Effect of Ti811 and TC4 titanium alloy substrate on microstructures and properties of laser cladding self-lubricating composite coatings
-
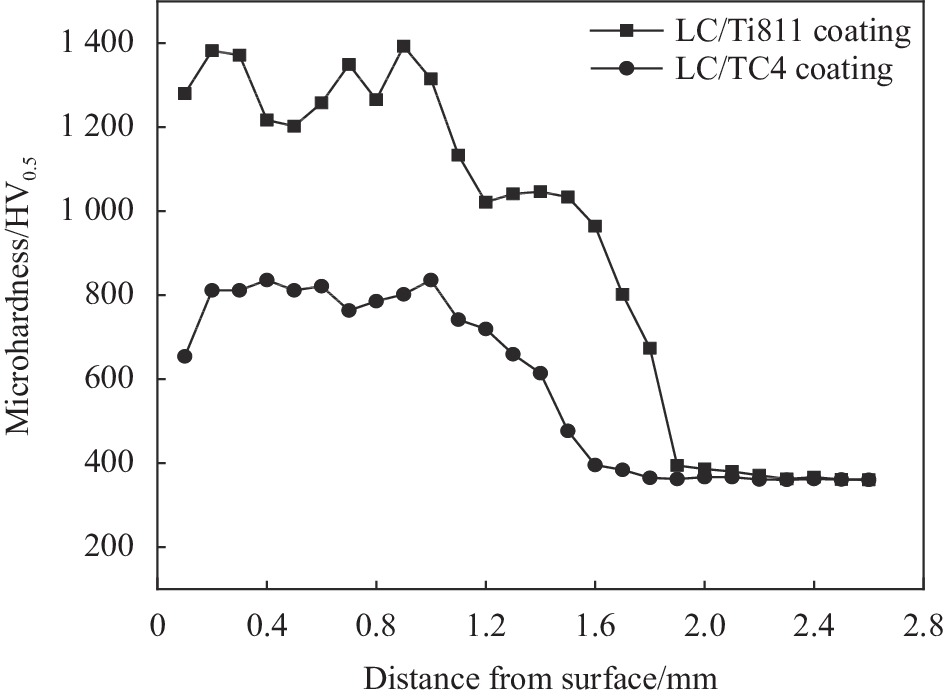
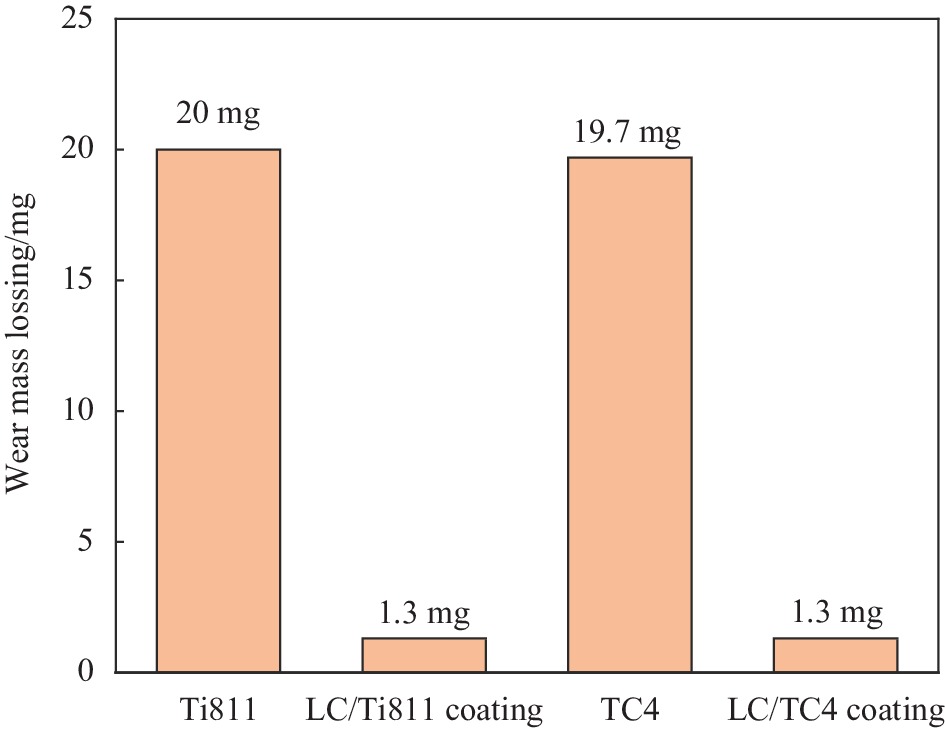
摘要: 为研究不同钛合金基材对激光熔覆自润滑耐磨涂层组织与性能的影响,采用同轴送粉技术,在Ti811合金和TC4合金表面分别熔覆TC4、Ni45、Al2O3、MoS2和稀土氧化物Y2O3混合粉末,用渗透测试观察熔覆层表面裂纹分布,利用SEM、EDS、XRD等测试技术分析激光熔覆层的元素分布及物相组成,并表征熔覆层的显微硬度和摩擦磨损性能。基材元素成分不同导致涂层物相差异,V元素含量高的TC4合金涂层α-Ti的析出比Ti811合金的少;并且基材的热物理性能对涂层裂纹分布、组织形貌与性能具有显著影响,导热系数低且密度高的TC4合金激光熔覆温度梯度较小,涂层裂纹面积较小,稀释率大,涂层组织更粗大;由于Ti811合金导热性好,冷却速度高,涂层组织更细小,硬度更高,平均硬度达到1303.5 HV0.5。两种熔覆层磨损量降低,摩擦系数均降至0.3以下。硬质相强化和软质相润滑的共同作用可提高熔覆表面的耐磨性能。Abstract: In order to research the effect of substrate on microstructure and properties of laser cladding self-lubricating coating, laser cladding was carried out on the surface of Ti811 alloy and TC4 alloy by coaxial powder-feeding laser cladding technology using TC4, Ni45, Al2O3, MoS2 and rare earth oxide Y2O3 powder mixture as cladding material. The surface crack distribution of cladding layer was observed by penetration test. The elemental distribution and microstructure of coatings were analyzed by SEM, EDS and XRD. Microhardness and tribological properties of the coatings were examined. The results show that the element composition on the substrate can cause the difference of cladding layer phases. Because of the high content of element V, the precipitation of α-Ti on TC4 alloy is less than that of the laser cladding layer on Ti811 alloy. The thermal conductivity of substrates has a significantly impact on the microstructure and performance of the coatings. Because of low thermal conductivity and high density, TC4 alloy has low temperature gradient during laser cladding. As a result, the coating on TC4 alloy has less cracks, higher dilution rate, and coarser microstructure. The average hardness of coating on Ti811 substrate reaches up to 1303.5 HV0.5 attributes to its good conductivity and high cooling rate. The wear mass losing of the cladding coatings on two alloys is significantly reduced, and the average friction coefficient drops to below 0.3. Due to the reinforcement of hard phase and anti-fiction of soft phase, laser cladding coatings on different substrates both have excellent wear resistance property.
-
Keywords:
- laser cladding /
- composite coatings /
- titanium alloy /
- microstructure /
- tribological properties
-
齿轮和轴类零件常被用于高速、振动、摩擦磨损等恶劣工况,易产生断裂和磨损等失效[1-2]。此类零件多采用20 CrMnTi低碳钢材料,为提高零件使用寿命,使用电沉积方法在零件表面制备镀层增强零件性能已成为常用方法。Ni-P合金镀层具有良好的耐磨、耐腐蚀性能,还具有较高的硬度,因此被广泛应用于化工、汽车和机械等行业[3-5]。随着行业的进步与发展,Ni-P镀层已难以满足复杂特殊的使用环境,向镀液中添加纳米颗粒针对性的提升镀层性能已成为研究的热门方向[6]。目前一元纳米颗粒复合电沉积技术已比较成熟,如添加Al2O3、WC、SiC等硬质颗粒提升复合镀层的硬度及耐磨损性能[7-10],添加具有自润滑特性的BN(h)、MoS2、PTFE等降低复合镀层的摩擦系数[11-13],添加部分纳米颗粒还可以提高复合镀层的耐腐蚀性能和抗高温氧化性能[14-18]。
近年来部分学者已经对二元纳米颗粒复合镀层进行研究,徐义库[19]等通过脉冲电沉积法制备Ni-Mo-SiC-TiN复合镀层,两种纳米颗粒均匀的分散在Ni-Mo基体中显著提升了镀层的耐磨和耐腐蚀性;张银[20]等使用电沉积法制备不同浓度配比的 Ni-Co-P-BN(h)-Al2O3复合镀层,结果表明二元纳米颗粒掺杂配比会对纳米复合镀层表面产生巨大影响,且二元纳米颗粒复合镀层的耐磨性优于一元纳米颗粒复合涂层;王浩鑫[21]采用单脉冲电沉积制备Ni-TiC-GO复合镀层,该镀层具有优秀的减摩擦和耐磨性能。目前,研究对于二元纳米复合电沉积技术尤其是电沉积Ni-P-WC-BN(h)二元纳米复合镀层的表面结构和减磨耐磨性能的研究未见报道。
因此本文采用超声-脉冲电沉积法制备不同浓度BN(h)纳米颗粒的Ni-P-WC-BN(h)二元纳米颗粒复合镀层,与Ni-P、Ni-P-WC复合镀层对比,探究BN(h)质量浓度对复合镀层组织结构和减磨耐磨性能的影响
1. 实 验
1.1 基材预处理
采用20 CrMnTi钢为基体,其尺寸为40 mm×16 mm×12 mm。表面使用320#、800#、
1200 #、2000#金相砂纸打磨→抛光→去离子水超声清洗→电净除油→去离子水超声清洗并吹干→强活化→去离子水超声清洗并吹干→弱活化→去离子水超声清洗并吹干待用。1.2 实验条件
试验采用单因素实验法,首先通过预实验确定电沉积工艺参数、基础镀液成分(表1所示)和WC颗粒的最优浓度(30 g/L,纯度99.9%,平均粒度为50 nm)。实验装置如图1所示,工艺参数:电流密度3 A/dm2,脉冲频率2 kHz,占空比0.8,镀液温度50℃,电镀时间60 min,超声功率210 W,搅拌速率150 r/min,;阳极为纯Ni板。
表 1 电沉积Ni-P镀液配方Table 1. Formulation of electrodeposition Ni-P plating solutionElement Concentration/(g·L−1) NiSO4·6H2O 230 NiCl2·6H2O 30 H3PO3 5 NaH2PO2·H2O 8 NaC6H8O7·H2O 80 H3BO3 30 C₁₂H₂₅NaSO₄ 0.1 SC(NH₂)₂ 0.02 C₇H₅NO₃S 1 以上述内容为基础向镀液中分别添加15 g/L、20 g/L、25 g/L、30 g/L的BN(h)纳米颗粒(纯度99.9%,平均粒度为200 nm)。探究BN(h)添加量对Ni-P-WC-BN(h)复合镀层表面形貌、组织成分、显微硬度及耐磨性能的影响。
1.3 测试方法
试样制备完成后,使用线切割将样品切割为10 mm×10 mm×6 mm的测试试样进行下一步测试。使用Quanta FEG250扫描电子显微镜、能谱仪X Flash Detector 5030 BRUKER)对试样表面的镀层形貌和元素分布进行观察。采用Rigaku SmartLab SE型X射线衍射仪对复合镀层的物相结构进行分析。采用斯特尔显微硬度仪(Struers)对镀层的显微硬度进行测试,实验载荷
1000 g,加载时间10 s,在不同位置测量五次取平均值。采用CFT-I型综合材料表面性能测试仪(兰州中科凯华科技)对复合镀层的摩擦系数进行测试,磨件为Si3N4对磨球(直径4 mm,表面粗糙度Ra=0.06 μm,硬度为1400 -1700 HV1),加载载荷100 g,往复次数200次/min,往复行程4 mm,时长30 min。采用日本Keyence VK-X1000激光显微镜拍摄磨痕处形貌及磨痕截面轮廓并计算镀层磨损体积损失。2. 结果与讨论
2.1 复合镀层的微观形貌及元素分布
图2展示了不同镀液配方复合镀层的表面微观形貌,(a)图Ni-P镀层表面呈胞状结构,胞状结构的直径较大且分布不均匀。在镀液中加入WC纳米颗粒后,(b)图Ni-P-WC复合镀层表面和(a) Ni-P镀层相比粗糙,这是由于部分WC团聚被Ni-P镀层包裹在镀层内部,镀层表面产生了单元凸起,改变了阳极和阴极的间距,凸起部分受到电场力较大优先生长因此形成不平整的胞状物结构[22]。(c1)到(c4)图为在镀液中进一步添加15 g~30 g/L的BN(h)纳米颗粒的Ni-P-WC-BN(h)复合镀层表面的微观形貌,与Ni-P-WC复合镀层相比,随着BN(h)含量的增加,镀层表面平整度略有提高,究其原因,一方面两颗粒协同作用在一定程度上减小了团聚[20],另一方面还可能与BN(h)颗粒具有自润滑特性,层与层之间靠爱德华力连接易产生滑动有关[23]。但BN(h)浓度超过某一极值,镀液中纳米颗粒浓度过高从而使纳米颗粒团聚,阴极附近导电性下降从而使沉积效率降低。
![]() 图 2 复合镀层表面SEM图像 (a) Ni-P,(b)Ni-P-WC,(c1)Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(15 g/L),(c2) Ni-P-WC-BN(h) (20 g/L),(c3) Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(25 g/L),(c4) Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(30 g/L)Figure 2. SEM image of composite plated surface (a)Ni-P,(b)Ni-P-WC,(c1)Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(15 g/L),(c2) Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(20 g/L),(c3) Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(25 g/L),(c4) Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(30 g/L)
图 2 复合镀层表面SEM图像 (a) Ni-P,(b)Ni-P-WC,(c1)Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(15 g/L),(c2) Ni-P-WC-BN(h) (20 g/L),(c3) Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(25 g/L),(c4) Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(30 g/L)Figure 2. SEM image of composite plated surface (a)Ni-P,(b)Ni-P-WC,(c1)Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(15 g/L),(c2) Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(20 g/L),(c3) Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(25 g/L),(c4) Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(30 g/L)图3为不同镀液配方复合镀层的截面形貌及元素分布。WC纳米颗粒的加入后镀层厚度有所增加,但镀层内部存在裂痕等缺陷;加入BN(h)纳米颗粒后,镀层平整性略有提高且镀层内部缺陷减少,镀层厚度先增加后减小,在BN(h)浓度为25 g/L时最厚达80.0 μm。随着BN(h)浓度进一步增加,镀液中纳米颗粒浓度过高导致阴极导电性下降从而降低沉积效率,镀层厚度减小。
![]() 图 3 复合镀层截面SEM图像及截面元素分布 (a)Ni-P,(b)Ni-P-WC,(c1)Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(15 g/L),(c2) Ni-P-WC-BN(h) (20 g/L),(c3) Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(25 g/L),(c4) Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(30 g/L)Figure 3. SEM image of composite plating cross-section and section element distribution (a)Ni-P,(b)Ni-P-WC,(c1)Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(15 g/L),(c2) Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(20 g/L),(c3) Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(25 g/L),(c4) Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(30 g/L)
图 3 复合镀层截面SEM图像及截面元素分布 (a)Ni-P,(b)Ni-P-WC,(c1)Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(15 g/L),(c2) Ni-P-WC-BN(h) (20 g/L),(c3) Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(25 g/L),(c4) Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(30 g/L)Figure 3. SEM image of composite plating cross-section and section element distribution (a)Ni-P,(b)Ni-P-WC,(c1)Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(15 g/L),(c2) Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(20 g/L),(c3) Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(25 g/L),(c4) Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(30 g/L)由图中元素分布可以看出,WC和BN(h)纳米镶嵌在镀层中,镀层和基体的界面交界处存在约50 μm的中间区,该区域元素相互渗透,有助于改善镀层和基体的结合。
图4为不同镀镀液配方复合镀层表面元素分布,从元素分布图中可以看出Ni、P、W、B均匀分散在镀层中,并无明显团聚现象,这说明在该工艺参数下WC纳米颗粒和BN(h)纳米颗粒在镀层中分散效果较好。
![]() 图 4 复合镀层表面元素分布 (a)Ni-P,(b)Ni-P-WC,(c1)Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(15 g/L),(c2) Ni-P-WC-BN(h) (20 g/L),(c3) Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(25 g/L),(c4) Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(30 g/L)Figure 4. Composite plating surface element distribution (a)Ni-P,(b)Ni-P-WC,(c1)Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(15 g/L),(c2) Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(20 g/L),(c3) Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(25 g/L),(c4) Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(30 g/L)
图 4 复合镀层表面元素分布 (a)Ni-P,(b)Ni-P-WC,(c1)Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(15 g/L),(c2) Ni-P-WC-BN(h) (20 g/L),(c3) Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(25 g/L),(c4) Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(30 g/L)Figure 4. Composite plating surface element distribution (a)Ni-P,(b)Ni-P-WC,(c1)Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(15 g/L),(c2) Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(20 g/L),(c3) Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(25 g/L),(c4) Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(30 g/L)2.2 复合镀层的EDS能谱及相结构
图5为二元纳米颗粒掺杂下Ni-P-WC-BN(h)复合镀层的EDS能谱图,从图中可以看出,所制备的二元纳米复合镀层表面均含有Ni、P、W、C、B等元素,各元素含量随着BN(h)浓度的变化而变化。随着BN(h)添加量从15 g/L增加到30 g/L,B元素质量分数呈先波动增大后减小趋势,在BN(h)浓度为25 g/L时B元素的质量分数达到最大值0.85%;镀层表面W元素质量分数先减小后增大,与B元素呈相反趋势;镀层中P元素质量分数逐渐减小。这说明通过超声-脉冲电沉积法制备了Ni-P-WC-BN(h)二元纳米复合镀层。Ni元素的质量分数随着BN(h)浓度的提升而增大,这是因为镀液中加入WC和BN(h)两种纳米颗粒后,不同纳米颗粒相互作用,减小团聚,镀层表面吸附的颗粒数目增加,为Ni原子提供更好的成核条件[23],从而增大Ni元素的沉积量。
图6所示为不同复合镀层的XRD图谱,镀层在2θ为44.507°、51.846°、76.370°的位置上出现了的Ni峰,分别对应(111)、(200)、(220)晶面,与Ni-P-WC复合镀层相比,随着BN(h)浓度的增加,Ni-P-WC-BN(h)复合镀层的三个晶面方向出现了明显的结晶取向,且生长晶面以(111)面为主,这是由于Ni的结晶取向同时受到生长速度、方向的影响外还受到晶体竞争模式的影响[24];Ni-P-WC复合镀层的衍射图谱中,2θ为31.474°、35.626°、48.266°的位置出现了WC的特征峰,这说明WC颗粒成功沉积在复合镀层中;在Ni-P-WC-BN(h)复合镀层的衍射图谱中并没有表现出明显的BN(h)峰,但是可以检测到BN(h),结合图5中B元素的质量分数可知这可能是BN(h)颗粒沉积量较少所致。
表2为不同配方镀层中Ni(111)元素的晶粒尺寸数据,其中FWHM为半幅宽,D为镀层中垂直于晶面的晶粒尺寸。随着BN(h)浓度的提升,Ni(111)的晶粒尺寸先减小后增大,最小晶粒尺寸为8.9 nm,这是因为BN(h)对晶粒有一定的细化作用[25],合适浓度的BN(h)可以减小晶粒尺寸,但是BN(h)浓度过高会使晶粒尺寸增大。
表 2 不同复合镀层中Ni(111)元素的晶粒尺寸Table 2. Grain size of Ni(111) elements in different composite coatingsType of plating 2θ/(°) FWHM Diameter/nm Ni-P 44.480 0.941 9.2 Ni-P-WC 44.670 0.848 10.2 Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(15 g/L) 44.480 0.894 9.7 Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(20 g/L) 44.340 0.908 9.5 Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(25 g/L) 44.660 0.968 8.9 Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(30 g/L) 44.710 0.677 12.8 2.3 复合镀层的硬度
不同复合镀层的显微硬度测试结果如图7所示,从图中可知,Ni-P镀层硬度在700 HV1左右,添加WC纳米颗粒后镀层的显微硬度为
1141 HV1,这是因为WC在镀层中弥散分布,对镀层起到弥散强化作用[26],根据晶界强化原理,晶粒越细小镀层的显微硬度越高,WC纳米颗粒自身硬度较高且可以使镀层晶粒细化从而提高硬度。加入BN(h)后,随着BN(h)浓度从15 g/L到30 g/L的过程中,Ni-P-WC-BN(h)复合镀层硬度呈先增大后减小的变化趋势,在BN(h)浓度为25 g/L时Ni-P-WC-BN(h)复合镀层的硬度达到最大值115 6HV1,硬度最大值与Ni-P-WC复合镀层相当。分析认为, 纳米粒子在沉积过程中分为弱吸附和强吸附[27],随着镀液中纳米颗粒浓度增加,更多的颗粒发生强吸附作用,从而使镀层中纳米颗粒的含量增加从而使镀层硬度提升,但当其添加量过大时镀层易产生析氢现象[28],使镀层厚度下降,因此硬度下降。2.4 复合镀层的减磨耐磨性能
不同配方复合镀层的摩擦系数如图8所示,各复合镀层的摩擦系数均存在明显的摩擦系数急剧上升后趋于平稳的“磨合”阶段[29]。分析认为随着磨损试验的进行镀层表面的磨屑不断在磨痕处堆积,最终在压应力的作用下产生塑性变形使摩擦阻力增大,从而导致摩擦系数增大。
相同条件下,未添加纳米颗粒的Ni-P镀层的摩擦系数较大。摩擦系数和复合镀层中的硬质颗粒的尺寸、均匀性和数量有关[30],添加WC纳米颗粒后,纳米WC嵌入镀层,使晶粒细化并致密镀层组织,且WC自身硬度较高,因此可以减小摩擦时的接触面积从而降低摩擦系数。在Ni-P-WC镀层基础上添加BN(h)颗粒,随着BN(h)浓度增加,Ni-P-WC-BN(h)复合镀层摩擦系数呈先减小后增大的变化趋势。
摩擦磨损实验结束后,各镀层的磨损体积如表3所示,由数据可以看出Ni-P镀层磨损体积最大;加入WC纳米颗粒后镀层的磨损体积显著减小;加入BN(h)纳米颗粒后,随着浓度的提升,复合镀层的磨损量先减小后增大,Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(25 g/L)复合镀层的磨损体积最小,与Ni-P-WC复合镀层相当,显著优于其他镀层。将磨损体积与图5硬度测试结果对比,可以得出镀层磨损量和镀层硬度呈负相关。
表 3 镀层磨损体积Table 3. Plating wear volumeType of plating Wear volume /μm3 Ni-P 459553 Ni-P-WC 51945 Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(15 g/L) 256137 Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(20 g/L) 135765 Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(25 g/L) 53587 Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(30 g/L) 102966 各镀层磨痕形貌、轮廓线如图9所示,不同区域元素分布如表4所示。由磨痕形貌与图3镀层厚度对比及磨痕元素分布可知,磨损区域均不含Fe元素,摩擦磨损试验过程中镀层并未磨穿。Ni-P镀层磨痕与其他镀层磨痕相比较为明显,且磨痕处呈明显的黏着现象和犁沟状形貌,取磨痕中部长度为310 μm的截面轮廓线可知磨损过程中Ni-P复合镀层的磨损量较大,Ni-P涂层的硬度较低,易产生剥落现象,磨痕处含有少量Si元素,这说明Si3N4对磨球在摩擦磨损试验中摩擦热的作用下转移到镀层表面产生黏着磨损现象。镀层中加入WC纳米颗粒后,Ni-P-WC复合镀层磨痕表面无明显的犁沟形貌,这是因为WC颗粒在镀层中起到弥散强化作用,大幅度提升了复合镀层的硬度,减小了摩擦的接触面积,在磨损过程中,镀层先产生塑形形变,当形变量过大时部分WC颗粒脱落,形成镀层、WC粉末、摩擦副之间的三体磨损[31],此过程中摩擦热大幅增加导致氧化磨损,涂层的氧含量大幅提高。
![]() 图 9 复合镀层磨痕SEM(左)、磨痕形貌(中)、磨痕轮廓线(右):(a)Ni-P (b)Ni-P-WC (c)Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(15 g/L) (d)Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(20 g/L) (e)Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(25 g/L) (f)Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(30 g/L)Figure 9. SEM of composite plating wear marks (left), wear mark morphology (center), and wear mark contour lines (right): (a) Ni-P (b) Ni-P-WC (c) Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(15 g/L) (d) Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(20 g/L) (e) Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(25 g/L) (f) Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(30 g/L)表 4 磨痕元素分布Table 4. Distribution of abrasion elements
图 9 复合镀层磨痕SEM(左)、磨痕形貌(中)、磨痕轮廓线(右):(a)Ni-P (b)Ni-P-WC (c)Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(15 g/L) (d)Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(20 g/L) (e)Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(25 g/L) (f)Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(30 g/L)Figure 9. SEM of composite plating wear marks (left), wear mark morphology (center), and wear mark contour lines (right): (a) Ni-P (b) Ni-P-WC (c) Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(15 g/L) (d) Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(20 g/L) (e) Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(25 g/L) (f) Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(30 g/L)表 4 磨痕元素分布Table 4. Distribution of abrasion elementsArea Atomic fraction of an element at% Ni O P Si W B Au 1 75.01 14.08 5.15 2.71 — — 2.34 2 90.1 — 6.4 — — — 3.49 3 23.16 70.39 1.49 — 2.87 — 1.28 4 84.64 2.48 3.43 — 6.14 — 3.31 5 56.59 31.00 3.36 1.35 5.41 0.35 1.93 6 63.12 4.00 3.58 — 3.13 23.59 2.60 7 37.49 53.33 2.07 1.16 3.40 0.76 1.79 8 37.68 52.95 2.56 1.06 4.05 0.2 1.50 9 66.25 9.97 4.38 0.01 4.05 14.04 1.29 10 72.42 15.68 3.59 0.15 5.63 0.13 2.42 11 58.76 7.96 3.03 0.11 4.56 20.69 4.88 12 46.65 27.96 1.23 4.89 4.47 8.99 5.82 BN(h)纳米颗粒加入后磨痕形貌如图9(c)-(f)所示,BN(h)添加量为15 g/L时,对比图8中摩擦系数曲线及磨痕处轮廓线可以发现Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(15 g/L)复合镀层发生了较为严重的剥落现象,剥落的镀层在磨痕处随摩擦副一起在镀层表面摩擦,从而导致摩擦系数短时内上升,随着摩擦实验的进行,剥落的镀层被压应力压碎,摩擦系数也逐渐减小到该涂层的正常水平;BN(h)添加量为20 g/L时,镀层的剥落现象大幅减少,磨痕处的Si元素含量增加,镀层存在黏着磨损现象,此时摩擦系数略小于Ni-P-WC复合镀层,但是由于BN(h)沉积量较少,因此减磨能力有限;BN(h)添加量为25 g/L时,镀层基本无剥落现象,磨痕较为平整,这是因为BN(h)微粒在镀层中和WC共沉积,呈弥散分布,由于BN(h)为六方结构,层与层之间靠范德华力连接,在摩擦中易产生滑动,一方面滑动的BN(h)可以在镀层和对磨球间形成固体润滑膜减小摩擦,另一方面BN(h)可以在摩擦过程中填补磨痕处的缺陷,使磨痕更加平整,此时摩擦形式为磨料磨损,伴随极微的黏着磨损;BN(h)添加量为30 g/L时,磨痕呈现较为明显的犁沟状并伴随着严重的黏着现象,此时纳米浓度颗粒浓度过高,电沉积效率下降,镀层硬度和厚度减小,镀层中Si元素含量大幅提高,镀层主要磨损形式为黏着磨损。
3. 结 论
(1)不同纳米颗粒的质量浓度对纳米复合镀层表面的微观形貌和物相结构有重要影响,Ni-P镀层表面呈现明显的胞状结构;加入WC纳米颗粒后,Ni-P-WC复合镀层表面呈不平整“菜花”状形貌;加入BN(h)纳米颗粒后,Ni-P-WC-BN(h)复合镀层微观形貌无明显变化,镀层平均晶粒尺寸先减小后增大,合适浓度的BN(h)对晶粒有一定的细化作用。
(2)试验范围内,纳米颗粒的添加可以有效的提升复合镀层的显微硬度和厚度。Ni-P-WC和Ni-P-WC-BN(h)(25 g/L)复合镀层硬度最大,平均硬度达到
1150 HV1,纳米颗粒浓度过低或者过高均会降低镀层的显微硬度。(3)试验范围内,Ni-P镀层在摩擦磨损实验中存在较为严重的黏着和剥落现象且磨损量较大;加入WC纳米颗粒后,镀层无黏着现象,磨损形式为磨料磨损和氧化磨损,此时摩擦系数较小且磨损量较低;进一步加入BN(h)纳米颗粒后,随着BN(h)浓度的提升,镀层的摩擦系数和磨损量先减小后增大,在BN(h)质量浓度为25 g/L时镀层的摩擦系数最低,在保证镀态高硬度的同时,摩擦系数较Ni-P-WC复合镀层降低22.6%,这说明二元纳米颗粒掺杂发挥了协同生长的优势,具有更好的减磨耐磨性能。
-
表 1 Ti811和TC4合金主要化学成分
Table 1 Main chemical composition of Ti811 and TC4 alloy
wt% Material Al V Mo C N Fe O Ti Ti811 8.10 0.99 1.05 0.03 0.01 0.05 0.06 Banlance TC4 6.01 3.80 – 0.10 0.05 0.30 0.20 Banlance 表 2 TC4和Ni45粉末主要化学成分
Table 2 Main chemical composition of TC4 and Ni45 powders
wt% Material Al V Fe C N O H Cr B Si Ni Ti TC4 5.5-6.8 3.5-4.5 0.30 0.10 0.05 0.20 0.015 – – – – Bal. Ni45 – – 3.00 0.35 – – – 8.9 1.8 4.0 Bal. – 表 3 激光熔覆试验工艺参数
Table 3 Process parameters of laser cladding experiment
Laser
power/WLaser scanning
velocity/(mm·min−1)Beam
diameter/mmPower feeding
rate/(r·min−1)Discharge of power
gas/(L·min−1)Protective gas
flow/(L·min−1)Laser focal
length/mmMulti-path
rate/%900 400 3 1.4 7 11 16 50 表 4 Ti811和TC4合金与熔覆层主要生成物在20℃下的性能[27-29]
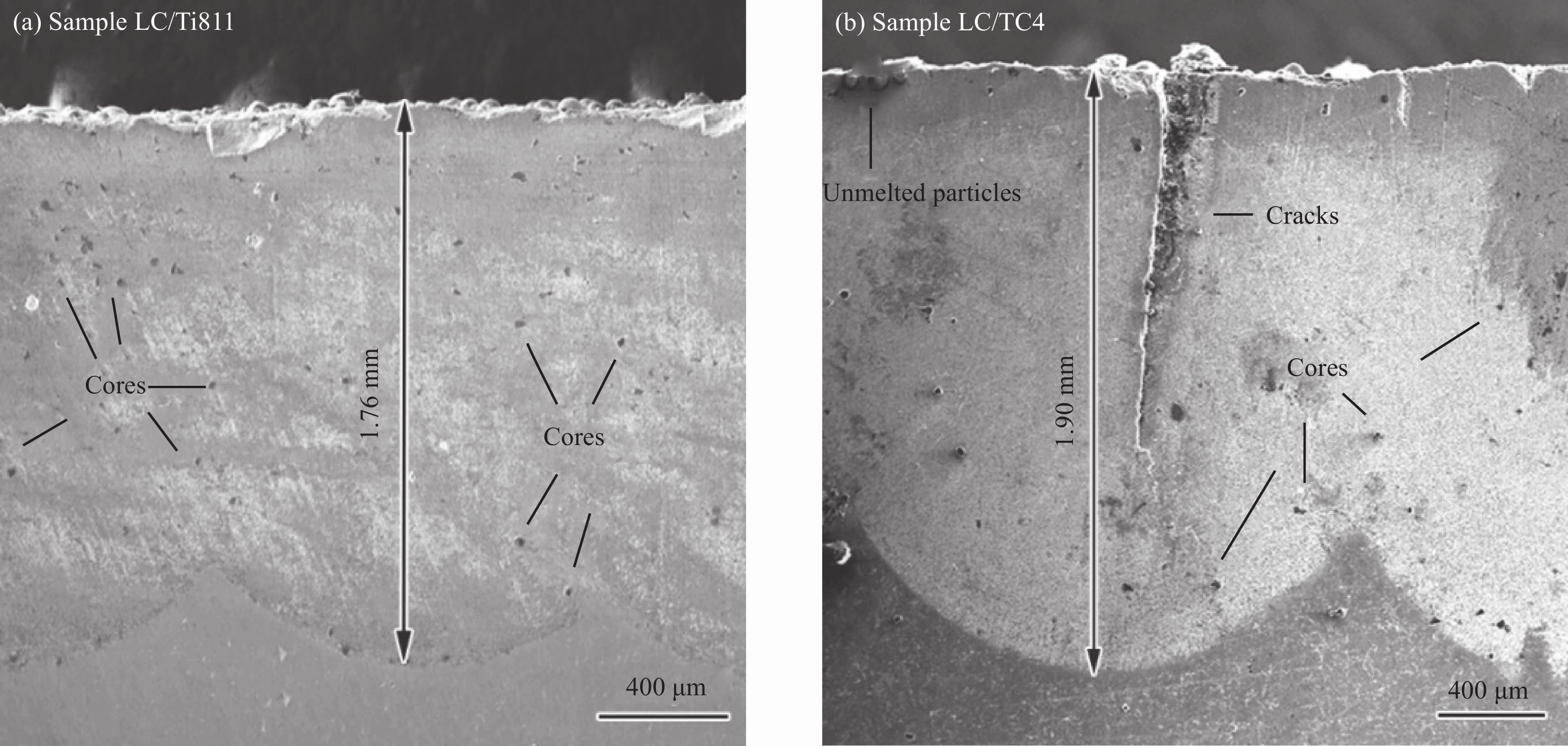
Table 4 Performances of Ti811 alloy, TC4 alloy and major products in cladding layer at 20℃[27-29]
Material Density/
(kg·m–3)Thermal conductivity/
(W·m−1·K−1)Coefficient of linear
expansion/(μm·℃−1)Elastic modulus/
GPaYield strength/ MPa Elongation/
%Hardness/
HVTi811 4350 7.25 8.53 118 950 17 390 TC4 4440 6.43 9.00 100 830 10 330 TiC 4990 – 6.50-7.15 440 – – – Ti2Ni 5770 – 4.05 128 – – – 表 5 不同基材激光熔覆层特征相能谱分析结果
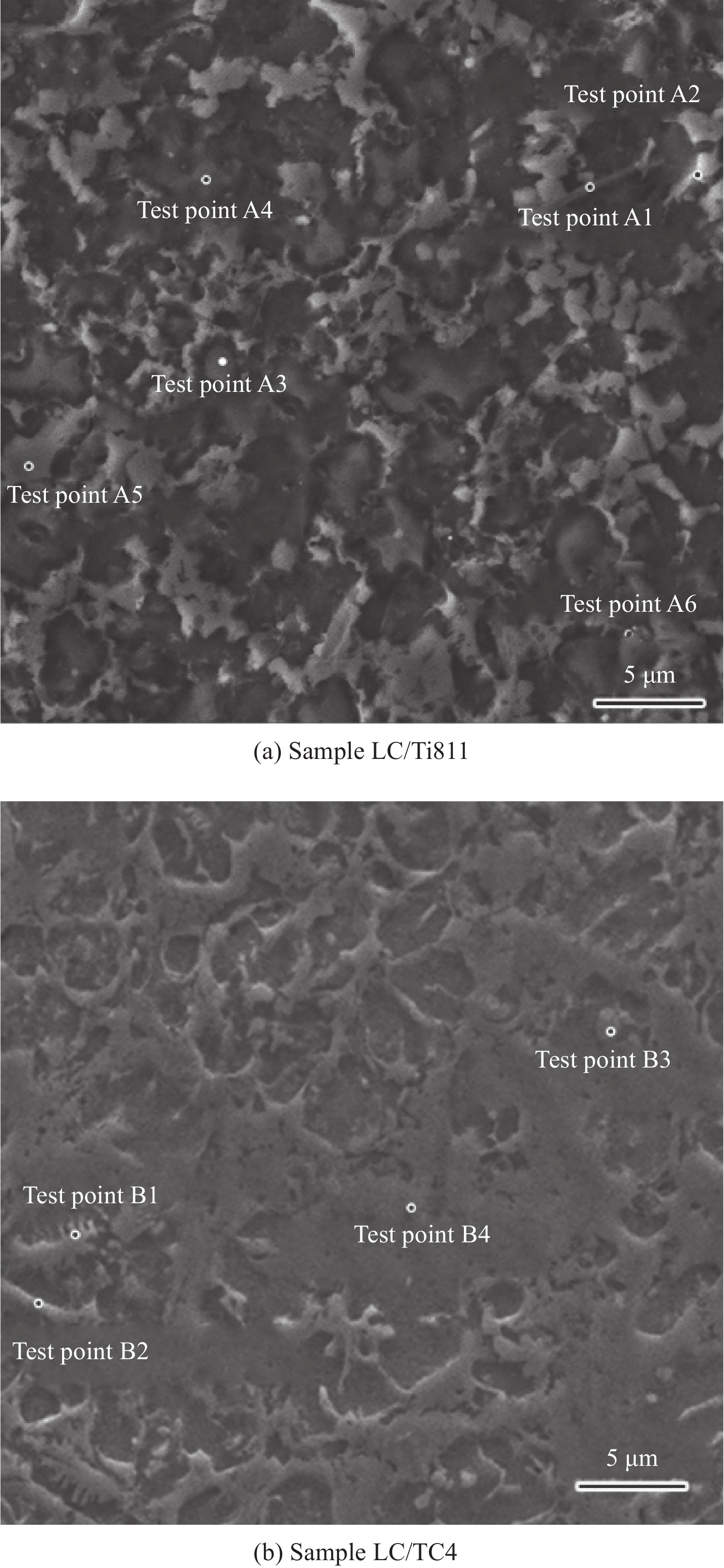
Table 5 Energy spectrum analysis results of feature phase of laser cladding coating with different substrate
C O Al Si Ti V Cr Ni Sample LC/Ti811 A1 wt% 17.34 – 4.4 – 65.42 1.94 1.99 8.91 at% 45.11 – 5.09 – 42.67 1.19 1.19 4.74 A2 wt% 12.66 – 6.05 – 56.1 1.99 2.38 20.82 at% 36.49 – 7.76 – 40.54 1.36 1.59 12.27 A3 wt% – – 7.89 1.83 55.22 2.29 3.27 29.17 at% – – 13.79 3.08 54.35 2.12 2.97 23.42 A4 wt% 7.51 – 3.93 – 85.24 0.28 0.47 2.58 at% 23.97 – 5.58 – 68.21 0.21 0.34 1.68 A5 wt% 4.27 – 4.49 – 88.38 – – 2.86 at% 14.72 – 6.89 – 76.38 – – 2.02 A6 wt% 7.31 6.85 7.43 – 60.98 – – 17.42 at% 21.13 14.86 9.55 – 44.17 – – 10.29 Sample LC/TC4 B1 wt% 14.43 – 3.01 – 65.42 0.74 1.47 14.93 at% 44.16 4.1 42.67 0.54 2.04 6.49 B2 wt% 13.32 – 5.2 – 57.15 1.13 2.68 20.52 at% 37.44 7.00 44.04 0.82 1.91 8.68 B3 wt% 2.84 – 4.9 – 86.51 0.88 2.57 2.92 at% 9.35 7.17 78.97 0.69 1.95 1.87 B4 wt% – 3.97 8 – 51.80 2.56 4.74 28.84 at% 10.98 13.11 47.81 2.22 4.03 21.72 -
[1] 张喜燕, 赵永庆, 白晨光. 钛合金及应用[M]. 北京: 化学工业出版社, 2005. ZHANG Xiyan, ZHAO Yongqing, BAI Chenguang. Titanium alloy and its application[M]. Beijing: Chemical Industry Press, 2005(in Chinese).
[2] 邓炬. 钛与航空[J]. 钛工业进展, 2004, 21(2):6-15. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9964.2004.02.001 DENG Ju. Titanium and aerospace[J]. Titanium Industry Progress,2004,21(2):6-15(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1009-9964.2004.02.001
[3] 刘彬, 刘延斌, 杨鑫, 等. TITANIUM 2008: 国际钛工业, 制备技术与应用的发展现状[J]. 粉末冶金材料科学与工程, 2009, 14(2):67-73. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0224.2009.02.001 LIU Bin, LIU Yanbin, YANG Xin, et al. TITANIUM 2008: The international titanium industry, preparation technology and application development[J]. Powder Metallurgy Materials Science and Engineering,2009,14(2):67-73(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-0224.2009.02.001
[4] 金和喜, 魏克湘, 李建明, 等. 航空钛合金研究进展[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2015, 25(2):280-292. JIN Hexi, WEI Kexiang, LI Jianming, et al. Research development of titanium alloy in aerospace industry[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals,2015,25(2):280-292(in Chinese).
[5] LÜTJERING G, WILLIAMS J C. Titanium (engneering materials and processes)[M]. Manchester: Springer, 2003: 251-255.
[6] MOLINARI A, STRAFFELINI G, TESI B, et al. Dry sliding wear mechanisms of the Ti6Al4V alloy[J]. Wear,1997,208(12):105-112.
[7] 张志强, 杨凡, 张宏伟, 等. 含稀土TiCx增强钛基激光熔覆层组织与耐磨性[J]. 航空学报, 2021, 42(7):624115. ZHANG Zhiqiang, YANG Fan, ZHANG Hongwei, et al. Microstructure and wear resistance of TiCx reinforced Ti-based laser cladding coating with rare earth[J]. Acta Aeronautica et Astronautica Sinica,2021,42(7):624115(in Chinese).
[8] 张蕾涛, 刘德鑫, 张伟樯, 等. 钛合金表面激光熔覆涂层的研究进展[J]. 表面技术, 2020, 49(8):97-104. ZHANG Leitao, LIU Dexin, ZHANG Weiqiang, et al. Research progress of laser cladding coating on titanium alloy surface[J]. Surface Technology,2020,49(8):97-104(in Chinese).
[9] SOUZA C A C, RIBEIRO D V, KIMINAMI C S. Corrosion re-sistance of Fe-Cr-based amorphous alloys: An overview[J]. Journal of Non-crystalline Solids,2016,442:56-66. DOI: 10.1016/j.jnoncrysol.2016.04.009
[10] 李响, 来佑彬, 于锦, 等. 高能束熔覆制备耐磨涂层技术研究现状与展望[J]. 表面技术, 2021, 50(2):134-159. LI Xiang, LAI Youbin, YU Jin, et al. Research status and prospect of wear-resistant coating prepared by high power density beam cladding[J]. Surface Technology,2021,50(2):134-159(in Chinese).
[11] ZHAO Y, YU T B, SUN J Y, et al. Microstructure and properties of laser cladded B4C/TiC/Ni-based composite coating[J]. International Journal of Refractory Metals and Hard Materials,2020,86:105112. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijrmhm.2019.105112
[12] 孙荣禄, 牛伟, 雷贻文, 等. 钛合金TC4激光熔覆NiCrBSi+Ni/MoS2涂层组织和摩擦磨损性能[J]. 材料热处理学报, 2014, 35(6):157-162. SUN Ronglu, NIU Wei, LEI Yiwen, et al. Microstructure and tribological properties of laser clad NiCrBSi+Ni/MoS2 coating on TC4 titanium alloy[J]. Transactions of Materials and Heat Treatment,2014,35(6):157-162(in Chinese).
[13] LIU X B, MENG X J, LIU H Q, et al. Development and characterization of laser clad high temperature self-lubrication wear resistant composite coatings on Ti-6Al-4V alloy[J]. Materials & Design,2014,55(6):404-409.
[14] 石皋莲, 吴少华, 陆小龙, 等. TA2钛合金表面激光熔覆Ti2SC/TiS自润滑耐磨复合涂层组织与性能[J]. 材料热处理学报, 2016, 37(7):198-202. SHI Gaolian, WU Shaohua, LU Xiaolong, et al. Microstructure and property of laser clad Ti2SC/TiS self-lubrication anti-wear composite coating on TA2 titanium alloy[J]. Transactions of Materials and Heat Treatment,2016,37(7):198-202(in Chinese).
[15] 刘亚楠, 孙荣禄, 张天刚, 等. CeO2含量对激光熔覆自润滑涂层微观组织和性能的影响[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2018, 55(11):277-284. LIU Yanan, SUN Ronglu, ZHANG Tiangang, et al. Effect of CeO2 content on microstructure and properties of laser cladded self-lubricant coatings[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers,2018,55(11):277-284(in Chinese).
[16] 王勇刚, 刘和剑, 回丽, 等. 激光熔覆原位自生碳化物增强自润滑耐磨复合涂层的高温摩擦学性能[J]. 材料工程, 2019, 47(5):72-78. DOI: 10.11868/j.issn.1001-4381.2018.000409 WANG Yonggang, LIU Hejian, HUI Li, et al. High tempera-ture tribological properties of laser cladding in-situ carbide reinforced self-lubricating[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering,2019,47(5):72-78(in Chinese). DOI: 10.11868/j.issn.1001-4381.2018.000409
[17] 刘发兰, 赵树森, 高文焱, 等. 基材属性对Ni60A-WC激光熔覆涂层性能的影响[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2014, 24(5):1319-1326. LIU Falan, ZHAO Shusen, GAO Wenyan, et al. Effect of substrate on Ni60A-WC laser cladding coatings[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals,2014,24(5):1319-1326(in Chinese).
[18] 高广睿, 刘道新, 张晓化. Ti811 合金的高温微动疲劳行为[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2005, 15(1):38-43. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1004-0609.2005.01.006 GAO Guangrui, LIU Daoxin, ZHANG Xiaohua. The high temperature of Ti811 alloy micro fatigue behavior[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals,2005,15(1):38-43(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1004-0609.2005.01.006
[19] 郑启池, 金亚娟, 李瑞峰, 等. 功率输入对激光熔覆镍基涂层组织和裂纹生成的影响[J]. 江苏科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 31(3):293-297. ZHENG Qichi, JIN Yajuan, LI Ruifeng, et al. Effect of power input on microstructure and crack formation of Ni based coating by laser cladding[J]. Journal of Jiangsu University Science and Technology (Natural Science Edition),2017,31(3):293-297(in Chinese).
[20] ZHOU S F, ZENG X Y, HU Q W, et al. Analysis of crack behavior for Ni-based WC composite coatings by laser cladding and crack-free realization[J]. Applied Surface Science,2008,255(5):1646-1653. DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2008.04.003
[21] 张磊, 陈小明, 刘伟, 等. 激光熔覆Ni基合金裂纹的形成机理及敏感性[J]. 激光与光电子学进展, 2019, 56(11):168-175. ZHANG Lei, CHEN Xiaoming, LIU Wei, et al. Formation mechanism and sensitivity of cracks in laser-cladded Ni-based-alloy coatings[J]. Laser & Optoelectronics Process,2019,56(11):168-175(in Chinese).
[22] KADOLKAR P B, WATKINS T R, DE HOSSON J T M, et al. State of residual stress in laser-deposited ceramic compo-site coatings on aluminum alloys[J]. Acta Materialia,2007,55(4):1203-1214. DOI: 10.1016/j.actamat.2006.07.049
[23] 余廷, 邓琦林, 张伟, 等. 激光熔覆NiCrBSi合金涂层的裂纹形成机理[J]. 上海交通大学学报, 2012, 46(7):1043-1048. YU Ting, DENG Qilin, ZHANG Wei, et al. Study on cracking mechanism of laser clad NiCrBSi coating[J]. Journal of Shanghai Jiaotong University,2012,46(7):1043-1048(in Chinese).
[24] 钟燕. 异种金属摩擦焊先顶后刹过程的数值模拟及工艺研究[D]. 西安: 西北工业大学, 2006. ZHONG Yan. Different metal friction welding numerical simulation on forging process and parameter study[D]. Xi'an: Northwestern Polytechnical University, 2006(in Chinese).
[25] 鲁耀钟, 雷卫宁, 任维彬, 等. 激光熔覆 Inconel718合金裂纹分析及裂纹控制研究[J]. 表面技术, 2020, 49(9):233-243. LU Yaozhong, LEI Weining, REN Weibin, et al. Crack analysis and control of laser cladding Inconel718 alloy[J]. Surface Technology,2020,49(9):233-243(in Chinese).
[26] 路世盛, 周建松, 王凌倩, 等. 钛合金表面激光熔覆陶瓷涂层的研究进展[J]. 表面技术, 2019, 48(11):82-90. LU Shisheng, ZHOU Jiansong, WANG Lingqian, et al. Development of laser cladding ceramic coatings on titanium alloy surface[J]. Surface Technology,2019,48(11):82-90(in Chinese).
[27] MARKOVSKY P E, SAVVAKIN D G, IVASISHIN O M, et al. Mechanical behavior of titanium-based layered structures fabricated using blended elemental powder metallurgy[J]. Journal of Materials Engineering and Performance,2019,28(9):5772-5792. DOI: 10.1007/s11665-019-04263-0
[28] 梁广冰, 朱锦洪, 尹丹青, 等. TC4钛合金激光熔覆路径选择数值模拟研究[J]. 河南科技大学学报(自然科学版), 2021, 42(6):12-18. LIANG Guangbing, ZHU Jinhong, YIN Danqing, et al. Numerical simulation of laser cladding path selection for TC4 titanium alloy[J]. Journal of Henan University of Science and Technology (Natural Science),2021,42(6):12-18(in Chinese).
[29] 王田. 航空发动机压气机叶片用Ti-811合金棒材热连轧工艺研究[D]. 西安: 西安建筑科技大学, 2019. WANG Tian. Research on the hot tandem rolling process of Ti-811 alloy in aero-engine compressor blade[D]. Xi’an: Xi’an University of Architecture and Technology, 2019(in Chinese).
[30] 谢映光, 王成磊, 张可祥, 等. 数值模拟和稀土调控改性结合优化铝合金表面激光熔覆[J]. 表面技术, 2020, 49(12):144-155. XIE Yingguang, WANG Chenglei, ZHANG Kejian, et al. Optimizing laser cladding on aluminum alloy surface with numerical simulation and rare earth modification[J]. Surface Technology,2020,49(12):144-155(in Chinese).
[31] 李德英, 张坚, 赵龙志, 等. 超声作用下激光熔覆SiC/316L复合涂层残余应力数值模拟[J]. 复合材料学报, 2016, 33(10):2270-2276. LI Deying, ZHANG Jian, ZHAO Longzhi, et al. Numerical simulation of residual stress in SiC/316L composite coating by ultrasonic aided laser cladding[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2016,33(10):2270-2276(in Chinese).
[32] 邹海贝. TC4钛合金热处理强化工艺及相变行为研究 [D]. 秦皇岛: 燕山大学, 2019. ZOU Haibei. Study on heat treatment strengthening and phase transformation behavior of TC4 titanium alloy[D]. Qinhuangdao: Yanshan University, 2019(in Chinese).
[33] QUAZIL M, FAZAL M, HASEEB A, et al. Effect of rare earth elements and their oxides on tribo-mechanical perfor-mance of laser claddings: A review[J]. Journal of Rare Earths,2016,34(6):549-564. DOI: 10.1016/S1002-0721(16)60061-3
[34] 张天刚, 庄怀风, 姚波, 等. Y2O3对钛基激光熔覆层组织与性能的影响[J]. 复合材料学报, 2020, 27(6):1390-1400. ZHANG Tiangang, ZHUANG Huaifeng, YAO Bo, et al. Effect of Y2O3 on microstructure and properties fo Ti-based laser cladding layer[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2020,27(6):1390-1400(in Chinese).
[35] 章小峰, 王爱华, 张祥林, 等. 激光熔覆Ni45-CaF2-WS2自润滑涂层组织与性能[J]. 中国有色金属学报, 2008, 18(2):215-219. DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1004-0609.2008.02.004 ZHANG Xiaofeng, WANG Aihua, ZHANG Xianglin, et al. Microstructure and tribological properties of laser cladding Ni45-CaF2-WS2 self-lubrication coating[J]. The Chinese Journal of Nonferrous Metals,2008,18(2):215-219(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3321/j.issn:1004-0609.2008.02.004
[36] 刘亚楠, 谷米, 孙荣禄, 等. 钛合金表面激光熔覆原位制备TiC/Ti2Ni复合涂层微观组织与性能研究[J]. 中国激光, 2021, 48(14):1402011. DOI: 10.3788/CJL202148.1402011 LIU Yanan, GU Mi, SUN Ronglu, et al. Micro structure and properties of in-situ TiC/Ti2Ni composite coating prepared via laser cladding on titanium alloy[J]. Chinese Journal of Lasers,2021,48(14):1402011(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3788/CJL202148.1402011
[37] ZHANG P L, LIU X P, LU Y L, et al. Microstructure and wear behavior of Cu-Mo-Si coatings by laser cladding[J]. Applied Surface Science,2014,311(30):709-714.
[38] 高秋实, 闫华, 秦阳, 等. 钛合金表面激光熔覆Ti-Ni+TiN+MoS2/TiS自润滑复合涂层[J]. 材料研究学报, 2018, 32(12):921-928. DOI: 10.11901/1005.3093.2018.163 GAO Qiushi, YAN Hua, QIN Yang, et al. Self-lubricating wear resistant composite coating Ti-Ni+TiN+MoS2/TiS prepared on Ti-6Al-4V alloy by laser cladding[J]. Chinese Journal of Materials Research,2018,32(12):921-928(in Chinese). DOI: 10.11901/1005.3093.2018.163
[39] 雷临苹, 叶宏, 宋坤, 等. Al2O3-TiO2对铝合金表面激光熔覆NiAl涂层组织性能的影响[J]. 表面技术, 2018, 47(10):145-150. LEI Linping, YE Hong, SONG Kun, et al. Effect of Al2O3-TiO2 on microstructure and properties of NiAl coating by laser cladding on aluminum alloy[J]. Surface Technology,2018,47(10):145-150(in Chinese).
-
期刊类型引用(12)
1. 贾宝惠,任鹏,宋挺,崔开心,肖海建. 湿热环境下端径比对复合材料螺栓连接结构静力拉伸失效的影响. 材料导报. 2024(05): 246-252 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 张宇,郭盼盼,熊婕,黄峰,王波. 循环湿热环境对树脂基复合材料弯曲性能的影响. 科学咨询(科技·管理). 2024(02): 135-138 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 牛存洋,寿文凯,顾海萍,孔德良. 以价值观为导向的生态学课程思政教学设计——以种群生活史对策为例. 科学咨询(教育科研). 2024(03): 134-137 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 刘鸿森,黄凯,黄金钊,韩晓剑,逯浩,骆杨,张莉,果立成. 考虑温度效应的复合材料紧固结构面外拉脱性能和失效机制. 复合材料学报. 2024(09): 4778-4790 .  本站查看
本站查看
5. 王慧敏,任亮,范微微,陈阳,孙丽. 基于锥体结构复合材料制品布带缠绕成型关键工艺参数优化. 宇航材料工艺. 2024(05): 87-92 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 樊俊铃,马国庆,焦婷,陈曾美,韩啸. 温度和湿度对碳纤维增强复合材料老化影响研究综述. 航空科学技术. 2023(09): 1-13 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 刘宋婧,冯宇,张腾,毕亚萍,张铁军. 航空复合材料加筋板湿热环境下吸湿性能. 航空动力学报. 2023(09): 2231-2240 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 王静,程健,肖存勇,贾松,任荣,熊需海. 先进聚合物基复合材料超声焊接研究进展. 高分子材料科学与工程. 2023(09): 166-173 .  百度学术
百度学术
9. 蒋平,吕太勇,吴丽华,José Pérez-Rigueiro,胡梦蕾,徐丽萍,黄诗怡,王安萍,郭聪. 形变导致的蜘蛛大壶状腺丝力学行为的记忆与变异. 材料导报. 2023(23): 237-245 .  百度学术
百度学术
10. 吴志猛. 聚四氟乙烯芳纶1313纤维树脂基复合材料的摩擦学性能研究. 化学工程与装备. 2022(09): 40-41+44 .  百度学术
百度学术
11. 王志平,陈灏,路鹏程. 电-湿耦合作用下碳纤维增强树脂基复合材料损伤机制. 中国塑料. 2022(10): 39-45 .  百度学术
百度学术
12. 史超帆,陈叔平,王洋,金树峰,于洋,何远新,杨帅,熊珍艳,史庆智. 纤维方向对环氧树脂/玻纤复合材料导热性能影响. 工程塑料应用. 2022(11): 108-116 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(9)
-




 下载:
下载: