Hydrothermal method of rGO/Mo0.7Co0.3S2 nanocomposites for high-performance supercapacitor electrodes
-
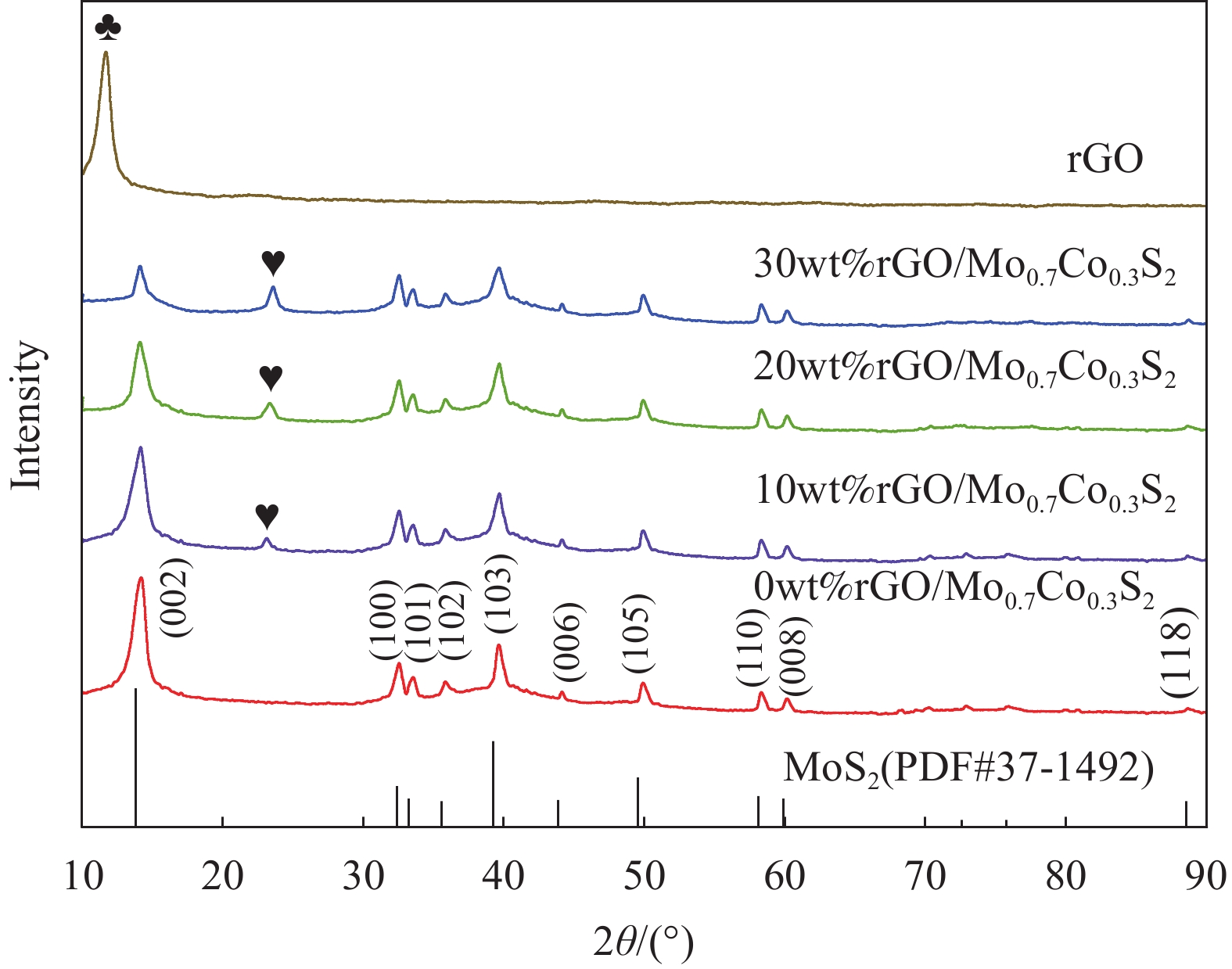
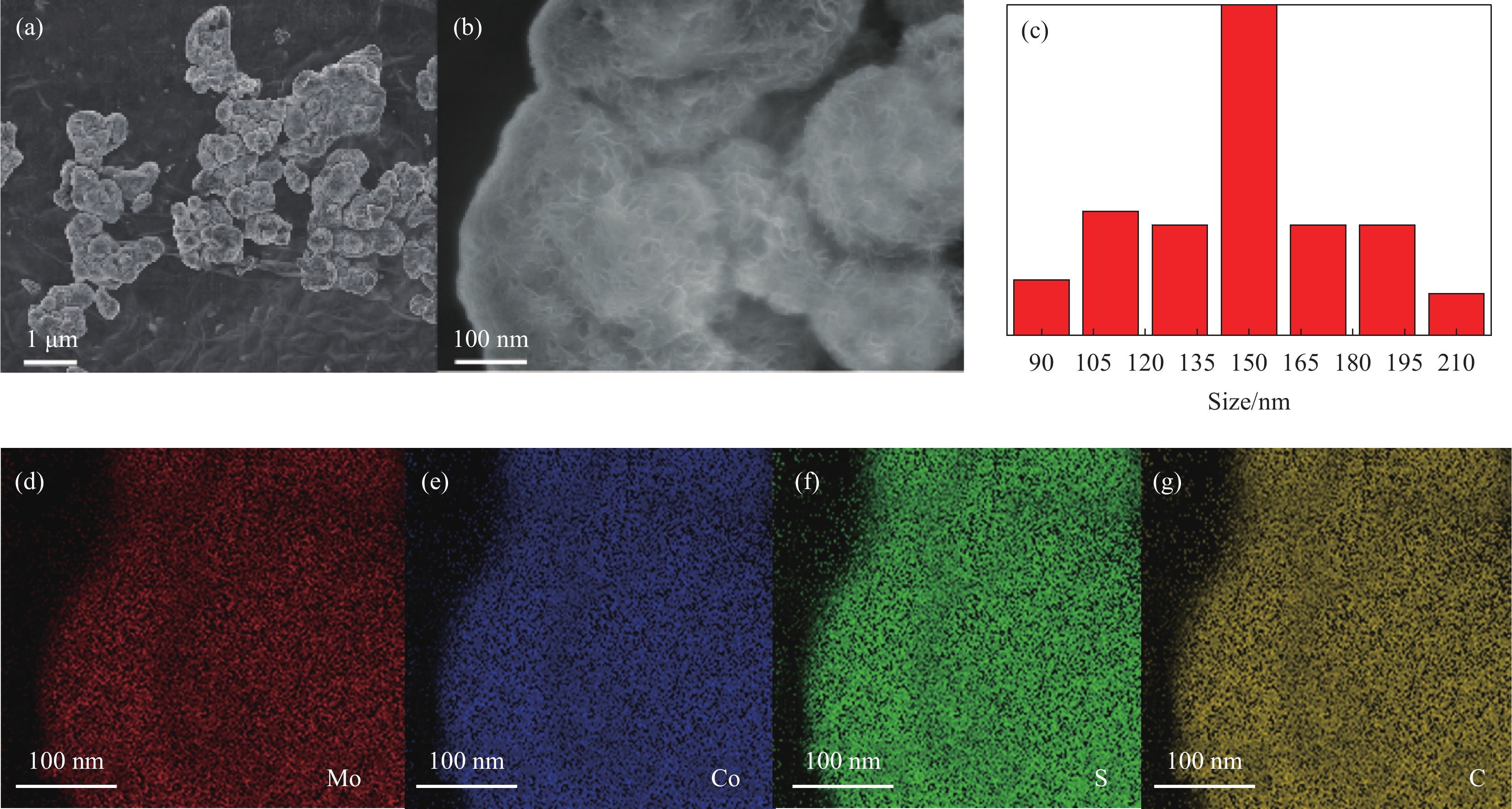
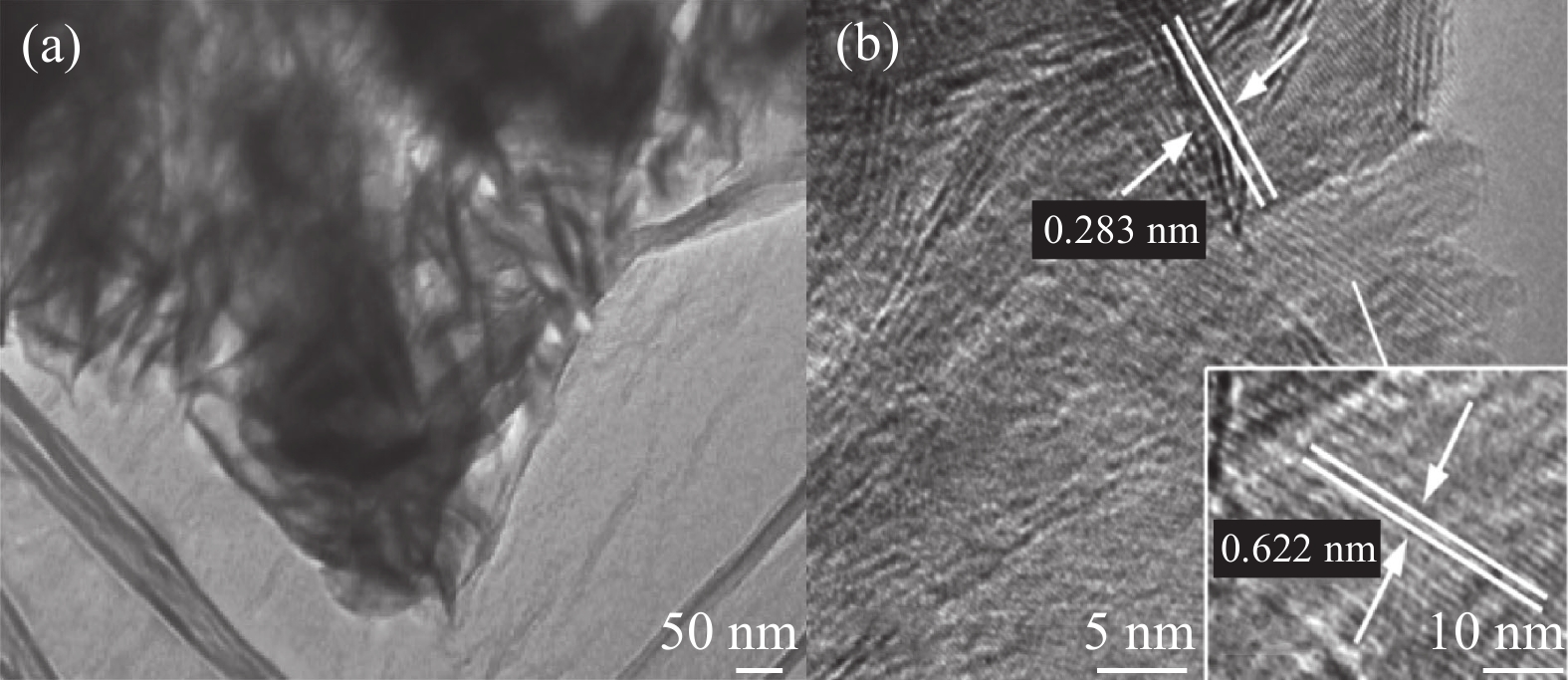
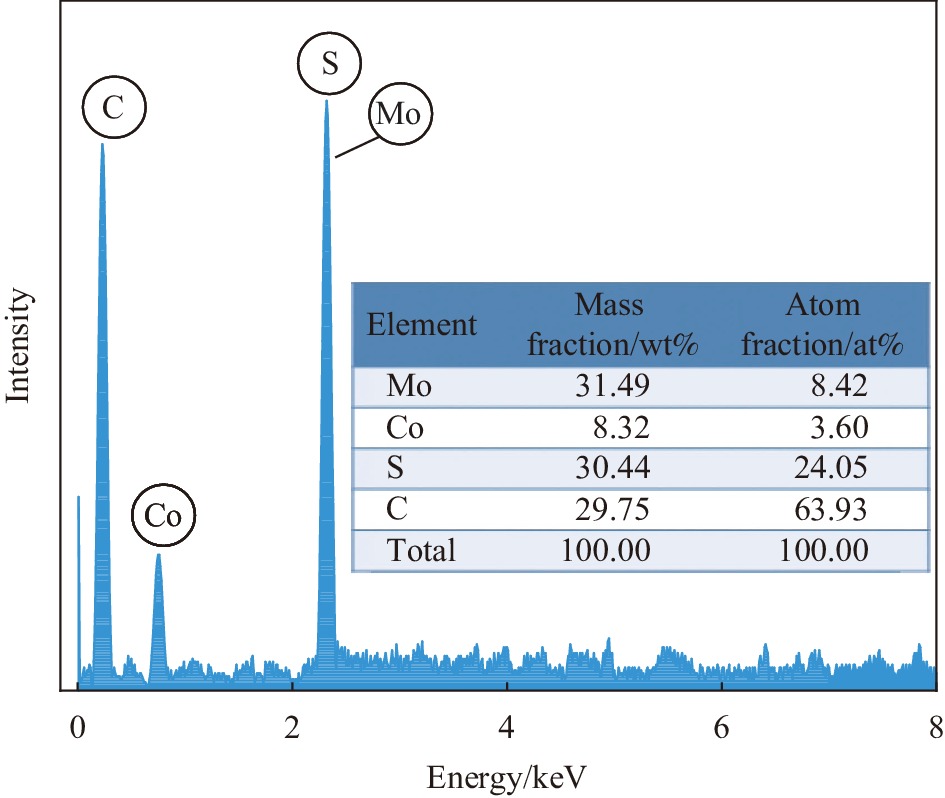
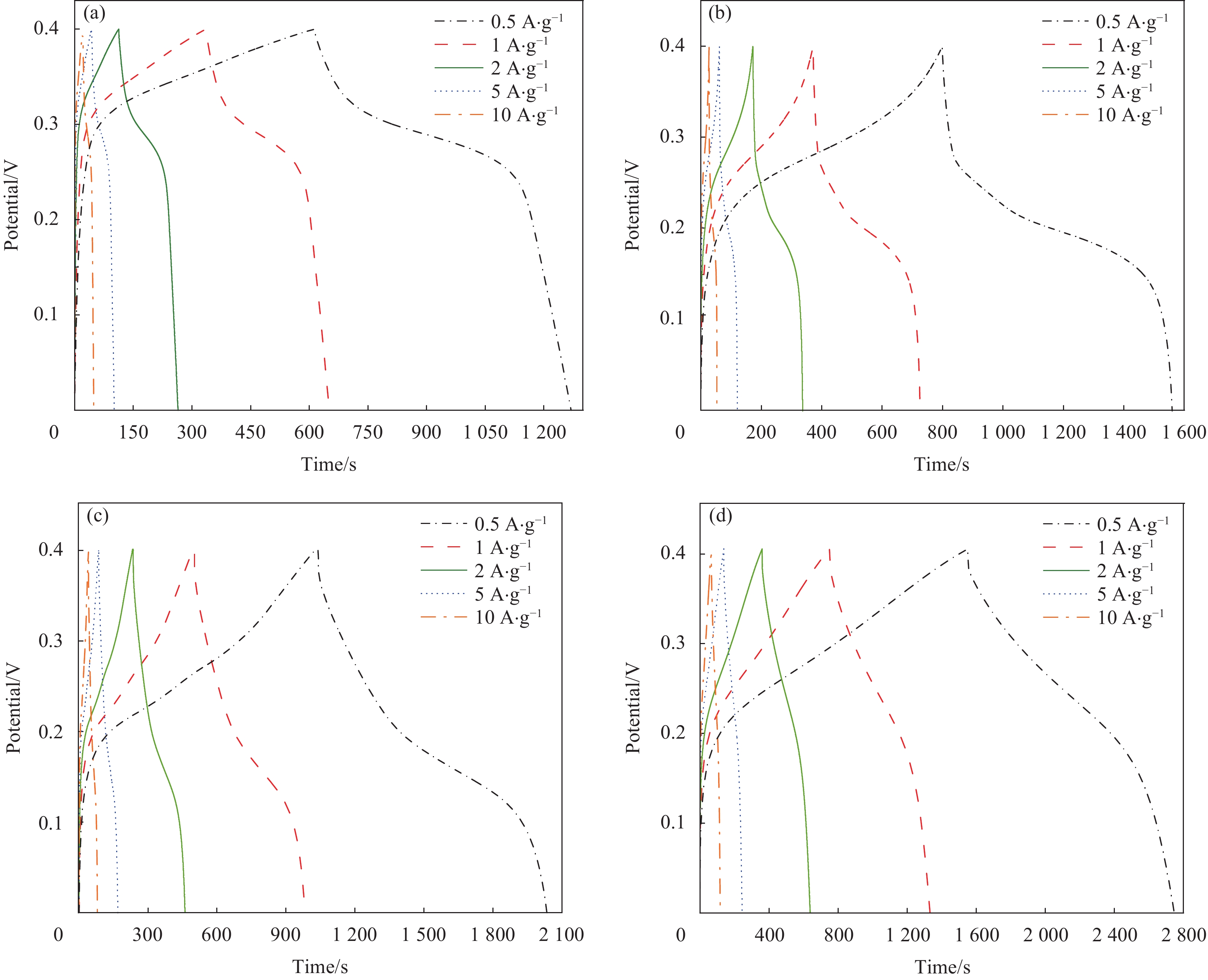
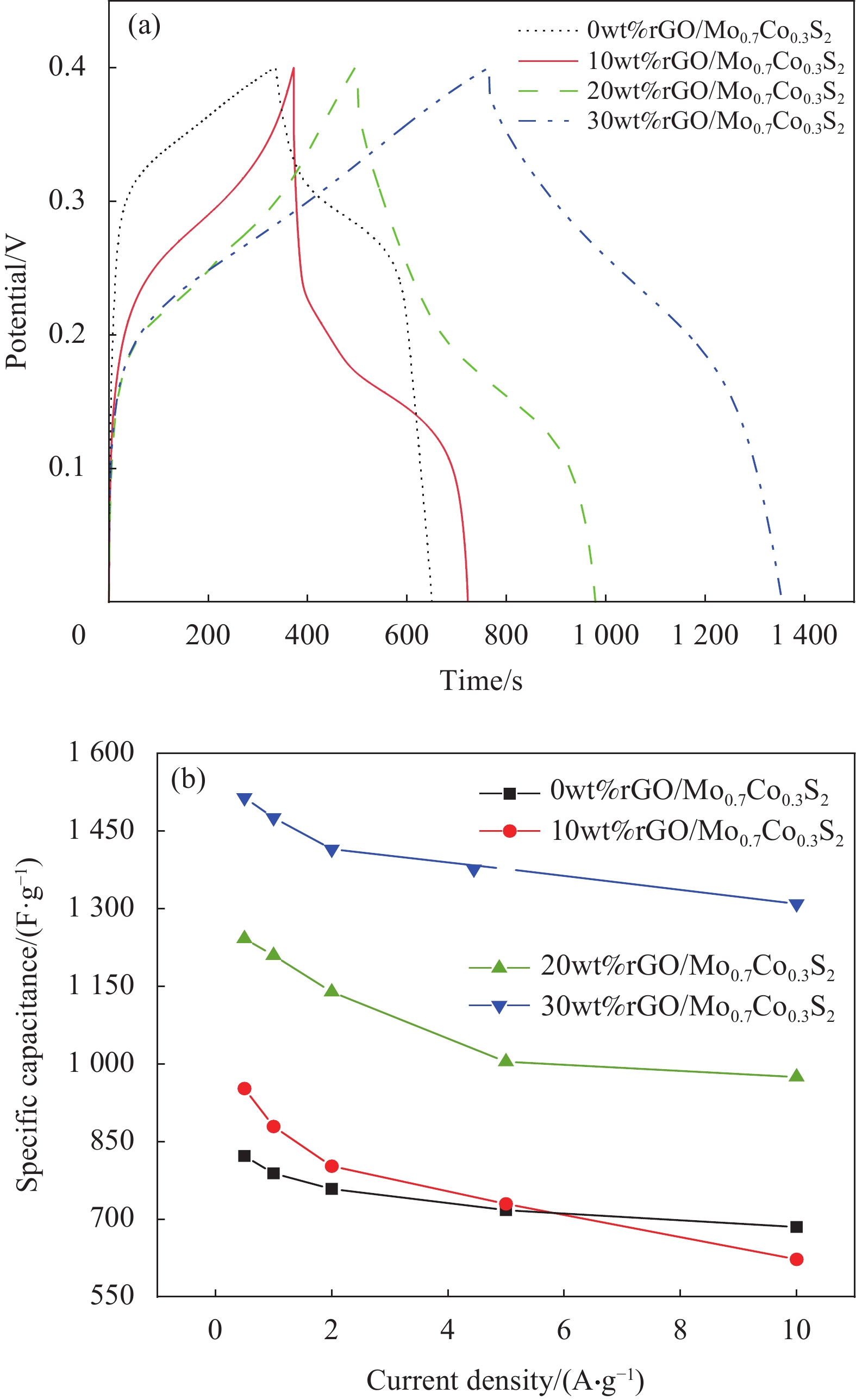
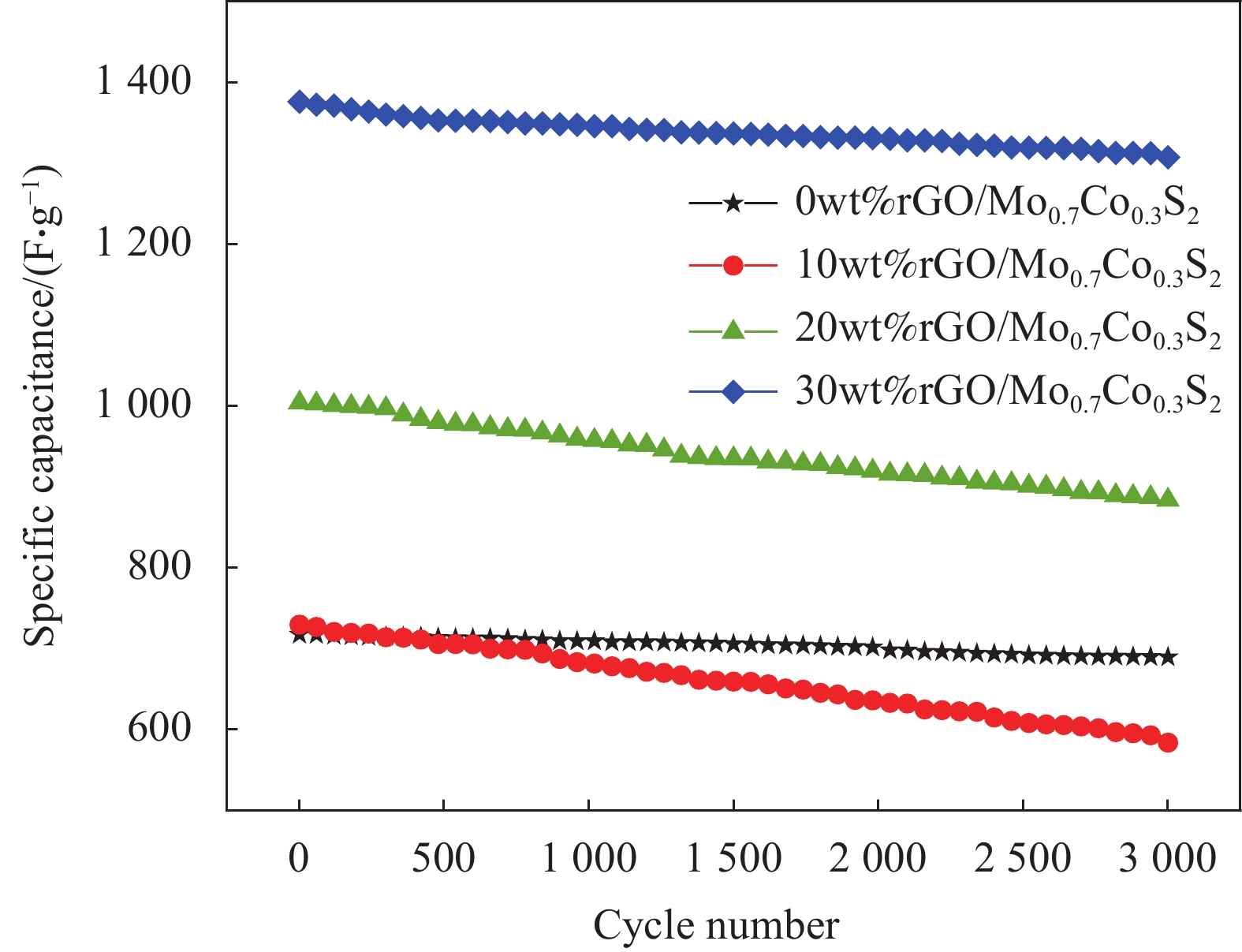
摘要: 氧化石墨烯(rGO)以广泛的比表面积(SSA)(2630 m2/g)、高电导率和化学稳定性及优异的力学、热和光学性能成为超级电容器中的佼佼者,但是氧化石墨烯本身导电性较差,因此本文通过rGO与Mo0.7Co0.3S2复合改善其性能,采用简单的水热法成功合成了rGO与Mo0.7Co0.3S2不同质量比的纳米复合材料rGO/Mo0.7Co0.3S2。通过XRD、SEM、HRTEM、EDS等手段对其物理结构进行表征。以泡沫镍为基底,聚偏氟氯乙烯为粘结剂,N-甲基吡咯烷酮作为辅助剂制作电极,在KOH为电解液的三电极电化学工作站上测试其电化学性能。实验结果表明, rGO/Mo0.7Co0.3S2纳米复合材料为六方结构,结晶良好,形貌主要为纳米花状微球结构,Mo0.7Co0.3S2纳米颗粒表面被一层纱似的rGO包裹着。rGO/Mo0.7Co0.3S2纳米复合材料表现出明显的赝电容行为,特别是rGO/Mo0.7Co0.3S2电极(rGO的含量为30wt%)表现出最大的比电容和最小的扩散阻抗,在电流密度5 A·g−1下循环3000次后rGO/Mo0.7Co0.3S2电极(rGO的含量为30wt%)的比电容值由1377.00 F·g−1降为1307.87 F·g−1,库伦效率为95%,这可能是由于Mo0.7Co0.3S2与rGO之间发生的耦合效应。Abstract: Graphene oxide (rGO) has become a leader in supercapacitors with a wide specific surface area (SSA) (2630 m2/g), high electrical conductivity and chemical stability, and excellent mechanical, thermal and optical properties. However, rGO itself has poor electrical conductivity, so in this paper, rGO is combined with Mo0.7Co0.3S2 to improve its performance. This paper was successfully synthesized different mass ratios of rGO and Mo0.7Co0.3S2 by a simple hydrothermal method. The microstructure was characterized by XRD, SEM, HRTEM, EDS. The electrode is made by using foamed nickel as the substrate, polyvinylidene chlorofluoride as the binder, and N-methyl pyrrolidone as the auxiliary agent. The electrochemical performance was tested on a three-electrode electrochemical workstation with KOH as the electrolyte. The experimental results show that all samples exhibit hexagonal system structure with good crystallization, the morphologies are flower-like microsphere shape with a certain degree of agglomeration. The surface of Mo0.7Co0.3S2 nanoparticles is wrapped by a layer of rGO like yarn. rGO/Mo0.7Co0.3S2 nanocomposite exhibits pseudo-capacitance behavior and excellent electrochemical performance, especially the Mo0.7Co0.3S2 electrode (30wt% rGO content) exhibits the largest specific capacitance and smallest impedance, and the Mo0.7Co0.3S2 electrode (30wt% rGO content) electrode reduced from 1377.00 F·g−1 to 1307.87 F·g−1 after 3000 cycles at a current density of 5 A·g−1, the coulombic efficiency is 95%, which may be due to the Coupling effect between Mo0.7Co0.3S2 and rGO.
-
Keywords:
- MoS2 /
- Co doping /
- graphene oxide /
- high specific capacitance /
- electrochemical properties /
- supercapacitor
-
-
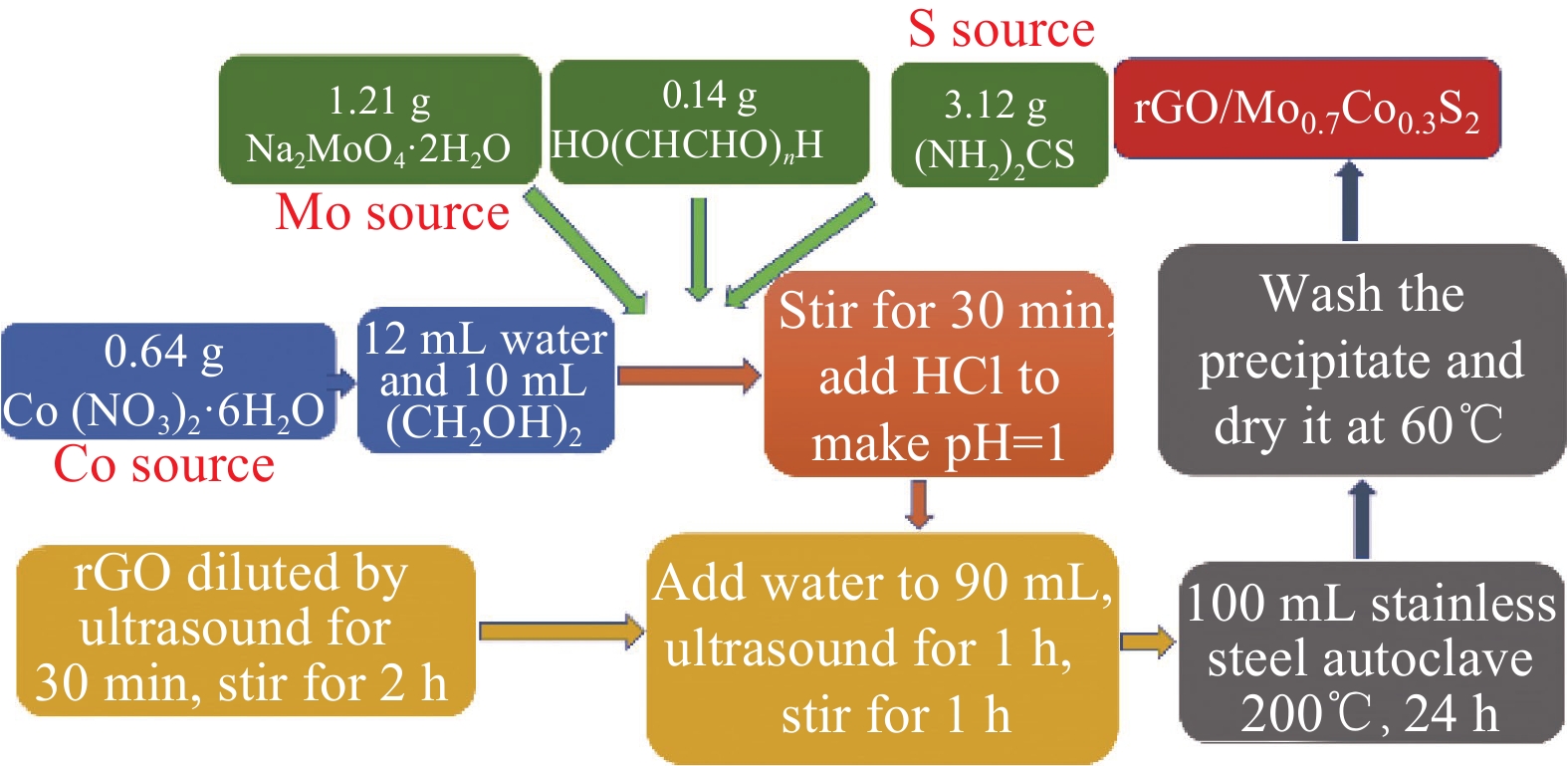
表 1 实验试剂
Table 1 Experimental reagents
Reagent Molecular formula Molecular weight Manufacturer Sodium molybdate Na2MoO4·2H2O 241.95 Sinopharm Chemical Reagent CO., LTD. Thiourea (NH2)2CS 76.12 Shanghai Aladdin Biochemical Technology CO., LTD. Hydrochloric acid HCl 36.5 Shanghai Aladdin Biochemical Technology CO., LTD. Graphite powder C 12 Sinopharm Chemical Reagent CO., LTD. Concentrated sulfuric acid H2SO4 98 Shanghai Aladdin Biochemical Technology CO., LTD. Potassium permanganate KMnO4 158.03 Sinopharm Chemical Reagent CO., LTD. Cobalt nitrate Co (NO3)2·6H2O 291.05 Shanghai Aladdin Biochemical Technology CO., LTD. Ethylene glycol (CH2OH)2 62.068 Shanghai Aladdin Biochemical Technology CO., LTD. Hydrogen peroxide H2O2 34.01 Shanghai Aladdin Biochemical Technology CO., LTD. -
[1] OUYANG T, HUANG S, WANG X T, et al. Nanostructures for electrocatalytic CO2 reduction[J]. Chemistry A European Journal,2020,26(62):14024-14035. DOI: 10.1002/chem.202000692
[2] 许进博, 董晓珠, 孔存辉, 等. SrTiO3/TiO2复合薄膜的制备及其光电化学阴极保护性能[J]. 复合材料学报, 2022, 39(8): 3929-3935. XU Jinbo, DONG Xiaozhu, KONG Cunhui, et al. Preparation of SrTiO3/TiO2 composite film and its photoelectrochemical cathodic protection performance [J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2022, 39(8): 3929-3935(in Chinese).
[3] NAZIR M S, ALI Z M, BILAL M, et al. Environmental impacts and risk factors of renewable energy paradigm—A review[J]. Environmental Science and Pollution Research,2020,27(27):33516-33526. DOI: 10.1007/s11356-020-09751-8
[4] LIPPKE B, PUETTMANN M E, JOHNSON L, et al. Carbon emission reduction impacts from alternative biofuels[J]. Forest Products Journal,2012,62(4):296-304. DOI: 10.13073/12-00021.1
[5] HUANG Y, ZHU M S, PEI Z X, et al. Extremely stable polypyrrole achieved via molecular ordering for highly flexible supercapacitors[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2016,8(3):2435-2440.
[6] CHEN W, XIA C, ALSHAREEF H N. Graphene based integrated tandem supercapacitors fabricated directly on separators[J]. Nano Energy,2015,15:1-8. DOI: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2015.03.040
[7] DONG L B, XU C J, LI Y, et al. Breathable and wearable energy storage based on highly flexible paper electrodes[J]. Advanced Materials,2016,28(42):9313-9319. DOI: 10.1002/adma.201602541
[8] ZHAO C H, ZHOU Y N, GE Z X, et al. Facile construction of MoS2/RCF electrode for high-performance supercapacitor[J]. Carbon,2018,127:699-706. DOI: 10.1016/j.carbon.2017.11.052
[9] UJJAIN S K, AHUJA P, BHATIA R, et al. Printable multi-walled carbon nanotubes thin film for high performance all solid state flexible supercapacitors[J]. Materials Research Bulletin,2016,83:167-171. DOI: 10.1016/j.materresbull.2016.06.006
[10] LI W, MA Y Q, WANG X L, et al. Electric field effects on the electronic structures of MoS2/antimonene van der Waals heterostructure.[J]. Solid State Communications,2019,293:28-32. DOI: 10.1016/j.ssc.2019.02.002
[11] WANG Y P, HUANG S, ZHAO H, et al. First principles study on properties of monolayer MoS2 under different strains[J]. Brazilian Journal of Physics,2021,51(4):1230-1236. DOI: 10.1007/s13538-021-00927-2
[12] 谢杭明, 吴汉卿, 何志伟, 等. MoS2/MXene纳米复合物的研究进展[J]. 复合材料学报, 2022, 39(3): 1005-1016. XIE Hangming, WU Hanqing, HE Zhiwei, et al. Research progress of MoS2/MXene nanocomposite [J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2022, 39(3): 1005-1016(in Chinese).
[13] BAFEKRY A, STAMPFL C, AKGENC B, et al. Control of C3N4 and C4N3 carbon nitride nanosheets' electronic and magnetic properties through embedded atoms[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics,2020,22(4):2249-2261. DOI: 10.1039/C9CP06031F
[14] VU T V, HIEU N V, THAO L T P, et al. Tailoring the structural and electronic properties of an SnSe2/MoS2 van der Waals heterostructure with an electric field and the insertion of a graphene sheet[J]. Physical Chemistry Chemical Physics,2019,21(39):22140-22148. DOI: 10.1039/C9CP04689E
[15] ACERCE M, VOIRY D, CHHOWALLA M. Metallic 1T phase MoS2 nanosheets as supercapacitor electrode materials[J]. Nature Nanotechnology,2015,10(4):313-318. DOI: 10.1038/nnano.2015.40
[16] KRIVOSHEEVA A V, SHAPOSHNIKOV V L, BORISENKO V E, et al. Theoretical study of defect impact on two-dimensional MoS2[J]. Journal of Semiconductors,2015,36(12):1220021-1220026.
[17] ZHOU Z B, ZHANG Y H, ZHANG X W, et al. Suppressing photoexcited electron-hole recombination in MoSe2/WSe2 lateral heterostructures via interface-coupled state engineering: A time-domainab initiostudy[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A,2020,8(39):20621-20628. DOI: 10.1039/D0TA06626E
[18] CHEN T T, WANG R, LI L K, et al. MOF-derived Co9S8/MoS2 embedded in tri-doped carbon hybrids for efficient electrocatalytic hydrogen evolution[J]. Journal of Energy Chemistry,2020,44:90-96. DOI: 10.1016/j.jechem.2019.09.018
[19] HU J Y, LI Y H, ZHANG S S, et al. MoS2 supported on hydrogenated TiO2 heterostructure film as photocathode for photoelectrochemical hydrogen production[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy,2019,44(59):31008-31019. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2019.09.238
[20] MISHRA R K, CHOI G J, SOHN Y, et al. A novel rGO/N-rGO supercapacitor architecture for a wide voltage window, high energy density and long-life via voltage holding tests[J]. Chemical Communications,2020,56(19):2893-2896. DOI: 10.1039/D0CC00249F
[21] CHITHAIAH P, RAJU M M, KULKARNI G U, et al. Simple synthesis of nanosheets of rGO and nitrogenated rGO[J]. Beilstein Journal of Nanotechnology,2020,11:68-75. DOI: 10.3762/bjnano.11.7
[22] AHAMED M, AKHTAR M J, KHAN M A M, et al. SnO2-doped ZnO/reduced graphene oxide nanocomposites: Synthesis, characterization, and improved anticancer activity via oxidative stress pathway[J]. International Journal of Nanomedicine,2021,16:89-104. DOI: 10.2147/IJN.S285392
[23] HE G P, BAI Y X, HUANG F, et al. Enhanced electrochemical energy storage of rGO@CoxSy through nanostructural modulation[J]. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics,2021,32(10):13639-13655. DOI: 10.1007/s10854-021-05942-2
[24] 叶喜葱, 欧阳宾, 杨超, 等. 石墨烯-羰基铁粉线材的制备及其吸波性能分析[J]. 复合材料学报, 2022, 39(7): 3292-3302. YE Xicong, OUYANG bin, YANG Chao, et al. Preparation of graphene-carbonyl iron powder wire and analysis of its absorbing properties [J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica, 2022, 39(7): 3292-3302(in Chinese).
[25] WEI Y, ZHANG X, ZHAO Z L, et al. Controllable synthesis of P-doped MoS2 nanopetals decorated N-doped hollow carbon spheres towards enhanced hydrogen evolution[J]. Electrochimica Acta,2019,297:553-563. DOI: 10.1016/j.electacta.2018.12.019
[26] GUO S N, MIN Y L, FAN J C, et al. Stabilizing and improving solar H-2 generation from Zn0.5Cd0.5S nanorods@MoS2/rGO hybrids via dual charge transfer pathway[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2016,8(5):2928-2934.
[27] ZHAO Y, ZHANG X, WANG T, et al. Fabrication of rGO/CdS@2H, 1T, amorphous MoS2 heterostructure for enhanced photocatalytic and electrocatalytic activity[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy,2020,45(41):21409-21421. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2020.05.217
[28] CHE Z Z, LI Y F, CHEN K X, et al. Hierarchical MoS2@rGO nanosheets for high performance sodium storage[J]. Journal of Power Sources,2016,331:50-57. DOI: 10.1016/j.jpowsour.2016.08.139
[29] JIA Y L, WANG Z H, WANG L Y, et al. Awakening solar hydrogen evolution of MoS2 in alkalescent electrolyte through doping with Co[J]. ChemSusChem,2019,12(14):3336-3342. DOI: 10.1002/cssc.201900936
[30] CHEN Z Y, YAN H X, LIU T Y, et al. Improved mechanical and tribological properties of bismaleimide composites by surface-functionalized reduced graphene oxide and MoS2 coated with cyclotriphosphazene polymer[J]. RSC Advances,2015,5(118):97883-97890. DOI: 10.1039/C5RA19101G
[31] EL-SHAHAT M, MOKHTAR M, RASHAD M M, et al. Electrical studies on a single, binary, and ternary nanocomposites of Mn3O4@TiO2@rGO[J]. Journal of Materials Science: Materials in Electronics,2021,32(8):10224-10239. DOI: 10.1007/s10854-021-05678-z
[32] KUMAR R. NiCo2O4 nano-/microstructures as high-performance biosensors: A review[J]. Nano-Micro Letters,2020,12(9):262-313.
[33] CHENG H, SHAPTER J G, LI Y Y, et al. Recent progress of advanced anode materials of lithium-ion batteries[J]. Journal of Energy Chemistry,2021,57(6):451-468.
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 柯俊,李志虎,秦玉林. 金属主簧-复合材料副簧复合刚度计算模型. 汽车实用技术. 2021(05): 39-43 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 曾婷,王咏莉,尹忠旺,苏婷慧,师志峰,饶猛. 端面凸轮下压机构支承轴承冲击失效分析及优化(英文). 机床与液压. 2017(24): 37-42 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(5)
-




 下载:
下载: