Preparation and characterization of aligned carbon nanotubes/epoxy composite films
-
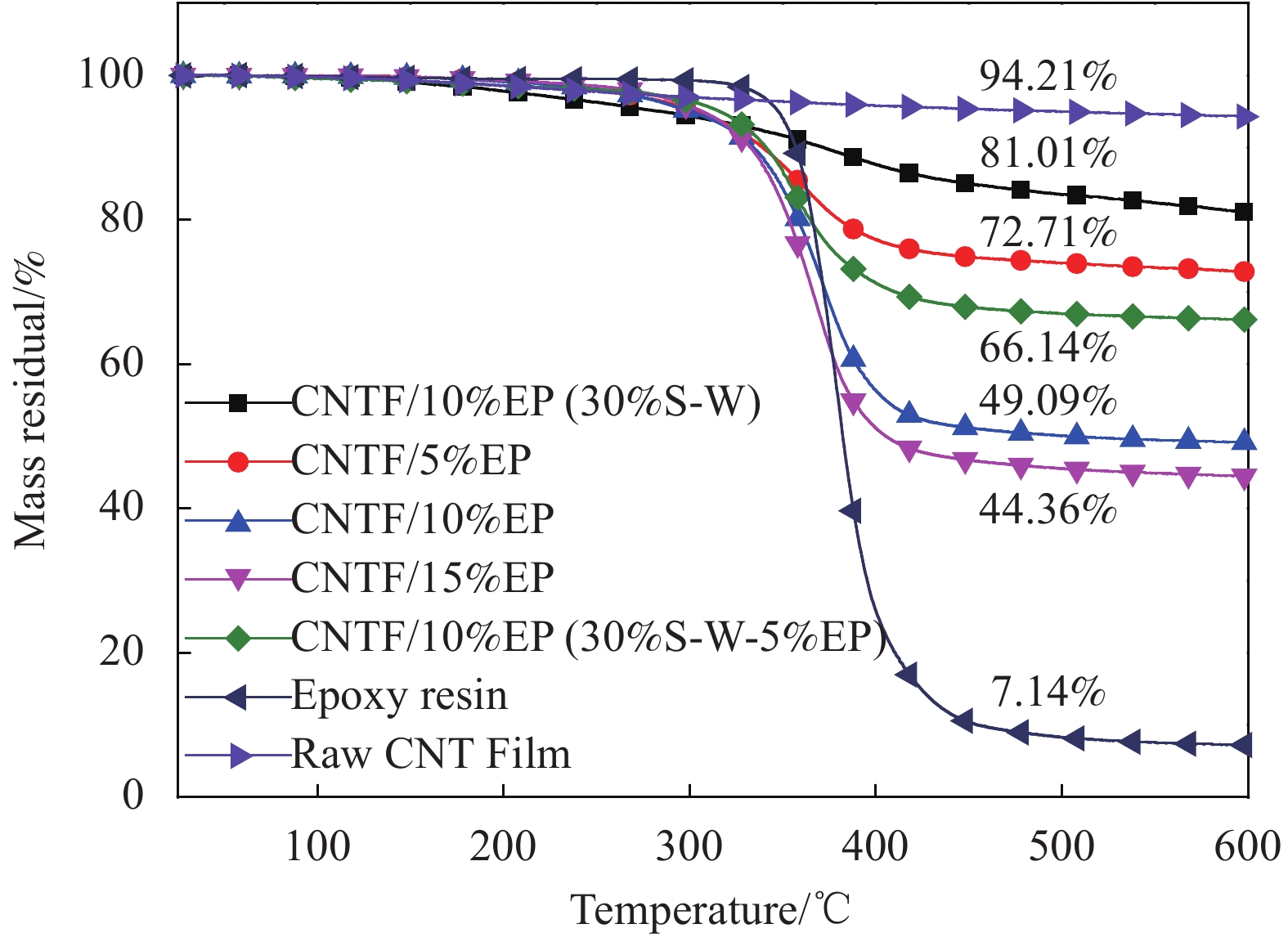
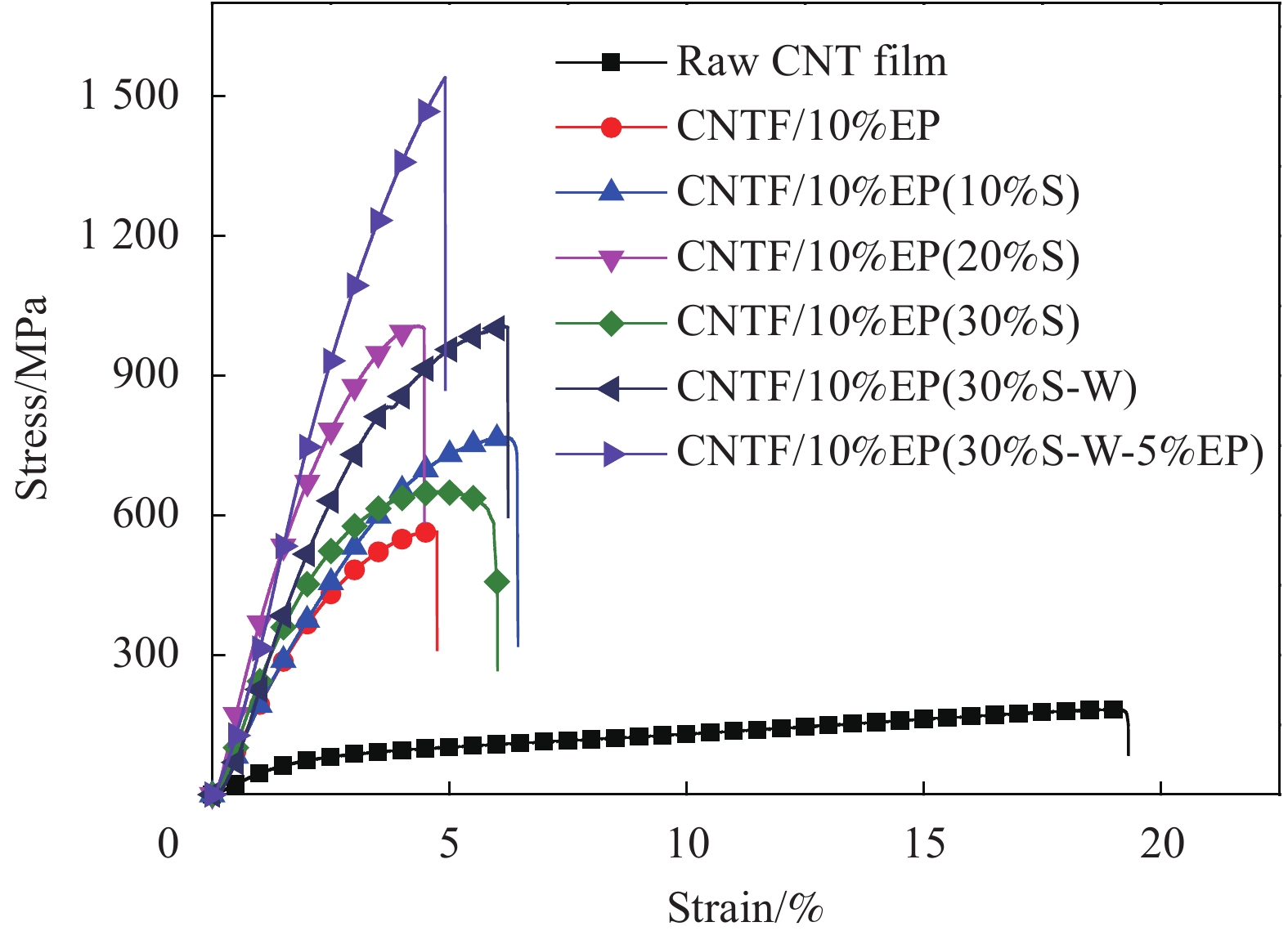
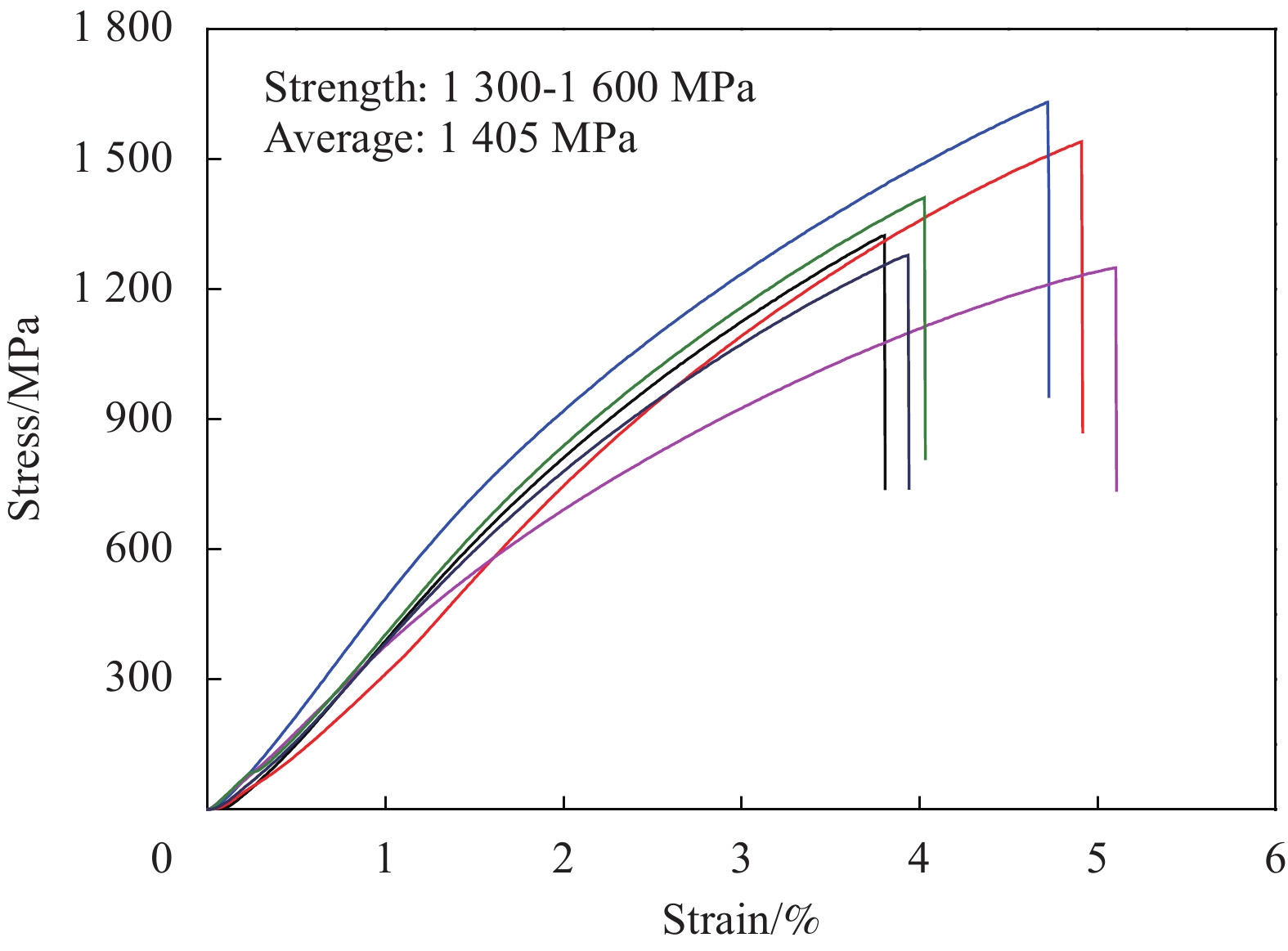
摘要: 碳纳米管(Carbon nanotube, CNT)/环氧树脂(Epoxy resin, EP)纳米复合材料中树脂含量、分布、CNT取向及其与树脂间界面结合是制备高性能纳米复合材料的关键因素。为了探究树脂分布和CNT/EP复合材料性能之间的关系,采用浮动催化化学气相沉积法制备的CNT薄膜和EP为原料,通过浸渍、牵伸、清洗和热压固化工艺制备CNT/EP复合薄膜。利用聚焦离子束结合扫描电子显微镜定性表征树脂在复合膜中的分布状态。结果表明,随着树脂含量增加,树脂在复合薄膜表面富集程度增加。在最优工艺条件下制备的纳米复合材料中CNT含量为66.14wt%, 拉伸强度和拉伸模量达到1405 MPa和46.7 GPa。Abstract: In carbon nanotube (CNT)/epoxy resin (EP) nanocomposites, the resin content and distribution, CNT orientation and CNT-resin interfacial strength are the key factors to fibrate the high-performance composites. In order to study the relationship between the resin distribution and the CNT/EP composite properties, CNT films prepared by floating catalytic chemical vapor deposition were impregnated by using EP and then stretched, washed and hot-press cured. The focus ion beam and scanning electron microscope were used to characterize the distribution of resin in the CNT/EP composites. The results show that, with the increase of resin content, the amount of resin on the composite surface is increasing and the average tensile strength and tensile modulus of CNT/EP composite with CNT content of 66.14wt% can be up to 1405 MPa and 46.7 GPa, respectively.
-
Keywords:
- carbon nanotubes /
- alignment /
- resin distribution /
- mechanical property /
- nanocomposites
-
-
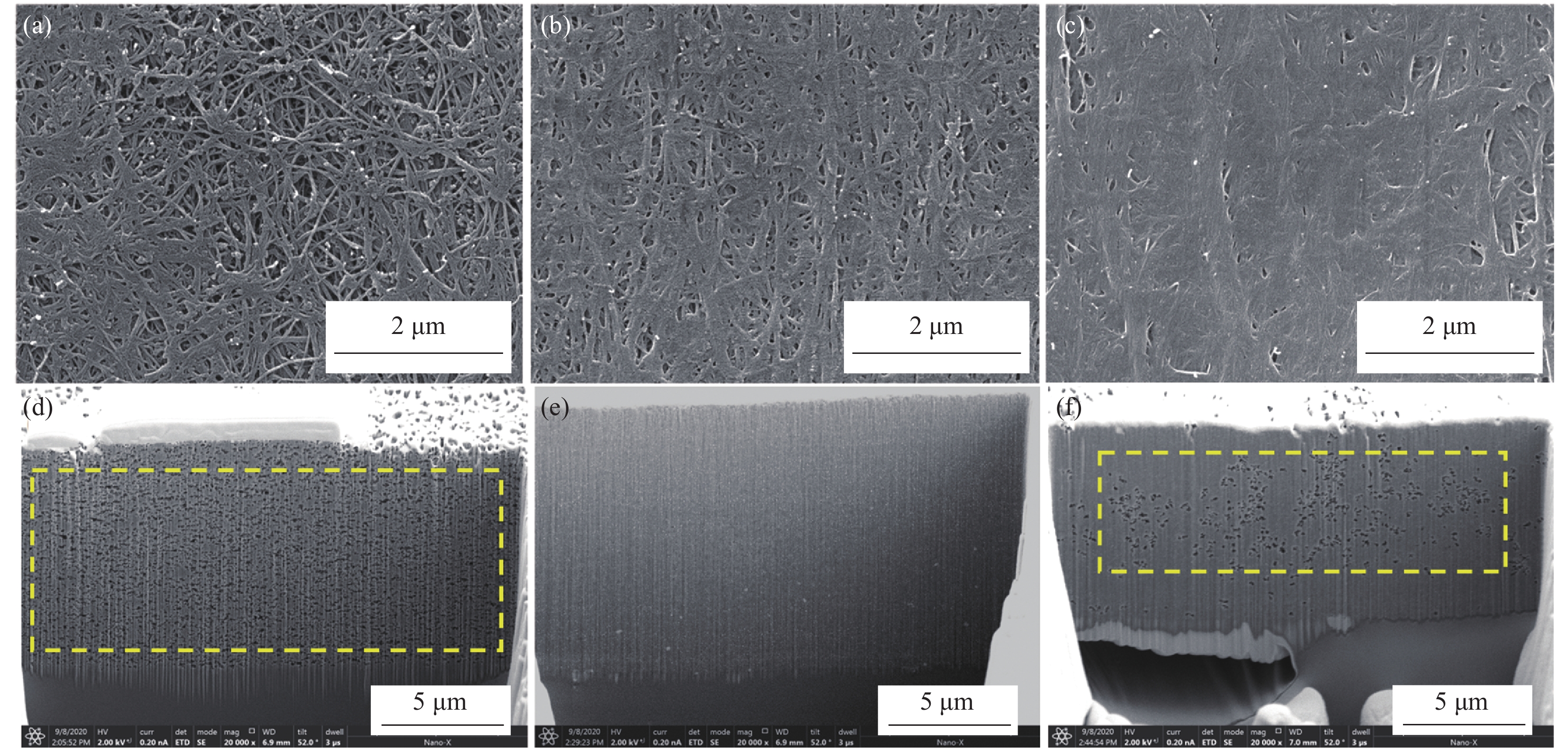
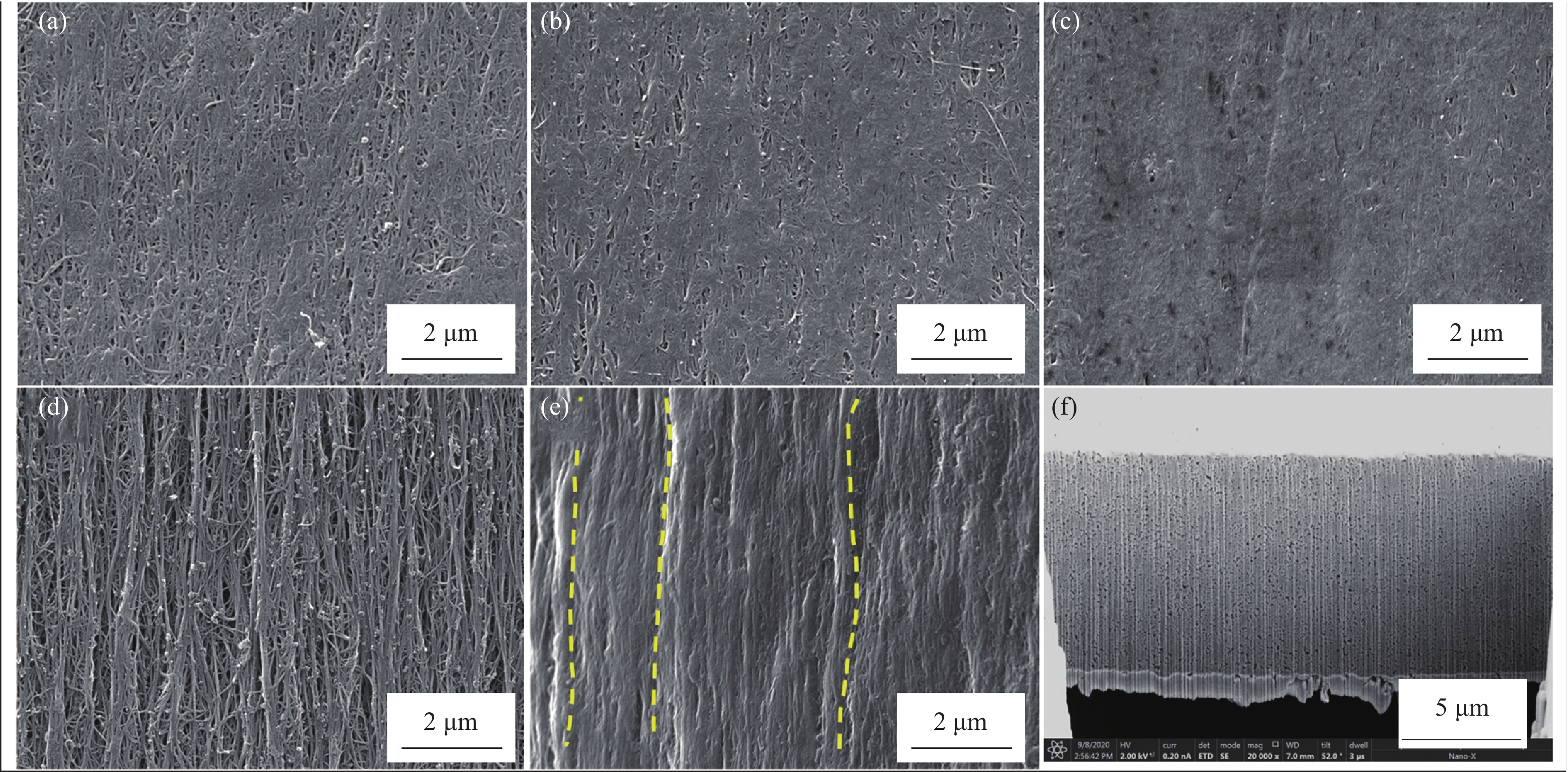
图 9 牵伸率10%、20%、30%CNTF/EP复合膜表面形貌((a)~(c));牵伸30%洗去树脂后表面形貌(d);再次浸渍5wt%树脂溶液CNTF/EP复合膜表面、截面形貌((e)、(f))
Figure 9. Surface morphology of CNTF/EP composite film with stretched 10%, 20% and 30% ((a)-(c)); Surface morphology of CNTF/EP composite film with 30% stretched after resin washing(d); Surface and section morphology of the CNTF/EP composite film impregnated with 5wt% resin solution again ((e), (f))
表 1 取向碳纳米管薄膜/环氧树脂(CNTF/EP)复合膜树脂含量
Table 1 Resin content of aligned carbon nanotube film/epoxy resin (CNTF/EP) composite film
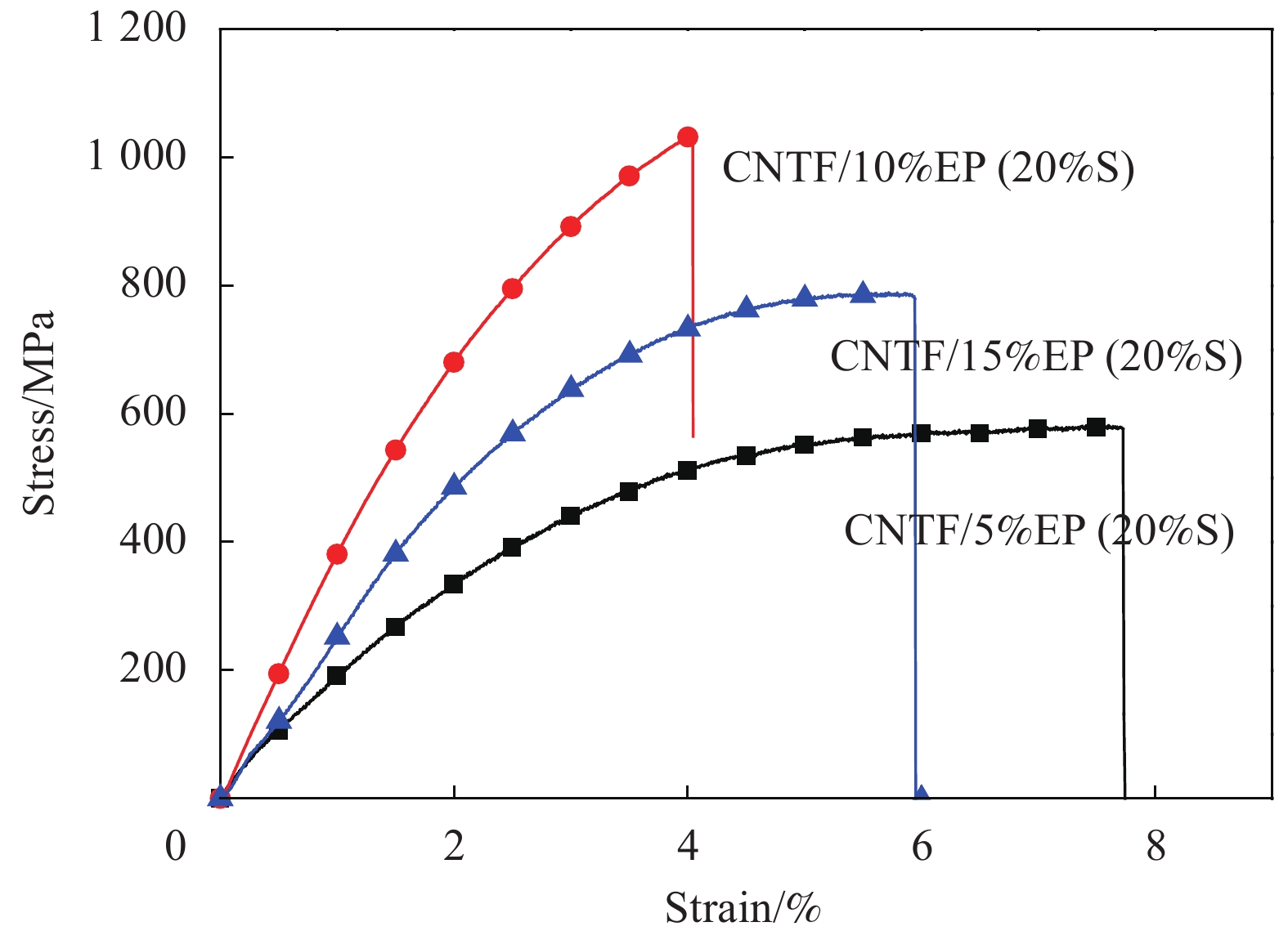
Name Sample Resin content /wt% CNTF/5%EP CNTF impregnated 5wt% EP solution 27.29 CNTF/10%EP CNTF impregnated 10wt% EP solution 50.91 CNTF/15%EP CNTF impregnated 15wt% EP solution 55.64 CNTF/5%EP (20%S) CNTF/5%EP stretched 20% - CNTF/10%EP (20%S) CNTF/10%EP stretched 20% - CNTF/15%EP (20%S) CNTF/15%EP stretched 20% - CNTF/10%EP (30%S) CNTF/10%EP stretched 30% - CNTF/10%EP (30%S-W) CNTF/10%EP stretched 30% washed by acetone 18.91 CNTF/10%EP (30%S-W-5%EP) CNTF/10%EP (30%S-W) impregnated 5wt% EP solution again 33.86 Notes:“W”means washing; 20%S and 30%S are stretching rates. 表 2 CNTF/EP复合薄膜力学性能
Table 2 Mechanical properties of CNTF/EP composite films
Sample Fracture force/N Strength/MPa Modulus/GPa Strain at break/% CNTF/5%EP 2.88-3.65 400-450 13.5-16 14.30-19.72 CNTF/10%EP 3.9-5.75 570-620 20-22 4.23-5.90 CNTF/15%EP 4.08-5.84 490-510 18-21 3.59-4.77 CNTF/5%EP (20%S) 4.72-5.49 580-650 18-22 5.54-8.48 CNTF/10%EP (20%S) 5.64-6.51 950-1040 40-49 3.86-4.38 CNTF/15%EP (20%S) 5.27-6.37 750-820 27-31 3.96-4.74 CNTF/10%EP (30%S) 4.36-5.44 581-651 21-24 5.94-6.01 CNTF/10%EP (30%S-W) 5.71-6.99 1005-1044 31-33 3.71-6.23 CNTF/10%EP (30%S-W-5%EP) 6.33-7.06 1300-1600 47-54 3.85-4.72 -
[1] PARK J G, SMITHYMAN J, LIN C Y, et al. Effects of surfactants and alignment on the physical properties of single-walled carbon nanotube buckypaper[J]. Journal of Applied Physics,2009,106(10):185710.
[2] YU M F, LOURIE O, DYER M J, et al. Strength and breaking mechanism of multiwalled carbon nanotubes under tensile load[J]. Science,2000,287(5453):637-640. DOI: 10.1126/science.287.5453.637
[3] IIJIMA S. Helical microtubules of graphitic carbon[J]. Nature,1991,354(6348):56-58. DOI: 10.1038/354056a0
[4] LI S, PARK J G, LIANG Z Y, et al. In situ characterization of structural changes and the fraction of aligned carbon nanotube networks produced by stretching[J]. Carbon,2012,50(10):3859-3867. DOI: 10.1016/j.carbon.2012.04.029
[5] THOSTENSON E T, LI C Y, CHOU T W. Nanocomposites in context[J]. Composite Science and Technology,2005,65(3-4):491-516. DOI: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2004.11.003
[6] EBBESEN T W, LEZEC H J, HIURA H, et al. Electrical conductivity of individual carbon nanotubes[J]. Nature,1996,382(6586):54-56. DOI: 10.1038/382054a0
[7] BERBER S, KWON Y K, TOMANEK D. Unusually high thermal conductivity of carbon nanotubes[J]. Physical Review Letters,2000,84(20):4613-4616. DOI: 10.1103/PhysRevLett.84.4613
[8] HAN Z D, FINA A. Thermal conductivity of carbon nanotubes and their polymer nanocomposites: A review[J]. Progress in Polymer Science,2011,36(7):914-944. DOI: 10.1016/j.progpolymsci.2010.11.004
[9] XIE X L, MAI Y W, ZHOU X P. Dispersion and alignment of carbon nanotubes in polymer matrix: A review[J]. Materials Science and Engineering R Reports,2005,49(4):89-112. DOI: 10.1016/j.mser.2005.04.002
[10] LIU J L, GONG W B, YAO Y G, et al. Strengthening carbon nanotube fibers with semi-crystallized polyvinyl alcohol and hot-stretching[J]. Composite Science and Technology,2018,164:290-295. DOI: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2018.06.003
[11] MA W J, LIU L Q, ZHANG Z, et al. High-strength composite fibers: Realizing true potential of carbon nanotubes in polymer matrix through continuous reticulate architecture and molecular level couplings[J]. Nano Letter,2009,9(8):2855-2861. DOI: 10.1021/nl901035v
[12] JOLOWSKY C, SWEAT R, PARK J G, et al. Microstructure evolution and self-assembling of CNT networks during mechanical stretching and mechanical properties of highly aligned CNT composites[J]. Composite Science and Technology,2018,166:125-130. DOI: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2018.04.003
[13] WANG X, BRADFORD P D, LIU W, et al. Mechanical and electrical property improvement in CNT/Nylon composites through drawing and stretching[J]. Composite Science and Technology,2011,71(14):1677-1683. DOI: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2011.07.023
[14] SEVERINO J, YANG J M, CARLSON L, et al. Progression of alignment in stretched CNT sheets determined by wide angle X-ray scattering[J]. Carbon,2016,100:309-317. DOI: 10.1016/j.carbon.2016.01.005
[15] LIU Qianli, WANG Xiaolei, LI Min, et al. Preparation and property strengthening mechanism of carbon nanotube membrane/cyanogen resin composites[J]. Acta Materiae Compositae Sinica,2017,34(12):2653-2660.
[16] DOWNES R, WANG S K, HALDANE D, et al. Strain-induced alignment mechanisms of carbon nanotube networks[J]. Advanced Engineering Materials,2015,17(3):349-358. DOI: 10.1002/adem.201400045
[17] DOWNES R D, HAO A, PARK J G, et al. Geometrically constrained self-assembly and crystal packing of flattened and aligned carbon nanotubes[J]. Carbon,2015,93:953-966. DOI: 10.1016/j.carbon.2015.06.012
[18] HUANG C J, CHENG Q F. Learning from nacre: Constructing polymer nanocomposites[J]. Composite Science and Technology,2017,150:141-166. DOI: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2017.07.021
[19] DIEZ-PASCUAL A M, GUAN J W, SIMARD B, et al. Poly(phenylene sulphide) and poly(ether ether ketone) composites reinforced with single-walled carbon nanotube buckypaper II:Mechanical properties, electrical and thermal conductivity[J]. Compos Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2012,43(6):1007-1015. DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2011.11.003
[20] DI J T, HU D M, CHEN H Y, et al. Ultrastrong, foldable, and highly conductive carbon nanotube film[J]. ACS Nano,2012,6(6):5457-5464. DOI: 10.1021/nn301321j
[21] SUN X M, CHEN T, YANG Z B, et al. The alignment of carbon nanotubes: An effective route to extend their excellent properties to macroscopic scale[J]. Accounts for Chemical Research,2013,46(2):539-549. DOI: 10.1021/ar300221r
[22] WANG J N, LUO X G, WU T, et al. High-strength carbon nanotube fibre-like ribbon with high ductility and high electrical conductivity[J]. Nature Communications,2014,5:3848.
[23] TRAN T Q, FAN Z, LIU P, et al. Super-strong and highly conductive carbon nanotube ribbons from post-treatment methods[J]. Carbon,2016,99:407-415. DOI: 10.1016/j.carbon.2015.12.048
[24] WANG S, HALDANE D, LIANG R, et al. Nanoscale infiltration behaviour and through-thickness permeability of carbon nanotube buckypapers[J]. Nanotechnology,2013,24(1):015704. DOI: 10.1088/0957-4484/24/1/015704
[25] CHENG Q F, BAO J W, PARK J, et al. High mechanical performance composite conductor: Multi-walled carbon nanotube sheet/bismaleimide nanocomposites[J]. Advanced Functional Materials,2009,19(20):3219-3225. DOI: 10.1002/adfm.200900663
[26] LI Z R, LIANG Z Y. Optimization of buckypaper-enhanced multifunctional thermoplastic composites[J]. Scientific Reports,2017,7:42423.
[27] LIU X H, XU F J, ZHANG K, et al. Characterization of enhanced interfacial bonding between epoxy and plasma functionalized carbon nanotube films[J]. Composite Science and Technology,2017,145:114-121. DOI: 10.1016/j.compscitech.2017.04.004
[28] MARRIAM I, XU F J, TEBYETEKERWA M, et al. Synergistic effect of CNT films impregnated with CNT modified epoxy solution towards boosted interfacial bonding and functional properties of the composites[J]. Composites Part A: Applied Science and Manufacturing,2018,110:1-10. DOI: 10.1016/j.compositesa.2018.04.011
[29] ZHANG L, XU W, LUO X G, et al. High performance carbon nanotube based composite film from layer-by-layer deposition[J]. Carbon,2015,90:215-221. DOI: 10.1016/j.carbon.2015.04.026
[30] GAO Y, LI L Y, TAN P H, et al. Application of Raman spectroscopy in carbon nanotube-based polymer composites[J]. Chinese Science Bulletin,2010,55(35):3978-3988. DOI: 10.1007/s11434-010-4100-9
[31] LEFRANT S, BAIBARAC M, BALTOG I. Raman and FTIR spectroscopy as valuable tools for the characterization of polymer and carbon nanotube based composites[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry,2009,19(32):5690-5704. DOI: 10.1039/b821136a
[32] ZHAO Q, WAGNER H D. Raman spectroscopy of carbon-nanotube-based composites[J]. Philosophical Transactions of the Royal Society A: Mathematical, Physical and Engineering Sciences,2004,362(1824):2407-2424. DOI: 10.1098/rsta.2004.1447
-
期刊类型引用(8)
1. 丁能鑫,侯夫庆,杨会康,张春辉. 石英纤维的表面改性及分散特性研究. 中国造纸. 2023(06): 56-63 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 杨娜,苏韬,黄锴荻,王文俊. 通过与苯乙烯共聚改善含硅芳炔树脂及其复合材料性能. 复合材料学报. 2023(09): 5002-5010 .  本站查看
本站查看
3. 束长朋,王茂源,周权,宋宁,倪礼忠. 苯并噁嗪-氨基稀释剂改性硅炔杂化树脂及其复合材料性能. 复合材料学报. 2020(11): 2718-2725 .  本站查看
本站查看
4. 成滨,扈艳红,邓诗峰,杜磊,周燕,杨藤,崔方旭. 一种含腈基的硅烷偶联剂改性石英纤维/含硅芳炔复合材料. 复合材料学报. 2019(03): 545-554 .  本站查看
本站查看
5. 王卓,王欢,任鹏刚,王明存. 硅氧烷杂化苯并恶嗪及其耐高温复合材料. 热固性树脂. 2019(02): 13-20 .  百度学术
百度学术
6. 杨海荟,崔丽平. 新型含醚酰亚胺端炔硅烷偶联剂的合成研究. 广东化工. 2019(18): 69-71+78 .  百度学术
百度学术
7. 宋来福,杨彩云. 复合材料界面理论及石英纤维表面处理与改性方法研究进展. 纺织科学与工程学报. 2018(01): 171-176 .  百度学术
百度学术
8. 杨海荟,扈艳红,杜磊,顾渊博,张芳芳. 新型硅烷偶联剂对石英纤维/含硅芳炔复合材料界面增强增韧改性. 玻璃钢/复合材料. 2016(08): 13-21 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(4)
-





 下载:
下载: