Preparation and microwave absorption properties of porous charcoal/ Fe3O4 composites
-
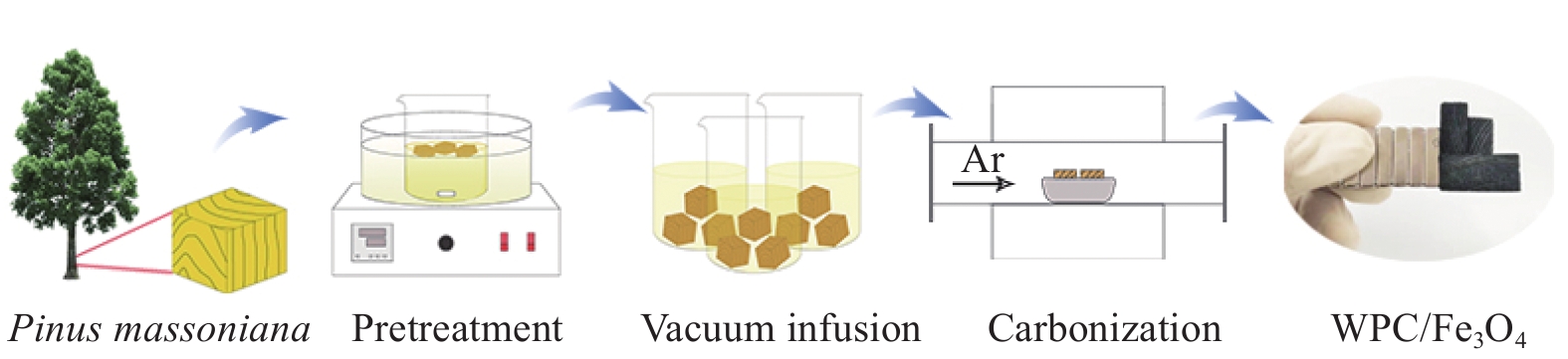
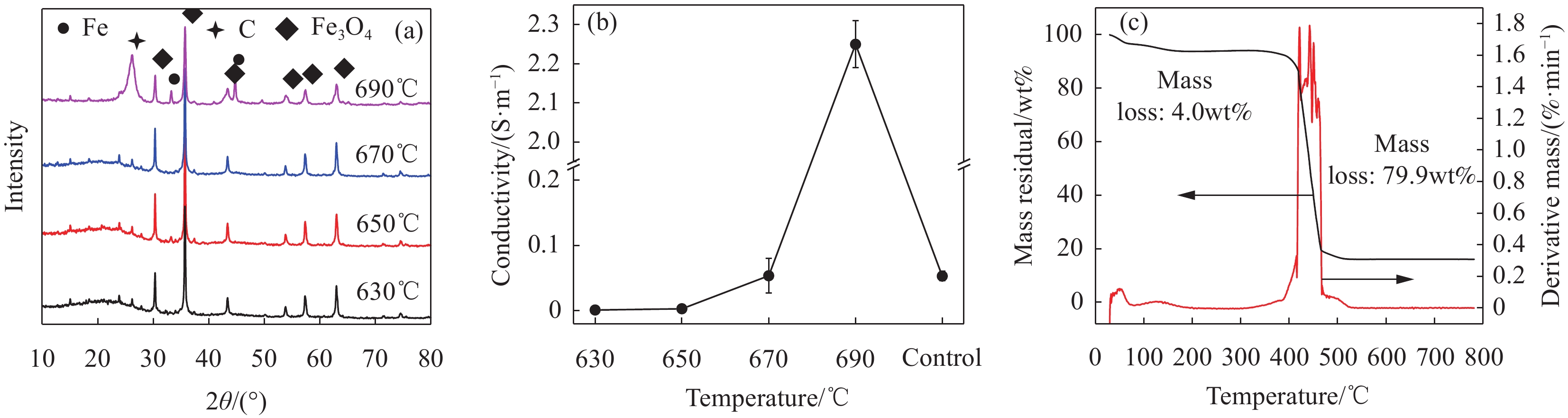
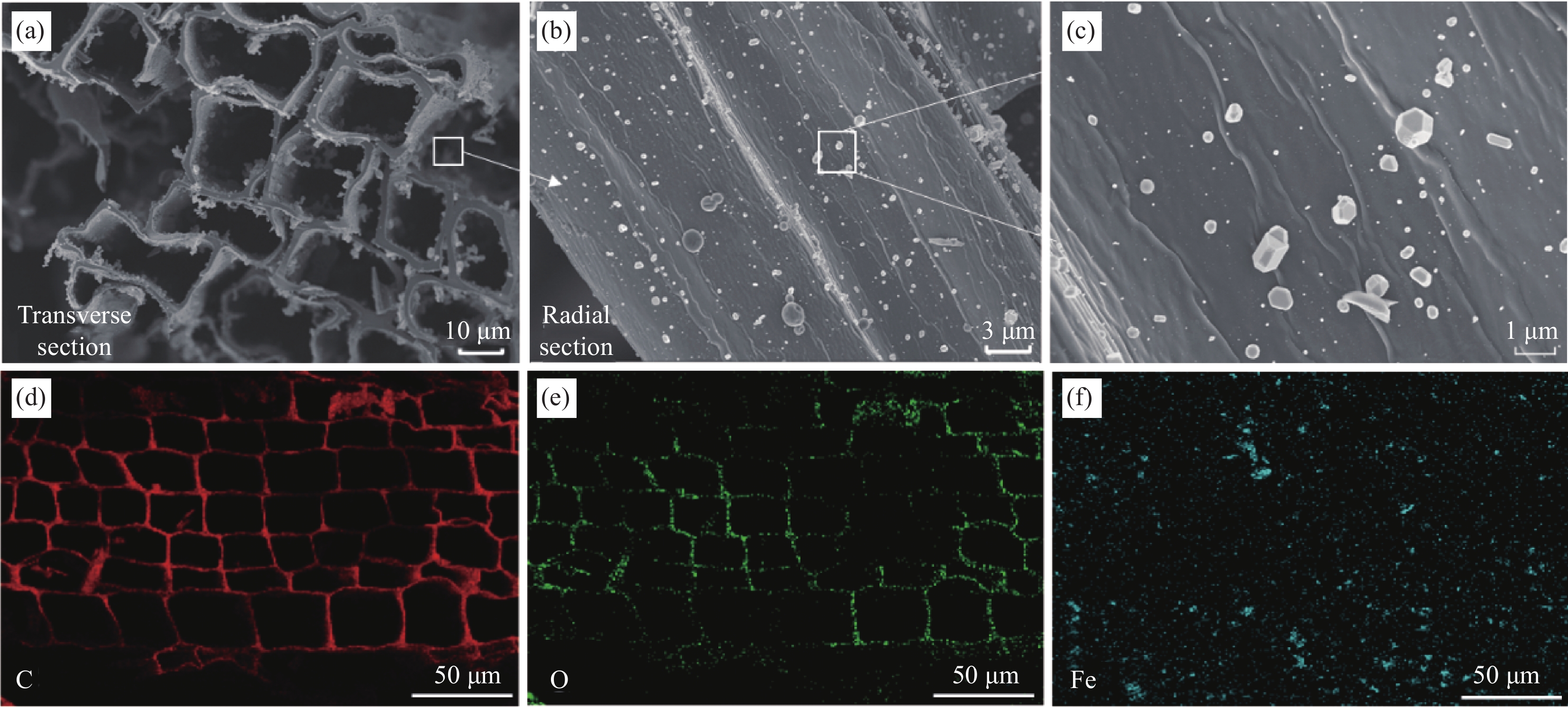
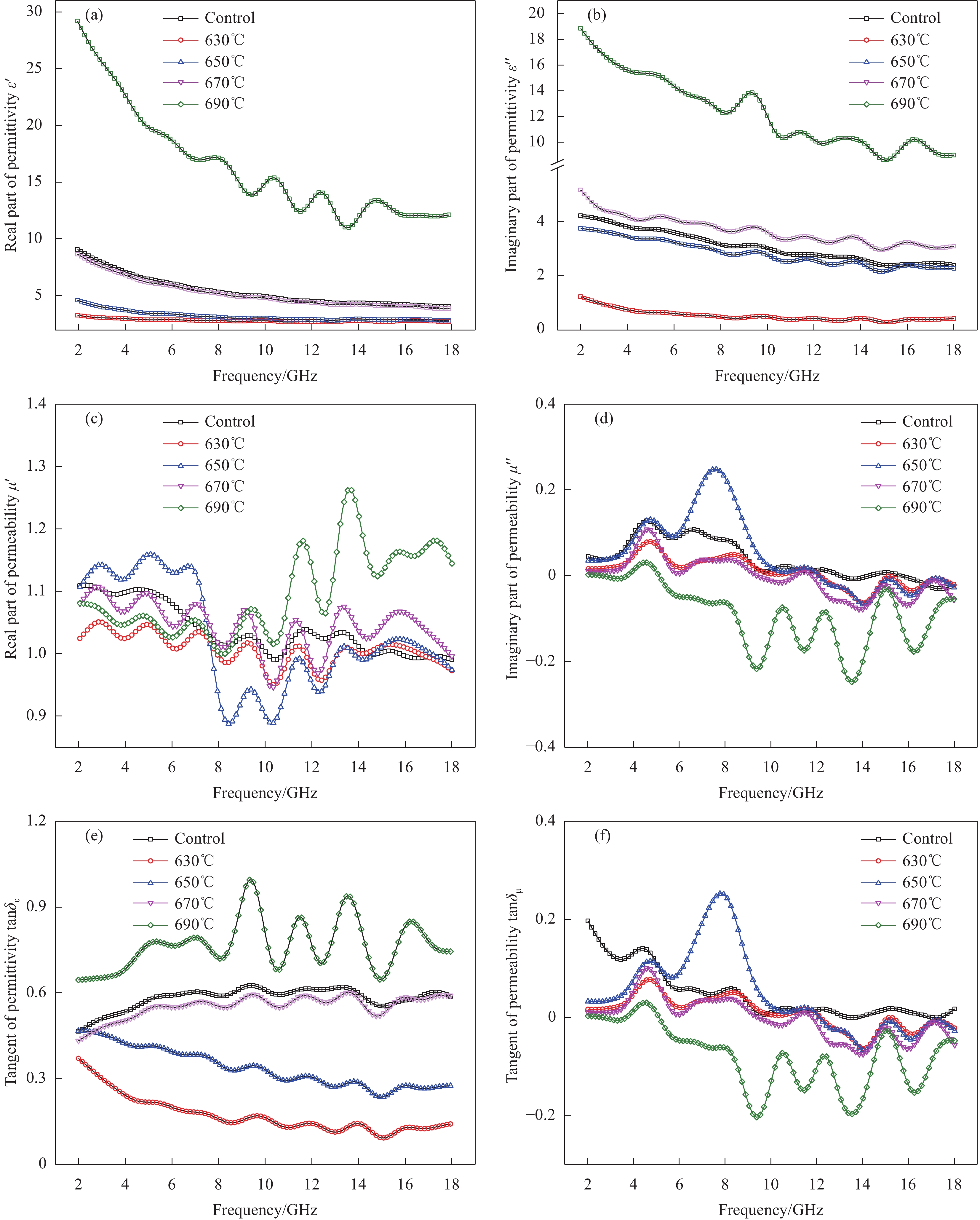
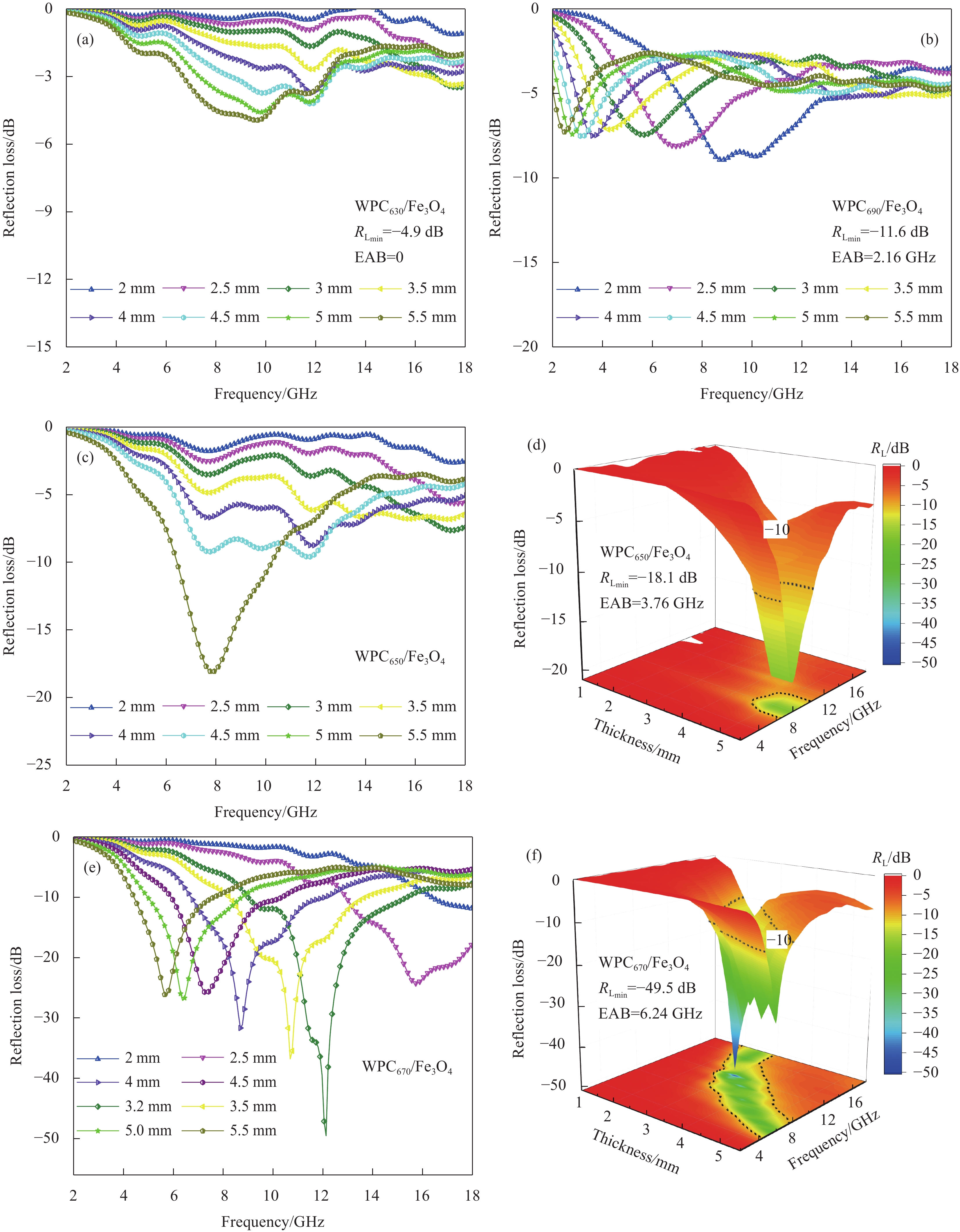
摘要: 为了改善Fe3O4吸波材料密度大和吸波频带窄等问题,以马尾松木材为原料,采用去木质素及高温原位生长法制备了多孔木炭(WPC)/Fe3O4复合材料,通过变化碳化温度来调控复合材料的电磁特性与微波吸收性能。微观形貌、结构和电磁参数等结果表明:WPC/Fe3O4复合材料保有木材天然的三维孔结构,Fe3O4粒子均匀负载于多孔木炭的炭壁与孔道中;升高碳化温度(630~690℃)可增强材料的电导率与电磁衰减能力,但温度过高会引起材料阻抗失配。670℃制备的复合材料微波衰减能力强且阻抗匹配特性好,最小反射损耗为−49.5 dB,有效吸收频宽为6.24 GHz(9.04~15.28 GHz),主要衰减机制归结于复合材料的电导损耗、极化弛豫及介电与磁损耗的协同作用。WPC/Fe3O4复合材料优异的吸波性能在电磁波吸收领域具有良好前景,可促进速生木材的高值化与功能化应用。Abstract: In order to improve the shortages of big density and narrow absorption bandwidth of Fe3O4 absorbing material, in this study, wood-based porous charcoal (WPC)/Fe3O4 composites were prepared from fast-growing masson pine wood by delignification and high temperature in-situ growth methods. The microwave absorption properties of the composites were regulated by tailoring the carbonization temperature. The results of micromorphology, structure and electromagnetic parameters show that, the WPC/Fe3O4 composites retain the natural three-dimensional porous structure of wood with Fe3O4 particles evenly loaded in the carbon walls and channels of WPC. The increment of carbonization temperature (630-690℃) can enhance the electric conductivity and microwave attenuation capacity of the composites, but too high temperature causes the impedance mismatching. The composite prepared at 670℃ exhibits excellent microwave absorption performance with a minimum reflection loss of −49.5 dB and an effective absorption bandwidth of 6.24 GHz (9.04-15.28 GHz), due to its strong attenuation capability and good impedance matching characteristics. The main dissipation mechanism includes conductive loss, polarization relaxation, and synergistic effect of dielectric and magnetic loss. The strong reflection loss and wide effective absorption bandwidth of WPC/Fe3O4 composite suggest a good prospect in electromagnetic absorption field, which can promote the value-added and functional application of fast-growing wood.
-
Keywords:
- pine wood /
- Fe3O4 /
- porous structure /
- impedance matching /
- wave absorption performance /
- attenuation mechanism
-
高性能热塑性复合材料具有能够快速成型、原材料可无限期存贮、制件可多次加热成型、废旧制件可回收利用等优点[1-3],符合经济型、环保性的发展要求,成为各个国家高端复合材料领域研究和发展的重点[4]。早在上个世纪80年代[5],国外科研院所、企业等在热塑性复合材料的应用方面投入了大量的研发力量[6],经过多年的发展,国外热塑性复合材料在军用、民用航空的应用已完成从飞机内饰、舱门、口盖、整流罩等非承力部件到飞机固定面前后缘、襟翼、副翼、方向舵等受载较小部位[7],再到机翼盒段、机身壁板、蒙皮等主承力结构的转变[8]。高性能热塑性复合材料的实际应用取得了显著的效果,有效弥补了热固性复合材料制造和使用过程中面临的诸多问题。
高性能热塑性复合材料中,碳纤维增强聚芳醚酮(CF/PAEK)复合材料,具有优异的韧性[9]、耐老化性能及耐疲劳性能[10],使CF/PAEK热塑性复合材料得以替代部分传统热固性复合材料,在航空、航天等领域取得成功应用,但是在使用的过程中仍然面临损伤、失效的风险。复合材料典型损伤模式包括层内损伤和层间损伤,层内损伤如基体开裂、纤维与基体脱粘和纤维断裂等,层间损伤如层间脱粘等[11],因此,复合材料的界面性能及层间性能得到了研究者们的关注。Lu等[12]研究了CCF300碳纤维与不同树脂基体间的界面剪切强度,结果显示聚醚醚酮(Polyetheretherketone,PEEK)与碳纤维间的界面强度约为44.87 MPa;一些研究者认为由于PEEK链惰性和碳纤维表面能较低,导致界面强度稍低,复合材料的界面强度仍然有提升的空间,Su等[13]采用碳纳米管优化了CF/PEEK复合材料的层间剪切性能,将复合材料的短梁剪切强度提高35.8%;Yan等[14]研制了水溶性胺化聚醚醚酮(PEEK-NH2)上浆剂将CF/PEEK复合材料的层间剪切强度提高了43.1%;除此之外,成型工艺也能够影响复合材料的界面及层间性能,Wu等[15]研究了孔隙率及树脂结晶度对CF/PEEK复合材料的层间剪切性能的影响,结果显示较低的孔隙率和较高的结晶度能够提高复合材料的层间剪切性能;史如静等[16]研究了成型工艺参数对CF/PEEK复合材料Ⅰ型断裂性能的影响,结果显示较高的成型温度、适当的成型压力及较快的降温速率能够提高复合材料的Ⅰ型断裂韧性。上述研究主要集中于研究工艺条件对复合材料性能的影响,而对树脂基体的特性对复合材料性能的影响研究较少,Chen等[17]研究了不同流动性能的PEEK树脂的流变行为,并根据结果优化了PEEK树脂基体对碳纤维的浸渍参数,并测试了优化浸渍参数后的复合材料的力学性能,但并未对比具有不同流动性能的PEEK基复合材料的力学性能。
本文中使用具有不同特性的PAEK树脂基体和国产T300级SCF35碳纤维制备了连续碳纤维增强PAEK热塑性复合材料,以微球脱粘性能、90°拉伸性能、短梁剪切性能、Ⅰ型断裂韧性、Ⅱ型断裂韧性为指标,研究了树脂基体的特性对复合材料的界面性能和层间性能的影响,为航空、航天领域所用轻质高强复合材料的设计和制造提供了选材参考。
1. 试验材料及方法
1.1 原材料
基体树脂为汤原县海瑞特工程塑料有限公司生产的聚芳醚酮(Polyaryletherketone,PAEK)树脂,其中流动性稍低的树脂基体牌号为PAEK-L,流动性稍高的树脂基体牌号为PAEK-H,树脂基体的性能如表1所示;碳纤维为中国石化上海石油化工股份有限公司生产的T300级碳纤维,牌号为SCF35,碳纤维性能如表2所示,表面形貌如图1所示;热塑性单向预浸料由黑龙江英创新材料有限公司生产,牌号分别为SCF35/PAEK-L及SCF35/PAEK-H,预浸料的纤维面密度约为147 g/m2,纤维体积分数约为52vol%,树脂质量分数约为40wt%。
表 1 聚芳醚酮(PAEK)树脂基体的性能Table 1. Properties of poly aryl ether ketone (PAEK) resin matrixProperty Tensile
strength/MPaTensile
modulus/GPaElongation/% Notched impact
strength/(kJ∙m–2)Apparent viscosity
(360℃)/(Pa·s)PAEK-L 96±0.5 4.0±0.2 109±7.2 5.7±0.2 1139 PAEK-H 95±0.5 3.9±0.2 101±4.4 5.7±0.2 399 Notes: PAEK-L—Low flow poly aryl ether ketone resin matrix; PAEK-H—High flow poly aryl ether ketone resin matrix. 表 2 国产T300级碳纤维(SCF35)的性能Table 2. Properties of domestic T300 grade carbon fiber (SCF35)Fibre Specification Tensile strength
/MPaTensile modulus
/GPaElongation
/%Bulk density
/(g∙cm−3)Linear density
/(g∙m−1)SCF35 12 K 4300 230 1.85 1.8 0.8 1.2 复合材料层压板制备
采用模压成型的方法制备复合材料层压板,首先将预浸料裁切成所需的长度规格,采用超声波焊机将预浸料铺贴为预成型体,然后将预制体放入高温脱模剂处理后的模具型腔,最后将模具放入平板硫化仪(LSVI-50 T,广州市普同实验分析仪器有限公司)进行模压成型,成型工艺如图2所示,图2(a)为薄板成型工艺,适用于铺层方式为[0°]14的90°拉伸试样;图2(b)为厚板成型工艺,适用于断裂韧性试样及铺层方式为[0°]42的短梁剪切试样。上述断裂韧性试样所用层压板的铺层方式为[0°]24,预制体中间层铺放厚度为0.03 mm的聚酰亚胺胶带作为预制缺陷,如图3所示。
1.3 测试与表征
SCF35碳纤维与聚芳醚酮(PAEK)树脂间界面强度的测试,采用微球脱粘实验测试纤维与树脂间的界面强度,所用设备为日本东荣株式会社生产的复合材料界面性能评价装置,设备型号为HM410。测试过程中首先将PAEK树脂330℃熔融成球,然后使树脂浸润单根纤维约10 s,待挂在纤维上的树脂由于表面张力形成微球后,再使用树脂熔体蘸取纤维表面上多余的树脂,将纤维上挂载的小球修理至长度为40~60 μm的小球,随后将纤维和树脂在330℃下保温10 min使树脂充分浸润纤维,最后将保温后的样品冷却至室温进行测试,测试原理如图4所示,界面剪切强度的计算公式如下所示:
τ=Fmaxπdl (1) 式中:τ为平均剪切强度;Fmax为小球剥脱时的力;d为纤维直径;l为纤维埋入树脂中的长度。
SCF35/PAEK复合材料的力学性能采用美国英斯特朗公司生产的万用材料试验机进行测试,设备型号为Instron 5982,90°拉伸性能采用测试标准ASTM D3039/D3039 M-14[18],测试样条尺寸为175 mm×25 mm×2 mm,测试加载速度为2 mm/min,90°拉伸强度计算公式如下所示:
σt=Pbd (2) 式中:σt为极限拉伸强度;P为破坏前最大载荷;b为试样宽度;d为试样厚度。
复合材料的短梁剪切性能测试采用标准ASTM D2344/D2344 M-16[19],试样长度∶跨距∶宽度∶厚度=6∶4∶2∶1,SCF35/PAEK-L的试样尺寸为36.6 mm×12.2 mm×6.1 mm,SCF35/PAEK-H的试样尺寸为35.4 mm×11.8 mm×5.9 mm,测试过程中加载头的半径为3.0 mm,支座的半径为1.5 mm,试样加载速度为1.0 mm/min,短梁剪切强度计算公式如下所示:
Fsbs=0.75Pmbd (3) 式中:
Fsbs 为短梁剪切强度;Pm 为试样破坏的最大载荷;b为试样宽度;d为试样厚度。Ⅰ型断裂韧性采用测试标准ASTM D5528/D5528 M-21[20],试样的尺寸为180 mm×25 mm,预制裂纹长度约为50 mm,测试过程中加载速度为2.0 mm/min,Ⅰ型断裂韧性的计算公式如下所示:
GIC=nPδ2ba (4) 式中:
GIC 为Ⅰ型断裂韧性;n为柔度标定系数,是lg(δi/Pi)与lg(ai)的最小二乘法拟合的直线斜率;i为测试过程中的取样点;P为裂纹扩展临界载荷;δ 为对应于P的加载点位移;a为裂纹长度。Ⅱ型断裂韧性采用测试标准ASTM D7905/D7905 M-19[21],采用预制试样的方法进行测试,试样的尺寸为140 mm×25 mm,预制裂纹长度约为40 mm,测试过程中加载速度为2.0 mm/min,Ⅱ型断裂韧性的计算公式如下所示:
GПC=3mP2Maxa2pc2B 式中:
GПC 为Ⅱ型断裂韧性;m为合规校准系数;PMax 为载荷的最大值;apc 为实际裂纹长度;B为试件宽度。除上述测试外,还采用日立Regulus 8230型场发射扫描电子显微镜及浩视RH 8800超景深显微镜对相关试样的微观形貌进行测试表征。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 SCF35/PAEK复合材料的界面性能
SCF35/PAEK复合材料的界面性能如表3所示,SCF35碳纤维与低流动性树脂PAEK-L的界面剪切强度约为64 MPa,接触角约为35.8°,90°拉伸强度约为55 MPa,90°拉伸模量约为8.6 GPa,短梁剪切强度约为86 MPa;SCF35碳纤维与高流动性树脂PAEK-H的界面剪切强度约为79 MPa,接触角约为34.4°,90°拉伸强度约为76 MPa,90°拉伸模量约为9.7 GPa,短梁剪切强度约为92 MPa。
表 3 SCF35/PAEK复合材料的界面性能Table 3. Interfacial properties of SCF35/PAEK compositesSystem Interfacial shear
strength/MPaContact angle/
(°)90° tensile
strength/MPa90° tensile
modulus/GPaShort beam shear
strength/MPaSCF35/PAEK-L 64±3.4 35.8±1.0 55±2.9 8.6±0.1 86±1.9 SCF35/PAEK-H 79±6.0 34.4±3.0 76±5.4 9.7±0.4 92±1.4 SCF35/PAEK复合材料界面剪切测试后,树脂剥脱后的表面形貌如图5所示,微球脱粘的截面形貌如图6所示,纤维与树脂间的接触角如图7所示。图5(a)中PAEK-L微球剥脱的前端呈现撕裂状,后端树脂呈现整体剥脱状;图5(b)中PAEK-H微球剥脱的前端和后端均呈现撕裂状。图6(a)中SCF35/PAEK-L复合材料界面处存在空隙,而图6(b)中SCF35/PAEK-H复合材料界面处树脂基体与纤维结合紧密。图7(a)中PAEK-L树脂在表面张力的作用下在纤维上形成独立的树脂微球,而图7(b)中PAEK-H树脂与纤维结合较紧密,出现树脂粘连、不能形成微球的现象,出现这种现象的原因是,在没有额外压力的作用下,树脂对带有沟槽的SCF35碳纤维浸润的驱动力主要来自于毛细管压力[22],流动性低的PAEK-L树脂具有较高的内摩擦阻力,毛细管压力不足以克服树脂的内摩擦阻力[23],树脂液滴与空气界面处的树脂分子不能克服自由能势垒[24],无法彻底的将纤维表面的沟槽浸润,从而与纤维表面沟槽形成Cassie接触状态[25],并且在表面张力的作用下,团聚成为独立的树脂微球;PAEK-H树脂基体具有较高的流动性能,即较低的内摩擦阻力,因此在毛细管压力的作用下,树脂液滴与空气界面处的树脂分子能够克服自由能势垒与纤维表面沟槽接触并发生黏附,形成Wenzel接触状态[26]。上述结果说明,造成SCF35/PAEK-L界面强度稍低于SCF35/PAEK-H的原因是PAEK-H树脂的流动性较好,能够与带有沟槽的SCF35碳纤维形成较好的结合能力。
![]() 图 5 SCF35/PAEK微球脱粘的表面形貌:(a) SCF35/PAEK-L:(1) 整体形貌、(2) 微球脱粘的示意图、(3) 微球脱粘的前端形貌、(4) 微球脱粘的后端形貌;(b) SCF35/PAEK-H:(1) 整体形貌、(2) 微球脱粘的示意图、(3) 微球脱粘的前端形貌、(4) 微球脱粘的后端形貌Figure 5. Surface morphologies of SCF35/PAEK microsphere debonding: (a) SCF35/PAEK-L: (1) Overall Shape, (2) Schematic diagram of microsphere debonding, (3) Shape of the front end of microsphere debonding, (4) Shape of the back end of microsphere debonding; (b) SCF35/PAEK-H: (1) Overall Shape, (2) Schematic diagram of microsphere debonding, (3) Shape of the front end of microsphere debonding, (4) Shape of the back end of microsphere debonding
图 5 SCF35/PAEK微球脱粘的表面形貌:(a) SCF35/PAEK-L:(1) 整体形貌、(2) 微球脱粘的示意图、(3) 微球脱粘的前端形貌、(4) 微球脱粘的后端形貌;(b) SCF35/PAEK-H:(1) 整体形貌、(2) 微球脱粘的示意图、(3) 微球脱粘的前端形貌、(4) 微球脱粘的后端形貌Figure 5. Surface morphologies of SCF35/PAEK microsphere debonding: (a) SCF35/PAEK-L: (1) Overall Shape, (2) Schematic diagram of microsphere debonding, (3) Shape of the front end of microsphere debonding, (4) Shape of the back end of microsphere debonding; (b) SCF35/PAEK-H: (1) Overall Shape, (2) Schematic diagram of microsphere debonding, (3) Shape of the front end of microsphere debonding, (4) Shape of the back end of microsphere debondingSCF35/PAEK复合材料的90°拉伸测试的破坏形貌如图8所示,可以看出,SCF35/PAEK-L复合材料的90°拉伸试样破坏后,在纤维表面存在不均匀分布的残留树脂;SCF35/PAEK-H复合材料的90°拉伸试样破坏后,纤维被树脂基体均匀包覆。造成复合材料界面呈现不同的破坏模式的原因是PAEK-H树脂基体相较于PAEK-L树脂基体具有较高的流动性,能够填充SCF35碳纤维表面的微小沟槽,形成较强的机械啮合作用,进而表现出较高的界面强度,破坏的过程中界面强度大于树脂的断裂强度时,裂纹在树脂基体中扩展,纤维表面粘连较多的树脂基体。
SCF35/PAEK热塑性复合材料短梁剪切测试的典型应力-应变结果如图9所示。相同的铺层条件下,SCF35/PAEK-H复合材料的短梁剪切强度略大于SCF35/PAEK-L,SCF35/PAEK-L试样达到最大载荷后,出现了载荷突降的现象,随着应变的增加,试样被迅速破坏,载荷快速下降;SCF35/PAEK-H试样的载荷达到最大值前缓慢增加,存在明显的屈服行为,试样的载荷在到达最大值后,试样通常出现一段载荷下降的过程,然后随着剪切形变量的增加,试样发生剪切破坏。
复合材料短梁剪切的截面形貌如图10所示,试样中压头下方的受载区域呈现锥形塑性变形,在剪切力的作用下塑性变形区域边缘萌生裂纹并发生裂纹扩展。短梁剪切试样压头处的表面形貌如图11所示,试样在压头施加的载荷的作用下呈现圆弧形的塑性变形,图11(a)中SCF35/PAEK-L复合材料表面较光滑,纤维随树脂的塑性变形发生弯曲,图11(b)中SCF35/PAEK-H复合材料表面存在纤维断裂痕迹,纤维随树脂的塑性变形发生弯曲与断裂。结合图9与图10、图11,分析造成短梁剪切强度出现差异的原因是,SCF35/PAEK-L复合材料的界面强度稍弱,试样在加载的过程中,复合材料中的纤维在稍低的载荷下发生滑移,导致试样的载荷降低,随着应变的增加,进而萌生裂纹并发生扩展;SCF35/PAEK-H复合材料的界面强度稍强,试样在加载的过程中,复合材料中的纤维较难发生滑移,而是随着试样应变的增加出现纤维弯曲、基体屈服等非线性硬化的效应[11],进而能够承受更高的载荷,当试样的应变达到极限时,试样在剪应力的作用下萌生裂纹并最终发生断裂。
2.2 SCF35/PAEK复合材料的层间性能
连续纤维增强树脂基复合材料中重要的破坏模式是层间破坏,SCF35/PAEK复合材料的层间性能如表4所示。其中SCF35/PAEK-L的Ⅰ型断裂韧性约为938 J/m2,Ⅱ型断裂韧性约为2232 J/m2;SCF35/PAEK-H的Ⅰ型断裂韧性约为638 J/m2,Ⅱ型断裂韧性约为1702 J/m2。
表 4 SCF35/PAEK复合材料的断裂韧性Table 4. Fracture toughness of SCF35/PAEK compositesSystem GIC/(J∙m−2) GIIC/(J∙m−2) SCF35/PAEK-L 938±38 2232±208 SCF35/PAEK-H 638±38 1702±46 Notes: GIC—Type I fracture toughness of SCF35/PAEK composites; GIIC—Type Ⅱ fracture toughness of SCF35/PAEK composites. 对比两种复合材料体系的典型加载曲线如图12所示,结果显示SCF35/PAEK-L复合材料的破坏载荷及其破坏曲线包络的面积均高于SCF35/PAEK-H复合材料,证明SCF35/PAEK-L复合材料的断裂韧性较高。两种复合材料体系的断裂形貌如图13所示,可以看出,SCF35/PAEK-L复合材料中树脂基体均呈现撕裂状,在Ⅱ型断裂韧性试样中树脂基体在剪切应力的作用下沿剪切力方向撕裂破坏;SCF35/PAEK-H复合材料中树脂基体同样呈现撕裂状,但不同的是,SCF35/PAEK-H复合材料中树脂基体撕裂的尺寸较小。研究认为复合材料层间断裂韧性是基体延展性和界面结合强度之间复杂相互作用的结果,而基体的塑性变形能力是影响复合材料韧性的主要因素[27],图14为表1中冲击试样及拉伸试样的破坏形貌。可以看出PAEK-L树脂试样的冲击断面形貌相对于PAEK-H树脂试样具有更大尺寸的断裂变形,PAEK-L树脂试样拉伸断面处存在因塑性变形而产生的齿状树脂残留,而PAEK-H树脂试样拉伸断面处存在片状树脂残留,对比两种树脂试样的断裂形貌及复合材料的断裂形貌可以发现,复合材料中PAEK-L树脂基体较大撕裂形貌将导致复合材料在破坏的过程中消耗更多的能量[28],这是造成SCF35/PAEK-L复合材料断裂韧性较高的原因。
![]() 图 13 SCF35/PAEK断裂形貌:(a) SCF35/PAEK-L Ⅰ型断裂形貌;(b) SCF35/PAEK-L Ⅱ型断裂形貌;(c) SCF35/PAEK-H Ⅰ型断裂形貌;(d) SCF35/PAEK-H Ⅱ型断裂形貌Figure 13. Fracture morphology of SCF35/PAEK: (a) Type I fracture morphology of SCF35/PAEK-L; (b) Type Ⅱ fracture morphology of SCF35/PAEK-L; (c) Type I fracture morphology of SCF35/PAEK-H; (d) Type Ⅱ fracture morphology of SCF35/PAEK-H
图 13 SCF35/PAEK断裂形貌:(a) SCF35/PAEK-L Ⅰ型断裂形貌;(b) SCF35/PAEK-L Ⅱ型断裂形貌;(c) SCF35/PAEK-H Ⅰ型断裂形貌;(d) SCF35/PAEK-H Ⅱ型断裂形貌Figure 13. Fracture morphology of SCF35/PAEK: (a) Type I fracture morphology of SCF35/PAEK-L; (b) Type Ⅱ fracture morphology of SCF35/PAEK-L; (c) Type I fracture morphology of SCF35/PAEK-H; (d) Type Ⅱ fracture morphology of SCF35/PAEK-H![]() 图 14 PAEK树脂试样断裂形貌:(a) PAEK-L冲击断面形貌;(b) PAEK-L拉伸断面形貌;(c) PAEK-H冲击断面形貌;(d) PAEK-H拉伸断面形貌Figure 14. Fracture morphology of PAEK resin specimens: (a) Impact section morphology of PAEK-L; (b) Tensile section morphology of PAEK-L; (c) Impact section morphology of PAEK-H; (d) Tensile section morphology of PAEK-H
图 14 PAEK树脂试样断裂形貌:(a) PAEK-L冲击断面形貌;(b) PAEK-L拉伸断面形貌;(c) PAEK-H冲击断面形貌;(d) PAEK-H拉伸断面形貌Figure 14. Fracture morphology of PAEK resin specimens: (a) Impact section morphology of PAEK-L; (b) Tensile section morphology of PAEK-L; (c) Impact section morphology of PAEK-H; (d) Tensile section morphology of PAEK-H3. 结 论
(1) 国产碳纤维增强聚芳醚酮(SCF35/PAEK)复合材料的界面性能受到树脂基体流动性的影响,流动性较高的PAEK-H树脂能够与纤维之间形成较好的界面结合及较高的界面强度。SCF35/PAEK-L的界面剪切强度约为64 MPa,接触角约为35.8°,90°拉伸强度约为55 MPa,90°拉伸模量约约为8.6 GPa,短梁剪切强度约为86 MPa;SCF35/PAEK-H的界面剪切强度约为79 MPa,接触角约为34.4°,90°拉伸强度约为76 MPa,90°拉伸模量约为9.7 GPa,短梁剪切强度约为92 MPa。
(2) SCF35/PAEK复合材料的层间性能受到树脂基体塑性变形能力的影响,基体塑性变形能力较强的PAEK-L相较于PAEK-H,其复合材料具有较高的断裂韧性。SCF35/PAEK-L的Ⅰ型断裂韧性约为938 J/m2,Ⅱ型断裂韧性约为2232 J/m2;SCF35/PAEK-H的Ⅰ型断裂韧性约为638 J/m2,Ⅱ型断裂韧性约为1702 J/m2。
-
表 1 碳基吸波材料的性能对比
Table 1 Comparison of microwave absorption properties of carbon-based materials
Sample Filler content/wt% RL
/dBThickness
/mmEffective absorption bandwidth/GHz Ref. PC 70 −42.4 2 1.76 [30] PFSL 50 −43.8 3 5.3 [20] RHPC/Fe 25 −21.8 1.4 5.6 [31] Fe3O4/rGO 50 −45 3 − [32] HPC/Co 30 −52.6 2.8 2.5 [24] Co/C fiber 33 −31 2 3.2 [33] Ni(OH)2/BPC 50 −23.6 6 2 [34] Fe3O4/WPC 50 −51.3 2 5.8 [35] HCF@CZ-CNTs 10 −53.5 2.9 2.64 [36] WPC670/Fe3O4 15 −49.5 3.20 6.24 (9.04-15.28) This work Notes: PC—Porous carbon; PFLS—Pyrolytic functionalized loofah sponge; RHPC—Rice husk-based porous carbon; rGO—Reduced graphene oxide; HPC—Hierarchical porous carbon; C fiber—Carbon fiber; BPC—Biomass porous carbon; HCF@CZ-CNTs—Hierarchical carbon fiber coated with Co/C nano-dodecahedron particles where CNTs were anchored. -
[1] XU H L, YIN X W, ZHU M, et al. Carbon hollow microspheres with a designable mesoporous shell for high-performance electromagnetic wave absorption[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2017,9(7):6332-6341. DOI: 10.1021/acsami.6b15826
[2] ZHANG N, HUANG Y, LIU X D, et al. High efficiency microwave absorption nanocomposites of multiple-phase core-shell CoNi alloy@C loaded on rGO conducting network[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2018,115:283-293. DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2018.10.012
[3] LIU P B, GAO S, ZHANG G Z, et al. Hollow engineering to Co@N-doped carbon nanocages via synergistic protecting-etching strategy for ultrahigh microwave absorption[J]. Advanced Functional Materials,2021,31(27):2102812. DOI: 10.1002/adfm.202102812
[4] ZHANG H X, SHI C, JIA Z R, et al. FeNi nanoparticles embedded reduced graphene/nitrogen-doped carbon composites towards the ultra-wideband electromagnetic wave absorption[J]. Journal of Colloid and Interface Science,2021,584:382-394. DOI: 10.1016/j.jcis.2020.09.122
[5] LIU X D, HUANG Y, DING L, et al. Synthesis of covalently bonded reduced graphene oxide-Fe3O4 nanocomposites for efficient electromagnetic wave absorption[J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology,2021,72:93-103. DOI: 10.1016/j.jmst.2020.09.012
[6] 赵佳, 姚艳青, 杨煊赫, 等. 铁氧体及其复合吸波材料的研究进展[J]. 复合材料学报, 2020, 37(11):2684-2699. ZHAO Jia, YAO Yanqing, YANG Xuanhe, et al. Research progress of ferrite and its composite absorbing materials[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2020,37(11):2684-2699(in Chinese).
[7] HUANG L, LI J J, WANG Z J, et al. Microwave absorption enhancement of porous C@CoFe2O4 nanocomposites derived from eggshell membrane[J]. Carbon,2019,143:507-516. DOI: 10.1016/j.carbon.2018.11.042
[8] SHAO Y Q, LU W B, CHEN H, et al. Flexible ultra-thin Fe3O4/MnO2 coreshell decorated CNT composite with enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption performance[J]. Composites Part B: Engineering,2018,144:111-117. DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesb.2018.02.015
[9] LIU J L, LIANG H S, WU H J. Hierarchical flower-like Fe3O4/MoS2 composites for selective broadband electromagnetic wave absorption performance[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2020,130:105760. DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2019.105760
[10] LI J S, XIE Y Z, LU W B, et al. Flexible electromagnetic wave absorbing composite based on 3D rGO-CNT-Fe3O4 ternary films[J]. Carbon,2018,129:76-84. DOI: 10.1016/j.carbon.2017.11.094
[11] ZHOU X F, ZHANG C H, ZHANG M, et al. Synthesis of Fe3O4/carbon foams composites with broadened bandwidth and excellent electromagnetic wave absorption performance[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2019,127:105627. DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2019.105627
[12] WANG H S, SHI P P, RUI M, et al. The green synthesis rGO/Fe3O4/PANI nanocomposites for enhanced electromagnetic waves absorption[J]. Progress in Organic Coatings,2020,139:105476. DOI: 10.1016/j.porgcoat.2019.105476
[13] 李焕然, 马关胜, 杨智伟, 等. Fe3O4/CNTs@Cf 复合材料的制备及其吸波性能的研究[J]. 功能材料, 2021, 52(4):4023-4029. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9731.2021.04.005 LI Huanran, MA Guansheng, YANG Zhiwei, et al. Preparation of Fe3O4/CNTs@Cf composite material and its microwave absorbing properties[J]. Functional Materials,2021,52(4):4023-4029(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1001-9731.2021.04.005
[14] XI J B, ZHOU E Z, LIU Y J, et al. Wood based straightway channel structure for high performance microwave absorption[J]. Carbon,2017,124:492-498. DOI: 10.1016/j.carbon.2017.07.088
[15] GUAN H, CHANG Z Y, WANG X Q. Highly compressible wood sponges with a spring-like lamellar structure as effective and reusable oil absorbents[J]. ACS Nano,2018,12(10):10365-10373. DOI: 10.1021/acsnano.8b05763
[16] LI X J, CAO M, PANG X N, et al. Microtubule-based hierarchical porous carbon for lightweight and strong wideband microwave absorption[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry C,2021,9(5):1649-1656. DOI: 10.1039/D0TC04486E
[17] WANG X X, MA T, SHU J C, et al. Confinedly tailoring Fe3O4 clusters-NG to tune electromagnetic parameters and microwave absorption with broadened bandwidth[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2018,332:321-330. DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2017.09.101
[18] GAO S, ZHANG G Z, WANG Y, et al. MOFs derived magnetic porous carbon microspheres constructed by core-shell Ni@C with high-performance microwave absorption[J]. Journal of Materials Science & Technology,2021,88:56-65. DOI: 10.1016/j.jmst.2021.02.011
[19] LI X J, HE L L, LI Y S, et al. Catalytic graphite mechanism during CVD diamond film on iron and cobalt alloys in CH4-H2 atmospheres[J]. Surface & Coatings Technology,2019,360:20-28. DOI: 10.1016/j.surfcoat.2018.12.120
[20] LIU L Y, SHUANG Y, HU H Y, et al. Lightweight and efficient microwave absorbing materials based on loofah sponge derived hierarchically porous carbons[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering,2019,7(1):1228-1238. DOI: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.8b04907
[21] MA F W, MA D, WU G, et al. Construction of 3D nanostructure hierarchical porous graphitic carbons by charge-induced self-assembly and nanocrystal-assisted catalytic graphitization for supercapacitors[J]. Chemical Communications,2016,52(40):6673-6676. DOI: 10.1039/C6CC02147F
[22] 张艳. 生物质碳材料及生物质碳/磁性粒子复合材料的微波吸收性能研究[D]. 秦皇岛: 燕山大学, 2020. ZHANG Yan. Research on the microwave absorption properties of biomass carbon materials and biomass carbon/magnetic particle composite materials[D]. Qinhuangdao: Yanshan University, 2020(in Chinese).
[23] LIU P B, GAO S, WANG Y, et al. Magnetic porous N-doped carbon composites with adjusted composition and porous microstructure for lightweight microwave absorbers[J]. Carbon,2021,173:655-666. DOI: 10.1016/j.carbon.2020.11.043
[24] LIU T S, LIU N, GAI L X, et al. Hierarchical carbonaceous composites with dispersed Co species prepared using the inherent nanostructural platform of biomass for enhanced microwave absorption[J]. Microporous and Mesoporous Materials,2020,302:110210. DOI: 10.1016/j.micromeso.2020.110210
[25] WANG C, HAN X J, XU P, et al. The electromagnetic property of chemically reduced graphene oxide and its application as microwave absorbing material[J]. Applied Physics Letters,2011,98:072906. DOI: 10.1063/1.3555436
[26] YAN F, ZHANG S, ZHANG X, et al. Growth of CoFe2O4 hollow nanoparticles on graphene sheets for high-performance electromagnetic wave absorbers[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry C,2018,6(47):12781-12787. DOI: 10.1039/C8TC04222E
[27] XU D W, XIONG X H, CHEN P, et al. Superior corrosion-resistant 3D porous magnetic graphene foam-ferrite nanocomposite with tunable electromagnetic wave absorption properties[J]. Journal of Magnetism and Magnetic Materials,2019,469:428-436. DOI: 10.1016/j.jmmm.2018.09.019
[28] NI S B, SUN X L, WANG X H, et al. Low temperature synthesis of Fe3O4 micro-spheres and its microwave absorption properties[J]. Materials Chemistry Physics,2010,124(1):353-358. DOI: 10.1016/j.matchemphys.2010.06.046
[29] CHENG Y, CAO J M, LI Y, et al. The out-side-in approach to construct Fe3O4 nanocrystals/mesoporous carbon hollow spheres core-shell hybrids toward microwave absorption[J]. ACS Sustainable Chemistry & Engineering,2018,6(1):1427-1435. DOI: 10.1021/acssuschemeng.7b03846
[30] QIU X, WANG L X, ZHU H L, et al. Lightweight and efficient microwave absorbing materials based on walnut shell-derived nanoporous carbon[J]. Nanoscale,2017,9(22):7408-7418. DOI: 10.1039/C7NR02628E
[31] FANG J Y, SHANG Y S, CHEN Z, et al. Rice husk-based hierarchically porous carbon and magnetic particles composites for highly efficient electromagnetic wave attenuation[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry C,2017,5(19):4695-4705. DOI: 10.1039/C7TC00987A
[32] ZHU L Y, ZENG X J, LI X P, et al. Hydrothermal synthesis of magnetic Fe3O4/graphene composites with good electromagnetic microwave absorbing performances[J]. Journal of Magnetism& Magnetic Materials,2016,426:114-120. DOI: 10.1016/j.jmmm.2016.11.063
[33] LI W X, QI H X, GUO F, et al. Co nanoparticles supported on cotton-based carbon fibers: A novel broadband microwave absorbent[J]. Journal of Alloys and Compounds,2019,772:760-769. DOI: 10.1016/j.jallcom.2018.09.075
[34] WANG H Y, ZHANG Y L, WANG Q Y, et al. Biomass carbon derived from pine nut shells decorated with NiO nanoflakes for enhanced microwave absorption properties[J]. RSC Advances,2019,9(16):9126-9135. DOI: 10.1039/C9RA00466A
[35] GAO S S, AN Q D, XIAO Z Y, et al. Significant promotion of porous architecture and magnetic Fe3O4 NPs inside honey comb like carbonaceous composites for enhanced microwave absorption[J]. RSC Advance,2018,8(34):19011-19023. DOI: 10.1039/c8ra00913a
[36] YANG M L, YUAN Y, LI Y, et al. Dramatically enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption of hierarchical CNT/Co/C fiber derived from cotton and metal-organic-framework[J]. Carbon,2020,161:517-527. DOI: 10.1016/j.carbon.2020.01.073
[37] LV H L, ZHANG H Q, ZHAO J, et al. Achieving excellent bandwidth absorption by a mirror growth process of magnetic porous polyhedron structures[J]. Nano Research,2016,9:1813-1822. DOI: 10.1007/s12274-016-1074-1
[38] WU Z C, TIAN K, HUANG T, et al. Hierarchically porous carbons derived from biomasses with excellent microwave absorption performance[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2018,10(13):11108-11115. DOI: 10.1021/acsami.7b17264
[39] ZHANG X J, WANG G S, WEI Y Z, et al. Polymer-composite with high dielectric constant and enhanced absorption properties based on graphene-CuS nanocomposites and polyvinylidene fluoride[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A,2013,1(39):12115-12122. DOI: 10.1039/c3ta12451g
[40] 谢文瀚, 耿浩然, 柳扬, 等. MoS2/生物质碳复合材料的制备与吸波性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2022, 39(5): 2238-2248. XIE Wenhan, GENG Haoran, LIU Yang, et al. Preparation and microwave absorbing properties of MoS2/biomass carbon composite [J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2022, 39(5): 2238-2248(in Chinese).
[41] TONG G X, LIU Y, CUI T T, et al. Tunable dielectric properties and excellent microwave absorbing properties of elliptical Fe3O4 nanorings[J]. Applied Physics Letters,2016,108(7):072905. DOI: 10.1063/1.4942095
[42] ZHAO B, SHAO G, FAN B B, et al. Investigation of the electromagnetic absorption properties of Ni@TiO2 and Ni@SiO2 composite microspheres with core-shell structure[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics,2015,17(4):2531-2539. DOI: 10.1039/C4CP05031B
[43] SHENG A, YANG Y Q, YAN D X, et al. Self-assembled reduced graphene oxide/nickel nanofibers with hierarchical core-shell structure for enhanced electromagnetic wave absorption[J]. Carbon,2020,167:530-540. DOI: 10.1016/j.carbon.2020.05.107
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 冯葆炜,王华清. 层合板和蜂窝夹心结构复合材料敲击特性研究. 新技术新工艺. 2024(02): 56-59 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 顾洋洋,张金栋,刘刚,刘衍腾,甘建,杨曙光. 聚芳醚酮(PAEK)树脂熔体黏度及冲击能量对其复合材料冲击损伤行为的影响. 复合材料学报. 2023(10): 5641-5653 .  本站查看
本站查看
其他类型引用(3)
-




 下载:
下载: