Effect of graphene oxide on the impermeability of cementitious capillary crystalline waterproofing
-
摘要: 研究了木质素磺酸钠(MN)对氧化石墨烯(GO)在模拟水泥水化孔隙液中的分散能力的影响,并研究了MN分散的GO对水泥基渗透结晶型防水材料(CCCW)对水泥砂浆抗渗性能的影响。通过吸光度试验、Zeta电位及原子力显微镜(AFM)研究表明,当MN与GO的质量比为3∶1时,GO在饱和氢氧化钙溶液中的分散性最佳;砂浆力学强度测试表明,当GO掺量为水泥质量的0.03%时,3天、28天的抗折抗压强度相较于不掺入MN的GO砂浆分别提高了39.13%和39.37%、33.84%和33.48%;砂浆抗渗压力和氯离子扩散系数比标准砂浆试件分别提高了160.0%和下降了50.6%;抗渗性能测试表明,当GO掺量为水泥质量的0.03%时,GO改性CCCW涂层抗渗压力比含CCCW的涂层提高了116.7%;微观测试表明,GO促进了水化反应,并在砂浆基质中发挥了填充作用和模板作用,增强了水化产物的密实度,使得砂浆和CCCW抗渗性能增加了。本文提供了一种GO改性CCCW来提升水泥砂浆的抗渗性能,在涂层防水效果和降低CCCW材料成本等应用价值得到提升。
-
关键词:
- 氧化石墨烯 /
- 分散 /
- 抗渗性能 /
- 水泥基渗透结晶型防水材料 /
- 力学性能
Abstract: The effect of sodium lignosulfonate (MN) on the dispersion ability of graphene oxide (GO) in simulated cement hydration pore solution was studied, and the effect of MN-dispersed GO on the impermeability of cementitious capillary crystalline waterproofing (CCCW) was studied. The results of absorbance test, Zeta potential and atomic force microscope (AFM) show that GO has the best dispersion in saturated calcium hydroxide solution when the mass ratio of MN and GO is 3:1. The mechanical strength test of mortar shows that when the GO content is 0.03% of the cement mass, the flexural and compressive strength of 3 days and 28 days are increased by 39.13% and 39.37%, 33.84% and 33.48%, respectively, compared with the GO mortar without MN. The impermeability pressure and chloride ion diffusion coefficient of mortar are 160.0% and 50.6% higher than those of standard mortar specimens, respectively. The impermeability test shows that when the GO content is 0.03% of the cement mass, the impermeability pressure of the GO modified CCCW coating is 116.7% higher than that of the CCCW coating. Micro-test shows that GO promotes the hydration reaction, plays a filling role and template role in the mortar matrix, enhances the density of hydration products, and increases the impermeability of mortar and CCCW. This study provides a GO modified CCCW to improve the impermeability of cement mortar, and its application value in coating waterproof effect and reducing CCCW material cost is improved. -
水泥基材料是一种应用广泛的土木工程材料,其内部存在诸多错综复杂、形状各异、尺寸不一的孔隙和微裂缝,这种多孔结构极大的影响了水泥基材料的抗渗能力[1]。目前,如何提升水泥基材料的抗渗性能是土木工程研究中的重点问题。以往研究表明,采用防水材料[2]如防水卷材[3-5]、防水涂料[6-7]、密封材料[8-9]、刚性防水材料[10-12]等,或者是掺入纳米粒子/聚合物[13]及添加纤维[14]能够增强建筑物的防水性能。但在工程应用中逐渐发现一些弊端,防水卷材、涂料与基体的相容性差、耐久性差、施工复杂、环保差等;聚合物可导致水泥水化延缓,引起水泥基材料早期强度下降;纤维对密实性和耐久性改善较少。随着进一步的大量研究表明[15-18],人们发现掺加氧化石墨烯(GO)是一种显著提高水泥基材料性能的有效途径,GO能起到提供模板与调控水泥水化产物形成规整微观结构[19],减少水泥基体的孔隙率、平均孔径及裂缝的作用[20-22]。由于GO能够良好的增强水泥基材料的密实性[22-24],关于其在抗渗性能方面的研究也随之增多[25-29]。Zeng等[30]使用两种不同组成GO,当GO-1和GO-2的用量均为0.06wt%时,水渗透深度分别显著降低了55.5%和23.2%,相对渗透系数分别降低了80.2%和41.0%。Liu等[31]发现当GO的剂量为0.03%时,砂浆的不渗透性增加了80%。此外,该砂浆在受到硫酸盐攻击时也具有较高的强度保留率。张友来等[32]利用硅烷渗透型防水材料的渗透性好、防水效果优良等优点,制备出GO/硅烷复合乳液,该复合乳液可有效阻止有害离子通过水溶液进入水泥中,进而提高混凝土的耐久性。说明GO可作为水泥基材料理想的防水剂和耐腐蚀剂。这些研究结果为解决某些结构的漏水问题和提高重盐碱区结构的耐久性提供了新的方法发现。
随着防水材料研究的逐渐深入,一种具备优异防水性能的新型刚性防水材料−水泥基渗透结晶型防水材料(CCCW)[33-35],进入人们的视野。这类材料不同于传统防水材料是其能工作于背水面潮湿基面,并且其1 cm厚的涂层能达到10~20 cm厚的聚合物水泥砂浆防水涂料的抗渗防水效果,且对基体还有修复功能。CCCW在潮湿环境下能够加速混凝土的水泥水化反应,生成不溶于水的结晶体,填补裂缝和孔隙,修补混凝土内部损伤和降低混凝土的渗透性,从而提高混凝土的密实性和抗氯离子侵蚀性能[36-37]。丁向群等[38]发现内掺渗透结晶防水材料混凝土的28天强度可达基准试块的123.06%,28天抗渗压力为基准试块的275%。其结构致密,结构中水化硅酸钙明显增多,抗渗性能明显提高。孙学志[39]发现经涂刷渗透结晶型涂层后试件的渗透深度相对于基准试件均有大小不等的减小且随水灰比的增大,无论是基准件还是涂有涂层的试件其渗透深度都有不同程度的增加。
通过查阅文献,目前有关CCCW的研究中多采用纳米二氧化硅[37]和掺入活性物质[40-41]来提升对其抗渗性能的影响,尚未有研究提出GO对CCCW抗渗性能的影响。基于GO对水泥基材料综合性能的提升作用及CCCW良好的抗渗性能,故本文研究了GO对CCCW抗渗性能的影响。
1. 实 验
1.1 原材料
GO原浆由常州第六元素材料科技股份有限公司提供,质量分数为3.18wt%,固含量为43.17%;CCCW由重庆中防德邦防水技术有限公司提供;木质素磺酸钠(MN),纯度为工业级,天津市光复精细化工研究所提供;水泥(C)为重庆永固新型建材有限公司生产,为PO42.5 R的普通硅酸盐水泥,主要化学成分列于表1;标准砂(S)由厦门艾思欧标准砂有限公司生产,为ISO标准砂;聚羧酸减水剂(PC)由重庆建研科之杰新材料有限公司生产,固含量为50wt%,减水率为26.7%。
表 1 水泥化学成分Table 1. Chemical composition of cementMineral Al2O3 SiO2 Fe2O3 CaO MgO SO3 NaO f-CaO Content/wt% 4.47 21.50 3.37 65.84 3.18 0.30 0.49 0.78 Note: f-CaO—Free calcium oxide. 1.2 GO悬浮液的制备
取定量氧化石墨与去离子水置于超声波细胞破碎仪(JY99-ⅡDN,宁波新芝生物科技股份有限公司)中超声分散2 h后静置,配制浓度为5.0 mg/mL的GO悬浮液作为储备液;取少量溶液加入去离子水稀释,再次超声2 h得到浓度为3.666 mg/mL的GO悬浮液,保存备用。
1.3 GO在饱和Ca(OH)2溶液中的分散性测试
分别配制浓度为10 mg/L的MN、GO,采用UV-3200 S型紫外可见分光光度计(UV-3200S,上海美谱达仪器有限公司)测试如表2所示溶液在200~900 nm波长范围内的光吸收情况,并测定其在波长230 nm的吸光度。溶液吸光度测试方法:向一定的去离子水中依次加入PC、MN、GO配制混合溶液,搅拌10 min后超声30 min,再将上述溶液加入澄清的饱和Ca(OH)2溶液中磁力搅拌10 min、超声30 min,静置10 min后在不同时间段测试吸光度。
表 2 用于吸光度和Zeta电位测试的氧化石墨烯(GO)溶液组成Table 2. Composition of graphene oxide (GO) solution for absorbance and Zeta potential testSample Water/g Ca(OH)2/g PC/mL GO①/mL MN② Y0 99.3 0.16 0 0.7 0 Y1 99.3 0.16 0.05 0.7 0 Y2 99.3 0.16 0.05 0.7 1∶1 Y3 99.3 0.16 0.05 0.7 2∶1 Y4 99.3 0.16 0.05 0.7 3∶1 Y5 99.3 0.16 0.05 0.7 4∶1 Y6 99.3 0.16 0.05 0.7 5∶1 Notes: PC—Polycarboxylic acid water reducer; MN—sodium ligninsulfonate; ①—GO concentration is 3.666 mg/mL; ②—Content of MN is its ratio to GO. 1.4 Zeta电位测试
按表2所示配制含不同MN和GO含量的饱和Ca(OH)2溶液。搅拌10 min后超声30 min,再静置10 min后取一定量的溶液在马尔文ZEN-3700电位仪(ZEN-3700,马尔文帕纳科公司)中测定表面电位。
1.5 原子力显微镜(AFM)测试
AFM测定MN分散GO的分散情况具体方法为:配制MN含量为0.3%、GO含量为0.1%的水溶液,分别磁力搅拌2 min和超声10 min混合均匀,再将配好溶液稀释1000倍,取上层清液滴在贴有云母片的载玻片上,取出晾干并保鲜膜密封后放置玻璃皿中待用。
1.6 砂浆力学性能、抗渗压力和抗氯离子渗透测试
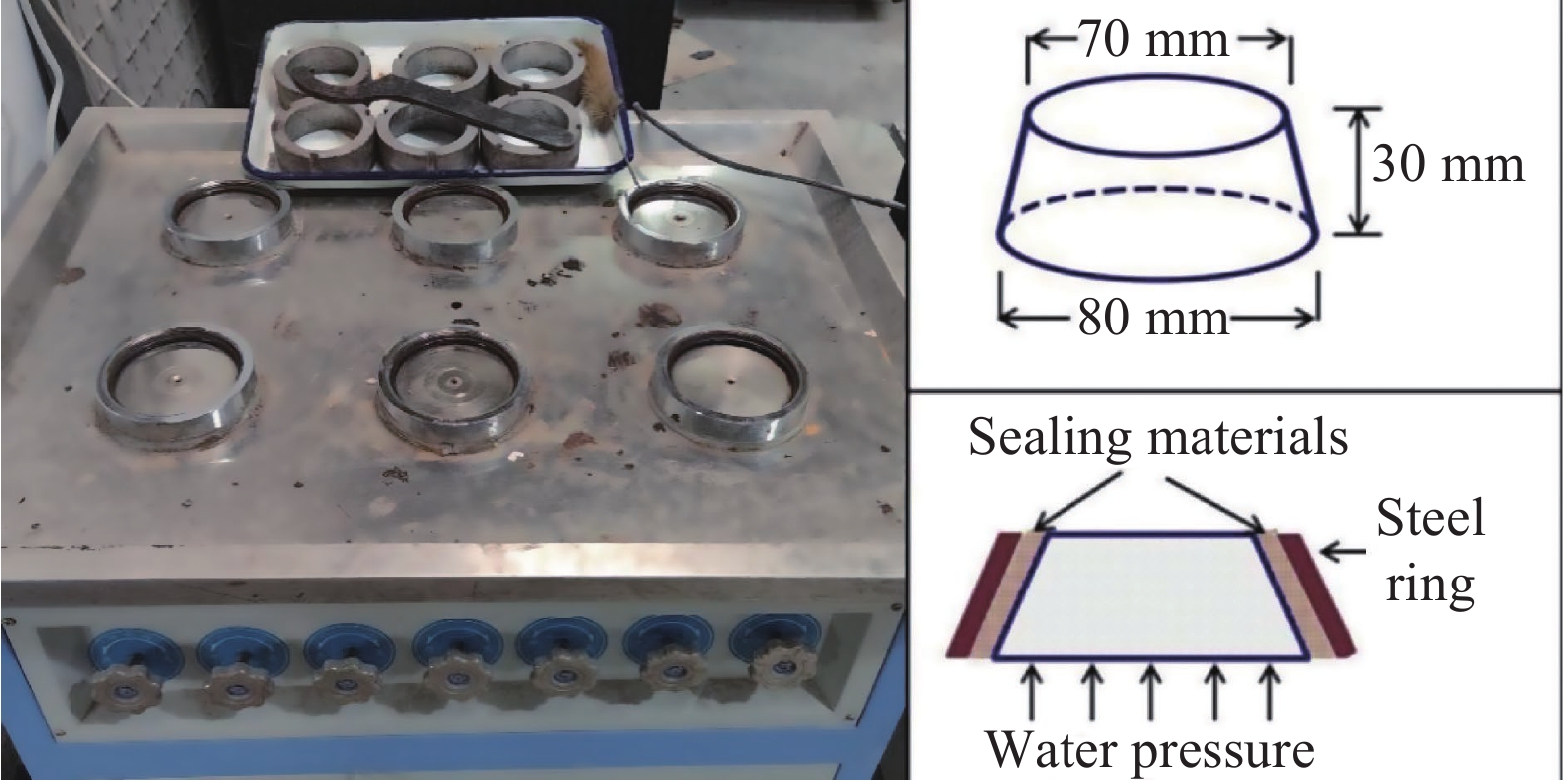
将定量PC、MN、GO分散液按比例混合,超声30 min后将分散液与拌合水混合进行砂浆成型,砂浆配合比如表3所示。水泥砂浆拌和、成型、养护及力学性能测试参照《水泥胶砂强度检验方法(ISO法)》(GB/T 17671—1999)[42]执行。其中水泥砂浆的力学性能测试采用抗折抗压一体试验机(YW-300 D,济南天辰试验机制造有限公司)如图1所示。
表 3 用于力学性能和抗渗压力测试的GO改性水泥砂浆配合比Table 3. Mix ratio of GO modified cement mortar for mechanical properties and impermeability pressure testSample Sand/g Cement/g PC/g Water/g GO①/% MN/% A1 1350 450 2.7 166 0 0 A2 1350 450 2.7 166 0 0.03 A3 1350 450 2.7 166 0.005 0.015 A4 1350 450 2.7 166 0.005 0 A5 1350 450 2.7 166 0.01 0.03 A6 1350 450 2.7 166 0.01 0 A7 1350 450 2.7 166 0.03 0.09 A8 1350 450 2.7 166 0.03 0 A9 1350 450 2.7 166 0.05 0.15 A10 1350 450 2.7 166 0.05 0 Note: ①—Mass ratio to cement. 砂浆制备及抗渗压力测试按《建筑砂浆基本性能试验方法标准》(JGJ/T 70—2009)[43]《砂浆、混凝土防水剂》(JC 474—2008)[44]执行。采用RCM法测试砂浆的抗氯离子渗透性能,试验按照《混凝土氯离子扩散系数测定仪》(JG/T 262—2009)[45]执行。
1.7 GO改性CCCW防水涂层的抗渗压力测试
用于涂层测试的基准砂浆配合比如表4所示,掺加CCCW的涂层配合比如表5所示,采用SS-15砂浆渗透仪(思拓锐(天津)测控技术有限公司)如图2所示,对涂敷防水涂层的砂浆试件进行抗渗压力试验。其中基准砂浆试件的成型制作和养护及涂层抗渗压力测试按照《砂浆、混凝土防水剂》(JC 474—2008)[44]标准执行,带涂层砂浆抗渗试件按照《水泥基渗透型防水材料》(GB/T 18445—2012)[46]进行养护。
表 4 基准砂浆配合比Table 4. Mix ratio of reference mortarCement/g Water/g Sand/g Cellulose ether/g 320 260 1350 0.5 表 5 涂层配合比Table 5. Mix ratio of coatingSample CCCW/g Water/g PC①/% GO②/% MN/% C1 20 6 0 0 0 C2 20 6 0.3 0.01 0 C3 20 6 0.3 0.01 0.03 C4 20 6 0.3 0.03 0 C5 20 6 0.3 0.03 0.09 C6 20 6 0.3 0.05 0 C7 20 6 0.3 0.05 0.15 Notes: CCCW—Cementitious capillary crystalline waterproofing material; ①—Mass ratio to CCCW; ②—Mass ratio to CCCW. 1.8 含CCCW的硬化浆体微观测试
取28天龄期CCCW涂层净浆样品浸泡在无水乙醇中终止水化后在65℃的烘箱中干燥24 h后用Sigma 300型场发射扫描电子显微镜(SEM,德国卡尔·蔡司股份公司)观察水泥石的微观形貌。将试件样品制成长1 cm×高1.5 cm,然后用压汞法(MIP)对涂层净浆进行孔隙率测试,样品粉碎后所得粉末采用德国Bruker公司的D8 Advance型X射线衍射仪进行XRD测试。
2. 结果与分析
2.1 MN对GO在饱和Ca(OH)2溶液中分散性能的影响
在波长180~700 nm范围下GO与MN水溶液的紫外可见吸收光谱如图3所示。可以看出,在230 nm处GO溶液有明显的吸收峰,而MN在该波长下几乎没有吸收,故可推测,当二者共存于同一溶液时,MN不会影响GO在波长230 nm处的光吸收。由比尔-朗伯定律可知,GO吸光度与其溶液浓度成正比。大量研究表明,GO在水泥水化介质中的分散性与其吸光度有直接的线性关联度[47]。故使用在波长230 nm处的溶液吸光度来考察MN对GO在饱和Ca(OH)2溶液中分散程度的影响。
以往研究表明PC能促进GO在水泥水化介质中的分散性[48],本实验研究了在PC存在时,MN对GO在饱和Ca(OH)2溶液中分散性的影响。不同含量MN对GO溶液吸光度的影响如图4所示,其中Y1为对照溶液,Y2~Y6为额外加入了不同含量MN的GO溶液。可以看出,相比对照溶液(Y1),当MN与GO质量比依次为1∶1、2∶1和3∶1时,Y2~Y4溶液的吸光度不断增大,表明加入少量MN能改变GO在溶液的聚集状态,防止GO的团聚。这可能是由于MN在溶液中能与Ca2+迅速配位络合,使能与GO配位并诱导GO聚沉的Ca2+有效浓度减少,导致更多的GO均匀分散在整个溶液中。对溶液Y5和Y6,随着MN掺量的增加,其吸光度发生了下降,这是由于MN掺量过多导致GO发生了聚沉。当MN与GO质量比为3∶1时,溶液的吸光度达到最大值,即此时MN对GO的分散效果最佳。此外,MN对GO的分散效果也会受时间的影响,相同条件下,随着时间的延长,溶液的吸光度呈现下降的趋势。根据吸光度的数据,后续研究中选择MN与GO的质量比为3∶1进行试验研究。
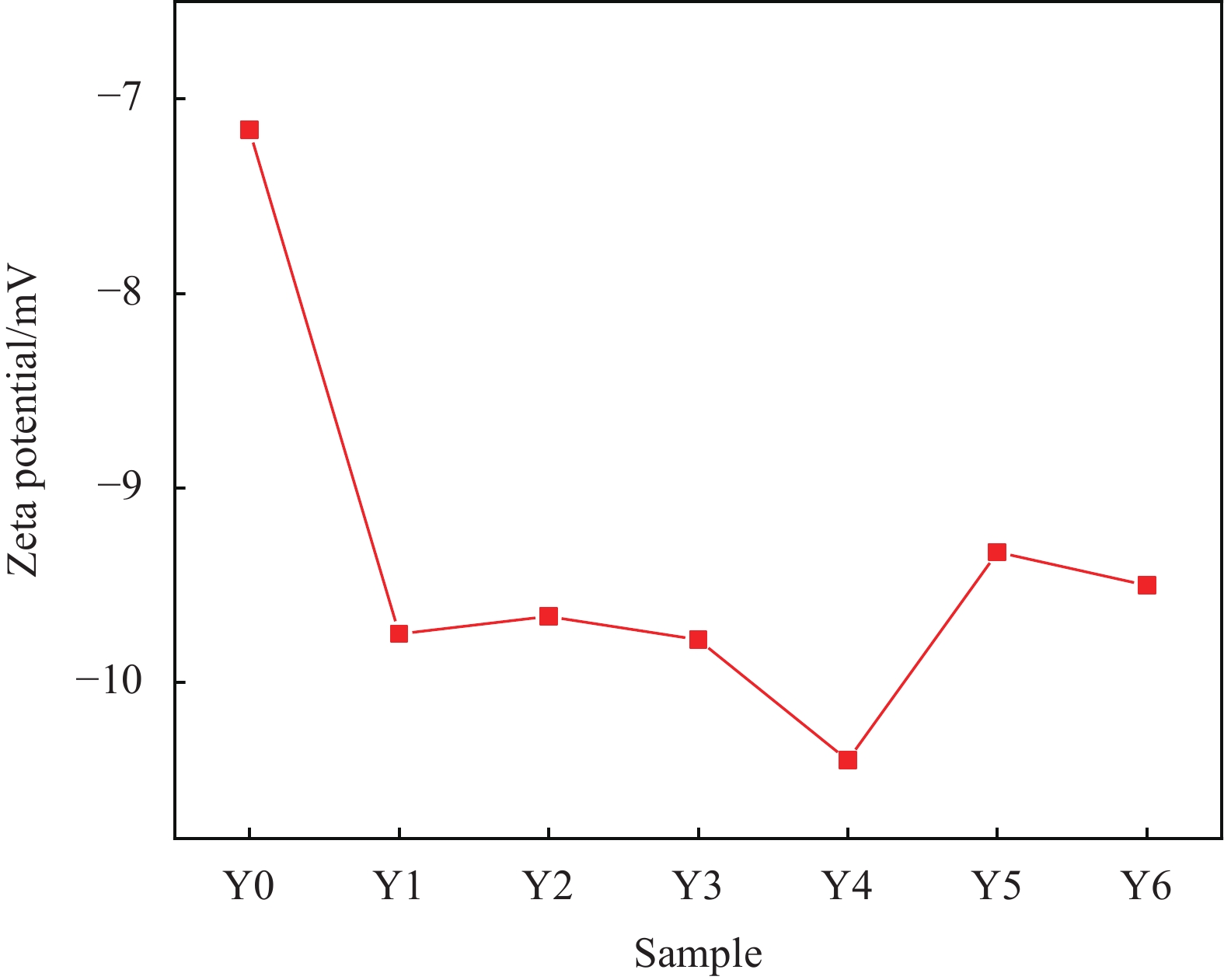
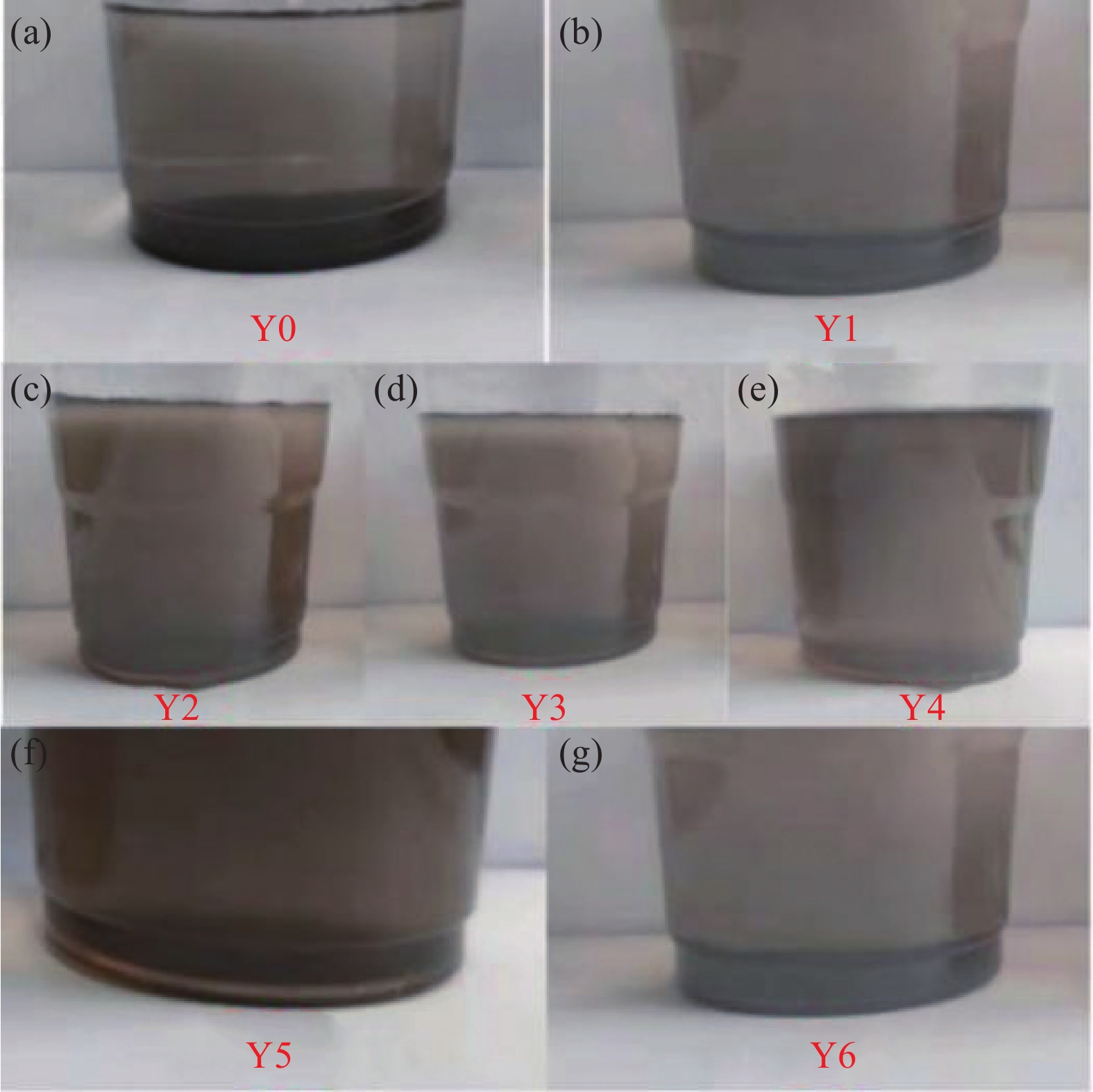
图5为不同GO溶液体系的Zeta电位图。Y0为基准溶液,GO在Y0溶液体系中的Zeta表面电位为−7.16 mV,表明GO在模拟水泥水化孔隙液的饱和Ca(OH)2溶液中表面带负电荷,电荷绝对值越小,表明分散液状态不稳定、易聚沉。在减水剂PC作用下GO在Y1溶液中电位值为−9.78 mV,相对Y0溶液,GO电位绝对值有所增长,说明PC能在一定程度上改善GO在饱和Ca(OH)2溶液中稳定分散的程度但其效果相当有限。当GO与MN的质量比从1∶1变化到1∶3时,表面电位从−9.66 mV逐渐减小到−10.4 mV。但进一步增大MN含量,溶液Zeta电位逐渐上升了。图6为不同GO溶液体系的60 min静置图。可以看出在不同体系中GO的分散情况,其中,当GO与MN质量比为1∶3时,溶液分散状态最佳,且与吸光度实验数据得出的结果一致,这不仅表明了MN能进一步促进GO在饱和Ca(OH)2溶液中均匀分散,还展示出了该比例来分散GO的可靠性。
2.2 MN分散的GO对片层厚度的影响
图7为掺加MN分散的上层清液中GO的AFM图像。所得的GO片层厚度在2~3 nm之间,由于单层GO厚度一般在0.6~1.2 nm[49-50],因此在MN做分散剂时分GO层数约为2~5层。说明了MN的存在分散有助于GO片层的稳定分散。
2.3 MN分散的GO对砂浆力学强度的影响
MN分散的GO对水泥砂浆的力学性能影响如表6所示,可知,单独掺加MN的试件A2相较于基准试件强度A1的3天和28天抗折强度分别减小了13.04%和9.23%,其原因是MN有部分缓凝作用[51-52],使水泥水化时间延迟,导致早期强度有所降低;3天和28天抗压强度相较于基准试件A1强度分别减小了20.05%和5.38%,与抗折强度现象类似,表明MN对水泥砂浆强度有劣化作用,这主要是由于掺加的MN对水泥水化具有缓凝作用,因此导致强度降低。单独掺加0.005%、0.01%、0.03%、0.05%的GO样品(A4、A6、A8、A10),3天抗折强度和抗压强度相较于基准试件分别提高了19.56%和5.23%、21.73%和16.8%、34.78%和28.94、34.78%和26%,28天抗折强度和抗压强度相较于基准试件分别提高了7.69%和13.04%、9.23%和17.57%、32.30%和28.88%、24.61%和20.11%说明一定掺量的GO能改善水泥砂浆的力学性能这是由于GO纳米填充效应及模板效应等使水泥砂浆内部结构变得紧密,从而提升了水泥砂浆的抗折强度和抗压强度;当MN与GO质量比为3∶1时(A3、A5、A7、A9),水泥砂浆3天、28天抗折强度和抗压强度随着GO的掺量增加先增后减的趋势。其中A7试件3天、28天抗折、抗压强度相较于基准试件分别可以最高提升39.13%和39.37%、33.84%和33.48%,在MN的助分散作用下,GO提升水泥砂浆强度的效果更加显著,其原因是MN是一种水溶性很好的物质,且分子结构式中具有大量的苯环,可与GO二维片层之间有很强的分子间作用力,极大提升在水化介质中GO的分散能力。本文和部分已发表GO提升砂浆抗压抗折强度的最佳结果进行对比如表7所示,可以表明,当GO掺量相同时水泥砂浆的抗折抗压强度增长幅度更大,进一步说明本文MN可以更有效地分散GO,发挥GO作用。
表 6 MN分散的GO对水泥砂浆抗折强度和抗压强度的影响Table 6. Effect of MN dispersed GO on the flexural and compressive strength of cement mortarSample Flexural strength (MPa)/Changing rate (%) Compressive strength (MPa)/Changing rate (%) 3 days 28 days 3 days 28 days A1 4.6±0.25/0 6.5±0.71/0 35.0±0.15/0 45.7±0.83/0 A2 4.0±0.34/13.04 5.9±0.85/9.23 27.98±0.35/20.05 43.24±0.85/5.38 A3 5.6±0.35/21.73 7.9±0.75/21.53 38.56±0.25/10.17 52.45±0.93/14.77 A4 5.5±0.55/19.56 7±0.95/7.69 36.83±0.44/5.23 51.66±1.15/13.04 A5 5.7±0.05/23.91 7.9±0.35/21.53 42.67±1.35/21.91 54.12±1.55/18.42 A6 5.6±0.35/21.73 7.1±0.45/9.23 40.88±0.84/16.80 53.73±0.75/17.57 A7 6.4±0.05/39.13 8.7±1.05/33.84 48.78±1.02/39.37 61.00±1.25/33.48 A8 6.2±0.65/34.78 8.6±0.84/32.30 45.13±0.05/28.94 58.90±0.55/28.88 A9 6.3±0.15/36.95 8.2±0.94/26.15 46.35±1.25/32.43 56.75±0.74/24.18 A10 6.2±0.45/34.78 8.1±0.35/24.61 44.10±0.85/26 54.89±0.65/20.11 表 7 GO提升水泥砂浆抗压抗折强度研究对比Table 7. Comparison of compressive and flexural strength of cement mortar improved by GO综上所述,在MN的存在下GO在水泥浆体中有更好的分散性,从而进一步利用模板效应[53]调控水泥水化产物的生长,从而使硬化水泥石结构更加密实。而这一结果与吸光度测试和Zeta电位测试正好吻合,也正由于这个结果可以利用MN和GO一起去改善CCCW的抗渗性能。
2.4 MN分散的GO对水泥砂浆抗氯离子渗透试验的影响
试件选用表3中A1、A2、A3、A4、A7、A8。保持MN与GO质量比为3∶1,不同GO掺量对砂浆的抗氯离子渗透影响如图8所示。从A1和A2可以看出,在水泥砂浆中加入了MN之后,水泥砂浆中的非稳态氯离子迁移系数降低,说明MN在一定程度上能改善水泥砂浆的抗渗性能,这是由于在MN能够有效填充水泥砂浆的孔隙,使水泥基体更加密实,从而改善了砂浆的抗渗性能;从A1、A4和A8中也可以看出,在水泥砂浆中加入GO后,迁移系数同样发生了降低,并且迁移系数随着GO掺量的增加而下降,说明GO改善水泥砂浆抗渗性能的效果与GO的掺量有关,随着GO掺量的增加,这种提升作用也愈加显著,在GO的掺量达0.03%时效果最佳,这是由于GO的掺入能够水泥水化产物的生长进程与晶体形貌,改善了水泥基体的孔隙结构;A3与A4相比,A7与A8相比,其迁移系数分别下降了3.7%和8.0%,且A7相比于A1其迁移系数下降了50.6%,说明在MN的助分散作用下,砂浆试件的抗渗性能得到了进一步的改善。这一方面是由于MN本身也对砂浆的抗渗性能有提升作用,另一方面是由于MN有利于GO在水泥基体中的稳定分散,从而使GO砂浆抗渗性能有更加显著的增强效果,这与MN分散的GO对砂浆力学强度的影响一样,更加说明MN分散的GO能更好地调控水化产物来改善砂浆试件的抗渗性能。
2.5 GO改性水泥砂浆及改性CCCW涂层的抗渗压力试验
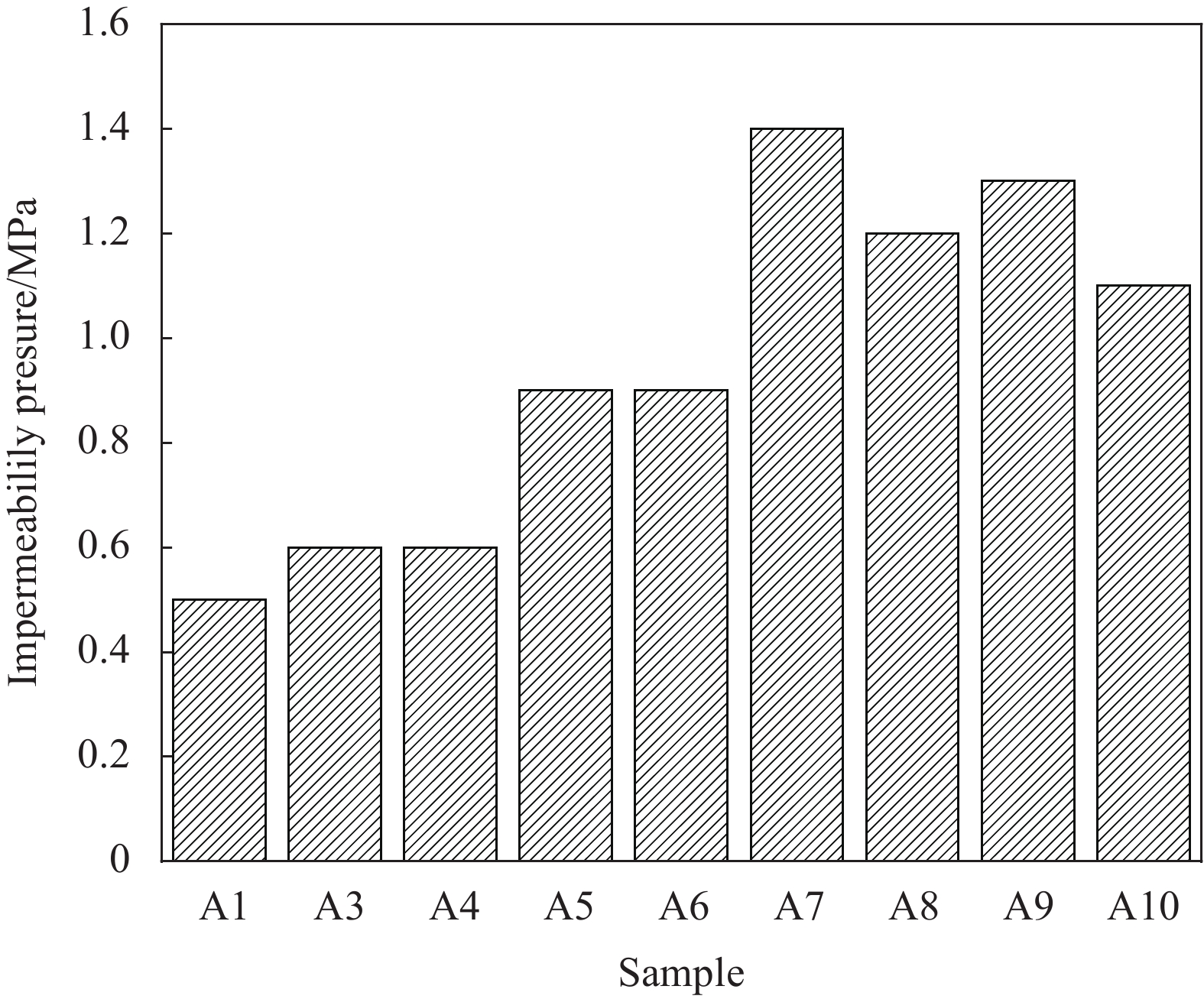
MN分散的GO对水泥砂浆抗渗压力的影响如图9所示。空白对照组A1的抗渗压力为0.5 MPa,从保持MN与GO质量比为3∶1,GO掺量分别为0.005%、0.01%(A3、A5)和分别单独掺加GO(A4、A6)可以看到,当GO掺量小的时候额外加入MN对抗渗压力的影响不是很明显,当GO掺量为0.03%、0.05%的时候(A7、A8)和(A9、A10)两组抗渗压力随着MN的掺入抗渗压力有所增加,而抗渗压力最高值在A7,此时的GO被MN分散得最好,即MN能提升GO对砂浆抗渗性能的改善作用,并且这个改善效果与GO的掺量有着密切的关系,当GO的掺量为0.03%,砂浆抗渗性能最好,抗渗压力为1.4 MPa,与A1的相比提高了160.0%。
目前对GO提升水泥砂浆抗渗性能的研究还很少。Zeng等[57]采用两种GO纳米片作为添加剂,以降低水泥砂浆的渗透性。试验结果表明,0.06wt%GO-1(纵横比50000)和GO-2(纵横比5000)的相对渗透率系数分别降低了80.2%和41.0%。Liu等[58]研究了把硅灰(SF)和粉煤灰(FA)加入到不同掺量的GO中研究抗渗性能,结果表明:当GO掺量为0.03%时抗渗性最好,渗透压与对照试件的比值达到180%。通过对比可以发现本文利用MN良好分散后的GO可以大幅度的提升水泥砂浆的抗渗性能。通过对GO改性水泥砂浆的抗渗性能研究结果,故提出对GO改性CCCCW涂层的抗渗性能进行研究。
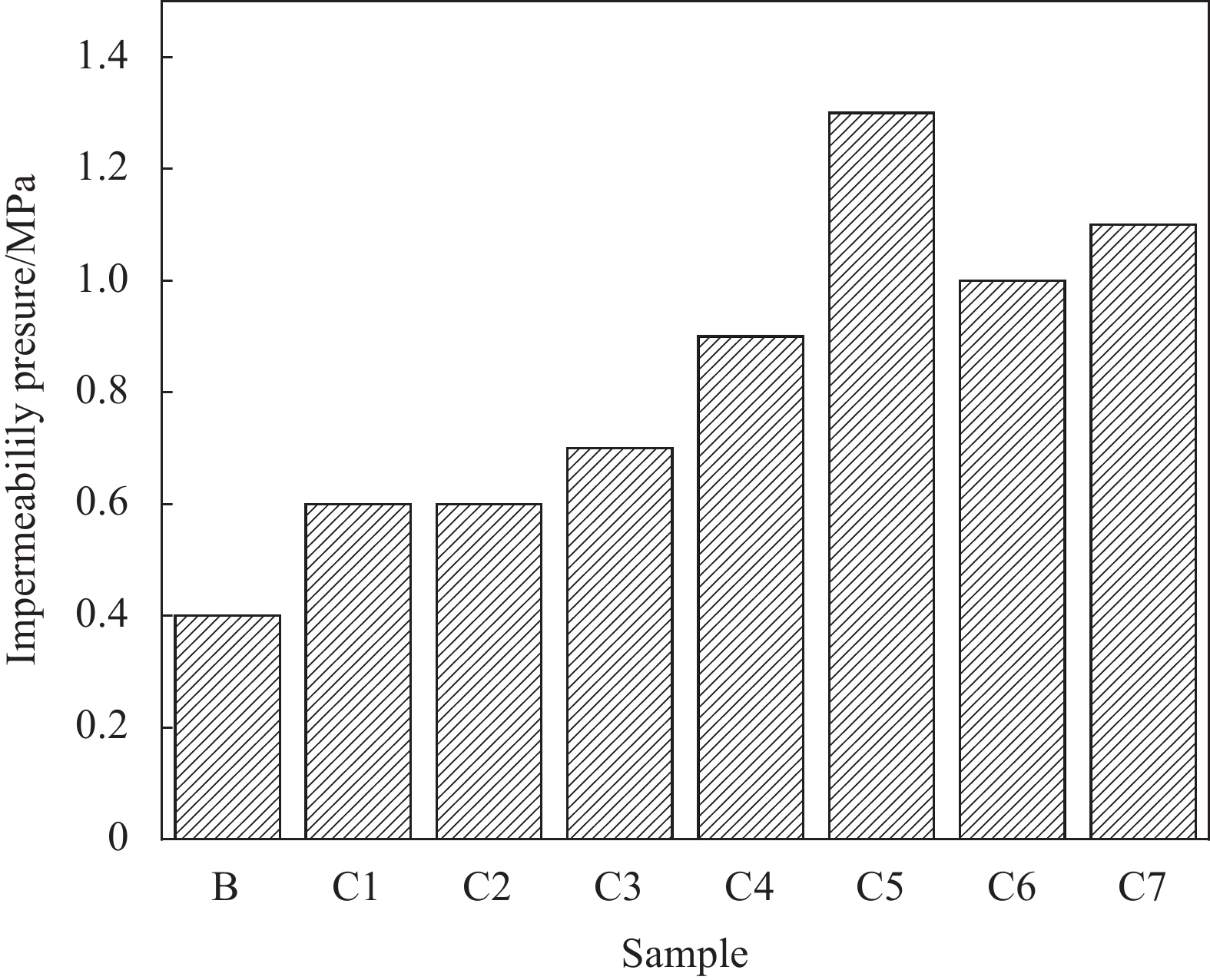
按照表4的配合比成型基准砂浆试件,按照表5的配合比成型GO改性CCCW涂层试件,图10为GO对CCCW抗渗性能的影响。从抗渗压力可以看出单独掺加CCCW(C1)的抗渗压力0.6 MPa比基准砂浆(B)的抗渗压力0.4 MPa高,由此说明,CCCW防水材料可有效增强水泥砂浆表面抗渗性能;从GO掺量为0.01%、0.03%、0.05%的CCCW涂层(C2、C4、C6)的抗渗压力可以看出,随着GO的掺量增加,涂层抗渗压力都比单独掺加CCCW试件的抗渗压力大,说明GO的掺入对CCCW涂层的抗渗性能有改善作用,且改善效果与GO的掺量有关;同时对比保持MN与GO质量比为3∶1(C2和C3、C4和C5、C6和C7),可以看到在加入MN后,涂层的抗渗压力均得到了提高,且在GO掺量为0.03%时,其涂层C5的抗渗压力比单独掺CCCW的涂层C1提高了116.7%,说明在MN的存在下,GO能够更好地改善CCCW涂层的抗渗性能。这个结果和本文研究MN对GO掺配水泥砂浆的性能提升相符合,为改善CCCW抗渗性能提供了一种新颖的研究思路。
2.6 水泥石微观形貌及结构
图11为28天不同CCCW涂层净浆的SEM图像。从图11(a)基准净浆看出水泥石结构不密实,存在大量的孔洞;图11(b)为C1试件的SEM图像。与图11(a)相比,变得较密实,但仍存在较多的孔洞,可能是由于加入了CCCW,能在水泥石之间形成晶体,能填充其细小的孔洞,从而密实水泥石的结构。因此CCCW涂层的防水效果较空白试件有一定程度的改善,但水泥石仍然存在较多大孔洞,导致其提升效果有限;图11(c)为单独掺加0.03%GO的试件,可见水化硅酸钙凝胶(C-S-H)明显比图11(b)多,而孔洞结构却变少了,这是由于GO在水泥净浆中的模板作用,使水化产物C-S-H凝胶生长密集,能填充并堵塞毛细孔道,使大孔洞变为小孔洞、小孔洞变裂缝、裂缝变得更加密实;图11(d)为C5试件的SEM图像。可以明显看出,水泥石中的C-S-H凝胶分散得更加均匀和密实,孔洞结构也变得更加少且小,这是由于加入了MN之后,GO分散的更加均匀,填充于孔洞中的GO借助其模板效应使C-S-H凝胶在孔洞中生长,使水泥石变得更加密实,之间的孔隙变得更小、更少,由此从微观上解释了C5涂层的抗渗、抵抗外界侵蚀的能力为何是所有样品中最好的。
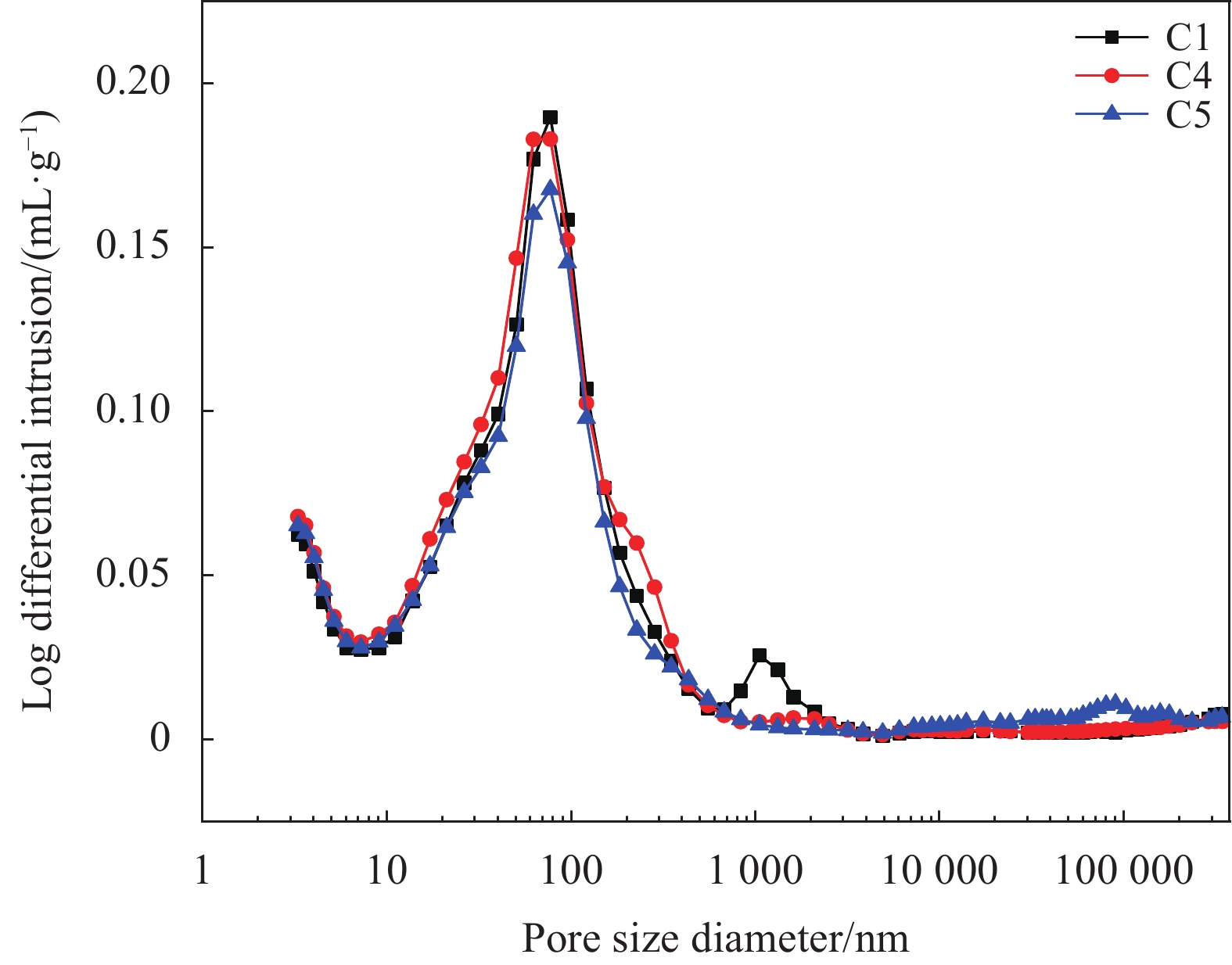
图12为28天不同CCCW涂层净浆的孔径分布图。能够看出3组试件MIP测试得到最可几孔径在60~70 nm,说明不管是加入MN还是GO对硬化后涂层净浆的最可几孔径并无明显影响。C5试件的最可几孔径体积与C1和C4试件相比,明显有减小。这主要是由于加入MN后,GO分散得更加均匀、能更好地调整孔结构,提高密实性,从而使涂层的抗渗性能提高。同样地,也可以看到,在10~1000 nm孔径范围内,C5曲线的各点纵坐标,均在C1和C4曲线之下,这同样说明了经过MN助分散的GO能改善水泥净浆的孔隙结构,同时也验证了前文加入MN分散GO能改善涂层抗渗性能的这一推断。
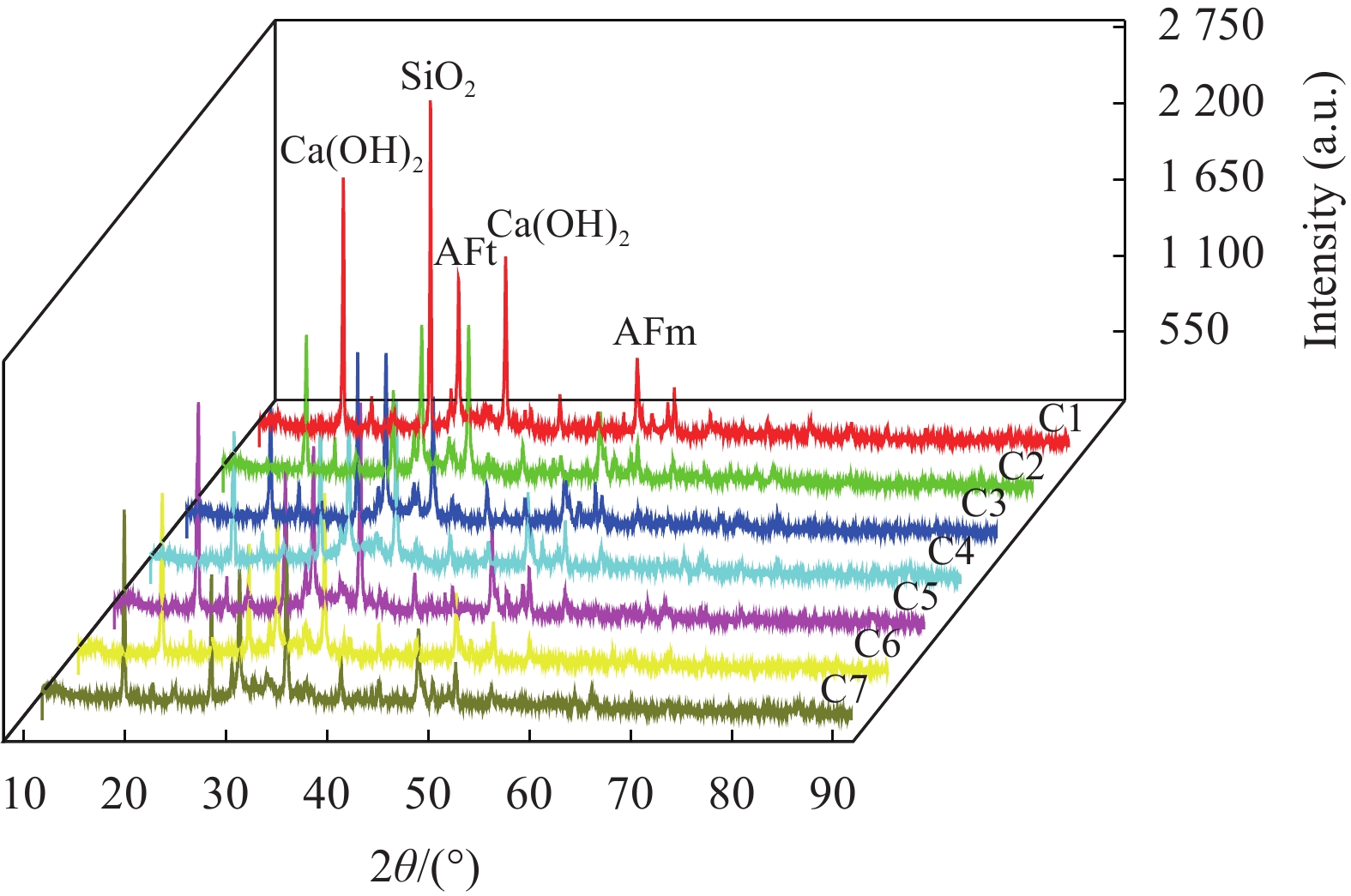
图13为28天不同CCCW涂层净浆的XRD图谱。可以看出,水泥水化产物主要是Ca(OH)2、SiO2、钙矾石(AFt)和单硫型水化硫铝酸钙(AFm)等。7个试件的吸收峰形状相似,无单独的吸收峰出现,这说明加入的GO和MN均不会改变水泥水化产物的种类。根据吸收峰的强弱变化可知水泥的水化程度,从图13中可以看到,质量比为3∶1、GO掺量分别为0.01%、0.03%、0.05%的试件(C3、C5、C7)的吸收峰在逐渐增高,这说明了GO促进了水泥水化产物的形成;试件C3比试件C2的吸收峰高、试件C5比试件C4的吸收峰高、试件C7比试件C6的吸收峰高,均说明了在含有GO的水泥砂浆试件中加入MN,能促进GO在水泥砂浆中的分散,更多均匀分散的GO调节了水泥水化产物的形成,最终使加入MN后的峰值比同掺量下没有加MN的高。
3. 结 论
(1) 木质素磺酸钠(MN)能促进氧化石墨烯(GO)在水泥水化孔隙液的饱和Ca(OH)2溶液中的分散,当MN与GO的质量比为3∶1,GO掺量为0.03%时,GO的在水泥水化孔隙液的饱和Ca(OH)2溶液中的分散最好,其抗折抗压强度相比于未掺GO的基准试件,3天和28天分别提高了39.13%,39.37%和33.84%,33.48%。
(2) 采用MN分散GO与水泥基渗透结晶型防水材料(CCCW)一起加入到涂层后,能改善涂层的抗渗压力,当GO掺量为0.03%时,涂层抗渗压力比纯粹CCCW涂层提高了116.7%,并且将MN分散的GO直接加入到由砂浆做成的抗渗试件中,也能改善它的抗渗压力和抗氯离子渗透性能,在掺量为0.03%时,砂浆抗渗压力和氯离子扩散系数比标准砂浆试件分别提高了160.0%和下降了50.6%。
(3) 微观测试结构表明,经MN改善均匀分散能力的GO能更好促进水泥水化的进程并能调控水化产物形貌和进一步密实水泥石的结构和优化水泥石的孔隙率,GO不仅能改善砂浆的抗渗性能,而且能提升CCCW的防水抗渗能力,因作为分散剂的MN改善GO分散能力,故掺入MN后,可进一步增强GO掺配的砂浆和CCCW的抗渗性能,从而改善水泥砂浆的抗渗能力和CCCW防水材料的防水性能。
本文采用廉价的MN改善GO在水泥浆的分散性,不仅能进一步发挥GO对水泥基材料的增强效果,最大限度提升石墨烯类材料对水泥基材料的抗渗透能力,还能增强在复杂环境中CCCW防水材料的防水效率,并为降低CCCW的成本提供了新的途径。
-
表 1 水泥化学成分
Table 1 Chemical composition of cement
Mineral Al2O3 SiO2 Fe2O3 CaO MgO SO3 NaO f-CaO Content/wt% 4.47 21.50 3.37 65.84 3.18 0.30 0.49 0.78 Note: f-CaO—Free calcium oxide. 表 2 用于吸光度和Zeta电位测试的氧化石墨烯(GO)溶液组成
Table 2 Composition of graphene oxide (GO) solution for absorbance and Zeta potential test
Sample Water/g Ca(OH)2/g PC/mL GO①/mL MN② Y0 99.3 0.16 0 0.7 0 Y1 99.3 0.16 0.05 0.7 0 Y2 99.3 0.16 0.05 0.7 1∶1 Y3 99.3 0.16 0.05 0.7 2∶1 Y4 99.3 0.16 0.05 0.7 3∶1 Y5 99.3 0.16 0.05 0.7 4∶1 Y6 99.3 0.16 0.05 0.7 5∶1 Notes: PC—Polycarboxylic acid water reducer; MN—sodium ligninsulfonate; ①—GO concentration is 3.666 mg/mL; ②—Content of MN is its ratio to GO. 表 3 用于力学性能和抗渗压力测试的GO改性水泥砂浆配合比
Table 3 Mix ratio of GO modified cement mortar for mechanical properties and impermeability pressure test
Sample Sand/g Cement/g PC/g Water/g GO①/% MN/% A1 1350 450 2.7 166 0 0 A2 1350 450 2.7 166 0 0.03 A3 1350 450 2.7 166 0.005 0.015 A4 1350 450 2.7 166 0.005 0 A5 1350 450 2.7 166 0.01 0.03 A6 1350 450 2.7 166 0.01 0 A7 1350 450 2.7 166 0.03 0.09 A8 1350 450 2.7 166 0.03 0 A9 1350 450 2.7 166 0.05 0.15 A10 1350 450 2.7 166 0.05 0 Note: ①—Mass ratio to cement. 表 4 基准砂浆配合比
Table 4 Mix ratio of reference mortar
Cement/g Water/g Sand/g Cellulose ether/g 320 260 1350 0.5 表 5 涂层配合比
Table 5 Mix ratio of coating
Sample CCCW/g Water/g PC①/% GO②/% MN/% C1 20 6 0 0 0 C2 20 6 0.3 0.01 0 C3 20 6 0.3 0.01 0.03 C4 20 6 0.3 0.03 0 C5 20 6 0.3 0.03 0.09 C6 20 6 0.3 0.05 0 C7 20 6 0.3 0.05 0.15 Notes: CCCW—Cementitious capillary crystalline waterproofing material; ①—Mass ratio to CCCW; ②—Mass ratio to CCCW. 表 6 MN分散的GO对水泥砂浆抗折强度和抗压强度的影响
Table 6 Effect of MN dispersed GO on the flexural and compressive strength of cement mortar
Sample Flexural strength (MPa)/Changing rate (%) Compressive strength (MPa)/Changing rate (%) 3 days 28 days 3 days 28 days A1 4.6±0.25/0 6.5±0.71/0 35.0±0.15/0 45.7±0.83/0 A2 4.0±0.34/13.04 5.9±0.85/9.23 27.98±0.35/20.05 43.24±0.85/5.38 A3 5.6±0.35/21.73 7.9±0.75/21.53 38.56±0.25/10.17 52.45±0.93/14.77 A4 5.5±0.55/19.56 7±0.95/7.69 36.83±0.44/5.23 51.66±1.15/13.04 A5 5.7±0.05/23.91 7.9±0.35/21.53 42.67±1.35/21.91 54.12±1.55/18.42 A6 5.6±0.35/21.73 7.1±0.45/9.23 40.88±0.84/16.80 53.73±0.75/17.57 A7 6.4±0.05/39.13 8.7±1.05/33.84 48.78±1.02/39.37 61.00±1.25/33.48 A8 6.2±0.65/34.78 8.6±0.84/32.30 45.13±0.05/28.94 58.90±0.55/28.88 A9 6.3±0.15/36.95 8.2±0.94/26.15 46.35±1.25/32.43 56.75±0.74/24.18 A10 6.2±0.45/34.78 8.1±0.35/24.61 44.10±0.85/26 54.89±0.65/20.11 表 7 GO提升水泥砂浆抗压抗折强度研究对比
Table 7 Comparison of compressive and flexural strength of cement mortar improved by GO
-
[1] SILVESTRE J, SILVESTRE N, BRITO J. Review on concrete nanotechnology[J]. European Journal of Environmental and Civil Engineering,2016,20(4):455-485. DOI: 10.1080/19648189.2015.1042070
[2] 熊琳强. 防水材料的发展及应用情况综述[J]. 建材发展导向, 2021, 19(12):2-3. XIONG Linqiang. Overview of development and application of waterproof materials[J]. Development Guide to Building Materials,2021,19(12):2-3(in Chinese).
[3] 徐建华. 屋面卷材防水施工技术在建筑工程中的应用[J]. 中国建筑装饰装修, 2021(6):42-43. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2167.2021.06.017 XU Jianhua. Application of roofing coil waterproofing construction technology in construction engineering[J]. Chinese Architectural Decoration,2021(6):42-43(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1672-2167.2021.06.017
[4] 李立, 霍胜旭, 罗林刚, 等. 聚氨酯防水涂料与自粘聚合物改性沥青防水卷材复合防水层剥离强度研究[J]. 新型建筑材料, 2021, 48(5):137-139, 142. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-702X.2021.05.032 LI Li, HUO Shengxu, LUO Lin'gang, et al. Study on peel strength of polyurethane waterproofing coating and self-adhesive polymer modified asphalt waterproofing membrane composite waterproofing layer[J]. New Building Materials,2021,48(5):137-139, 142(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-702X.2021.05.032
[5] 龚建国, 聂芹, 柯昌银. 弹性体改性沥青防水卷材的性能及应用技术[J]. 江西化工, 2021, 37(1):17-19. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-3103.2021.01.006 GONG Jianguo, NIE Qin, KE Changyin. The performance and application technology of elastomer modified asphalt waterproofing membrane[J]. Jiangxi Chemical Industry,2021,37(1):17-19(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1008-3103.2021.01.006
[6] 彭方灵. 防水涂料复合使用时粘接性能研究[J]. 江西建材, 2020(12):183-184. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2890.2020.12.111 PENG Fangling. Study on bonding properties of waterproof coatings in composite use[J]. Jiangxi Building Materials,2020(12):183-184(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1006-2890.2020.12.111
[7] 程赟, 罗健林, 滕飞, 等. 改性防水聚氨酯涂料的性能评价[J]. 聚氨酯工业, 2021, 36(3):41-43. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-1902.2021.03.013 CHENG Yun, LUO Jianlin, TENG Fei, et al. Performance evaluation of modified waterproof polyurethane coatings[J]. Polyurethane Industry,2021,36(3):41-43(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1005-1902.2021.03.013
[8] 余奕帆. 防水与密封材料绿色产品评价国家标准修订方向探讨[J]. 中国建筑防水, 2021(S01):46-50. YU Yifan. Discussion on the revision direction of national standard for green product evaluation of waterproofing and sealing materials[J]. Waterproofing of Buildings in China,2021(S01):46-50(in Chinese).
[9] 李华, 姜勇. 沥青基防水涂料及密封粘结材料探讨[J]. 建材发展导向, 2021, 19(20):82-83. LI Hua, JIANG Yong. Discussion on asphalt base waterproof coating and sealing adhesive material[J]. Development Guide to Building Materials,2021,19(20):82-83(in Chinese).
[10] 纪宪坤, 徐可. 防水混凝土, 结构自防水, 刚性防水及工程应用[J]. 中国建筑防水, 2020(10):49-57. JI Xiankun, XU Ke. Waterproof concrete, structural self-waterproofing, rigid waterproofing and engineering application[J]. Waterproofing of Chinese Buildings,2020(10):49-57(in Chinese).
[11] 胡骏. 论刚性防水[J]. 中国建筑防水, 2020(7): 1-7, 13. HU Jun. On rigid waterproofing[J]. Waterproof Building, 2020(7): 1-7, 13(in Chinese).
[12] 程福星, 邓小旭, 向飞, 等. 新型刚性结构自防水材料对混凝土抗渗防裂性能的影响研究[J]. 新型建筑材料, 2021, 48(4):119-122, 126. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-702X.2021.04.029 CHENG Fuxing, DENG Xiaoxu, XIANG Fei, et al. Study on the influence of new rigid structure self-waterproof materials on the impermeability and crack resistance of concrete[J]. New Building Materials,2021,48(4):119-122, 126(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-702X.2021.04.029
[13] 张鹏, 赵士坤, 陈继周, 等. 纳米粒子和PVA纤维增强水泥基复合材料抗渗性能研究[J]. 硅酸盐通报, 2017(S1):153-157. ZHANG Peng, ZHAO Shikun, CHEN Jizhou, et al. Study on the impermeability of nano-particles and PVA fiber reinforced cement matrix composites[J]. Silica Notification,2017(S1):153-157(in Chinese).
[14] 刘金秀, 戴涛, 徐子芳. 不同纤维改性水泥基复合材料的试验研究[J]. 非金属矿, 2021, 44(6):42-44. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8098.2021.06.011 LIU Jinxiu, DAI Tao, XU Zifang. Experimental study on different fiber modified cement-based composites[J]. Nonmetallic Ore,2021,44(6):42-44(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-8098.2021.06.011
[15] 程志海, 杨森, 袁小亚. 石墨烯及其衍生物掺配水泥基材料研究进展[J]. 复合材料学报, 2021, 38(2):339-360. CHENG Zhihai, YANG Sen, YUAN Xiaoya. Research progress on cement-based materials doped with graphene and its derivatives[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2021,38(2):339-360(in Chinese).
[16] 李建仙. 氧化石墨烯对水泥基复合材料性能影响研究[J]. 人民黄河, 2020, 42(2):54-57, 62. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1379.2020.02.011 LI Jianxian. Study on the effect of graphene oxide on the properties of cement-based composites[J]. Renmin Yellow River,2020,42(2):54-57, 62(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1000-1379.2020.02.011
[17] XU G, DU S, HE J, et al. The role of admixed graphene oxide in a cement hydration system[J]. Carbon,2019,148:141-150. DOI: 10.1016/j.carbon.2019.03.072
[18] 魏致强, 王远贵, 齐孟, 等. 没食子酸协同聚羧酸减水剂分散氧化石墨烯及其对水泥砂浆性能的影响[J]. 材料导报, 2021, 35(10):10042-10047. DOI: 10.11896/cldb.20040258 WEI Zhiqiang, WANG Yuangui, QI Meng, et al. gallic acid and polycarboxylate superplasticizer dispersed graphene oxide and its influence on the performance of cement mortar[J]. Material Report,2021,35(10):10042-10047(in Chinese). DOI: 10.11896/cldb.20040258
[19] 袁小亚, 曾俊杰, 高军, 等. 氧化石墨烯与石墨烯复掺对水泥砂浆性能影响研究[J]. 重庆交通大学学报: 自然科学版, 2019, 38(9):45-50. YUAN Xiaoya, ZENG Junjie, GAO Jun, et al. Study on the effect of graphene oxide and graphene on the properties of cement mortar[J]. Journal of Chongqing Jiaotong University: Natural Science Edition,2019,38(9):45-50(in Chinese).
[20] 杜涛. 氧化石墨烯水泥基复合材料性能研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2014. DU Tao. Graphene oxide cement-based composites performance research[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2014(in Chinese).
[21] 王明刚. 氧化石墨烯改善水泥基复合材料性能的影响研究[J]. 公路交通技术, 2020, 36(3): 37-41. WANG Minggang. Study on the effect of graphene oxide on the properties of cement-based composites[J]. Highway, Transportation Technology, 2020, 36(3): 37-41(in Chinese).
[22] CHINTALAPUDI K, PANNEM R M R. An intense review on the performance of graphene oxide and reduced graphene oxide in an admixed cement system[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2020,259:120598-120617. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.120598
[23] ZHAO L, GUO X, SONG L, et al. An intensive review on the role of graphene oxide in cement-based materials[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2020,241:117939-117956. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.117939
[24] LIN Y, DU H. Graphene reinforced cement composites: A review[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2020,265:120312-120328. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2020.120312
[25] GAO Y, JING H, ZHOU Z, et al. Reinforced impermeability of cementitious composites using graphene oxide-carbon nanotube hybrid under different water-to-cement ratios[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2019,222:610-621. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2019.06.186
[26] ZHANG Q, QIAN X, THEBO K H, et al. Controlling reduction degree of graphene oxide membranes for improved water permeance[J]. Science Bulletin,2018,63(12):788-794. DOI: 10.1016/j.scib.2018.05.015
[27] ZHANG Y T, ZUO L, YANG J C, et al. Influence of cementitious capillary crystalline waterproofing material on the water impermeability and microstructure of concrete[J]. Materials Science Forum,2019,953:209-214. DOI: 10.4028/www.scientific.net/MSF.953.209
[28] ZHENG W, CHEN W G, FENG T, et al. Enhancing chloride ion penetration resistance into concrete by using graphene oxide reinforced waterborne epoxy coating[J]. Progress in Organic Coatings,2020,138:105389-105398. DOI: 10.1016/j.porgcoat.2019.105389
[29] ZHU Q, HUANG Y, LI Y, et al. Aluminum dihydric tripolyphosphate/polypyrrole-functionalized graphene oxide waterborne epoxy composite coatings for impermeability and corrosion protection performance of metals[J]. Advanced Composites and Hybrid Materials,2021,4(3):780-792. DOI: 10.1007/s42114-021-00265-6
[30] ZENG H Y, LAI Y, QU S, et al. Effect of graphene oxide on permeability of cement materials: An experimental and theoretical perspective[J]. Journal of Building Engineering,2021,41:102326-102339. DOI: 10.1016/j.jobe.2021.102326
[31] LIU C J, HUANG X, WU Y Y, et al. The effect of graphene oxide on the mechanical properties, impermeability and corrosion resistance of cement mortar containing mineral admixtures[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2021,288:123059-123070. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2021.123059
[32] 张友来. 氧化石墨烯/硅烷复合乳液的制备及其对混凝土耐久性能的影响研究[D]. 青岛: 青岛理工大学, 2018. ZHANG Youlai. Preparation of graphene oxide/silane composite emulsion and its effect on durability of concrete[D]. Qingdao: Qingdao University of Technology, 2018(in Chinese).
[33] 高飞, 刘清, 姚国友, 等. 水泥基渗透结晶型防水材料的试验研究[J]. 低温建筑技术, 2021, 43(6):7-10, 15. GAO Fei, LIU Qing, YAO Guoyou, et al. Experimental study on cement-based permeable crystalline waterproofing materials[J]. Low Temperature Building Technology,2021,43(6):7-10, 15(in Chinese).
[34] 傅杰, 孙振平. 水泥基渗透结晶型防水材料的种类及作用机理[J]. 江西建材, 2020(S1): 4-5, 9. FU Jie, SUN Zhenping. Types and mechanism of cement-based permeable crystalline waterproofing materials[J]. Jiangxi Building Materials, 2020(S1) : 4-5, 9(in Chinese).
[35] 刘月雷, 杨洋, 李福海, 等. 水泥基渗透结晶型防水材料作用机理及性能评价[J]. 市政技术, 2021, 39(11):146-151, 156. LIU Yuelei, YANG Yang, LI Fuhai, et al. Mechanism and performance evaluation of cement-based permeable crystalline waterproofing materials[J]. Municipal Technology,2021,39(11):146-151, 156(in Chinese).
[36] ALMUSALLAM A A, KHAN F M, DULAIJAN S U, et al. Effectiveness of surface coatings in improving concrete durability[J]. Cement and Concrete Composites,2003,25(4-5):473-481. DOI: 10.1016/S0958-9465(02)00087-2
[37] 姚嘉诚, 延永东, 徐鹏飞, 等. 水泥基渗透结晶型防水材料和纳米二氧化硅改性混凝土自修复性能的研究[J]. 硅酸盐通报, 2020, 39(6):1772-1777. YAO Jiacheng, YAN Yongdong, XU Pengfei, et al. Study on self-healing properties of cement-based permeable crystalline waterproofing materials and nano-silica modified concrete[J]. Silicate Notification,2020,39(6):1772-1777(in Chinese).
[38] 丁向群, 邢进, 刘东涛. 内掺渗透结晶防水材料混凝土的渗透性能研究[J]. 混凝土, 2016(9):120-123. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3550.2016.09.032 DING Xiangqun, XING Jin, LIU Dongtao. Study on the permeability of concrete with permeable crystalline waterproofing materials[J]. Concrete,2016(9):120-123(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1002-3550.2016.09.032
[39] 孙学志. 渗透结晶型涂料对普通混凝土抗渗性能的影响[J]. 新型建筑材料, 2011(4):53-55. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-702X.2011.04.016 SUN Xuezhi. Effect of penetration crystalline coating on impermeability of ordinary concrete[J]. New Building Materials,2011(4):53-55(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-702X.2011.04.016
[40] 郭璞. 高粘结高抗渗水泥基渗透结晶型防水材料的研究[J]. 山西建筑, 2016, 42(12):95-96. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6825.2016.12.052 GUO Pu. Research on high bond and high impermeability cement-based permeable crystalline waterproofing materials[J]. Shanxi Building,2016,42(12):95-96(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-6825.2016.12.052
[41] 鲁宗平, 李海斌. 水泥基渗透结晶型防水材料的正交优化及抗渗性能研究[J]. 安徽建筑大学学报, 2019, 27(1):5-49, 89. LU Zongping, LI Haibin. Orthogonal optimization and impermeability of cement-based permeable crystalline waterproofing materials[J]. Journal of Anhui Jianzhu University,2019,27(1):5-49, 89(in Chinese).
[42] 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 水泥胶砂强度检验方法(ISO法): GB/T 17671—2021[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2021. China National Standardization Management Committee. Strength test method of cement mortar (ISO method): GB/T 17671—2021[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2021(in Chinese).
[43] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 建筑砂浆基本性能试验方法标准: JGJ/T 70—2009[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2009. Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People's Republic of China. Standard test method for basic performance of building mortar: JGJ/T 70—2009[S]. Beijing: China Building Industry Press, 2009(in Chinese).
[44] 中华人民共和国国家发展和改革委员会. 砂浆、混凝土防水剂: JC 474—2008[S]. 北京: 中国建筑材料科学研究总院, 2008. National Development and Reform Commission. Mortar, concrete waterproofing agent: JC 474—2008[S]. Beijing: China Academy of Building Materials Science Research, 2008(in Chinese).
[45] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 混凝土氯离子扩散系数测定仪: JG/T 262—2009[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2009. Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of the People's Republic of China. Concrete chloride diffusion coefficient tester: JG/T 262—2009[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2009(in Chinese).
[46] 中国国家标准化管理委员会. 水泥基渗透结晶型防水材料: GB/T 18445—2012[S]. 北京: 中国标准出版社, 2012. China National Standardization Management Committee. Cementitious capillary crystalline waterproof material: GB/T 18445—2012[S]. Beijing: China Standards Press, 2012(in Chinese).
[47] YUAN X Y, NIU J W, ZENG J J, et al. Cement-induced coagulation of aqueous graphene oxide with ultrahigh capacity and high rate behavior[J]. Nanomaterials,2018,8(8):574-588. DOI: 10.3390/nano8080574
[48] 袁小亚, 曾俊杰, 牛佳伟, 等. 不同减水剂对氧化石墨烯掺配水泥胶砂力学性能及微观结构的影响[J]. 功能材料, 2018, 49(10):10184-10189. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9731.2018.10.032 YUAN Xiaoya, ZENG Junjie, NIU Jiawei, et al. Effect of different water reducing agents on mechanical properties and microstructure of grapene oxide doped cement mortar[J]. Functional Materials,2018,49(10):10184-10189(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9731.2018.10.032
[49] 郭畅. 氧化石墨烯及其两种功能化材料的制备与表征[D]. 昆明: 昆明理工大学, 2019. GUO Chang. Preparation and characterization of graphene oxide and its two functional materials[D]. Kunming: Kunming University of Technology, 2019(in Chinese).
[50] 苏恒. 石墨烯制备中氧化及非水介质中还原方法的研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉理工大学, 2019. SU Heng. Study on oxidation and reduction methods in non-aqueous medium in the preparation of graphene[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University of Technology, 2019(in Chinese).
[51] 程连勇, 龚建贵, 曾艳, 等. 不同缓凝剂对水泥凝结时间的影响[J]. 混凝土世界, 2017(7):86-93. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7011.2017.07.016 CHENG Lianyong, GONG Jiangui, ZENG Yan, et al. Effects of different retarders on setting time of cement[J]. Concrete World,2017(7):86-93(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1674-7011.2017.07.016
[52] 马聪, 韩伟, 周桂政. 改性磷铝酸盐水泥缓凝剂优选试验研究[J]. 新型建筑材料, 2014(5):7-10. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-702X.2014.05.002 MA Cong, HAN Wei, ZHOU Guizheng. Modified pho-sphoaluminate cement retarder optimization experimental research[J]. New Building Materials,2014(5):7-10(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-702X.2014.05.002
[53] LV S, HU H, HOU Y, et al. Investigation of the effects of polymer dispersants on dispersion of GO nanosheets in cement composites and relative microstructures/perfor-mances[J]. Nanomaterials,2018,8(12):964-982. DOI: 10.3390/nano8120964
[54] 袁小亚, 杨雅玲, 周超, 等. 氧化石墨烯改性水泥砂浆力学性能及微观机理研究[J]. 重庆交通大学学报: 自然科学版, 2017, 36(12):36-42. YUAN Xiaoya, YANG Yaling, ZHOU Chao, et al. Research on mechanical properties and microscopic mechanism of graphene oxide modified cement mortar[J]. Journal of Chongqing Jiaotong University: Natural Science Edition,2017,36(12):36-42(in Chinese).
[55] 盛况, 杨森, 毕俊峰, 等. 有机染料辅助分散氧化石墨烯及其对水泥砂浆强度和耐久性的影响[J]. 复合材料学报, 2022, 39(11):5486-5498. SHENG Kuang, YANG Sen, BI Junfeng, et al. Organic dye-assisted dispersion of graphene oxide and its influence on the strength and durability of cement mortar[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2022,39(11):5486-5498(in Chinese).
[56] 王远贵, 袁小亚, 高军, 等. 蔗糖对氧化石墨烯掺配砂浆流动性与力学性能影响研究[J]. 硅酸盐通报, 2020, 39(11):3453-3462. WANG Yuangui, YUAN Xiaoya, GAO Jun, et al. Research on the influence of sucrose on the fluidity and mechanical properties of graphene oxide doped mortar[J]. Silica Notification,2020,39(11):3453-3462(in Chinese).
[57] ZENG H, LAI Y, QU S, et al. Effect of graphene oxide on permeability of cement materials: An experimental and theoretical perspective[J]. Journal of Building Engineering,2021,41(4):102326-102339.
[58] LIU C J, HUANG X, WU Y Y, et al. The effect of graphene oxide on the mechanical properties, impermeability and corrosion resistance of cement mortar containing mineral admixtures[J]. Construction and Building Materials, 2021, 12(288): 123059-123070.
-
期刊类型引用(12)
1. 张惠一,蒲云东,张逸舟,苏俊儒,袁小亚,胡兵兵. 氧化石墨烯助分散的碳纤维对水泥砂浆强度及电热性能的影响. 化工新型材料. 2025(03): 272-280 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 郑寒,董玉文,王宗波. 渗透结晶型防水剂对混凝土抗冻性能的影响. 水力发电. 2025(04): 104-110 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 曹济,陈晓庭,张文涛,孙绿林,宋永胜. 活性剂增强改性水泥基渗透结晶型防水材料抗渗试验. 粘接. 2024(02): 104-107 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 桂尊曜,蒲云东,张惠一,袁小亚,黎少伟,邵伟升. 石墨烯量子点对水泥砂浆流动度、强度和耐盐腐蚀性的影响. 复合材料学报. 2024(04): 2043-2054 .  本站查看
本站查看
5. 李大芳,郭鑫,鲁义,施式亮,李贺. 煤层瓦斯抽采钻孔封孔材料研究进展与展望. 安全. 2024(05): 44-51 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 王黎,陶文彬. 反渗透自粘防水卷材对高层医院建筑工程的应用研究. 粘接. 2024(09): 27-29+40 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 陈宾,袁洋,胡杰铭,张召,张涛. 冲击荷载下氧化石墨烯改性珊瑚砂浆破碎分形特征研究. 兵器装备工程学报. 2024(10): 25-33 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 程文通,秦拥军,李东锦. 渗透结晶型防水材料活性母料制备与优化试验. 科学技术与工程. 2024(29): 12684-12690 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 陈韫钒. 活性剂增强改性水泥基渗透结晶型防水材料抗渗试验研究. 江西建材. 2024(08): 41-43 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 张惠一,桂尊曜,蒲云东,齐孟,曹蔚琦,袁小亚. 羟基化石墨烯对水泥基渗透结晶型防水材料力学性能的影响. 硅酸盐通报. 2023(05): 1569-1577+1588 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 陈宾,张涛,张召,袁洋,卢艺伟. 冲击荷载作用下氧化石墨烯改性珊瑚砂浆的动态力学特性与微观机制. 复合材料学报. 2023(08): 4682-4693 .  本站查看
本站查看
12. 陈妤,董凯,张文杰,李国浩,李创创,唐丽. 干湿交替氯盐环境下氧化石墨烯水泥砂浆抗侵蚀研究. 硅酸盐通报. 2022(12): 4147-4153 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(7)
-




 下载:
下载: