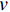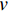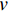Application of TiO2-g-C3N4-Bi2O3 composite heterogeneous catalytic materials in water treatment
-
摘要: 异质结光催化材料在降解有毒有害污染物方面体现出优良的效果。以苯酚有机废水作为研究对象,球磨法所制备的TiO2-g-C3N4和TiO2-g-C3N4-Bi2O3两种光催化材料作为实验材料,探究不同光源条件下TiO2-g-C3N4、TiO2-g-C3N4-Bi2O3的光催化特性及其对苯酚废水处理效果。结果表明,在可见光和紫外光单独照射条件下,三元体系的TiO2-g-C3N4-Bi2O3均比TiO2-g-C3N4具有更高的光催化活性,并且可见光条件下,TiO2-g-C3N4-Bi2O3比TiO2-g-C3N4的优势更明显;在可见光和紫外光同时照射时,TiO2-g-C3N4-Bi2O3、TiO2-g-C3N4对苯酚废水的降解效率分别达到99.44%、96.67%。表征结果表明,Bi2O3的掺杂有效地增强了催化剂在全光谱范围内对光的吸收,并且三元体系的构建有效地促进了光生电子与空穴的分离。研究结果表明,通过简单可控的球磨-微波加热-煅烧工艺,可以实现TiO2-g-C3N4-Bi2O3的制备,并且证实了TiO2-g-C3N4-Bi2O3材料在有机废水处理方面的良好前景。Abstract: Heterojunction photocatalytic materials show excellent ability in degrading toxic and harmful pollutants. In this study, we prepared TiO2-g-C3N4 and TiO2-g-C3N4-Bi2O3 heterostructure photocatalytic materials by ball milling. The photocatalytic performance of TiO2-g-C3N4 and TiO2-g-C3N4-Bi2O3 towards phenol organic wastewater were investigated under different light source, as well as the effects of light source on the degradation performance. Under the single visible light or ultraviolet light, the ternary TiO2-g-C3N4-Bi2O3 shows higher photocatalytic activity than TiO2-g-C3N4. And under visible light conditions, the degradation performance of TiO2-g-C3N4-Bi2O3 is much better than TiO2-g-C3N4. Under the simultaneous irradiation of visible light and ultraviolet light, the degradation efficiency of TiO2-g-C3N4-Bi2O3 and TiO2-g-C3N4 on phenol wastewater reached 99.44% and 96.67%, respectively. The characterization results show that the doping of Bi2O3 remarkably enhances the absorption of light by the catalyst in the full spectrum, and the construction of the ternary system promotes the separation of photogenerated electrons and holes. The research results show that the ternary TiO2-g-C3N4-Bi2O3 can be achieved through a feasible ball method of milling-microwave heating-calcination process, and confirms the promising prospects of TiO2-g-C3N4-Bi2O3 in organic wastewater treatment.
-
Keywords:
- phenol /
- organic wastewater /
- visible light /
- ultraviolet light /
- heterojunction /
- photocatalytic
-
随着大量工业和城市有毒有害物质累积并释放到水资源中,环境问题日益严重,绿色处理技术引起了越来越多的关注。半导体光催化材料因具有利用太阳能潜能及能够将有机污染物完全矿化的优势,使其在水处理领域有着广阔的应用前景[1]。尽管基于半导体的光催化技术具有绿色、环保、经济等优势,但由于单一半导体材料具有载流子复合率高和对可见光响应不高等缺陷,限制了其光催化活性[2]。TiO2作为目前应用最广泛的催化剂之一,存在光生电子与空穴分离效率低及禁带宽度较大(Eg=3.2 eV)等缺陷,使其仅在小于400 nm的波长范围内有响应(该波长范围仅占太阳光谱的3%~5%)。因此,非金属元素掺杂、金属掺杂、结构调控和构建异质结等方法被用于提升半导体材料的光催化活性,其中构建异质结的方法被广泛应用,用以提升半导体的可见光响应和光激发电子空穴对的分离效率。目前,许多研究集中在二元复合材料的制备和光催化应用上,如Yan等[3]制备的g-C3N4-TiO2异质结材料在紫外线和可见光下的光催化性能得到较大提升,而对三元体系的研究相对较少。氧化铋(Bi2O3)是一种重要的金属氧化物半导体,其直接带隙为2.8 eV[4],能被可见光激发,但单独使用Bi2O3会造成严重的光腐蚀,因此它常与其他半导体复合形成异质结[5]。Zhang等[6]制备了Bi2O3-g-C3N4材料,发现在可见光照射下其光催化性能远高于纯g-C3N4,但光吸收效率和电荷转移速率仍有待提高。根据半导体吸光规律可知,想提高材料的光能利用率,使催化效果更好,增大其受光面积是较有效的操作之一[7]。Dong等[8]构造了ZnO-ZnS-g-C3N4三元物质材料,其比表面积较g-C3N4而言,大幅提升,最大可达到76.2 m2/g。在光照下4 h下,H2产量是g-C3N4的17.1倍。众多研究表明,与二元复合材料相比,三元体系能够更加有效的拓宽可见光响应,并且其交错的能带结构能进一步促进光生载流子的分离[9],已经成为环境修复应用领域的研究热点。但目前对三元复合异质结光催化材料应用于实际污水的光催化降解性能研究鲜见报道。
鉴于此,本文以苯酚有机废水作为目标污染物,采用Wang等[10]前期所制备的TiO2-g-C3N4复合材料,构建TiO2-g-C3N4-Bi2O3新型异质结光催化材料,考察三元复合异质结光催化材料在实际水处理应用中的效率和价值,并进一步探究在不同光照下污染物降解的效果,剖析其复合催化剂的光催化机制和特性。
1. 实验部分
1.1 主要试剂
试剂:苯酚(纯度为99.5%)、氯化铵(纯度为98.0%)、4-氨基安替比林(纯度为98.0%)、铁氰化钾(纯度为99.0%)、浓硫酸(纯度为98.0%)均产自阿拉丁;LH-DE试剂购自成都连华环保科技有限公司。
1.2 光催化材料制备
1.2.1 TiO2-g-C3N4材料的制备
(1) 将TiO2和适量三聚氰胺混合物按照球料比为10∶1分别加入球磨罐,采用去离子水(四川沃特尔水处理设备有限公司,WP—UP—1810型沃特浦实验室专用超纯水机制备)为分散液,以400 r/min的转速球磨2~3 h;(2) 将球磨后的悬浮液放于700 W微波炉中,微波反应10~30 min;(3) 用玛瑙研钵将所得淡黄色材料进一步研磨,之后放置 2~3 h;(4) 将样品放在马弗炉中,于空气气氛下,以5℃/min的升温速率,升温至500℃并保温2 h,自然冷却后,用玛瑙研钵再次研磨即为TiO2-g-C3N4材料。
1.2.2 TiO2-g-C3N4-Bi2O3材料的的制备
(1) 在TiO2-g-C3N4基础上,取适量Bi(NO)3·5H2O混合,并按照球料比为10∶1分别加入球磨罐,采用去离子水为分散液,以400 r/min的转速球磨2~3 h;(2) 将球磨后的悬浮液放于700 W微波炉中,微波反应10~30 min;(3) 用玛瑙研钵将所得淡黄色材料进一步研磨,之后放置2~3 h;(4) 将样品放在马弗炉中,于空气气氛下,以5℃/min的升温速率,升温至450℃并保温2 h,自然冷却后,用玛瑙研钵再次研磨即为TiO2-g-C3N4-Bi2O3新型异质结光催化材料。
1.3 测试与表征
材料的晶型组成采用Empyrean型X射线衍射仪(XRD)(日本Shimadzu公司)分析,以Cu-Kα辐射。采用JSM-7500F型场发射扫描电子显微镜(SEM)(日本JEOL公司)测定材料的表面形态结构。材料内部的形貌结构及晶格结构采用TecnaiG20-Stwin型透射电子显微镜(TEM)(美国FEI公司)测定。材料的光学性能则通过UV-3600型的紫外可见漫反射分光光度仪(DRS)(日本Shimadzu公司)测定。
1.4 苯酚光催化性能测试
分别称取TiO2-g-C3N4和TiO2-g-C3N4-Bi2O3光催化材料样品各50.0 mg至干燥透明的100 mL烧杯中,加入20 mg/L的苯酚溶液各50.0 mL,加入深圳市洁盟清洗设备有限公司生产的JP-060型超声波清洗机中超声分散5 min后加入搅拌子,放于LC-TN-1型磁力搅拌机(力辰科技有限公司机)上先在暗室条件下搅拌1 h(暗反应),当吸附-脱附达到动态平衡的时候,取第一次样;之后打开可见光(或紫外光)光源继续反应,每隔2 h,取样5 mL,在上海安亭科学仪器厂生产的TGL-16B型离心机中采用10 000 r/min的转速离心20 min取上清液。采用4-氨基安替比林分光光度法[11]测定溶液中的苯酚浓度。其中,可见光光源采用60 W的LED灯带,紫外光光源采用60 W的家用消毒灯(UVC,波长100~275 nm)。用下式计算降解率,表征材料的降解能力。
η=Co−CCo×100% (1) 式中:η为降解率(%);Co和C分别是初始浓度和反应t min后的浓度(mg/L)。
2. 结果与讨论
2.1 TiO2-g-C3N4和TiO2-g-C3N4-Bi2O3材料的表征情况对比
图1为TiO2-g-C3N4和TiO2-g-C3N4-Bi2O3复合材料的XRD图谱。可以看出,TiO2-g-C3N4在衍射角2θ=27.5°处有较锋利的衍射峰,对应于g-C3N4的(002)晶面(PDF#21-1272)[12]。在TiO2-g-C3N4样品中除了存在g-C3N4的特征衍射峰,还发现存在金红石相TiO2的特征衍射峰。在2θ=36.22°、39.29°、41.34°、44.14°、54.42°、56.72°、62.96°、64.18°、69.08°和69.93°处的衍射峰与金红石型TiO2标准卡PDF#21-1276的特征衍射峰一致,依次对应于金红石型TiO2的(101)、(200)、(111)、(210)、(211)、(220)、(002)、(310)、(301)和(112)晶面[13]。
图1中TiO2-g-C3N4-Bi2O3复合材料在衍射角2θ=30.283°、31.761°、32.691°、46.218°、46.903°、54.269°和55.487°处出现了较强的衍射峰,依次对应于四方相β-Bi2O3的(211)、(002)、(220)、(222)、(400)、(203)和(421)晶面(JCPDS No.27-0050)[14]。另外与TiO2-g-C3N4对比看出,Bi掺杂后的TiO2-g-C3N4-Bi2O3样品仍然存在金红石相TiO2和g-C3N4的特征峰。在TiO2-g-C3N4-Bi2O3中,TiO2某些特征衍射峰的强度(如2θ=36.22°、54.42°)被减弱,可能是由于TiO2-g-C3N4-Bi2O3中TiO2的含量相较于TiO2-g-C3N4少。并且Bi2O3的引入并没有带来其他的杂峰,表明Bi2O3的引入没有改变TiO2-g-C3N4中g-C3N4和TiO2的晶型。
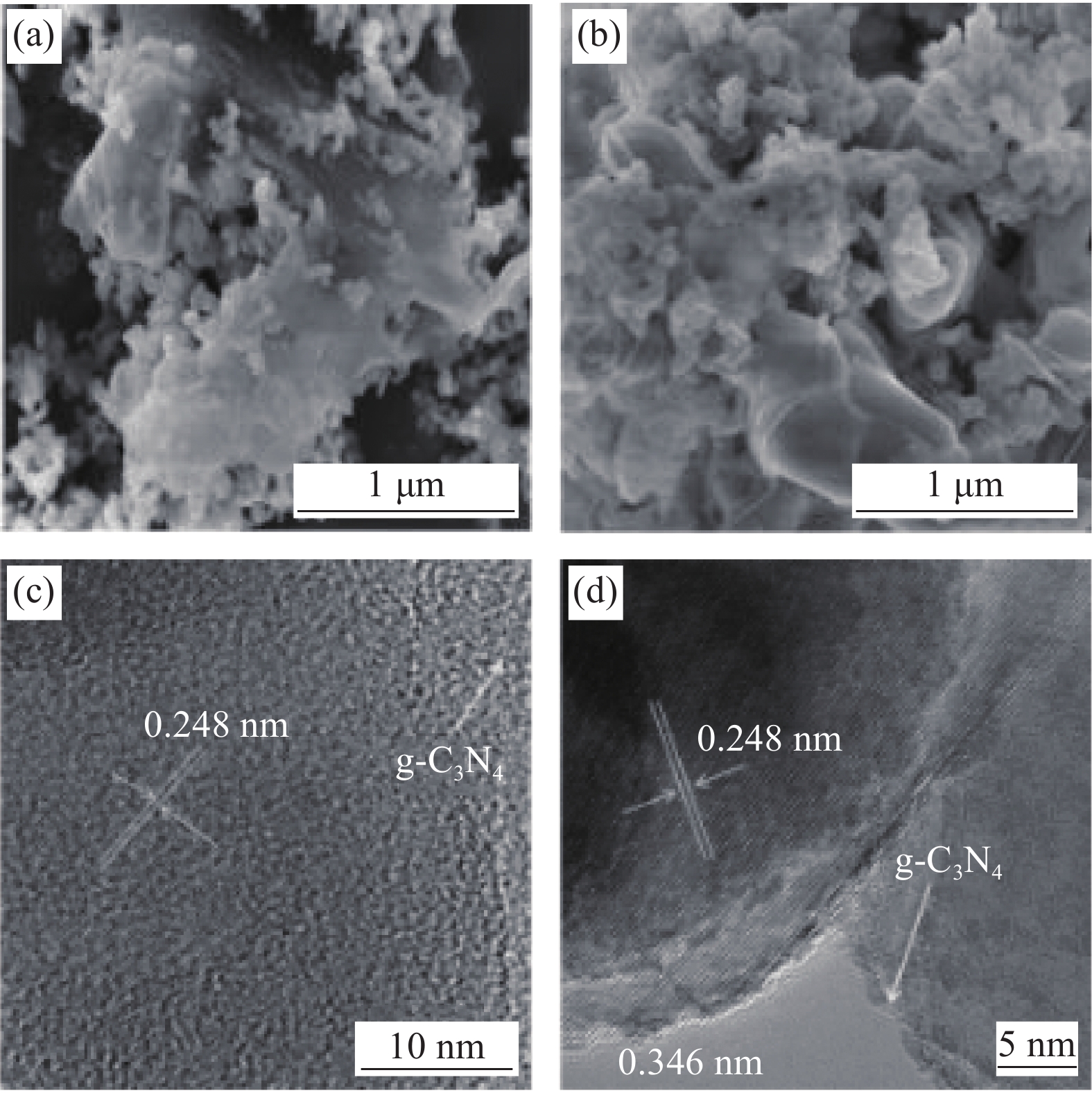
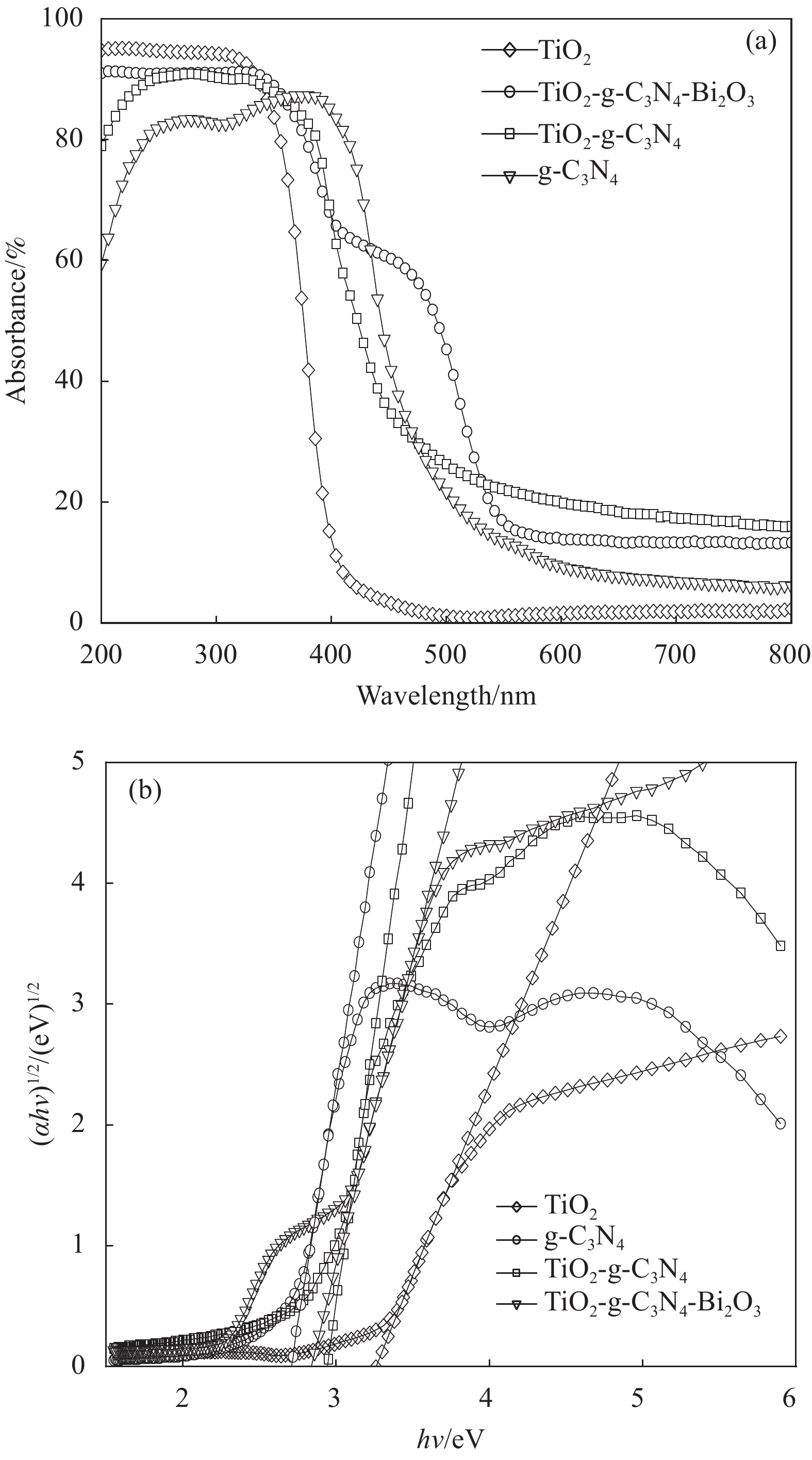
图2为TiO2-g-C3N4和TiO2-g-C3N4-Bi2O3的SEM图像和TEM图像。从图2(a)即TiO2-g-C3N4的SEM图像中可以发现有颗粒物分散在褶皱状薄膜材料中,通过以往研究成果和XRD的结果分析可知,褶皱状结构材料为g-C3N4[10],且在图2(c)中发现清晰晶格条纹的间距为0.248 nm,对应的是金红石相TiO2的(101)晶面,这与XRD的分析结果一致。从样品TiO2-g-C3N4-Bi2O3的TEM图像(图2(b))中可以进一步证明TiO2和Bi2O3颗粒均匀附着在g-C3N4薄膜上,只是相对于TiO2-g-C3N4其上的颗粒堆积更紧密,且有絮状结构产生,这可能是在烧结形成Bi2O3时大量放热,增加了整个反应的实际温度,使三聚氰胺生成的g-C3N4薄膜边缘发生絮状变化,同时增加了各物质间的聚合作用,从而使物质之间结合更加紧密。图2(d)中发现了长度0.248 nm的晶格间距,即为金红石相TiO2的(101)晶面;还发现了长度为0.346 nm的晶格间距,对比PDF#27-0050标准卡,可知这是Bi2O3的(210)晶面,进一步说明在样品TiO2-g-C3N4-Bi2O3中存在金红石相TiO2、Bi2O3和g-C3N4。
2.2 紫外可见吸收光谱结果及其分析
图3为样品的紫外-可见漫反射光谱图。可以看到样品均在紫外光区域(波长400 nm以下)有很强的吸收,在可见光区(波长范围在400~760 nm)的吸收能力相对较弱。TiO2-g-C3N4/和TiO2-g-C3N4-Bi2O3相对于TiO2均有红移现象,且TiO2-g-C3N4-Bi2O3最明显。紫外-可见漫反射光谱图除了可以表征半导体对光的吸收能力,还可以表征其带隙(Eg)和能带结构。半导体的漫反射吸收系数(α)和Eg之间存在以下关系:
(αhv)1/2=C(hv−Eg) (2) 式中:h为普朗克常量;
v 为光的频率;C为吸收系数。将紫外-可见漫反射光谱的数据以(αhv )1/2为纵坐标,hv 为横坐标,得到Tauc曲线[15]如图3(b)所示,将Tauc曲线线性部分延长至X轴,延长线在X轴上的截距即为Eg,得到各材料的Eg,如表1所示。表 1 各样品的禁带宽度(Eg)Table 1. Energy gap (Eg) of all samplesSample TiO2 g-C3N4 Bi2O3[19] TiO2-g-C3N4 TiO2-g-C3N4-Bi2O3 Eg/eV 3.18 2.70 2.80 2.91 2.83 计算可知,TiO2-g-C3N4和TiO2-g-C3N4-Bi2O3样品的Eg相对于TiO2均有所降低(表1),这使TiO2-g-C3N4和TiO2-g-C3N4-Bi2O3的光催化效率有望得到提高。Nasir等[16]证实采用稀土元素铈掺杂改性可以减小TiO2的Eg,提高其对太阳光的利用率。复合材料的能带间隙变窄和对可见光的吸收也相应的增加[17],这与表1分析结果相符合。在可见光区,Bi2O3的掺杂使复合材料对光的吸收能力增强,同时三元异质结的结构,能够使光生电子与空穴有效分离,进而提升催化效率[18]。
2.3 可见光照射下TiO2-g-C3N4和TiO2-g-C3N4-Bi2O3对苯酚的降解情况
图4为可见光照射下 TiO2-g-C3N4和TiO2-g-C3N4-Bi2O3对苯酚的降解效果。可以看出,经过可见光照射8 h后,TiO2-g-C3N4-Bi2O3和TiO2-g-C3N4对苯酚的降解率分别为47.43%、35.43%。结合材料的表征分析,在降解苯酚有机废水时,TiO2-g-C3N4-Bi2O3增加的光催化活性可能是由于在TiO2-g-C3N4-Bi2O3中TiO2和Bi2O3颗粒附着在g-C3N4薄膜上(图2(b)、图2(d)),TiO2-g-C3N4-Bi2O3中的g-C3N4、TiO2、Bi2O3形成交错的能带结构,使光生电子与空穴梯级传输至不同的半导体表面,有效地实现了光生电子与空穴的分离,提升了光催化性能。另外从表1中也可以看出TiO2-g-C3N4-Bi2O3材料的禁带宽度Eg相对较低,复合材料的能带间隙变窄对光生电子是有利的[20]。具有不同带隙的光催化材料进行复合,利用具有窄带隙的材料敏化具有较宽带隙的材料,从而能改善具有较宽带隙的光催化材料的光催化活性[21]。Asahi等[22]研究发现,TiO2-g-C3N4中N元素的掺入可以有效减小其禁带宽度,使其吸收光谱向可见光部分延伸,并同时保持紫外区的高催化吸收活性,这与图3分析结果也相符。
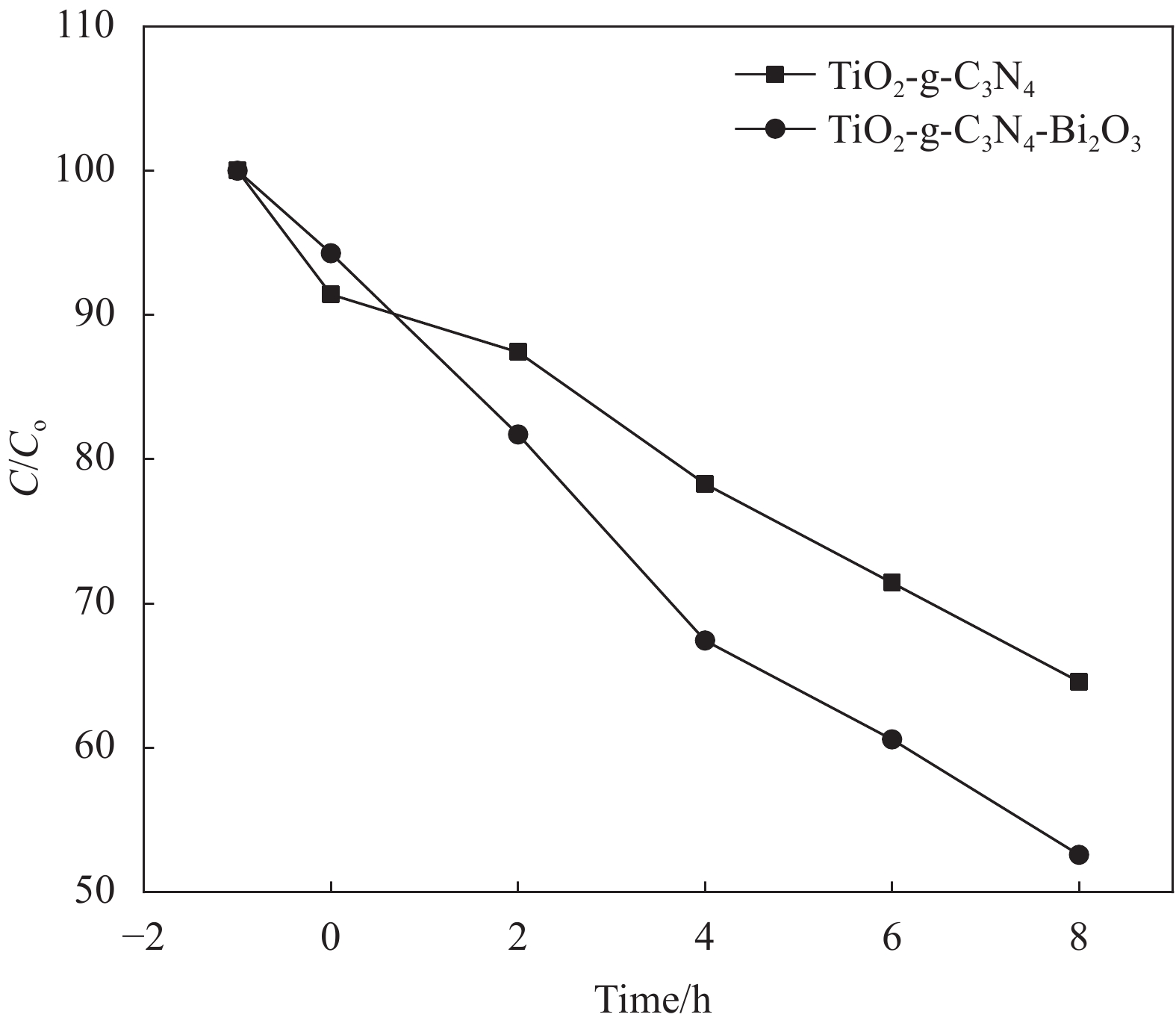
2.4 紫外光单独照射下TiO2-g-C3N4和TiO2-g-C3N4-Bi2O3对苯酚的降解情况
图5为紫外光照射下TiO2-g-C3N4和TiO2-g-C3N4-Bi2O3对苯酚的降解效果。可以看出,在紫外光照射下,TiO2-g-C3N4-Bi2O3随着反应时间增加,降解效果也逐渐高于TiO2-g-C3N4。在反应经过8 h后,TiO2-g-C3N4-Bi2O3和TiO2-g-C3N4对苯酚的降解率分别为62.56%和58.13%。此外,与可见光下的降解效果对比可以看到,在紫外光照射条件下两种材料对苯酚的降解效率更高,这也与样品在紫外光区域的吸收均高于在可见光区域(图3)的分析结果相符。Irie等[23]发现氮掺杂引起可见光活性的机制为氮置换氧,在价带上方形成一个独立的窄带,紫外光可在价带及该窄带上激发电子,而可见光只能在窄带上激发电子,因此其在可见光下的活性不如紫外光的活性高。
大部分有机物,其最大吸收波长主要分布于紫外光区域,使其能直接进行光降解的光源通常都是紫外光源,而约占太阳光谱45%的可见光由于光子能量无法被有机物直接吸收利用,并且难以激发水域环境中的物质形成强氧化自由基,因此不能仅仅通过可见光降解作用有效去除水体中的有机污染物[24]。
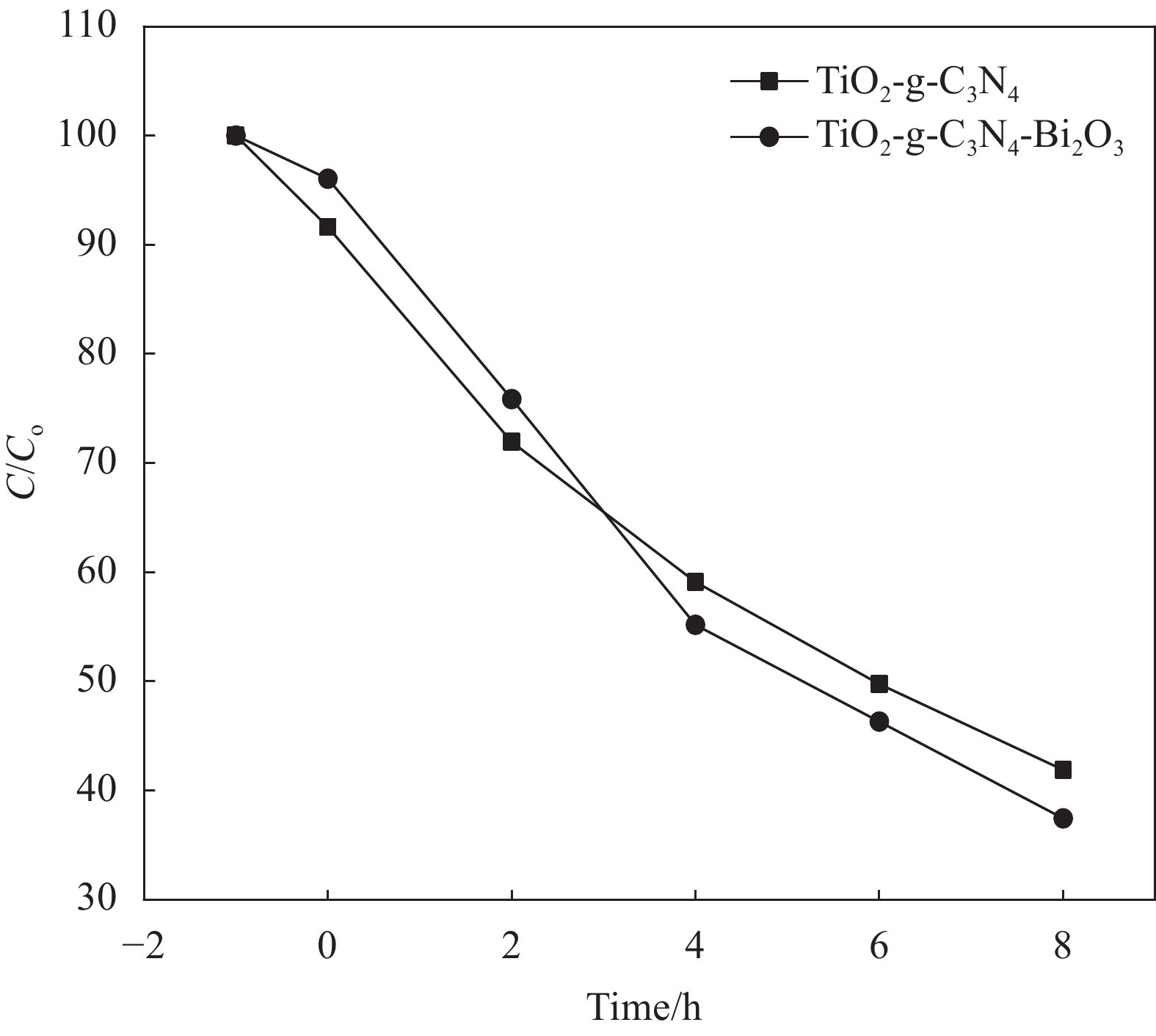
2.5 复合光源照射下TiO2-g-C3N4和TiO2-g-C3N4-Bi2O3对苯酚的降解情况
图6为可见光和紫外光同时照射下TiO2-g-C3N4和TiO2-g-C3N4-Bi2O3对苯酚的降解效果。可知,在复合光源同时照射下降解苯酚时,反应进行2 h,TiO2-g-C3N4-Bi2O3材料表现出优于TiO2-g-C3N4的光催化降解性能。此外,对比单一光源照射下的降解效果可以发现,在可见光和紫外光同时照射反应经过8 h后,TiO2-g-C3N4-Bi2O3和TiO2-g-C3N4对苯酚的降解效率分别达到99.44%、96.67%。结合UV-vis的结果分析,这可能是由于TiO2-g-C3N4-Bi2O3在全波长范围内的光吸收强度都高于TiO2-g-C3N4,从而产生更多的光生载流子参与光化学反应;此外由于TiO2-g-C3N4-Bi2O3材料中引入了Bi,形成交错的特殊能带结构,其载流子输送特性,在光催化反应中能有效抑制光生电子和空穴复合,提高量子效率,两种机制共同作用,促进了光催化降解苯酚的效率提升。比较其反应8 h的降解效率还可以发现,在可见光和紫外光同时照射下的降解效率刚好接近两种单独光源照射效率的加和,说明在混合光源下的光催化效率存在叠加效应。
2.6 催化反应动力学
材料光催化降解污染物反应在动力学上符合一级动力学反应,为了定量的比较光催化反应速率,则需模拟进行动力学反应。经推导其反应公式为
−lnCCo=kt (3) 式中,k为动力学中的比例常数,其数值能够量化光催化反应的速率的快慢,t为光催化反应持续进行的时间。根据式(3)对两种复合材料在不同光源条件下光催化降解有机废水(苯酚)的反应过程做线性拟合,结果如图7所示的紫外光和可见光条件下TiO2-g-C3N4和TiO2-g-C3N4-Bi2O3对苯酚的动力学曲线,结果显示-ln(C/Co)和t符合线性关系,催化反应过程符合一级反应动力学,其参数如表2所示。
表 2 TiO2-g-C3N4和TiO2-g-C3N4-Bi2O3对苯酚的反应动力学参数Table 2. Reaction kinetic parameters of TiO2-g-C3N4 and TiO2-g-C3N4-Bi2O3 for phenolSample K R2 TiO2-g-C3N4 (UV ligh) 0.0967±0.0042 0.9925 TiO2-g-C3N4/Bi2O3 (UV light) 0.1189±0.0066 0.9880 TiO2-g-C3N4 (visible light) 0.0449±0.0031 0.9816 TiO2-g-C3N4-Bi2O3 (visible light) 0.0734±0.0035 0.9909 Notes: K—Slope of straight line; R2—Goodness of fit. 从表2可以看出,TiO2-g-C3N4-Bi2O3的所有反应速率常数均大于TiO2-g-C3N4,光催化活性与其一阶反应速率常数k值变化规律一致。经过计算,在紫外光条件下,TiO2-g-C3N4和TiO2-g-C3N4-Bi2O3对苯酚的反应速率常数分别为0.0967 h−1、0.1189 h−1,TiO2-g-C3N4-Bi2O3在紫外光条件下对苯酚降解的反应速率常数是TiO2-g-C3N4的1.17倍;在可见光条件下,TiO2-g-C3N4和TiO2-g-C3N4-Bi2O3对苯酚的反应速率常数分别为0.0449 h−1、0.0734 h−1。不管是紫外光还是可见光照射,两种材料的反应速率常数均以TiO2-g-C3N4-Bi2O3较高,与材料的降解率分析结果是一致的。
2.7 光催化降解机制
半导体的价带(EVB)和能带位置(ECB)可以通过以下公式近似计算得到[25]:
EVB=X−EC+0.5Eg (4) ECB=EVB−Eg (5) 式中:X为半导体的电负性,g-C3N4、TiO2和Bi2O3的电负性分别为4.73 eV、5.81 eV和6.23 eV;EC为自由电子能,其值约为4.5 eV,Eg的值可由表1得到。计算得到g-C3N4、TiO2、Bi2O3的导带位置,结果如表2所示。
表 3 各样品的能带位(ECB)Table 3. Conduction band edge (ECB) of all samplesg-C3N4 Bi2O3 TiO2 Eg/eV 2.70 2.80 3.18 ECB/eV −1.12 0.33 −0.28 EVB/eV 1.58 3.13 2.90 根据g-C3N4、TiO2、Bi2O3半导体能带的位置,推测TiO2-g-C3N4-Bi2O3三元异质结的结构及催化机制,如图8所示。
TiO2-g-C3N4-Bi2O3中的g-C3N4、TiO2、Bi2O3形成交错的能带结构,使光生电子与空穴梯级传输至不同的半导体表面,有效地实现了光生电子与空穴的分离,提升了光催化性能[26]。三种半导体都能够受到紫外光的激发产生光生电子与空穴[27],光生电子从g-C3N4流向TiO2,最终到达Bi2O3的表面,g-C3N4产生的部分光生电子被表面吸附的氧气捕获,而生成具有强氧化性的超氧自由基(·O2)[28],进而将污染物(苯酚)氧化,而由于Bi2O3和TiO2导带的位置要低于(O2/·O2)的氧化电位,因此在Bi2O3和TiO2的表面并不能产生超氧自由基(·O2);光生空穴与光生电子传输的方向相反,由Bi2O3流向TiO2,最终到达g-C3N4的表面,Bi2O3和TiO2价带上的光生空穴具有较高的还原电位,能够将OH—还原成具有强氧化性的羟基自由基(·OH),进而与吸附在催化剂表面的苯酚进行反应,将其氧化降解。同时,三种半导体价带上的光生空穴也具有氧化能力,能够将污染物降解[29]。当受到可见光激发时,TiO2由于带隙过大而不能产生光生电子与空穴,此时,TiO2在Bi2O3与g-C3N4之间起到了导体的作用,促进电子与空穴的分离,从而提高光催化性能。
3. 结 论
(1) TiO2-g-C3N4-Bi2O3复合材料相较于TiO2-g-C3N4均表现出较高的光催化活性。样品掺杂Bi2O3后禁带宽度从2.91 eV减少为2.83 eV,较窄的禁带宽度能够更有效地利用太阳光,从而促进对污染物的降解。
(2) TiO2-g-C3N4-Bi2O3样品的三元体系能带呈现梯度交错,光生空穴和电子对能够有效分离,能够产生更多的·O2、·OH等超氧活性物质,在光催化降解污染物中起到关键作用。
(3) 在紫外光照射下TiO2-g-C3N4-Bi2O3复合材料光催化效果优于可见光,TiO2-g-C3N4-Bi2O3在紫外光条件下对苯酚降解的反应速率常数是TiO2-g-C3N4的1.17倍;在可见光和紫外光同时照射反应经过8 h后,TiO2-g-C3N4-Bi2O3材料在混合光源照射下对苯酚的降解效率达到99.44%,且刚好接近两种单独光源的照射效率的加和,表明在混合光源下的光催化效率存在叠加效果。
(4) TiO2-g-C3N4-Bi2O3复合材料相比TiO2-g-C3N4材料在有机废水处理方面具有良好的应用前景。
-
表 1 各样品的禁带宽度(Eg)
Table 1 Energy gap (Eg) of all samples
Sample TiO2 g-C3N4 Bi2O3[19] TiO2-g-C3N4 TiO2-g-C3N4-Bi2O3 Eg/eV 3.18 2.70 2.80 2.91 2.83 表 2 TiO2-g-C3N4和TiO2-g-C3N4-Bi2O3对苯酚的反应动力学参数
Table 2 Reaction kinetic parameters of TiO2-g-C3N4 and TiO2-g-C3N4-Bi2O3 for phenol
Sample K R2 TiO2-g-C3N4 (UV ligh) 0.0967±0.0042 0.9925 TiO2-g-C3N4/Bi2O3 (UV light) 0.1189±0.0066 0.9880 TiO2-g-C3N4 (visible light) 0.0449±0.0031 0.9816 TiO2-g-C3N4-Bi2O3 (visible light) 0.0734±0.0035 0.9909 Notes: K—Slope of straight line; R2—Goodness of fit. 表 3 各样品的能带位(ECB)
Table 3 Conduction band edge (ECB) of all samples
g-C3N4 Bi2O3 TiO2 Eg/eV 2.70 2.80 3.18 ECB/eV −1.12 0.33 −0.28 EVB/eV 1.58 3.13 2.90 -
[1] HU C, PENG T, HU X, et al. Plasmon-lnduced photodegradation of toxic pollutants with Ag-Agl/Al2O3 under visible-light irradiation[J]. Journal of the American Chemical Society,2010,132(2):857-862. DOI: 10.1021/ja907792d
[2] ZENG Q, BAI J, LI J, et al. A low-cost photoelectrochemical tandem cell for highly-stable and efficient solar water splitting[J]. Nano Energy,2017,41:225-232. DOI: 10.1016/j.nanoen.2017.09.032
[3] YAN J, WU H, CHEN H, et al. Fabrication of TiO2/C3N4 heterostructure for enhanced photocatalytic Z-scheme overall water splitting[J]. Applied Catalysis B Environmental,2016,191:130-137. DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.03.026
[4] SOITAH T N, YANG C H, YU Y, et al. Properties of Bi2O3 thin films prepared via a modified Pechini route[J]. Current Applied Physics,2010,10(6):1372-1377. DOI: 10.1016/j.cap.2010.04.006
[5] 张洋洋. 几种铋基光催化剂的微结构调控及光催化性能研究[D]. 上海: 上海交通大学, 2016. ZHANG Y Y. Microstructure tuning and photocatalytic activity of several Bismuth-based photocatalysts[D]. Shanghai: Shanghai Jiao Tong University, 2016(in Chinese).
[6] ZHANG J, Hu Y, JIANG X, et al. Design of a direct Z-scheme photocatalyst: Preparation and characterization of Bi2O3/g-C3N4 with high visible light activity[J]. Journal of Hazardous Materials,2014,280:713-722. DOI: 10.1016/j.jhazmat.2014.08.055
[7] 叶仕雄. g-C3N4基三元复合材料的制备及光催化性能研究[D]. 赣州: 江西理工大学, 2020. YE S X. Preparation and photocatalytic properties of g-C3N4 based ternary composites[D]. Ganzhou: Jiangxi University of Science and Technology, 2020(in Chinese).
[8] XIAO P, JIANG D, JU L, et al. Construction of RGO/CdIn2S4/g-C3N4 ternary hybrid with enhanced photocatalytic activity for the degradation of tetracycline hydrochloride[J]. Applied Surface Science,2018,433(1):388-397.
[9] DONG Z F, WU Y, THIRUGNANAM N, et al. Double Z-scheme ZnO/ZnS/g-C3N4 ternary structure for efficient photocatalytic H2 production[J]. Applied Surface Science,2018,430:293-300. DOI: 10.1016/j.apsusc.2017.07.186
[10] WANG Y, Yu J, PENG W, TIAN J, et al. Novel multilayer TiO2 heterojunction decorated by low g-C3N4 content and its enhanced photocatalytic activity under UV, visible and solar light irradiation[J]. Scientific Reports,2019,9(1):5932. DOI: 10.1038/s41598-019-42438-w
[11] 全国环境保护部科技标准司. 水质. 挥发酚的测定. 4-氨基安替比林分光光度法: HJ 503—2009[S]. 北京: 中国环境科学出版社, 2009. Department of Science and Technology Standards. Ministry of Environmental Protection. Water quality. Determination of volatile phenolic compounds. 4-AAP spectrophotometric method: HJ 503—2009[S]. Beijing: China Environmental Press, 2009(in Chinese).
[12] DONG F, WU L, SUN Y, et al. Efficient synthesis of polymeric g-C3N4 layered materials as novel efficient visible light driven photocatalysts[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry,2011,21(39):15171-15174. DOI: 10.1039/c1jm12844b
[13] 牛宪军, 白杨, 田振勇等. Cu2+掺杂的金红石/锐钛矿型TiO2复合光催化材料的制备及性能研究[J]. 云南大学学报:自然科版, 2019, 41(5):1001-1008. ZHU X J, BAI Y, TIAN Z Y, et al. Preparation and properties of Cu2+ doped rutile/anatase TiO2 composite photocatalytic material[J]. Ournal of Yunnan University: Natural Sciences Edition,2019,41(5):1001-1008(in Chinese).
[14] 李婷婷. 含铋氧化物复合光催化材料的制备及其光催化降解有机污染物[D]. 长沙: 湖南大学, 2015. LI T T. Bimuth-containing oxide composite photocatalytic materials: Preparation and their application of organic pollutants’degradation[D]. Changsha: Hu'nan Uninversity, 2015(in Chinese).
[15] SUN J, LI X, ZHAO Q, et al. Quantum-sized BiVO4 modified TiO2 microflower composite heterostructures: Efficient production of hydroxyl radicals towards visible light-driven degradation of gaseous toluene[J]. Journal of Materials Chemistry A,2015,3(43):21655-21663. DOI: 10.1039/C5TA05659D
[16] NASIR M, ZHANG J, CHEN F, et al. Detailed study of Ce and C codoping on the visible light response of titanium dioxide[J]. Research on Chemical Intermediates,2015,41(3):1607-1624. DOI: 10.1007/s11164-013-1297-7
[17] AFROZE T, BHUIYAN A H. Infrared and ultraviolet-visible spectroscopic studies of plasma polymerized 1, 1, 3, 3-tetramethoxypropane thin films[J]. Thin Solid Films,2011,519(6):1825-1830. DOI: 10.1016/j.tsf.2010.10.006
[18] BENSAID, SAMIR, SACCO, et al. Photo-catalytic activity of BiVO4 thin-film electrodes for solar-driven water splitting[J]. Applied Catalysis A. General: An International Journal Devoted to Catalytic Science and Its Applications, 2015, 504: 266-271.
[19] 李卫, 周科朝, 杨华. 氧化铋的应用研究进展[J]. 材料科学与工程学报, 2004, 22(1):154-156. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2812.2004.01.040 LI W, ZHOU K L, YANG H. Application research progress of bismuth oxide[J]. Journal of Materials Science and Engineering,2004,22(1):154-156(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.1673-2812.2004.01.040
[20] ZHU J, XIAO P, LI H, et al. ChemInform abstract: Graphitic carbon nitride: Synthesis, properties, and applications in catalysis[J]. ACS Applied Materials & Interfaces,2014,6(19):16449-16465.
[21] HU J, XU, WANG J, et al. Photocatalytic property of a Bi2O3 nanoparticle modified BiOCl composite with a nanolayered hierarchical structure synthesized by in situ reactions[J]. Dalton Trans,2015,44(12):5386-5395. DOI: 10.1039/C4DT03953J
[22] ASAHI R, MORIKAWA T, OHWAKI T, et al. Visible-light photocatalysis in nitrogen-doped titanium Oxides[J]. Science,2001,293(5528):269-271. DOI: 10.1126/science.1061051
[23] IRIE H, WATANABE Y, HASHIMOTO K. Nitrogen-concentration dependence on photocatalytic activity of TiO2-xNx powders[J]. Journal of Physical Chemistry B,2003,107(23):5483-5486. DOI: 10.1021/jp030133h
[24] 张一兵, 陈博, 谈军. 铁掺杂二氧化钛的结构及其可见或紫外光下对有机物催化降解的行为分析[J]. 稀有金属, 2013, 37(1):92-96. DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7076.2013.01.017 ZHANG Y B, CHEN B, TAN J. Structure of Fe3+-doping titanium dioxide and photocatalytic degeneration of organic compound radiated by Vis or UV[J]. Chinese Journal of Rare Metals,2013,37(1):92-96(in Chinese). DOI: 10.3969/j.issn.0258-7076.2013.01.017
[25] SHAN W, HU Y, BAI Z, et al. In situ preparation of g-C3N4/bismuth-based oxide nanocomposites with enhanced photocatalytic activity[J]. Applied Catalysis B: Environmental,2016,188:1-12. DOI: 10.1016/j.apcatb.2016.01.058
[26] ZHANG F J, XIE F Z, ZHU S F, et al. novel photofunctional g-C3N4/Ag3PO4 bulk heterojunction for decolorization of Rh. B[J]. Applied Physics Letters,2013,102(12):14613-14619.
[27] 杨慧娟, 邵铭哲, 周健兴等. Ag2O/TiO2异质结的光催化活性及耐光腐蚀性研究[J]. 人工晶体学报, 2017, 46(2):56-63. YANG H J, SHAO M Z, ZHOU J X, et al. Photocatalytic activity and anti-photocorrosion properties of Ag2O/TiO2 heterojunction[J]. Journal of Synthetic Crystals,2017,46(2):56-63(in Chinese).
[28] SUN Y, YANG J, YANG S, et al. Development of an immunochromatographic lateral flow strip for the simultaneous detection of aminoglycoside residues in milk[J]. Rsc Advances,2018,8(17):9580-9586. DOI: 10.1039/C8RA01116H
[29] DONG G, ZHAO K, ZHANG L. Carbon self-doping induced high electronic conductivity and photoreactivity of g-C3N4[J]. Chemical Communications,2012,48(49):6178-6180. DOI: 10.1039/c2cc32181e
-
期刊类型引用(2)
1. 赵瑞,刘艳君,翟媛媛,王进. ACF制备工艺优化对微观结构和吸波性能的影响. 纺织科学与工程学报. 2021(03): 42-48 .  百度学术
百度学术
2. 赵世怀,杨紫博,赵晓明,张旭平,张翠翠,陶超. 活性炭纤维在防护领域的应用进展. 化工新型材料. 2019(02): 15-17+21 .  百度学术
百度学术
其他类型引用(0)
-






 下载:
下载: