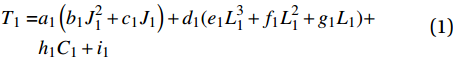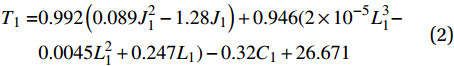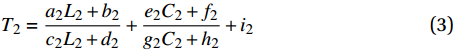Nonlinear regression models of compressive performance and pore structure of rubber aggregate alkaline mortar
-
摘要: 废旧轮胎的弃置会导致诸多环境问题,而粉碎制得的橡胶粉可在建筑砂浆中替代细骨料。砂浆中橡胶骨料的掺量和粒径是橡胶混凝土强度的主要影响因素,利用碱激发矿渣材料可替代普通硅酸盐水泥,提升砂浆的环境友好性。研究多因素耦合作用对橡胶骨料砂浆抗压性能的影响,通过测试砂浆的抗压强度,对试验结果进行显著性分析及多元非线性回归,建立了多因素与砂浆抗压强度的多元非线性回归模型。对砂浆试样进行细观孔隙测量和SEM表征,探究橡胶骨料对砂浆抗压强度的劣化机制。结果表明:砂浆中橡胶骨料掺量的提升会造成砂浆抗压强度的下降,40vol%骨料替代率下碱激发类砂浆抗压强度均值相比对照组降低了49.93%,硅酸盐类降低了66.62%;在碱激发类砂浆的高碱性环境下,使用0.38 mm粒径橡胶骨料的砂浆抗压强度均值为对照组的69.65%,取得试验组中最优值;而在硅酸盐类砂浆的低碱性环境中,随着橡胶骨料粒径的减小,砂浆抗压强度均值由对照组的61.46%降至37.98%。Abstract: The disposal of used tires causes many environmental problems, and the crushed rubber powder can replace fine aggregate in building mortar. The content and particle size of rubber aggregate in mortar are the main factors affecting the strength of rubber concrete. Alkali-activated slag can replace ordinary Portland cement and improve the environmental friendliness of mortar. The influence of multi-factor coupling on the compressive properties of rubber aggregate mortar was studied. By testing the compressive strength of mortar, significance analysis of the test results was completed and the multivariate nonlinear regression model was established. The microscopic pore measurement and SEM test of mortar samples were carried out to explore the degradation mechanism of rubber aggregate on the compressive strength of mortar. The results show that the increase of rubber aggregate content in mortar will cause the decrease of compressive strength of mortar. Compared with the control group, the average compressive strength of alkali activated mortar decreases by 49.93% and the silicate mortar decreases by 66.62% under 40vol% aggregate replacement rate. Under the high alkaline environment of alkali-activated mortar, the average compressive strength of mortar using 0.38 mm rubber aggregate is 69.65% of the control group, which is the optimal value in the test group. In the low alkaline environment of silicate mortar, with the decrease of rubber aggregate size, the average compressive strength of mortar decreased from 61.46% of the control group to 37.98%.
-
废旧轮胎回收利用的多方面研究使这种工业固废产生了各种富有前景的用途,减少了原油消耗和化工排放带来的环境影响[1]。根据中国橡胶工业协会废橡胶综合利用分会统计数据,2021年全年29家协会会员单位生产废旧轮胎处理量全年约为111.8万吨,其中再生橡胶粉产量约为20.5万吨。由旧轮胎磨碎制成的再生橡胶建筑骨料的性能研究始于20世纪90年代初并发展至今,已成为再生胶粉的一种高效应用手段。用再生橡胶骨料替代混凝土中的细骨料,其具有成本低、技术复杂性小的优点[2-5]。
在全球低碳限排的背景下,混凝土产业的可持续性、低碳友好性已成为世界工程界关注的焦点。橡胶混凝土具有将废弃物有效利用的特点,可以减少自然资源的消耗,并生产出更优质的材料[6]。因此,橡胶混凝土常用于浇筑混凝土板,如混凝土地板、隔墙等。此外也用于密封筒仓与防波堤的建设,在道路工程中,含有再生橡胶骨料的路面对温度变化的敏感度更低,同时也获得了更好的透水性能[7-8]。Shao等[9]和Liu等[10]进行了掺橡胶颗粒混凝土力学性能、减缩性能等试验研究。
在混凝土的配制中,通常作为主要原材料的普通硅酸盐水泥具有易于取材、成本低、易于制造、耐久性好等因素,但硅酸盐水泥的生产会导致大量的碳排放,约占全球CO2排放的7%,已经成为全球变暖潜在的原因之一[10-12]。此外,硅酸盐水泥制造也导致了石灰石等矿物的过度采掘,因此需要寻找一种低碳环保的胶凝材料对硅酸盐水泥进行替代,同时又可以使混凝土在工程中发挥同样甚至更好的作用[13-15]。
碱激发矿渣水泥作为普通硅酸盐水泥的替代物,因其快硬早强、耐久性高、低能耗的特点在过去的几十年间被广泛的开发利用[16-17]。碱激发矿渣水泥常用的激发剂有NaOH、Na2SiO3、Na2CO3等,其中最基础常用的就是NaOH,通过使胶凝体系中增加大量OH−,从而激发粒化高炉矿渣的火山灰活性,使碱激发矿渣水泥快速凝结[18]。同时,NaOH作为强碱,对于橡胶表面具有显著的改性作用[19-20],可以改善砂浆与橡胶骨料的交界面形貌,提升混凝土的力学性能。Segre等[21]研究了用于水泥砂浆再生轮胎橡胶的表面特征,经过饱和NaOH溶液的浸泡,轮胎橡胶颗粒表面的硬脂酸锌含量降低,增强了橡胶与砂浆之间的附着力。因此,使用NaOH溶液作为激发剂的碱激发矿渣砂浆可减轻橡胶骨料对砂浆抗压强度带来的负面影响。
目前在橡胶骨料混凝土的研究中,将多因素控制下橡胶骨料混凝土砂浆抗压强度影响程度进行量化对比的研究仍需深化,将胶凝体系的碱性、橡胶骨料的掺量和粒径的变化对于砂浆抗压强度的影响规律进行准确的描述,对于后续理论研究和配合比设计具有重要意义[22]。鉴于该试验具有多种因素,因此采用完全试验方案,在将所有可能组别进行试验之后,排除可能存在的试验误差,提高数据精度,并可通过采集完整的数据库,结合统计分析方法定量评估强度值变化幅度[23]。同时,根据所采集数据库,使用多元非线性回归分析方法建立砂浆强度预测模型[24-26],从而可通过给定试验参数对橡胶骨料砂浆抗压强度进行高可信度的预测。
试验创新使用多种胶凝环境下的橡胶骨料砂浆,通过控制激发剂pH值、骨料粒径和骨料掺量这3个主要因素,进行完全试验。通过对试样的细观与微观多尺度表征,分析了各因素对橡胶骨料砂浆抗压强度的影响机制,对砂浆抗压强度主导因素进行了考虑因素之间交互作用的显著性分析,建立了可预测砂浆抗压强度值的多元非线性回归模型,为工程中进行橡胶骨料砂浆配合比设计提供理论依据。
1. 碱性砂浆正交实验方法及材料
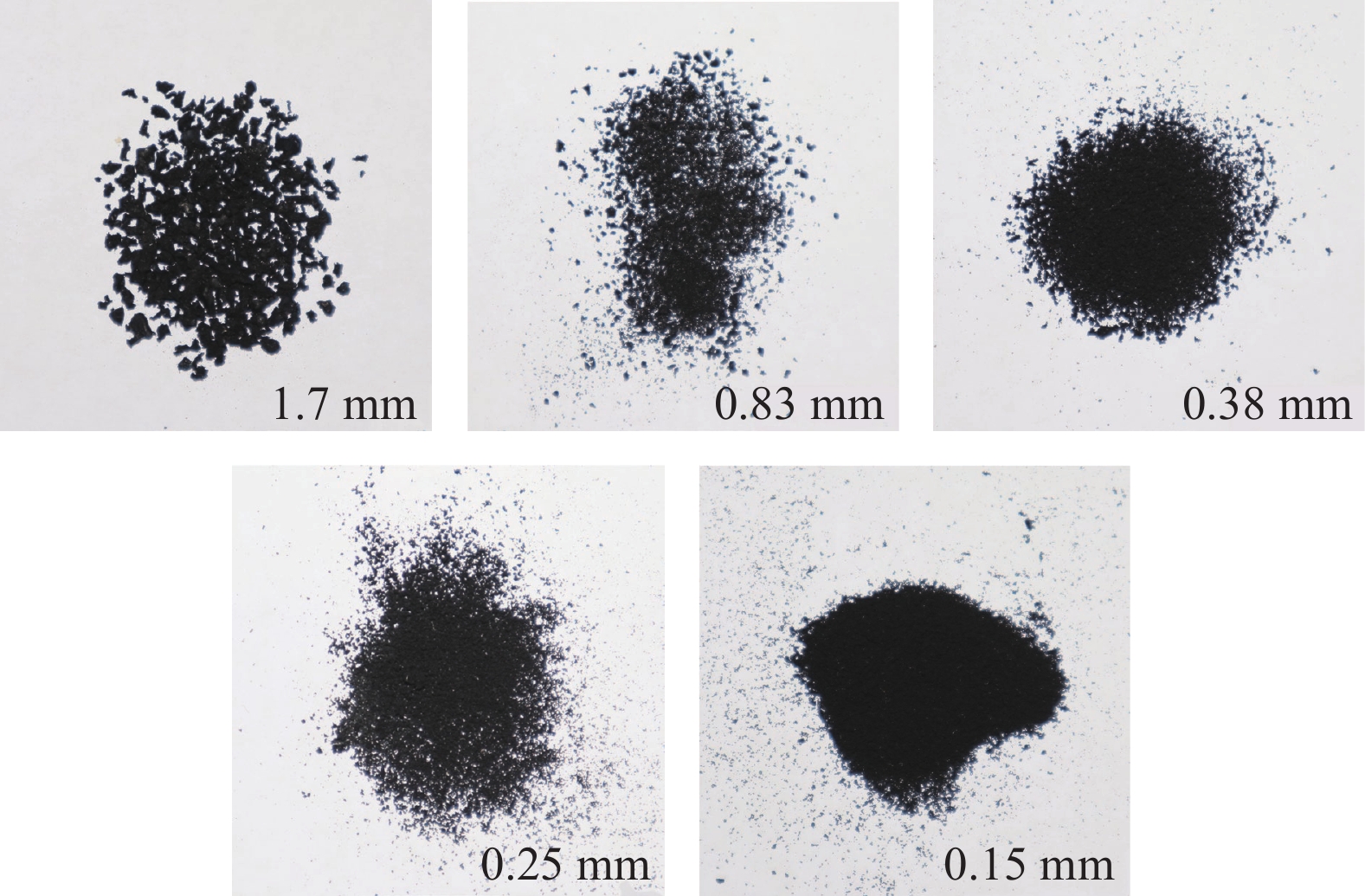
试验用水泥为八公山牌P·O 42.5普通硅酸盐水泥,矿渣粉采用怡然矿产品加工厂S95级矿渣粉。使用PANalytical Axios型X 射线荧光光谱分析仪(XRF)对矿渣粉的氧化物和单质含量进行了测定,测试结果如表1所示。橡胶细骨料采用陕西宏瑞橡胶制品厂产废旧橡胶轮胎再生橡胶粉,如图1所示。试验用砂为过2.36 mm方孔砂石筛天然中砂,试验用水为城市自来水。碱激发类试验的激发剂使用双双化工有限公司生产片状分析纯氢氧化钠,与自来水搅拌至完全融化,冷却至23℃备用。
表 1 高炉矿渣主要氧化物成分Table 1. Main oxide components of blast furnace slagOxide component CaO SiO2 Al2O3 MgO SO3 TiO2 Fe2O3 Content/wt% 49.51 25.61 13.23 5.51 2.34 2.131 0.421 在碱激发类砂浆完全试验方案3个影响因素中,橡胶骨料粒径设5个水平,橡胶骨料掺量设4个水平,激发剂pH值设3个水平,分别采用质量分数为8wt%、12wt%、16wt%的NaOH溶液,换算成OH− mol/L后可求得激发剂pH值为14.3、14.5、14.6。此外另有3组以激发剂pH值为单一变量的纯砂浆作为对照组试验,故总样本数为正交样本5×4×3=60组+对照组3组,空白对照组水灰比为0.45,砂率为50%,具体方案见表2。
表 2 碱激发类砂浆变量名称分类Table 2. Designation and classification of alkali-activated mortar group's variablesFactor Symbol of variable Level Designation pH value of sodium
hydroxide solutionJ1 1 pH≈14.3 2 pH≈14.5 3 pH≈14.6 Volume substitution
rate of rubber aggregateC1 1 10vol% 2 20vol% 3 30vol% 4 40vol% Particle size of
rubber aggregateL1 1 1.70 mm 2 0.83 mm 3 0.38 mm 4 0.25 mm 5 0.15 mm 采用普通硅酸盐水泥砂浆类与碱激发类的数据进行对比和印证,设置橡胶骨料掺量与粒径为试验变量,采用普通硅酸盐水泥对矿渣进行等水灰比替代,将等水灰比硅酸盐水泥净浆试样制得后,使用广州基准科仪DF牌精密pH试纸(pH=9.5~13)对新拌净浆试样进行测试,测得浆液pH值为12.5。试验分为对照组1组加5×4=20组正交变量试验,每个类别各有21组样本,组别命名方案见表3。
表 3 硅酸盐类砂浆变量名称分类Table 3. Designation and classification of silicate mortar group's variablesFactor Symbols of variable Level Designation Volume substitution
rate of rubber aggregateC2 1 10vol% 2 20vol% 3 30vol% 4 40vol% Particle size of
rubber aggregateL2 1 1.70 mm 2 0.83 mm 3 0.38 mm 4 0.25 mm 5 0.15 mm 砂浆试块制样时,将再生橡胶骨料与砂子预先充分拌和、烘干,防止橡胶细骨料吸水结团。将S95矿渣粉与骨料一同加入砂浆搅拌机中,将干料搅拌3 min拌和均匀,加入室温放置24 h后的NaOH溶液,再搅拌3 min至无结块浆体,将砂浆倒入预先刷脱模油的砂浆模具中。由于再生橡胶粉为轻质骨料,故统一设定电动震动台(圣科,0.5x220)对所制试样振动20 s消除气泡,将浇筑面抹平并静置24 h脱模。
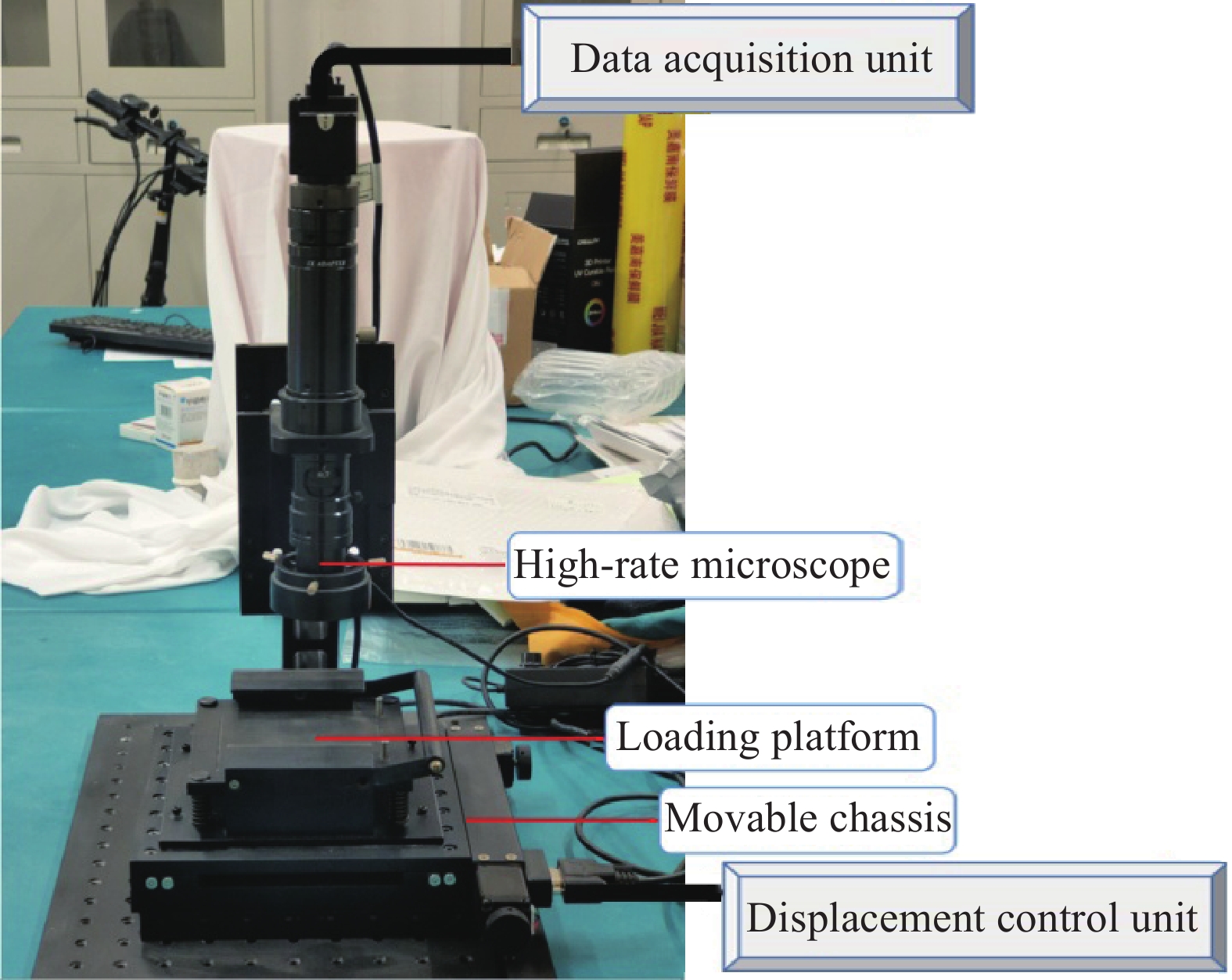
试样单轴抗压强度按照ASTM C109/C109 M-02标准[27]进行测试,依据该标准使用每组3个、边长为50 mm立方体模具进行制样,在试块标准条件养护至28天后,使用单轴压力机(SUNS,WDW-1000)测定抗压强度。使用直径Φ50 mm×20 mm的薄片试样对砂浆试样进行细观孔结构数据的采集,实验方法为:用标号数为240#、320#、400#、600#、800#、1000#、1500#、2000#到3000#的金刚石磨抛盘在精密研磨抛光机(砼瑞,TR-1Y)上对试样进行打磨处理,随后使用抛光块进行抛光,用流水洗净烘干后,在抛光表面涂布黑色醇基颜料,干透后将硫酸钡粉末均匀涂抹在试样表面,抹去浮粉待测,硬化混凝土气孔结构分析仪(砼瑞,TR-ASH),其组成部件如图2所示。试块真空干燥后取样进行SEM (Hitachi,FlexSEM 1000)微观形貌分析。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 碱激发类砂浆抗压试验
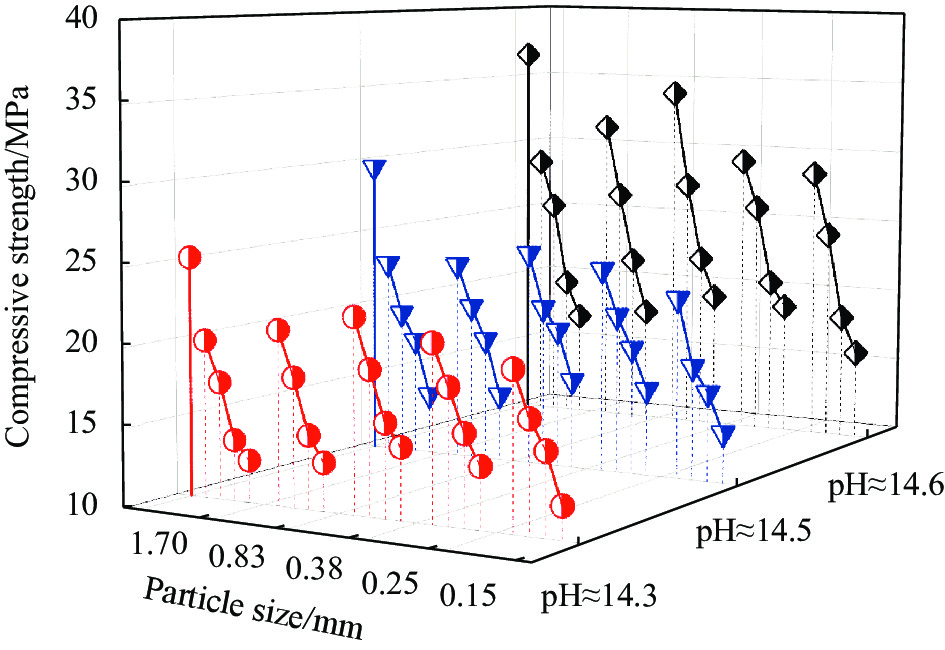
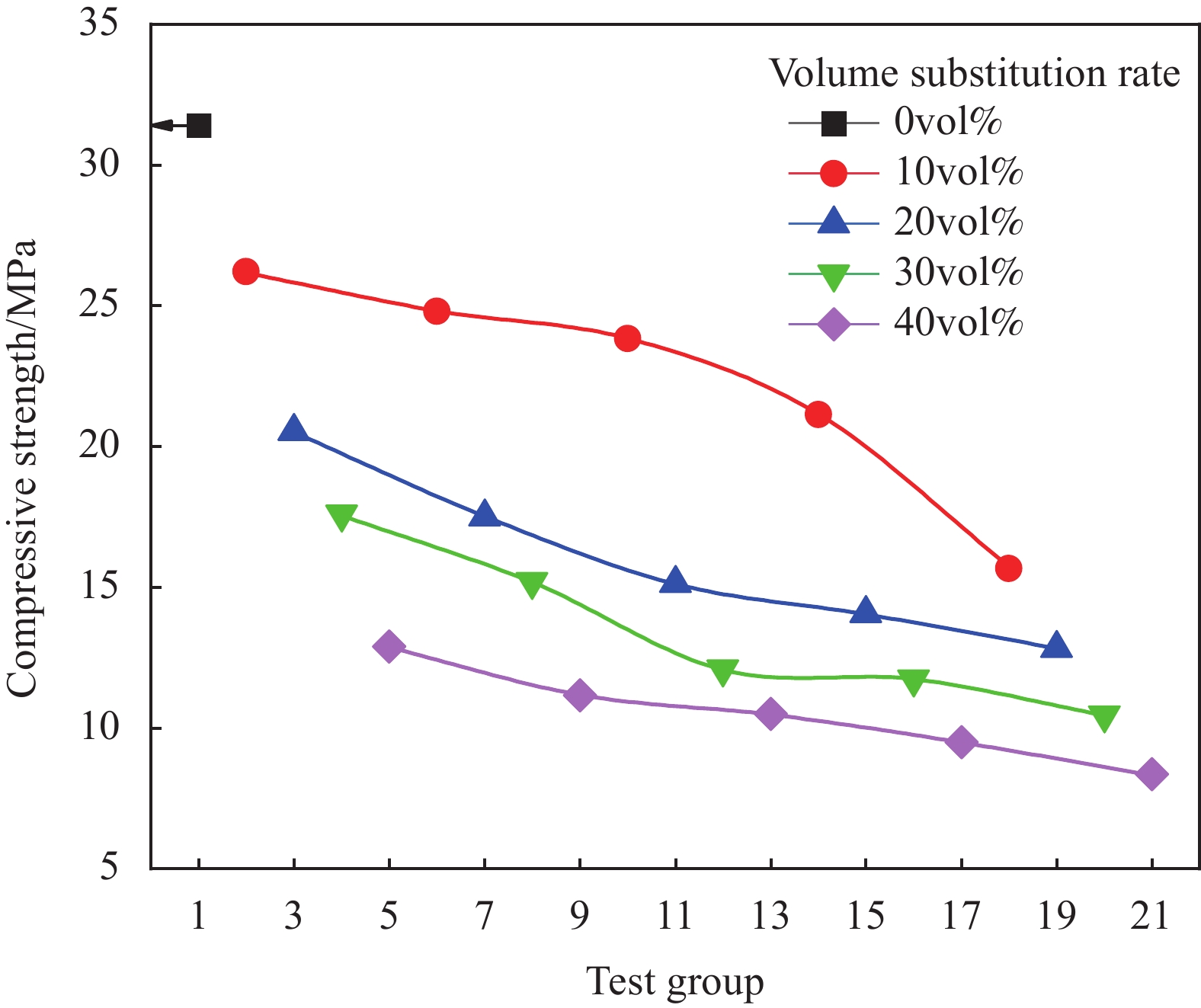
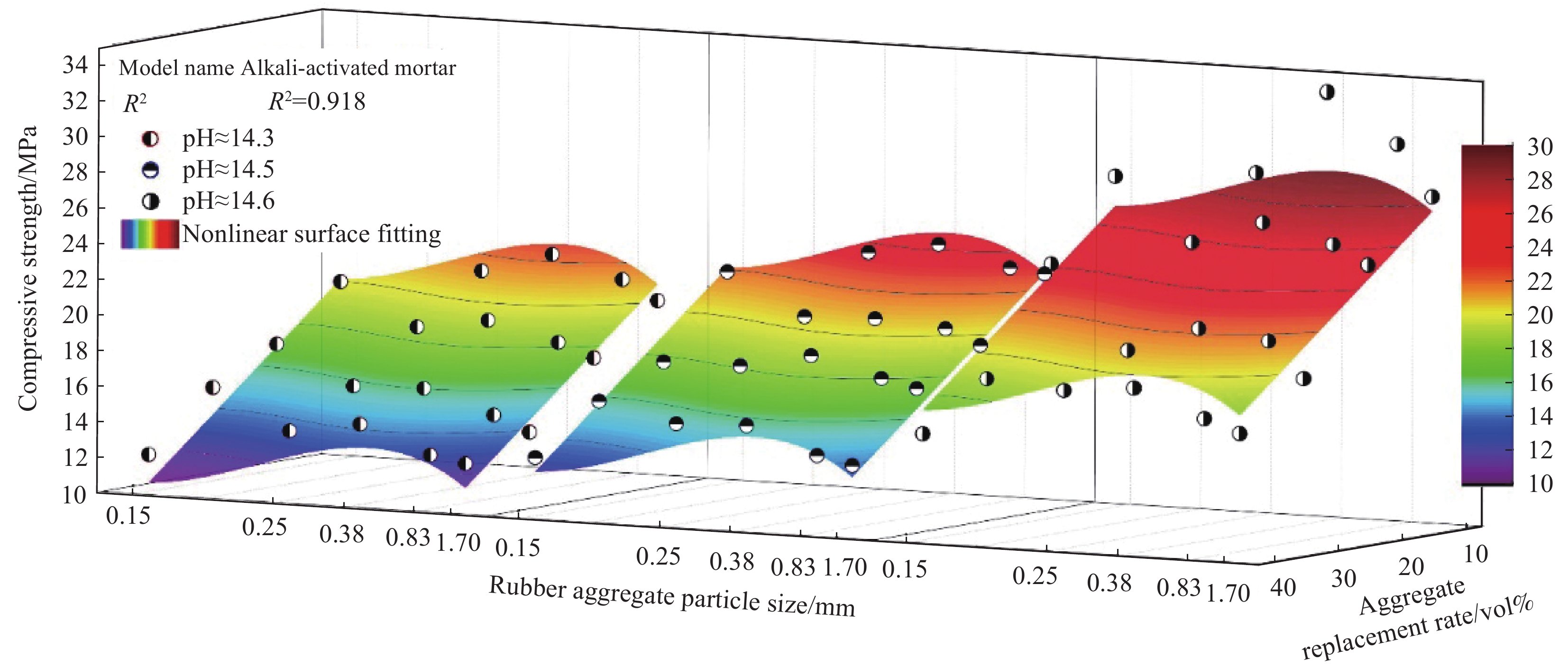
将碱激发类抗压强度测量并采集后可以得到,3组不同激发剂pH值的空白对照组试件的抗压强度随着激发剂pH值的增加而提升,且都高于同一激发剂pH值下掺有橡胶骨料的其他试验组别。将同样橡胶骨料粒径与掺量的试验组别进行对比,即pH≈14.3、pH≈14.5、pH≈14.6,3个数据区域橡胶骨料粒径与掺量相同的数据置于同轴,如图3所示,可以得到:激发剂pH值的提升与砂浆抗压强度的提升之间的关系是非线性的。在对比中,每一区域的强度最高值为掺量10vol%、粒径为0.38 mm的组别,随着激发剂pH值的提升,其基于浓度最低组的强度增长率为8.6%、52.94%;而最低值为粒径为0.15 mm、掺量40vol%的组别,随着激发剂pH值的提升,其基于浓度最低组的强度增长率为9.9%、32.03%。且该掺量下碱激发类砂浆抗压强度均值相比对照组降低了49.93%。
将相同激发剂pH值和橡胶骨料粒径的试样进行对比可看出,随着橡胶骨料掺量的增加,试样强度呈近似线性降低的趋势。例如在pH≈14.6、橡胶骨料粒径为0.38 mm的这4组中,试样强度随着橡胶骨料掺量的增加,相比于该激发剂pH值对照组分别下降了6.95%、25.25%、39.9%、47.29%。由此可见,橡胶骨料在碱激发类砂浆试样抗压方面起到的负面影响,且与胶凝体系内橡胶所占体积比存在似线性关系。
将pH≈14.3、pH≈14.5、pH≈14.6 3个数据区域中相同橡胶掺量的抗压数据分为一组,将橡胶骨料粒径因素对试块抗压强度造成的影响进行趋势的判断与分析。如图4所示,随着橡胶骨料粒径的逐渐缩小,试样强度呈现出先提升再下降的趋势,且在粒径为0.38 mm时取得最高值。在激发剂pH值最高、橡胶掺量最小的5组数据中,骨料粒径为1.70 mm的试样比0.38 mm的抗压强度约降低16.11%;在激发剂pH值最低、橡胶掺量最大的5组数据中,骨料粒径为1.70 mm的试样比0.38 mm的抗压强度约降低12.8%。使用0.38 mm粒径橡胶骨料的砂浆抗压强度均值为对照组的69.65%。
2.2 硅酸盐类砂浆抗压试验
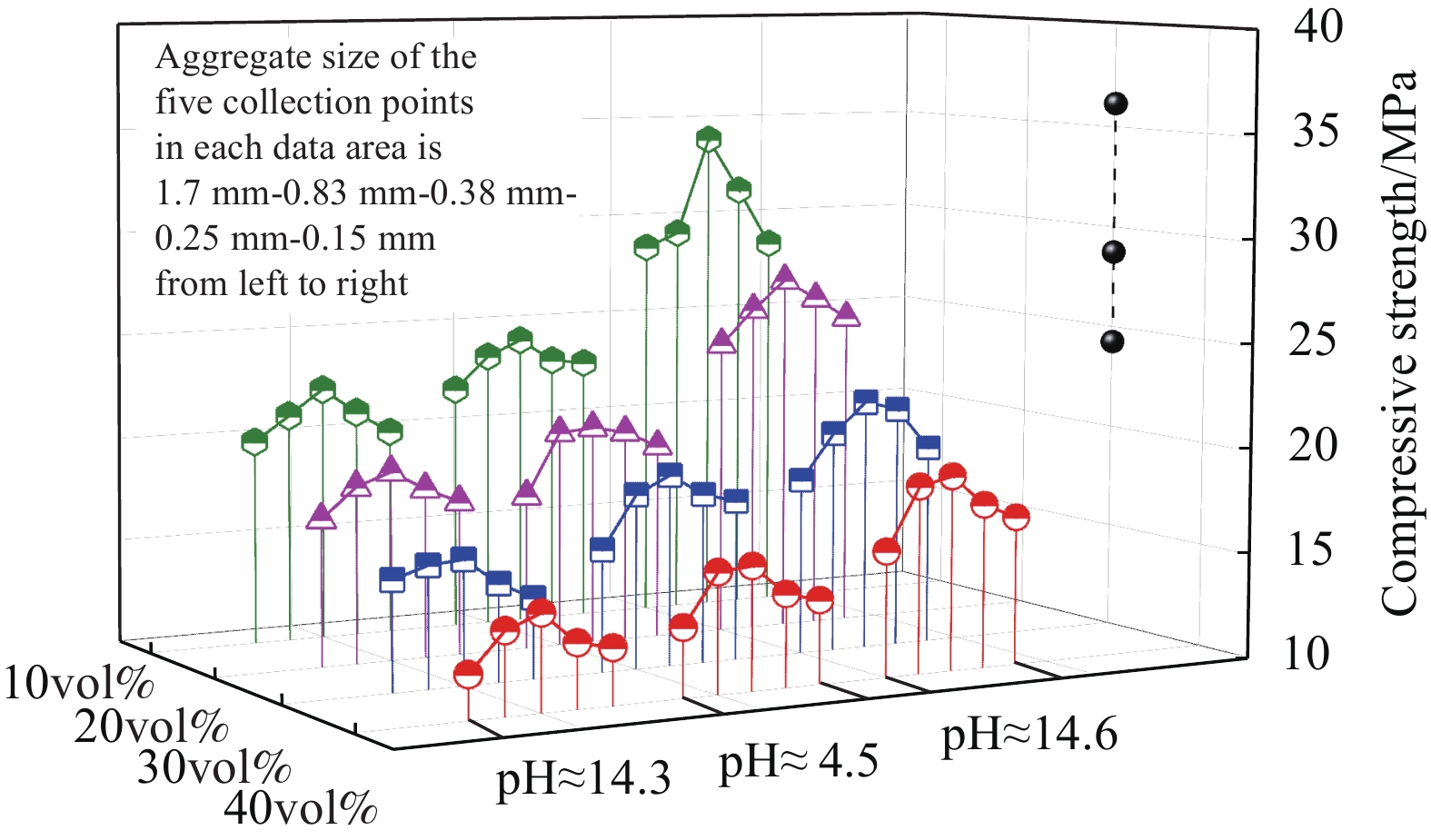
除63组碱激发类正交试验外,对21组硅酸盐类砂浆也进行了抗压强度测试以及数据采集。如图5所示,在硅酸盐类试验中,砂浆试样抗压强度主要影响因素为橡胶骨料掺量与粒径。随着橡胶粒径的不断减小,试块的抗压强度呈现出下降的趋势,说明橡胶的粒径会影响试块的抗压强度表现,在橡胶掺量为骨料体积10vol%、20vol%、30vol%、40vol%时,0.15 mm橡胶粒径的试样抗压强度约为1.70 mm橡胶粒径试样抗压强度的59.54%、63.32%、59.32%、64.88%,这表明在硅酸盐类砂浆的橡胶骨料粒径变化时,增大橡胶骨料掺量会使砂浆抗压强度降低,但幅度没有明显变化。40vol%骨料替代率下硅酸盐类砂浆抗压强度均值相比对照组降低了66.62%。
同时,橡胶骨料掺量的增加也是导致抗压强度降低的主要因素。在粒径相同时,砂浆中的橡胶在骨料中占比越大,试块的抗压强度越低。在橡胶粒径为1.70、0.83、0.38、0.25和0.15 mm时,橡胶掺量为骨料体积40vol%的硅酸盐类砂浆试样是橡胶掺量为骨料体积10vol%的试样抗压强度的49.24%、45.04%、44.06%、44.96%和53.41%。总体来看,橡胶骨料在硅酸盐类砂浆抗压强度中起到了明显的消极作用,且粒径越小,对硅酸盐类砂浆抗压强度产生的负面效果越强。
由碱激发类砂浆和硅酸盐类砂浆不同橡胶骨料体积替代率但粒径相同试件的抗压强度取均值,可得到抗压强度均值对比如图6。根据数据趋势可以得出:通过控制激发剂中NaOH的质量百分比,碱激发类砂浆可取得与同水灰比硅酸盐类砂浆相似的抗压强度。当粒径逐渐变细,碱激发类砂浆的抗压强度显示出与硅酸盐类砂浆不同的变化趋势,在使用0.38 mm橡胶骨料时,碱激发类砂浆的抗压强度均值是硅酸盐类砂浆的133.08%,这是由于硬脂酸锌在高OH−浓度的环境下更少地存在于橡胶骨料表面[21],骨料与浆体的界面过渡区亲水性提升,因此遏制了碱激发类砂浆强度的下降趋势。
2.3 碱激发类砂浆微观形貌
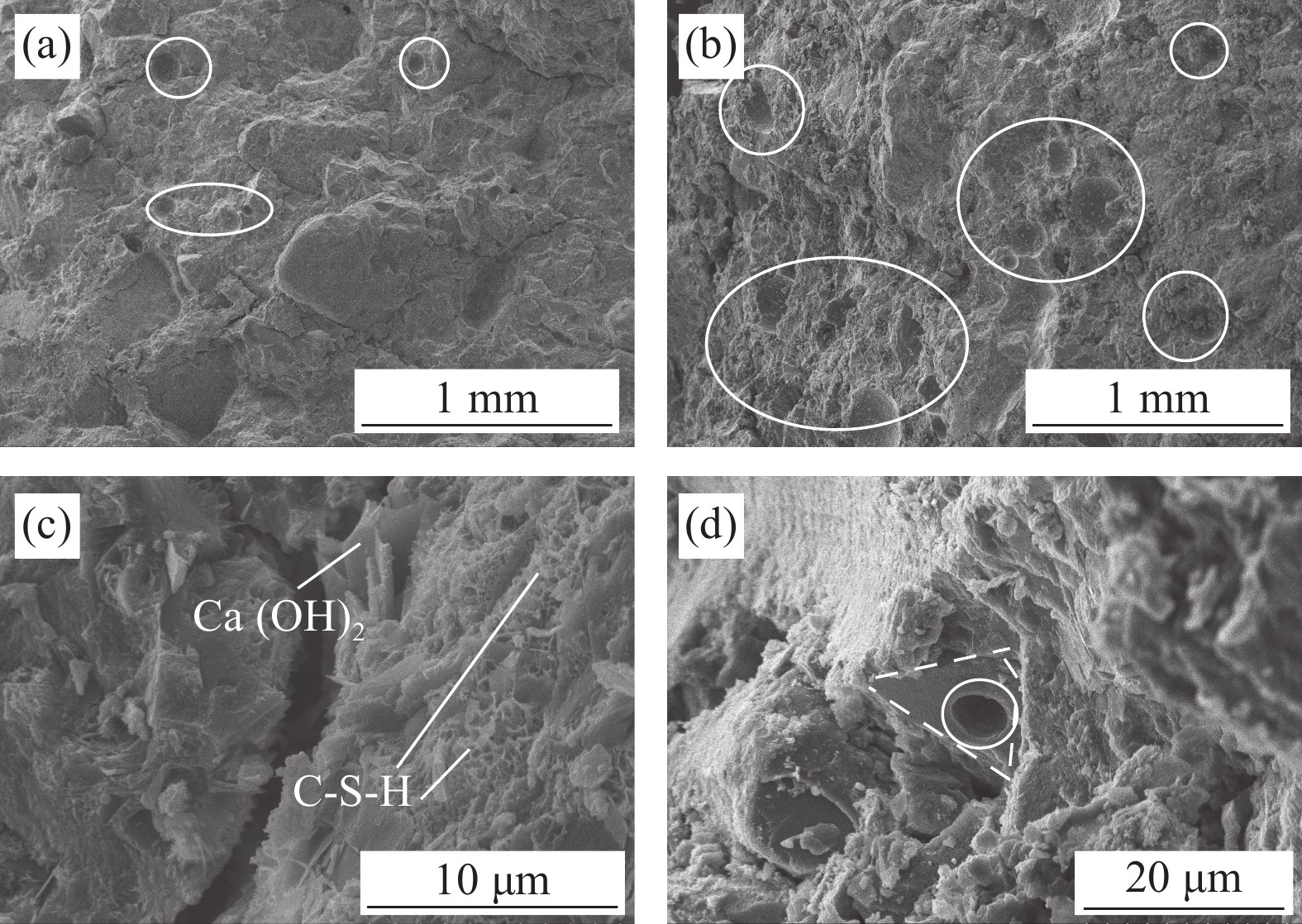
将碱激发类砂浆样品通过SEM来观测样品晶体的组成以及骨料界面过渡区形貌,如图7所示。在50倍的放大倍率下(图7(a)) 可以看出,橡胶骨料细度最粗时气泡的密集程度明显低于橡胶骨料细度最细时(图7(b));在5000倍的放大倍率下(图7(c)),可观测到碱激发矿渣砂浆的水化产物。砂浆中含有大量交错纤维状的水化硅酸钙(C-S-H)凝胶,同时也富集有板状Ca(OH)2晶体;在2000倍的放大倍率下(图7(d)),仍可观测到橡胶骨料剥离后平整的界面过渡区以及界面存在的气泡,这种骨料界面过渡区大量存在的小型气泡会增加界面过渡区的孔隙率,从而使砂浆试样的峰值抗压强度大幅度下降。
2.4 碱激发类砂浆细观孔隙结构
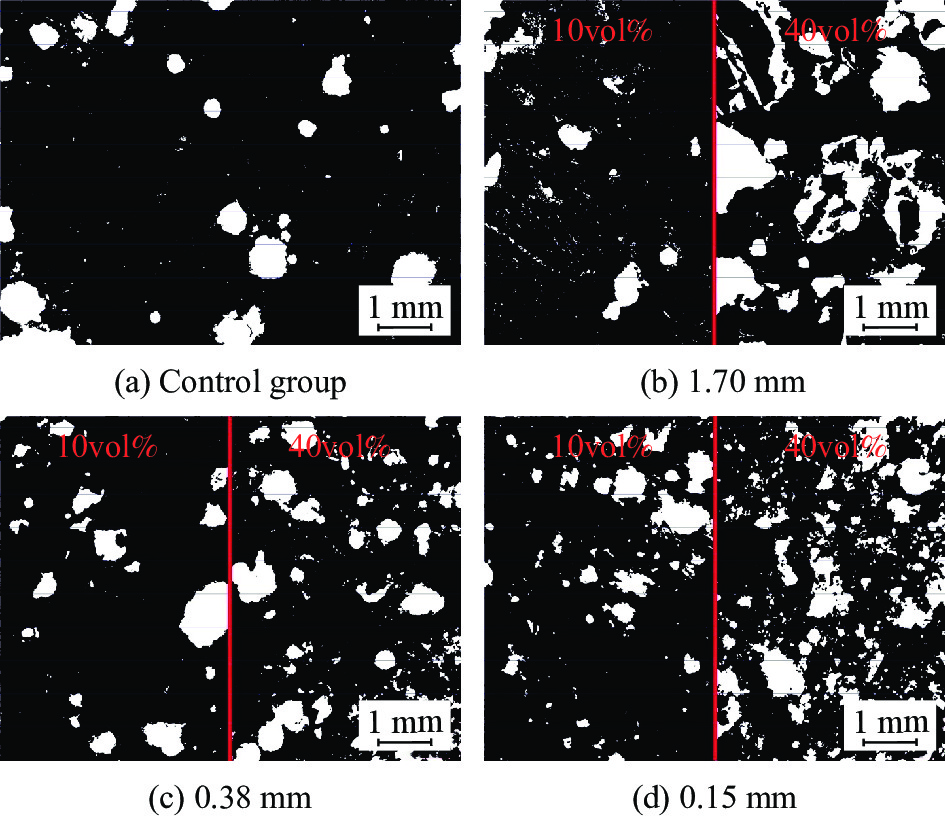
在孔隙分析仪采集到的碱激发类砂浆样品的细观孔隙图片中,选取激发剂pH值最高,掺量差别最大的组别(10vol%和40vol%)进行对比,如图8所示。图8(a)为碱激发类砂浆的对照组。可以看到平面中存在有少数中等大小的独立气孔以及均匀散布的小气孔。在骨料粒径1.70 mm组别的对比中,如图8(b)可以观察到1.70 mm的橡胶骨料会使砂浆内大型的独立气泡增多,这是由于粗粒度的橡胶骨料具有较大的连续面,且表面的憎水性使大型气泡可以依附于橡胶骨料之上。
使用0.38 mm粒径橡胶骨料的砂浆抗压强度是所有碱激发类砂浆除对照组以外的最高值,所以有必要研究该数据区间孔隙分布的特征及规律。从样品的采集影像图8(c)可以看出,橡胶骨料为0.38 mm时,由于骨料粒径的缩小,相同总体积下比表面积有所增大,一方面避免了类似于1.70 mm粒径的橡胶骨料由于单体太大可吸附大型气泡;另一方面又使碱性溶液与橡胶骨料的接触实际面积增加,橡胶骨料获得了更多的表面改性面积,从而改善了骨料与砂浆的界面过渡区形貌,因此砂浆中气泡与孔隙的存在都较少,获得了与对照组相似的孔隙环境。随着橡胶骨料体积比在砂浆中不断的增加,如图8(c)右侧橡胶体积比达到40vol%时,气泡密度明显增加,降低了试件的均匀性。
当橡胶骨料的粒径进一步变小直至0.15 mm时,如图8(d)所示,孔隙形貌相较于骨料粒径较粗的组别有所差异。此时,过量增加的比表面积导致在砂浆中橡胶-砂浆界面过渡区总面积进一步增大,这导致了抗压强度的下降,同时,由于橡胶骨料单体数量的增多,更多的小气泡被引入砂浆,如图8(d)右侧40vol%组别中的气泡密度比10vol%显著增长,加剧了砂浆抗压强度的损失。
2.5 硅酸盐类砂浆孔隙结构
图9为硅酸盐类砂浆的孔隙形貌图。相比于碱激发类砂浆,硅酸盐类砂浆在同水灰比情况下对照组的大孔稍多,如图9(a)所示。当橡胶骨料开始替代普通骨料时,砂浆的孔隙结构会发生不同程度的改变。用掺量差别最大的组别进行对比(10vol%和40vol%)。在1.70 mm的橡胶骨料掺入砂浆时,随着橡胶掺量的提升,砂浆试样会出现越来越多的大型孔隙,当1.70 mm橡胶掺量达到骨料体积40vol%时,由图9(b)右侧40vol%组别中可以看出砂浆中存在大量贯通型气泡,使砂浆强度不断降低。将碱激发类的最优组别图8(c)左侧10vol%组别与配方图9(c)左侧对比,可以看出大气泡既比同水灰比、同橡胶骨料粒径与掺量的碱激发类砂浆要多,同时也比硅酸盐类的对照组更密集,这展现出了与碱激发类砂浆完全不同的气泡形貌变化规律。
随着橡胶骨料的进一步变细,如图9(d)所示,可观察到的现象是:硅酸盐类砂浆的不良孔隙明显多于碱激发类,且随着骨料粒径的变化,气泡的密集程度也在加剧。其根本原因在于,橡胶骨料在碱激发类砂浆富含OH−的孔隙溶液中,其表面被充分地改性,而碱性较低的硅酸盐类砂浆不能满足这一点。因此,在硅酸盐类砂浆中橡胶骨料的变细并不能带来界面过渡区可改性面积的增加,相反地,由于橡胶颗粒的强憎水性,随着孔隙水溶液的碱性变低,细颗粒的橡胶骨料更易于产生团聚并吸附更大体积气泡,这就导致了硅酸盐类砂浆抗压强度随着骨料粒径的减小而不断下降。
3. 砂浆强度与各因素多元非线性回归分析
3.1 三因素作用下碱激发类砂浆抗压强度多元非线性回归分析
经过对碱激发类砂浆抗压试样的各项表征与分析,可得出初步结论:激发剂pH值、橡胶骨料粒径、橡胶骨料掺量3个因素对试样的抗压强度都有非常显著的影响。为了对不同因素产生的影响进行量化分析及趋势预测,对三因素进行考虑交互作用的显著性分析。将碱激发类砂浆激发剂pH值因素设为J1,橡胶骨料粒径设为L1,橡胶骨料掺量设为C1,碱激发类砂浆抗压强度设为T1,将试验数据整合后导入SPSS软件中进行显著性分析,可以得到J1、L1、C1、J1L1、L1C1、J1C1、J1L1C1的F值。F值是方差齐性检验的检测结果, 在显著性分析中,若计算得F值大于F0.01时,可定义该因素为显著因素,使用代号“***”表示;若计算得F值小于F0.1时,可定义该因素为不显著因素,使用代号“//”表示。对各因素对应F临界值进行检索对比后将结果整合记录于表4。
表 4 碱激发类砂浆因素显著性分析Table 4. Significance analysis of alkali-activated mortar's factorsSource Sum of squares Degree of freedom Mean square F-value Significance J1 1464.388 2 732.194 758.883 *** L1 171.936 4 42.984 44.551 *** C1 2313.327 3 771.109 799.216 *** J1 L1 23.364 8 2.920 3.027 *** L1C1 13.789 12 1.149 1.191 // J1C1 160.447 6 26.741 27.716 *** J1L1C1 20.204 24 0.842 0.873 *** Error 115.780 120 0.965 — — Total 74288.445 180 — — — Notes: ***—Significant factor; //—Not significant factor; F—Test results of homogeneity of variance. 通过上述显著性分析可得出:J1、L1、C1 3个单因素对碱激发类砂浆抗压强度都具有较高的显著性水平。在二阶交互作用中,粒径和掺量的交互作用是不具有显著性的,其余的二阶以及三阶交互作用都具有较高的显著性水平。在3个单因素中,掺量对碱激发类砂浆强度的影响最大。
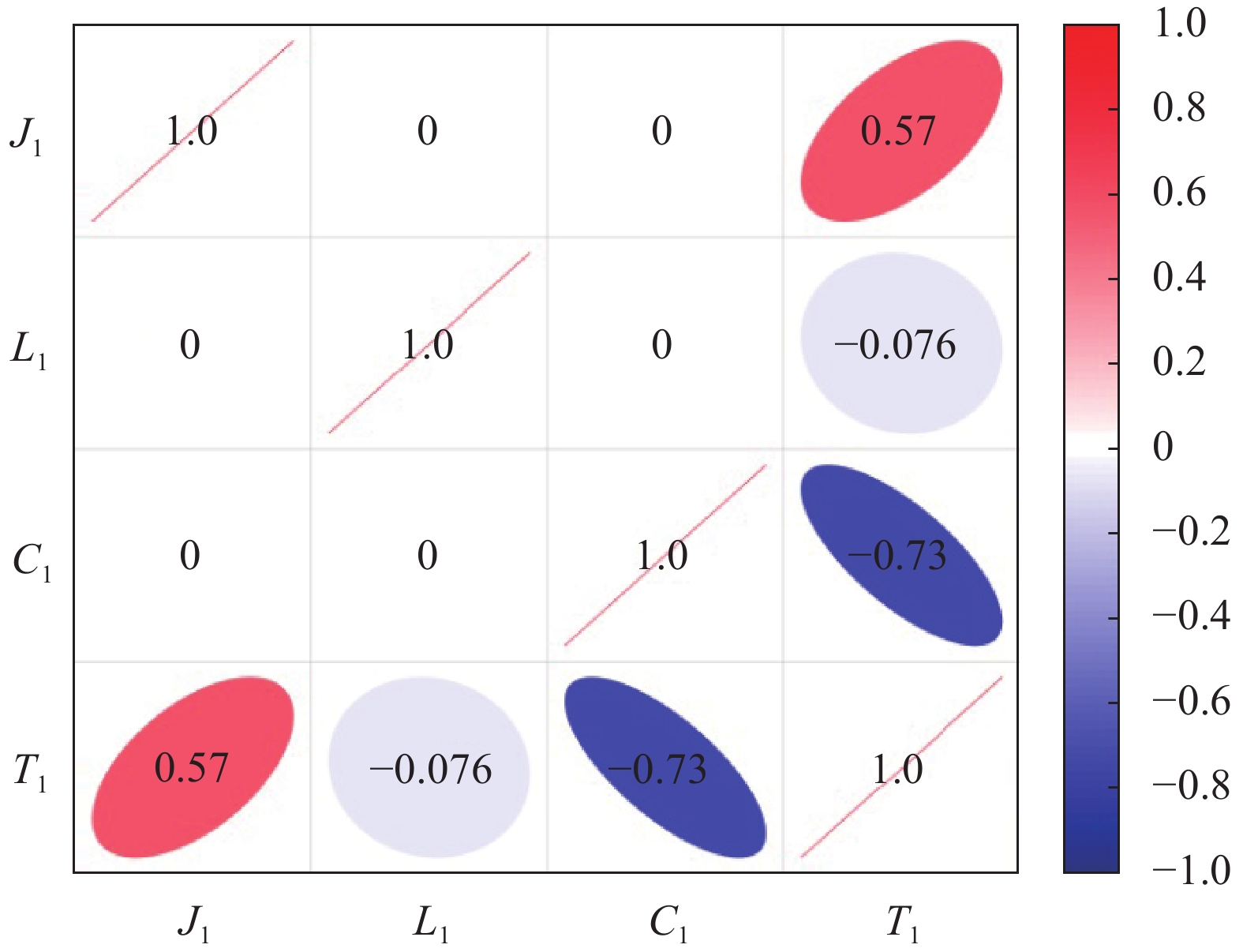
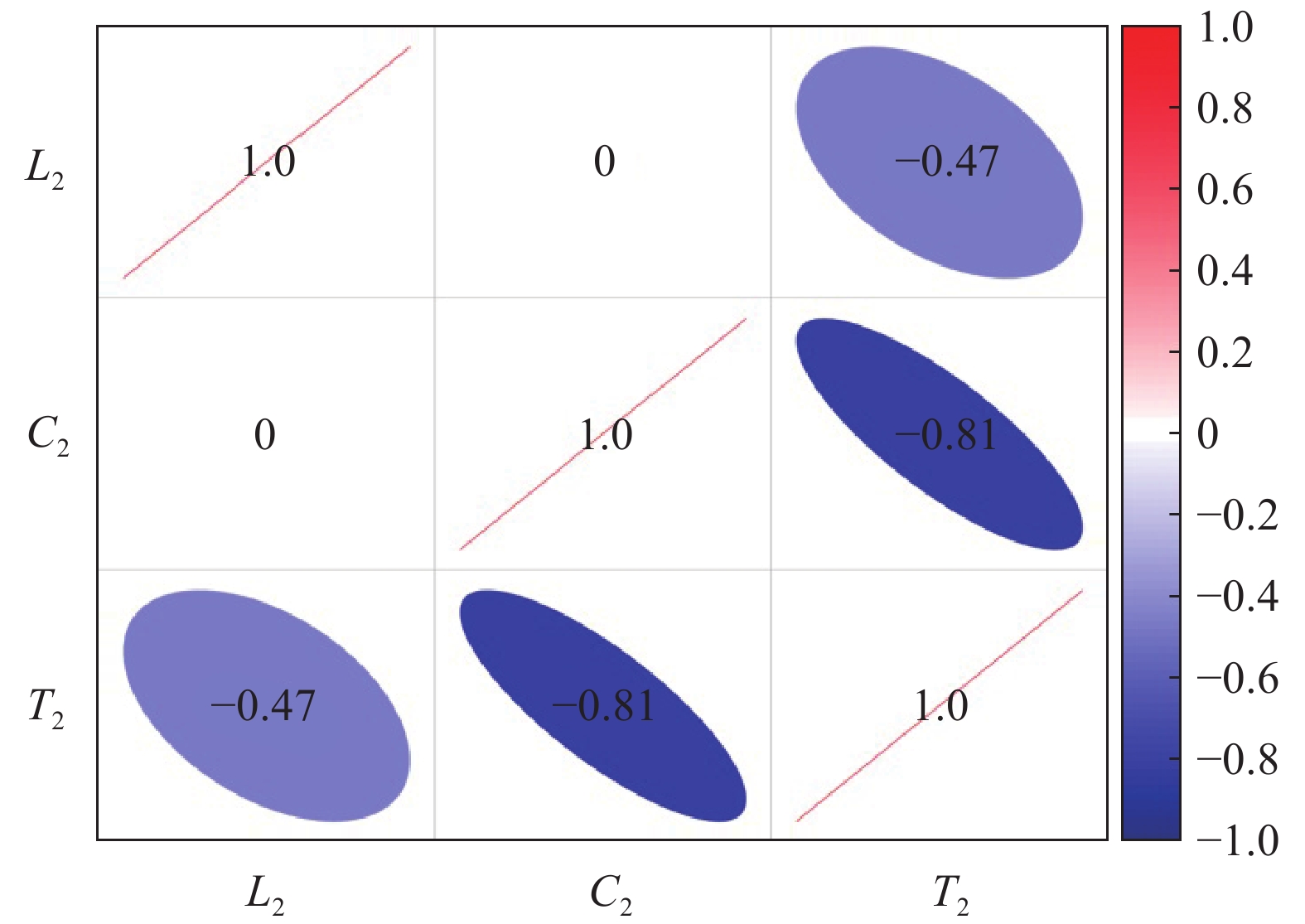
为了建立碱激发类砂浆强度与三因素间的回归模型,有必要对3个因素与抗压强度间的相关系数进行分析,使用SPSS软件计算出相关系数后,得到相关系数矩阵如图10所示。
由相关系数的计算结果可得:碱激发类砂浆的激发剂pH值与抗压强度呈现出正相关的规律,橡胶骨料掺量与抗压强度呈现出负相关的规律,而橡胶骨料粒径的相关系数为负值,但绝对值较小。在因素的交互作用中,J1、L1、C1两两间相关系数均为0,完全不相关。这为建立预测碱激发组砂浆抗压强度的回归模型的形式上提供了依据,即针对三因素J1、L1、C1建立多元非线性回归模型。
根据图3、图4中的数据走势,可以判断出碱激发类砂浆三因素的影响规律并以此设计多元非线性回归模型。对J1采用二次型函数进行模拟,L1采用三次型函数进行模拟,而C1则采用线性函数进行模拟。因此,碱激发类砂浆抗压强度T1的多元非线性回归模型可设为
T1=a1(b1J21+c1J1)+d1(e1L31+f1L21+g1L1)+h1C1+i1 (1) 其中,a1~i1为待定系数,将设定好的多元非线性回归模型导入SPSS软件中进行计算各项待定系数的估计值,得出结果如下式:
T1=0.992(0.089J21−1.28J1)+0.946(2×10−5L31−0.0045L21+0.247L1)−0.32C1+26.671 (2) 为了确保碱激发类砂浆抗压强度回归模型的可靠性,对模型进行了非线性曲面拟合。模型的相关性表示自变量与因变量的线性关系,可以用相关系数R2来表示其相关程度,通过将模型预测值与实测值比较可观测到,该回归模型与实际实验数据有一致的数据趋势,且相关系数接近1,证明该模型具有较高的准确性。将预测值与碱激发类砂浆实测抗压强度值进行对比,如图11所示,显示出其具有良好的重合度与相似的数据规律。
3.2 双因素作用下硅酸盐类砂浆抗压强度二元非线性回归分析
完全试验中,硅酸盐类砂浆抗压试样的各项测试结果表明:橡胶骨料粒径和橡胶骨料掺量这两个因素对试样的抗压强度都有非常显著的影响。为了对不同因素产生的影响进行量化分析及趋势预测,对双因素进行了考虑交互作用的显著性分析。将硅酸盐类砂浆橡胶骨料粒径设为L2,橡胶骨料掺量设为C2,硅酸盐类砂浆抗压强度设为T2,将试验数据整合后导入SPSS分析软件中进行显著性分析,可以得到L2、C2、L2C2的F值。对各因素对应F临界值进行检索对比后将结果整合记录于表5中。显著性分析表明:L2、C2、L2C2对硅酸盐类砂浆抗压强度都具有较高的显著性水平。
表 5 硅酸盐类砂浆因素显著性分析Table 5. Significance analysis of silicate mortar’s factorsSource Sum of squares Degree of
freedomMean
squareF-value Significance L2 391.441 4 97.860 61.322 *** C2 1173.307 3 391.102 245.077 *** L2C2 72.638 12 6.053 3.793 *** Error 63.833 40 1.596 — — Total 16296.580 60 — — — 使用SPSS软件对硅酸盐类砂浆抗压强度双因素与抗压强度间的相关系数进行分析,计算出相关系数后,得到相关系数矩阵如图12所示。由相关系数的计算结果可得:硅酸盐类砂浆的橡胶骨料掺量及橡胶骨料粒径与抗压强度呈现出负相关的规律。在因素的交互间,L2、C2间相关系数均为0,完全不相关。因此,在建立预测硅酸盐类砂浆抗压强度的回归模型的形式上,应使用双因素L2、C2建立二元非线性回归模型。
由数据统计得出的规律对硅酸盐类各因素的拟合函数型进行判断。经过从图5中汇总的数据实际情况可以得出,双因素L2、C2都适宜使用渐近线函数型。因此,硅酸盐类砂浆抗压强度T2的二元非线性回归模型可设为下式:
T2=a2L2+b2c2L2+d2+e2C2+f2g2C2+h2+i2 (3) 其中,a2~i2为系数,将设定好的二元非线性回归模型导入SPSS软件中进行计算各项待定系数的估计值,可求得硅酸盐类砂浆双因素非线性回归模型如下:
T2=3092.09−166.48L216.33L2+899.3−94.75C2+441.711.46C2+16.99+68.79 (4) 对硅酸盐类砂浆抗压强度回归模型进行了相关性检验和非线性曲面拟合,通过计算可得到,该回归模型相关系数接近1,证明该模型具有较高的准确性。将正交试验的变量值带入模型中,可以得到该模型计算出的预测值,将预测值与硅酸盐类砂浆实测抗压强度值进行对比,如图13所示,可以观测到拟合值与预测值具有较高的相似性。
4. 结 论
(1) 碱激发类砂浆抗压强度受到激发剂pH值、橡胶骨料粒径、橡胶骨料掺量3个因素的影响,在试验中取得的最优配合比是激发剂pH值14.6,橡胶骨料粒径为0.38 mm,橡胶骨料掺量为10vol%的组别,其抗压强度约为对照组强度的93%。硅酸盐类砂浆抗压强度受到橡胶骨料粒径、橡胶骨料掺量两个因素的影响,且均为负相关因素。
(2) 碱激发类砂浆的孔隙随着橡胶掺量的提升而逐渐增加,孔隙的尺寸随着橡胶粒径的减小而增大,孔隙的密度与橡胶骨料粒径变量非线性相关,在0.38 mm时,橡胶骨料的孔隙形貌与对照组类似。在实验组中孔隙密度最低。
(3) 硅酸盐类砂浆中孔隙的尺寸和数量随着橡胶粒径的减小而增大,尺寸也同样随着橡胶粒径的减小而增大。与碱激发类砂浆抗压强度均值进行比较,硅酸盐类砂浆具有相似的抗压强度,且碱激发类砂浆在高橡胶掺量时具有更高的抗压性能。
(4) 建立的碱激发类砂浆抗压强度多元非线性回归模型、硅酸盐类砂浆抗压强度二元非线性回归模型,能直观地表现各因素间的函数关系,回归显著,为再生橡胶骨料在碱性环境砂浆中的应用与配合比设计提供了理论支撑。
-
表 1 高炉矿渣主要氧化物成分
Table 1 Main oxide components of blast furnace slag
Oxide component CaO SiO2 Al2O3 MgO SO3 TiO2 Fe2O3 Content/wt% 49.51 25.61 13.23 5.51 2.34 2.131 0.421 表 2 碱激发类砂浆变量名称分类
Table 2 Designation and classification of alkali-activated mortar group's variables
Factor Symbol of variable Level Designation pH value of sodium
hydroxide solutionJ1 1 pH≈14.3 2 pH≈14.5 3 pH≈14.6 Volume substitution
rate of rubber aggregateC1 1 10vol% 2 20vol% 3 30vol% 4 40vol% Particle size of
rubber aggregateL1 1 1.70 mm 2 0.83 mm 3 0.38 mm 4 0.25 mm 5 0.15 mm 表 3 硅酸盐类砂浆变量名称分类
Table 3 Designation and classification of silicate mortar group's variables
Factor Symbols of variable Level Designation Volume substitution
rate of rubber aggregateC2 1 10vol% 2 20vol% 3 30vol% 4 40vol% Particle size of
rubber aggregateL2 1 1.70 mm 2 0.83 mm 3 0.38 mm 4 0.25 mm 5 0.15 mm 表 4 碱激发类砂浆因素显著性分析
Table 4 Significance analysis of alkali-activated mortar's factors
Source Sum of squares Degree of freedom Mean square F-value Significance J1 1464.388 2 732.194 758.883 *** L1 171.936 4 42.984 44.551 *** C1 2313.327 3 771.109 799.216 *** J1 L1 23.364 8 2.920 3.027 *** L1C1 13.789 12 1.149 1.191 // J1C1 160.447 6 26.741 27.716 *** J1L1C1 20.204 24 0.842 0.873 *** Error 115.780 120 0.965 — — Total 74288.445 180 — — — Notes: ***—Significant factor; //—Not significant factor; F—Test results of homogeneity of variance. 表 5 硅酸盐类砂浆因素显著性分析
Table 5 Significance analysis of silicate mortar’s factors
Source Sum of squares Degree of
freedomMean
squareF-value Significance L2 391.441 4 97.860 61.322 *** C2 1173.307 3 391.102 245.077 *** L2C2 72.638 12 6.053 3.793 *** Error 63.833 40 1.596 — — Total 16296.580 60 — — — -
[1] 姚韦靖, 刘雨姗, 王婷雅, 等. 橡胶/混凝土盐冻循环后性能劣化及微观结构[J]. 复合材料学报, 2021, 38(12):4294-4304. YAO Weijing, LIU Yushan, WANG Tingya, et al. Performance degradation and microscopic structure of rubber/concrete after salt freeze-thaw cycles[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2021,38(12):4294-4304(in Chinese).
[2] BRAVO M, DE BRITO J. Concrete made with used tyre aggregate: Durability-related performance[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production,2012,25:42-50. DOI: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2011.11.066
[3] SIDDIKA A, AL MAMUN M A, ALYOUSEF R, et al. Properties and utilizations of waste tire rubber in concrete: A review[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2019,224:711-731. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.07.108
[4] KHALOOA R, DEHESTANI M, RAHMAYABADI P. Mechanical properties of concrete containing a high volume of tire–rubber particles[J]. Waste Management,2008,28(12):2472-2482. DOI: 10.1016/j.wasman.2008.01.015
[5] GIRSKAS G, NAGROCKIENĖ D. Crushed rubber waste impact of concrete basic properties[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2017,140:36-42. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2017.02.107
[6] GUPTA T, CHAUDHARY S, SHARMA R K. Assessment of mechanical and durability properties of concrete containing waste rubber tire as fine aggregate[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2014,73:562-574. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2014.09.102
[7] INCE C, SHEHATA B M H, DEROGAR S, et al. Towards the development of sustainable concrete incorporating waste tyre rubbers: A long-term study of physical, mechanical & durability properties and environmental impact[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production,2022,334:130223. DOI: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.130223
[8] VALENTE M, SAMBUCCI M, CHOUGAN M, et al. Reducing the emission of climate-altering substances in cementitious materials: A comparison between alkali-activated materials and Portland cement-based composites incorporating recycled tire rubber[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production,2022,333:130013. DOI: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2021.130013
[9] SHAO J, ZHU H, XUE G, et al. Mechanical and restrained shrinkage behaviors of cement mortar incorporating waste tire rubber particles and expansive agent[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2021,296:123742. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.123742
[10] LIU M, LU J, MING P, et al. Study of fracture properties and post-peak softening process of rubber concrete based on acoustic emission[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2021,313:125487. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.125487
[11] SHAO J, ZHU H, ZHAO B, et al. Combined effect of recycled tire rubber and carbon nanotubes on the mechanical properties and microstructure of concrete[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2022,322:126493. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2022.126493
[12] GRAVINA R J, XIE T. Toward the development of sustainable concrete with crumb rubber: Design-oriented models, life-cycle-assessment and a site application[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2022,315:125565. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.125565
[13] NOCERA F, WANG J, FALESCHINI F, et al. Probabilistic models of concrete compressive strength and elastic modulus with rubber aggregates[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2022,322:126145. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.126145
[14] AL-FASIH M Y M, HUSEIEN G F, BIN IBRAHIM I S, et al. Synthesis of rubberized alkali-activated concrete: Experimental and numerical evaluation[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2021,303:124526. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.124526
[15] SOUZA T B, LIMA V M E, ARAÚJO F W C, et al. Alkali-activated slag cellular concrete with expanded polystyrene (EPS)-physical, mechanical, and mineralogical properties[J]. Journal of Building Engineering,2021,44:103387. DOI: 10.1016/j.jobe.2021.103387
[16] WANG H, WU Y, CHENG B. Mechanical properties of alkali-activated concrete containing crumb rubber particles[J]. Case Studies in Construction Materials,2022,16:e00803. DOI: 10.1016/j.cscm.2021.e00803
[17] KONG L, ZHAO W, XUAN D, et al. Application potential of alkali-activated concrete for antimicrobial induced corrosion: A review[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2022,317:126169. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.126169
[18] BANDYOPADHYAY S, DE P P, TRIPATHY D K, et al. Influence of surface oxidation of carbon black on its interaction with nitrile rubbers[J]. Polymer,1996,37(2):353-357. DOI: 10.1016/0032-3861(96)81110-4
[19] DOU Y, FENG G, XU L, et al. Modification of rubber particles and its application in rubberized concrete[J]. Journal of Building Engineering,2022,51:104346. DOI: 10.1016/j.jobe.2022.104346
[20] MA D D, ZHANG W P, WANG X P, et al. Effects of curing temperature on mechanical properties and pore size distribution of cement clay modified by metakaolin and basalt fiber[J]. Journal of Building Engineering, 2023, 68: 106232.
[21] SEGRE N, MONTEIRO P J M, SPOSITO G. Surface characterization of recycled tire rubber to be used in cement paste matrix[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science,2002,248(2):521-523. DOI: 10.1006/jcis.2002.8217
[22] AMRAN M, FEDIUK R, ABDELGADER H S, et al. Fiber-reinforced alkali-activated concrete: A review[J]. Journal of Building Engineering,2022,45:103638. DOI: 10.1016/j.jobe.2021.103638
[23] MOHAMMED A, RAFIQ S, SIHAG P, et al. ANN, M5 P-tree and nonlinear regression approaches with statistical evaluations to predict the compressive strength of cement-based mortar modified with fly ash[J]. Journal of Materials Research and Technology,2020,9(6):12416-12427. DOI: 10.1016/j.jmrt.2020.08.083
[24] GOLAFSHANI E M, BEHNOOD A, ARASHPOUR M. Predicting the compressive strength of normal and high-performance concretes using ANN and ANFIS hybridized with grey wolf optimizer[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2020,232:117266. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.117266
[25] XIAO Y, MENG M, CHEN H, et al. Nonlinear regression model for peak-failure strength of rockfill materials in general stress space[J]. Geoscience Frontiers,2018,9(6):1699-1709. DOI: 10.1016/j.gsf.2017.07.001
[26] XU J, ZHAO X, YU Y, et al. Parametric sensitivity analysis and modelling of mechanical properties of normal-and high-strength recycled aggregate concrete using grey theory, multiple nonlinear regression and artificial neural networks[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2019,211:479-491. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.03.234
[27] ASTM. Standard test method for compressive strength of hydraulic cement mortars: ASTM C109/C109 M-02[S]. West Conshohocken: ASTM International, 2002.
-




 下载:
下载: