Application of photocatalytic degradation of formaldehyde by g-C3N4-Ag/SiO2 heterostructure composites
-
摘要: 将Ag、薄层石墨相氮化碳(g-C3N4)和硅铝胶球(SiO2)通过液相超声剥离-光化学沉积法-浸渍法合成复合光催化材料。设计甲醛降解密闭实验舱,探究g-C3N4、Ag-g-C3N4和g-C3N4-Ag/SiO2材料的光催化特性及其对甲醛的降解效果。结果表明,在可见光源条件下,对于g-C3N4-Ag/SiO2材料,降解甲醛的效率最高可达到65.6%。40%的相对湿度可有效提升降解效果。负载30 mg 4%Ag/g-C3N4的硅铝胶球循环使用16次时,甲醛降解效率仅下降9.71%。结合材料表征结果表明,通过超声剥离和Ag的引入,提升了材料可见光的吸收强度和吸收范围,并且有效促进了光生电子和空穴的分离,有效提升甲醛分子的降解效率。研究结果表明g-C3N4-Ag/SiO2材料具有优异的稳定性和良好的光催化性能,为实际有机污染物治理的应用提供了较好的科学基础。Abstract: Composite photocatalytic materials were synthesized by liquid-phase ultrasonic exfoliation-photochemical deposition method-impregnation method of monolithic Ag, thin layer of graphitic phase carbon nitride (g-C3N4) and silica-alumina colloidal spheres (SiO2). A formaldehyde degradation hermetic chamber was designed to investigate the photocatalytic properties of g-C3N4, Ag-g-C3N4 and g-C3N4-Ag/SiO2 materials and their degradation effects on formaldehyde. The results show that the efficiency of degradation of formaldehyde can reach up to 65.6% for SAG materials under visible light source conditions. 40% relative humidity can effectively enhance the degradation efficiency.The formaldehyde degradation efficiency decreases by only 9.71% when the silica-alumina spheres load with 30 mg 4%Ag/g-C3N4 are recycled for 16 times. The results of material characterization show that the visible light absorption intensity and absorption range of the material are enhanced by ultrasonic stripping and the introduction of Ag, and the separation of photogenerated electrons and holes are effectively promoted, which effectively enhance the degradation efficiency of formaldehyde molecules. The results show that the g-C3N4-Ag/SiO2 material has excellent stability and good photocatalytic performance, which provides a better scientific basis for the application of practical organic pollutant treatment.
-
挥发性有机物(VOCs)由于其种类多、挥发性强、毒性强、刺激性强等特点已日益成为室内污染的主要元凶。家具、板材、油漆、车内饰品等环境中多含有并释放甲醛[1-4],甲醛于2005年被国际癌症研究机构列为I类致癌物,人类吸入高浓度甲醛可导致支气管哮喘、肺炎等呼吸道疾病,若经口摄入10~20 mL的甲醛溶液会致死[5]。从某种意义上讲,甲醛的存在已与人们的生命安全息息相关[6]。
甲醛治理技术主要有吸附法[7]、低温等离子体技术[8]、微生物过滤法[9]、光催化技术,其中光催化技术由于其操作方便和成本低的优点逐渐被人们所关注。石墨相氮化碳(g-C3N4)作为光催化材料,化学合成方法简单,成本低廉,并且具有较窄的带隙(2.7 eV)、较高的可见光响应,但由于其比表面积较小且具有光生载流子的复合率较高的缺陷,导致其光催化活性偏低,因此g-C3N4材料难以单独作为光催化剂[10-11]。增强材料光催化活性的常见方法有形态结构调整、金属/非金属掺杂、异质结工程等方法[10]。较小尺寸的颗粒具有更高的光催化性能和活性,Wang等[12]成功制备了具有较大比表面积的g-C3N4材料,作为催化剂在可见光条件下的产氢速率比块状g-C3N4高出1个数量级。Ag的修饰可以提升光生电子和空穴分离,Zhou等[13]利用光还原沉积法将纳米Ag颗粒成功负载到g-C3N4的表面,并且该材料在可见光下降解罗丹明B的效率为单一g-C3N4的7倍。硅铝胶球的主要成分为SiO2和Al2O3,虽然硅铝胶球化学性质稳定,主要成分不参与光催化过程,但其中SiO2[14]以其优异的机械强度、高的内表面积和均匀的孔径,被广泛用作载体和稳定的介孔载体。对其扩孔可增加催化剂负载量,提供更多反应位点,是优秀的催化剂载体。
为此,本研究采用扩孔硅铝胶球作为光催化剂载体负载Ag掺杂的薄层g-C3N4光催化降解甲醛,探究了合成材料的最佳影响参数和提升光催化性能的机理,选取最佳光催化材料进行了循环稳定性实验和不同湿度梯度的降解实验,以期为光催化降解甲醛及其他有机污染物提供科学依据和技术支持。
1. 材料与方法
1.1 原材料
本实验采用的二氰二胺、乙二醇、乙醇、硝酸银、酚试剂指示剂、硫酸铁铵、硫代硫酸钠、甲醛标准溶液等化学试剂均为分析纯,购自上海阿拉丁生化科技股份有限公司。
1.2 材料制备
1.2.1 薄层g-C3N4的制备
块状g-C3N4制备:将10 g二氰二氨固体置于氧化铝坩埚中后放入马弗炉,在空气气氛下煅烧,540℃加热2 h(升温速率2℃/min),冷却至室温,得到淡黄色固体研磨成粉末,g-C3N4粉末标记为g-C3N4-B。
薄层g-C3N4制备:取150 mg g-C3N4粉末于玻璃瓶中,加入200 mL无水乙醇和水的混合液,超声处理一定时间使其分散均匀,离心分离固体,经洗涤、烘干和研磨得到薄层g-C3N4,标记为g-C3N4-F。
1.2.2 薄层g-C3N4掺杂Ag的制备
分别取500 mg g-C3N4-F粉末于6支100 mL玻璃管中,加入25 mL蒸馏水,磁力搅拌10 min,加入5 mL浓度分别为0、1 mg/mL、2 mg/mL、4 mg/mL、8 mg/mL、12 mg/mL、16 mg/mL的AgNO3溶液。再加入2 mL浓度为1 mg/mL硫化钠溶液作为空穴牺牲剂,然后通10 minN2。将玻璃管置于光反应器中,300 W氙灯照射2 h后,洗涤、烘干、研磨,获得g-C3N4掺杂不同质量比的Ag的粉末。分别记为0、1%Ag-g-C3N4-F、2%Ag-g-C3N4-F、4%Ag-g-C3N4-F、8%Ag-g-C3N4-F、12%Ag-g-C3N4-F、16%Ag-g-C3N4-F(见表1)。
1.2.3 g-C3N4-Ag/SiO2光催化材料的制备
扩孔硅铝胶球:将一定量的硅铝胶球(粒径8 mm,孔径范围为10~50 nm)置入40 mg/L碳酸钠溶液中,磁力搅拌30 min,80℃烘干,放入马弗炉中300℃煅烧2 h (1℃/min升温),冷却至室温,用乙醇和蒸馏水洗涤,80℃烘干后备用。
g-C3N4-Ag/SiO2:取2.2.1节中甲醛降解效率最高的Ag-g-C3N4-F样品10 mg、20 mg、30 mg、40 mg、50 mg加入100 mL无水乙醇,超声分散均匀,然后分别加入30 g经过扩孔处理的硅铝胶球,磁力搅拌30 min,80℃烘干,置于马弗炉中200℃煅烧2 h(升温速率1℃/min)。将样品分别标记为g-C3N4-Ag/SiO2-10、g-C3N4-Ag/SiO2-20、g-C3N4-Ag/SiO2-30、g-C3N4-Ag/SiO2-40、g-C3N4-Ag/SiO2-50(见表2)。
表 1 Ag-薄层石墨相氮化碳(g-C3N4-F)复合材料的命名Table 1. Naming of Ag-thin layer graphite phase carbon nitride (g-C3N4-F) compositesSample g-C3N4-F/mg Concentration of AgNO3/(mg·mL−1) AgNO3/mL Na2S/mL 0 500 0 5 2 1%Ag-g-C3N4-F 500 1 5 2 2%Ag-g-C3N4-F 500 2 5 2 4%Ag-g-C3N4-F 500 4 5 2 8%Ag-g-C3N4-F 500 8 5 2 12%Ag-g-C3N4-F 500 12 5 2 16%Ag-g-C3N4-F 500 16 5 2 表 2 石墨相氮化碳(g-C3N4)-Ag/SiO2复合材料的命名Table 2. Naming of graphite phase carbon nitride (g-C3N4)-Ag/SiO2 compositesSample Ag-g-C3N4-F/mg SiO2/g Ethyl alcohol/mL g-C3N4-Ag/SiO2-10 10 30 100 g-C3N4-Ag/SiO2-20 20 30 100 g-C3N4-Ag/SiO2-30 30 30 100 g-C3N4-Ag/SiO2-40 40 30 100 g-C3N4-Ag/SiO2-50 50 30 100 1.3 材料的表征
利用X射线衍射(X-Ray Diffraction,XRD,日本岛津公司,Empyrean型,测试条件:Cu Kα射线,加速电压40 kV,2θ范围20°~90°)对材料的晶体结构、晶格缺陷和组成成分表征。利用场发射扫描电子显微镜(JSM-7900F,日本电子株式会社(JEOL))和场发射透射电子显微镜(Tecnai G2 F20 S-TWIN,美国FEI公司)展示材料微观形态。采用X射线能谱仪(EDS,Escalab 250Xi型,美国费希尔公司)对材料进行元素分析。利用紫外-可见漫反射光谱(UV-vis DRS,Cary 5000,以BaSO4为标准白板,分辨率低于0.2 nm,平均停留时间为0.2 s,数据间隔1 nm)测试样品对光的吸收能力及分析能带结构。利用荧光光谱(PL,Cary 100,Xe灯为激发光源)分析半导体光生电子-空穴负荷率,探究其分离效率。采用电化学工作站(LK1100A,300 W Xe灯,波长范围420~780 nm)作为激发光源对样品的电化学特性进行表征,测试样品的光电流响应曲线和电化学阻抗。
1.4 光催化降解甲醛实验
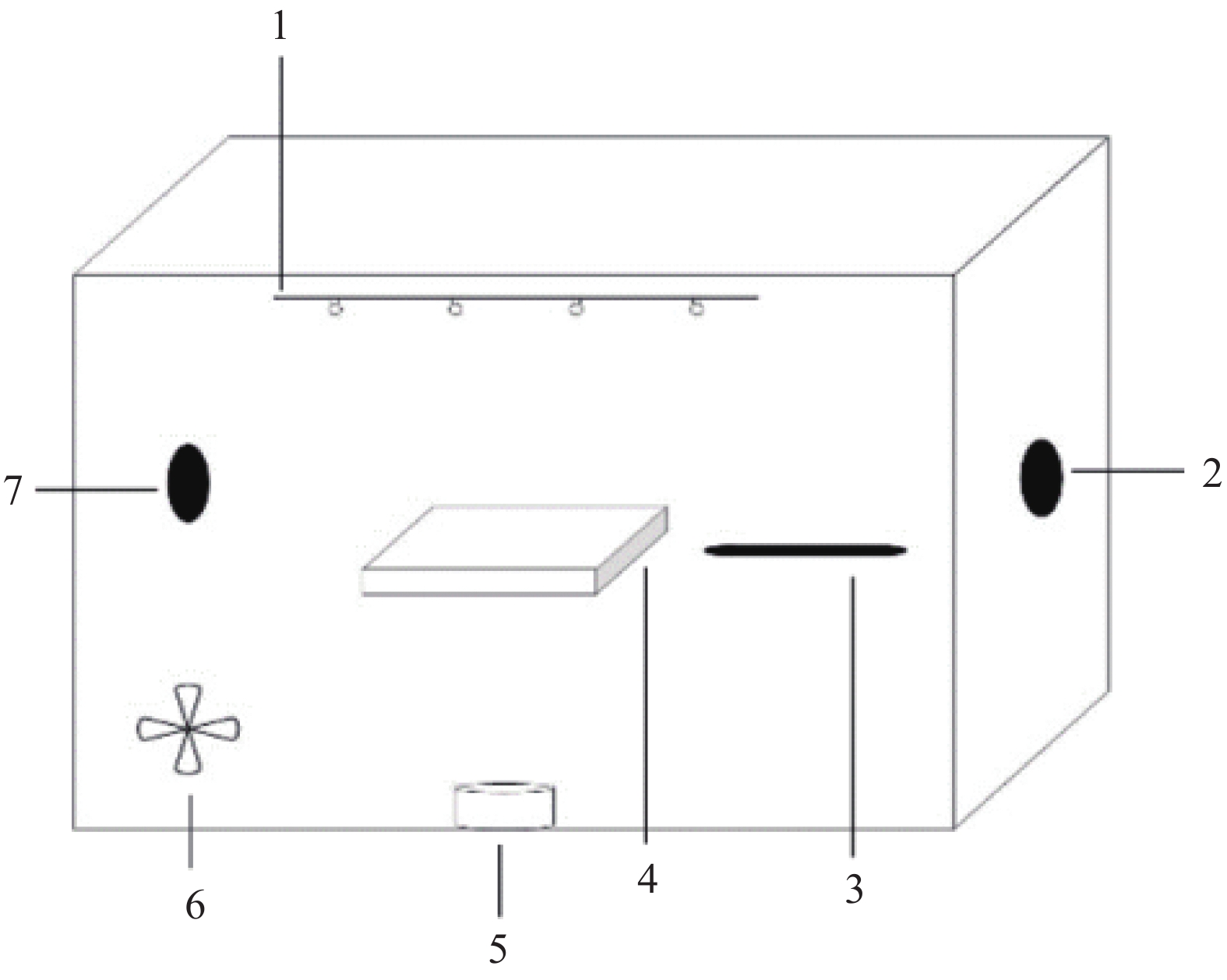
图1为自制的甲醛降解实验舱,光催化降解甲醛实验在此中进行,测试时,将光催化剂放入支架,密封后注入甲醛,打开风扇和甲醛挥发装置,待甲醛完全挥发且混合均匀后,进行暗反应,然后打开灯照射光催化剂,进行光催化反应2 h,采用酚试剂分光光度法测量甲醛浓度,甲醛的初始浓度为0.5 mg/m3。光源为家庭常用8 W白光LED灯,波长范围为450~460 nm。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 g-C3N4-Ag/SiO2材料的表征结果与分析
2.1.1 成分组成与分析
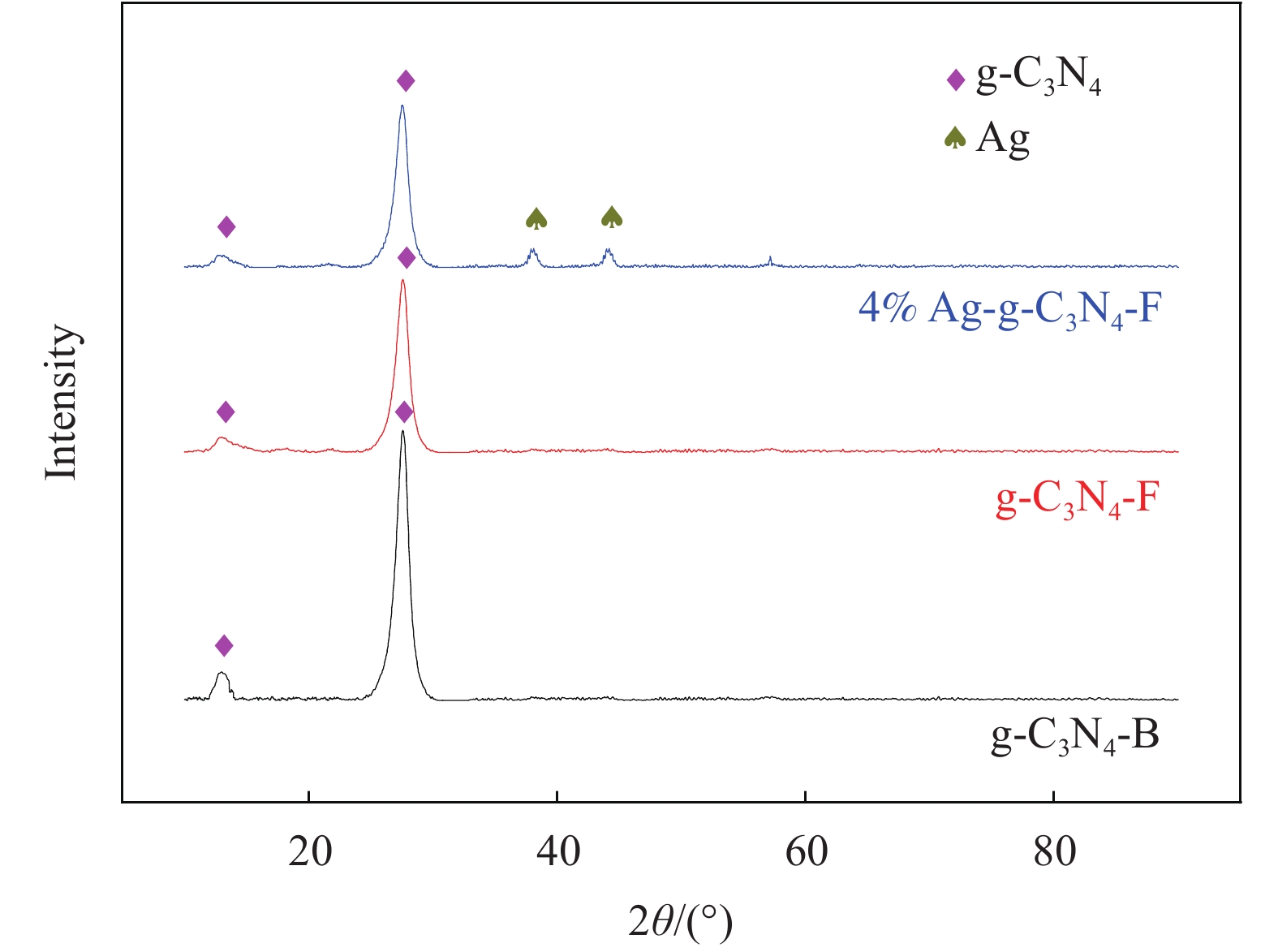
图2为g-C3N4-B、g-C3N4-F和4%Ag-g-C3N4-F材料的XRD图谱。可见,g-C3N4-B、g-C3N4-F和4%Ag-g-C3N4-F在2θ为13.6°和27.3°处存在g-C3N4的特征衍射峰,依次对应g-C3N4的碳氮杂环结构的(100)晶面和层间堆叠结构的(002)晶面[15-16],峰型尖锐且没有其他杂峰,说明g-C3N4结晶度较高,超声处理和光沉积没有改变g-C3N4的晶型,在2θ=13.6°的特征衍射峰位置上,g-C3N4-F明显低于g-C3N4-B,说明超声处理破坏了(002)晶面对应的层状堆叠结构,纵向尺寸减小[17],薄层g-C3N4制备成功;4%Ag-g-C3N4-F的XRD图谱在2θ为38.1°和44.2°的位置上出现Ag的特征衍射峰,依次对应Ag面心立方晶型的(111)和(200)晶面[18],另外与g-C3N4-B/g-C3N4-F对比看出,Ag掺杂后的4%Ag-g-C3N4-F材料,仍然存在明显且尖锐的g-C3N4特征衍射峰,没有其他杂峰,表明超声处理和光沉积没有改变4%Ag-g-C3N4-F中g-C3N4的晶型。
2.1.2 微观形貌与分析
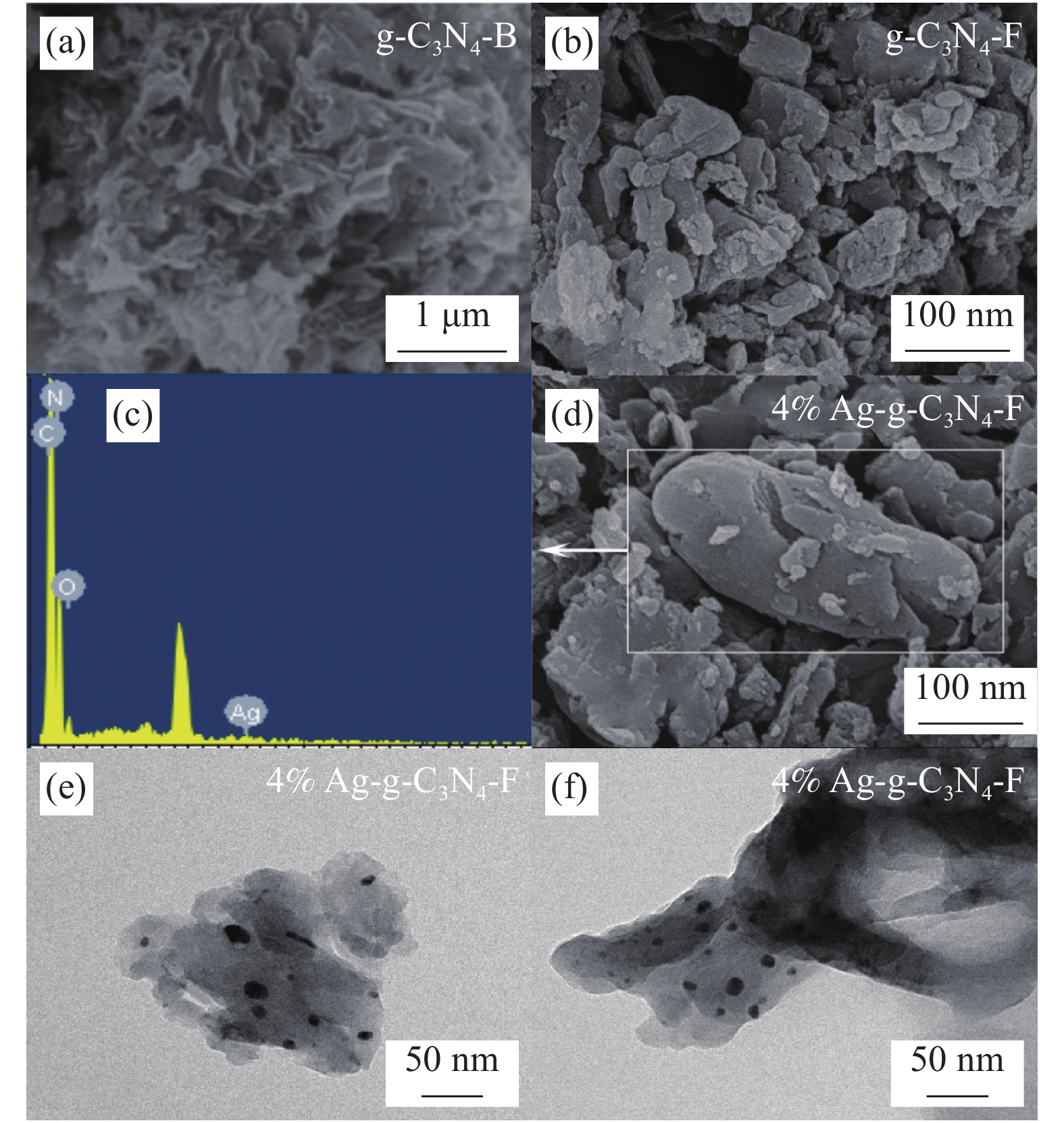
图3为g-C3N4-B、g-C3N4-F和4%Ag-g-C3N4-F材料的SEM、TEM图像和EDS图谱。如图3(a)所示,g-C3N4-B表面呈现弯曲褶皱,横向尺寸达到微米级以上。图3(b)显示g-C3N4经过超声处理后,横向尺寸减小,并且材料表面均匀光滑,没有破碎和褶皱。如图3(d)所示,g-C3N4-F表面负载了椭球体和不规则片层状的颗粒,TEM图像表明该纳米级颗粒分散均匀,结合EDS结果说明成功将纳米级单质Ag负载到4%Ag-g-C3N4-F表面。
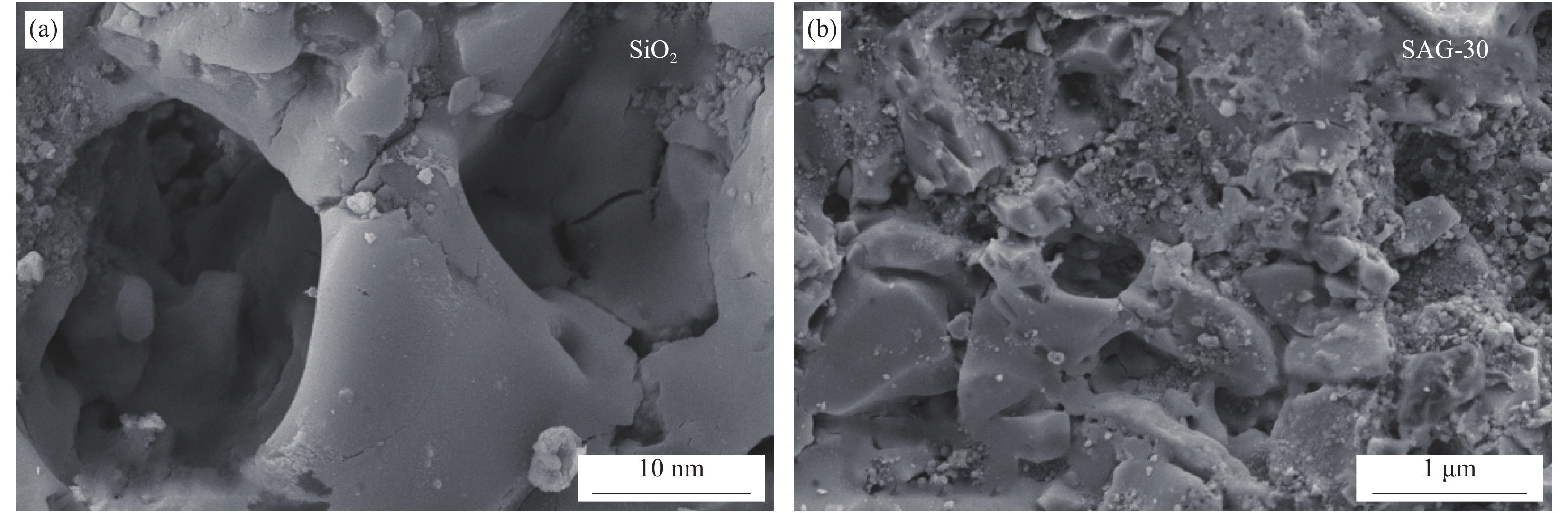
图4为SiO2和g-C3N4-Ag/SiO2-30的SEM图像。如图4(b)所示,经扩孔处理的硅铝胶球(g-C3N4-Ag/SiO2-30)的孔容积增大,孔径最大达到微米级,负载了Ag-g-C3N4的SiO2表面更粗糙,表明4%Ag-g-C3N4-F成功负载到扩孔硅铝胶球的表面和部分孔道结构中。但是可以看出部分孔道和表面没有Ag-g-C3N4的负载,负载的并不均匀。
2.1.3 紫外可见光吸光性与分析
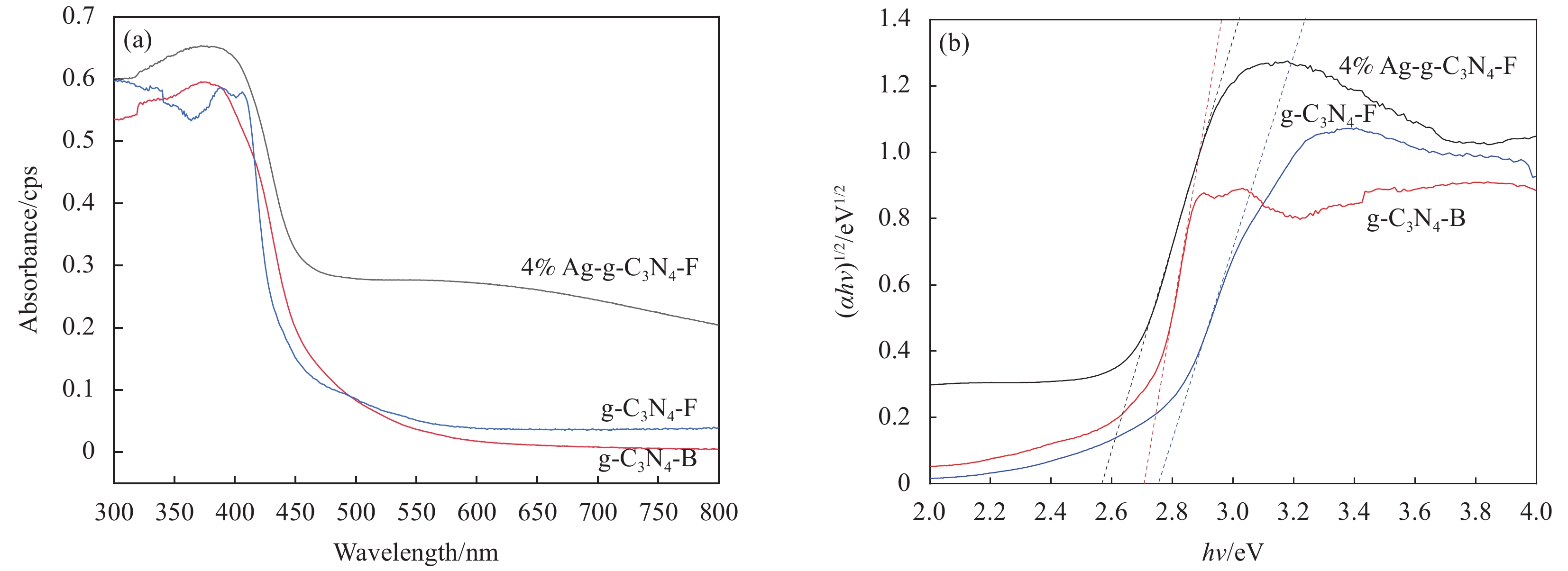
图5为g-C3N4-B、g-C3N4-F和4%Ag-g-C3N4-F材料的紫外可见光吸收光谱图。如图5(a)所示,g-C3N4-B、g-C3N4-F和4%Ag-g-C3N4-F这3种材料都有吸收带边。g-C3N4-B吸收带边位于460 nm附近,能带间隙为2.69 eV,说明g-C3N4-B有可见光响应,与文献[19]报道一致。g-C3N4-F的吸收带边相对g-C3N4-B,发生蓝移在450 nm附近,带隙约为2.75 eV,这是由于超声处理后g-C3N4-F的量子尺寸效应导致能隙变大,使其吸收带边发生蓝移[15,20]。4%Ag-g-C3N4-F的吸收带边相对于g-C3N4-F,发生了明显的红移,在480 nm附近,带隙为2.58 eV,说明掺杂的纳米单质Ag,能显著地提升g-C3N4-F对可见光的吸收强度和吸收范围,出现这种情况的原因在于纳米单质Ag的等离子体产生了共振效应[18,21]。
2.1.4 荧光光谱结果与分析
图6为g-C3N4-B、g-C3N4-F和4%Ag-g-C3N4-F材料的荧光光谱图。可见,3种材料均在450 nm附近有明显的g-C3N4特征峰,与Zhou等[22]和Shi等[23]研究结果一致。g-C3N4-F的荧光强度明显低于g-C3N4-B,表明经超声处理后的g-C3N4-F比g-C3N4-B具有更低的光生载流子复合率,更高的分离率和迁移率,从而产生更多的光生电子和空穴参与光催化。g-C3N4主要依靠范德华力和氢键作用于材料的层状结构,因此具有较高的势垒,阻碍了光生电子与空穴的迁移,而超声剥离使g-C3N4纵向尺寸变小,降低了层与层之间的氢键和范德华力,减小了势垒[20],促进光生电子和空穴的分离和迁移,进而增强了光催化效率。4%Ag-g-C3N4-F的荧光强度明显低于g-C3N4-F,表明纳米单质Ag的掺杂,极大地提升了光生电子和空穴的分离率和迁移率,这是由于Ag具有较大的电负性,可在g-C3N4与Ag的交界处形成电子势阱,进而提升光生电子向交界处的迁移率。同时Ag具有优异的导电性,迁移到交界处的光生电子会迅速迁移到Ag表面并传递给受体,从而提升了光催化效率[21]。
2.1.5 电化学结果与分析
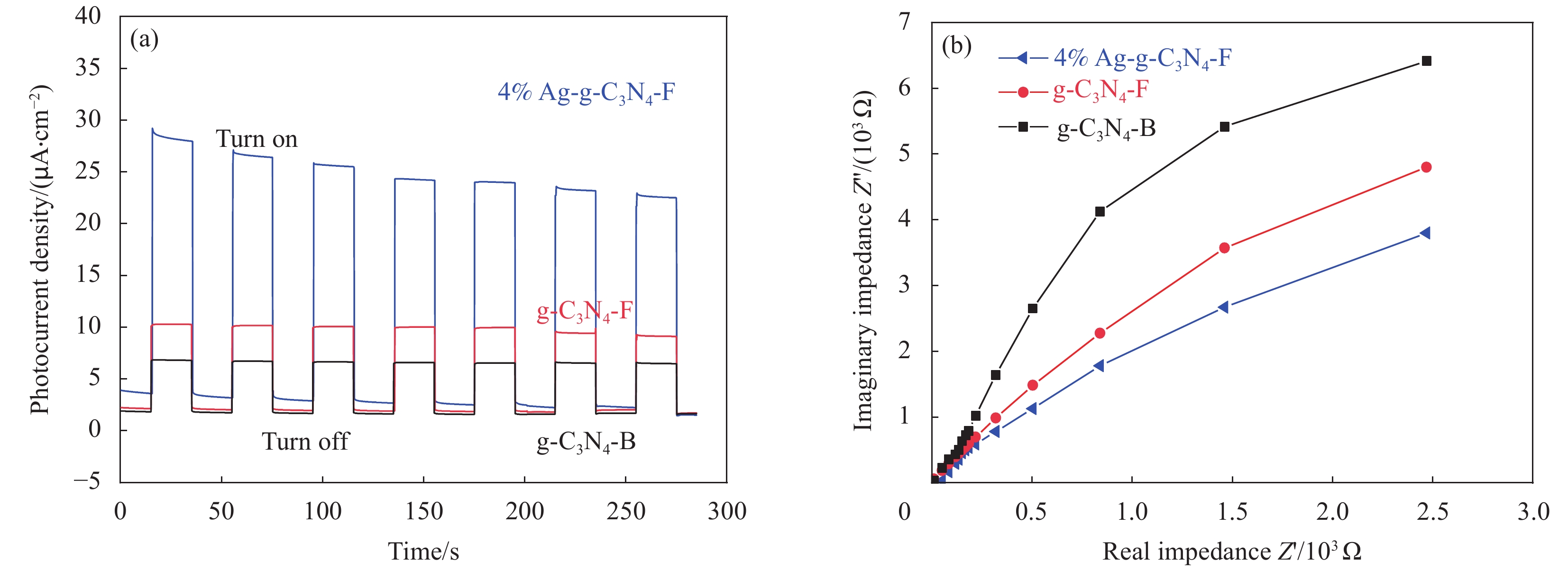
图7是g-C3N4-B、g-C3N4-F和4%Ag-g-C3N4-F材料的光电流响应曲线和电化学阻抗曲线。光电流响应曲线显示光催化材料在光照条件下产生光电流的强度,电化学阻抗显示光生载流子在材料内部转移的阻抗大小。如图7(a)所示,3种材料在光照条件下均产生了光电流,g-C3N4-F和4%Ag/g-C3N4-F的光电流密度分别达到了g-C3N4-B的1.7倍和4倍,这是由于调控g-C3N4的尺寸和掺杂纳米单质Ag可以有效提高其光生电子和空穴的分离效率,并且Ag的掺杂可以显著加快光生载流子的迁移效率。图7(b)所示,3种材料的化学阻抗曲线均为圆弧状曲线,圆弧半径越大电荷迁移阻抗就越大,圆弧半径的大小排列顺序为g-C3N4-B>g-C3N4-F>4%Ag-g-C3N4-F,说明尺寸调控和纳米单质Ag的掺杂能够降低阻抗,加快光生载流子的迁移效率,这与荧光光谱和光电流响应曲线的结果一致。
2.2 g-C3N4掺杂Ag、SiO2对光催化性能的影响
2.2.1 薄层g-C3N4掺杂不同质量比Ag对甲醛光催化降解效果的影响
图8是薄层g-C3N4掺杂不同质量比Ag对甲醛光催化降解效果图。可见,随着Ag质量比的增加,甲醛的降解率先上升后下降,在Ag质量比为4%时,为甲醛降解率的最大值52.82%。当Ag的质量比超过4%时,Ag较容易聚集成较大颗粒,使Ag与g-C3N4接触面积减少,进而减降低了Ag与g-C3N4交界面光电子的迁移效率[24],因此在Ag质量比超过4%时,光催化效率下降。可以得出适量掺杂Ag,能有效地提升量子产率,提升光催化降解效率。
2.2.2 g-C3N4-Ag/SiO2对甲醛光催化降解效果的影响
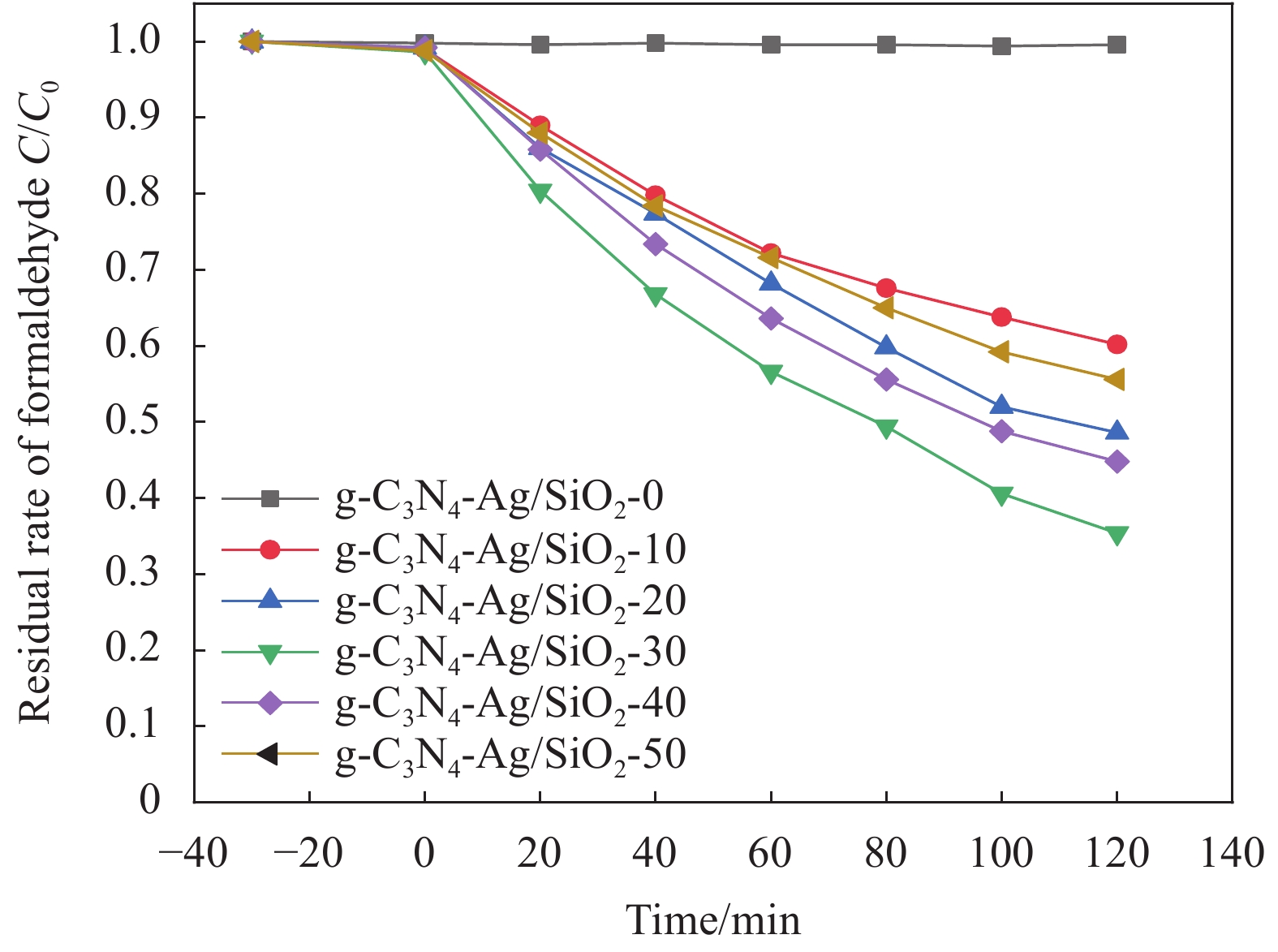
图9是g-C3N4-Ag/SiO2对甲醛光催化降解效果图。可见,降解甲醛的效率最好的是g-C3N4-Ag/SiO2-30,120 min后降解率达到65.6%。随着4%Ag-g-C3N4-F含量的增加,甲醛降解率先增加后降低。因为活性组分4%Ag-g-C3N4-F的增加,使降解甲醛的活性位点增多,所以甲醛降解率升高。而随着其负载量的继续增加,使硅铝胶球的部分孔道堵塞,从而抑制了甲醛的吸附和降解产物的脱附,进而导致甲醛降解率降低。
2.3 环境湿度对甲醛降解效果的影响
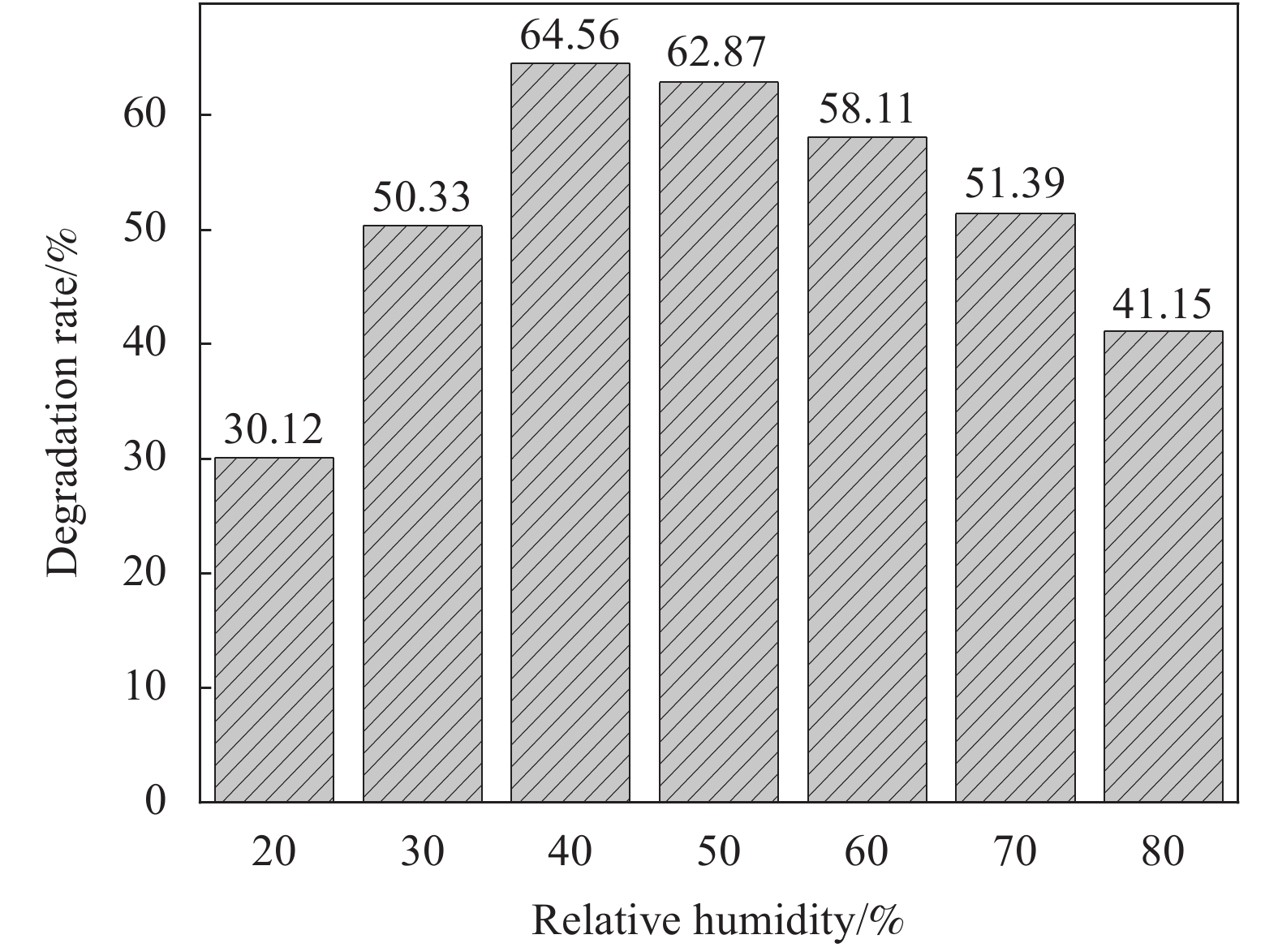
图10是相对湿度对甲醛降解效果的影响。因为空气中的水分子会一定程度地影响光催化反应,而不同地区的相对湿度不同,所以相对湿度作为环境因素有一定的代表性和重要性。选择g-C3N4-Ag/SiO2-30作为催化剂,探究相对湿度对甲醛光催化降解的影响。可见,随着相对湿度的增加,甲醛降解率呈显先上升后下降的趋势。这是由于在光催化反应中,水分子作为空穴的受体,与光生空穴反应会生成羟基自由基,随着水分子的增加,会产生更多的羟基自由基来氧化甲醛分子;随着相对湿度的继续增加,水分子和甲醛分子变成竞争关系,而SiO2表面的硅氧键更容易与水分子结合形成氢键,使水分子占据更多的吸附点位,从而削弱了对甲醛分子的吸附,同时由于水分子在较高的相对湿度下会液化,在硅铝胶球的表面形成液膜,使甲醛分子的传质阻力增大,阻碍了甲醛分子与催化剂的接触,导致甲醛的降解效率降低。
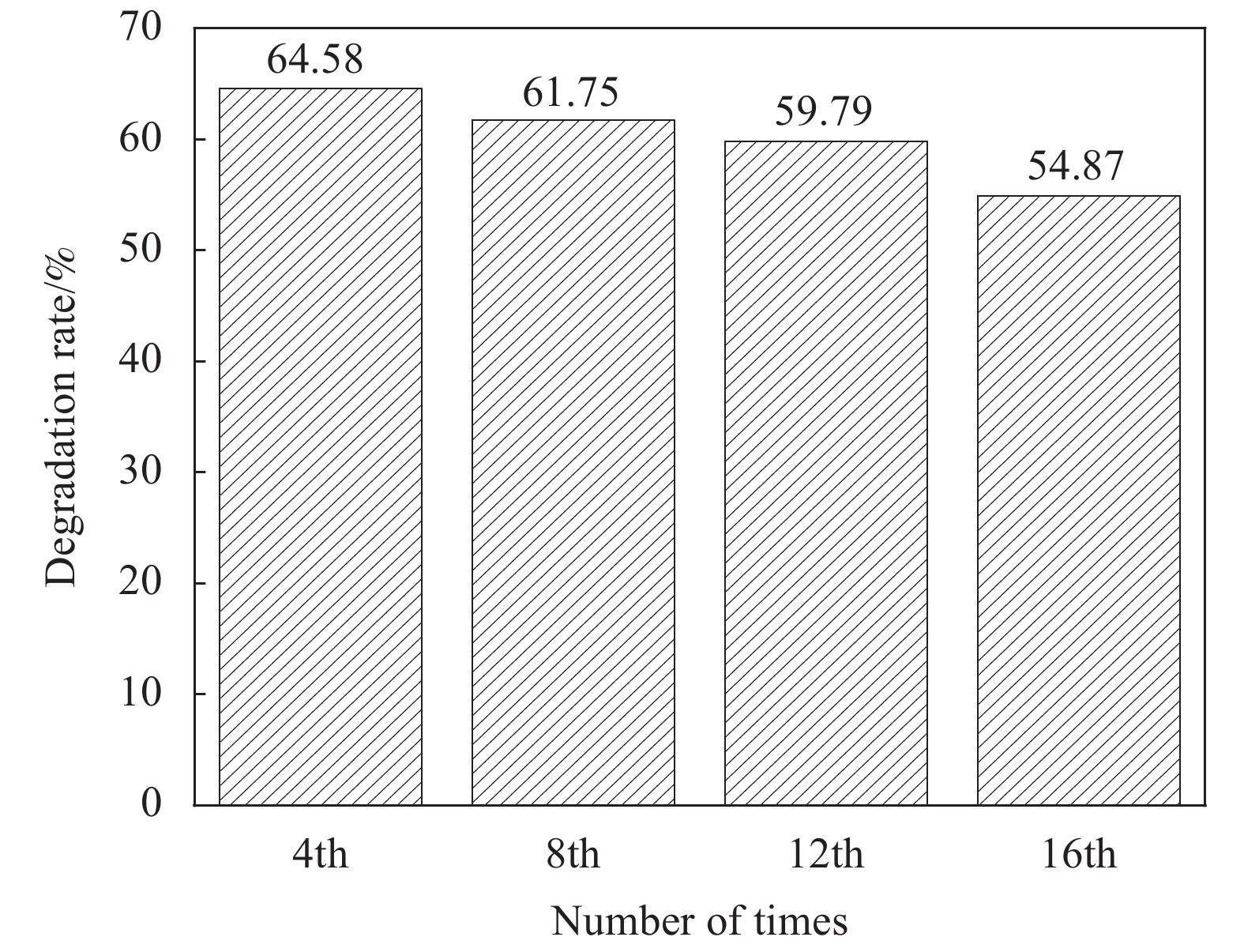
2.4 催化剂使用次数对甲醛降解效果的影响
图11是催化剂使用次数对甲醛降解效果的影响。催化剂的循环稳定性是评价其实际应用的重要指标。本试验使用g-C3N4-Ag/SiO2-30样品进行重复降解甲醛实验,每个周期降解时间为120 min,甲醛初始浓度均为0.5 mg/m3,催化剂每次循环前不作处理。可见,随着催化剂使用次数的增加,甲醛降解率呈缓慢下降趋势,16次使用过后,甲醛的降解率仅降低了9.71%,说明g-C3N4-Ag/SiO2-30的循环稳定性较好。使用多次催化效率下降的原因是由于SiO2 内部的孔道形状不平整,容易阻碍气体流动,不利于气体分子的脱附和扩散,进而导致降解产物逐渐在催化剂上积累,抑制了光催化活性[25]。
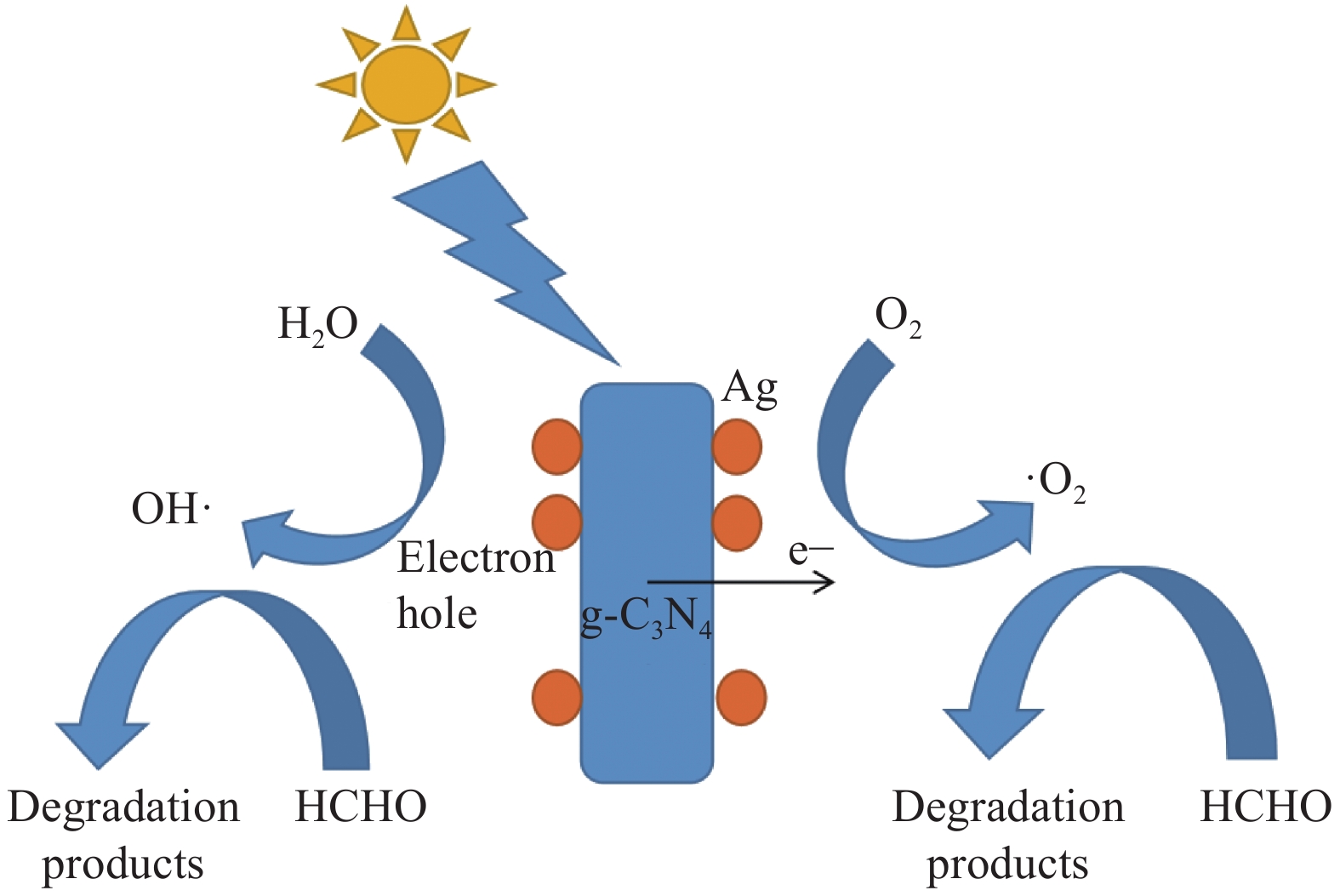
2.5 g-C3N4-Ag/SiO2光催化降解机制
图12是g-C3N4-Ag/SiO2材料光催化降解机制图。可见,经超声处理后的g-C3N4具有更低的光生载流子复合率,更高的分离率和迁移率,产生更多的光生电子流向g-C3N4表面,同时Ag具有优异的导电性,迁移到交界处的光生电子会迅速迁移到Ag表面并被空气中的氧气捕获,产生超氧自由基(·O2)[26],从而将甲醛氧化。超声处理降低了g-C3N4的势垒,促进了光生电子和空穴的分离,纳米单质Ag等离子体的共振效应增强了g-C3N4对可见光的吸收强度和吸收范围,并且Ag较大的电负性在g-C3N4与Ag的交界处形成电子势阱,提升光生电子向交界处的迁移率。因此g-C3N4-Ag/SiO2材料在LED白光光源下表现出良好的催化能力。
扩孔硅铝胶球可供降解产物吸附的位点较多,而水分子作为空穴的受体,与光生空穴反应会生成羟基自由基来氧化甲醛分子。
3. 结 论
(1) 成功制备薄层石墨相氮化碳(g-C3N4)-Ag/SiO2光催化复合材料,通过XRD、SEM、DES、TEM、紫外可见光吸收光谱、荧光光谱和电化学等表征显示材料光催化性能良好。
(2) g-C3N4-Ag/SiO2材料对甲醛具有良好的催化降解性能。超声处理使g-C3N4的势垒降低,促进了光生电子和空穴的分离,纳米单质Ag的掺杂通过等离子体的共振效应提升了光的吸收强度和吸收范围,依靠其较大的电负性加快光生电子的迁移速度,g-C3N4-Ag/SiO2-30催化降解率达到65.6%。
(3) g-C3N4-Ag/SiO2材料有良好的应用前景,g-C3N4-Ag/SiO2-30(Ag-薄层g-C3N4(g-C3N4-F)为30 mg)循环使用16次时,甲醛降解效率仅下降9.71%;g-C3N4-Ag/SiO2材料对环境因素具有一定的选择性,其中环境湿度对甲醛降解效果影响比较明显,相对湿度为40%时,甲醛降解效率达最大值64.56%。
-
表 1 Ag-薄层石墨相氮化碳(g-C3N4-F)复合材料的命名
Table 1 Naming of Ag-thin layer graphite phase carbon nitride (g-C3N4-F) composites
Sample g-C3N4-F/mg Concentration of AgNO3/(mg·mL−1) AgNO3/mL Na2S/mL 0 500 0 5 2 1%Ag-g-C3N4-F 500 1 5 2 2%Ag-g-C3N4-F 500 2 5 2 4%Ag-g-C3N4-F 500 4 5 2 8%Ag-g-C3N4-F 500 8 5 2 12%Ag-g-C3N4-F 500 12 5 2 16%Ag-g-C3N4-F 500 16 5 2 表 2 石墨相氮化碳(g-C3N4)-Ag/SiO2复合材料的命名
Table 2 Naming of graphite phase carbon nitride (g-C3N4)-Ag/SiO2 composites
Sample Ag-g-C3N4-F/mg SiO2/g Ethyl alcohol/mL g-C3N4-Ag/SiO2-10 10 30 100 g-C3N4-Ag/SiO2-20 20 30 100 g-C3N4-Ag/SiO2-30 30 30 100 g-C3N4-Ag/SiO2-40 40 30 100 g-C3N4-Ag/SiO2-50 50 30 100 -
[1] ABU J B, MOURAD A H, HITTINI W, et al. Traditional, state-of-the-art and renewable thermal building insulation materials: An overview[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2019,214:709-735.
[2] HUANG S, WEI W, WESCHLER L B, et al. Indoor formaldehyde concentrations in urban China: Preliminary study of some important influencing factors[J]. Science of the Total Environment,2017,590:394-405.
[3] WI S, PARK J H, KIM Y U, et al. Evaluation of environmental impact on the formaldehyde emission and flame-retardant performance of thermal insulation materials[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2020,402:123463.
[4] XIAN Q X, YING Y Y, YI T N, et al. Development of a cornstarch adhesive for laminated veneer lumber bonding for use in engineered wood flooring[J]. International Journal of Adhesion and Adhesives,2019,98:102534.
[5] 尚丽新, 朴丰源. 环境有害因素的生殖和发育毒性[M]. 郑州: 河南科学技术出版社, 2017: 1-312. SHANG L X, PU F Y, ed. Reproductive and developmental toxicity of environmental harmful factors[M]. Zhengzhou: Henan Science and Technology Press, 2017: 1-312(in Chinese).
[6] IARC. IARC monographs on the evaluation of carcinogenic risks to humans[R]. Switzerland:World Health Organization, 2006, 95: 27-50.
[7] CHAE J N, MI J, DANIEL C W, et al. High-performance materials for effective sorptive removal of formaldehyde in air[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2018,27(2):442-470.
[8] KUAN L P, DAI L C, GUAN T P, et al. Removal of phenol from gas streams via combined plasma catalysis[J]. Journal of Industrial and Engineering Chemistry,2017,52:108-120. DOI: 10.1016/j.jiec.2017.03.031
[9] PATRICIO A, MORENO C, FELIPE S, et al. Computational tomography and CFD simulation of a biofilter treating a toluene, formaldehyde and benzo[α]pyrene vapor mixture[J]. Chemosphere,2020,240:124924. DOI: 10.1016/j.chemosphere.2019.124924
[10] ISMAEL M, WU Y. A mini-review on the synthesis and structural modification of g-C3N4 -based materials, and their applications in solar energy conversion and environmental remediation[J]. Sustainable Energy & Fuels,2019,3(12):8946-8968.
[11] LI Y, WU S, HUANG L, et al. Synthesis of carbon-doped g-C3N4 composites with enhanced visible-light photocatalytic activity[J]. Materials Letters,2014,137:281-284. DOI: 10.1016/j.matlet.2014.08.142
[12] WANG X, MAEDA K, CHEN X, et al. Polymer semiconductors for artificial photosynthesis: Hydrogen evolution by mesoporous graphitic carbon nitride with visible light[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society,2009,131(5):1680-1681. DOI: 10.1021/ja809307s
[13] ZHOU T, XU Y G, XU H. In situ oxidation synthesis of visible-lightdriven plasmonic photocatalyst Ag/AgCl/g-C3N4 and its activity[J]. Ceramics International,2014,40(7):9293-9301. DOI: 10.1016/j.ceramint.2014.01.152
[14] LIANG K, ZHANG C H, XIANG H W, et al. Effects of modified SiO2 on H2 and CO adsorption and hydrogenation of iron-based catalysts[J]. Journal of Fuel Chemistry and Technology,2019,47(7):769-779. DOI: 10.1016/S1872-5813(19)30033-7
[15] WAN J W, YU J C, DEHUA X, et al. Graphene and g-C3N4 nanosheets cowrapped elemental α-sulfur as a novel metal-free heterojunction photocatalyst for bacterial inactivation under visible-light[J]. Environmental Science & Technology,2013,47(15):8724-8732.
[16] WANG X C, MAEDA K, THOMAS A, et al. A metal-free polymeric photocatalyst for hydrogen production from water under visible light[J]. Nature Materials,2009,8(1):76-80. DOI: 10.1038/nmat2317
[17] LIU L, QI Y, YANG J, et al. An AgI@ g-C3N4 hybrid core@shell structure: stable and enhanced photocatalytic degradation[J]. Applied Surface Science,2015,358(A):319-327.
[18] CHENG B, LE Y, YU J. Preparation and enhanced photocatalytic activity of Ag@TiO2 core-shell nanocomposite nanowires[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2010,177(1-3):971-977. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2010.01.013
[19] JI H, CHANG F, HU X, et al. Photocatalytic degradation of 2, 4, 6-trichlorophenol over g-C3N4 under visible light irradiation[J]. Chemical Engineering Journal,2013,218:183-190. DOI: 10.1016/j.cej.2012.12.033
[20] CAO S W, YUAN Y P, FANG J, et al. In-situ growth of CdS quantum dots on g-C3N4 nanosheets for highly efficient photocatalytic hydrogen generation under visible light irradiation[J]. International Journal of Hydrogen Energy,2013,38(3):1258-1266. DOI: 10.1016/j.ijhydene.2012.10.116
[21] CHEN Y, HUANG W, HE D, et al. Construction of heterostructured g-C3N4/Ag/TiO2 microspheres with enhanced photocatalysis performance under visible-light irradiation[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2014,6(16):17523-17539.
[22] ZHOU C, SHI R, SHANG L, et al. Template-free large-scale synthesis of g-C3N4 microtubes for enhanced visible light-driven photocatalytic H2 production[J]. Nano Research,2018,11(6):3462-3468. DOI: 10.1007/s12274-018-2003-2
[23] SHI H, CHEN G, ZHANG C, et al. Polymeric g-C3N4 coupled with NaNbO3 nanowires toward enhanced photocatalytic reduction of CO2 into renewable fuel[J]. Acs Catalysis,2014,4(10):3637-3643. DOI: 10.1021/cs500848f
[24] WEN X J, NIU C G, ZHANG L, et al. In-situ synthesis of visible-light-driven plasmonic Ag/AgCl-CdWO4 photocatalyst[J]. Ceramics International,2016,43(2):1922-1929.
[25] JO B W, KIM C H, TAE G H, et al. Characteristics of cement mortar with nano-SiO2 particles[J]. Construction and Building Materials,2007,21(6):1351-1355. DOI: 10.1016/j.conbuildmat.2005.12.020
[26] SUN Y, YANG J, YANG S, et al. Development of an immunochromatographic lateral flow strip for the simultaneous detection of aminoglycoside residues in milk[J]. Rsc Advances,2018,8(17):9580-9586. DOI: 10.1039/C8RA01116H
-
期刊类型引用(7)
1. 陈楚晓,郝京华. AuPt/还原氧化石墨烯/氮化碳的制备及其在室内挥发性有机物处理中的应用. 环境工程学报. 2025(01): 178-187 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 崔春丽,郝振华,舒永春,徐继香,王磊. MoO_3-Cu_2O/CN三相复合光催化剂的制备及其降解四环素性能. 复合材料学报. 2025(03): 1361-1374 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 孙术博,于海瀚,李强,葛慎光,姜葱葱,王丹,张丽娜,程新,高超民. NaNbO_3@g-C_3N_4复合材料的可控构筑及其压电光催化性能. 复合材料学报. 2023(03): 1534-1540 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 陈书航,郝亚超,赵阳灿,杨潘,王斯琰,徐宏妍. 硫酸改性g-C_3N_4的制备及其光催化产氢性能研究. 功能材料. 2023(07): 7126-7130 .  百度学术
百度学术
5. 徐凯旋,亢玉龙,高晓明,贺红斌,袁中强,胡亚楠. 内电场增强S型异质结N-C_3N_4/BiOCl_xI_(1-x)的制备及其光催化性能. 复合材料学报. 2023(09): 5134-5144 .  本站查看
本站查看
6. 肖力光,杨子力. Ag改性的g-C_3N_4基纳米复合光催化材料的研究进展. 现代化工. 2022(03): 37-40+45 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 范新容,李成,许岩. 多酸基分子材料在图书馆清洁与用户环境保护中的应用研究. 化学研究与应用. 2022(07): 1674-1679 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(6)
-




 下载:
下载: