2-6 h 100 6 18.71 TiO2/Bi2WO6-6 h TiO2-8 h 100 8 21.64 TiO2/Bi2WO6-8 h TiO2-10 h 100 10 22.18 TiO2/Bi2WO6-10 h TiO2-12 h 100 12 24.40 TiO2/Bi2WO6-12 h TiO2-14 h 100 14 36.41 TiO2/Bi2WO6-14 h TiO2-60℃ 60 10 24.08 TiO2/Bi2WO6-60℃ TiO2-80℃ 80 10 21.23 TiO2/Bi2WO6-80℃ TiO2-100℃ 100 10 21.92 TiO2/Bi2WO6-100℃ TiO2-120℃ 120 10 22.96 TiO2/Bi2WO6-120℃ TiO2-140℃ 140 10 30.51 TiO2/Bi2WO6-140℃ Notes: Tcor and time—Corroding temperature and maintaining time during the synthesis of TiO2 nanobelts substrates; Sample TiO2-10 h and TiO2-100℃—Prepared using the same procedure, except the concentration of H2SO4 solution has a small error between them. -
[1] YAN Q S, XU M M, LIN C P, et al. Efficient photocatalytic degradation of tetracycline hydrochloride by Ag3PO4 under visible-light irradiation[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research,2016,23(14):14422-14430. DOI: 10.1007/s11356-016-6588-2
[2] MIRANDA-GARCIA N, SUAREZ S, MALDONADO M I, et al. Regeneration approaches for TiO2 immobilized photocatalyst used in the elimination of emerging contaminants in water[J]. Catalysis Today,2014,230:27-34. DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2013.12.048
[3] ZHANG X, YANG P, YANG B, et al. Synthesis of novel Bi/Bi4O5Br2 via a UV light irradiation for decomposing the oil field pollutants[J]. Inorganic Chemistry Communications,2020,122:108297. DOI: 10.1016/j.inoche.2020.108297
[4] BAO J J, DAI Y, LIU H, et al. Photocatalytic removal of SO2 over Mn doped titanium dioxide supported by multi-walled carbon nanotubes[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy,2016,41(35):15688-15695. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2016.03.174
[5] ZHANG Y, XIONG M Y, SUN A R, et al. MIL-101(Fe) nanodot-induced improvement of adsorption and photocatalytic activity of carbon fiber/TiO2-based weavable photocatalyst for removing pharmaceutical pollutants[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production,2021,290:125782. DOI: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.125782.
[6] LOU W B, ZHANG Y, ZHENG S L, et al. Efficient recovery of scrapped V2O5-WO3/TiO2 SCR catalyst by cleaner hydrometalurgical process[J]. Hydrometallurgy,2019,187:45-53. DOI: 10.1016/j.hydromet.2019.05.003
[7] KAVINKUMAR V, VERMA A, UMA K, et al. Plasmonic metallic silver induced Bi2WO6/TiO2 ternary junction towards the photocatalytic, electrochemical OER/HER, antibacterial and sensing applications[J]. Applied Surface Science,2021,569:150918. DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2021.150918
[8] LOW J X, YU J G, MIETEK J, et al. Heterojunction photocatalysts[J]. Advanced Materials,2017,29:1601694. DOI: 10.1002/adma.201601694
[9] TONG H, OUYANG S, BI Y, et al. Nano-photocatalytic materials: Possibilities and challenges[J]. Advanced Materials,2012,24:229-251. DOI: 10.1002/adma.201102752
[10] NICOSIA D, CZEKAJ I, KROCHER O. Chemical deactivation of V2O5-WO3/TiO2 SCR catalysts by additives and impurities from fuels, lubrication oils and urea solution: Part II. Characterization study of the effect of alkali and alkaline earth metals[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental,2008,77(15):228-236.
[11] LI K, CHAI B, PENG T, et al. Preparation of AgIn5S8/TiO2 heterojunction nanocomposite and its enhanced photocatalytic H2 production property under visible light[J]. ACS Catalysis,2013,3(2):170-177. DOI: 10.1021/cs300724r
[12] LIU S Z, ZHANG Y C. Synthesis of CPVC-modified SnS2/TiO2 composite with improved visible light-driven photocatalysis[J]. Materials Research Bulletin,2021,135:111125. DOI: 10.1016/j.materresbull.2020.111125
[13] ZHANG J, HUANG L H, YANG L X, et al. Controllable synthesis of Bi2WO6(001)/TiO2(001) heterostructure with enhanced photocatalytic activity[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compound,2016,676:37-45. DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2016.03.090
[14] SHANG M, WANG W Z, ZHANG L, et al. 3D Bi2WO6/TiO2 hierarchical heterostructure: Controllable synthesis and enhanced visible photocatalytic degradation performances[J]. The Journal of Physical and Chemisity C,2009,113:14727-14731. DOI: 10.1021/jp9045808
[15] LOPEZ S M, HIDALGO M C, NAVIO J A, et al. Novel Bi2WO6/TiO2 heterostructures for rhodamine B degradation under sunlike irradiation[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2011,185(2-3):1425-1434. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.10.065
[16] YANG C, HUANG Y, LI F, et al. One-step synthesis of Bi2WO6/TiO2 heterojunctions with enhanced photocatalytic and superhydrophobic property via hydrothermal method[J]. Journal of Materials Science,2016,51:1032-1042. DOI: 10.1007/s10853-015-9433-y
[17] LI H X, LIANG L, NIU X, et al. Construction of a Bi2WO6/TiO2 heterojunction and its photocatalytic degradation performance[J]. New Journal of Chemistry, 2022, 46: 8185-8194.
[18] FANG G L, LIU J, WU J D, et al. A generic strategy for preparation of TiO2/BixMyOz (M=W, Mo) heterojunctions with enhanced photocatalytic activities[J]. Applied Surface Science,2019,475:785-792. DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2018.12.297
[19] HINOJOSA-REYES M, CAMPOSECO-SOLIS R, RUIZ F, et al. Promotional effect of metal doping on nanostructured TiO2 during the photocatalytic degradation of 4-chlorophenol and naproxen sodium as pollutants[J]. Materials Science in Semiconductor Processing,2019,100:130-139. DOI: 10.1016/j.mssp.2019.04.050
[20] SHIVANI V, HARISH S, ARCHANA J M, et al. Highly efficient 3D hierarchical Bi2WO6 catalyst for environmental remediation[J]. Applied Surface Science,2019,488:696-706. DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2019.05.072
[21] ZHANG L, NIE Y, HU C, et al. Enhanced fenton degradation of rhodamine B over nanoscaled Cu-doped LaTiO3 perovskite[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental,2012,12:418-424.
[22] 李小燕, 何登武, 李冠超, 等. Bi2O3-Bi2WO6直接Z-scheme异质结的制备、表征及光催化还原U(VI) 的性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2021, 38(8):2646-2654. LI Xiaoyan, HE Dengwu, LI Guanchao, et al. Preparation and characterization of Bi2O3-Bi2WO6 direct Z-scheme heterojunction and photocatalytic reduction of U(VI) under visible light irradiation[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2021,38(8):2646-2654(in Chinese).
[23] XU Y, LIN D, LIU X, et al. Electrospun BiOCl/Bi2Ti2O7 nanorod heterostructures with enhanced solar light efficiency in the photocatalytic degradation of tetracycline hydrochloride[J]. ChemCatChem,2018,10:2496-2504. DOI: 10.1002/cctc.201800100
[24] HOU Y F, LIU S J, ZHANG J, et al. Facile hydrothermal synthesis of TiO2/Bi2WO6 hollow superstructures with excellent photocatalysis and recycle properties[J]. Dalton Transactions,2014,43(3):1025-1031. DOI: 10.1039/C3DT52046C
[25] ZHU Y, SHAH M W, WANG C, et al. Insight into the role of Ti3+ in photocatalytic performance of shuriken-shaped BiVO4/TiO2-x heterojunction[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental,2017,203:526-532. DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.10.056
[26] LI W, DING X, WU H, et al. In-situ hydrothermal synthesis of TiO2/Bi2WO6 heterojunction with enhanced photocatalytic activity[J]. Materials Letters,2018,227:272-275. DOI: 10.1016/j.matlet.2018.05.107
[27] YANG Z, WANG J, CHEN L, et al. In situ fabrication of TiO2/Bi3.64Mo0.36O6.55 nanocomposite with high visible-light-driven photocatalytic efficiency[J]. Nano,2017,12:1750059. DOI: 10.1142/S179329201750059X
[28] BAI J, REN X, CHEN X, et al. Oxygen vacancy-enhanced ultrathin Bi2O3-Bi2WO6 nanosheets' photocatalytic performances under visible light irradiation[J]. Langmuir,2021,37(16):5049-5058. DOI: 10.1021/acs.langmuir.1c00576
-
期刊类型引用(12)
1. 龙国文,曾开华,谢帮华,田海,邱智坚. 相变混凝土复合材料的性能研究综述及展望. 功能材料. 2024(10): 10038-10046 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 陈春鸣,张燕,彭建山. 轻质相变混凝土物理力学性能研究进展. 化工新型材料. 2024(S2): 294-298 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 肖桐,刘庆祎,张家豪,赵佳腾,刘昌会. 热固性树脂基复合相变材料的制备及其储能强化研究进展. 复合材料学报. 2023(03): 1311-1327 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 张宇,恽定康,邱菊. 冻融循环下相变混凝土剪力墙抗震性能研究. 徐州工程学院学报(自然科学版). 2023(01): 42-49 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 张家玮,黄玮,黄大建,李旭辉,马建虎,郑永. 基于微孔漂珠的相变微胶囊制备及其对砂浆力学和热性能影响. 复合材料学报. 2023(08): 4703-4719 .  本站查看
本站查看
6. 于文艳,殷凯. 复合相变蓄热涂层的蓄放热调温特性. 科学技术与工程. 2023(31): 13492-13498 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 蔡昕辰,刘志彬,张云,白梅,刘锋. 相变材料在道路工程中的应用研究进展. 功能材料. 2021(12): 12013-12021 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 周建庭,聂志新,郭增伟,杨娟,郑忠. 相变混凝土的制备与性能研究综述. 江苏大学学报(自然科学版). 2020(05): 588-595 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 刘朋,缪正坤,田国华,刘伟,王东. 不同工况下陶粒吸附相变石蜡试验研究. 江苏科技信息. 2019(04): 44-46 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 司亚余,马芹永,罗小宝,顾皖庆,白梅. 癸酸-正辛酸与活性炭复合相变材料的制备. 安徽理工大学学报(自然科学版). 2019(03): 66-72 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 马芹永,白梅. 珍珠岩基相变骨料混凝土断裂特性试验与分析. 建筑材料学报. 2018(03): 365-369 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 顾皖庆,马芹永,白梅,罗小宝,司亚余. 月桂醇膨胀珍珠岩复合相变材料吸附试验与分析. 科学技术与工程. 2018(25): 230-235 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(21)
-





 下载:
下载: