Fe3O4/PDMS modified collagen sponge and its oil-water separation performance
-
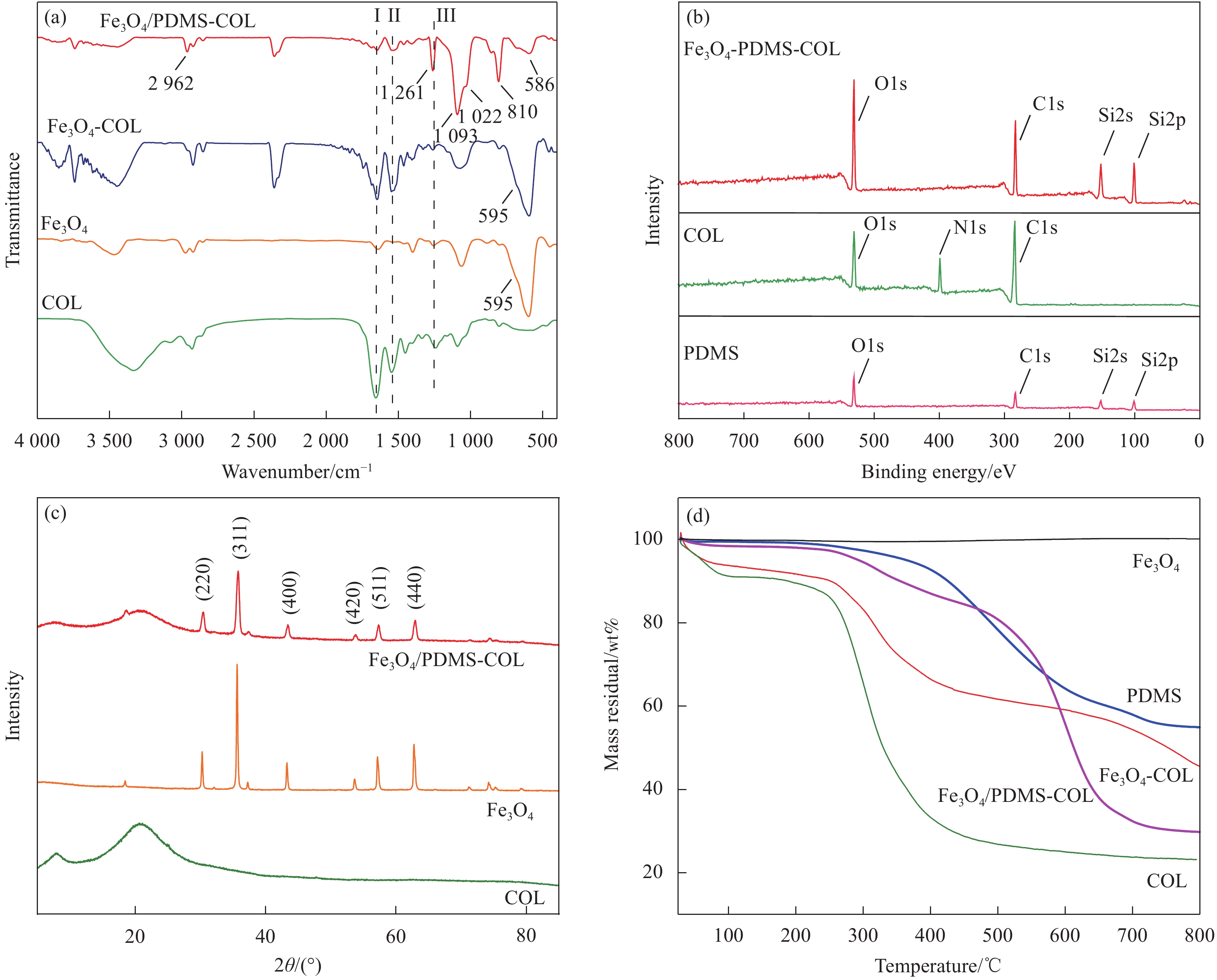
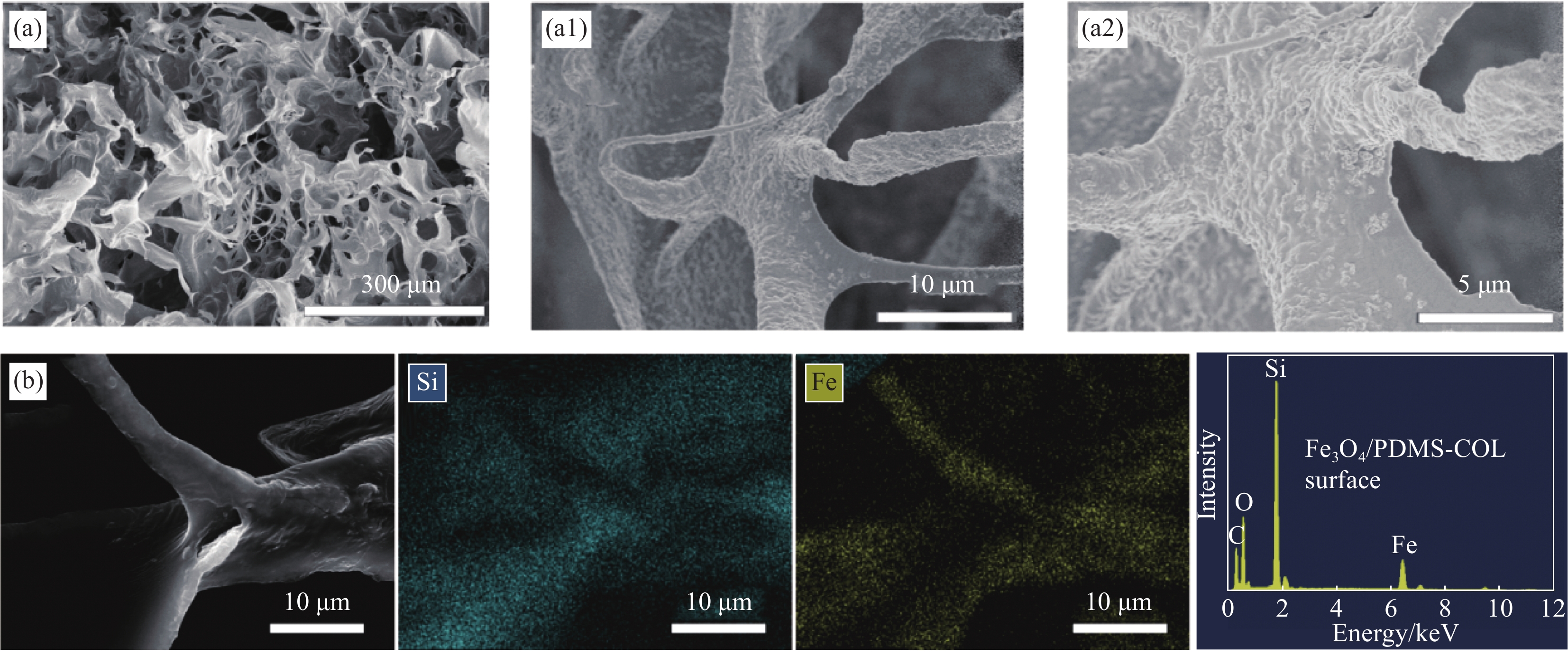
摘要: 为发展一种原料丰富、绿色环保、易于在复杂环境中操控使用、循环使用性好的多功能油水分离用海绵材料,采用浸渍法对胶原海绵进行聚二甲基硅氧烷(PDMS)/四氧化三铁(Fe3O4)纳米颗粒复合改性,制备了超疏水胶原基复合海绵(Fe3O4/PDMS-COL),表征了改性后化学结构与微观结构的变化,研究了油水分离性能。通过接触角测量可知:当胶原(COL)浓度为10 mg/mL、PDMS浓度为15vol%时,复合海绵的水接触角为150.3°。FTIR、XPS、XRD及TG测试结果表明Fe3O4/PDMS与胶原海绵成功发生复合,FE-SEM观察结果表明Fe3O4纳米粒子的加入可有效构造表面粗糙结构。海绵可吸附多种不同类型的油相如苯、正己烷、乙酸乙酯、真空泵油、花生油等,其中对乙酸乙酯的吸附量达47 g/g,且对不同油相的分离效率在99%以上。以苯为吸附物,连续循环使用20次后,海绵的接触角与磁性均未发生明显下降。海绵还可有效分离水包油乳液。在外加磁场作用下实施多种场景下的油水分离实验,Fe3O4/PDMS-COL表现出良好的磁操控性。此外,海绵还具有较好的阻燃性能。利用近红外光热响应性,Fe3O4/PDMS-COL还具备了吸附分离复杂环境中固体状油脂/水体系的潜力。Abstract: In order to develop a multi-functional oil-water separation sponge that is rich in raw materials, environmentally friendly, easy to operate in complex environment, and of good reusability, superhydrophobic collagen-based composite sponge (Fe3O4/PDMS-COL) was prepared by impregnating collagen sponge with polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS)/ferroferric oxide nanoparticles (Fe3O4). The changes of chemical structure and microstructure after modification were characterized, and the oil-water separation performance was studied. According to the measurement of contact angle, when the concentration of collagen (COL) is 10 mg/mL and the concentration of PDMS is 15vol%, the water contact angle of the composite sponge reaches 150.3°. The results from FTIR, XPS, XRD and TG show that Fe3O4/PDMS compounds with collagen sponge successfully. FE-SEM observation shows that the addition of Fe3O4 nanoparticles construct rough surface structures effectively. Fe3O4/PDMS-COL can adsorb a variety of oil phases, including benzene, n-hexane, ethyl acetate, vacuum pump oil, peanut oil, among which the adsorption capacity (47 g/g) toward ethyl acetate is the highest, meanwhile the separation efficiency towards various oil phases reaches no less than 99%. After recycling for 20 times for absorbing benzene, both of the contact angle and magnetism of the sponge do not reduce significantly. Moreover, Fe3O4/PDMS-COL has a desirable emulsion separation ability and can effectively separate oil-in-water emulsion. Oil-water separation experiments were carried out in various scenarios under the action of external magnetic field, demonstrating the favourable magnetic responsiveness and manipulation. In addition, Fe3O4/PDMS-COL exhibits a good flame retardant performance. Furthermore, Fe3O4/PDMS-COL possesses an excellent separation capacity toward solid oil/water system in a complex environment, due to its near infrared photothermal effect.
-
纤维增强树脂复合材料具有显著和丰富的细观结构特征,在制造成型过程中不可避免或无法完全消除内部含有的缺陷,如夹杂、孔隙、纤维褶皱、分层等[1-3]。复合材料结构内部缺陷种类多、特征尺寸分散[4-6]、危害程度不一,检测难度大。缺陷检测的最终目的是对含缺陷构件的机械力学性能给出适应性评价。现有的无损检测技术(包括射线检测技术[7-9]、超声检测技术[10-14]、热成像技术[15, 16]等)在面对具有紧密多层细观结构的纤维复合材料时,缺陷识别存在一定的困难或障碍。
在复合材料界面缺陷检测方面,Li等[17]利用微CT技术对复合材料在冲击剪切载荷作用下的裂纹、脱粘和层间分层等损伤进行了检测。Chen [18]利用CT技术对复合材料桨叶蒙皮分层缺陷进行了试验研究和分析。虽然断层扫描CT技术对纤维褶皱及脱粘、分层缺陷的检测能力较好,但该方法受测试材料几何形状的限制,采集数据规模大,检测非常耗时,此外射线检测过程中存在辐射污染。超声波信号在遇到分层、孔隙这类缺陷时明显衰减,传统的超声检测方法可以较好地识别这类缺陷,而在识别褶皱缺陷方面有很大的困难。Larrañaga-Valsero等[11]比较了三种不同的超声技术在检测和表征用于风力涡轮机叶片的典型玻纤-碳纤混杂层合板内褶皱缺陷的有效性:基于全聚焦方法的全矩阵捕捉技术、相控阵检测技术和超声波水浸聚焦探测。试验结果表明,全矩阵捕捉方法得到了较好的试验结果,而相控阵技术和水浸聚焦测试应用于褶皱检测时误差较大,面临更多的挑战。值得一提的是激光剪切散斑技术在航空工业的复合结构无损检测方面已经有较成熟的应用,对复合材料层间的剥离可以进行可靠的评定[19],但对于其他缺陷类型的识别,并未形成公认可靠有效的方法。
另一方面,运用上述缺陷检测方法,即使在一定程度上探查到局部缺陷位置和形貌,仍需借助大量数据经验的积累或复杂的仿真分析才能获得含缺陷的构件在给定工况下的行为响应 [20-22]。因此,从传统缺陷检测方法到结构性能评价之间,仍存在巨大的鸿沟需要跨越。为此,本文提出了一种特别适合于纤维增强树脂复合材料的集缺陷检测和性能评价为一体的微应力无损检测方法。
首先,该方法将缺陷视为对复合材料刚度矩阵的一种扰动,考虑缺陷的种类、严重程度和空间概率分布建立扰动的数学力学模型,并将该模型植入自主研发的三维复合材料有限元程序,获得以概率分布和统计信息表征的缺陷分布及其对复合材料结构的机械力学响应影响规律,以此奠定微应力无损检测的理论基础。
理论预测发现,复合材料中不同类型的缺陷对不同的载荷具有特殊的响应模式,这种特殊响应模式往往表现为位移场的畸变和扭曲。以褶皱缺陷为例,对含褶皱缺陷的层合板施加面内拉伸载荷,离面位移会产生明显的特殊响应如位移场的畸变或扭曲,而当施加横向压力载荷时,褶皱缺陷对板的挠度响应几乎没有影响[22]。这种高度敏感的响应和完全不敏感的响应,可分别称之为“敏感”响应和“钝感”响应,同时这种“敏感”响应和“钝感”响应也为我们提供了一种缺陷检测和性能评价的可能途径。
根据理论预测,可以为复合材料构件设计特定的加载方式并确定合适的载荷大小,使构件处于微应力水平,且对应的全场变形处于光学非接触测量方法可测范围内,通过对变形信息中蕴含的畸变信息的判断和提取,获知缺陷的位置。同时由于使用了光-力学的综合检测方法,可以跨越对缺陷具体形貌尺寸的探查,而直接获得含缺陷构件在给定工况下的力学行为响应,为构件适应性评价提供参考依据。
1. 纤维增强树脂复合材料的褶皱缺陷特征响应
1.1 纤维增强树脂复合材料中均匀型褶皱的细观力学模型
从几何描述上有均匀型和线性梯度型褶皱。由于本文中考虑的含褶皱试样整体厚度较薄,沿厚度方向每层褶皱的高度变化可近似忽略,因此文中的褶皱模型简化为均匀型褶皱,如图1所示。
褶皱的形状由余弦公式描述[23],其具体表达式如下:
z(x)=z0+Acos(2πx/λ),|x|⩽λ/2 (1) 式中:x 是平行于纤维的方向;z是沿厚度方向;z0是对应于无褶皱时层合板每层的高度;A和λ分别是褶皱的波幅和波长。
当一个代表性体积单元(RVE)包含一个完整的均匀型褶皱时,可以通过两步均匀化方法计算RVE的等效刚度矩阵,如图2所示。首先假设层合板不存在褶皱缺陷,进行沿厚度方向的均匀化计算,得到一个等效的层合板的刚度矩阵
C∗ ;其次,令该等效层合板的纤维弯曲形成褶皱,在水平方向离散化并进行水平方向的均匀化计算得到最终的等效刚度矩阵C∗∗ 。垂直方向均匀化和水平方向均匀化具体计算过程可作者论文参考文献[24]附录A。![]() 图 2 纤维增强树脂复合材料中含均匀型褶皱的RVE等效刚度计算模型Figure 2. Calculation model of equivalent stiffness of RVE with uniform wrinkle in fiber-reinforced resin compositesCij—Ply stiffness matrix; C*—Equivalent stiffness matrix of wrinkle-free laminates; C**—Equivalent stiffness matrix of laminates with uniform wrinkle; θk—Orientation angle of kth ply; φ—Out-of-plane misalignment
图 2 纤维增强树脂复合材料中含均匀型褶皱的RVE等效刚度计算模型Figure 2. Calculation model of equivalent stiffness of RVE with uniform wrinkle in fiber-reinforced resin compositesCij—Ply stiffness matrix; C*—Equivalent stiffness matrix of wrinkle-free laminates; C**—Equivalent stiffness matrix of laminates with uniform wrinkle; θk—Orientation angle of kth ply; φ—Out-of-plane misalignment1.2 纤维增强树脂复合材料中褶皱缺陷的分散性
在实际的复合材料构件中,褶皱的物理形态及其空间分布具有分散性,事先一般不能预知缺陷所在的位置。如Mukhopadhyay等[25]对弯曲复合材料结构内部的褶皱缺陷检测发现其呈现随机性特点,Lemanski等[26]利用多场影像分析技术对局部小范围的复合材料层合板截面处的纤维偏转角的分布特点进行统计学研究,纤维偏转角呈现近似正态分布的特点。此外,Riddle等[27]对已经完成制造或运行中的叶片缺陷进行了大量的统计与分析,发现褶皱波长、波幅及其偏转角度均近似呈现正态分布或威布尔分布。
基于上述理由,褶皱缺陷检测所采取的方法应该是一全场测量方法,同时还需考虑对构件施加合适的载荷类型及大小,使缺陷所造成的异常能够被显示出来并处于测量所覆盖的范围内。
为此本文建立了含分散性褶皱的纤维增强树脂复合材料薄板模型,如图3所示,该层合板长250 mm,宽25 mm,采用对称铺层,铺层顺序为[0/90/0/90]s,每层的厚度为0.1 mm,总厚度为0.8 mm。
在下文的算例与实验中,组成该层合板的单向板采用碳纤维(CF)增强环氧树脂(EP)复合材料,其性能参数如表1所示。其中褶皱的几何尺寸服从下式所示的正态分布,而褶皱在结构上为随机分布。
表 1 碳纤维(CF)/环氧树脂(EP)复合材料弹性参数Table 1. Elastic parameters of carbon fiber (CF)/epoxy (EP) compositesE11 /GPa (E22 /E33) /GPa G23 /GPa G31 /GPa G12 /GPa ν21 ν32 ν31 133.3 9.09 3.16 7.24 7.23 0.261 0.436 0.261 Notes: E11, E22, E33—Elastic modulus (direction 11, 22, 33); G12, G23, G31—Shear modulus (direction 12, 23, 31); v21, v32, v31—Poisson’s ratio (direction 21, 32, 31). F(γ)=1√2πSexp[−(γ−γ0)22S2] (2) 式中:γ表示褶皱的波幅与波长之比(A/λ称为波纹比);γ0表示波纹比的均值。当γ为正数时,表示纤维在厚度方向的偏转沿z轴正向。相反地,当
γ 为负数时,意味着纤维在厚度方向的偏转沿z轴负方向。由于褶皱的方向有可能朝z轴的正向或负向,故此处波纹比的均值为0。1.3 CF/EP复材层合板特征响应分析
对含分散性褶皱缺陷的CF/EP复材层合板模型考虑不同的加载方式,如图4所示。
基于作者自主开发的含分散性褶皱缺陷的有限元计算程序,图5给出了拉伸载荷下含分散性褶皱缺陷的层合板面内和离面位移响应。其中面内位移u、v分别表示沿x和y方向的位移,用位移等值线表示,离面位移w则采用三维曲面显示。作为对比,图6是不含缺陷的层合板在拉伸载荷下的位移。
比较图5和图6可见当复合材料层合板内部存在褶皱缺陷时,在单轴拉伸载荷作用下,其面内位移和离面位移均会产生特殊响应如位移场的畸变或扭曲,且离面位移的畸变程度尤为显著。
图7、图8分别为含随机褶皱缺陷及不含缺陷层合板的在弯曲载荷下的位移响应。对比可知,含随机褶皱缺陷层合板的沿y方向的面内位移响应对弯曲载荷敏感,而沿x方向的面内位移及离面位移不受褶皱缺陷的影响,其响应与无缺陷的理想材料一致。
图9、图10分别为含随机褶皱缺陷及不含缺陷层合板的剪切位移响应。对比可知,含随机褶皱缺陷层合板的面内位移响应对剪切载荷作用不敏感,无论是否含有缺陷,两种情况下面内位移响应非常接近。而含褶皱缺陷的层合板离面位移在靠近根部约束区域的两翼出现了独特的边缘扭曲现象,这与褶皱缺陷及各向异性复合材料的变形耦合有关。
上述结果表明,CF/EP复材层合板中的褶皱缺陷导致结构不同方向的位移对不同的加载方式具有完全不同的响应,在给定载荷下,某些方向的位移在分布模式和数量级上均出现显著的改变,而其他方向的位移可能完全不受缺陷影响。
这种高度敏感的响应和完全不敏感的响应,我们分别称之为“敏感”响应和“钝感”响应,同时这种“敏感”响应和“钝感”响应也为我们提供了一种用于缺陷检测和识别的工具。
根据上述三种载荷响应的计算,对于褶皱缺陷,其不同载荷下的位移响应敏感性如表2所示。
表 2 CF/EP复材层合板中褶皱缺陷对不同载荷的响应敏感性Table 2. Response sensitivity of wrinkle defects to different loading modes in CF/EP composite laminatesLoading mode Uniaxial tensile Bending Shearing Response sensitivity In-plane displacement u 


v 


Out-of-plane displacement w 


Note: *Sensitivity: 


位移响应敏感度反映了位移畸变的程度,畸变程度越大,越容易被检出。从现实应用角度,应选择位移响应最敏感的方式进行加载荷和测量。因此对于褶皱缺陷可采用单轴拉伸或剪切加载方式,通过检测层合板的离面位移即可凸显褶皱缺陷引起的位移畸变。
课题组至今已针对褶皱和层间弱粘结缺陷开展了大量的理论分析工作[28-30],作为比较,表3为含有层间弱粘结缺陷时,层合板在不同加载方式下的响应敏感性。
表 3 CF/EP复材层合板中层间弱粘结缺陷对不同载荷的响应敏感性[30]Table 3. Response sensitivity of weak bonding defects to different loading modes in CF/EP composite laminatesLoading mode Uniaxial tensile Bending Shearing Response sensitivity In-plane displacement u 


v 


Out-of-plane displacement w 


综合表2与表3结论可见,单轴拉伸载荷下,褶皱或者弱粘结缺陷均导致离面位移的畸变,虽然此处不能根据位移的畸变反演缺陷的类型和具体形状尺寸,但反之,通过测量拉伸载荷下的离面位移,可以揭示畸变区域存在多种缺陷的可能性。
因此,本文所提出的方法,不是传统意义上的缺陷检测方法,而是为大型复材结构提供了一种全场测量快速识别异常区域以及越过缺陷的具体形式识别而直接根据位移畸变程度量化评价材料结构性能退化程度的一种方法。
2. CF/EP复材层合板检测方案的数值验证
尽管在实际纤维增强树脂复合材料结构中,褶皱的分布呈分散性,但是为了便于对上述检测理论进行分析计算和试验验证,本文制作了含单个确定性褶皱的试样进行相应的分析。
根据表2结论,考虑到单轴拉伸可以方便地在万能试验机上实现,因此本文选择拉伸加载方式和离面位移测量的组合作为检测的手段。
2.1 CF/EP复材层合板中褶皱缺陷制样
为形成不同程度的褶皱缺陷,本文采用钢棒法来制造缺陷,通过使用不同直径钢棒置入不同预浸料板之间,将褶皱缺陷波纹比引入CF/EP试样中。试样从底部往上共8层,试样I的钢棒放置在第2层与第3层的中间,试样II的钢棒放置在最底层。同时该钢棒使用聚四氟乙烯布包覆,固化过程完成后,由于聚四氟乙烯材料摩擦系数极小,因此可轻松将钢棒从层合板中取出。在制造过程中,由于树脂流动性较强,会聚集到由钢棒产生的凹槽中,待取出钢棒之后,可进一步将环氧树脂添加到由于钢棒拔出而留下的空腔中。钢棒法制作褶皱缺陷的示意图和制作过程如图11所示。
2.2 CF/EP试样结构与参数
含缺陷的CF/EP试样如图12所示,褶皱缺陷位于试样中部位置,缺陷的设计参数见表4。试样长250 mm,宽25 mm,采用对称铺层,铺层顺序为[0/90/0/90]s,共8层,厚度为0.8 mm。预浸料采用威海光威复合材料股份有限公司生产的USN 10000型号,单向纤维预浸料厚度为0.1 mm,纤维单位面积质量为100 g/m2,树脂含量为20%~40%。该单向板的力学性能与表1所示一致。
表 4 CF/EP试样中的缺陷参数Table 4. Defect parameters of the CF/EP specimensSpecimen number Layup sequences Wrinkle parameters Wavelength/mm Amplitude/mm Wrinkle ratio I [0/90/0/90]s 6.0 1.2 0.200 II [0/90/0/90]s 12.0 0.8 0.067 2.3 检测方案的有限元验证
对于图12所示的含褶皱缺陷试样,图13(a)、图13(b)给出了单轴拉伸下的离面位移有限元分析结果。对于试样Ⅰ,图13(a)表明当拉伸载荷大小为600 N时,对应的最大离面位移为0.169 mm,图13(b)表明当拉伸载荷大小为1200 N时,试样Ⅰ对应的最大离面位移为0.228 mm。作为对比,图13(c)是不含缺陷的理想试样在1200 N时的离面位移,由图可见,当结构中存在褶皱缺陷时,不但离面位移分布模式发生了显著改变,且离面位移的最大值增加了104的数量级,离面位移的最大值与褶皱缺陷所在的区域一致。
有限元分析结果也说明,在600~1200 N的拉伸载荷下,含褶皱缺陷试样离面位移的大小与下文中光学变形检测的范围相适应,因此根据有限元分析结果可合理设计拉伸试验的检测方案,包括加载方式、载荷大小和测试值的预估计。
3. 双目结构光检测
光栅投影向来被用于三维表面的测量,其测量范围较大,测量精度可调,对环境要求不高。近年来,有文献将DIC(数字图像相关)方法与光栅投影方法相结合用以测量三维变形,其中光栅投影用于变形前后的三维曲面测量,DIC用于变形前后的图像数据匹配[31-32]。考虑到缺陷检测的应用场景往往面临大尺寸、大曲率结构及现场检测等实际需求,本文创新性地提出了独立利用双目结构光测量离面位移的新方法,即利用变形前后点云数据本身携带的信息进行数据重建和匹配。
根据上文分析结果,含褶皱缺陷的层合板试样,应通过检测其拉伸过程中的离面位移畸变情况以判断缺陷所在的位置。双目结构光检测直接得到的是表面高度信息,因此本文分别对加载前后的试样采集其表面高度信息z0和z1,从测试原理上可得离面位移d= z1− z0。但在实际测量中,试件拉伸后,在光测系统中物面相对位置发生变化,不仅试件本身的三维形貌发生变化,而且采集到的表面三维点云的数据量也发生变化,变形前后的点云不再存在一一对应的关系,本文创新性地提出了三维点云重构算法提取离面位移场,从而实现了基于光栅投影位移场测量的微应力缺陷检测方法。图14是点云重构算法的基本框架,该算法吸收了无网格法中形函数的构造方法,规格化节点上的点云数据取决于其邻域的半径、邻域内原始点云的数值及原始点云到该节点的距离作为权重,经最小二乘法拟合得到。
3.1 实验装置
对褶皱缺陷试样进行轴向拉伸试验,拉伸试验采用双立柱台式Instron 3369型电子万能试验机进行,试验机负荷范围为0~50 kN。光学测试系统采用多频相移结构光投影结合三角测量法(见图15)获取试样表面的空间三维信息。
3.2 实验结果
图16(a)为I号试样未加载时表面形貌点云,图16(b)是该试样加载到1200 N并保持稳定时采集的试样表面形貌点云。
由于点云边缘数据误差较大,故提取图16中线框内有效区域数据进行分析。图17(a)和图17(b)将加载前后所检测到的试样表面有效点云信息分别以等高线的形式给出,由于复合材料试样为手工制样,表面平整度较差,在未施加载荷的情况下,其表面等高线并非理想的光滑曲线。
图17(c)是经点云数据处理并相减后,得到试样表面的离面位移分布。由于手工制造的褶皱缺陷在形式上也并非理想的余弦曲线,因此试样I实测的离面位移分布与图13所示的有限元分析结果有一定的偏差,有限元给出的理想褶皱缺陷所引起的离面位移在试样上分布较为均匀,但实测结果说明实际褶皱所造成的影响集中分布在试样中部的有限区域,这一分布与缺陷所在的区域吻合较好,在无缺陷区域,等值线显示其实际位移数值为0,说明远离缺陷区域,其位移的变化相对缺陷区域的变化是可以忽略的。
图18(a)、图18(b)是试样II加载前后的表面等高线,图18(c)是基于加载前后的点云信息所提取的离面位移,由图18可见:通过加载前后表面高度的测量并提取离面位移,可以很好地捕捉到缺陷所在的位置,离面位移的分布与缺陷位置具有对应一致的关系,且与计算预测结果符合较好。
表5为从200 N到1200 N的拉伸载荷下实测位移响应与有限元分析得到的缺陷处最大离面位移结果的对比。可见,两件试样在1200 N下的离面位移误差分别约为10.0%和18.3%,试样II误差相对较大可能与手工制样的缺陷形状误差及试样夹持端表面平整度较差造成加载过程中引起的附加载荷等有关。
表 5 CF/EP试样离面位移实测结果与有限元结果比较Table 5. Comparison of out-of-plane displacement of CF/EP specimens between measurement results and finite element resultsSpecimen number Load/N Measurement results/cm Finite element results/cm Error I 200 0.01078 0.0089 17.7% 500 0.01806 0.0154 14.7% 800 0.02093 0.0193 7.8% 1 000 0.02359 0.0212 10.1% 1 200 0.02508 0.0228 10.0% Ⅱ 200 0.00218 0.0027 20.1% 500 0.00918 0.0101 8.6% 1 200 0.01361 0.0115 18.3% 上述结果说明:由于褶皱缺陷导致的离面位移异常现象,可以由本文提出的双目结构光方法检测出来,且实测值与有限元结果的误差也在可接受范围内。
本文研究表明:针对大型纤维增强树脂复合材料构件,建立合理的缺陷细观力学模型并展开深入的力学响应分析可能是其缺陷检测理论中重要的一环,而在该理论的指导下通过光学全场测量方法,快速捕获响应异常区域,为后续在该异常区域进行精细化的缺陷识别和检测提供了一条可行的路径。
4. 量化评价
缺陷导致的位移畸变程度可以由缺陷区域的离面位移与无缺陷区域的离面位移之比(位移比)表示,以试样I为例,由于波纹比A/λ可以表征褶皱的严重程度,固定褶皱区范围,即取λ值为6 mm,调整波幅A作为变量来控制褶皱参数,使得A/λ取值范围为0.04~0.2。
图19为位移畸变程度随波纹比的变化趋势。虚线表示远离缺陷处的远场归一化位移(离面位移值与板厚比值),实线表示缺陷区域的归一化位移。褶皱区域与远场非褶皱区域的位移比值表征了位移畸变程度。可见,随着波纹比的增加,远场位移几乎保持水平不变,而缺陷处的位移显著增大,因此位移畸变程度随波纹比增大而增加,同时说明畸变主要集中在缺陷所在的局部区域,对远场位移几乎没有影响。因此将位移比作为量化评价指标,可以实现不同严重程度的缺陷的比较与评价。
此外,图20为CF/EP复材层合板离面位移及位移比随载荷的变化。可知,当波纹比为0.1875时,随着拉伸载荷在弹性范围内的增加,褶皱区域和非褶皱区域的归一化离面位移均呈线性增大的趋势,但其比值并不随加载而变化,因此若采用光-力学方法对试样进行加载,只要在弹性范围内,具体所施加的载荷大小并不会影响结论。
5. 结 论
本文建立了以概率分布和统计信息表征的缺陷力学模型,开展了含分散性缺陷的纤维增强树脂复合材料结构的力学响应规律研究,提出了一种集缺陷检测与性能评价为一体的方法,并以褶皱缺陷为例进行了具体的实施。研究结果表明:
(1) 含缺陷层合板在不同加载下对位移具有“敏感”或“顿感”响应特征,“敏感”响应反映了较大的位移畸变程度,可以为缺陷检测和识别提供理论指导。由本文数值预测结果可知,含褶皱缺陷的层合板在拉伸载荷下的离面位移响应最敏感。
(2) 针对含褶皱缺陷构件的“敏感”响应特征,创新性地提出了基于光栅投影测量技术的全场离面位移测量方法,所探测到的位移场畸变直观地反映了缺陷在试样上的位置。与剪切散斑等光测方法对大型结构的变形而导致过度的刚体运动使得散斑之间相关性丧失相比,本文基于双目结构光所提出的间接位移测量方法,测量视野大,不受刚体位移影响。
(3) 含褶皱层合板在拉伸加载下的光栅投影测量结果显示,褶皱缺陷处的离面位移异常增大,且实测的褶皱区域离面位移值印证了有限元预测结果。实测位移响应的畸变程度也为含缺陷复材结构性能评价提供了直接的参考依据。
(4) 当前纤维增强树脂复合材料的缺陷检测仍具有一定的难度和挑战性,一些复杂的复合材料构件仍依靠手工铺层裁剪,因此其表面平整度、尺寸精度与机加工产品具有很大的差距。与其他直接检测位移的方法相比,本文所提出的检测方法,可以消除表面初始误差对位移的影响,非常适合复合材料结构的变形检测。利用该方法首先在大型结构上快速发现位移畸变区域,然后再结合超声、CT等手段对该区域进行细致的扫描探查,为大型复材结构的缺陷检测工业化提供了一种可行的方法途径。
-
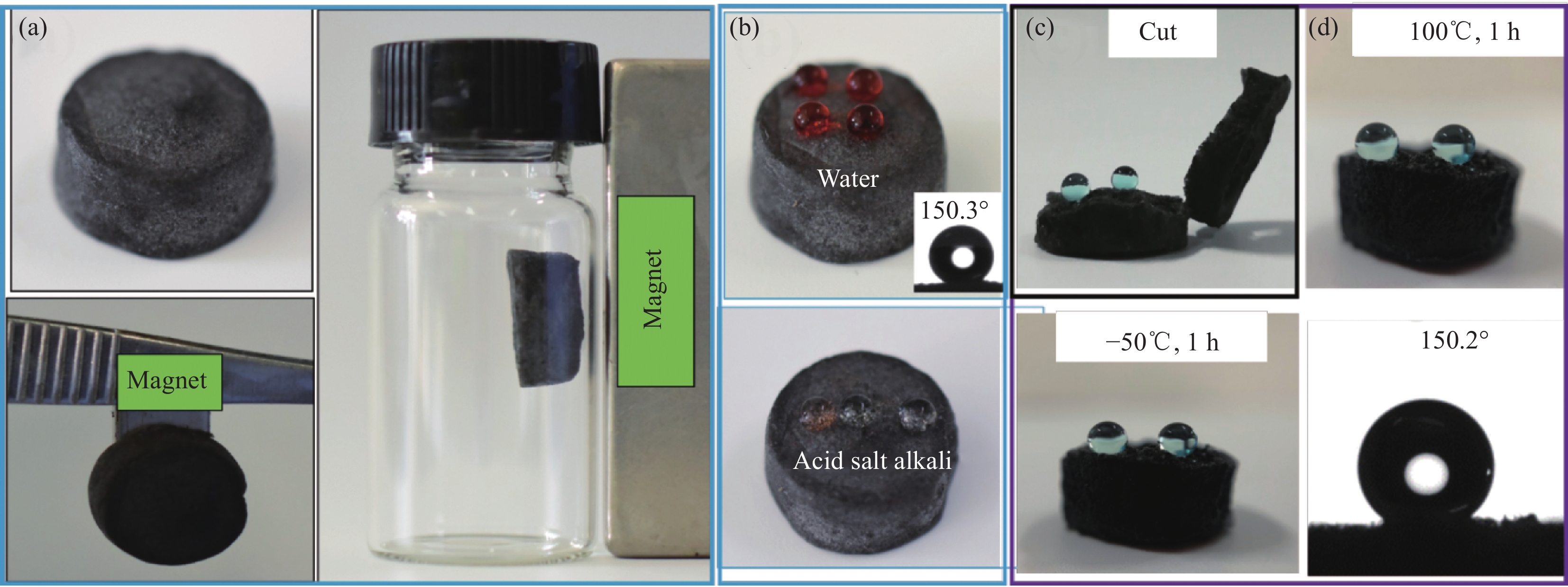
图 4 Fe3O4/PDMS-COL海绵的磁性表现 (a)、对不同液滴的疏水表现 (b)、海绵内部的疏水表现 (c) 及在极端条件(冷冻、加热)下的疏水表现 (d)
Figure 4. Magnetic performance (a), hydrophobic performance toward different droplets (b), hydrophobic performance of the interior (c) and hydrophobic performance under different conditions (freezing, heating) (d) of Fe3O4/PDMS-COL sponge
图 6 Fe3O4/PDMS-COL海绵在重力作用下的油水分离实验 ((a1)~(a3))、外部驱动作用下的抽滤实验 ((b1)~(b3)) 和外部驱动作用下的连续性油水分离实验 ((c1)~(c3))
Figure 6. Oil-water separation experiment under gravity ((a1)-(a3)), filtration experiment under external drive ((b1)-(b3)) and continuous oil-water separation experiment under external drive ((c1)-(c3)) of Fe3O4/PDMS-COL sponge
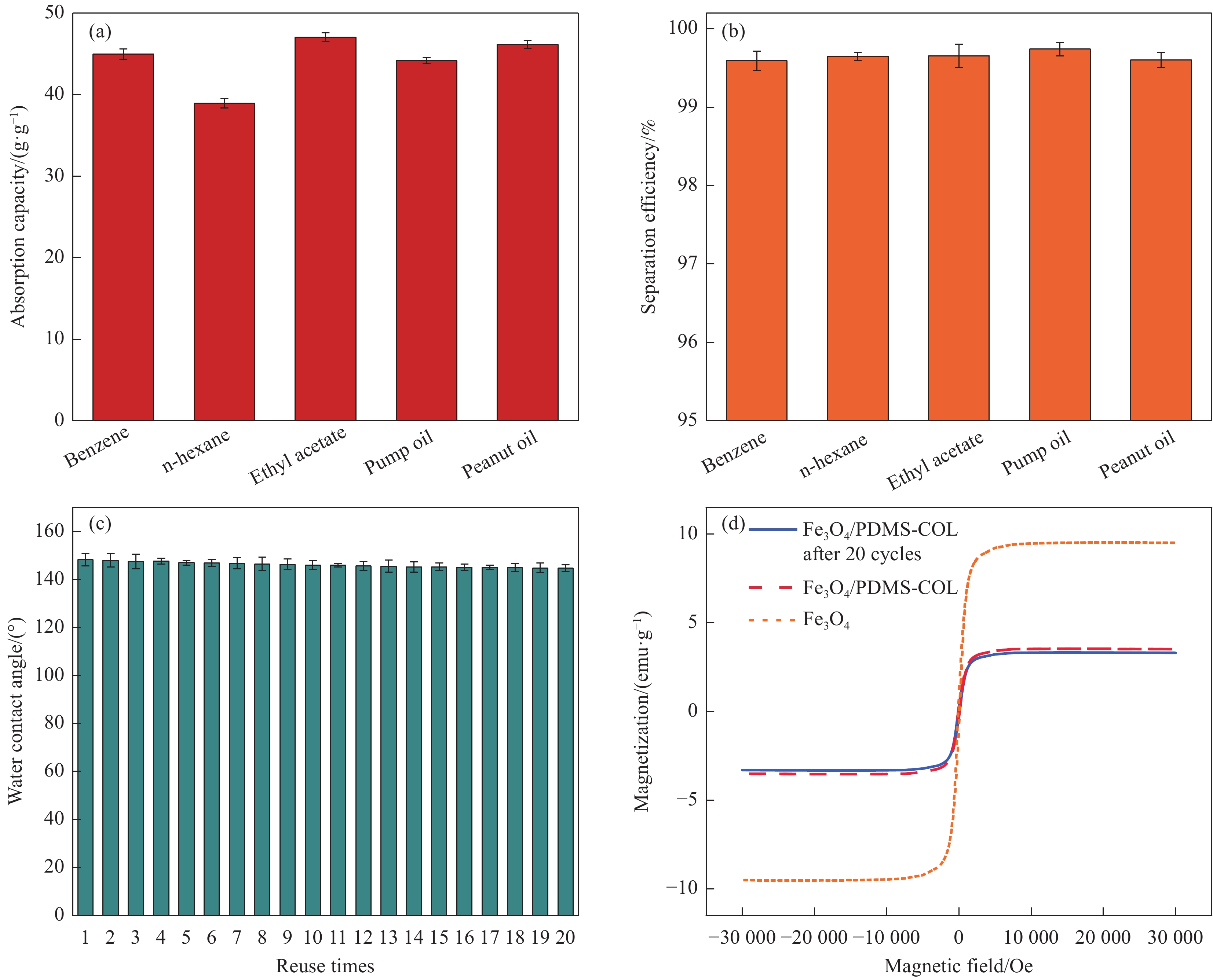
图 7 Fe3O4/PDMS-COL海绵对不同油相的吸附容量 (a)、对不同油相的分离效率 (b)、苯每次循环利用后的水接触角 (c) 和20次循环利用后的磁性图 (d)
Figure 7. Absorption capacity toward different oils (a), adsorption efficiency toward different oils (b), water contact angle after each recycling from benzene (c) and magnetic diagram after 20 cycles of recycling (d)
图 9 ((a1)~(a3)) Fe3O4/PDMS-COL海绵在弯管内的油水分离实验;((b1)~(b5)) 在U形管中水层下方重油的去除情况(该管中包含三相液体,分别为:正己烷(上层,透明,轻油)、水(中层,蓝色)和三氯甲烷(下层,红色,重油))
Figure 9. ((a1)-(a3)) Oil-water separation experiment of Fe3O4/PDMS-COL sponge on curved track; ((b1)-(b5)) Removal of heavy oil under the water layer in the U-shaped tube (The tube contains three-phase liquids, namely n-hexane (upper layer, transparent, light oil) , water (middle layer, blue) and chloroform (lower layer, red, heavy oil))
表 1 不同聚二甲基硅氧烷(PDMS)与胶原浓度下海绵的接触角
Table 1 Contact angles of sponges at different concentrations of polydimethylsiloxane (PDMS) and collagen
PDMS
concentration/
vol%Contact
angle/(°)Collagen
concentration/
(mg·mL−1)Contact
angle/(°)5 114.7±0.2 3 109.0±0.3 10 120.1±0.5 6 114.6±0.5 15 150.3±0.6 10 150.3±0.5 20 149.0±0.3 15 140.3±0.4 30 150.5±0.3 20 125.7±0.7 -
[1] DUBANSKY B, WHITEHEAD A, MILLER J T, et al. Multitissue molecular, genomic, and developmental effects of the deepwater horizon oil spill on resident gulf killifish (Fundulus grandis)[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2013,47(10):5074-5082. DOI: 10.1021/es400458p
[2] SU L, WANG H J, NIU M, et al. Ultralight, recoverable, and high-temperature-resistant SiC nanowire aerogel[J]. ACS Nano,2018,12(4):3103-3111. DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.7b08577
[3] JAYARAMULU K, GEYER F, PETR M, et al. Shape controlled hierarchical porous hydrophobic/oleophilic metal-organic nanofibrous gel composites for oil adsorption[J]. Advanced Materials,2017,29(12):1605307. DOI: 10.1002/adma.201605307
[4] 纪浩楠, 易昌凤, 徐祖顺, 等. 二氧化钛/ZIF-8复合超疏水海绵的制备及其油水分离性能[J/OL]. 复合材料学报: 1-10[2022-08-30]. DOI: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20211217.001. JI Haonan, YI Changfeng, XU Zushun, et al. Preparation of titanium dioxide/ZIF-8 composite superhydrophobic sponge and its oil-water separation performance[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica: 1-10[2022-08-30](in Chinese). DOI: 10.13801/j.cnki.fhclxb.20211217.001.
[5] 管浩, 戴鑫建, 王鑫, 等. 木基多孔油水分离材料研究进展[J]. 木材科学与技术, 2022, 36(1):1-8. DOI: 10.12326/j.2096-9694.2021183 GUAN Hao, DAI Xinjian, WANG Xin, et al. Research review of wood-based porous materials for oil/water separation[J]. Chinese Journal of Wood Science and Technology,2022,36(1):1-8(in Chinese). DOI: 10.12326/j.2096-9694.2021183
[6] 叶泽权, 吴青芸, 顾林. 纤维素基油水分离材料研究进展[J]. 化工进展, 2022, 41(6): 3038-3050. YE Zequan, WU Qingyun, GU Lin. Recent progress in cellulose-based materials for oil-water separation[J]. Chemical Industry and Engineering Progress, 2022, 41(6): 3038-3050(in Chinese).
[7] YANG Q, TANG L, GUO C, et al. A bioinspired gallol-functionalized collagen as wet-tissue adhesive for biomedical applications[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2021,417:127962. DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.127962
[8] LI Y, ZHANG H, MA C, et al. Durable, cost-effective and superhydrophilic chitosan-alginate hydrogel-coated mesh for efficient oil/water separation[J]. Carbohydrate Polymers,2019,226:115279. DOI: 10.1016/j.carbpol.2019.115279
[9] LI L, LIU L, LEI J, et al. Intelligent sponge with reversibly tunable super-wettability: Robust for effective oil–water separation as both the absorber and filter tolerate fouling and harsh environments[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A,2016,4(31):12334-12340. DOI: 10.1039/C6TA03581G
[10] WU J, DING Y, WANG J, et al. Facile fabrication of nanofiber- and micro/nanosphere-coordinated PVDF membrane with ultrahigh permeability of viscous water-in-oil emulsions[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A,2018,6(16):7014-7020. DOI: 10.1039/C8TA01539B
[11] SUREWICZ W K, MANTSCH H H, CHAPMAN D. Determination of protein secondary structure by Fourier transform infrared spectroscopy: A critical assessment[J]. Biochemistry,1993,32(2):389-394. DOI: 10.1021/bi00053a001
[12] YANG K, PENG H, WEN Y, et al. Re-examination of characteristic FTIR spectrum of secondary layer in bilayer oleic acid-coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles[J]. Applied Surface Science,2010,256(10):3093-3097. DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2009.11.079
[13] ZHOU D, WANG L, CHEN X, et al. Reaction mechanism investigation on the esterification of rosin with glycerol over annealed Fe3O4/MOF-5 via kinetics and TGA-FTIR analysis[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2020,401:126024. DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.126024
[14] JEON H, LEE C S, PATEL R, et al. Well-organized meso-macroporous TiO2/SiO2 film derived from amphiphilic rubbery comb copolymer[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2015,7(14):7767-7775. DOI: 10.1021/acsami.5b01010
[15] LIU Y, WANG X, FENG S. Nonflammable and magnetic sponge decorated with polydimethylsiloxane brush for multitasking and highly efficient oil-water separation[J]. Advanced Functional Materials,2019,29(29):1902488. DOI: 10.1002/adfm.201902488
[16] RADU G L, BAIULESCU G L. Surface analysis of collagen membranes by X-ray photoelectron spectroscopy[J]. Journal of Molecular Structure,1992,293:265-268. DOI: 10.1016/0022-2860(93)80064-3
[17] SHARAN J, KOUL V, DINDA A K, et al. Bio-functionalization of grade V titanium alloy with type I human collagen for enhancing and promoting human periodontal fibroblast cell adhesion—An in-vitro study[J]. Colloids and Surfaces B: Biointerfaces,2018,161:1-9. DOI: 10.1016/j.colsurfb.2017.10.024
[18] SCHNYDER B, LIPPERT T, KÖTZ R, et al. UV-irradiation induced modification of PDMS films investigated by XPS and spectroscopic ellipsometry[J]. Surface Science,2003,532-535:1067-1071.
[19] LI J J, ZHOU Y N, LUO Z H. Mussel-inspired V-shaped copolymer coating for intelligent oil/water separation[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2017,322:693-701. DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2017.04.074
[20] SU X, LI H, LAI X, et al. Dual-functional superhydrophobic textile with asymmetric roll-down/pinned states for water droplet transportation and oil-water separation[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2018,10(4):4213-4221. DOI: 10.1021/acsami.7b15909
[21] ZHANG Y, CHAI C P, LUO Y J, et al. Synthesis, structure and electromagnetic properties of mesoporous Fe3O4 aerogels by sol-gel method[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: B,2014,188:13-19. DOI: 10.1016/j.mseb.2014.06.002
[22] NEWBURY D E. Mistakes encountered during autom-atic peak identification in low beam energy X-ray microanalysis[J]. Scanning,2007,29(4):137-151. DOI: 10.1002/sca.20009
[23] YU T, HALOUANE F, MATHIAS D, et al. Preparation of magnetic, superhydrophobic/superoleophilic polyurethane sponge: Separation of oil/water mixture and demulsification[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2020,384:123339. DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2019.123339
[24] GE J, JIN Q, ZONG D, et al. Biomimetic multilayer nanofibrous membranes with elaborated superwettability for effective purification of emulsified oily wastewater[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2018,10(18):16183-16192. DOI: 10.1021/acsami.8b01952
[25] 许亮鑫. 特殊浸润性海绵的制备及油水分离应用研究[D]. 北京: 清华大学, 2016. XU Liangxin. Research on preparation of special wettable sponge and application of oil-water separation[D]. Beijing: Tsinghua University, 2016(in Chinese).
[26] 贺兵. 高抗污油水分离膜制备及分离性能的研究[D]. 哈尔滨: 哈尔滨工业大学, 2019. HE Bing. Preparation of superantifouling membrance for oil-water separation and study of separation performance[D]. Harbin: Harbin Institute of Technology, 2019(in Chinese).
[27] LEI Z, DENG Y, WANG C. Multiphase surface growth of hydrophobic ZIF-8 on melamine sponge for excellent oil/water separation and effective catalysis in a Knoevenagel reaction[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A,2018,6(7):3258-3263. DOI: 10.1039/C7TA10566E
[28] WANG F, LI X S, LI W T, et al. Dextran coated Fe3O4 nanoparticles as a near-infrared laser-driven photothermal agent for efficient ablation of cancer cells in vitro and in vivo[J]. Materials Science and Engineering: C,2018,90:46-56. DOI: 10.1016/j.msec.2018.04.030
-
期刊类型引用(3)
1. 凌圣博,姚启,王乐蓬,梅杰,吴振. 褶皱缺陷对复合材料拉伸性能的影响规律:试验及数值模型. 力学学报. 2024(06): 1740-1751 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 陈正东,张启灿,吴周杰. 基于条纹投影的复杂结构多维度信息传感技术(内封面文章·特邀). 红外与激光工程. 2024(09): 81-99 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 王风全,梁森,吴召琦,田程. 基于分子动力学模拟异氰酸酯接枝改性热塑性树脂/纤维复合材料界面结合机理研究. 化工新型材料. 2023(12): 154-159 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)
-





 下载:
下载: