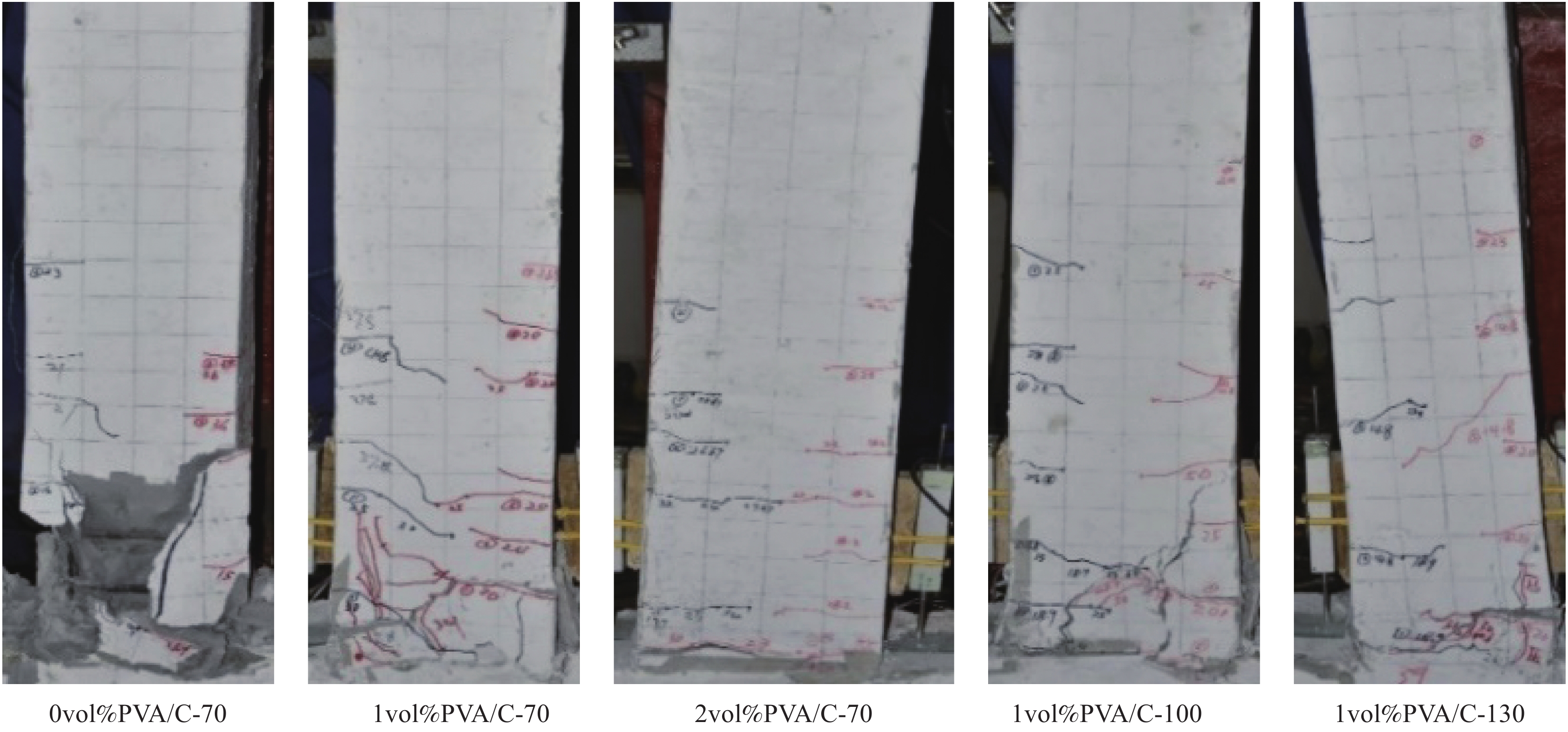
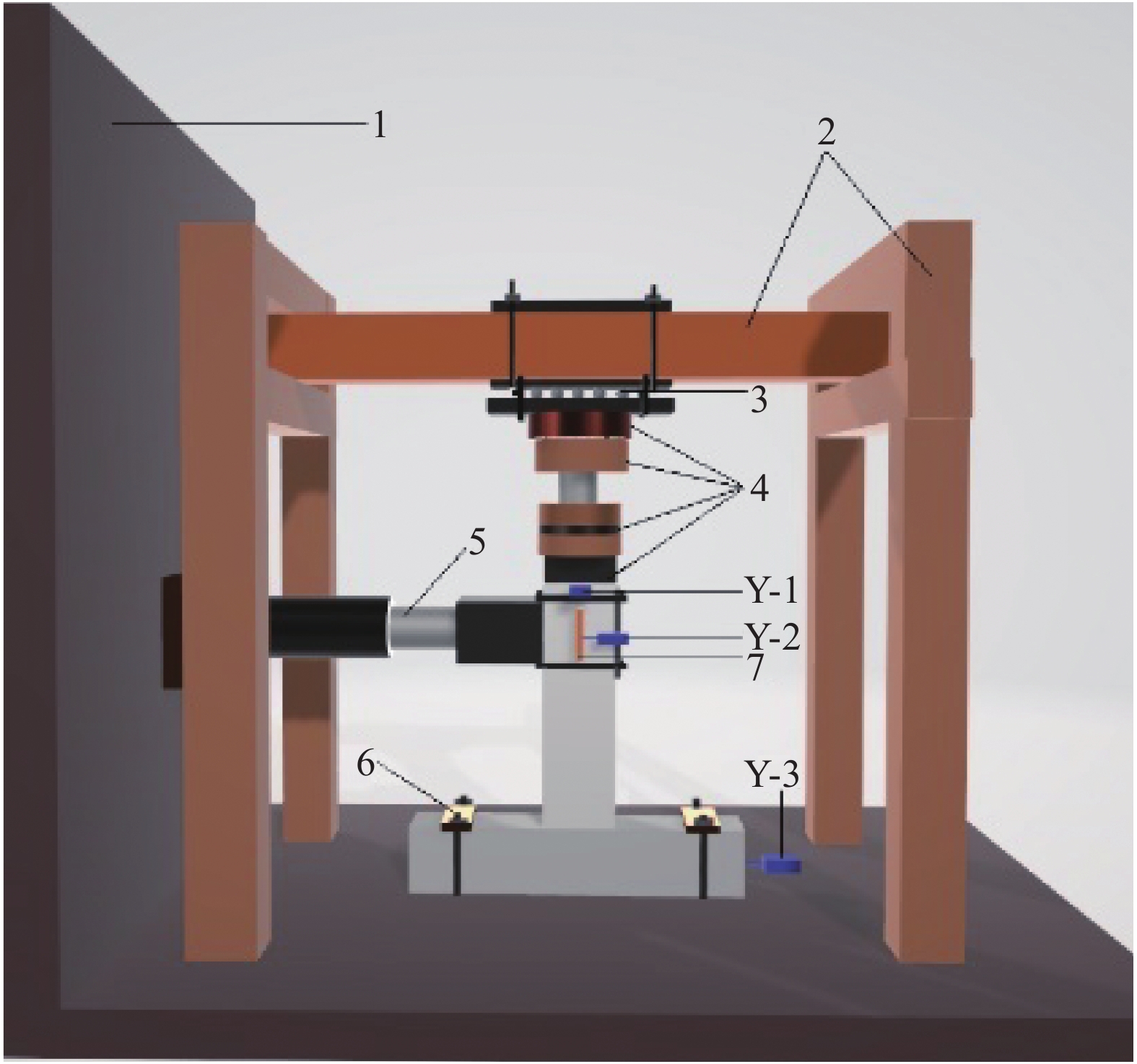
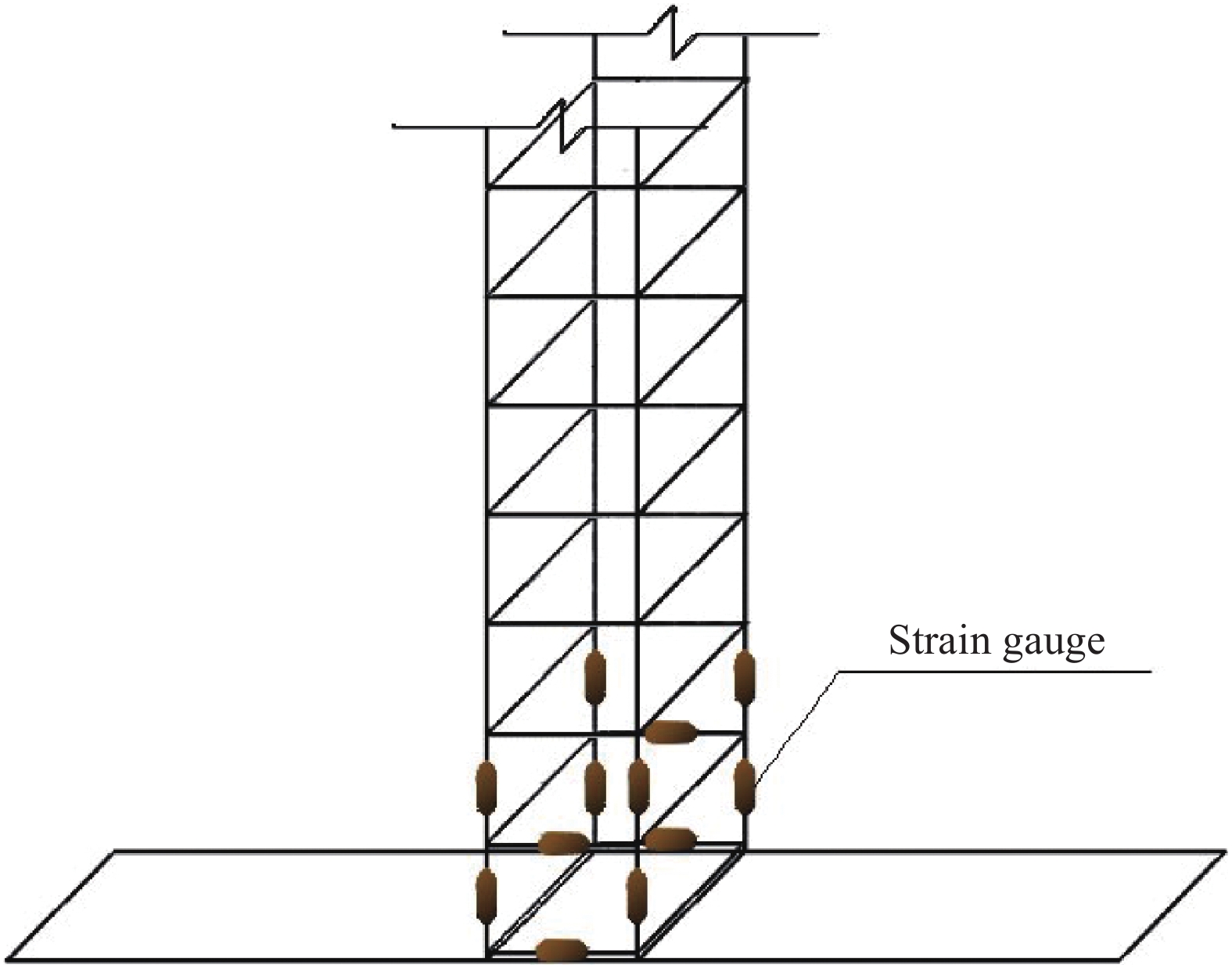
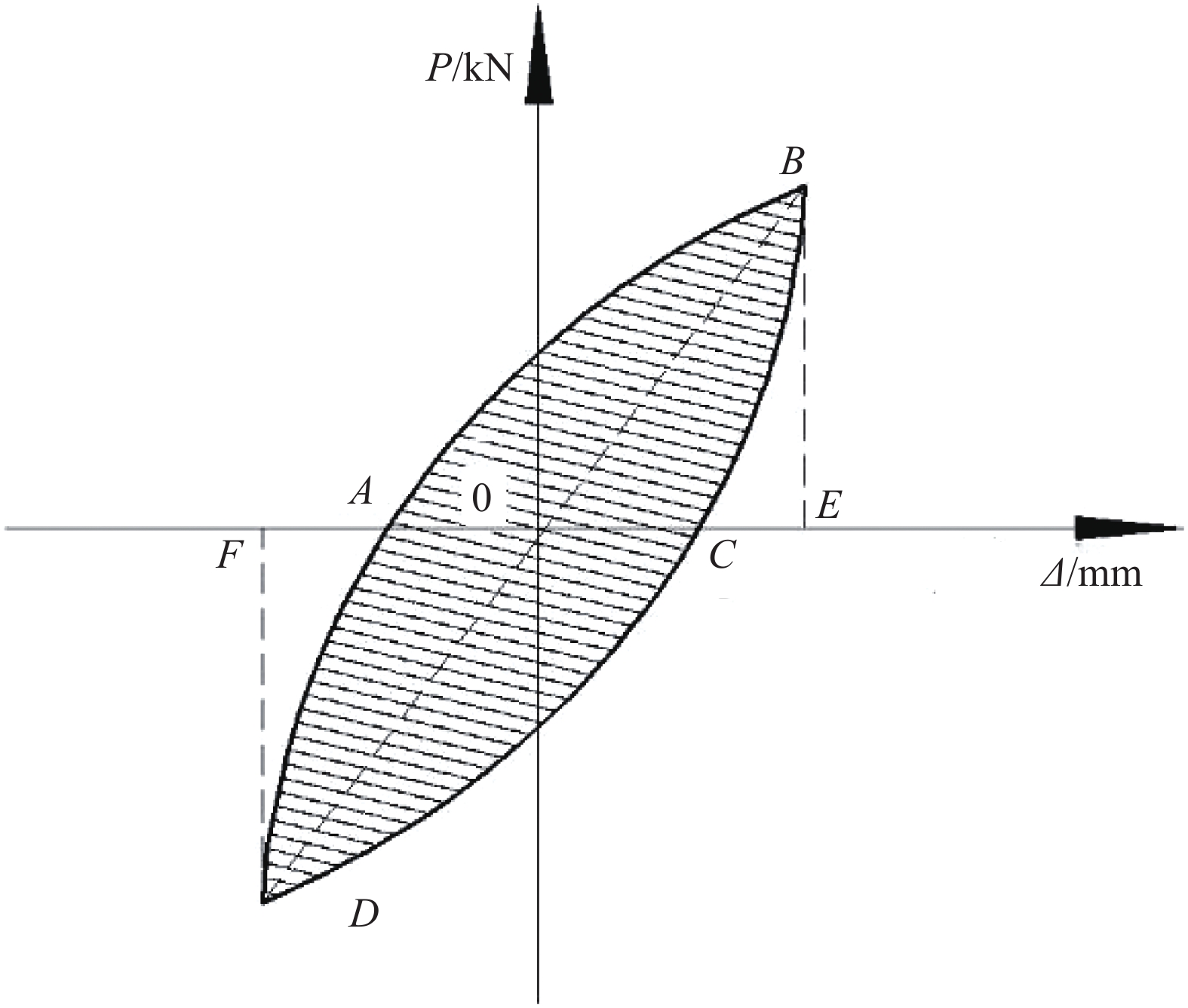
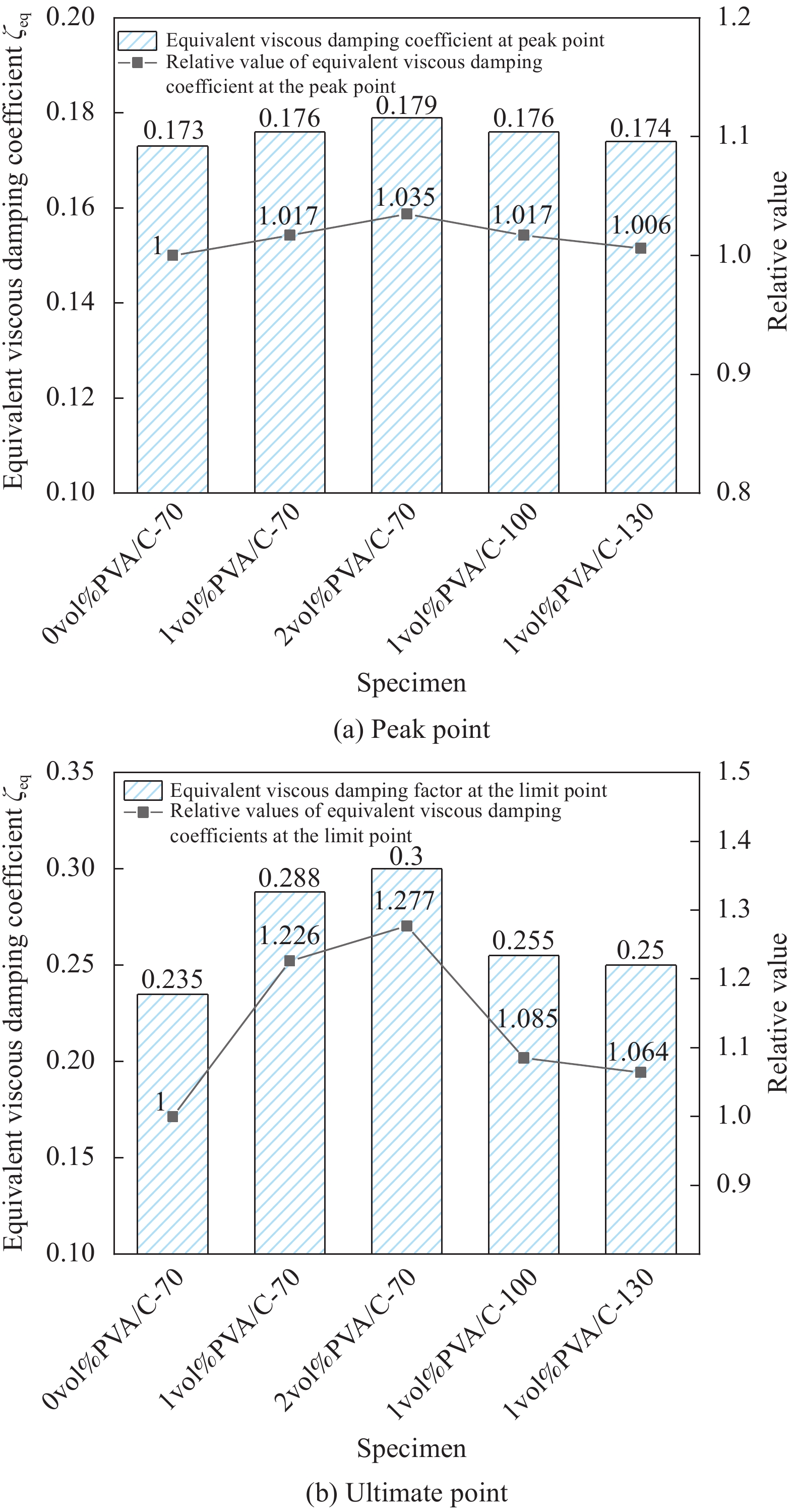
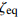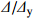Experimental study on seismic performance of polyvinyl alcohol fiber reinforced cementitious composite medium-length columns with low axial pressure ratio
-
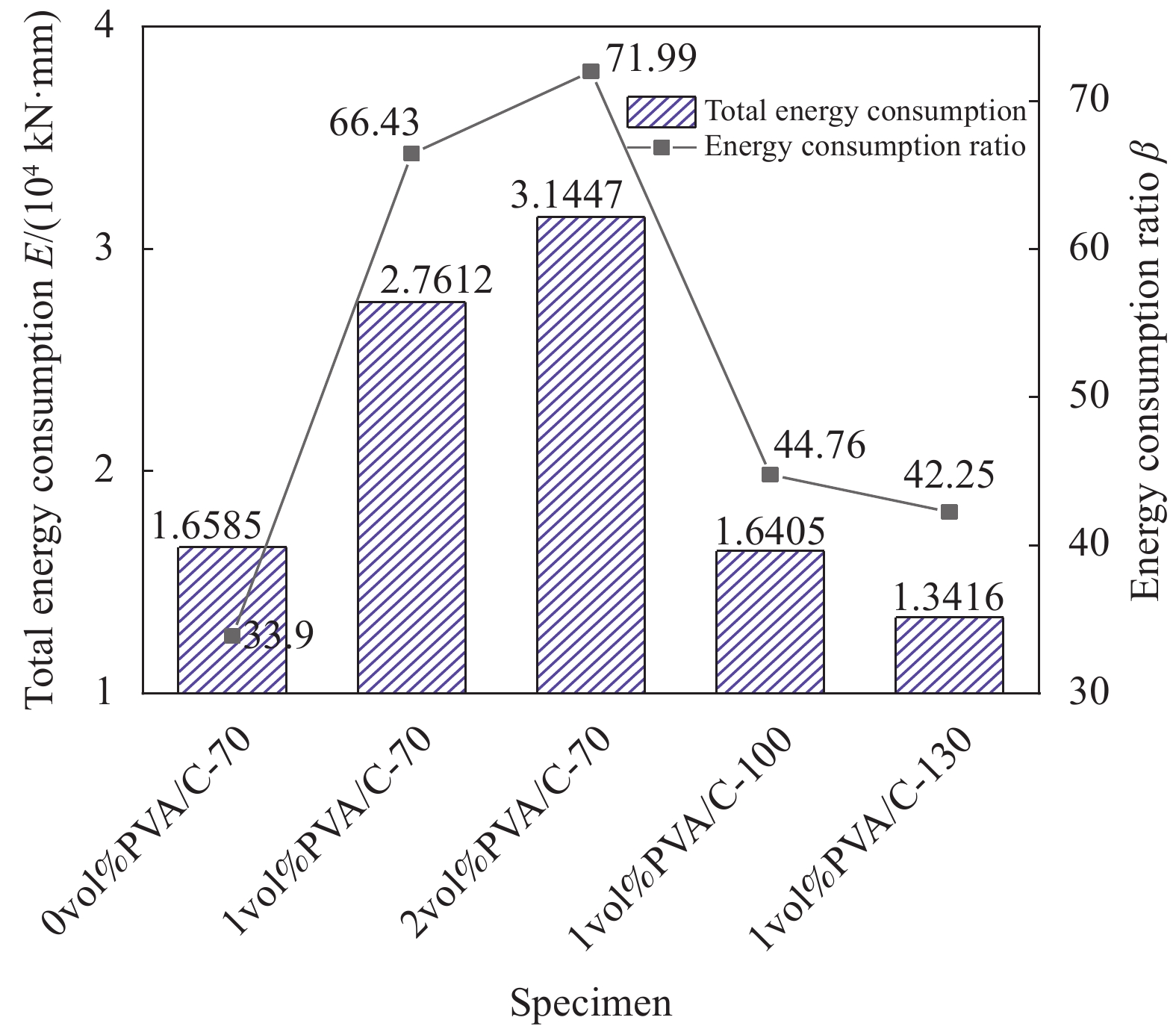
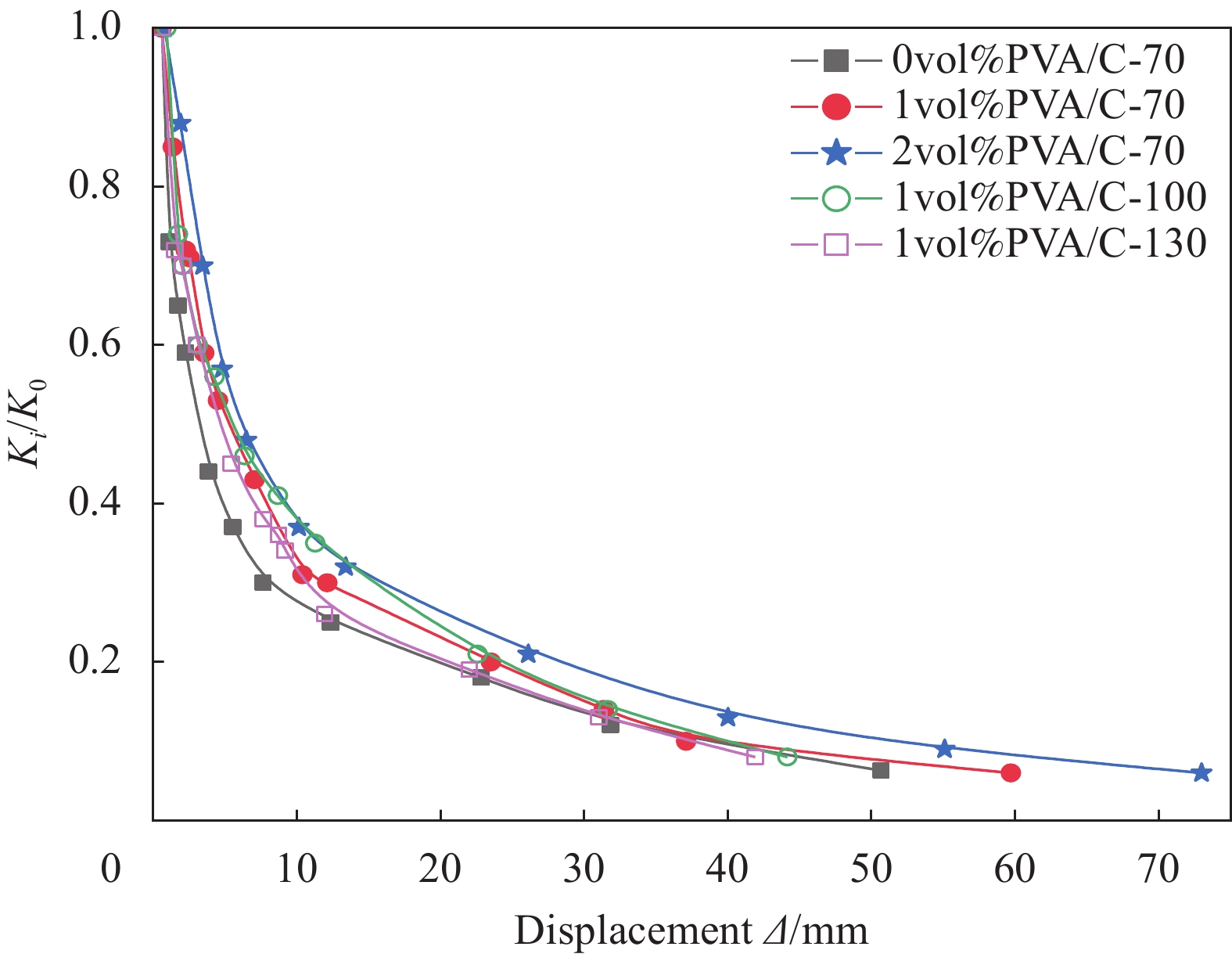
摘要: 已有对聚乙烯醇纤维增强水泥基复合材料(PVA/C)柱抗震性能的研究大多针对短柱,且PVA/C一般只在节点及其邻近部位局部设置。基于此,本文对低轴压比且沿柱全高设置的PVA/C中长柱进行低周反复荷载试验,变化参数为纤维体积分数ρf和体积配箍率ρv。通过试验,得出以下结论:所有试件均发生弯曲破坏;当ρf和ρv分别在试验设计范围内增大时,试件的裂缝控制能力、延性、截面转动能力及耗能能力均提高,刚度退化及承载力衰减速度减小;ρf的增大可较大程度提高试件开裂荷载,而对峰值荷载影响较小;ρf由0 vol%提高到2 vol%,位移延性系数、耗能比及开裂荷载分别提高52.9%、112.3%和51.1%;掺加适量纤维后,即使降低配箍率,试件也可保持良好的抗震性能和裂缝形态。根据本文试验数据并收集其他相关文献试验数据,拟合得出位移延性系数与ρf和ρv之间的关系式。最后总结了各类PVA/C柱抗震性能差异。Abstract: Previous studies on the seismic performance of polyvinyl alcohol fiber reinforced cementitious compo-site (PVA/C) columns mostly focused on short columns, and PVA/C was usually set locally in the joint and its adjacent parts. Based on this, low-cycle reversed loading tests on medium-length PVA/C columns with low axial pressure ratio were carried out, and PVA/C was set along the full height of the column. Test variation parameters are fiber volume fraction ρf and volume-stirrup ratio ρv. The following conclusions can be drawn through the test: Bending failure occurs in all specimens. When ρf and ρv increase within the test condition range respectively, the crack controlling ability, ductility, section rotation ability and energy dissipation ability of specimens are improved. While the rate of stiffness degradation and decay of bearing capacity are decreased. The increase of ρf can greatly improve the cracking load of specimens, but has little effect on the peak load. When ρf increases from 0 vol% to 2 vol%, the displacement ductility coefficient, the energy consumption ratio and the cracking load increase 52.9%, 112.3% and 51.1%, respectively. The PVA/C columns can maintain good seismic performance and crack morphology even if the stirrup ratio is reduced. According to the experimental data of this paper and other relevant literature, the relationship between displacement ductility coefficient and ρf and ρv is obtained. Differences of seismic performance of various PVA/C columns were summarized.
-
纤维增强复合材料(Fiber reinforced composite,FRC)是由高比强度、比模量的纤维增强体(碳纤维、玻璃纤维、芳纶纤维和玄武岩纤维等[1])和质地软、韧性强的基体(聚合物、金属和无机非金属等[2-3])经过各种复合加工工艺制造而成的新型材料。强而脆的纤维提供高强度,主要起承受载荷的作用,基体主要起黏结增强体并提供支撑与保护作用,在承受载荷时使应力集中减弱,能够提供较强的断裂韧性[4]。
由FRC组成的零部件因其具有质量轻、刚性高、强度高、尺寸稳定、导热性好等诸多优点,在航空航天、武器装备、汽车领域得到了广泛的应用,其应用量占比已成为衡量新一代先进航空航天装备先进性的重要标志[5-6]。根据相关报告显示,空客公司的A380飞机构件大量采用了碳纤维增强复合材料,A380的外翼、发动机、平尾翼和垂直尾翼等部位都采用了FRC,FRC的质量占到整体结构质量的25%[7]。波音787主体结构的复合材料用量更是达到了50%,这极大地减轻了波音787的质量,使其能够在同航程下比同类型飞机减少15%~20%燃料使用量[8]。近年来国内外大型飞机的复合材料的用量呈现井喷式增长趋势,先进FRC在航空装备发展中具有举足轻重的地位与作用[9]。
FRC具有较多而复杂的成形工艺,主要包括预浸料、拉挤成型、增材制造等[10-11],但成形的FRC结构件通常需要进行以钻孔为主的二次加工以满足与其他航空结构件进行铆接、螺接等装配需求[12]。以飞机上的FRC零部件为例,制造一架波音747飞机需要加工300多万个连接孔,制孔工序占总加工量的80%以上。在实际加工与装配中,60%的FRC零件因钻孔质量差而报废,追其溯源是由于FRC具有各向异性、层间强度低、导热性差的特点。在钻削过程中由于钻头和工件的接触产生机械损伤和热损伤,钻削产生的钻屑仅能通过钻头的螺旋槽排出,钻屑、钻头与工件产生摩擦热主要是沿着纤维方向进行传导,垂直纤维方向上的热量则是通过树脂及树脂/纤维间的界面传导,又因FRC中树脂基体导热性差,且其玻璃转化温度不高,产生的热量促使基体性能下降,进而出现工件材料烧蚀、刀具热疲劳磨损等问题,最终影响工件的加工质量和刀具的使用寿命[13-15]。因此连接孔的加工质量直接影响构件的强度、刚度和可靠性,研究钻削热对FRC加工质量的影响具有重要意义[16]。
对不同工艺参数下FRC工件预制孔的钻削热对钻削质量影响的研究一直都是国内外学者的重要研究方向。Mu等[17]使用红外摄像机测量了对FRC的常规钻削工况下的工件温度,结果表明转速和进给速度增大都会使钻削温度升高。蔡建国等[18]进行了FRC的常规钻削测温实验,使用热电偶对钻削温度进行测量,建立了钻削温度与钻削参数的指数模型经验公式。陈文成等[19]进行了FRC钻削实验,并分别使用热电偶和红外热像仪测量了钻削温度,结果表明当钻削温度高于玻璃转化温度时,FRC性能下降,钻孔质量变差。Santiuste等[20]建立了FRC正交切削的有限元模型,预测结果表明FRC面内机械损伤和热损伤主要受纤维方向影响,而且热损伤影响区域比机械损伤影响区域大。王福吉等[21]研究了FRC钻削区域的热量分配问题,建立了FRC切削温度场模型,得出随纤维方向增大,FRC的热能分配比例表现为先增大后减小的结论。Geng等[22]对FRC开展了常规钻削和超声振动钻削对比实验,使用红外摄像机对钻削温度进行了测量,当进给速度等于75 mm/min和150 mm/min时,超声振动钻削能使最高温度降低约18.8%和13.1%。
根据上述描述,对FRC钻削热的形成机制,钻削热的数值模拟、工艺参数对热损伤的优化分析及钻削热控制方法等研究一直是国内外研究重点,FRC钻削加工中的许多经济和技术问题大都直接或间接地由钻削热所引起,它不仅影响刀具的磨损及耐用度,还影响工件的加工精度、已加工表面的质量和生产效率等。因此了解FRC切削热的形成机制、精确测量方法与降低钻削热并减少制孔损伤等研究,无论是对钻削机制的研究、刀具磨损机制的探讨,还是刀具的设计与制造、加工参数的选择及加工表面质量的控制等都是相当重要的。
故本文对国内外FRC钻削过程相关研究进行系统性的整理与分析,概述了近年来关于FRC钻削过程产生的切削热研究,主要包含钻削热理论研究、钻削热对加工质量的影响研究、温度的影响因素与辅助加工控制钻削热方法研究3个方面的分析与总结,最后探讨并总结了当前对FRC钻削热研究存在的问题及今后研究的发展趋势。
1. FRC钻削热理论研究
1.1 钻削热形成机制
FRC钻削热的形成过程,是纤维产生断裂,基体被破坏、发生老化、软化的复杂难分析过程。以碳纤维增强树脂基复合材料(Carbon fiber reinforced polymer,CFRP)为例,CFRP是典型的各向异性材料,具有非均质、层间强度低的特点。由于碳纤维增强相和基体的材料属性存在较大差异的原因,在钻削过程中两者的切屑断裂模式在细观尺度下表现不同,使在CFRP热力耦合作用下具有更复杂的钻削缺陷形成机制[23]。研究表明钻削力是影响CFRP制孔质量的重要因素,当主轴转速不变时,进给速度与轴向力呈现正比例关系,从而加剧撕裂和分层损伤[24]。如果为了降低轴向力,保持进给速度不变,增大主轴转速,则钻削温度会显著升高,从而导致加剧基体烧伤、孔径偏差增大、刀具磨损增大等问题[25],例如热塑性复合材料还容易出现热结晶问题[26]。若此时采用冷却辅助加工技术,虽然能有效降低钻削温度,改善毛刺和烧蚀现象,但又容易因温度过低导致CFRP材料力学性能增强,增大了轴向力[27]。因而研究钻削力对FRC制孔质量影响时需充分考虑钻削温度对各钻削缺陷的影响机制。
与此同时,学者研究发现FRC钻削热的形成与纤维排布方向有很大关联,为了简化FRC的钻削热形成过程,便于钻削热形成机制的研究,从微观层面更深层次地研究钻削过程中切削热、切削力的作用机制,学者们按照纤维分布方向与刀具运动方向的夹角将其分为3种切削模式:(1) 切削方向与纤维方向平行,材料发生层间分离而断裂产生切削热;(2) 切削方向与纤维方向形成锐角,纤维被切断而形成切屑而产生切削热;(3) 切削方向与纤维方向为钝角,纤维的弯曲作用和剪切作用交互作用,材料断裂而形成切削热[12]。如图1所示,可采用微元法将单向(Unidirectional,UD)层合板结构的CFRP按照刀具运动方向与纤维方向的夹角将微观切削加工机制分为0°、45°、90°和135°这4种模式[28]。在纤维方向角约为0°时,刀具尖端的纤维被压缩,而前刀面的纤维主要被挤压弯曲。这一过程中由于分层减少了刀具去除材料时的纤维断裂数量,刀具去除材料所需的力变小,且具有较好的表面粗糙度;在纤维方向角约为45°时,刀具尖端和前刀面的纤维受到挤压直至挤压剪切断裂,又由于塑性作用,加工后纤维会产生回弹,这使表面粗糙度增大;在纤维方向角约为90°时,刀具垂直于纤维进行切削,当一根纤维被切削时,其周围起支撑作用的纤维与基体也同时受到挤压弯曲变形,此时切削过程中塑性作用比45°时更明显,表面粗糙度进一步增大;在纤维方向角约为135°时,纤维主要受弯曲作用,纤维去除模式主要为弯曲断裂,此时表面粗糙度较差。
![]() 图 1 单向(UD)-碳纤维增强树脂基复合材料(CFRP)切削加工机制:(a) 刀具与纤维夹角;(b) 微观切削模型;(c) 四种切削模式[28]θ—Cutting direction; →Vc—Cutting speed; →k—Fiber directionFigure 1. Unidirectional (UD)-carbon fiber reinforced polymer (CFRP) cutting mechanism: (a) Angle between cutter and fiber; (b) Micro-cutting model; (c) Four cutting modes[28]
图 1 单向(UD)-碳纤维增强树脂基复合材料(CFRP)切削加工机制:(a) 刀具与纤维夹角;(b) 微观切削模型;(c) 四种切削模式[28]θ—Cutting direction; →Vc—Cutting speed; →k—Fiber directionFigure 1. Unidirectional (UD)-carbon fiber reinforced polymer (CFRP) cutting mechanism: (a) Angle between cutter and fiber; (b) Micro-cutting model; (c) Four cutting modes[28]以CFRP切削加工过程为例,如图2所示,切削热主要产生于以弹性变形和塑性变形消耗变形功生热为主的第一变形区、前刀面与切屑摩擦生热的第二变形区、后刀面与工件表面摩擦生热的第三变形区。其中,第三变形区由于刀具在切削CFRP时,已加工表面会产生回弹现象,产生较高的切深抗力,在切深抗力的作用下,刀具会与工件摩擦产生大量切削热,因而切削热主要来源于第三变形区[29]。因此在简化的微观切削过程中,纤维方向约为90°时纤维受刀具挤压断裂,纤维与刀具之间具有明显的摩擦,会产生大量切削热。而纤维方向约为0°时,纤维更容易被去除,摩擦较小,因此产生的切削热也较少[30]。
基于能量守恒定律,切削过程中摩擦产生的热量会传入工件、刀具和切屑。Wang等[32]根据傅里叶定律计算得到单位时间传入刀具的热量Qtool可表示为
Qtool=kΔTLA (1) 其中:k为刀具导热系数;∆T为刀具的温升;L为热电偶预埋孔中心到刀尖的距离;A为接触区域面积。进一步地,A可表示为
A=(90∘+α0+γ0180∘πRe+1sinα0(3Fy4E∗√Re)2/3)lt (2) 其中:α0为刀具后角;γ0为刀具前角;Re为刀具切削刃半径;Fy为法向切削力;E*为刀具和工件的等效弹性模量;lt为CFRP工件的厚度。
因此,最终传入刀具的热量λ1可由下式计算:
λ1=QtoolQtotal (3) {\lambda }_{1}=\frac{k{l}_{\mathrm{t}}}{{F}_{{x}}{V}_{{{\rm{c}}}}} \frac{\Delta T}{L}\left[\frac{90°+{\alpha }_{0}+{\gamma }_{0}}{180°}{\text{π}} {R}_{\mathrm{e}}+\frac{1}{{\sin}{\alpha }_{0}} {\left(\frac{3{F}_{y}}{4{E}^*\sqrt{{R}_{\mathrm{e}}}}\right)}^{2/3}\right] (4) 其中:Qtotal为摩擦产生的总热量;Fx为水平切削力;Vc为切削速度。
式(4)为研究切削区热量分配机制、适温切削散热量确定方法提供了重要依据。
通过上述对钻削热形成机制的分析可以看出:FRC钻孔过程中的材料去除机制可简化为刀具不断地切削不同纤维排布方向的UD-FRC。刀具在对UD-FRC进行切削进给时,由于纤维具有高强度、高硬度,刀具与工件摩擦产生大量的热,而这些热量主要来自于已加工表面的第三变形区。钻削过程产生的热量会传入刀具、工件和被切屑带走,其中切屑带走的热量可忽略不计。
1.2 热传导与损伤预测
目前关于FRC的钻孔工艺中涉及的切削热理论大多基于传热学的温度场模型分析。Bao等[33]建立了图3中的单向碳纤维增强树脂基复合材料(Unidirectional carbon fiber reinforced polymer,UD-CFRP)钻孔的热传导模型,并推导建立了其温度场模型用于预测钻削温度。杨帆等[34]基于传热学原理,建立了CFRP/Ti(钛合金,简称Ti)叠层的钻削温度场模型,并采用有限差分方法进行求解,最后通过实验测量叠层钻削中的界面温度验证了模型的正确性。Liu等[35]建立了CFRP轨道铣孔的热传导模型,指出铣孔过程中主要有两个热源,位于刀具边缘切削刃与工件接触区域和刀具底部切削刃与工件接触区域,其几何形状分别为半圆形和线形。在Liu等[35]学者的研究基础上,刘亚军等[15]使用有限差分法对CFRP/Ti轨道铣孔过程的温度场模型进行数值仿真求解,并最后通过实验测量确定了Ti与CFRP的界面温度传导率为6%。
![]() 图 3 UD-CFRP钻削热传导模型[33]ω—Angular velocity; νf—Feed velocity of the drill; q1—Heat flux load which comes from the major cutting edges and chisel edge; q2—Heat flux load generated from the side edges; lx—CFRP length; ly—CFRP width; lz—CFRP thickness; d—Tool diameterFigure 3. UD-CFRP drilling heat conduction model[33]
图 3 UD-CFRP钻削热传导模型[33]ω—Angular velocity; νf—Feed velocity of the drill; q1—Heat flux load which comes from the major cutting edges and chisel edge; q2—Heat flux load generated from the side edges; lx—CFRP length; ly—CFRP width; lz—CFRP thickness; d—Tool diameterFigure 3. UD-CFRP drilling heat conduction model[33]学者们不仅建立了用于温度预测的热传导理论模型,还建立了考虑了温度影响、可用于预测钻削损伤的损伤理论模型。Sikiru等[36]考虑了钻头几何形状(横刃和顶角)对推出分层的影响和温度对工件力学性能的影响,基于钻头切削刃上受力为均布载荷,横刃上受到一个集中力的假设,建立了CFRP层合板钻孔的分层损伤数值模型,有效预测了发生分层的临界轴向力。贾振元等[37]建立了考虑树脂及界面温变特性和被切纤维周围支撑材料对被切纤维约束作用的单纤维切削数值模型,揭示了CFRP的微观切削机制,但该模型基于双参数弹性地基梁理论,其预测宏观切削力的误差可达20%。Fattahi 等[38]建立了考虑热力耦合作用的分层损伤预测模型,解释了分层损伤如何从入口处的圆形截面演化成出口处的椭圆形截面。
从相关学者对热传导与损伤预测的研究可知,近年来关于钻削热模型的建立大多只考虑了宏观结构的热传导,且尚未充分考虑切削力对温度场的影响。而实际钻削加工过程中,FRC工件钻削预制孔形成的分层、撕裂、毛刺等损伤受温度影响显著,FRC的钻孔过程是复杂的热力耦合作用过程。目前FRC钻孔的微观尺度下的切削模型揭示了FRC的微观切削机制,但其对切削热、切削力的预测与实际结果相比有较大偏差。更深次的切削热理论模型来解释温度场分布及变化规律需进一步探讨,进而能够准确预测热力耦合作用下的不同损伤。
1.3 基于数值模拟分析的切削热分析
近年来,除了试验和解析法,基于数值模拟的有限元法(Finite element method,FEM)对FRC在钻削工况下的钻削热求解越来越受到复合材料领域的学者们重视。针对FRC全过程钻孔工艺的分析,FEM具有可以节省大量人力物力和时间,可实现钻削温度的数值可视化、预测材料加工中的表面缺陷、优化钻削加工工艺参数和指导钻削刀具的设计与刀具参数的优化等优点[39-40]。同时,FEM可以从微观尺度上模拟材料的去除,直接获取微观应力、应变、温度分布等云图[3,41],而这些都是在实验中难以实现的。因而,采用FEM使研究者们能够直接研究纤维和基体在刀具作用下的微观损伤过程,以便于更深入、准确地解释宏观切削去除机制[42]。
虽然近年来计算机计算能力有了很大的进步,对于FRC钻孔的模拟仍需耗费较长时间,其中的缘由是复杂结构的有限元模型必须要有足够多的精细网格来保证模型精度,而网格数量的增加将导致模拟时间呈指数性增长。为了确保有限元模型的可靠性,并尽可能提高模型计算效率与计算精度,学者们做出了大量的具有重要指导意义的研究[43-44]。
在微观层面,学者们直接对纤维进行建模,主要模拟了纤维单向分布的FRC微观切削过程。齐振超等[45]模拟了正交切削过程中不同纤维方向角下CFRP切削温度分布的差异,结果显示切削温度的峰值受纤维方向角影响,当方向角为90°时切削温度最高,并且其应力和温度的分布具有相似性。Gao等[46]研究了CFRP三维细观直角切削热力耦合模型,如图4所示,在不同切削参数下对比分析了4种典型纤维方向角下切屑形成机制、表面质量,并与实际加工表面轮廓进行了对比。Xu等[47]实现了超声振动辅助CFRP正交切削的热力耦合仿真,其建模方式如图5所示,结果表明相比无振动辅助加工,超声振动辅助加工条件下的切削温度始终更低,其模拟结果如图6所示,并指出切削力受温度影响不大,切削力数值的震荡是由于刀具间歇性地切割纤维,且只有当进给量小于进给方向上的最大振动速度,超声振动能够有效地减小切削力。Han等[31]模拟了不同预处理温度下UD-CFRP的正交切削过程,阐述了其微观变形机制、切削力演化与切削温度演化之间的关系,研究结果表明低温预处理会加剧纤维和基体以脆性断裂为主的面下损伤,加热预处理会导致基体软化,从而加剧以纤维断裂为主的面下损伤。
对微观结构更复杂的编织FRC,学者们主要模拟了其微观尺度下的热物理行为。Dong等[48]模拟了三维编织CFRP的多尺度热传导行为,结果表明,热导率随温度的增加而增大,并近似呈线性增长。Zhai等[49]模拟了编织角与温差对FRC热物理属性的影响,并提出了一种优化的多尺度渐近均质化方法来,有效减少了有限元建模工作量。He等[50]建立了三维编织复合材料的多尺度模型,揭示了其在高温下的失效机制,使用了弹塑性损伤本构定律来表征微观结构和细观结构的力学行为。Cheng等[51]模拟了UD-CFRP的热力耦合作用下的微观切削,模拟结果显示UD-CFRP切削过程中工件存在两个应力集中区,如图7(a)所示,区域(I)靠近刀具尖端,区域(II)处于加工表面下,是纤维之间相互作用力主要作用区域。
在宏观层面,学者们建立了FRC的均质化模型,主要模拟了FRC钻削温度场分布变化规律。Díaz-Álvarez等[52]建立了一种简单高效的二维CFRP钻孔热传导有限元模型,模拟结果如图8所示,相比新刀具,磨损后的刀具会引起更高的切削温度,具有更大范围的切削高温区。Sadek等[53]认为FRC的钻孔过程中,热传导受刀具的几何形状、刀具上力与力矩分布的影响,提出将刀具分成K个等厚层,刀具所受总的轴向力与力矩可由主切削刃和横刃上每层的力与力矩求和得到,该理论模型对刀具设计具有指导意义。Sorrentino等[54]建立了二维轴对称的钻削热热传导有限元模型,极大地减少了仿真所需计算时间,但模型只能预测温度,不能反应钻削过程中损伤、应力等其他状态。Bao等[55]将建立的预测钻削过程中温度分布的三维数值模型运用于芳纶纤维增强树脂基复合材料(Aramid fiber reinforced polymer composites,AFRP)的钻孔仿真,结果表明,编织结构的AFRP钻削热云图呈近圆形的菱形,仿真结果与实验结果有较好的一致性。Kubher等[56]的研究中指出多向(Multidirectional,MD)CFRP热力耦合钻削仿真模型中层内损伤应考虑正应力σ33和剪应力σ13、σ23,并认为附加层间损伤模式中,黏性单元的损伤起始基于二次强度准则,仿真结果更加符合实验所测得结果。
![]() 图 8 CFRP钻孔时的二维热传导有限元模拟结果(高温区由尺寸标注,温度高于180°C):(a) 新刀具;(b) 磨损刀具[52]Figure 8. Two-dimensional finite element simulation results of heat conduction during drilling with CFRP (The high temperature zone is marked by dimensions, the temperature is higher than 180 C): (a) New tool; (b) Wear the cutting tools[52]
图 8 CFRP钻孔时的二维热传导有限元模拟结果(高温区由尺寸标注,温度高于180°C):(a) 新刀具;(b) 磨损刀具[52]Figure 8. Two-dimensional finite element simulation results of heat conduction during drilling with CFRP (The high temperature zone is marked by dimensions, the temperature is higher than 180 C): (a) New tool; (b) Wear the cutting tools[52]基于上述分析,近年来有关于不同尺度下的切削热的数值模拟主要研究的统计如表1所示,其研究类型可按图7进行分类,学者们从微观尺度和宏观尺度对不同FRC模拟了其材料性能影响因素、加工质量影响因素、温度场分布变化规律和损伤本构优化。但由于计算机计算能力限制,目前对FRC的钻削热、传热机制的仿真模拟大多只模拟了机械损伤或热传导,而对钻孔缺陷或损伤进行热力耦合模拟的研究又较理想化,与实际结果存在一定偏差。关于FRC的有限元模型中使用的损伤判据与损伤演化与实际情况仍存在一定偏差,从更深层次建立热力耦合作用下的损伤模型预测FRC的钻孔缺陷与损伤是目前的难点。
表 1 切削热的数值模拟分析Table 1. Numerical simulation analysis of cutting heatSimulation scale Object Keyword Reference Micro-scale UD-CFRP Fiber orientation angle [41] UD-CFRP Ultrasonic vibration [43] UD-CFRP Temperature
pretreatment[26] 3D braided composites Thermal conductivity [44] 3D braided composites Braiding angle [45] 3D braided composites Elastic-plastic damage constitutive laws [46] UD-CFRP Stress concentration [47] Macro-scale CFRP Thermal damage area prediction [48] Tool Cutting tool structure
design[49] CFRP, GFRP Temperature prediction [50] AFRP Temperature prediction [51] CFRP Intralaminar damage [52] 2. FRC钻削热的影响及其控制策略分析
2.1 钻削热测量方法研究
由于FRC特殊的材料性能(各向异性、不均质性、层间强度低)及半封闭式的钻削加工特点,一般的金属切削测温方法对FRC钻削温度测量是不适用的。Liu等[35]研究指出,钻削CFRP的过程中,K型热电偶的测温精确度与可靠性比高温计、红外测温仪高。Kerrigan等[57]在边缘切削实验中,通过在刀具中嵌入无线热电偶测量刀具温度,同时使用热成像测量工件温度的方法,研究了进给量、工件厚度和轴向切削深度对切削温度的影响。Sorrentino等[58]使用热电偶测温的方法,研究了CFRP和玻璃纤维增强树脂基复合材料(Glass fiber reinforced polymer,GFRP)钻削温度与进给速度的关系,指出进给速度与钻削温度呈现出正比关系。Merino-Pérez等[59]在研究钻削热过程中比较了利用热成像测量温度和动态热电偶测量温度两种测温方法,指出与热成像相测量温度相比,热电偶测量温度的方法由于其响应时间低和测温设备更复杂而存在一定的局限性。Loja等[60]使用热成像测温方法研究证明了分层损伤的形成是热力耦合作用的过程,研究结果发现温度升高,分层损伤具有加重的趋势。Takeshi等[61]结合使用多种温度测量方法:(1) 刀具-工件间热电偶直接测量切削点的温度;(2) 热成像仪测量全局温度;(3) 预埋K型热电偶测量层间温度,提高了温度测量的精确度。
根据上述研究可以看出:当前FRC钻削测温方法主要有刀具-工件热电偶法[62]、工件嵌入热电偶法[63-64]和热像仪测温法3种方法[61],其测量装置示意图分别如图9所示。实现钻削温度的精准测量是目前研究的难题,而直接测量钻头的温度,让工件旋转也仅能在低速钻削中实现,且与实际加工的工况存在一定的差别。因而采用更先进、更简便的方法实现钻削温度的精准测量是近10年的研究热点。例如,采用多种测温方法相结合、或采用多点、多角度测量方法测量同一加工工况下温度的办法,从而获取更可靠的数据,这将有助于分析各种影响钻削热因素的权重系数,进一步探究热损伤机制,从而建立更精准的传热数值模型、多尺度下的有限元损伤等其他预测模型,最终实现工艺的优化等目的。
![]() 图 9 三种不同测温方法的实验原理图:(a) 刀具-工件热电偶法;(b) 工件嵌入热电偶法;(c) 热像仪测量法[61]PC—Personal computerFigure 9. Experimental schematic diagram of three different temperature measurement methods: (a) Tool-workpiece thermocouple method; (b) Workpiece embedding thermocouple method; (c) Thermal imager measurement method[61]
图 9 三种不同测温方法的实验原理图:(a) 刀具-工件热电偶法;(b) 工件嵌入热电偶法;(c) 热像仪测量法[61]PC—Personal computerFigure 9. Experimental schematic diagram of three different temperature measurement methods: (a) Tool-workpiece thermocouple method; (b) Workpiece embedding thermocouple method; (c) Thermal imager measurement method[61]2.2 钻削热对制孔质量影响研究
制孔加工质量包括孔壁表面质量、制孔尺寸精度和分层、毛刺、撕裂等损伤缺陷程度,其主要损伤形式如图10所示。FRC具有温度敏感性,特别是环氧基体其力学性能和变形行为显著受温度影响,因此钻削热对制孔加工质量有重要影响。以分层损伤为例:一方面由于纤维增强体和基体的热导率、热膨胀系数都存在显著差异,在钻孔过程中,随着工件和刀具的温度升高,工件容易由于受热而发生应力集中,进而使工件内部产生局部应变导致分层缺陷。另一方面由于基体与纤维均为传热的不良导体,钻孔过程产生的热量难及时向外传导,因此易产生热量积聚,导致刀具因温度过高产生热疲劳磨损,而刀具磨损也会加重分层缺陷[65]。
为了探究温度对FRC加工质量的影响,许多学者研究了温度变化对FRC物理性能的影响。Luigi等[67]研究指出碳纤维增强聚苯二甲酸乙二醇酯复合材料的抗冲击性能随温度升高而增强,但弯曲强度随温度升高而下降。Xavier等[68]研究指出UD碳纤维/聚酰亚胶树脂复合材料在达到玻璃化转变温度之前具有高温稳定性,当温度达到玻璃化温度后,材料的储能模量、强度都显著下降。Um等[69]研究了碳纤维增强聚对苯二甲酸乙二酯复合材料在不同温度影响下结晶后的力学性能变化,结果表明温度升高纤维方向拉伸模量、拉伸强度、面内剪切模量、面内剪切强度都降低。
基于FRC温度变化与物理性能的研究基础,许多学者更进一步研究了切削热与加工质量之间的关联。Siddharth等[70]系统地研究了CFRP钻削分别在干钻和低温条件下的可加工性,并提出了一种引入最大轴向力与临界轴向力的比值的新分层损伤评价方法,结果表明分层因子和表面粗糙度随着温度的降低均呈减小趋势,而轴向力呈增大趋势。Fu等[71]使用热成像测温的方法,详细揭示了UD和MD-CFRP钻出口温度分布与变化机制,并指出UD和MD-CFRP钻出口的最高温度都在纤维方向角为–25°到25°,公称直径向内约0.5 mm处。Ge等[72]研究了热塑性碳纤维/聚醚醚酮(CF/PEEK)复合材料的制孔性能,首次系统地阐明了碳纤维增强热塑性塑料制孔过程中,热力耦合作用对钻孔损伤的影响机制,并指出CF/PEKK的分层损伤在低进给速率时温度对分层损伤的影响较大,在高进给速率时轴向力对分层损伤影响更大。
综上所述,由于FRC的基体有着传递热载荷与机械载荷的作用,而基体的力学性能和变形行为受温度影响显著,当温度升高,FRC的弯曲强度、刚度、储能模量和拉伸强度都会降低,导致分层损伤加重、孔壁表面粗糙度增大和纤维拔出增多等问题,并且温度升高会加剧刀具磨损,刀具磨损则又会影响孔壁形貌等加工质量,因此钻削温度与钻孔损伤存在着千丝万缕的联系,研究钻削热的影响因素及其冷却控制策略依旧是控制孔损伤的首要工作[73]。
2.3 钻削刀具对钻削热的影响
在FRC钻孔加工过程中,由于纤维具有很高的硬度和强度,钻头会受到强烈的摩擦磨损,又加之钻孔是半封闭加工过程,易造成热量聚集。在高温条件下钻孔不仅会增加热损伤和刀具磨损,还会造成黏刀等问题,严重影响制孔质量。因此FRC制孔加工对刀具材料的硬度、强度及耐磨性有很高要求[74]。通过改变刀具的几何尺寸与形貌或优化涂层的方法来降低温度对孔的加工质量的影响,大量研究人员对此方面研究做出了贡献,并取得了一些突破性的结果[75]。
在刀具结构方面,以对现有刀具结构进行改型及其微结构修整为主的研究已成为现阶段的研究重点。例如,陈浩等[76]研究了麻花钻几何参数对钻削温度的影响,结果表明钻尖角和螺旋角对钻削温度无明显影响,钻削温度随横刃长度的减小有所降低。Shu等[28]基于减小前角从而改变切削机制的原理设计了一种新钻孔刀具,其刀具结构如图11(a)中右侧所示,相比传统麻花钻,该刀具横刃更薄,并具有锯齿结构,能够有效降低钻削温度,如图11(b)所示,使用新型刀具的CFRP钻出口处温度更低。同年,Kong等[77]更进一步设计了一种新的螺旋钻孔刀具,如图12所示,其设计的新型刀具特点在于使用轨道磨削制孔中刀具的运动轨迹并采用类似阶梯钻的结构。
![]() 图 11 CFRP钻出口热像图:(a) 实验所用刀具;(b) 钻出口处随钻孔深度变化的热像图(其中左侧使用常规刀具,右侧为新型刀具)[28]Figure 11. Thermal images of CFRP drill hole: (a) Tool used in the experiment; (b) Thermal image of the drilling outlet with the change of drilling depth (In which conventional tools are used on the left side and new tools are used on the right side)[28]
图 11 CFRP钻出口热像图:(a) 实验所用刀具;(b) 钻出口处随钻孔深度变化的热像图(其中左侧使用常规刀具,右侧为新型刀具)[28]Figure 11. Thermal images of CFRP drill hole: (a) Tool used in the experiment; (b) Thermal image of the drilling outlet with the change of drilling depth (In which conventional tools are used on the left side and new tools are used on the right side)[28]![]() 图 12 轨道钻孔及其刀具示意图[77]ap—Screw pitch of the helical path; D—Diameter of the peripheral cutting edges; e—Eccentricity of the helical path; d—Diameter of the milling part; R—Radius of the arc of the ODR tool; ODR—Orbital drilling and reamingFigure 12. Schematic diagram of track drilling and its tools[77]
图 12 轨道钻孔及其刀具示意图[77]ap—Screw pitch of the helical path; D—Diameter of the peripheral cutting edges; e—Eccentricity of the helical path; d—Diameter of the milling part; R—Radius of the arc of the ODR tool; ODR—Orbital drilling and reamingFigure 12. Schematic diagram of track drilling and its tools[77]除了以上研究,Xu等[78]设计了一种排屑槽平行于刀具轴线的新型聚晶金刚石(PCD)匕首钻,并研究指出该匕首钻有助于减少分层损伤、降低孔壁粗糙度和延长刀具寿命,但匕首钻排屑槽空间较小,易造成排屑不畅。Xu等[14]研究了使用具有金刚石涂层烛心钻和阶梯钻的CFRP钻孔可加工性,结果表明由于第二切削刃的扩孔效应,阶梯钻比烛心钻具有更好的孔壁形貌和较低的表面粗糙度值,并指出为了减小孔径偏差,烛心钻适合采用高转速和中速进给,而阶梯钻适合采用中转速和小进给。
在刀具材料与涂层方面,由于刀具磨损会导致热量积聚,钻削温度升高,降低制孔质量,因此控制刀具磨损是学者们的重点研究方向[74]。Xu等[78]研究指出,PCD刀具相对于高速钢和硬质合金刀具钻削CFRP时具有更高的加工质量和刀具寿命。伍俏平等[79]对比了超细晶硬质合金钻头与普通硬质合金钻头钻削AFRP的性能,结果表明超细晶硬质合金钻头相比普通硬质合金钻头具有更高耐磨性,钻削温度和钻削力都更低。Gaugel等[80]研究指出金刚石涂层刀具比无涂层具有更高的耐磨性,但只有在加工高质量复合材料时具有显著寿命优势。但有涂层刀具并不总是性能优于无涂层刀具,Xu等[81]的研究指出在钻削CFRP/Ti时,相同切削条件下,TiAIN涂层钻头并没有比无涂层钻头有明显优势,反而无涂层钻头具有更低的轴向力、更好的孔出口边缘处加工质量。Redouane等[82]研究了金刚石涂层与纳米复合多层涂层对加工温度和刀具磨损的影响,结果表明涂有金刚石层或纳米复合层的刀具具有良好的导热系数与更小的摩擦系数,可以降低加工温度,减少基体的热降解。
由于设计特殊钻头降低FRC钻削热的成本较高,仅有少数学者针对特殊结构刀具设计进行研究,关于优化刀具控制钻削热的相关研究类型如图13所示,学者主要从改变刀具结构、几何尺寸和涂层的角度研究了控制钻削热方法。钻孔过程中,钻削温度会随着刀具与工件接触面积增大而升高,这可以通过减小钻头直径来降低钻削热。刀具与工件间的后角大小也会影响钻削温度,当后角较小时,刀具与工件的接触面积会增大,导致摩擦力增大,产生更多的热量,这可以通过减小切削刃半径的方法来降低钻削温度。改变刀具几何尺寸控制钻削热的研究已经比较成熟,针对考虑钻孔过程中切削机制的刀具结构设计和刀具几何尺寸参数优化分析从而控制切削热是以后研究的重要方向。在刀具材料方面,目前刀具基体材料主要以硬质合金和PCD为主,刀具涂层材料则以金刚石涂层为主。虽然综合考虑金刚石涂层耐磨性最优,但单一涂层无法满足硬度、耐磨性和耐热性等综合性能,刀具的多层、复合涂层研究是目前的主要方向[83]。
2.4 工艺参数对钻削热的影响
在常规的FRC钻削加工中,大量研究成果指出切削速度和进给量是影响切削热最显著的两个因素[85]。早在Chen等[86]研究中,结果表明钻削温度受切削速度和进给速度的影响,当切削速度过高或进给速度太低时,钻削温度均会升高,钻削温度与加工参数的关系可参考图14[28]。王福吉等[21]的研究结果显示当每齿进给的增大,最大切削力、温升速率都会随之会增加。除了以加工参数为变量,学者们还针对不同类型FRC,以其他工艺参数为变量做了进一步研究。
对于热固性复合材料,Merino-Pérez等[59]研究了交联密度和结晶度对CFRP钻孔过程中的最高温度的影响,结果表明具有更高交联密度和更紧密的分子网络的树脂表现出更强的散热性、更高的玻璃化转变温度和热稳定性。Wang等[87]建立了不同纤维方向角下UD-CFRP的热导率数值模型,并通过边缘铣削实验研究了热导率对CFRP切削温度的影响,结果表明当纤维方向角为45°时CFRP有最大的有效散热区,而135°时最小,因此在不同切削速度下45°角的切削温度始终为较低,135°角的切削温度始终较高。Hou等[88]使用陶瓷片加热待切削区域后,通过正交切削实验观测CFRP的切屑形成与面下损伤,结果表明纤维方向角在约150°时,孔出口处表面松弛、基体开裂和纤维拉出较明显。
对于热塑性复合材料,王福吉等[89]研究了进给速度对玻璃纤维增强聚丙烯复合材料的出口温度的影响,结果表明在低速进给时钻削出口温度随进给速度增加显著升高,在高速进给时钻出口温度受进给速度影响较小,并研究指出进给速度过高或过低都会加重钻出口处撕裂,而入口处撕裂损伤随进给速度增加基本呈单调递增趋势。Xu等[90]研究了碳纤维增强聚酰亚胺(CF/PI)和CF/PEEK钻削加工的可加工性,结果表明以CF/PI和CF/PEEK为代表的热塑性复合材料具有与热固性复合材料相似的切削热规律,钻削温度会随切削速度增加而增加,分层因子随进给量增大而增大,分层因子随切削速度增大而减小,并指出相比CF/PI,CF/PEEK具有更好的孔壁形貌和尺寸精度,但是刀具磨损更剧烈。
综上所述,传统钻削工艺下,钻削的主轴速度和进给量是影响钻削热的主要因素。由于基体有着传递热载荷与机械载荷的作用,FRC在进给方向上的热物理性能主要由基体决定,因此FRC工件的材料属性本身很大程度上影响钻削热,质地较硬、工艺较好的材料其产生的钻削热较多,FRC的结晶度、材料交联密度、基体热物理属性和纤维排布方式也会影响钻削热。相比于热固性树脂基复合材料,以基体使用PEEK、聚苯硫醚(PolyphenyleneSulfide,PPS)和聚醚酰亚胺(Polyetherimide,PEI)为代表的先进热塑性复合材料因其具有低吸湿、损伤容限高等独特优势,目前已成为FRC研究的主流[91-93]。
2.5 辅助加工控制钻削热方法
对于FRC的制孔方式有多种,例如水射流、高能粒子束、电火花制孔是常用的制孔方式,但综合考虑加工质量、加工效率和成本等因素,实际生产中FRC制孔仍以机械切削为代表的接触式加工为主[94]。由于FRC具有硬度高、强度大、导热性差、层间强度低等特点,在孔加工时易产生分层、毛刺、撕裂,刀具极易磨损,加工表面质量低。除了上述单一FRC制孔容易产生的问题外,叠层结构的复合材料有额外的制孔难题:(1) 铝/钛合金本身就是难加工材料,钻孔加工过程中会产生极高的热量,增加热损伤;(2) 叠层顺序会影响加工质量;(3) 金属和复合材料接合面处切削力、切削热呈现阶跃变化,刀具受力热冲击,易磨损崩刃。针对上述问题,国内外许多学者尝试优化加工方法减少切削热[90]。
2.5.1 最小润滑辅助钻削加工
为了克服钻削加工中热交换困难、温升过快、保证零件加工精度等问题,采用最小润滑(Minimum quantity lubrication,MQL)辅助加工技术也在FRC加工中逐步采用。其原理是将压缩气体与少量润滑油(通常小于100 mL/h)混合,形成微米大小的液滴油雾,通过喷嘴高速喷射到切削区域从而实现充分润滑[95]。MQL辅助加工技术原理如图15所示,传统润滑液无法靠近刀具切削的尖端部分,而最小润滑技术能够使刀具切削区域得到充分润滑。
进一步地,MQL辅助加工技术可以通过添加纳米增强生物润滑剂改善刀具-工件界面的摩擦状态,减少刀具磨损,且切削区域与外界的传热效率会由于纳米增强剂的布朗运动的作用得到提高。此外MQL辅助加工技术可大大减少冷却介质的用量,极大地减少了加工成本。但是MQL辅助加工还存在一些问题,比如MQL辅助加工会增大加工表面粗糙度[96]。关于MQL辅助钻FRC,相关学者做了一些尝试性的探索研究。Gao等[66]研究结果表明MQL能显著防止毛刺缺陷和热损伤,但润滑剂会使粉末状CFRP切屑很容易黏附在刀具表面和孔壁上,并研究指出高空气流速和低油流速的结合更有助于液滴的细化和喷雾效果,从而提高加工精度与减少刀具磨损。Xu等[97]比较了不同加工方式与刀具涂层对CFRP/Ti6 Al4 V层叠结构复合材料钻孔加工质量的影响,结果表明MQL辅助加工相比干钻能够提高孔的表面质量并有利于抑制Ti毛刺的形成,同时指出虽然金刚石涂层刀具能够降低钻孔扭矩并具有较低的比切削能,然而在MQL加工条件下,金刚石涂层钻头相比TiALN涂层钻头更容易导致Ti屑的堵塞,TiALN涂层更有利于抑制Ti毛刺的形成。基于先前的研究,Xu等[98]又发现MQL加工比干钻有更高的轴向力,认为这是由于纤维的脆性断裂和基体的吸水性使FRC表面吸收了润滑剂,而没有在钻头-工件界面形成稳定润滑膜,并且MQL加工会导致CFRP切屑堵塞,使轴向力更大,因此MQL加工不能有效减少分层损伤。Arjun等[99]比较了CFRP在干钻、MQL加工和低温冷却条件下的钻孔性能,结果表明低温冷却钻孔的轴向力比干钻高36%,MQL加工比干钻高17.6%,低温冷却钻孔的扭矩比干钻高15%,MQL加工比干钻低17%,干钻分层最轻微,低温冷却钻孔最严重,低温冷却钻孔的圆度误差最小。
综上所述,MQL辅助加工技术能够有效减少FRC钻孔的毛刺、热损伤和刀具磨损,并且相比于低温冷却辅助钻削加工(如液氮、液氧、冷风等冷却方式)技术,MQL辅助钻削加工技术能够极大地减少冷却介质的用量,降低了加工成本。但由于其对润滑剂的种类、颗粒尺寸和流速有高技术要求、基体材料的吸水性使刀具-工件界面不能形成稳定的润滑膜、切屑易排出不畅导致加工质量不稳定,因此目前关于MQL辅助加工的应用和研究较少,也是有待进一步突破的难点。
2.5.2 低温冷却辅助钻削加工
FRC的低温冷却辅助钻孔加工通常使用液氮、二氧化碳或冷冻空气作为冷却介质来实现快速散热,从而降低切削温度。低温冷却辅助通过降低切削温度,增加了工件在钻削时的杨氏模量和抗拉强度,提高了抗断裂强度、刚度、层间的剪切强度和硬脆性,从而提高了分层临界轴向力,增强了抗分层失效的能力。此外,低温冷却辅助钻孔在抑制毛刺、裂纹、热损伤和减少刀具磨损方面也有明显优势[66],国内外学者对此也做了深入的研究分析。
关于液氮冷却辅助加工,Gültkein等[100]采用液氮低温冷却加工方法钻削CFRP,研究指出该方法降低了孔壁表面粗糙度和刀具磨损,但增加了轴向力和分层系数。Marcelo等[101]对热塑性和热固性CFRP分别进行干钻和液氮冷却辅助钻削,结果表明对于热塑性和热固性CFRP,低温冷却辅助加工都均能改善孔的表面质量、保证孔径尺寸,但热塑性CFRP在低温环境下具有更高的刚度,钻孔时的轴向力和扭矩更大,导致其分层因子受冷却条件影响更大。Navneet等[102]研究指出,与干钻相比液氮冷却钻孔的圆柱度和圆度偏差更大,但表面形貌更好,反分层因子数值更优。王晋宇等[103]研究了液氮作为冷却介质的AFRP复合材料钻孔试验,结果表明低温冷却辅助加工能有效减少毛刺面积,抑制烧蚀现象,改善AFRP的孔加工质量。
关于液化二氧化碳冷却辅助加工,Rodríguez等[104]学者的研究指出在对CFRP-Ti6 Al4 V钻削时使用液化二氧化碳作为低温冷却剂,可保证孔径偏差在0.5%以内、刀尖温度显著降低、CFRP相的表面完整性增加、刀刃磨损减少、刀具寿命延长,并研究指出相比干钻使用液化二氧化碳低温冷却会增加能耗,但随着钻孔数量增加,能耗逐渐降低。邹凡等[105]为了减少冷却介质用量,研究了超临界二氧化碳低温冷却方法应用于CFRP复合材料机械加工的可行性,结果表明相比干式切削超临界二氧化碳低温冷却辅助加工能明显提高表面质量。
关于冷风辅助加工,王福吉等[106]比较了干式切削、正向冷风冷却和逆向冷风冷却条件下钻削CFRP加工质量,结果表明相比干钻正逆向冷风冷却均能够有效抑制刀具磨损,并研究指出在使用逆向冷风冷却时,由于孔内气流运动情况更加稳定,切屑去除能力更强,换热效果更明显,因此逆向冷风冷却能够更好地抑制刀具磨损,延长刀具寿命。由于正向冷风冷却的气流对出口纤维有顶出作用,因此其引起的毛刺高度最大,干式切削的毛刺高度次之,由于逆向冷风的气流对纤维有拉回作用,因此逆向冷风冷却的毛刺高度最小。此外,采用冷风冷却不论气流流向如何,由于气流对纤维的牵扯作用,都会导致撕裂损伤的增加。
根据以上学者的研究,表2总结了近年来低温冷却辅助加工控制切削热的相关研究,以上学者的研究表明了通过低温冷却辅助加工方法控制切削热已经是一种成熟的加工技术。不同辅助加工方法的实验装置如图16所示[107],相比于常用的干式切削,液氮低温冷却剂更有助于降低刀具损伤,但会增大切削力和扭矩,二氧化碳为冷却剂的节流低温冷却钻孔更有助于提高孔的表面质量和尺寸精度(孔径尺寸和圆柱度等),而冷风辅助加工更有利于抑制毛刺损伤。
表 2 辅助加工控制温度研究Table 2. Study on control temperature of auxiliary machiningAuxiliary method Object Subject Reference MQL CFRP/Ti6Al4V Torque, specific cutting energy, hole wall morphologies, burr [89] CFRP/Ti6Al4V Thrust force, delamination damage, tool wear, [90] CFRP torque, thrust force, delamination damage, hole diameter, roundness [91] LN2 CFRP Hole wall morphologies, hole wall surface roughness, tool wear, thrust force [92] CFRP, CFRPs Torque, thrust force, delamination damage, hole diameter, roundness [93] CFRPs Hole wall surface roughness, roundness, cylindricity, delamination damage [94] AFRP Thrust force, delamination damage, burr, ablation [95] LCO2 CFRP/Ti6Al4V Hole diameter, power consumption [96] CFRP Hole wall morphologies, hole wall surface roughness, torque [97] Air CFRP Burr, tear, tool wear [98] Ultrasonic vibration CFRPs Hole wall surface roughness, thrust force, torque, delamination damage, burr, tear [108] CFRP Thrust force [43] CFRPs Hole wall morphologies [22] CFRP Hole wall surface roughness, thrust force, delamination damage, burr, tear [110] 2.5.3 振动辅助钻削加工
振动辅助钻削技术充分利用了超声/低频振动加工技术中的锤击、磨抛及划擦等机制,利用瞬间的振动切削快速切断纤维,实现在钻削过程中反复的切削。这种加工方式可有效降低钻削硬脆材料时的钻削力,降低了材料的加工难度,从而显著提升刀具使用寿命[108-110]。振动辅助加工技术可分为低频振动辅助和超声振动辅助,其中多维的旋转超声振动辅助钻削技术是一种新兴的复合加工技术,在FRC切削领域已有较多的应用,国内外学者尝试了采用两种振动技术降低切削热,并取得了一定得研究成果。
在低频振动辅助方面,Sadek等[111]研究指出采用低频振动辅助钻削CFRP可降低切削温度约50%,轴向力约40%,有效减少了撕裂和分层损伤。Oliver等[112]研究指出低频振动钻削工艺也适用于CFRP/Ti6 Al4 V叠层材料,可有效降低切削温度,从而减少刀具磨损。张世杰等[113]研究指出高低频复合振动钻削可有效抑制CFRP/Ti中CFRP入口处撕裂损伤,提高孔壁质量。但是陈冒风等[114]研究表明CFRP/Ti低频振动钻削会使Ti切屑在排出过程中对CFRP孔壁造成二次切削作用,扩大CFRP的孔径,而Ti层的孔径变化很小,导致孔径存在阶差。谢大叶等[115]分析了低频振动辅助钻削的运动学原理,总结了提高制孔质量及断屑的机制,指出低频振动装置的加工参数需满足使切削刃轨迹发生干涉的条件才能实现断屑,断屑有助于减少切屑对CFRP孔壁的划伤和切屑与孔壁的摩擦,从而降低切削热的产生。
在超声振动辅助方面,Liu等[116-117]研究指出纵向扭转耦合旋转超声辅助钻孔会随着振幅的增加,孔出口处的表面粗糙度和缺陷都具有先减小后增大的变化趋势,并且当振幅为7~9 μm时,毛刺因子、撕裂因子和分层因子最小,遗憾的是未对钻削热进行研究并控制。Xu等[47]研究指出,超声振动切削中,由于工件与刀具接触时间短和切屑被快速去除,温升速率被有效抑制,进而工件的温度可以始终保持在基体玻璃化转变温度以下。Geng等[22]测量了旋转超声椭圆振动加工(Rotary ultrasonic elliptical machining,RUEM)和磨削钻孔的切削温度,如图17所示,与磨削钻孔相比,RUEM有效地改善了切屑去除方式,切削区有更好的散热条件,并且RUEM中刀刃的间歇性切削减少了刀具与工件接触时间,使钻孔过程中产生的热量更少,降低了切削温度。为了进一步降低钻削热引起的损伤,李树健等[118]提出一种将超声振动、超低温液氮和超低温环境相结合的辅助加工方法,结果表明超声振动能够降低轴向钻削力,而超低温液氮及形成的冰冻支撑层能够为出口层提供支撑,并降低钻削温度。
综上所述,目前振动辅助加工技术已经被成熟地应用到FRC钻孔加工过程中以控制钻削热的产生。作为先进复合加工技术,旋转超声振动辅助钻削技术在常规纵向振动的基础上实现轴向的振动切削加工有助于大幅度减少切削热,纵扭耦合振动、旋转超声振动和旋转椭圆超声振动则在多维振动工况下进一步减少了切削热,提高了加工质量。学者们更多地研究了多维旋转超声振动辅助钻削,但主要内容是不同钻削方式下的对比实验研究,且部分学者的研究结果存在差异性,钻削参数与钻削温度的影响规律研究尚未深入研究,对于钻削参数与钻削温度之间的拟合模型也有待进一步的突破。
![]() 图 17 旋转超声椭圆振动加工原理:(a) 旋转超声振动加工;(b) 旋转超声椭圆振动加工;(c) 切屑排出示意图[22]vf—Feed speed; ns—Spindle speed; A—Vibration amplitude; H—Local section view H—HFigure 17. Principle of rotary ultrasonic elliptical vibration machining: (a) Rotary ultrasonic vibration machining; (b) Rotary ultrasonic elliptical vibration processing; (c) Schematic diagram of chip discharge[22]
图 17 旋转超声椭圆振动加工原理:(a) 旋转超声振动加工;(b) 旋转超声椭圆振动加工;(c) 切屑排出示意图[22]vf—Feed speed; ns—Spindle speed; A—Vibration amplitude; H—Local section view H—HFigure 17. Principle of rotary ultrasonic elliptical vibration machining: (a) Rotary ultrasonic vibration machining; (b) Rotary ultrasonic elliptical vibration processing; (c) Schematic diagram of chip discharge[22]3. 结 论
重点对纤维增强复合材料(Fiber reinforced composite,FRC)钻削加工中切削热理论研究、钻削热对加工质量影响研究、钻削热影响因素及控制策略等研究进行了综述。目前,虽然国内外学者在FRC钻孔加工过程中热量的产生及其控制策略方面开展了一定的研究,但着眼于有效提高加工质量和优化加工工艺方面仍存在一定的挑战,具体可描述为
(1) 需建立考虑热力耦合作用的FRC钻削损伤形成理论。目前FRC钻孔切削热理论的研究内容主要集中在通过仿真及实验相结合的方法探究单向(UD)-FRC的切削去除机制、切削力、切削温度及切屑的宏观形貌观察上。而关于FRC钻削的热传导理论模型大多基于均质化的理想假设,通过实验观测直接建立FRC钻削过程中的损伤形成理论模型较难实现,而基于有限元法的数值模拟则能有效帮助研究者们分析FRC微观切削过程,建立考虑热力耦合作用的FRC钻削损伤形成理论;
(2) 尚未形成完善的理论来指导多尺度的FRC热力耦合钻削模型的建立。受计算机能力限制,大多数模型只模拟了机械损伤或热传导,而对钻孔缺陷或损伤进行热力耦合模拟的研究大多将工件理想化为均质化模型,不能模拟出FRC钻孔过程中的毛刺、撕裂和分层等微观损伤。FRC的有限元模型中使用的损伤判据与损伤演化也存在一定局限性,一般只能有效预测单一损伤类型。建立更准确的热力耦合作用下的损伤模型从而更全面地预测FRC钻孔缺陷与损伤是目前的难点;
(3) 需要建立“刀具-工艺-控制策略-数据库”一体化研究方法。关于在钻削热对FRC钻孔加工质量影响方面的研究主要停留在表层直观的实验观测层面,已经有大量研究说明了加工参数、材料属性等变量对钻削温度和加工质量的影响。目前控制钻削热的策略主要从刀具、工艺参数和辅助加工技术3个角度考虑。由于FRC的钻削缺陷与损伤由复杂的热力耦合作用引起,单一的控制策略无法实现综合制孔质量的最优,需采用先进的刀型、刀具材料和涂层并配合先进钻削工艺来解决问题。因此需针对FRC从材料的切削机制和刀具疲劳磨损的角度建立系统的刀具设计理论、建立钻削数据库和专家系统、优化辅助加工控制钻削热方法,从而实现刀具、工艺参数和辅助控制方法的快速选择;
(4) 需要优化新型复合振动辅助加工策略与新工艺相互结合的钻削热控制方法。钻削热控制策略中采用有效辅助加工工艺控制FRC切削热已是当前研究的热点问题。其中低温冷却辅助加工和超声振动辅助加工技术被广泛采用来控制切削热。但单一的辅助加工技术存在一定局限性,低温冷却辅助加工会增加钻削轴向力,而超声振动辅助加工对叠层结构工件的制孔质量提升效果不显著,最小润滑(MQL)辅助加工则对设备的技术要求较高,加工系统复杂,且加工质量不稳定。因而学者们多尝试使用复合辅助加工技术控制钻削热,如低温冷却与超声振动相结合,但针对控制FRC钻削热的新型工艺的开发仍任重道远。
-
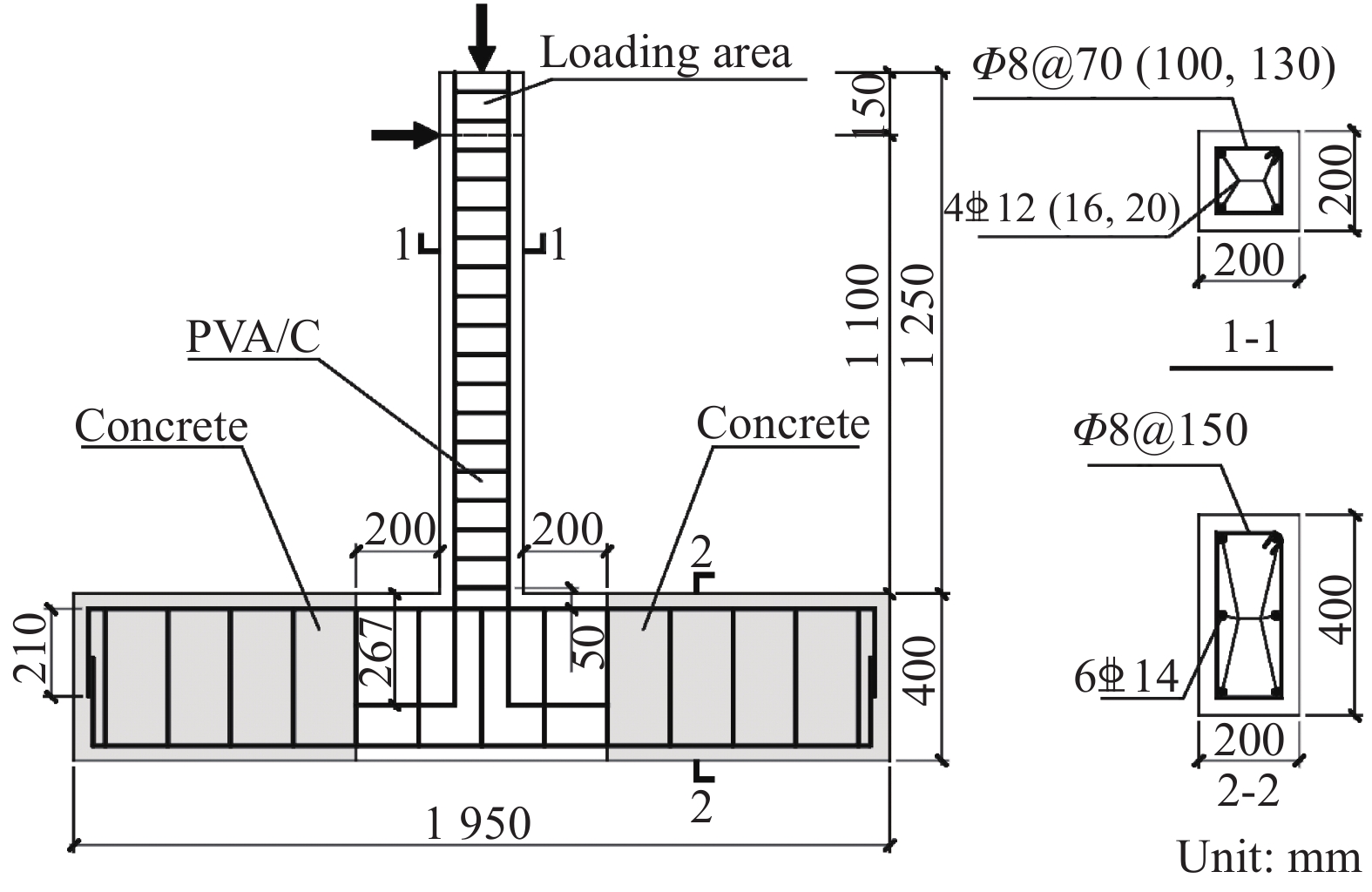
表 1 试验工况
Table 1 Test conditions
Specimen Fiber volume
fraction
\rho _{\rm{f}} /vol%Designed axial
compression
ratio nText axial
compression ratio ntShear
span
ratioRebar Stirrup Stirrup volume
ratio \rho _{\rm{v}} /%0vol%PVA/C-70 0 0.3 0.179 5.5 4 
Φ8@70 1.74 1vol%PVA/C-70 1.0 0.3 0.179 5.5 4 
Φ8@70 1.74 2vol%PVA/C-70 2.0 0.3 0.179 5.5 4 
Φ8@70 1.74 1vol%PVA/C-100 1.0 0.3 0.179 5.5 4 
Φ8@100 1.22 1vol%PVA/C-130 1.0 0.3 0.179 5.5 4 
Φ8@130 0.94 Note: PVA/C—Polyvinyl alcohol fiber reinforced cementitious composite. 表 2 PVA/C配合比
Table 2 Mix proportion of PVA/C
Cement Fly ash Water Sand Thickener/% Defoamer/% Plasticizer/% Fiber content/vol% 0.8 0.2 0.5 0.8 0.05 1 0.1 0, 1, 2 Notes: Fiber content—Volume fraction, other materials are mass ratio; Water/cement mass ratio is 0.5. 表 3 PVA纤维性能
Table 3 Properties of PVA fiber
Fineness/dtex Density/(g·cm−3) Diameter/mm Elongation/% Length/mm Tensile strength/MPa Elastic modulus/GPa 15 1.3 0.04 6 12 1600 40 表 4 钢筋受拉力学性能参数
Table 4 Tensile mechanical properties of rebar
Steel grade Diameter/mm Yield strength/MPa Ultimate strength/MPa Elongation after fracture/% HRB400 12 442 635 25.0 16 449 640 23.0 20 450 640 22.5 表 5 PVA/C材料力学性能
Table 5 Mechanical properties of PVA/C
Fiber content/vol% fcu/MPa fc/MPa ft/MPa 0 46.63 42.66 2.25 1 46.31 41.18 4.70 2 46.12 40.81 5.08 Notes: fcu—Cube crushing strength; fc—Prism compressive strength; ft—Axial tensile strength. 表 6 PVA/C试件特征值
Table 6 Characteristic values of PVA/C specimens
Specimen Loading direction Cracking point Yield point Peak point Ultimate point Pcr/kN \varDelta _{\rm{cr}}/mm Py/kN \varDelta_{\rm{y}}/mm Pm/kN \varDelta_{\rm{m}}/mm Pu/mm \varDelta_{\rm{u}}/mm 0vol%PVA/C-70 Positive direction 6.60 1.86 24.20 16.43 29.40 22.24 14.95 51.00 Negative direction −11.2 −0.29 −38.30 −14.83 −43.40 −23.45 −36.90 −50.54 1vol%PVA/C-70 Positive direction 17.60 3.41 26.70 11.38 31.70 22.7 13.66 59.04 Negative direction −9.60 −0.84 −37.70 −14.44 −45.40 −24.31 −38.60 −60.39 2vol%PVA/C-70 Positive direction 17.50 3.40 25.50 11.31 31.10 25.19 18.40 68.92 Negative direction −9.40 −1.43 −33.70 −18.20 −41.00 −27.06 −34.90 −77.73 1vol%PVA/C-100 Positive direction 11.80 2.57 26.20 10.40 30.60 22.06 17.36 46.06 Negative direction −11.80 −1.56 −38.1 −12.44 −45.10 −23.12 −38.30 −44.15 1vol%PVA/C-130 Positive direction 10.00 2.74 25.40 11.89 29.10 18.65 16.06 43.00 Negative direction −13.30 −1.44 −32.20 −10.16 −39.50 −25.39 −33.60 −41.04 Notes: Pcr—Column cracking load; \varDelta _{\rm{cr}}—Column cracking displacement; Py—Yield load of longitudinal reinforcement; \varDelta_{\rm{y}}—Specimen yield displacement; Pm—Peak load; \varDelta_{\rm{m}}—Displacement when the column reached peak load; Pu—Loads of specimens in both positive and negative directions decreased to 85% of peak load; \varDelta_{\rm{u}}—Displacement when the column reached ultimate load. 表 7 PVA/C试件位移参数汇总
Table 7 Summary of displacement parameters of PVA/C specimens
Specimen Yield displacement {\varDelta}_{\rm{y}} /mm Ultimate displacement {\varDelta}_{\rm{u}} /mm Displacement ductility coefficient {{\mu }} Elastic-plastic limit displacement angle \mathop \theta \nolimits_{\rm{u}} Absolute value Relative value Absolute value Relative value 0vol%PVA/C-70 15.63 50.77 3.25 1 1/22 1 1vol%PVA/C-70 12.91 59.72 4.63 1.42 1/19 1.16 2vol%PVA/C-70 14.76 73.33 4.97 1.53 1/15 1.47 1vol%PVA/C-100 11.42 45.11 3.95 1.22 1/24 0.92 1vol%PVA/C-130 11.03 42.02 3.81 1.17 1/26 0.85 表 8 PVA/C位移延性系数试验结果与计算结果对比
Table 8 Comparison between test results and calculated values of displacement ductility coefficient of PVA/C
Specimen Test value {{\mu }_{\rm{e}}} Calculated value {{\mu }_{\rm{c}}} {{{{\mu }_{\rm{c}}}} / {{{\mu }_{\rm{e}}}}} 1vol%PVA/C-70 4.63 4.63 1.00 2vol%PVA/C-70 4.97 5.10 0.97 1vol%PVA/C-100 3.95 2.60 1.52 1vol%PVA/C-130 3.81 4.39 0.87 R/FRC3[10] 3.44 3.39 1.01 R/FRC4[10] 3.35 3.39 0.99 R/FRC5[10] 3.58 3.21 1.11 R/FRC6[10] 3.48 3.21 1.08 S1[19] 3.11 3.80 0.82 S3[19] 3.71 3.80 0.98 S6[20] 6.09 5.54 1.09 S7[20] 5.15 5.39 0.96 表 9 PVA/C曲率计算值
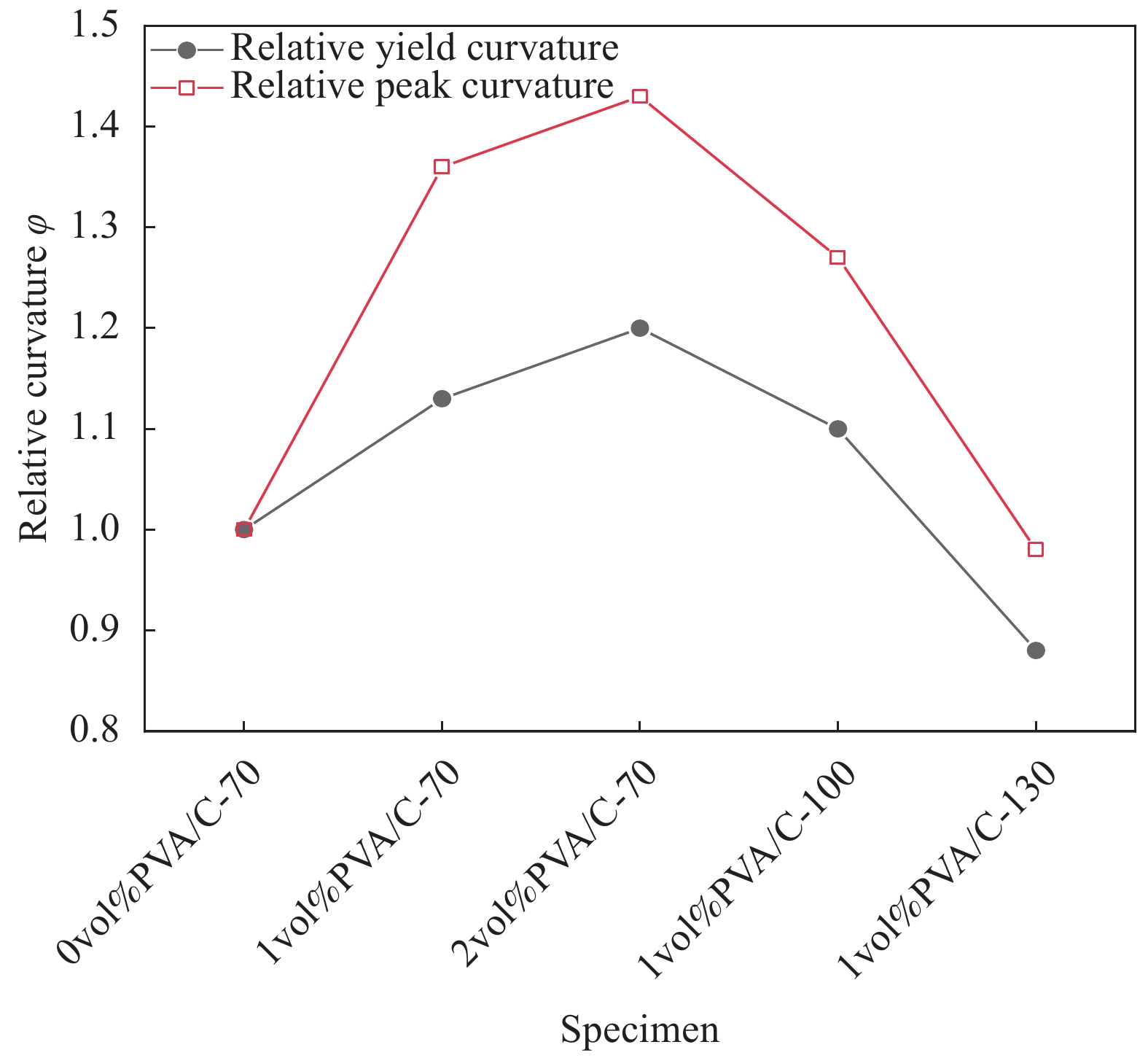
Table 9 Curvature calculation values of PVA/C
Specimen Yield curvature \mathop {\varphi }\nolimits_{\rm{y}} Relative yield curvature Peak curvature \mathop \varphi \nolimits_{\rm{p}} Relative peak curvature 0vol%PVA/C-70 2.71×10−5 1.00 3.43×10−5 1.00 1vol%PVA/C-70 3.05×10−5 1.13 4.68×10−5 1.36 2vol%PVA/C-70 3.26×10−5 1.20 4.89×10−5 1.43 1vol%PVA/C-100 2.99×10−5 1.10 4.36×10−5 1.27 1vol%PVA/C-130 2.39×10−5 0.88 3.36×10−5 0.98 -
[1] HANIF F, KANAKUBO T. Shear performance of fiber-reinforced cementitious composites beam-column joint using various fibers[J]. Journal of the Civil Engineering Forum,2017,9(3):383.
[2] MU Y, ANDO M, YASOJIMA A, et al. Influence of fiber orientation on structural performance of beam-column joints using PVA FRCC[C]//Strain-Hardening Cement-Based Composites. SHCC4, 2017.
[3] MU Y, YASOJIMA A, KANAJUBO T. Shear performance of FRCC beam-column joints using various polymer fibers[J]. Journal of Engineering and Architecture,2019,13(9):562-571.
[4] PAN J, MO C, XU L, et al. Seismic behaviors of steel reinforced ECC/RC composite columns under low-cyclic loading[J]. Journal of Southeast University (English Edition),2017,33(1):70-78.
[5] 梁兴文, 康力, 车佳玲, 等. 局部采用纤维增强混凝土柱的抗震性能试验与分析[J]. 工程力学, 2013, 30(9):243-250. LIANG Xingwen, KANG Li, CHE Jialing, et al. Experiments and analyses of seismic behavior of columnswith fiber-reinforced concrete in bottom region[J]. Engineering Mechanics,2013,30(9):243-250(in Chinese).
[6] 梁兴文, 王英俊, 邢朋涛, 等. 局部采用纤维增强混凝土梁柱节点抗震性能试验研究[J]. 工程力学, 2016, 33(4):67-76. LIANG Xingwen, WANG Yingjun, XING Pengtao, et al. Experimental study on seismic performance of beam-column joints with fiber-reinforced concrete in joint core and plastic hinge zone of beam and column end[J]. Engineering Mechanics,2016,33(4):67-76(in Chinese).
[7] 路建华, 张秀芳, 徐世烺. 超高韧性水泥基复合材料梁柱节点的低周往复试验研究[J]. 水利学报, 2012, 43(S1):135-144. LU Jianhua, ZHANG Xiufang, XU Shilang. Cyclic-loading experiment for investigating seismic performance of beam-column connections with high toughness cementitious composites[J]. Journal of Hydraulic Engineering,2012,43(S1):135-144(in Chinese).
[8] 邓明科, 张辉, 梁兴文, 等. 高延性纤维混凝土短柱抗震性能试验研究[J]. 建筑结构学报, 2015, 36(12):62-69. DENG Mingke, ZHANG Hui, LIANG Xingwen, et al. Experimental study on seismic behavior of high ductile fiber reinforced concrete short column[J]. Journal of Building Structures,2015,36(12):62-69(in Chinese).
[9] 姜睿, 徐世烺, 贾金青. 高轴压比PVA纤维超高强混凝土短柱延性的试验研究[J]. 土木工程学报, 2007(8):54-60. JIANG Rui, XU Shilang, JIA Jinqing. An experimental study on the seismic ductility of PVA fiber super-high-strength concrete columns with high axial load ratios[J]. China Civil Engineering Journal,2007(8):54-60(in Chinese).
[10] 韩建平, 刘文林. 高轴压比配筋PVA纤维增强混凝土柱抗震性能试验研究[J]. 工程力学, 2017, 34(9):193-201. HAN Jianping, LIU Wenlin. Experimental investigation on seismic behavior of PVA fiber reinforced concrete columns with high axial compression ratios[J]. Engineering Mechanics,2017,34(9):193-201(in Chinese).
[11] 汪梦甫, 张旭. 高轴压比下PVA-ECC柱抗震性能试验研究[J]. 湖南大学学报(自然科学版), 2017, 44(5):1-9. WANG Mengfu, ZHANG Xu. Experimental study on seismic performance of PVA-ECC columns with high axial load ratio[J]. Journal of Hunan University (Natural Sciences),2017,44(5):1-9(in Chinese).
[12] 邓明科, 方超, 代洁, 等. 高延性纤维混凝土低矮剪力墙抗震性能试验研究[J]. 建筑结构, 2017, 47(2):57-63. DENG Mingke, FANG Chao, DAI Jie, et al. Experimental study on seismic behavior of high ductile fiber reinforced concrete low-rise shear walls[J]. Building Structure,2017,47(2):57-63(in Chinese).
[13] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 建筑抗震设计规范: GB 50011—2010[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2010. Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of People's Republic of China. Code for seismic design of buildings: GB 50011—2010[S]. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 2010(in Chinese).
[14] 陕西省建筑科学研究院. 建筑砂浆基本性能试验方法: JGJ/T 70—2009[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2009. Shaanxi Provincial Building Research Institute. Standard for test method of performance on building mortar: JGJ/T 70—2009[S]. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 2009(in Chinese).
[15] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 普通混凝土力学性能试验方法标准: GB/T 50081—2002[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2002. Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of People's Republic of China. Standard for test method of mechanical properties on ordinary concrete: GB/T 50081—2002[S]. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 2002(in Chinese).
[16] 中华人民共和国住房和城乡建设部. 建筑抗震试验方法规程: JGJ/T 101—2015[S]. 北京: 中国建筑工业出版社, 2015. Ministry of Housing and Urban-Rural Development of People's Republic of China. Specification of testing methods for earthquake resistant building: JGJ/T 101—2015[S]. Beijing: China Architecture & Building Press, 2015(in Chinese).
[17] 徐浩然. 钢-聚丙烯混杂纤维混凝土柱抗震性能研究[D]. 武汉: 武汉大学, 2013. XU Haoran. Seismic performance of steel-polypropylene fiber reinforced concrete columns[D]. Wuhan: Wuhan University, 2013(in Chinese).
[18] 李凤兰, 黄承逵, 温世臣, 等. 低周反复荷载下钢纤维高强混凝土柱延性试验研究[J]. 工程力学, 2005(6):159-164. LI Fenglan, HUANG Chengkui, WEN Shichen, et al. Ductility of steel fiber reinforced high-strength concrete columns under cyclic loading[J]. Engineering Mechanics,2005(6):159-164(in Chinese).
[19] 陈梦成, 陈利平, 袁方. 复合筋增强ECC混凝土组合柱抗震性能研究[J]. 混凝土, 2020(4):1-4, 8. CHEN Mengcheng, CHEN Liping, YUAN Fang. Seismic performance of reinforced with hybrid FRP and steels ECC concrete composite column[J]. Concrete,2020(4):1-4, 8(in Chinese).
[20] LI Xu, PAN Jinlong, CHEN Junhan. Mechanical behavior of ECC and ECC/RC composite columns under reversed cyclic loading[J]. Journal of Materials in Civil Engineering,2017,29(9):04017097. DOI: 10.1061/(ASCE)MT.1943-5533.0001950
[21] SHI Q X, WANG P, TIAN Y, et al. Experimental study on seismic behavior of high-strength concrete columns with high-strength stirrups[J]. Engineering Mechanics, 2014, 31(8):161-167.
[22] 赵国藩, 周氐. 高等钢筋混凝土结构学[M]. 北京: 机械工业出版社, 2005. ZHAO Guofan, ZHOU Di. Advanced reinforced concrete structures[M]. Beijing: Published By Mechanical Indu-stries, 2005(in Chinese).
[23] 邓明科. 高性能混凝土剪力墙基于性能的抗震设计理论与试验研究[D]. 西安: 西安建筑科技大学, 2006. DENG Mingke. Theory and experimental reseach on performance-based seismic design of high performance concrete shear wall[D]. Xi’an: Xi’an University of Architecture and Technology, 2006(in Chinese).
[24] 李建委, 李汉春, 田承昊. 低周反复荷载作用下钢筋混凝土异形柱框架的延性分析[J]. 世界地震工程, 2016, 32(3):53-57. LI Jianwei, LI Hanchun, TIAN Chenghao. Ductility analysis of reinforced concrete special-shaped column frame under low reversed cyclic loading[J]. World Earthquake Engineering,2016,32(3):53-57(in Chinese).
[25] 李忠献. 工程结构试验理论与技术[M]. 天津: 天津大学出版社, 2004. LI Zhongxian. Theory and technique of engineering structure experiments[M]. Tianjin: Tianjin University Press, 2004(in Chinese).
[26] 姜睿. 超高强混凝土组合柱抗震性能的试验研究[D]. 大连: 大连理工大学, 2007. JIANG Rui. Experimental study on seismic performance of reinforced super-high-strength concrete composite columns[D]. Dalian: Dalian University of Technology, 2007(in Chinese).
[27] 吴畅. 考虑剪切效应的RECC柱及框架结构抗震性能研究[D]. 南京: 东南大学, 2016. WU Chang. Study on seismic behavior of RECC col-umns and frames considering shear effect[D]. Nanjing: Southeast University, 2016(in Chinese).
-
期刊类型引用(4)
1. 陶能如,蔡颂,陈根余,肖铮铭,韦怡. 碳纤维复合材料皮秒激光旋切制备大孔工艺. 光学学报. 2024(14): 218-230 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 束静,廖文和,郑侃,董松,孙连军. 旋转超声加工碳纤维复合材料研究现状与展望. 航空学报. 2024(13): 114-138 .  百度学术
百度学术
3. 李玉峰,赵积鹏,张海,于斌. 高低温对碳纤维/环氧树脂复合材料高压气瓶的性能影响. 工程塑料应用. 2024(09): 119-125 .  百度学术
百度学术
4. 邹喆. 镁合金层合板麻花钻削工艺对轴向力的影响. 山西冶金. 2024(10): 63-64+67 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(2)
-





 下载:
下载: