Preparation of BiOI/BiOBr0.9I0.1 photocatalyst and its degradation performance on 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid
-
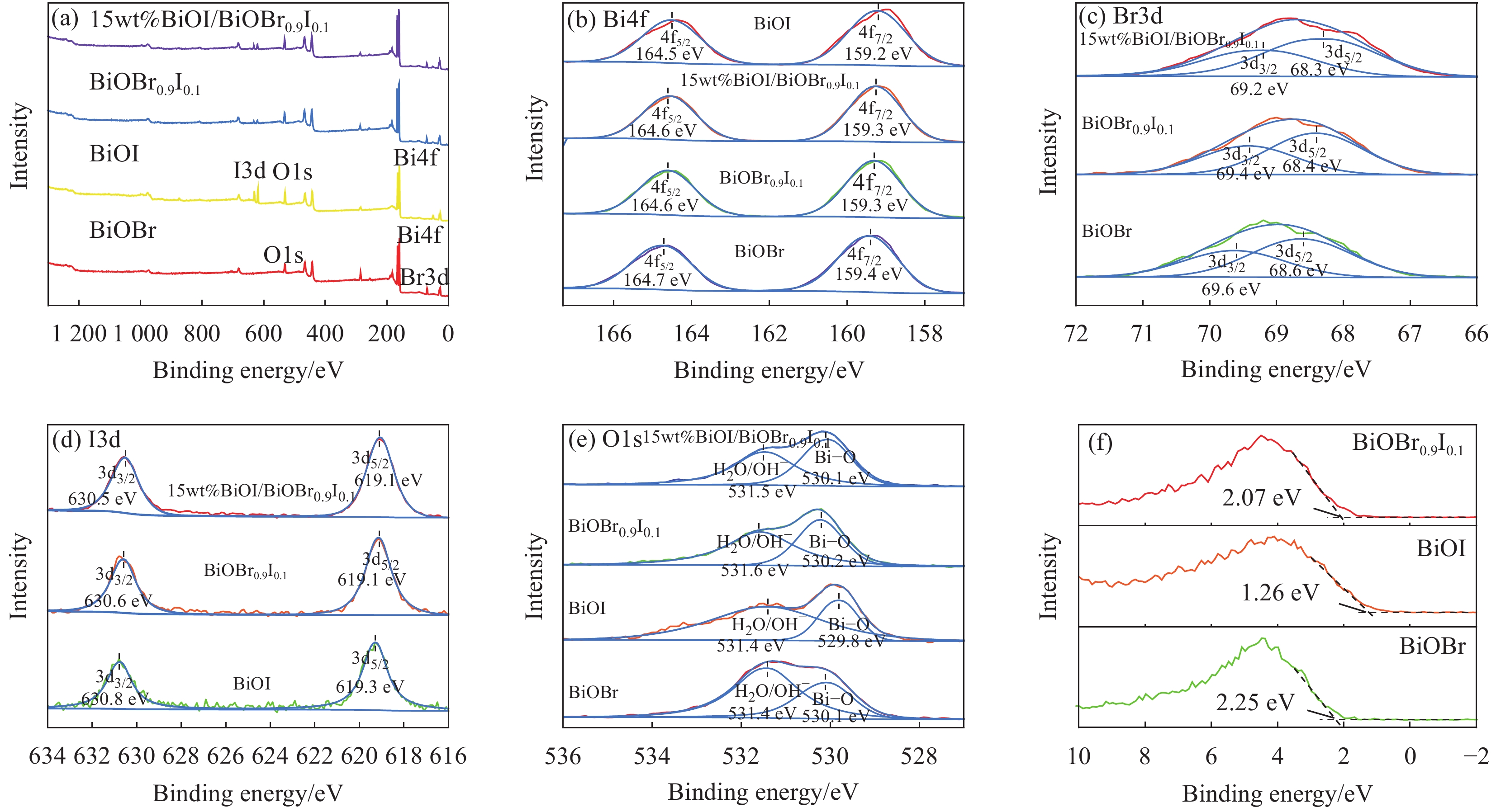
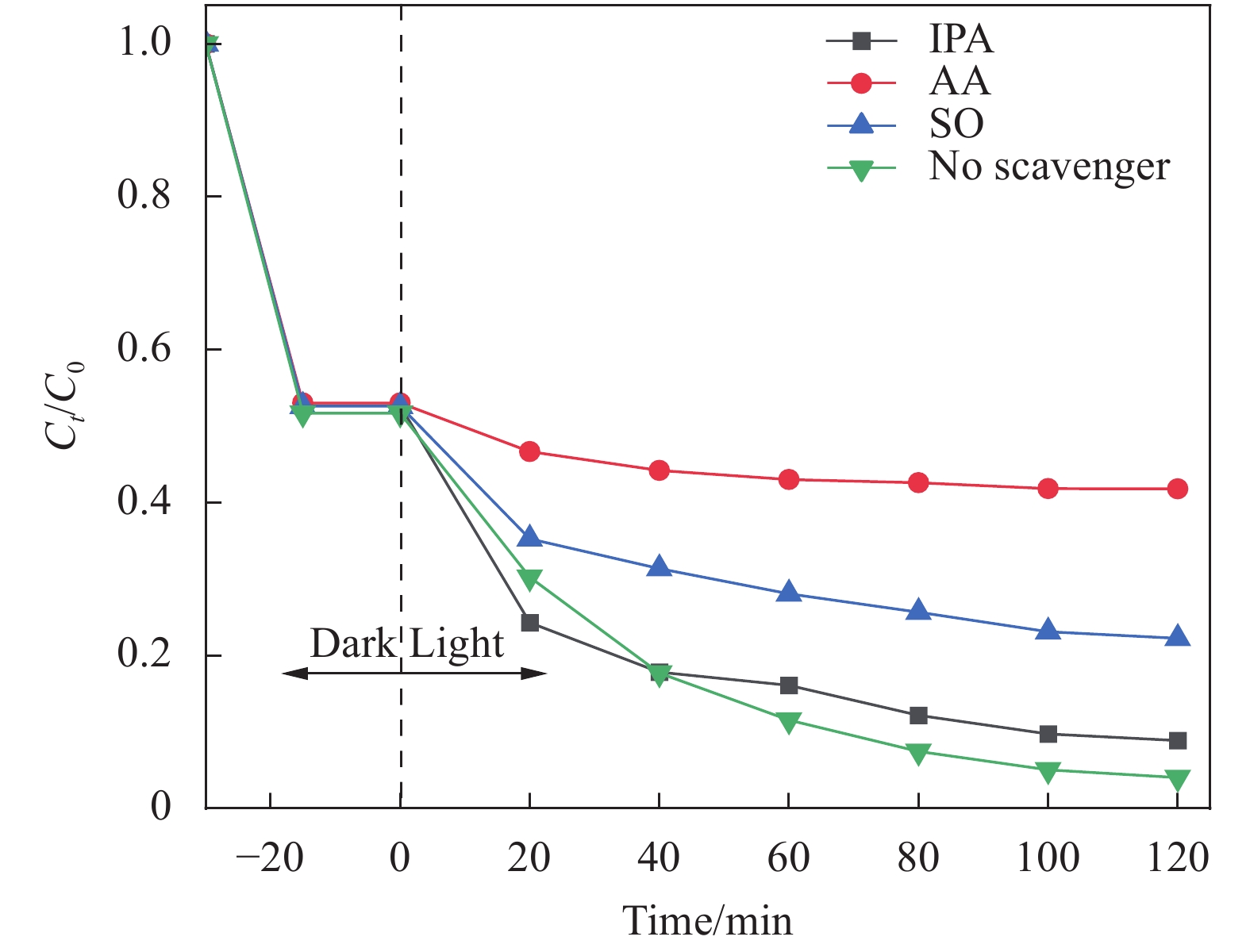
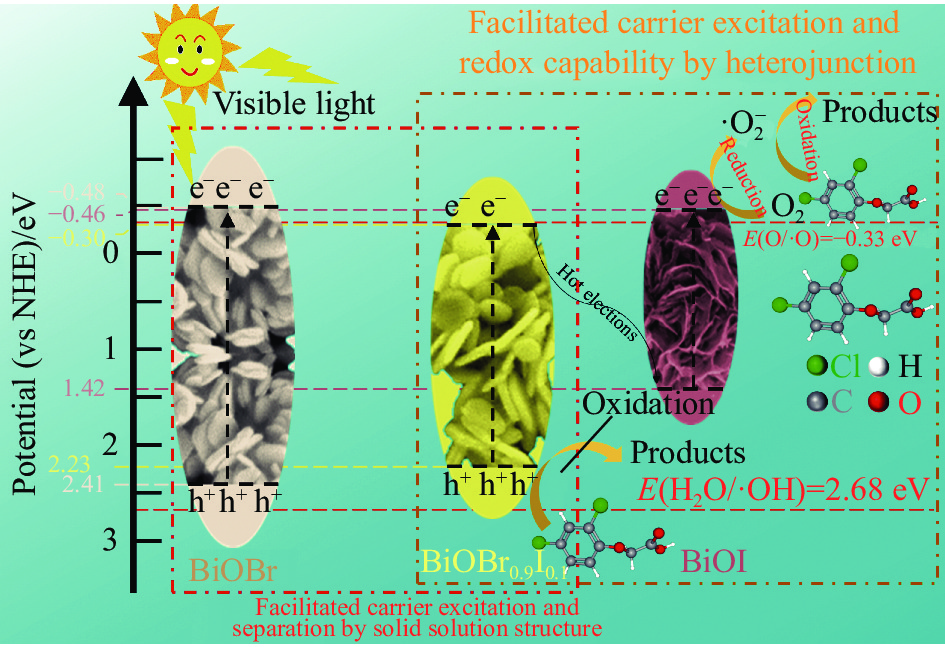
摘要: 农药污染严重危害生态环境和饮用水安全。采用溶剂热法制备一种新型高效的BiOI/BiOBr0.9I0.1光催化剂。通过XRD、SEM、XPS、UV-vis DRS、PL、EIS等手段表征其结构、形貌和光学性能等理化性质。制备的BiOI/BiOBr0.9I0.1呈团簇状堆积结构,有助于活性位点的增加,固溶体和异质结两种策略的结合拓宽了BiOBr的光响应范围,有效防止光生电子-空穴对在BiOI/BiOBr0.9I0.1内部复合并提高产生光生载流子的氧化还原能力。光催化实验结果表明,合成的15wt%BiOI/BiOBr0.9I0.1在可见光下对2,4-二氯苯氧乙酸(2,4-D)有最佳的光催化性能,120 min降解2,4-D效率最高可达95%,4次循环实验后降解率仍达到80.9%。结合捕获实验与电子自旋共振(ESR)技术结果可以证实•O2−和h+是主要的活性物种。制备的BiOBr0.9I0.1能有效调节BiOBr能带结构。BiOBr0.9I0.1和BiOI构成的异质结符合Z型异质结特点,构建异质结和固溶体两方法之间可在增强BiOBr光催化活性上产生协同作用。
-
关键词:
- BiOBr /
- 固溶体 /
- 异质结 /
- 农药 /
- 光催化 /
- 2,4-二氯苯氧乙酸 /
- BiOBr0.9I0.1
Abstract: The pollution of pesticides seriously threatens the ecological environment and drinking water safety. A novel and efficient photocatalyst of BiOI/BiOBr0.9I0.1 was prepared through solvothermal method. The physicochemical properties, such as structure, morphology and optical properties, were characterized by detections of XRD, SEM, XPS, UV-vis DRS, PL, EIS, etc. The BiOI/BiOBr0.9I0.1 synthesized has a cluster-like accumulation structure, which facilitates the increase of active sites. The combination of solid solution and heterojunction broadens the photoresponse range of BiOBr, effectively prevents the recombination of photogenerated electron-hole pairs inside BiOI/BiOBr0.9I0.1 and improves the redox ability of photogenerated carriers. The results of photocatalytic experiments show that 15wt%BiOI/BiOBr0.9I0.1 reaches the best photocatalytic performance for 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) under visible light, and the degradation efficiency of 2,4-D can reach 95% within 120 min. Furthermore, the degradation rate still reaches 80.9% after four cycles of experiments. According to the results of capture experiments and electron spin-resonance (ESR) tests, it can be confirmed that •O2− and h+ are the main active species. The BiOBr0.9I0.1 synthesized can effectively modulate the energy band structure of BiOBr. The heterojunction composed of BiOBr0.9I0.1 and BiOI is consistent with the characteristics of Z-scheme heterojunction, and the synergistic effect between the two strategies of constructing heterojunction and solid solution can be produced in enhancing the photocatalytic activity of BiOBr.-
Keywords:
- BiOBr /
- solid solution /
- heterojunction /
- pesticide /
- photocatalysis /
- 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid /
- BiOBr0.9I0.1
-
碳纤维增强聚合物复合材料(CFRP)具有高强、质轻、抗疲劳性能好和施工方便等优点,目前不仅被广泛应用于钢筋混凝土结构的加固中,同时也用在砌体结构的加固中[1-6]。CFRP加固砌体结构是通过CFRP与砌体材料界面间的粘结力,使两种材料组合在一起协同工作并传递荷载。因此,CFRP与砌体材料之间良好的粘结性能是保证CFRP与砌体结构共同受力变形的基础[7-8]。关于CFRP加固砌体结构,国内外学者做了大量研究,而关于CFRP-砌体界面性能只有少部分学者进行了研究并提出不同的界面粘结-滑移模型,这些模型基本上能准确模拟粘结界面的受力情况[9],但对于冻融环境下界面粘结-滑移模型未见公开报道。在冻融环境中,粘土砖的性能会随着时间的推移有所退化,在一定程度上会影响界面粘结性能,最终引起不可避免的耐久性问题[10-12]。因此,对冻融循环作用下CFRP与粘土砖之间粘结性能进行相应研究具有十分重要的意义。
通过简单可靠的单剪试验探究了冻融循环作用下CFRP-粘土砖界面在外力作用的破坏过程及破坏形态,得到了界面剥离承载力在循环作用下的变化规律,通过试验测得的应变得到了冻融循环过程中剪应力的发展及分布规律,并给出了考虑冻融循环影响的界面粘结-滑移关系。
1. 实验材料及方法
1.1 试件设计及制作
试验所使用碳纤维增强聚合物复合材料(CFRP)和树脂均为上海滠口实业有限公司生产,其主要性能如表1所示。试验所使用粘土砖的抗压强度平均值为9.28 MPa,吸水率约为17.58%,平均密度约为1 700 kg/m3。试验所用胶粘剂为SKO-碳纤维浸渍胶,其主要性能如表2所示。
表 1 碳纤维增强聚合物复合材料(CFRP)的性能Table 1. Properties of carbon fiber reinforced polymer(CFRP)Sample Tensile
strength/MPaModulus/
GPaElongation/
%Thickness/
mmCFRP ≥3 500 220 1.458 0.111 表 2 粘结树脂的性能Table 2. Properties of impregnation resinTensile shear strength/MPa Tensile strength/GPa Compressive strength/MPa Bending strength/MPa Positive tensile bond strength/MPa Modulus/MPa Elongation/% 24.29 40.12 73.62 72.95 4.44 2 605.7 2.45 本试验选用的粘土砖尺寸为235 mm×115 mm×55 mm,CFRP片材粘贴在粘土砖的一个表面(如图1所示),CFRP粘贴尺寸设计为6种规格,试件的具体参数如表3所示。
表 3 CFRP-粘土砖单剪试验试件参数Table 3. Specimen parameters of CFRP-clay brick specimens for single shear testCFRP size(Length×width)/mm Number of CFRP-clay brick specimen 0 cycle 20 cycles 40 cycles 60 cycles 80 cycles 80×50 5 5 5 5 5 100×80 5 5 5 5 5 80×80 5 5 5 5 5 100×80 5 5 5 5 5 80×100 5 5 5 5 5 100×100 5 5 5 5 5 参照CECS 146—2003[13]中相关要求将CFRP粘贴在粘土砖表面。为防止粘土砖出现局部拉剪破坏,粘结CFRP时在加载端留出30 mm非粘结区,制作完成的试件如图1所示,标准试件示意图如图2所示。
1.2 实验装置及加载程序
冻融循环试验参照GB/T 2542—2012[14]进行。将试件清理干净,在鼓风干燥箱内烘干达到质量要求后,将其在20℃的水中浸泡24 h后取出拭干水分,在冷冻箱内温度降至−15℃时开始计时。每次冷冻时间为3 h,融化2 h,控制冷冻温度为(−17±2)℃,融化水的温度控制在(15±2)℃。冻融循环次数分别取0次、20次、40次、60次和80次。
所有试件的单剪试验均在济南恒思盛大仪器有限公司生产的WDW-50微机控制电子万能试验机上通过自制单剪试验盒进行(如图3(a)所示),通过电脑控制加载速度,由荷载传感器输出CFRP与粘土砖的粘结荷载,CFRP的应变值通过江苏东华DH3816静态应变测试系统采集(如图3(b)所示)。为了使CFRP片材在加载过程中受力均匀,在试件加载端片材上下各粘贴一层30 mm长的CFRP加强片,加强片与试件同宽。加载过程采用位移控制,加载速率为0.5 mm/min。在CFRP试件拉伸前,先施加约为破坏荷载5%的预拉荷载(约为0.4 kN),检查夹具、拉力机和应变采集系统运行是否正常。
2. 试验现象
2.1 冻融循环对CFRP-烧结粘土砖界面的作用效果
试验发现,在经过若干次冻融循环后,CFRP-烧结粘土试件界面发生了较为明显的变化,以粘贴长度×宽度为80 mm×50 mm的单剪试件为例,图4为不同冻融循环作用下CFRP-烧结粘土砖界面破坏情况。可知,室温下试件破坏发生后,CFRP片材上粘有大颗粒粘土砖碎屑(如图4(a)所示);冻融20次和40次的试件破坏后,CFRP片材上粘有的粘土砖颗粒较小(如图4(b)所示);冻融60次后,其中2个试件破坏面较40次严重,界面上粘有大量粘土砖颗粒(如图4(c)所示),另1个试件与冻融40次的形态基本相同;冻融80次后,试件破坏发生在粘土砖,界面发生剪切破坏(如图4(d)所示),说明冻融循环作用对界面粘结性能有不利影响。
表4为粘贴长度×宽度为80 mm×50 mm的CFRP-粘土砖单剪试件试验结果。可以看出,随着冻融次数的增加,界面承载力逐渐降低,60次冻融后减小了约12%,表明冻融循环作用对CFRP-粘土砖的界面承载力有着不利影响。因此,当使用CFRP对粘土砖结构进行加固时,如果是在北方寒冷地区应适当考虑界面粘结折减系数。
表 4 CFRP-粘土砖界面承载力平均值和降低幅度Table 4. Average interfacial bearing capacity and reduction of CFRP-brick specimensCFRP size(Length×width)/mm Interfacial baring capacity/kN Decrease of bearing capacity/% 0 cycle 20 cycles 40 cycles 60 cycles 80 cycles 0 cycle 20 cycles 40 cycles 60 cycles 80 cycles 80×50 7.63 7.52 6.85 5.93 5.34 — 1.44 10.22 22.28 30.01 100×50 7.95 7.88 7.07 6.95 6.43 — 0.88 11.07 12.58 19.12 120×50 8.12 8.15 7.26 7.06 6.65 — –0.37 10.59 13.05 18.10 80×80 12.40 12.00 11.40 11.00 10.30 — 3.23 8.06 11.29 16.94 100×80 13.00 12.80 12.30 11.60 10.50 — 1.54 5.38 10.77 19.23 120×80 13.50 13.20 12.50 11.70 11.00 — 2.22 7.41 13.33 18.52 从试验及文献分析可知,造成界面承载力降低的原因主要有两点:(1)冻融作用导致粘土砖自身材料强度降低而引起CFRP-粘土砖试件粘结强度降低;(2) CFRP-粘土砖之间的胶体面层的粘结性能退化。由于CFRP的特殊构造,其聚合物基体的孔径较小,冻融循环作用下,其孔隙中的水不会冻结[15]。因此,可能是胶体吸水后,在冻融作用下,当溶胀和温度应力共同作用时,界面产生微裂纹,从而导致介质水在界面上冻结产生应力。
2.2 CFRP-粘土砖单剪试验破坏形态
由于本次试验在CFRP-粘土砖试件加载端预留了30 mm非粘结区,所有CFRP-粘土砖试件均是CFRP与粘土砖之间发生界面剥离而破坏的,没有发生CFRP布的撕裂破坏,也没有发生粘土砖的拉剪破坏。
所有CFRP-粘土砖试件剥离破坏是由纤维布传递荷载到粘土砖,从而使粘土砖内部产生的微小裂缝逐渐发展导致的。对于没有经过冻融循环的CFRP-粘土砖试件,其破坏过程是初始加载时除了碳纤维布开始绷紧外,试件并无明显变化,加载端的应变基本呈线性增加;当荷载增加至剥离荷载的40%左右时,可以听到“噼啪声”,加载端附近的应变迅速增加,粘土砖内部微裂缝逐渐开展,试件开始发生局部粘结破坏,总的粘结面积开始减少;随着荷载的进一步增大,应变急速增加,剥离深度也在加大,距离加载端较远处应变片的应变也逐渐增大,说明剥离逐渐向自由端发展。当剩余的粘结面积不足以抵抗荷载时,破坏瞬间发生。而在冻融循环作用下,破坏具有相似性,只是由于粘土砖与胶层之间的界面被削弱、粘土砖材料本身强度降低,开裂速度较未经循环试件更迅速,破坏更突然。
3. 结果与分析
3.1 冻融循环作用下粘土砖孔隙结构损伤
粘土砖为多孔材料,在水冻作用下,粘土砖内部孔隙中的水分子会出现冻结现象,造成孔隙体积膨胀,从而使粘土砖内部出现较大的微孔隙损伤和拉应力,使砖体的缝隙和节理出现加深和扩大;当粘土砖处于融化状态时,粘土砖内部微孔隙会出现迁移现象。当粘土砖在不同温度下进行反复冻结和溶解时,张力使孔隙壁的损伤不断加剧,最终造成砖体损伤。这种损伤反映到CFRP-粘土砖的粘结上,便会出现粘结退化现象。
图5为不同冻融循环作用下粘土砖孔隙度变化。图6为不同冻融循环作用下粘土砖弛豫时间T2谱分布。从图5可以看出,随着冻融循环次数的增加,粘土砖的孔隙度逐渐增大。由图6可知,随着冻融循环次数的增加,T2谱的峰值向右移动,说明大孔径比例增加,冻融使冻胀力逐渐大于颗粒间的粘聚力,造成砖样的孔隙发育和扩展程度加剧。
由CFRP-粘土砖单剪试验结果分析可知,冻融作用下,粘结界面破坏模式的变化与粘土砖微观变化是相统一的(如图4所示)。从单剪试件的破坏过程可以看出,不同冻融次数下,CFRP-粘土砖试件破坏后,粘土砖的表层破坏模式不尽相同。未经冻融的CFRP-粘土砖试件以CFRP粘结区域内靠近加载端部位的粘土砖剪切破坏为主。剪切破坏面被拉出的近似三角形粘土砖块与CFRP粘结较好,其余部位CFRP粘有大量被拉下的粘土砖碎屑与颗粒,破坏面一般在粘土砖基层一侧,深度约为2~5 mm。经过冻融循环的CFRP-粘土砖试件在冻融次数较低时,破坏模式与未受冻融的CFRP-粘土砖试件基本一致,冻融达到40次后,在加载端出现三角破坏区的概率随之减小,破坏以界面剥离破坏为主;当冻融时间达到60次时,所有试件均为剥离破坏,加载端不再出现三角破坏区,在CFRP上粘下的粘土砖层越来越均匀;当冻融时间达到80次时,在加载端出现类似三角区域的破坏情况,说明粘土砖的强度减弱。
3.2 CFRP-粘土砖界面承载力及平均粘结强度
图7为CFRP-粘土砖界面承载力随冻融循环次数的变化曲线。由表4和图7可知,随着冻融循环次数的增加,CFRP-粘土砖界面承载力总体呈下降趋势,而后期的下降速度要快于前期。同时,还可以看到,在CFRP的粘结宽度及冻融循环次数相同的情况下,当粘结长度从80 mm增加至120 mm时,CFRP-粘土砖界面承载力增加的幅度并不大,但当粘结宽度从50 mm增加到80 mm时,CFRP-粘土砖界面承载力却提高了60%~70%,说明CFRP的粘结宽度是影响界面承载力的主要因素之一,与以混凝土为基材的复合材料结果相似[16-18]。
在不考虑相关几何参数因素对试件界面粘结性能的影响下,通过界面粘结强度平均值来考察界面在冻融循环作用下的劣化情况,界面粘结强度平均值计算如下:
τf=PuA (1) 式中:
τf 为试件平均粘结强度(MPa);Pu为CFRP-粘土砖界面承载力(kN);A为粘结面积(mm2)。图8为CFRP-粘土砖界面平均粘结强度曲线。可知,平均粘结强度曲线根据长度和宽度组合分为三组,同一长度不同宽度的图形在位置上比较接近,再次证明粘结宽度对承载力的贡献较大,即只要保证粘结长度足够,CFRP-粘土砖试件的平均粘结强度基本和粘结宽度呈正相关关系。
3.3 CFRP-粘土砖界面剪应力的分布规律
由于试验无法得到粘结界面上任意点的应变值,因此在计算中以两个相邻应变片之间的平均剪应力作为界面剪应力。由于CFRP非常薄,可以假定CFRP在轴向力方向上的应力
σf 在横截面内是均匀分布的,并假定相邻两应变片间的应变线性分布,现取长度为微元长度dx的CFRP单元作为对象进行研究,CFRP-烧结粘土砖界面单元体剪应力分布如图9所示。由力的平衡条件可以得到粘结剪应力的计算公式为
τ(x)=dFbfdx=dσfdxtf=Eftfdεxdx=Eftfεi+1−εiΔxi (2) 式中:F为界面承载力;
bf 、tf 、Ef 和εi 分别为CFRP片材的宽度、厚度、弹性模量和应变。由于各个试件剪应力的分布具有一定相似性,因此以粘贴长度×宽度为80 mm×50 mm的单剪试件为例,其不同冻融循环作用下的剪应力分布如图10所示。可知,当荷载较小时,剪应力的峰值出现在加载端,而粘结剪应力只分布在距加载端20 mm左右的范围内;当荷载逐渐增加时,加载端附近的剪应力也随之逐渐增加,增加到峰值后剪应力开始向远端传递,此时的剪应力集中分布在一定区域内,区域外剪应力几乎为零,这一区域即为有效粘结区域,该区域的长度称为“有效粘结长度”,本试验中有效粘结长度基本保持不变,大约为60~80 mm,且其不随CFRP粘结尺寸及冻融循环次数而变化,说明随着荷载的增加,有效粘结区域在破坏过程中会以近似不变的长度由加载端向自由端平行移动,从而使剥离区域逐渐增加,直至试件破坏,与CFRP-混凝土试件的研究结果一致[19-20]。
3.4 CFRP-粘土砖界面粘结-滑移本构关系
为建立准确可靠的粘结-滑移曲线,需要进一步了解界面剥离机制及破坏过程中粘结剪应力与滑移值的变化情况,即
ττmax−ss0 曲线。其中,滑移值为CFRP与粘土砖的位移差,计算如下:s(x)=s(0)+∫x0ε(u)du (3) 式中:
s(0) 为最大剪应力对应的滑移值;s(x) 为CFRP上任一点滑移值;ε 为应变值。关于粘结-滑移关系,目前国内外学者对纤维增强聚合物复合材料(FRP)-混凝土界面深入研究较多,而对于FRP-粘土砖的研究鲜见报道。粘结-滑移模型的提出有试验方法、有限元模拟方法、理论推导方法等,图11为几种典型粘结-滑移关系模型曲线。由图11(a)可以看到,直角三角形模型属于早期模型,把界面近似看做弹性体,缺点是忽略了界面在加载后期的软化行为;由图11(b)~11(d)可知,粘结-滑移关系模型均为两阶段曲线模型,曲线由上升段和下降段组成,目前对CFRP-混凝土界面的研究大多采用该类型曲线模型。通过对比发现,图11(d)的Popovics模型比较适合本试验数据,如下式:
ττmax (4) 通过式(4)拟合效果较好(拟合系数n=3.032),可以较准确地表示CFRP-粘土砖面粘结-滑移的有关特征,如图12所示。可以看出,CFRP-粘土砖界面粘结-滑移曲线分为上升段和下降段,上升段为强化阶段,下降段为软化阶段。开始加载时,界面粘结剪应力和滑移均不大,粘结-滑移曲线近似呈线性关系,试件处于弹性状态;随着粘结剪应力逐步增大,粘结-滑移曲线表现出非线性,此时滑移量增加速度较剪应力增加速度要快,当界面逐渐达到最大剪应力,界面的粘结不足以抵抗剪应力时,试件开始出现滑移;当粘结剪应力增大至最大后,曲线进入下降段,此时剪应力下降速度和滑移量增加的速度均较快,且滑移量增加的速度越来越大,当粘结应力几乎为零时,滑移量达到最大值,此时CFRP和粘土砖在界面处完全剥离。对比Popovics曲线和实验数据可以发现,Popovics模型可以较好地描述CFRP-粘土砖界面粘结-滑移关系,上升段试验数据点几乎与Popovics模型曲线重合,下降段的试验数据分布于Popovics模型曲线两侧,但偏差较小,表明采用Popovics模型来描述CFRP-粘土砖界面的粘结-滑移本构关系是较准确的。
4. 结 论
分析了冻融循环作用和粘结尺寸对CFRP-粘土砖界面承载力及粘结强度的影响,通过试验数据和理论比较,建立了考虑冻融循环影响下的CFRP-粘土砖界面粘结-滑移模型。
(1)在冻融循环作用下,CFRP-粘土砖界面的破坏模式是由剪切破坏转变为粘结剥离破坏,剥离是从CFRP加载端开始逐渐向自由端发展。相对于长度,CFRP的宽度对试件界面承载力影响更为显著。
(2)随着冻融循环次数的增加,CFRP-粘土砖界面承载力总体呈下降趋势,而后期的下降速度要快于前期。
(3) CFRP-粘土砖界面粘结剪应力分布曲线具有相似性,当荷载水平逐渐增加,剪应力也随之逐渐增大,并从加载端向自由端传递,且所有剪应力集中分布在一定的“有效粘结区域”内,而区域外的剪应力几乎为零,有效粘结区域的长度约为60~80 mm,且与冻融循环次数无关。
(4) CFRP-粘土砖界面粘结-滑移关系有明显的上升段和下降段,上升段为强化阶段,下降段为软化阶段,Popovics模型可以很好地描述CFRP-粘土砖的界面粘结-滑移关系。
-
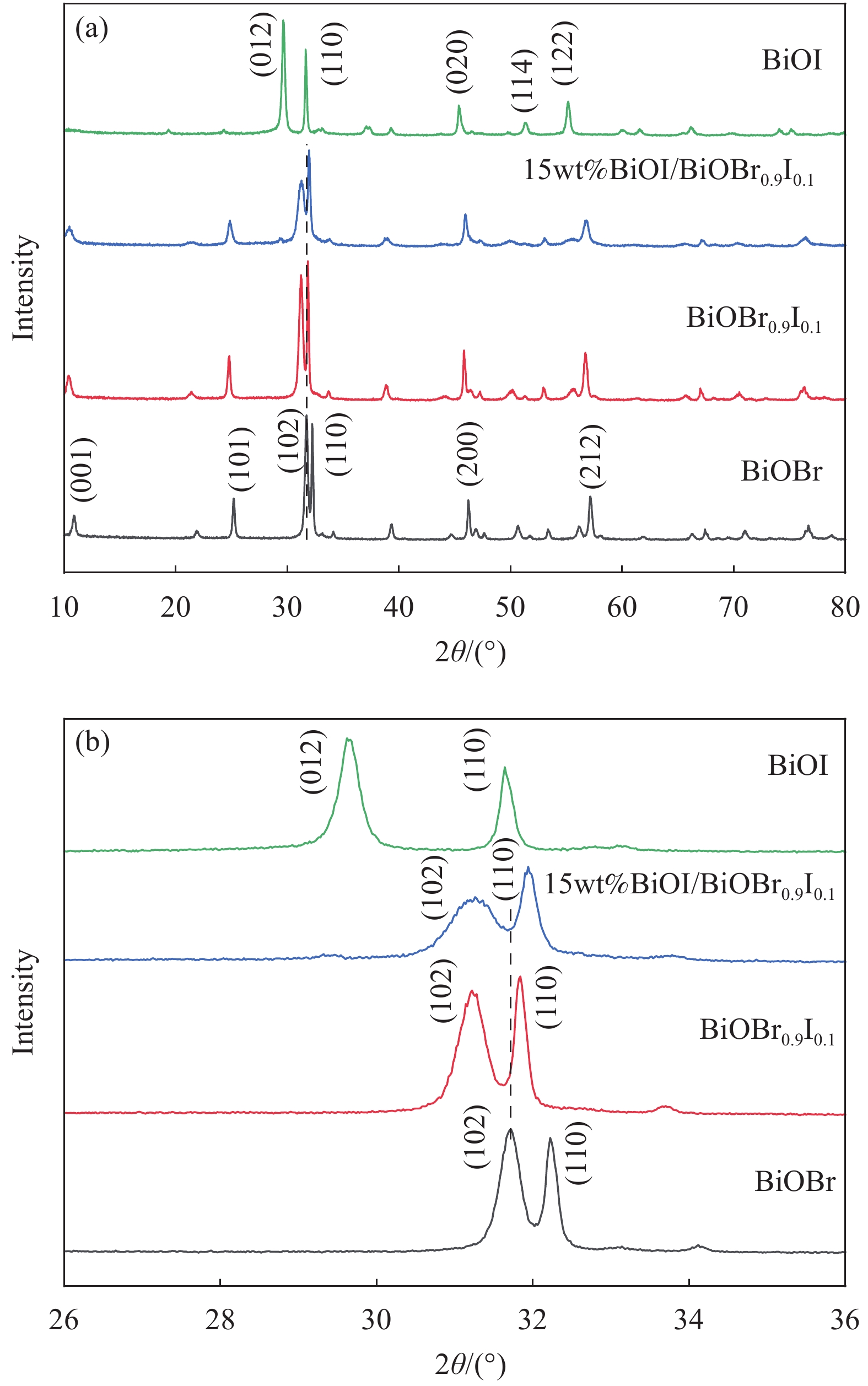
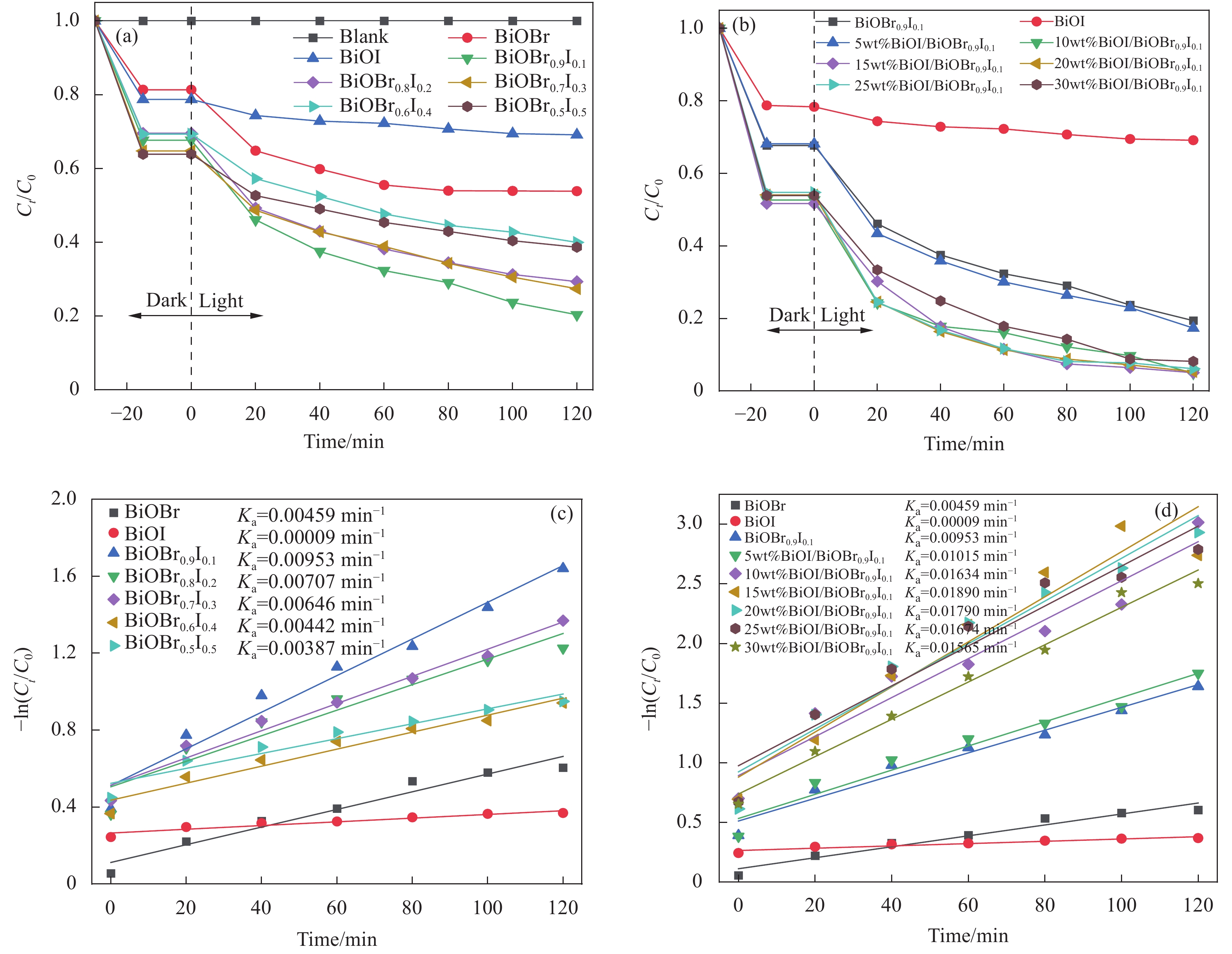
图 7 BiOBr、BiOI、BiOBrxI1-x和Pwt%BiOI/BiOBr0.9I0.1可见光降解2,4-二氯苯氧乙酸(2,4-D)曲线((a)、(b))及对应样品准一级动力学拟合((c)、(d))
Figure 7. Visible light degradation curves of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyaceticacid (2,4-D) by BiOBr, BiOI, BiOBrxI1-x and Pwt%BiOI/BiOBr0.9I0.1 ((a), (b)) and quasi-first-order kinetic fitting of corresponding samples ((c), (d))
Ct—Concentration of 2,4-D at different time t; C0—Initial concentration of 2,4-D; Ka—Apparent rate constants
-
[1] ALIKHANI N, FARHADIAN M, GOSHADROU A, et al. Photocatalytic degradation and adsorption of herbicide 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid from aqueous solution using TiO2/BiOBr/Bi2S3 nanostructure stabilizedon the activated carbon under visible light[J]. Environmental Nanotechnology, Monitoring & Management,2021,15:100415. DOI: 10.1016/j.enmm.2020.100415
[2] HA D D. Anaerobic degradation of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid by Thauera sp. DKT[J]. Biodegradation,2018,29(5):499-510. DOI: 10.1007/s10532-018-9848-7
[3] SONG W J, WAN Y, JIANG Y, et al. Urinary concentrations of 2,4-D in repeated samples from 0-7 year old healthy children in central and south China[J]. Chemosphere,2021,267:129225. DOI: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2020.129225
[4] VINAYAGAM R, PAI S D, MURUGESAN G, et al. Magnetic activated charcoal/Fe2O3 nanocomposite for the adsorptive removal of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) from aqueous solutions: Synthesis, characterization, optimization, kinetic and isotherm studies[J]. Chemosphere,2022,286:131938. DOI: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2021.131938
[5] MOREIRA R A, ROCHA G S, DA SILVA L C M, et al. Exposure to environmental concentrations of fipronil and 2,4-D mixtures causes physiological, morphological and biochemical changes in Raphidocelis subcapitata[J]. Ecotoxicolgy and Environmental Safety,2020,206:111180. DOI: 10.1016/j.ecoenv.2020.111180
[6] SALCEDO M F, MANSILLA A Y, COLMAN S L, et al. Efficacy of an organicallymodified bentonite to adsorb 2, 4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid (2,4-D) and prevent its phytotoxicity[J]. Journal of Environmental Management,2021,297:113427. DOI: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.113427
[7] WANG J S, ZHANG C, POURSAT B A J, et al. Unravelling the contribution of nitrifying and methanotrophic bacteria to micropollutant cometabolism in rapid sand filters[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2022,424:127760. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.127760
[8] LI Y, LIN R Y, LV F J, et al. Tannic acid-Fe complex derivative-modified electrodewith pH regulating function for environmental remediation by electro-Fenton process[J]. Environmental Research,2022,204:111994.
[9] UDDIN A, MUHMOOD T, GUO Z, et al. Hydrothermal synthesis of 3D/2D hetero-junctions of ZnIn2S4/oxygen doped g-C3-N4 nanosheet for visible light driven photocatalysis of 2,4-dichlorophenoxyacetic acid degradation[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2020,845:156206. DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.156206
[10] LIU H J, WANG B J, CHEN M, et al. Simple synthesis of BiOAc/BiOBr heterojunction composites for the efficient photocatalytic removal of organic pollutants[J]. Separation and Purification Technology,2021,261:118286. DOI: 10.1016/j.seppur.2020.118286
[11] HU M, YAN A H, LI F, et al. Z-scheme indium sulfide/bismuth oxybromide heterojunctions with enhanced visible-light photodegradation of organics[J]. Applied Surface Science,2021,547:149234. DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2021.149234
[12] LIANG Y J, ZENG Z K, YANG J, et al. Designing heterointerface in BiOBr/g-C3-N4 photocatalyst to enhance visible-light-driven photocatalytic performance in water purification[J]. Colloids and Surfaces A: Physicochemical and Engineering Aspects,2021,624:126796. DOI: 10.1016/j.colsurfa.2021.126796
[13] YAN X M, JI Q J, WANG C, et al. In situ construction bismuth oxycarbonate/bismuth oxybromide Z-scheme heterojunction for efficient photocatalytic removal of tetracycline and ciprofloxacin[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science,2021,587:820-830. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcis.2020.11.043
[14] GUO J Q, LIAO X, LEE M H, et al. Experimental and DFT insights of the Zn-doping effects on the visible-light photocatalytic water splitting and dye decomposition over Zn-doped BiOBr photocatalysts[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental,2019,243:502-512. DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2018.09.089
[15] WU Y Y, JI H D, LIU Q M, et al. Visible light photocatalytic degradation of sulfanilamide enhanced by Mo doping of BiOBr nanoflowers[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2022,424:127563. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.127563
[16] HE J Y, LIU Y L, WANG M, et al. Ionic liquid-hydrothermal synthesis of Z-scheme BiOBr/Bi2WO6 heterojunction with enhanced photocatalytic activity[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2021,865:158760. DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2021.158760
[17] ZHANG Y P, CAO P Y, ZHU X H, et al. Facile construction of BiOBr ultra-thin nano-roundels for dramatically enhancing photocatalytic activity[J]. Journal of Environtal Management,2021,299:113636. DOI: 10.1016/j.jenvman.2021.113636
[18] ZHANG H W, TEE J C L, JAENICKE S, et al. BiOBrnI1-n solid solutions as versatile photo oxidation catalysts for phenolics and endocrine disrupting chemicals[J]. Catalysis Today,2021,375:547-557. DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2020.01.009
[19] ZHOU P W, ZHANG L P, DAI Y M, et al. Construction of a metallic silver nanoparticle-decorated bismuth oxybromide-based composite material as a readily recyclable photocatalyst[J]. Journal of Cleaner Production,2020,246:119007. DOI: 10.1016/j.jclepro.2019.119007
[20] DENG F, LUO Y B, LI H, et al. Efficient toxicity elimination of aqueous Cr(VI) by positively-charged BiOClxI1-x, BiOBrxI1-x, and BiOClxBr1-x, solid solution with internal hole-scavenging capacity via the synergy of adsorption and photocatalytic reduction[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2020,383:121127. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2019.121127
[21] SHAO Y F, JI M X, ZHANG Y, et al. Integration of double halogen atoms in atomically thin bismuth bromide: Mutative electronic structure steering charge carrier migration boosted broad-spectrum photocatalysis[J]. Applied Surface Science,2021,541:148477. DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2020.148477
[22] HUSSAIN M B, KHAN M S, LOUSSALA H M, et al. The synthesis of a BiOCl-xBr1-x nanostructure photocatalyst with high surface area for the enhanced visible light photocatalytic reduction of Cr(VI)[J]. RSC Advances,2020,10(8):4763-4771. DOI: 10.1039/C9RA10256F
[23] ZHOU K H, LIU Y, HAO J Y. One-pot hydrothermal synthesis of dual Z-scheme BiOBr/g-C3N4/Bi2WO6 and photocatalytic degradation of tetracycline under visible light[J]. Materials Letters,2020,281:128463. DOI: 10.1016/j.matlet.2020.128463
[24] FENG C Y, TANG L, DENG Y C, et al. Synthesis of branched WO3@W18O49 homojunction with enhanced interfacial charge separation and full-spectrum photocatalytic performance[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2020,389:124474. DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2020.124474
[25] TONG Y H, YE S B, FANG X T, et al. ZnO-dispersedly-hybridizing BiOBr0.9I0.1 nanoflakes with p-type semiconducting character for improved photocatalysis[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2021,851:156888. DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.156888
[26] YU H B, HUANG J H, JIANG L B, et al. In situ construction of Sn-doped structurally compatible heterojunction with enhanced interfacial electric field for photocatalytic pollutants removal and CO2 reduction[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental,2021,298:120618. DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2021.120618
[27] WANG J Z, WANG Y N, CAO C S, et al. Decomposition of highly persistent perfluorooctanoic acid by hollow Bi/Bi-OI1-x-Fx: Synergistic effects of surface plasmon resonance and modified band structures[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2021,402:123459.
[28] ZHENG Q, CAO Y H, HUANG N J B, et al. Selective exposure of BiOI oxygen-rich {110} facet induced by BN nanosheets for enhanced photocatalytic oxidation performance[J]. Acta Physico-Chimica Sinica,2020,37(8):2009063.
[29] YU Q Q, CHEN J Y, LI Y X, et al. In situ decoration of metallic Bi on BiOBr with exposed (110) facets and surface oxygen vacancy for enhanced solar light photocatalytic degradation of gaseous n-hexane[J]. Chinese Journal of Catalysis,2020,41(10):1603-1612. DOI: 10.1016/S1872-2067(19)63496-0
[30] ZHAO C, LI Y, CHU H Y, et al. Construction of direct Z-scheme Bi5O7I/UiO-66-NH2 heterojunction photocatalysts for enhanced degradation of ciprofloxacin: Mechanism insight, pathway analysis and toxicity evaluation[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2021,419:126466. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2021.126466
[31] KONG L, GUO J Q, MAKEPEACE J W, et al. Rapid synthesis of BiOBrxI1-x photocatalysts: Insights to the visible-light photocatalytic activity and strong deviation from Vegard's law[J]. Catalysis Today,2019,335:477-484. DOI: 10.1016/j.cattod.2019.02.013
[32] REN X J, LI J B, CAO X Z, et al. Synergistic effect of internal electric field and oxygen vacancy on the photocatalytic activity of BiOBrxI1-x with isomorphous fluorine substitution[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science,2019,554:500-511. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcis.2019.07.034
[33] KOU M P, DENG Y, ZHANG R M, et al. Molecular oxygen activation enhancement by BiOBr0.5I0.5/BiOI utilizing the synergistic effect of solid solution and heterojunctions for photocatalytic NO removal[J]. Chinese Journal of Catalysis,2020,41(10):1480-1487. DOI: 10.1016/S1872-2067(20)63607-5
[34] ZHONG S T, ZHOU H, SHEN M, et al. Rationally designed a g-C3N4/BiOI/Bi2O2CO3 composite with promoted photocatalytic activity[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2021,853:157307. DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2020.157307
[35] GENG Q, XIE H T, HE Y, et al. Atomic interfacial structure and charge transfer mechanism on in-situ formed BiOI/Bi2O2SO4 p-n heterojunctions with highly promoted photocatalysis[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental,2021,297:120492. DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2021.120492
[36] LI X B, KANG B B, DONG F, et al. Enhanced photocatalytic degradation and H2/H2O2 production performance of S-pCN/WO2.72 S-scheme heterojunction with appropriate surface oxygen vacancies[J]. Nano Energy,2021,81:105671. DOI: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2020.105671
[37] 杜春艳, 宋佳豪, 谭诗杨, 等. 石墨烯桥联的ZnO/Ag3PO4复合材料的制备及其对环丙沙星的降解性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2021, 38(7):2254-2264. DU Chunyan, SONG Jiahao, TAN Shiyang, et al. Preparation of graphene bridged ZnO/Ag3PO4 compositeand its degradation performance for ciprofloxacin[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2021,38(7):2254-2264(in Chinese).
-




 下载:
下载: